3 minute read
PRECEDENTS EVOLVING AMPHITHEATER


Advertisement
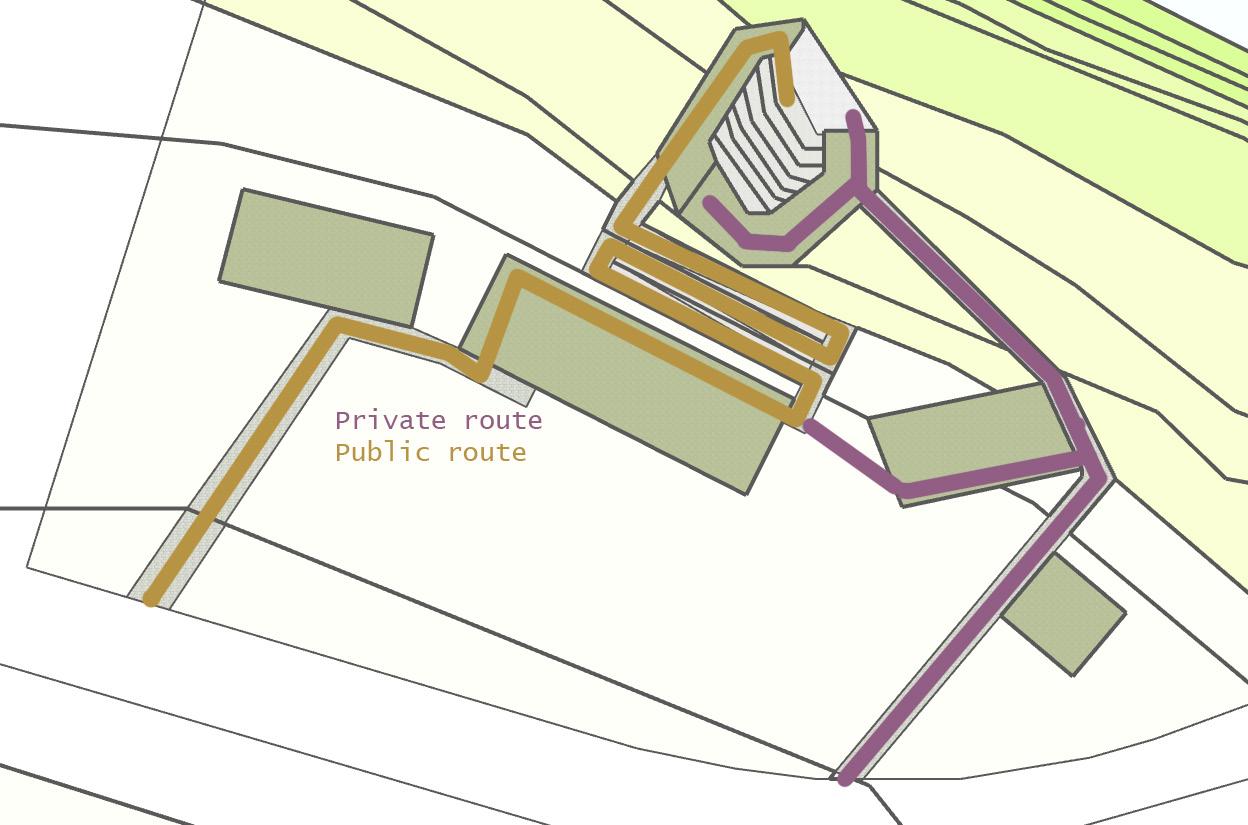
Browning Day, Bloomington, Indiana University Amphitheater - the lowrise amphitheater was designed to fit into the existing natural topogophy of the site inorder to connect the performacne to the environmnet, but also be less disriptive to a near by river tributary.
The first iteration, Inspired by the Indian University precedent, looks at adding in an amphitheater that follows the contour lines so the seating is almost embedded in the ground. This, however, creates a undefined threshold at the ends of the seating which is abrupt.


Ant Sudio, Delhi - Natural air coolers make out of terracotta pots
Anupama kundoo, Auroville, Sawchu - Open pavillion with dramatic water spouts and channels that connect the lowrise amphitheather to the ponds and landscaping that extend beyond it
The second iteration looks at curving the seating so that it creates a focus on the stage and landscape following it, inspired by Sawchu. Contours, however, are still used to determine levels of each seat. Ramps follow regulations of 1:20, with stairs beside them for direct acess.
Inspired by both Sawachu and Ant Studio, this iteration aims to incoperae teracotta pot wall to act as railings, a stage wall, and bring water as an actor of the space. The wall, facing south west, will also cool the space during warm summer days when it will be used the most. Over time, it will become a space of shelter for insects and small birds.

Water Flow Stratergy
1. Settlement and Flushing Chambers
Allow waste water to be dispersed across the surface of reedbed at regular time intervals, after being filtered. The Settlement Chamber works to filter out any unnecessary settlement and dispose of it outside the reedbed. The Flushing chamber disperses the remaining water over the bed once the water volume reaches a threshold value

2. Vertical Flow Reedbed
A 1.75m sand layer traps bacteria and pathogens. Ammonium is converted into nitrate through a nitrification process done by microbes in airspaces.
3. Settling Pond
Roof water is inserted directly into this layer. Sedimentation of dead bacteria, microorganisms and debris allow for decantation of cleaner water. Nitrate is converted to nitrogen gas by bacteria for further purification

4. Flowforms and Stream
Re-oxygenation of water is achieved by letting decanted water flow through 21 ‘flow forms’ that cause the water to splash and become turbulent, allowing air bubbles to be incorporated. Re-oxygenation allows for nitrification processes to restart
5. Horizontal Flow Reedbed
Acts as a feeding ground for wildlife as pure, nutrient rich water flows slowly though a horizontally oriented reedbed, which emulates natural reedbed systems. Dense reeds filter out any new sediments deposited into the water
6. The Wildlife Pond Water flows into a robust ecosystem with algae, insects and animals
7. The Lake
Water flows into a larger lake system. At this point water is safe to use by European water standards and can be reintroduced into the natural environment.
Gutter
The gutters are exposed chain gutters to expose the water and engage it as another actor. To passer bys from the chains hitting them in winds, a metal bracket holds it in place. As water trickles down, it will create noise and visuals.
Sensory Landscape Stratergy



Placing the landscaping stratergies on site and looking at opportunities of interconnecting with bat landscapes
Smell, comfort, and foraging
Placed fruit trees south-west of the site by the pond. As the wind blows, the pond first cools and humidifies it, the air then passes fruit trees which leave aroma onto the wind. This air finally passes the teracotta wall fence to yet again cool the air so that in summer (when the space is most used), i is comfortable and ambient. The fruit trees and pond also double as foraging space for bats
Passive Heating and nesting
Decidious trees are predominantly used around the building. During summer, it prvides shading and prevents overheating internally. During winter, the leaves fall letting light in, and heating up rammed earth which is an excellent thermal mass. This means, heating costs are lowered. The trees also are naturally spaces of nesting. Winter is when many birds migrate and when they return in the summer, it engages those inside the building to the homes of the birds.

Sound and travelling
Hedges are planted all around the border of the site to reduce and block traffic sounds from the road. This really drives the focus and importance of sound inside, and also is adventageous to bats who rely on sound to hunt and place themselves. Hedgerows by the road also act as ways urban fauna travel around safetly, and hence encourages that.