
SEP Consulting Ltd. introduction Palcsó Attila & Dr. Polgár Balázs attila.palcso@sepconsulting.hu phone: +36-20-823 5703 skype: apalcso
Overview
2
We provide services to domestic and international markets • Requirement specification based on Model Based System Engineering method • Development from scratch based on client specification. • Interim & transition management for JAVA development team • Specific recruitment & evaluation process for potential developer • Developer leasing (architect, senior, junior) • Software developer junior&trainee conversion and/or JAVA workframe catch-up course, • Training course for model based system engineering Services • Our customers will get financially significant value in management of sw development project, from requirements specification & system design to implementation phase. Mission
Software Project Management










3
IT strategy and management experience, Enterprise software development project experience, , Complex model-based thinking, We can do complex integration projects Collaborative work style, It is important that we understand software development context! strategy business challenges Information Technology level tasks / issues / challenges business IT opera tion
Systems Modeling Qualification


Qualification in 2010 OMG Certified Systems Modeling Professional Dr. Polgár Balázs (OCSMP) Model Builder Advanced level http://www.omg.org/ocsmp/ Certified Professionals Directory 4
Project References Chatolic World Youth Day Registration system development (2016.03 - 08 ) iBlue remote lock system req. specification and final system design (2016.01-02) EDF - Smart Metering impelementation support at EDF-DEMASZ zrt. (2012 – present ) Smart Metering complex integration project to SAP IS-U system (2015) Smart Metering Energy Engagement Portal implementation (2014) Smart Metering small power plan calculation model implementation (2016) Participation in MAVIR energy optimization project for the reserve market (2015) Safety critical system design for railway market (2014-2016) DECOS – Dependable Components and Systems, EU FP6 IP research pr. (2004–2007) o Main partners: Audi (DE), Airbus (DE), Fiat (IT), TTTech (AT), Esterel (FR), Austrian Institute of Technology (AT) (totally 20 partners from 6 European countries) MOGENTES – Model-based Generation of Tests for Dependable Embedded Systems (2008 – 2011), an EU FP7 STREP research project o Main partners: Ford (DE), Thales Railway (AT), Austrian Institute of Technology (AT), Prolan R3-COP – Resilient Reasoning Robotic Co-operating Systems (2012 – 2013), ARTEMIS pr. o Main partners: Fraunhofer Institute (DE), Siemens AG (DE), Austrian Institute of Technology (AT), Elettric 80 Spa (IT) (totally 28 partners from 11 European countries) 5
6 Domain knowledge of the team Energy: EDF Démász Zrt., Mátrai Erőmű, RWE, MAVIR Railway: Prolan Zrt. IT&Teleco: IBM Magyarországi kft. Vodafone, TATA Consulting Services Banking: ABN AMRO, ING, Manufacturing: Ganz Ansaldo Zrt, Transelectro, Coca Cola, IBM Storage, Electronics: Schneider Electric, Siemens Austria, Others: 25+ years experience in Software Development 20+ years experience IT consulting 10+ years experience in Research & Development in academia 20 years experience in software and systems modeling UML, SysML (= UML for Systems Engineering), domain specific modeling, formal models, etc.
Smart Metering is key to the Smart Grid journey, bringing together the Customer, Grid and Work & Asset domains
Smart Metering
Improving billing accuracy Reducing operational costs
Providing meaningful consumption information
Reducing overall and peak demand
Enabling more micro-generation Supporting implementation of smart grids
Operation of “virtual power plants”
Accelerate electric vehicle adoption
Utilising electric vehicle storage capability
Improving efficiency of industry processes Proactively managing customer debt
Integrating intelligent devices and appliances for demand management Enabling increased use of intermittent energy supplies Services beyond the meter
Trends in Smart Metering Industry
Smart Metering is no longer just meter to cash
o Premise-to-Participant end-to-end meter information network
o Grid Operations vendors designing metering into their systems
o Advent of Smart meter data hubs, increased multi-party access, underpinned by retail markets
o Impact of Meter information on Customer.
o New wave of CIS systems
Smart Metering Requirements Increase
o Increased granularity of data and frequency of reading
o Increase in the number and types of devices to manage
o Extreme High Volume processing on the immediate horizon
o Premise gateways and demand response
Smart Metering as a Service
Vendors repositioning
o Major MDM vendors are all moving into analytics, operational, customer, grid
o Meter communications vendors moving into Distribution automation
Security and Privacy are very important
Trends in Smart Metering Industry
Customer Domain Work and Asset Domain Grid Operations Domain Communications Security Integration Process Automation Regulatory Compliance Smart Metering HAN Portal Electric Vehicles Distributed Energy Resources Substation Automation Line Automation Distribution Mgmt. System Outage Mgmt. System Planning Construction Demand Response Control Room Remote Asset Monitoring Condition Based Monitoring Remote Device Monitoring Scheduling Crew Optimization Asset Mgt Mobile Workforce Managment Enterprise Optimization Customer Analtyics Work and Asset Analytics Grid Analytics Mobile devices
reference

EnergyIP – SAP IS-U
integration
Knowledge path of the JAVA roles
11
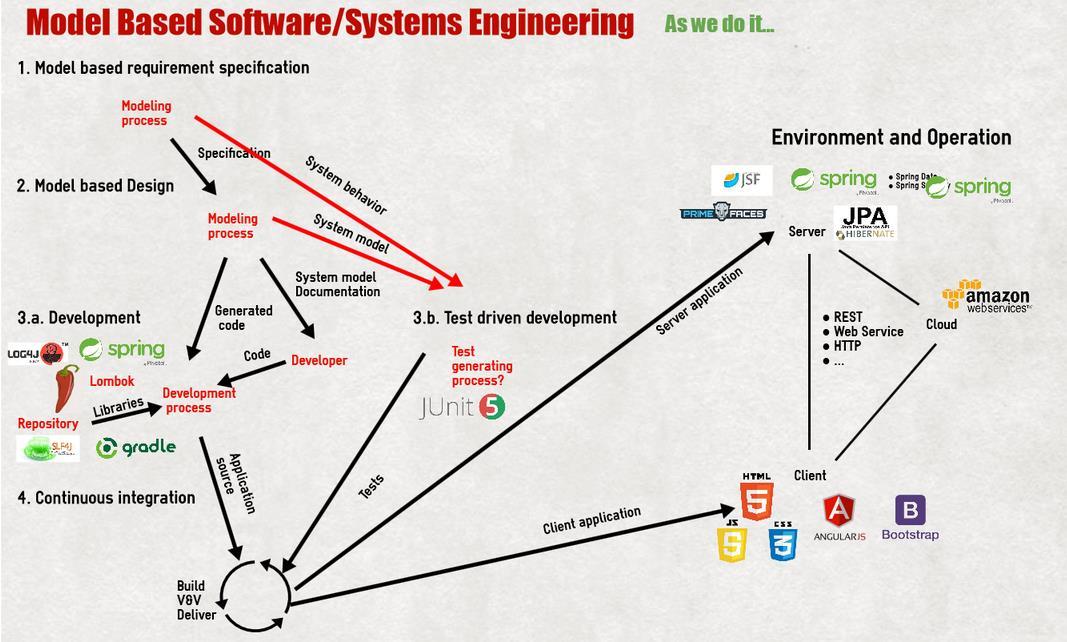
Model Based System Development
requirements modelling processes modelling Definition of Data Model Architecture and components System internal Interactions & interfaces Modelling of the state (state machine)
Java frameworks and directories Gradle dependences & build Lombok (java) Spring console application Log4J, Slf4J logging Spring Data WS & REST client development o JAX-B data link
Server-side Java technologies (Servlet, Filter) (Spring MVC) JSF Spring security WS & REST services development
User interfaces HTML, CSS, JS JSF details & Primefaces AngularJS (+Angular 2) Bootstrap
Modeling with SysML

17
Modeling
Requirements with






















Functional
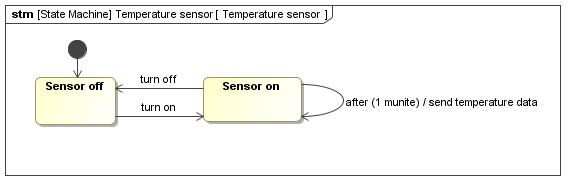
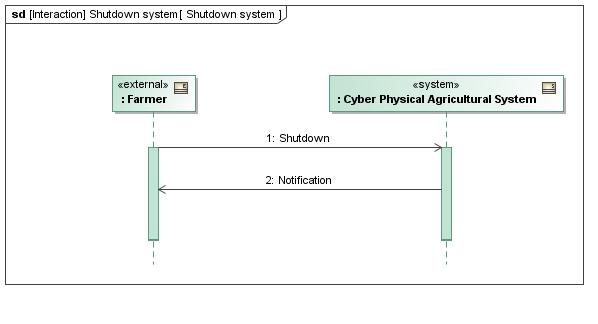
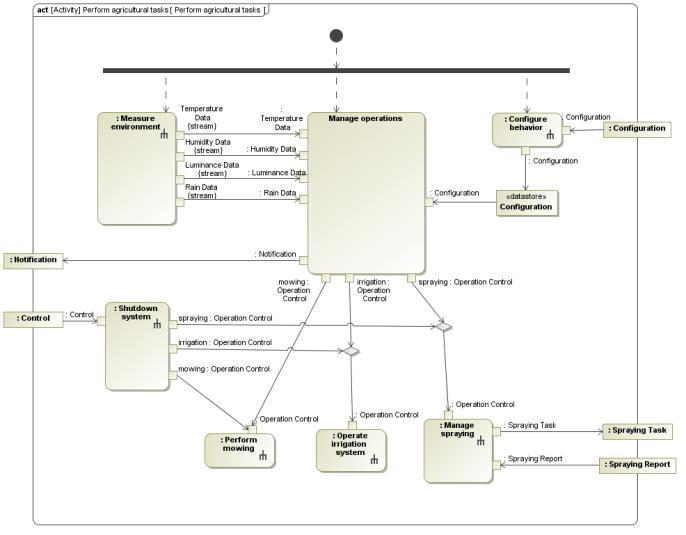
SysML 18 Requirement Activity: Process/flow diagram State Machine Sequence: Communication Use Case refines refines What to do?
Modeling Components with











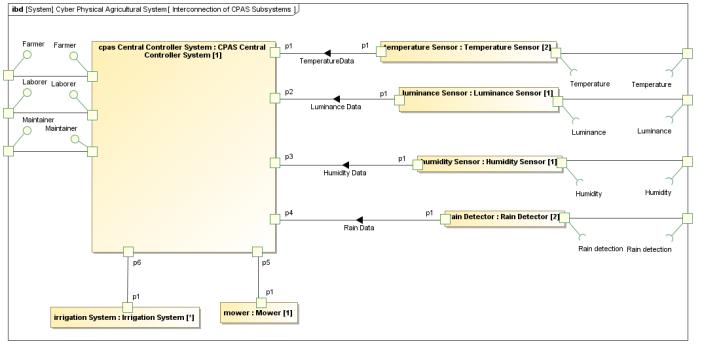







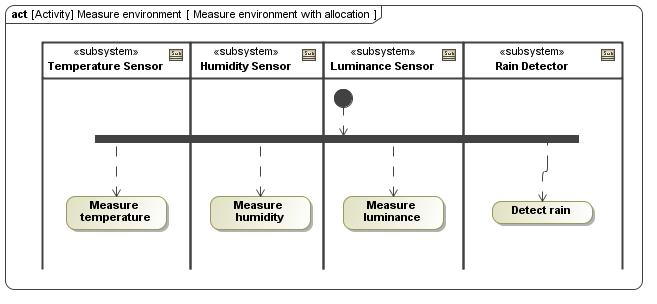

Activity
SysML 19
State Machine Sequence Block Definition Internal Block With what components and how?
Modeling Information with



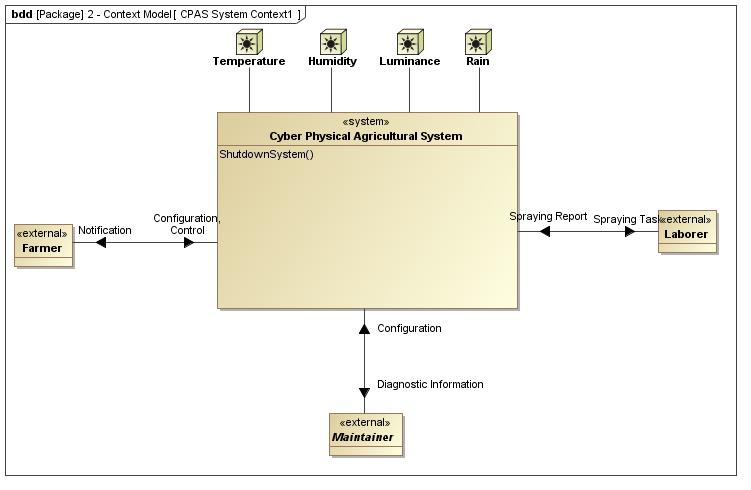





















SysML 20 Activity State Machine Sequence Block Definition Internal Block describes object flow Block Definition What information is handled and how?
How to apply Model Driven Development?
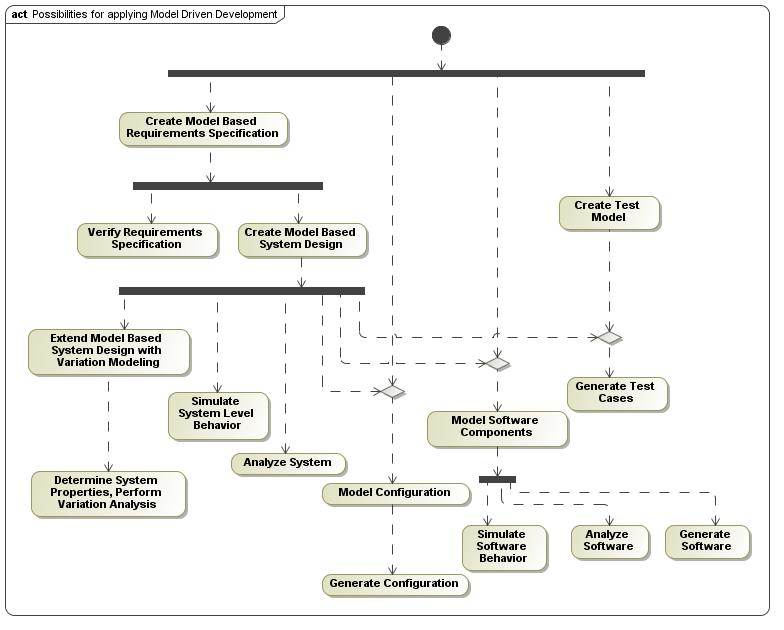
21














22 Possibilities o Platform independent platform specific o Configuration generation o Code generation o Monitor generation o Test Case generation o Documentation generation Tool Support o Workflow Based Execution Synthesis in Model Driven Development Configuration MDD framework Platform specific model (PSM) Platform model Platform independent model (PIM) Program code Test cases Monitor program Application / HW Tests MonitorsConfigures Application / System
Three pillars are needed for model-based work?
1. Modeling Language
o What types of elements can be used during modeling?
o Defines elements and their relationship
o Defines syntax and semantics
o E.g. SysML
2. Development Methodology
o How shall the model be built?
o Defines the steps of analyzing and designing the system
o Defines the usage of the model elements and diagrams
o E.g. SYSMOD (SYStem MODeling) by Tim Weilkiens, OOSEM, Rational Harmony
3. Tool
o E.g. MagicDraw, Enterprise Architect, IBM Rational Rhapsody
23





































































































