| Health Financing Reform in Ukraine
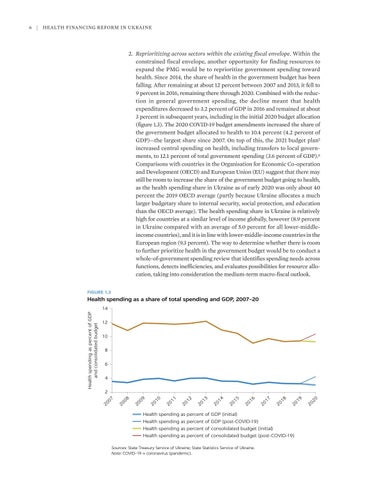
2. Reprioritizing across sectors within the existing fiscal envelope. Within the constrained fiscal envelope, another opportunity for finding resources to expand the PMG would be to reprioritize government spending toward health. Since 2014, the share of health in the government budget has been falling. After remaining at about 12 percent between 2007 and 2013, it fell to 9 percent in 2016, remaining there through 2020. Combined with the reduction in general government spending, the decline meant that health expenditures decreased to 3.2 percent of GDP in 2016 and remained at about 3 percent in subsequent years, including in the initial 2020 budget allocation (figure 1.3). The 2020 COVID-19 budget amendments increased the share of the government budget allocated to health to 10.4 percent (4.2 percent of GDP)—the largest share since 2007. On top of this, the 2021 budget plan5 increased central spending on health, including transfers to local governments, to 12.1 percent of total government spending (3.6 percent of GDP).6 Comparisons with countries in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and European Union (EU) suggest that there may still be room to increase the share of the government budget going to health, as the health spending share in Ukraine as of early 2020 was only about 40 percent the 2019 OECD average (partly because Ukraine allocates a much larger budgetary share to internal security, social protection, and education than the OECD average). The health spending share in Ukraine is relatively high for countries at a similar level of income globally, however (8.9 percent in Ukraine compared with an average of 5.0 percent for all lower-middle- income countries), and it is in line with lower-middle-income countries in the European region (9.3 percent). The way to determine whether there is room to further prioritize health in the government budget would be to conduct a whole-of-government spending review that identifies spending needs across functions, detects inefficiencies, and evaluates possibilities for resource allocation, taking into consideration the medium-term macro-fiscal outlook. FIGURE 1.3
Health spending as a share of total spending and GDP, 2007–20 14 12 10 8 6 4
Health spending as percent of GDP (initial) Health spending as percent of GDP (post-COVID-19) Health spending as percent of consolidated budget (initial) Health spending as percent of consolidated budget (post-COVID-19) Sources: State Treasury Service of Ukraine; State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Note: COVID-19 = coronavirus (pandemic).
20 20
19 20
18 20
17 20
16 20
15 20
14 20
13 20
12 20
11 20
10 20
09 20
08 20
07
2
20
Health spending as percent of GDP and consolidated budget
6