Inside the Groove Navigating the Music Industry



Introducing "Inside the Groove: Navigating the Music Industry" - an insightful guide that peels back the curtain on the captivating world of music. This book dives deep into the inner workings of the industry, unraveling its intricate mechanisms, and providing invaluable knowledge for aspiring musicians, producers, and industry professionals alike. From crafting your unforgettable melodies to record labels, promoting your work, and understanding the complexities of royalties and licensing.
Title: Inside the Groove: Navigating the Music Industry
Author: Coco & Cwtsh
All rights reserved. This ebook was produced by Coco & Cwtsh in 2023. coocwtsh.com

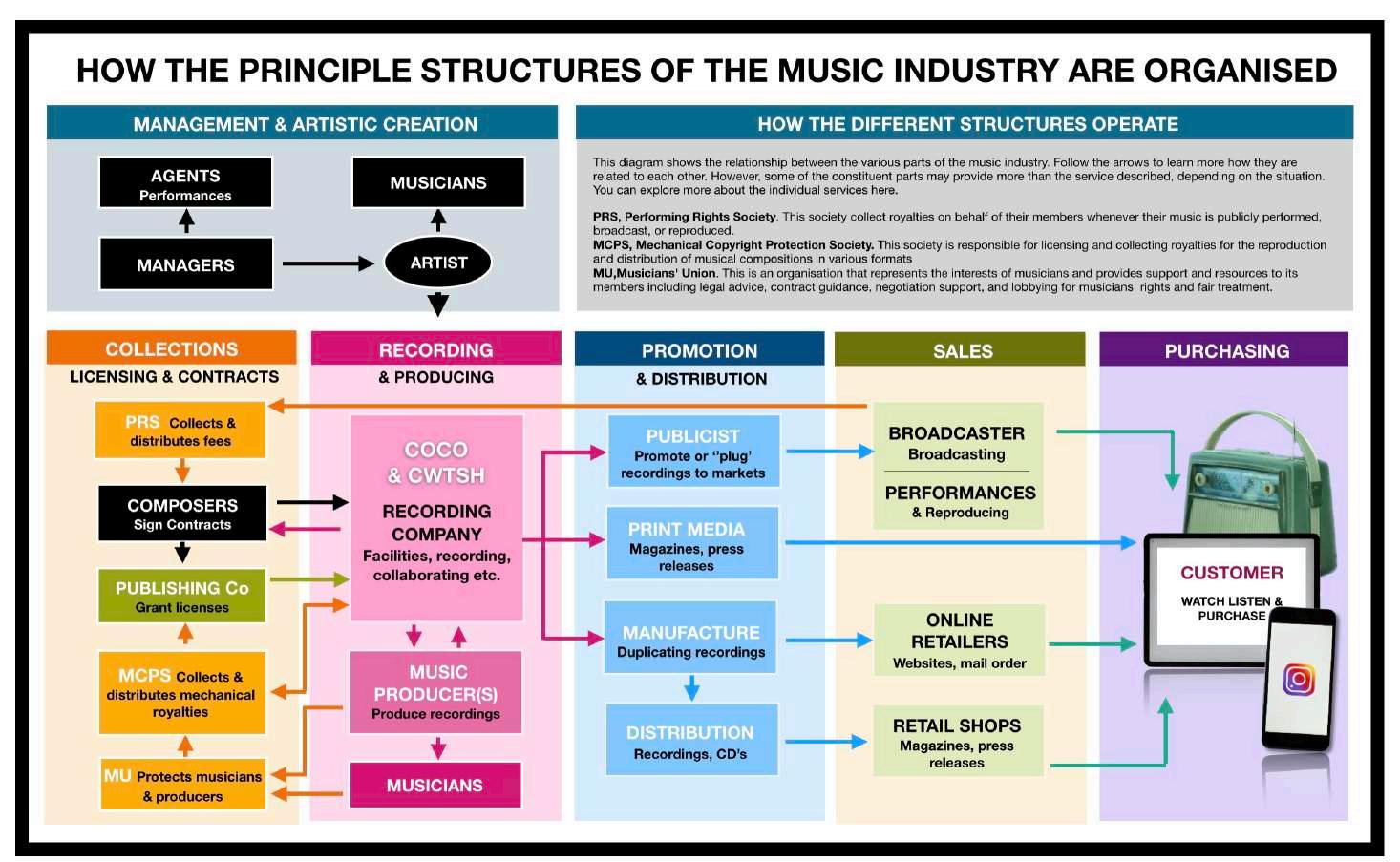
The Music Industry Coco & Cwtsh Where magic happens Artistic Creation 01 The Music Pathway 02 Artisticc Creation Record Label 03 Record Label 04 Music Producer 05 Musicians Promotion 06 Publicist 07 Print Media 08 Manufacture 09 Distribution Sales 10 Broadcasting 11 Online Sales 12 Retail Shops Purchase 13 Purchase Collections 14 PRS 15 Composers 16 Publishing Company 17 MCPS 18 Musicians Union
01 The Music Pathway
If you have a song that you would like the world to hear, there are several steps you can take to bring it to fruition. On the following page is a flow chart outlining the process from creating your song to how the customer purchases.
Find a Manager or Agent: If you have a manager or agent, they can assist you in navigating the music industry. They will help you connect with a recording company that has the necessary facilities and record producers to bring your song to life.
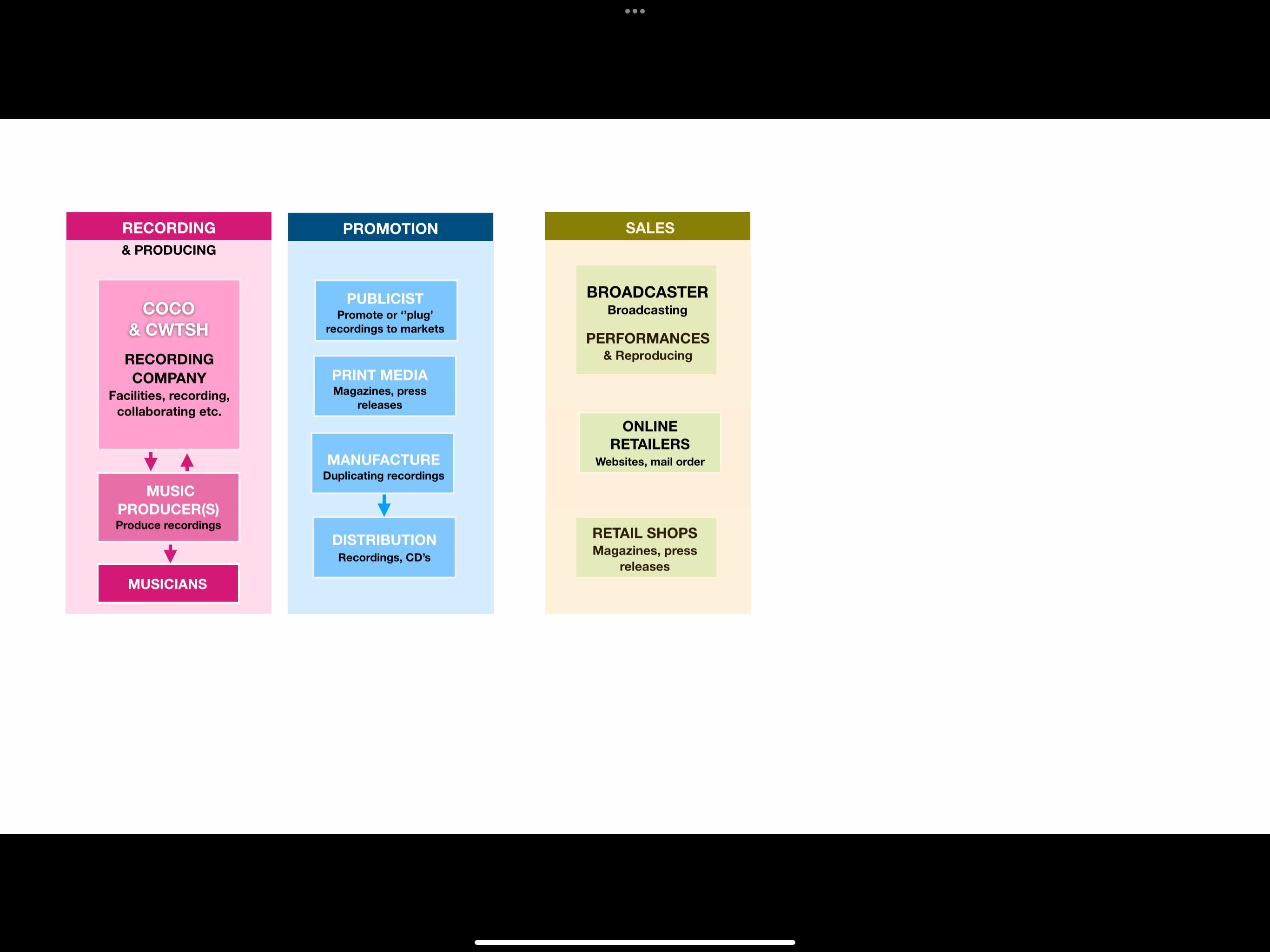
Recording Company:
Once you have identified a suitable recording company, they will work with you to create a high-quality recording of your song. They may provide access to talented composers who can help refine your music and sign necessary contracts. Additionally, they will collaborate with a publisher who can grant you a license to protect your song's rights.
Promotion:
Once your finished song is ready, the recording company takes on the role of promoting your music. They will reach out to organizations that specialize in promoting songs to broadcasters, such as radio stations or music supervisors for film and television. These organizations will help "plug" your song, meaning they will advocate for its inclusion in broadcasts and other media formats. The recording company may also develop promotional materials such as literature, photographs, or videos to
support the song's marketing efforts.
Distribution:
The recording company will handle the manufacturing and duplication of recordings. This includes producing physical copies, such as CDs or vinyl records if desired, as well as making the song available on digital platforms. The final recording of your song will be distributed to online retailers and retail shops, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Royalties:
In terms of revenue collection, two key organizations play a role: the Performing Rights Society (PRS) and the Mechanical Copyright Protection Society (MCPS). The PRS collects fees from broadcasters who use your song in their broadcasts, ensuring that you receive appropriate compensation for your work. The MCPS, on the other hand, collects fees from mechanical royalties, which encompass the reproduction and distribution of your song's recordings.
By following these steps, you can navigate the music industry and increase the chances of your song reaching a wider audience. Keep in mind that the specifics may vary depending on the region and individual circumstances, but this general outline should provide you with a helpful framework for pursuing your musical aspirations.
 Ffion Gruffudd Flockhart Coco&Cwtsh 2023
Ffion Gruffudd Flockhart Coco&Cwtsh 2023
INTRODUCTION AND GUIDE
O2 Artistic Creation
Agents
Artist Representation:
• Agents act as representatives for artists and work on their behalf to secure various opportunities, such as live performances, endorsements, and media appearances.
Booking Gigs:
• Agents are responsible for booking concerts, festivals, and other live performances for their clients. They negotiate contracts, handle logistics, and ensure that artists are compensated appropriately Industry
Networking:
• Agents establish and maintain relationships with industry professionals, including venue owners, promoters, and record labels, to create opportunities for their clients.
Career Development:
• Agents provide guidance and advice to artists regarding their career trajectory, helping them make strategic decisions and navigate the music industry.
Promoters
Event Organization:
• Promoters are responsible for organizing and staging live events, such as concerts, music festivals, and tours. They coordinate the logistics, including securing venues, arranging production elements, and managing ticket sales.
Marketing and Promotion:
• Promoters work to promote events, build anticipation, and attract audiences. This involves advertising campaigns, public relations efforts, and utilizing various media channels to generate awareness and ticket sales.
Financial Management:
• Promoters handle financial aspects, including budgeting, negotiating artist fees, and managing revenue streams from ticket sales, sponsorships, and merchandise.
In the music industry, agents and promoters play important roles in representing and promoting artists, organizing concerts and tours, and facilitating business opportunities. Here's a brief overview of what agents and promoters do:

Risk Management:
• Promoters assess potential risks associated with events, such as security concerns or adverse weather conditions, and take necessary measures to mitigate those risks.
Both agents and promoters play crucial roles in connecting artists with audiences, facilitating collaborations, and ensuring the smooth execution of live events. They contribute to the success and growth of artists' careers by managing their bookings, promoting their work, and creating opportunities for exposure in the music industry.
O3 Record Label
Arecord label or record company, is a company that specializes in various aspects of the music industry, particularly the production, distribution, marketing, and promotion of recorded music. Here's an overview of what a recording company typically does:
Artist Development:
• Record labels often play a role in discovering and developing new musical talent. They may scout for promising artists, sign them to recording contracts, and provide resources and support to help them refine their sound, create albums, and shape their artistic identity.
Recording and Production:
• Record labels oversee the process of recording and producing music albums. They may provide recording studios, engineers, and producers to work with artists in creating high-quality recordings.
Distribution and Manufacturing:
• Record labels handle the distribution and manufacturing of physical copies of music albums, such as CDs and vinyl records. They may coordinate with distributors and retailers to ensure that albums reach stores and online platforms for sale or streaming.
Marketing and Promotion:
• Record labels are responsible for promoting their artists and their music. They develop marketing strategies, create promotional materials, and engage in various marketing channels to increase awareness and reach a wider audience. This includes activities like organizing press campaigns, radio and TV appearances, online marketing, and social media promotion.
Contract Negotiations and Legal Matters:
• Record labels negotiate contracts with artists, which outline the terms of the recording agreement, including issues like royalties, advances, and ownership rights. They also handle legal matters related to copyright, licensing, and intellectual property protection.
Financial Support and Management:
• Record labels invest in the production, marketing, and promotion of music albums. They provide financial resources to cover recording costs, music videos, promotional activities, and tour support. They also manage the financial aspects of album sales, collect revenue, and distribute royalties to the artists according to the terms of their contracts.
RECORDING

COCO & CWTSH
Touring and Live Performances:
• Some record labels have departments or partnerships dedicated to organizing and supporting artists' live performances, tours, and concert bookings. They may collaborate with booking agents and promoters to secure tour dates and handle logistics.
It's important to note that the specific functions and roles of a recording company can vary depending on the size, structure, and genre focus of the label. Independent labels may have a more hands-on and personalized approach, while major labels often have more extensive resources and global reach.

MUSIC PRODUCER
Produce recordings
MUSICIANS
LABEL Facilities, recording, collaborating etc.
Music Producer
Amusic producer plays a crucial role in the creation and development of recorded music. They work closely with artists and are responsible for overseeing and managing various aspects of the music production process. Here's an overview of what a music producer typically does:
Pre-production Planning:
• Producers collaborate with artists to discuss and refine their creative vision for the project. This may involve selecting songs, determining the sound and style, and arranging musical elements.
Recording and Engineering:
• Producers oversee the recording process, working with engineers to capture high-quality sound recordings. They help create the desired sonic atmosphere, guide musicians in their performances, and make technical decisions related to microphone placement, instrument choices, and overall sound aesthetics.
Arrangement and Composition:
• Producers contribute to the arrangement and composition of songs. They may suggest changes to song structures, melodies, chord progressions, or instrumentation to enhance the overall impact and cohesiveness of the music.

04
Instrumentation and Session Musicians:
• Producers can assist in selecting appropriate instrumentation and recommend session musicians if needed. They ensure that the right musicians and instruments are employed to achieve the desired sound.
Sound Design and Production Techniques:
• Producers utilize their expertise in sound design and production techniques to shape the overall sonic landscape of the recording. This involves working with effects, synthesizers, samples, and other production tools to create unique textures and sonic elements.
Performance Guidance:
• Producers provide guidance and support to artists during recording sessions, helping them deliver their best performances. They offer feedback on vocal delivery, instrumental technique, and overall musical expression.
Mixing and Audio Post-production:
• Producers work closely with mixing engineers to achieve a balanced and polished sound. They make decisions regarding levels, panning, EQ, and other audio processing to achieve the desired sonic outcome.
Creative Decision-making:
• Producers make artistic decisions throughout the production process, including selecting the best takes, determining the final song order for an album, and overseeing the overall creative direction of the project.
Project Management:
• Producers often manage the logistical aspects of a recording project. This can involve scheduling recording sessions, coordinating with session musicians and engineers, and overseeing budget and timelines.
Collaborations and Networking:
• Producers may collaborate with songwriters, artists, and other industry professionals to bring their creative visions to life. They also build relationships with record labels, publishers, and other industry figures to create opportunities for their artists.
It's important to note that the specific responsibilities and roles of a music producer can vary based on the producer's style, genre, and the dynamics of their collaboration with artists. Some producers may have a more hands-on approach, while others focus primarily on technical aspects or specialize in specific genres.
Musicians
Musicians are the artisans who harness the power of sound to create captivating melodies and evoke emotions that transcend words. They are the magicians who transform notes into symphonies, rhythms into anthems, and lyrics into soul-stirring poetry. Musicians are the heartbeat of the music industry, captivating audiences with their extraordinary talent and unwavering dedication to their craft
At their core, musicians possess an innate ability to express their innermost thoughts, feelings, and experiences through the universal language of music. They channel their creativity and technical prowess to bring compositions to life, infusing them with their unique musicality and personal touch. Whether they are skilled instrumentalists, vocalists, or both, musicians possess the remarkable ability to transport listeners to different realms and connect with them on a profound level.
Behind every captivating musical performance lies countless hours of practice, discipline, and unwavering dedication. Musicians continually refine their skills, exploring new techniques, honing their craft, and seeking mastery. They collaborate with fellow musicians, composers, and producers, merging their talents to create breathtaking compositions that stand the test of time In today's digital age, musicians navigate a vast array of opportunities. They connect with fans through social media, share their music on streaming platforms, and engage in live performances that bring their artistry to life. They harness technology to innovate, experiment, and reach global audiences with their mesmerizing sounds. The world of musicians is a vibrant tapestry of creativity, passion, and boundless expression. They forge connections, spark conversations, and leave an indelible mark on the human experience. So, join us in celebrating the musicians who grace our lives with their melodic magic, and let their music be the soundtrack to our journey through life.
05


The Music Industry
Coco & Cwtsh

Where magic happens
Promotion
In the music industry, promotion refers to strategic activities aimed at increasing the visibility, reach, and success of musical artists, albums, or songs. It encompasses various marketing efforts, such as media campaigns, radio and TV appearances, online promotion, social media engagement, live performances, and collaborations. Effective promotion helps artists connect with audiences, build a fan base, and ultimately achieve recognition and success in the competitive music landscape.
PROMOTION
PUBLICIST
Promote or ‘’plug’ recordings to markets
PRINT MEDIA
Magazines, press publications
MANUFACTURE
Duplicating recordings
DISTRIBUTION
Recordings, CD’s
In the music industry, a publicist, also known as music pluggers or radio pluggers, are individuals or companies responsible for promoting and securing airplay for songs on radio stations. Their primary goal is to generate exposure and increase the chances of a song being played on radio, which can help boost its popularity and reach a wider audience. Here's an overview of what pluggers typically do:
Radio Promotion Strategy:
• Pluggers develop a radio promotion strategy to increase the chances of a song receiving airplay. This involves analyzing the target audience, identifying appropriate radio stations and programs, and determining the best timing for promotional efforts.
Building Relationships:
• Pluggers establish and maintain relationships with radio station personnel, including music directors, program directors, DJs, and other key decision-makers. They aim to develop rapport and credibility to enhance the chances of their songs being considered for airplay.
PUBLICIST Promote or ‘’plug’ recordings to markets PRINT MEDIA Magazines, press publications MANUFACTURE Duplicating recordings DISTRIBUTION
CD’s PROMOTION 06
Recordings,
Publicist
Pitching Songs:
• Pluggers pitch songs to radio stations, aiming to persuade them to add the songs to their playlists. They provide promotional materials, such as press releases, artist biographies, and high-quality recordings, to showcase the song's potential appeal and commercial viability.
Radio Interviews and Promotional Opportunities:
• Pluggers help secure radio interviews and other promotional opportunities for artists. They work to arrange appearances on radio shows, where artists can discuss their music, share their stories, and build a connection with listeners.
Monitoring Airplay and Chart Performance:
• Pluggers monitor the airplay of songs on radio stations. They track the number of spins, chart positions, and overall performance of the songs to assess the effectiveness of their promotional efforts. This information helps inform future strategies and promotional campaigns.
Feedback and Reporting:
• Pluggers provide feedback and reports to artists and their management teams. They share information about which radio stations are playing the song, the frequency of airplay, and any audience response or feedback received from radio stations.
Industry Networking:
• Pluggers actively network within the music industry, attending industry events, conferences, and showcases. They aim to expand their network of contacts and stay up-to-date with industry trends, which can help in identifying new promotional opportunities for their artists
It's important to note that pluggers primarily focus on promoting songs to radio stations and securing airplay. Other aspects of music promotion, such as online marketing, social media campaigns, and press outreach, may be handled by separate professionals or teams within an artist's management or marketing setup.
Print Media
In the music industry, print media refers to publications that specialize in reporting on music-related news, features, reviews, interviews, and other content. Print media outlets play an important role in promoting artists, albums, concerts, and industry trends. Here's an overview of what print media does in the music industry:
Music Journalism:
• Print media outlets employ music journalists who write articles and reviews about artists, albums, concerts, and other music-related topics. These journalists provide critical analysis, interviews, and features that inform and entertain music enthusiasts.
Album Reviews:
• Print media publishes album reviews, offering their assessment and critique of new releases. These reviews can influence public perception and help guide consumers in their music purchasing decisions.

Artist Interviews and Features:
• Print media often conducts interviews with musicians and artists, providing insights into their creative process, inspirations, and personal stories. These interviews and features help readers connect with artists on a deeper level and build interest in their music.
07
Concert and Festival Coverage:
• Print media outlets cover live concerts, music festivals, and other events, providing reviews, highlights, and photo galleries. This coverage helps create buzz around performances, promote upcoming shows, and share the experiences of music fans
Industry News and Trends:
• Print media reports on industry news, including updates on record labels, music technology, industry events, and emerging trends. This information keeps readers informed about the broader music landscape and helps industry professionals stay up-to-date.
Print Magazines and Newspapers:
• Print media outlets often publish magazines and newspapers dedicated to music. These publications may be general music-focused or cater to specific genres. They provide a tangible platform for in-depth coverage and feature articles that readers can enjoy and collect.
Promotion and Advertising:
• Print media offers advertising opportunities for record labels, music promoters, concert organizers, and other industry entities. Advertisements in print publications help raise awareness about artists, albums, tours, and related products or services
Music Charts and Listings:
• Some print media outlets publish music charts and listings, showcasing the most popular songs, albums, and artists based on sales, airplay, or other metrics. These charts and listings can influence industry perceptions and consumer preferences
While digital media and online platforms have become increasingly prevalent, print media remains a significant part of the music industry, providing in-depth and tangible content for music enthusiasts and serving as a platform for music promotion and critical analysis
Manufacture
In the music industry, manufacturers play a vital role in the production and distribution of musical instruments, audio equipment, and related products. They are responsible for designing, producing, and delivering instruments, equipment, and accessories that musicians and audio professionals use in their performances, recordings, and productions. Here's an overview of what manufacturers typically do in the music industry:
Instrument Manufacturing:

• Manufacturers produce musical instruments such as guitars, keyboards, drums, brass instruments, woodwinds, and more. They design and engineer instruments to meet the needs of musicians, ensuring functionality, quality, and playability.
Equipment Manufacturing:
• Manufacturers produce audio equipment and gear used in music production, recording studios, live sound reinforcement, and performance setups. This includes items like microphones, mixers, amplifiers, speakers, headphones, audio interfaces, studio monitors, and signal processors.
Product Development and Innovation:
• Manufacturers engage in research and development to introduce new products, improve existing ones, and innovate in terms of technology, design, and performance. They invest in exploring new materials, manufacturing techniques, and features to meet the evolving needs of musicians and audio professionals.


08
Quality Control and Testing:
• Manufacturers implement quality control measures to ensure that their products meet industry standards and customer expectations. They conduct rigorous testing and inspections throughout the manufacturing process to maintain consistent quality and performance.
Distribution and Supply Chain Management:
• Manufacturers coordinate the distribution and supply chain logistics to ensure their products reach retailers, dealers, and customers efficiently. This involves managing inventory, shipping, and working with distributors to make products available in various markets
•
Artist Endorsements and Partnerships:
• Manufacturers often collaborate with musicians, artists, and industry professionals through endorsement and partnership programs. They provide instruments or equipment to artists for promotional purposes, and in turn, benefit from the exposure and association with renowned musicians
Customer Support and Service:
• Manufacturers provide customer support services, such as technical assistance, repairs, and warranty services. They have dedicated customer service departments or work through authorized service centers to address inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and ensure customer satisfaction.
Product Marketing and Promotion:
• Manufacturers develop marketing strategies to promote their products. This includes advertising campaigns, participation in trade shows, endorsements by artists, product demonstrations, and digital marketing efforts to raise awareness and generate interest among potential customers
Manufacturers are essential in providing musicians, audio professionals, and enthusiasts with the instruments and equipment they need to create, perform, and record music. They contribute to the advancement of music technology, offer options for various budgets and skill levels, and play a significant role in shaping the overall music industry.
Distribution
In the music industry, distribution refers to the process of making recorded music available to the public through various channels and platforms. It involves getting music from artists, labels, or producers to consumers, allowing them to access and purchase the music in different formats. Here's an overview of what distribution entails in the music industry:
Physical Distribution:
Physical distribution involves manufacturing, shipping, and delivering physical formats of music, such as CDs, vinyl records, and cassettes, to retailers, distributors, and directto-consumer sales. This includes managing inventory, coordinating with manufacturing plants, and ensuring timely delivery to various sales outlets.
Digital Distribution:
Digital distribution involves making music available through online platforms and streaming services. This includes distributing music to digital music stores, such as iTunes, Amazon, and streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music. Digital distributors facilitate the uploading, encoding, and delivery of music files to these platforms.
Licensing and Sync Distribution:
Licensing and sync distribution refers to the process of granting permission for music to be used in films, TV shows, commercials, video games, and other audiovisual productions. Music distributors negotiate licensing deals on behalf of artists or labels, ensuring proper compensation for the use of their music in these mediums.
Global Distribution:
Global distribution involves making music available worldwide, ensuring that it reaches audiences in different countries and territories. Distribution companies often have agreements with international partners or use global distribution networks to reach markets beyond their home region.
Distribution Agreements:
Distribution agreements are contracts between artists, labels, or producers and distribution companies. These agreements outline the terms, rights, and responsibilities of both parties regarding the distribution of music. They cover aspects such as royalty rates, territory restrictions, marketing support, and sales reporting.
09
Promotional Support:
Some distribution companies provide promotional support to artists and labels. This may include marketing campaigns, playlist placements, advertising, and other promotional activities to increase the visibility and discoverability of the music being distributed.
Reporting and Royalty Collection:
Distribution companies collect sales data, streaming data, and other usage information to generate reports and statements for artists, labels, and rights holders. These reports outline the sales or streaming activity of the music and form the basis for royalty calculations and payments
Distribution plays a crucial role in connecting artists and their music with audiences. It ensures that music is available through various channels and platforms, both physically and digitally. By facilitating the availability and accessibility of music, distribution helps artists and labels reach a wider audience, generate revenue, and build their careers in the music industry

The Music Industry
Coco & Cwtsh

Where magic happens
Sales
Welcome to the dynamic realm of music sales, where the melodies that captivate our hearts find their way into the hands and ears of eager listeners. From broadcasting enchanting tunes over the airwaves to electrifying live performances that ignite the senses, music sales encompass a diverse ecosystem. Online retailers and retail shops serve as gateways, making musical treasures accessible, allowing melodies to find their forever home in the hearts of music enthusiasts.

While the method of delivery differs between traditional broadcasting and streaming services, they both serve the purpose of making music accessible to listeners on a mass scale. Streaming services have become an integral part of the music industry's distribution model, allowing artists to reach a global audience without the limitations of geographical boundaries.
It's worth noting that streaming services operate differently from traditional broadcasters in terms of revenue generation. Traditional broadcasters, such as radio stations, may pay performance royalties to songwriters and publishers through organizations like the Performing Rights Society (PRS). Streaming services, on the other hand, typically license music from record labels and pay royalties to rights holders based on factors like the number of streams or subscription revenue.
In summary, while broadcasting in the music industry traditionally referred to radio and television broadcasts, it now includes digital platforms and streaming services like Spotify. These services serve as digital broadcasters, enabling artists to distribute their music to a wide audience through online streaming.
Online Retailers

11
Online retailers in the music industry are platforms or websites that sell music-related products and services over the internet. These retailers provide a convenient and accessible way for consumers to discover, purchase, and consume music in various formats. Here are some common types of online retailers in the music industry:
Digital Music Stores:
• Online retailers like iTunes, Amazon Music, Google Play Music, and Bandcamp offer digital downloads of music. They allow consumers to purchase and download individual songs or complete albums in digital audio formats such as MP3, AAC, or FLAC. These platforms often offer a wide selection of music across different genres.
Streaming Platforms:
• Streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, Tidal, and Deezer offer on-demand access to a vast library of music through subscription-based services. Users can stream music online, create playlists, discover new artists, and access personalized recommendations. These platforms typically offer both free ad-supported tiers and premium subscription options.
Online Music Marketplaces:
• Online marketplaces like Discogs and eBay specialize in selling physical music formats such as CDs, vinyl records, cassettes, and music memorabilia. They connect buyers and sellers, facilitating the buying and selling of both new and used music items.
Merchandise Retailers:
• Many music artists and bands have their own online stores or partnerships with merchandise retailers. These online retailers offer a wide range of music-related merchandise such as t-shirts, posters, vinyl records, concert tickets, and other branded items.
Sheet Music Retailers:
• Online retailers like Sheet Music Plus and Musicnotes specialize in selling digital or physical sheet music. They provide a wide selection of sheet music for various instruments, genres, and skill levels, allowing musicians to purchase and download sheet music for personal or professional use.
Instrument and Equipment Retailers:
• Online retailers that focus on musical instruments, equipment, and accessories offer a wide range of products for musicians and music enthusiasts. Platforms like Sweetwater, Guitar Center, and Thomann provide online shopping for instruments, audio gear, recording equipment, and related accessories.
These online retailers play a crucial role in the music industry by providing a global marketplace for music consumption, sales, and merchandise. They offer convenience, choice, and accessibility for consumers, while also providing opportunities for artists, labels, and other industry professionals to reach a broader audience and monetize their music.
Retail Shops
In the music industry, distribution refers to the process of making recorded music available to the public through various channels and platforms. It involves getting music from artists, labels, or producers to consumers, allowing them to access and purchase the music in different formats. Here's an overview of what distribution entails in the music industry:
Physical Distribution:
• Physical distribution involves manufacturing, shipping, and delivering physical formats of music, such as CDs, vinyl records, and cassettes, to retailers, distributors, and direct-to-consumer sales. This includes managing inventory, coordinating with manufacturing plants, and ensuring timely delivery to various sales outlets.
Digital Distribution:
• Digital distribution involves making music available through online platforms and streaming services. This includes distributing music to digital music stores, such as iTunes, Amazon, and streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music. Digital distributors facilitate the uploading, encoding, and delivery of music files to these platforms.
Licensing and Sync Distribution:
• Licensing and sync distribution refers to the process of granting permission for music to be used in films, TV shows, commercials, video games, and other audiovisual productions. Music distributors negotiate licensing deals on behalf of artists or labels, ensuring proper compensation for the use of their music in these mediums.
Global Distribution:
• Global distribution involves making music available worldwide, ensuring that it reaches audiences in different countries and territories. Distribution companies often have agreements with international partners or use global distribution networks to reach markets beyond their home region.
Distribution Agreements:
• Distribution agreements are contracts between artists, labels, or producers and distribution companies. These agreements outline the terms, rights, and responsibilities of both parties regarding the distribution of music. They cover aspects such as royalty rates, territory restrictions, marketing support, and sales reporting.
12

The Music Industry
Coco & Cwtsh

Where magic happens
Purchasing
Experience the music we've meticulously crafted at our studio in a multitude of ways. Tune in to your favorite radio stations and let our melodies grace the airwaves, captivating listeners near and far. Access our music conveniently on your mobile phone, whether through streaming platforms or digital downloads, allowing you to carry our harmonies wherever you go. For those seeking a tangible connection, discover our tunes at retail shops, where CDs and vinyl records preserve the nostalgic joy of physical music ownership. Explore the diverse avenues we've embraced to ensure our music reaches your ears, leaving a lasting imprint on your soul.
CUSTOMER



PURCHASING WATCH, LISTEN & PURCHASE



Purchasing
Streaming services like Spotify, iTunes, and Amazon play a significant role in the distribution and accessibility of music in today's digital landscape. These platforms provide a convenient way for users to discover, stream, and purchase music online. Here's an explanation of their relationship to the song distribution process and how songs are sent to these platforms:
Aggregators or Digital Distributors:
• To get your song on streaming services, you typically work with an aggregator or digital distributor. These are companies that specialize in delivering music to various online platforms. Examples of popular aggregators include TuneCore, CD Baby, DistroKid, and The Orchard
Song Submission:
• As an artist, you would sign up with one of these aggregators or digital distributors and provide them with your finished song, along with the necessary metadata (e.g., song title, artist name, album name, genre, etc.). The aggregator/distributor will then facilitate the process of submitting your song to the streaming services
Distribution Network:
• Aggregators have established relationships and distribution networks with streaming services and online retailers. They handle the technical requirements and formatting necessary for your song to be accepted by these platforms. They ensure your song meets the specific audio format, quality, and metadata standards set by each streaming service.
Content Delivery:
• Once the aggregator has successfully submitted your song to the streaming services, it enters the platforms' content delivery pipeline. This process can take a variable amount of time, typically ranging from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the platforms and their internal procedures.
Availability on Streaming Services:
• After the content delivery process, your song becomes available for streaming, downloading, and purchase on the supported platforms. Users of services like Spotify, iTunes, Amazon Music, and others can then search for and listen to your song, either through free or premium subscriptions, or by purchasing individual tracks or albums
13
PURCHASING
It's important to note that the specific procedures and requirements may vary slightly between aggregators and streaming services. Some aggregators charge a fee or take a percentage of your earnings, while others operate on a flat fee or subscription model. It's recommended to research and compare different aggregators to find the one that best suits your needs and goals as an artist.
CUSTOMER


WATCH, LISTEN & PURCHASE



Overall, aggregators and digital distributors act as intermediaries between artists and streaming services, facilitating the process of making songs available on platforms like Spotify, iTunes, and Amazon Music.

The Music Industry
Coco & Cwtsh

Where magic happens
Collections
Welcome to the crucial stage of music collection in the music industry. Here, the intricate web of rights, royalties, and contracts intertwines to ensure that creators and rights holders receive their fair dues. The Performing Rights Society (PRS) diligently collects fees from broadcasters, ensuring songwriters and publishers are appropriately compensated for their work. The Mechanical Copyright Protection Society (MCPS) focuses on gathering fees from mechanical royalties. Composer contracts come into play, securing the rights of composers while publishing company licenses grant the necessary permissions for the use and distribution of music. It's through this intricate process that the music industry ensures a fair and balanced ecosystem for creators and their intellectual property.
LICENSING & CONTRACTS COLLECTIONS
PRS Collects & distributes fees
COMPOSERS
Sign Contracts
PUBLISHING
Co Grant licenses
MCPS Collects & distributes mechanical royalties
MU Protects musicians & producers
PRS. Performing Rights Society
PRS stands for Performing Rights Society, and it is a prominent music royalty collection society based in the United Kingdom. It is responsible for collecting and distributing royalties to songwriters, composers, and music publishers for the public performance, broadcast, and reproduction of their musical works. Here are some key points about PRS in the music industry:
Royalty Collection:
• PRS acts as an intermediary between music creators (songwriters, composers) and music users (such as radio stations, TV networks, live venues, streaming platforms). They collect royalties on behalf of their members whenever their music is publicly performed, broadcast, or reproduced.
Performing Rights:
• PRS collects performance royalties for live performances of musical works, including concerts, gigs, and public events. This includes both ticketed and non-ticketed events.
Broadcast Rights:
• PRS collects royalties for the public performance of musical works on television, radio, and other broadcasting platforms. This includes royalties from radio airplay, TV shows, commercials, and online streaming services.
Reproduction Rights:
• PRS also manages the reproduction rights of musical works, which refers to the mechanical reproduction of music on physical formats like CDs, vinyl records, and digital downloads. They collect royalties when these works are reproduced and sold.
International Royalty Collection:
• PRS has reciprocal agreements with similar organizations worldwide, allowing them to collect royalties for performances of their members' works in other countries. Likewise, they distribute international royalties to their members when their music is performed abroad.
14
LICENSING & CONTRACTS COLLECTIONS
PRS Collects & distributes fees
COMPOSERS
Sign Contracts
PUBLISHING
Co Grant licenses
Distribution of Royalties:
• PRS collects royalties from various sources, including license fees paid by music users, and distributes them to their members. The distribution is based on various factors such as the frequency of performances, broadcast data, and reporting by music users.
Member Services:
• PRS provides services to its members, including music copyright registration, royalty tracking and reporting, industry advocacy, and support for music creators. They also offer resources and educational materials to help members understand royalty collection and music publishing.
It's important to note that PRS specifically represents music creators and rights holders in the United Kingdom. Other countries have their own collective management organizations that perform similar functions, such as ASCAP and BMI in the United States or APRA AMCOS in Australia.
MCPS Collects & distributes mechanical royalties
MU Protects musicians & producers
Composers
Acomposer is an individual who creates music by combining and arranging various musical elements such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and instrumentation. Composers are responsible for writing original musical compositions, which can encompass a wide range of genres and styles, including classical music, film scores, popular music, jazz, and more. Here are some key aspects of what a composer does:
Writing Original Music:
• Composers create new musical pieces, either instrumental or vocal, by composing melodies, harmonies, and rhythms. They craft the structure and form of the composition, making decisions about sections, transitions, and overall flow.
Musical Notation:
• Composers use musical notation to write down their compositions, typically using sheet music. This notation includes information about pitch, duration, dynamics, articulation, and other musical instructions to guide performers in interpreting and playing the music.
Instrumentation and Orchestration:
• Composers choose the instruments and voices that will perform their compositions. They consider the timbre, range, and expressive capabilities of different instruments to achieve the desired sound and emotional impact. This process is known as orchestration.
Collaboration:
• Composers often collaborate with performers, such as orchestras, bands, or individual musicians, to bring their compositions to life. They may work closely with performers during rehearsals to provide guidance and make adjustments to the music as needed.
15
Film and Media Scoring:
• Composers in the film and media industry create original music scores to accompany visual content. They compose music that enhances the emotional impact of scenes, supports the narrative, and complements the overall audiovisual experience.
Adaptation and Arrangement:
• Composers may also adapt or arrange existing musical works to fit different settings or ensembles. This can involve rearranging a piece for a different instrumentation or creating variations on existing themes.
Personal Artistic Expression:
• Composers bring their own creative voice and artistic expression to their work. They express emotions, explore musical ideas, and communicate through their compositions, often drawing inspiration from personal experiences, cultural influences, or the world around them.
It's worth noting that composers can have diverse backgrounds, training, and styles. Some composers may specialize in specific genres or eras, while others may experiment with innovative techniques and genres.
Publishing Company
Apublishing company, in the context of the music industry, is a company that focuses on the administration and exploitation of musical compositions and their associated rights. Music publishing companies play a vital role in managing the business aspects of music composition, including the collection of royalties, licensing, and promotion. Here's an overview of what a music publishing company typically does: Administration of Copyrights:
• Publishing companies help composers, songwriters, and music creators protect and administer their copyrights. They assist in registering compositions with copyright offices, ensuring that the rights to the music are properly established and maintained.
Royalty Collection:
• Publishing companies actively collect royalties on behalf of their composers and songwriters. They monitor and track the usage of musical compositions in various contexts, such as radio airplay, streaming services, live performances, and synchronization in audiovisual productions. They work with performance rights organizations (PROs) and mechanical rights organizations to collect and distribute royalties to the rights holders.
Licensing and Permissions:
• Publishing companies handle licensing of musical compositions for various uses. This can include granting mechanical licenses for reproduction and distribution of compositions, synchronization licenses for use in films, TV shows, commercials, and video games, and public performance licenses for live performances and broadcast usage. They negotiate the terms of these licenses and ensure that the appropriate permissions and fees are obtained.
16
Royalty Distribution:
• Publishing companies calculate and distribute royalties to the composers and songwriters they represent. They use performance data, royalty statements from PROs and other sources, and their own tracking systems to allocate royalties based on the usage and popularity of compositions.
Promotion and Creative Support:
• Publishing companies may actively promote their catalog of compositions, seeking opportunities for placements in films, TV shows, advertisements, and other media. They may also provide creative support and guidance to composers and songwriters, assisting in the development of their careers and connecting them with other industry professionals.
Catalog Management:
• Publishing companies maintain and manage a catalog of musical compositions. They handle the administrative tasks associated with adding new compositions to the catalog, tracking changes in ownership or copyright splits, and ensuring accurate data and metadata for each composition.
Copyright Licensing Enforcement:
• Publishing companies monitor and enforce copyright licenses to protect the rights of the composers and songwriters they represent. They take action against unauthorized use or infringement of copyrighted works, which can include issuing cease-and-desist letters or pursuing legal actions if necessary.
Publishing companies play a crucial role in helping composers and songwriters monetize and protect their musical creations. They handle the business side of music composition, allowing creators to focus on their artistic work while ensuring that they receive fair compensation for their musical contributions.
MCPS. Mechanical Copyright
MCPS stands for Mechanical Copyright Protection Society. It is a collective management organization that operates in the United Kingdom and represents the mechanical rights of music publishers and songwriters. MCPS is responsible for licensing and collecting royalties for the reproduction and distribution of musical compositions in various formats. Here are some key points about MCPS in the music industry: Mechanical Rights:
• Mechanical rights refer to the right to reproduce and distribute copyrighted musical compositions. MCPS administers these rights on behalf of its members, who are primarily music publishers and songwriters.
Licensing:
• MCPS grants licenses to individuals, businesses, and organizations that wish to reproduce and distribute musical compositions in physical or digital formats. This includes licensing for the production of CDs, vinyl records, digital downloads, streaming services, and other forms of music reproduction.
Royalty Collection:
• MCPS collects royalties from licensees on behalf of its members. This includes mechanical royalties, which are payments made for the use of compositions in physical or digital reproductions. MCPS tracks the usage of musical compositions and ensures that the appropriate royalties are collected and distributed to the rights holders.
17
Protection Society
Distribution of Royalties:
• MCPS distributes the royalties it collects to its members. The distribution is based on the usage data provided by licensees, which indicates the number of reproductions and distribution channels involved. MCPS uses this data to calculate and allocate the royalties to the appropriate rights holders.
International Royalty Collection:
• MCPS has reciprocal agreements with similar organizations around the world, allowing them to collect royalties for the use of their members' compositions in other countries. This enables international royalty collection and distribution for global usage of musical works.
Work Registration:
• MCPS encourages its members to register their musical works with the organization. By registering compositions, members provide essential information that helps in tracking and distributing royalties accurately
It's important to note that MCPS primarily focuses on the mechanical rights of musical compositions. Performance rights, synchronization rights (music used in audiovisual productions), and other rights are typically managed by separate organizations, such as performing rights organizations (PROs) and synchronization licensing agencies. MCPS works alongside PRS for Music (Performing Rights Society), which represents the performing rights of composers, songwriters, and publishers in the United Kingdom. Together, MCPS and PRS for Music provide comprehensive copyright management and licensing services for music creators and rights holders in the UK.
MCPS. Musicians Union
In the context of the music production business, "MU" refers to the Musicians' Union. The Musicians' Union is an organization that represents the interests of musicians and provides support and resources to its members. It is commonly found in countries like the United Kingdom (MU UK), the United States (AFMAmerican Federation of Musicians), and other regions.
The Musicians' Union offers a range of services, including legal advice, contract guidance, negotiation support, and lobbying for musicians' rights and fair treatment in the industry. They also provide access to professional development opportunities, networking events, and healthcare benefits for their members. Musicians' Union membership can be beneficial for music producers who work closely with musicians, as it can help ensure fair compensation, proper contracts, and overall protection of rights for both the producers and the musicians involved in a project.
18
How it all fits together 19

Inside the Groove Navigating the Music Industry

This publication by Coco & Cwtsh aims to throw light on the music industy and help you navigate the complexities of the various parts that make it work.






 Ffion Gruffudd Flockhart Coco&Cwtsh 2023
Ffion Gruffudd Flockhart Coco&Cwtsh 2023



















