4. FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE
4.1 History of forests and wildlife institutes

There are several forest research institutes in India offering various research courses and projects. One of the most popular forest research institutes in the country is Forest Research Institute which is located at Dehradun in Uttrakhand. Forest Research Institute Dehradun is regarded as one of the oldest in the respective field in India. in 1991, it was declared a deemed university by the University Grants Commission and is managed by the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE).
The forest research institutes in India are broadly classified into three categories which are - Institutes under India's Ministry of Environment and Forests, Institutes under the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education and Institutes Under state governments. There are various forest research projects and courses such as Environment Management, Forestry Management, Wood Science Technology, and others offered by forest research institutions in India.
4.2 Importance of Institutes in Conservation
Institute as a strategy to conserve biodiversity aims to provide critical, sensitive understanding of biodiversity science and the socio-economic political, cultural and institutional environment within which policies and decision making is done.
Biodiversity is best learnt in the place where it is situated which should be done with sensitivity and hence architecture becomes important aspect.
4.3 Forest Research Institute in India
No Forest Research Institute Name Location Forest Research Institutes under India's Ministry of Environment and Forests
1 Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun Dehradun, Uttrakhand
2 Govind Ballabh Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development, Almora Almora, Uttrakhand
3 Indian Institute of Forest Management, Bhopal Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh Forest Research Institutes under State Governments
4 Kerala Forest Research Institute Thrissur, Kerala
5 Forest College and Research Institute, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University Mettupalayam, Tamil Nadu
6 Forest Research Institute, Kanpur Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh Forest Research Institutes under the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education
7 Forest Research Institution Dehradun Dehradun, Uttrakhand
8 Arid Forest Research Institute, Jodhpur Jodhpur, Jaipur
9 Centre for Forest-based Livelihoods and Extension (CFLE), Agartala Agartala, Tripura
10 Himalayan Forest Research Institute, Shimla Shimla, Himachal Pradesh
11 Institute of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding, Coimbatore Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu
12 Institute of Wood Science and Technology, Bangalore Bengaluru, Karnataka
13 Tropical Forest Research Institute, Jabalpur Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh
14 Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy, Dehradun Dehradun, Uttrakhand
15 National Institute of Animal Welfare, Faridabad Faridabad, Haryana
16 Advanced Research Centre for Bamboo and Rattan Aizawl, Mizoram
17 Centre for Forestry Research and Human Resource Development Chhindwara, Madhya Pradesh
18
Centre for Social Forestry and EcoRehabilitation Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh

19 Institute of Forest Biodiversity Hyderabad, Telangana
20 Institute of Forest Productivity Ranchi, Jharkhand
21 Rain Forest Research Institute Jorhat, Assam



5. CASE STUDY
5.1 Forest Research Institute
Location - Dehradun, Uttarakhand
Built by - Sir C.G. Blomfield
Style - Greco-Roman and Colonial styles of architecture
Area - 7 acres

Is an institute of the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education and is a premier institution in the field of forestry research in India. It is located at Dehradun in Uttarakhand, and is among the oldest institutions of its kind. In 1991, it was declared a deemed university by the University Grants Commission

This organization has led to the evolution of scientific forestry not only in our country but the entire Indian Subcontinent.
it is the home to a large amount of biodiversity including some endangered species of flora and fauna. It stores an impressive research history in the field of forestry of more.
a) Aim and objectives of the Institute
• Conservation of biodiversity
• Production, certification and supply of quality seeds of fuel, fodder and timber species.
• Social forestry/ Agroforestry.

• Conservation and eco-restoration of ecologically fragile and disturbed areas.
• Utilization of non-conventional woods and weeds for manufacture of forest products.
• Development of technology for reclamation of wastelands.
• Planting stock improvement program of different species.
• Geological, geomorphological and micro-morphological studies on sketetal and sodic soils.
• Reclamation and ecological monitoring of mined areas.
• Development of technology for eco-friendly preservatives.
• To impart education in such branches of forestry and environment as it may deem fit.
• To provide for research and for the advancement of and dissemination of knowledge in the forestry and environment. The disciplines pursued in the Institute are Silviculture, Resource Survey and Management, Social forestry, Minor forest produce, Ecology and conservation, Genetics and tree propagation, Forest protection, Forest Botany, Forest products and Forest Operations. The thrust areas are bio-diversity, tree improvement & quality seed production, non-wood forest products, social forestry & wasteland afforestation, design development of modern forestry tools, etc.
• To create consciousness about forest and environment among the people through extension programs.
• To do all such other acts and things as may be necessary or desirable to further the safeguarding of environment and protection of forest & wildlife.
• The Institute caters, in particular, to the research needs of the Indo-Gangetic plains of Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh, Delhi and Western Uttar Pradesh, as Well as the U.P. Himalayas. Forest research at the FRI is organized under fourteen divisions.
b) Programs
• laboratories, library, herbarium, arboreta, experimental field area for research, computer lab, botanical museum
• The place is dedicated for studying the plants, animals, climate and topography of the Himalaya




• The Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy and the head office of the Indian Council of Forestry Research are also housed in its premises.


• This building houses six museums related to forestry, which include museums on social forestry, pathology, silviculture, timber, non-wood forest products and entomology.
• the place also houses a Botanical Garden, which is a popular picnic spot among travelers
• The other 4 museums designed in the British era with heavy display cases and handwritten labels

c) Architecture

The institute’s main building is an impressive example hybrid architecture of GrecoRoman and Colonial styles of architecture, with a plinth area of 2.5 hectares.
The main façade of the building is almost 1,000 ft long
The building was listed for a time, in the Guinness Book of Records, as the largest purely brick structure in the world.
The main parking and ticket counters are on the eastern side/back of the FRI building
Blomfield had earlier worked with Edwin Lutyens on many projects in Delhi. Thus, the Lutyen’s touch to the forest research institute’s architecture can’t be missed. In fact, I would say that the courtyards are archetypal of Indian and oriental architecture,too.


Groin vault is a long tube of arches.
A large central avenue bisects the lawns, while the Tons river forms the northern boundary of the campus.

There are Domed towers built on both side of the central entrance.
The entrance leads to the convocation hall with elegant wooden interior


The Pediment is again very typical of the classical architecture. The triangular area enclosed the pediment known as the tympanum, some of them have an ovel-shaped vent, covered with glass.
The windows on the ground floor are huge and on the 1st floor are smaller, It is a typical feature of colonial architecture.


Wood and brick interiors with symmetrical layout are used in FRI according to British architectural style

There are 6 central courtyards, surrounded by wide corridors on all sides. These open to various museums, washrooms and offices.




TSC - Ticket sale counter I C - Information centre
M-1 - Social forestry museum M-4 - Timber museum
M-2 - Forest pathology museum M-5 - Non wood forest products museum
M-3 - Silviculture museum M-6 - Entomology museum
Classical architectural form such as Arcaded and airy corridors are designed around the courtyards

The FRI is made entirely of bricks. The bricks and mortar used in forest research institute are arranged in repetitive patterns





The drain pipe look rust-free and intact.

d) Research, Activities and Achievements

According to the present report, 410 mammal species are present in India. 13 of them are reported in FRI campus, including the top predator, the leopard. The presence of species like leopard in human dominated landscape invariably leads to some predation on domestic animals. They thrive on the abundant resources present in the FRI campus.











Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology gave the task to Forest Research Institute to develop a Biodiversity park. It was done under Forest Ecology and Climate Change Division. It was one of the best example of conversion of riverine ecosystem to Biodiversity park.

The Campus Bird Count is a significant component of GBBC which runs every year during 16-19th February. It is a coordinated effort of the volunteers to document the birdlife in multiple campus across India and Forest Research Institute (FRI) is a part of it. Campus Bird Count is a great way to introduce the student to birds and birding.

In 450 hectare area of FRI, a tremendous avian diversity was reported making the species count 186 in four days, which constitute important habitats for birds resulting in record of some new species such as, Sirkeer malkoha (Phaenicophaeus leschenaultii) and Short-toed snake eagle (Circaetus gallicus) reported in the FRI New Forest Campus. Documenting of avian richness was done in accordance with the protocol of eBird. Such events add to the cognizance of the students and inculcate the will to conserve nature, these events reveal the great biodiversity which is bestowed upon the campus of FRI.

Documenting of avian richness was done in accordance with the protocol of eBird. Such events add to the cognizance of the students and inculcate the will to conserve nature, these events reveal the great biodiversity which is bestowed upon the campus of FRI.


Research importance of understanding the intricate relationship between plants and why they grow where they grow. how a particular plant affected its immediate surrounding and in turn the entire ecosystem. The basic concepts of how slope, aspect, temperature, etc. effects the vegetation were also explained to us. Along the way, many species were identified at Maldevta which is approximately 25 km from Dehradun city such as Rumex hastatus, Adhatoda vasica, Lantana camara, Pogostemon benghalensis, Woodfordia fruticosa, Mallotus philippensis.
The wetland of the Asan and Yamuna Rivers covering an area of 4.44 sq km. The wetland is listed as an Important Bird Area and serves as a prominent wintering spot for migrating birds. The birds listed as globally threatened species and in the IUCN Red Data Book have been observed at Asan.

Asan Wetland Conservation Reserve, Uttarakhand Situated at the confluence of the rivers Yamuna and Asian is an important transition zone between riverine and forest ecosystems. Forest Research Institute was aimed to understand wetland ecology with special reference to avian and plant diversity
e) How to reach
Distance from main town is 5km
Connected by buses, taxis, cars and autos within 30 min
5.2 Wildlife Institute of India


Ownership
It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate change, Government of India.
Research Areas
Biodiversity, Endangered Species, Wildlife Policy, Wildlife Management, Wildlife Forensics, Spatial Modeling, Ecodevelopment, Ecotoxicology, Habitat Ecology and Climate Change.
Research Facility
Forensics, Remote Sensing and GIS, Laboratory, Herbarium, and an Electronic Library.
Founder
V. B. Saharia while the first Director was Hemendra Singh Panwar who remained the director from 1985 to 1994.
a) Mission
To nurture the development of Wildlife Science and promote its application in conservation, in consonance with our cultural and socio-economic milieum







b) Aims and objectives
● Build up scientific knowledge on wildlife resources.
● Train personnel at various levels for conservation and management of wildlife.
● Carry out research relevant to management including the development of techniques appropriate to Indian conditions.
● Provide information and advice on specific wildlife management problems.

● Collaborate with international organizations on wildlife research, management and training.
c) Courses offered in the institute
• Masters in Wildlife science
• Advanced Wildlife Management at diploma and Post grad level.
• Heritage conservation and management
• Other short-term courses
d) Programs
Lecture room, museum, library, computer lab, research lab, forensics lab, meeting hall, seminar hall, auditorium, guest house, dining hall, kitchen, artificial lake, nature trail




e) Various departments in the institute



• Animal Ecology and Conservation Biology: This department is dedicated to gaining an understanding of the ecology of wild fauna and their conservation issues. This discipline cuts across subject areas of animal population ecology, behavioral ecology, biogeography, community ecology, trophic interactions, systematics, conservation genetics and meta-population dynamics. The department also strives to use modern technology, development of methods for monitoring animal populations, and survey of rare and elusive species.
• Ecodevelopment Planning: Ecodevelopment is a multi-disciplinary and multi-stakeholder strategy to link the conservation values of protected areas (PAs) with the livelihoods of local people and development processes in the surrounding landscapes.
1. To develop an understanding of the issues involved in community participation in wildlife conservation.

2. To build the capacity of the state forest departments and other stakeholders in involving local communities in PA management while working with multiple stakeholders to arrive at a consensus for integrating conservation and development at the landscape level.

• Endangered Species Management: The Department of Endangered Species Management (ESM) has the mandate to work for the conservation of rare and endangered species of India through status surveys, research, monitoring, development of conservation action plans and advocacy.
• Habitat Ecology is a fascinating area of natural sciences that helps to advance our understanding of the interactions that determine the distribution and abundance of organisms. This knowledge is essential to refine our conservation efforts and management decisions for wildlife species and their habitats.
• Landscape planning and Management: The Department of Landscape Level Planning and Management was established to stimulate interest and capacity in this respect by offering training modules for managers and biologists in landscape ecology, landscape level policy development and human–wildlife interface options. The department has both field managers and biologists, providing for integration of different perspectives towards translating theoretical models to practical management solutions. The faculty members are involved in research and training programs in a variety of landscapes, providing new dimensions to wildlife management in the country.
• Wildlife health management: The department provides veterinary medical services to wildlife managers, biologists and veterinary specialists in projects where ecological studies on endangered species require highly professional services for immobilization, restraint and telemetry in wildlife. The department coordinates activities with several veterinary medical institutions for investigation, monitoring, researching and controlling diseases affecting the health and survival of wildlife and livestock across the country.

5.3 California Academy of Sciences


Architects - Renzo Piano
Location - Golden Gate Park, San Francisco, United States
Category – University
Project Year - 2008

• one of the few institutes of natural sciences in which public experience and scientific research occur at the same location.

• The entire 37,000 sq. m complex is like a piece of the park that has been cut away and lifted 10 m up above the ground.
• All concrete contains 30% fly ash, a by-product of coal-fi red power plants. It also contains 20% slag

• The choice of materials, recycling, the positioning of the spaces with respect to the natural lighting, natural ventilation, water usage, rainwater recovery and energy production: all of these design issues became an integral part of the project itself, and helped the museum obtain LEED platinum certification.



• California Academy of Sciences Discovers Hundreds of New Species in the Philippines California Academy of Sciences uncovered more than 300 new species. The discovery included new species of plants and fish, as well as numerous crabs and a unique species of shark.
• The two main domes cover the planetarium and rain forest exhibitions. all the functions laid out around a central courtyard exhibition space, Natural History Museum, African Hall, the North American Hall, Steinhart Aquarium, planetarium, research offices, dioramas, house exhibit and teaching spaces, café, retail store, research library, laboratories, Storage facilities, offices
• The roof is flat at its perimeter and, like a natural landscape, becomes increasingly undulating as it moves away from the edge to form a series of domes of various sizes rising up from the roof plane.
• These hills, which feature slopes in excess of 60 degrees, will draw cool air into the open Piazza at the center of the building, naturally ventilating the surrounding exhibit spaces.


• The domes are speckled with a pattern of skylights automated to open and close for ventilation.

a) Main Lobby

The space also features two-story columns, customizable flat screens, and floor-toceiling windows. Impressive Tyrannosaurus Rex skeleton at the centre of lobby, with the information desk to yourleft and the academy store and photo services to your right.



live entertainment, presentations, DJs, and proms, the Piazza of the California Academy of Sciences is an open-air space for fair-weather events. Glass walls and ceilings allow for views of the evening sky and surrounding exhibits. Four large trees feature prominently in the space, which is. Well suited to creative decor


Seated






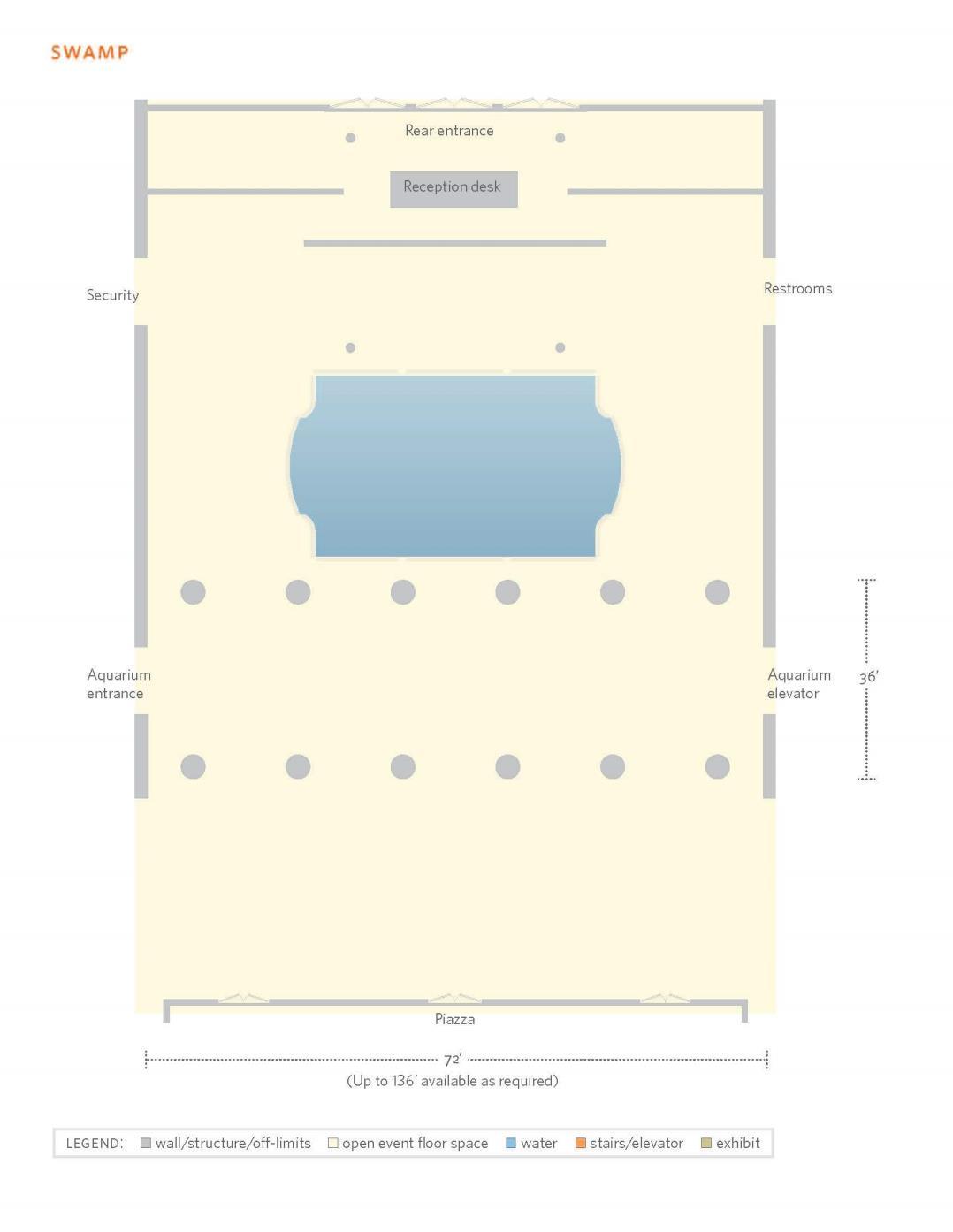
d) Swamp

Featuring tall columns and other impressive architectural elements, the Swamp at the California Academy of Sciences is ideal for seated dinners and presentations during the events. turtles, colourful freshwater fish & the albino alligator highlighting ecosystems of the South eastern United States.


e) East & West Halls
east halls are interactive exhibitions and live animals.it combines well with the adjacent African Hall space.

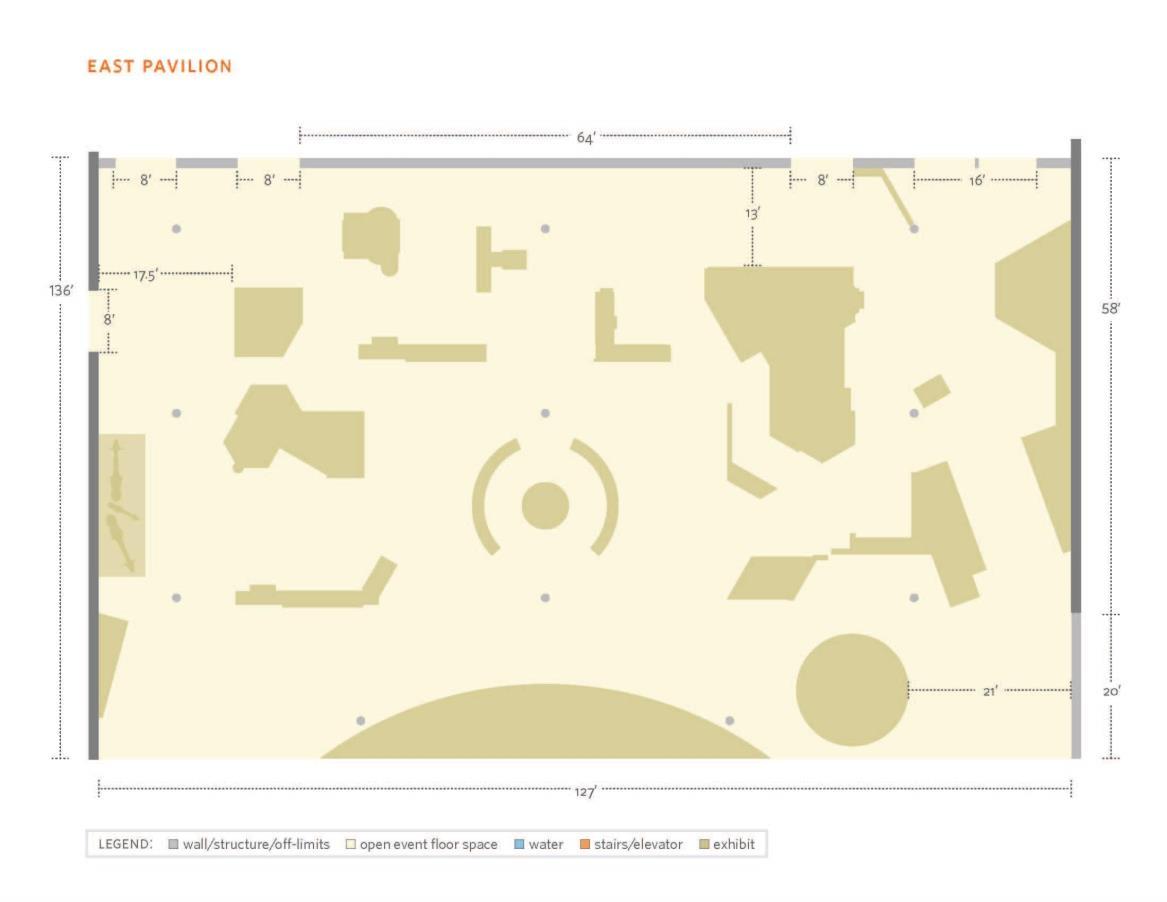
The West Hall space features immersive natural history exhibits and views into the Rainforest and the West Garden. Garden terrace included.

f) Osher Rainforest

Osher Rainforest spectacular 90-foot-diameter glass dome. More than 1,600 live animals reside in rainforest dome. Four story rainforest contains free-flying birds to exotic reptiles, amphibians, golden silk orb-weaver spiders, and enormous Amazonian fish. The rainforest's living plants include trees like the Brazilian beauty leaf and West Indies mahogany etc.
Strategically placed skylights will automatically open and close to allow heat to escape through the tops of the domes. These skylights will also allow sunlight to reach the living rainforest and coral reef exhibits below, reducing the energy requirements for artificial lighting.



g) Kimball Natural History Museum
Natural History Museum explores some of the most significant discoveries as well as T. rex and 87-foot-long blue whale skeleton.

h) Steinhart Aquarium

Steinhart Aquarium is most biologically diverse and interactive aquarium. Home to nearly 40,000 live animals, representing more than 900 unique species it offers guests view of underwater


Seated capacity: 100

i) Moss Room

Featuring a decorative rock wall, the California Academy of Sciences' Moss Room is an ideal location for luncheons, meetings, receptions, and more.


Square footage: 1,100
Seated capacity: 75+

j) Morrison Planetarium
75-foot dome displays digital Universes.


Square footage: 1,300

Theatre seating: 290

k) Tusher African Hall



African Hall, where you can compare fossils of early human ancestors. African landscapes & wildlife dioramas through the glass windows of their detailed displays.

l) Research & Training Facility



more than 100 dedicated scientists, researchers, and support staff. Together, we travel the world in our efforts to discover new knowledge about Earth's biodiversity, and to rapidly apply that knowledge to a wide range of protections.








n) Board Room
The board room is an intimate space well suited for lectures, presentations, and seated or buffet lunches. Tables and chairs included, along with state-of the-art (audio vision) capabilities and an adjacent reception area.


Square footage: 1,250


Reception capacity: 120
Seated capacity: 70
o) Living Roof

Living Roof providing 2.5 acres of habitat of native species. Allows the guest to view golden gate park from the observation deck at 360 degree. This “living roof” is covered with 1,700,000 selected native plants species planted in specially conceived biodegradable coconut fibre containers


The soil’s moisture, keeping interior temperatures about 10 degrees cooler than a standard roof and reducing low frequency noise by 40 decibels.thus avoiding the need for air-conditioning in the ground-floor public areas and the research offices along the facade.It absorb about 98% of all storm water, preventing up to 3.6 million gallons of runoff each year.

p) East Garden



The East Garden at the California Academy of Sciences is an outdoor space that features sculptures and the beauty of Golden Gate Park. Photovoltaic cells are contained between the two glass panels that form the transparent canopy around the perimeter of the green roof, they provide more than 5% of the electricity required by the museum. Glass is used extensively in the exterior walls, allowing visitors to look through the museum to the surrounding green space


q) Terrace


Terrace is freestanding steel and glass cafe building located in the West Garden. The structure is sited at the south end of the existing garden using its placement and simple form to visibly connect the interior of the café to the museum.

Square footage: 5,000

Seated capacity: 200+
Piano’s goal was to create a sense of transparency and connection between the building and the park through both a careful selection of materials and a thoughtful arrangement of space.

The lightweight roof form and translucent back wall allows to view of museum, implying one continuous space. Two tall all-glass sliding doors along the entire length of two sides can open completely for a direct connection between inside and out, and offer an enjoyable al fresco dining experience. Skylights allows natural light and blue shadow boxes made of recycled resin recall a bright blue sky even on the foggy days.




5.4 Comparative table of case studies
INSTITUTES IN INDIA
Institute Name Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun
Kerala Forest Research Institute Forest Research Institution, Dehradun
M.Sc. And Ph.D. Courses
Biodiversity hotspot location
M.Sc. And Ph.D. in Wildlife Science Wildlife management, Forest Management, Botany, Ecology, Zoology, Entomology
M.Sc. And Ph.D. in Forestry
Wildlife management, Zoology, Botany
Himalaya
Amenities & Facilities laboratories, museum, computer lab, library, meeting hall, auditorium, guest house, dining hall, kitchen, artificial lake, nature trail
Institute Name
Research Courses
Forest Management, Zoology, Botany, Geology, Entomology

Western Ghat Himalaya
laboratories, museum, library, lecture hall, seminar hall, meeting room, computer lab, herbarium, arboretum, guest house, nurseries, green house,
INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE
California Academy of Sciences
laboratories, museum, computer lab, library, lecture hall, herbarium, arboreta, experimental field area for research, Botanical Garden
Biodiversity Science, anthropology, marine, biology, botany, entomology, herpetology, ichthyology, invertebrate zoology, mammalogy, ornithology, geology, and paleontology
Amenities & Facilities laboratories, lectures & workshops area, exhibitions area, museum, aquarium, dining area, lecture hall, meeting, dry and wet collection roof garden, cafe
