
3 minute read
Chapter 10: Searching and evaluating
CHAPTER 10
Searching and Evaluating
LEARNING INTENTION
To learn steps to efficiently search for and evaluate sources.
LEARNING OUTCOME
2.3 Search the internet to gather information on a specific topic of interest.
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
Classroom Based Assessments make up a big part of the new Junior Cycle and an important aspect of all these assessments across every subject is research. The internet has a lot of information on it and you need to be able to navigate it and decide what makes your research good. Knowing how to search the web appropriately and efficiently is a useful skill to develop not only for the Junior Cycle but also for life. The language used to describe research terms can be difficult for students to understand at first.
SAMPLE

MATERIALS
Digital devices with internet access eLearning platform: Microsoft Teams, Google Classroom Microsoft Word RTE article: https://www.rte.ie/sport/soccer/2020/0831/1162365-forget-barca-or-city-well-do-it-ourway-randolph/
ACTIVE LEARNING METHODOLOGIES
Debate Paired research Reflection journal
PRACTICAL SKILLS
Online dictionary Snipping tool Searching the internet using operators Referencing
OBJECTIVES
By the end of this chapter students will be able to:
Define
Valid In-depth Sources Describe Debate Explain Evaluate Create Effective questioning Accurate Appropriate Varied Preliminary research Clickbait Domain name How to search the internet effectively using operators How different domain names (.com, .gov) affect the information given Whether Wikipedia should be allowed as a source Research terminologies The sources that are generally more reliable and accurate A referencing form SAMPLE
ACTIVITY 1: ONLINE DICTIONARY Using an online dictionary such as www.dictionary.com students will look up the search terms in the table below and then copy and paste the definitions into the table.

ACTIVITY 2: USE EACH OF THESE RESEARCH TERMS IN A SENTENCE. Alternatively, students could find sentences online and use the snipping tool to copy and paste the sentence into the spaces below.

Example: I didn’t agree
with my friend but the arguments she made were valid.
SAMPLE
ACTIVITY 3: SEARCH TERMS
i) Which phrase is the most appropriate to look up if you are doing a research project on the relationship between Religion and Science? Highlight the correct one.
a. Religion vs Science
b. “Religion” and “Science”
c. Religion and science
ii) Translate the following search phrases into sentences
Romeo+Juliet
+Shakespeare-Romeo

+Germany history-Hitler Ask the students to Google search the sentences they had translated to demonstrate how many results are returned versus the search term. ACTIVITY 4: PAIRED RESEARCH In pairs, students will choose a topic they are interested in. Try to find sources from each of the different domain names on your topic. Remind students to use operators when creating their search terms for the best results.SAMPLE


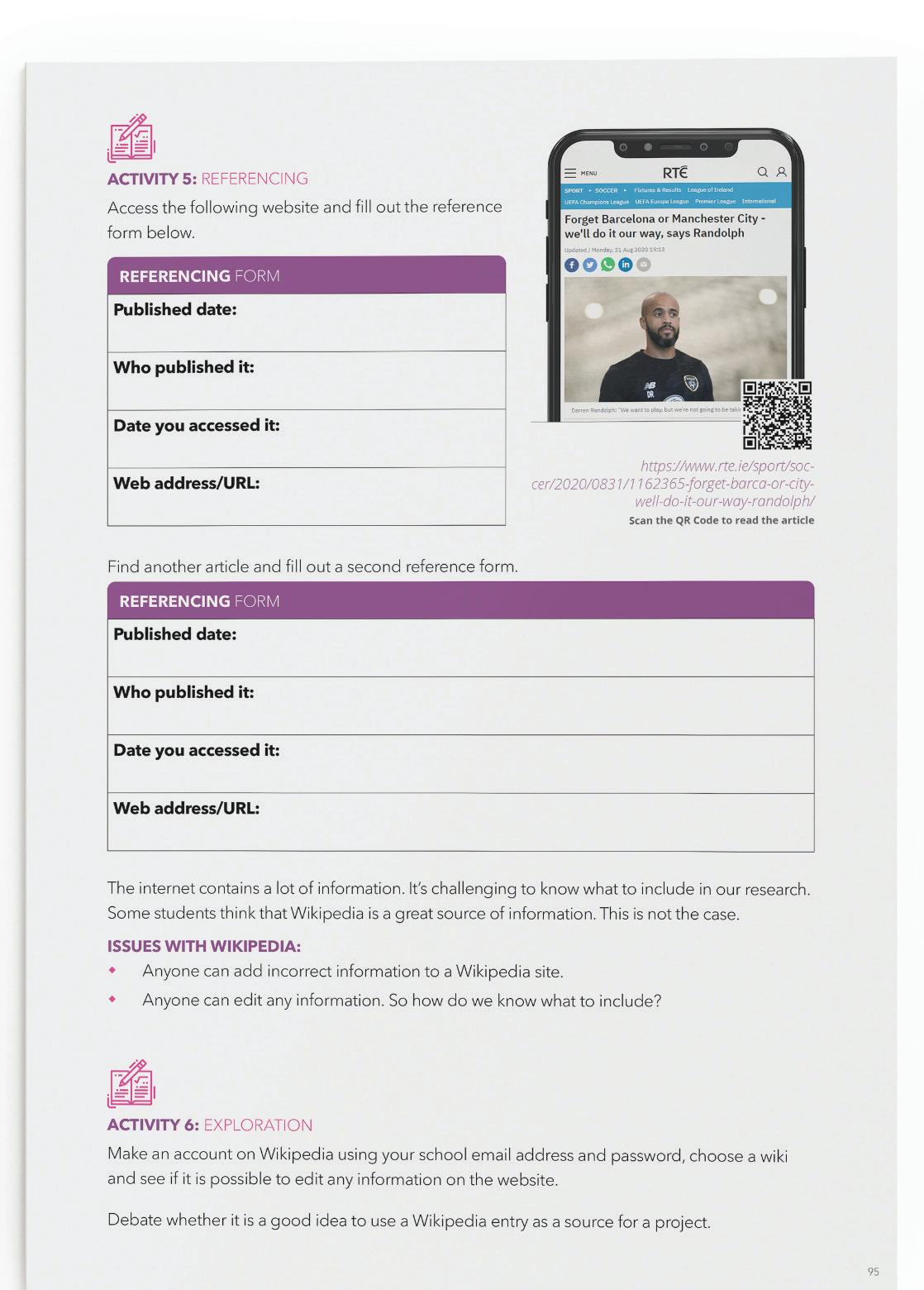
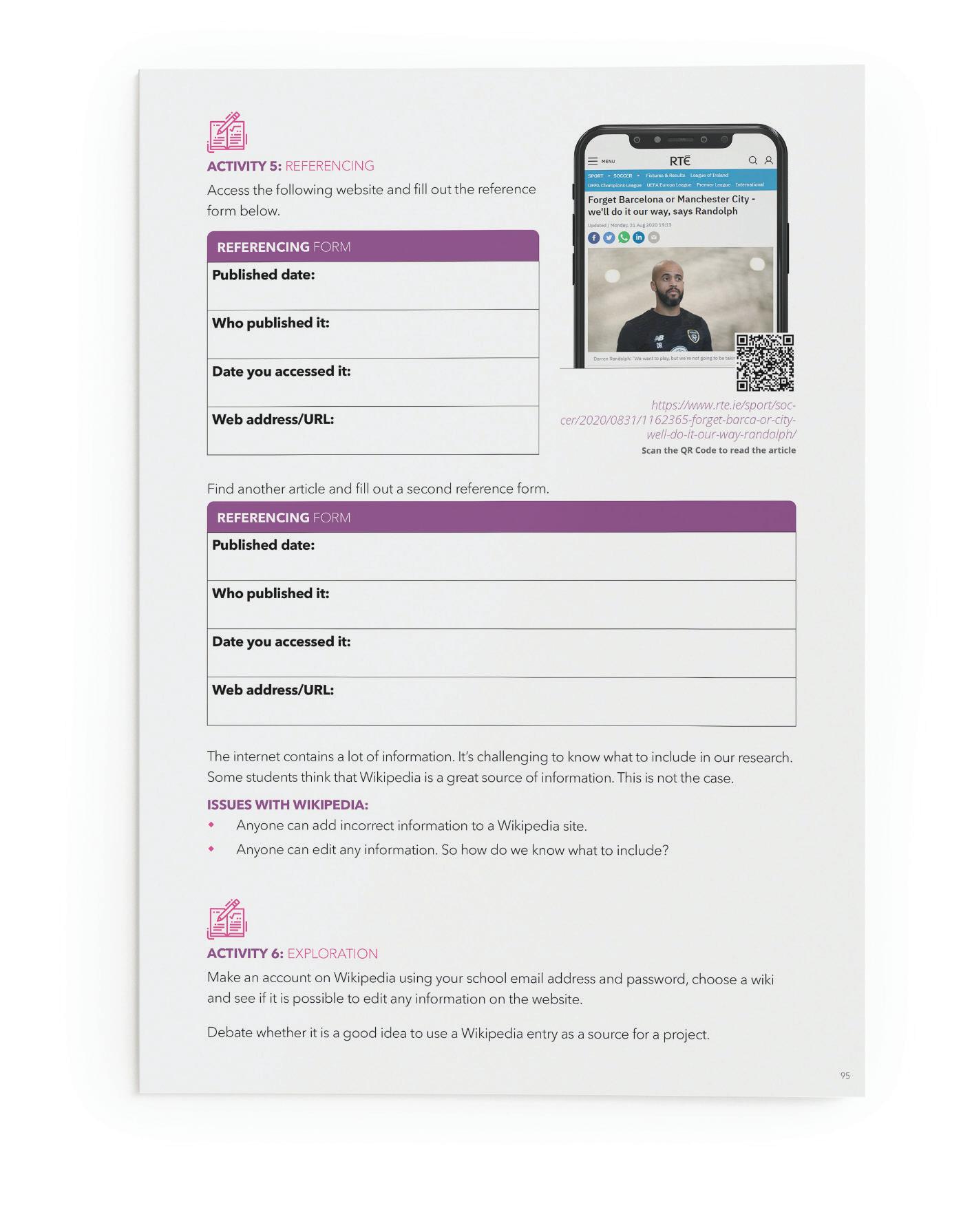
ACTIVITY 5: REFERENCING Students will access the following website and fill out the reference form.
31/08/2020
By Anthony Pyne, RTE Sport journalist
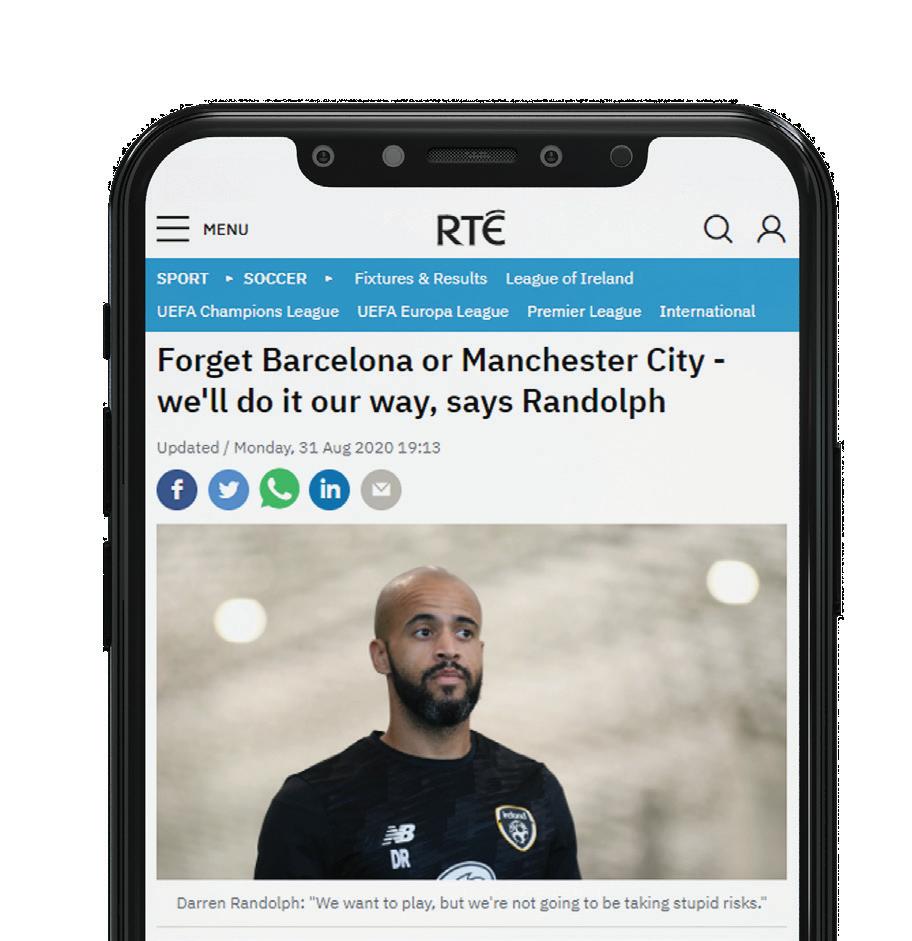
https://www.rte.ie/sport/soccer/2020/0831/1162365-forget-barca-or-citywell-do-it-our-way-randolph/
Scan the QR Code to read the article
31/08/2020
www.rte.ie/sport/soccer/2020/0831/1162365forget-barca-or-city-well-do-it-our-way-randolph/
Students will find another article and fill out a second reference form. ACTIVITY 6: EXPLORATION Students will set up an account on Wikipedia using their school email addresses and passwords, choose a wiki and see if it is possible to edit any information on the website. Students will then debate whether it is a good idea to use a Wikipedia entry as a source for a project.SAMPLE PAUSE & REFLECT In your reflection journal describe: Three things you learned in this section Two things you already knew One thing you would like to learn more about










