
3 minute read
Chapter 16: Media formats
CHAPTER 16
Media formats
15k

LEARNING INTENTION
Compare and contrast different media formats and analyse what information gets distributed.
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
LEARNING OUTCOME
3.2 Analyse how the choice of digital media format influences the kind of information accessed/ transmitted. All digital media content is created by a person who decides what to leave in and what to take out. This will influence the style and substance of the content and determine how it is presented to the intended audience. Understanding the theme, purpose and intended audience can help us become more informed consumers. Another way we can analyse digital media is by examining how it is distributed to the public. Media can be classed as formal or informal. Formal media outlets are traditional ways of receiving information, such as online newspapers and government websites. Informal media outlets are less traditional ways of receiving information such as blogs, vlogs, social media and YouTube videos.
SAMPLE
MATERIALS
Digital devices with internet access eLearning platform: Microsoft Teams, Google Classroom Microsoft Word Mentimeter.com Flip chart paper
ACTIVE LEARNING METHODOLOGIES
Reflection journal Digital brainstorm Think-pair-share Flip chart Paired research
PRACTICAL SKILLS Venn diagrams
OBJECTIVES
By the end of this chapter students will be able to:
Define
Digital media formats Formal media Informal media
Describe Why organisations use multiple digital formats to spread the same information How digital influencing works The differences between formal and informal media
Explain How digital influencing works How our choice of digital media formats influences the type of information we receive
Evaluate How different media outlets report on the same news story.
Create Venn diagram SAMPLE
ACTIVITY 1: BRAINSTORM Using mentimeter.com students will brainstorm:
1. Formal media that you receive information from.
2. Informal media that you receive information from.
Let’s look at two examples of how Governments use different media formats to educate the public about Covid19. These digital advertisements are not designed to help governments make money. Instead, the purpose of these adverts is to influence and educate the public about a global pandemic.
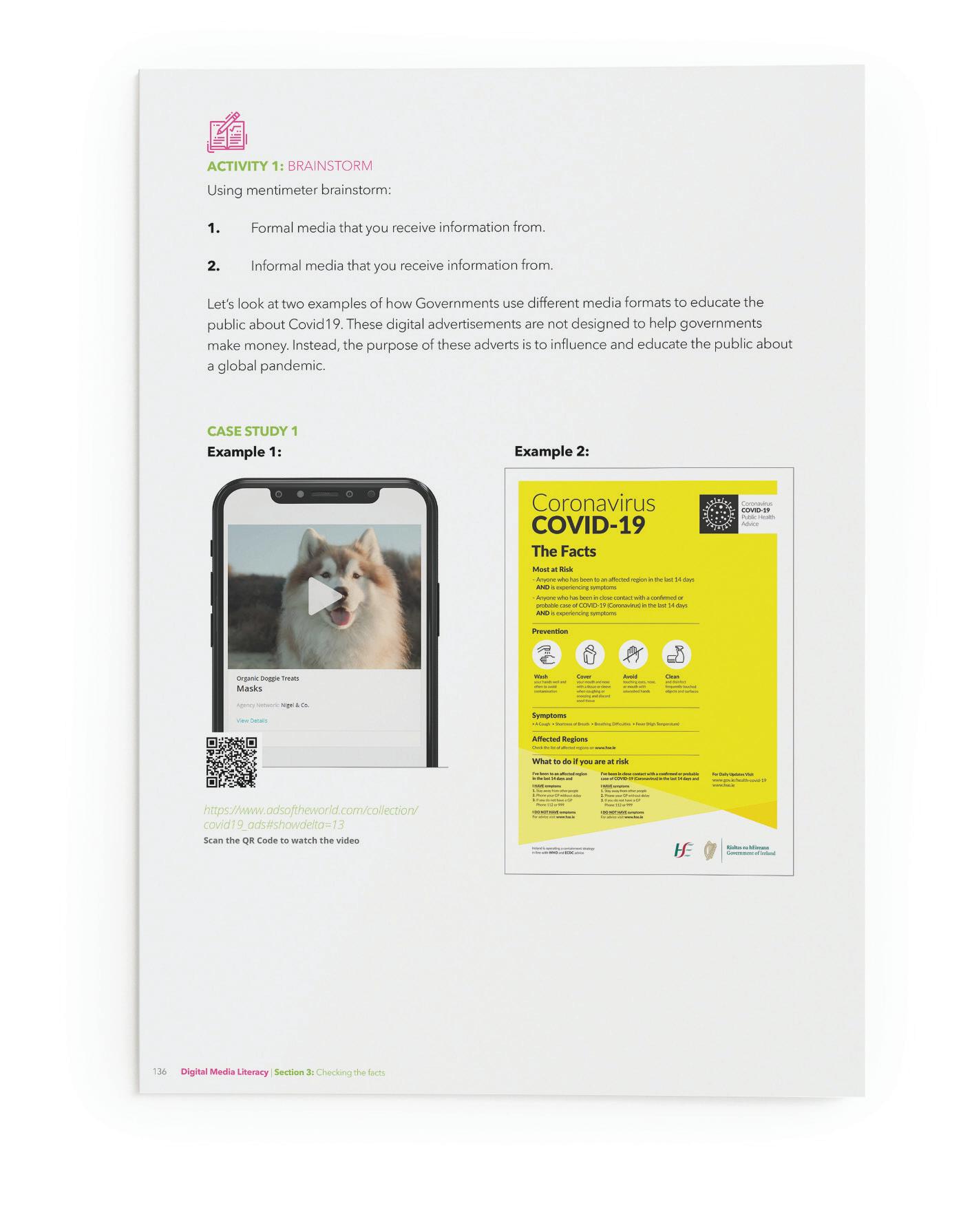
ACTIVITY 2: THINK-PAIR-SHARE Case study one uses one formal and one informal technique to try and spread awareness and advice about the coronavirus pandemic.
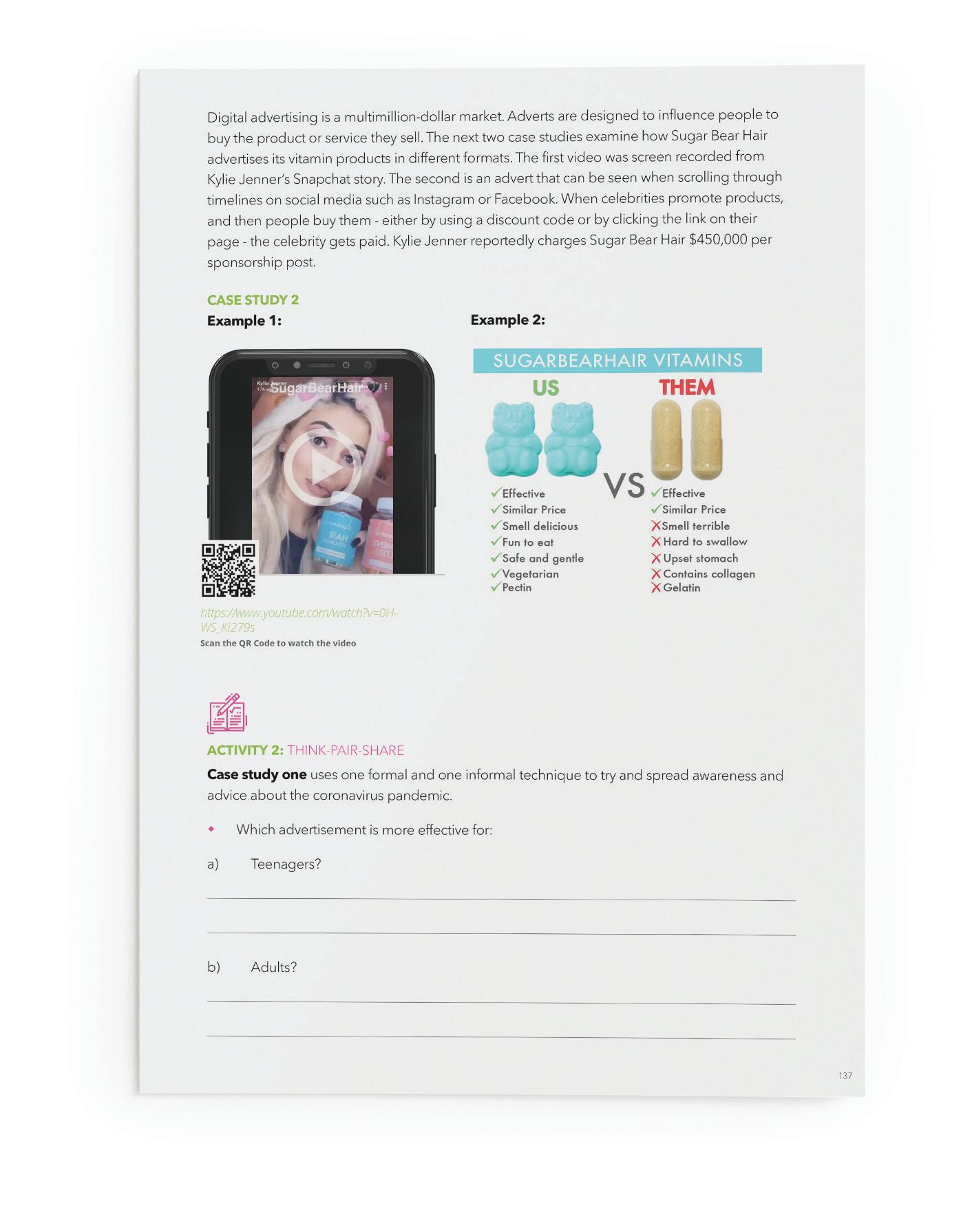
Which advertisement is more effective for: a) Teenagers? b) Adults? Case study two also uses two different formats to influence people to buy their products. One employs an influencer, and the other advert can be seen on traditional news websites. Why, in your opinion, does Sugar Bear Hair advertise using: a) online influencers? b) formal marketing techniques? Who is the intended market for this product? In your opinion, which of the adverts is the most effective?
SAMPLE
ACTIVITY 3: VENN DIAGRAM Students will create a Venn diagram to compare (similarities) and contrast (differences) the information received from one of the case studies.

DIGITAL MEDIA LITERACY for Secondary Students www.4schools.ie Creating a basic Venn Diagram TUTORIAL: VENN DIAGRAMSAMPLE

https://vimeo.com/578089538/58fa5ab74c
Scan the QR Code to watch the video
ACTIVITY 4: FLIP CHART In groups of 4, students will draw a table on flip sheet paper and determine some differences between the two articles.
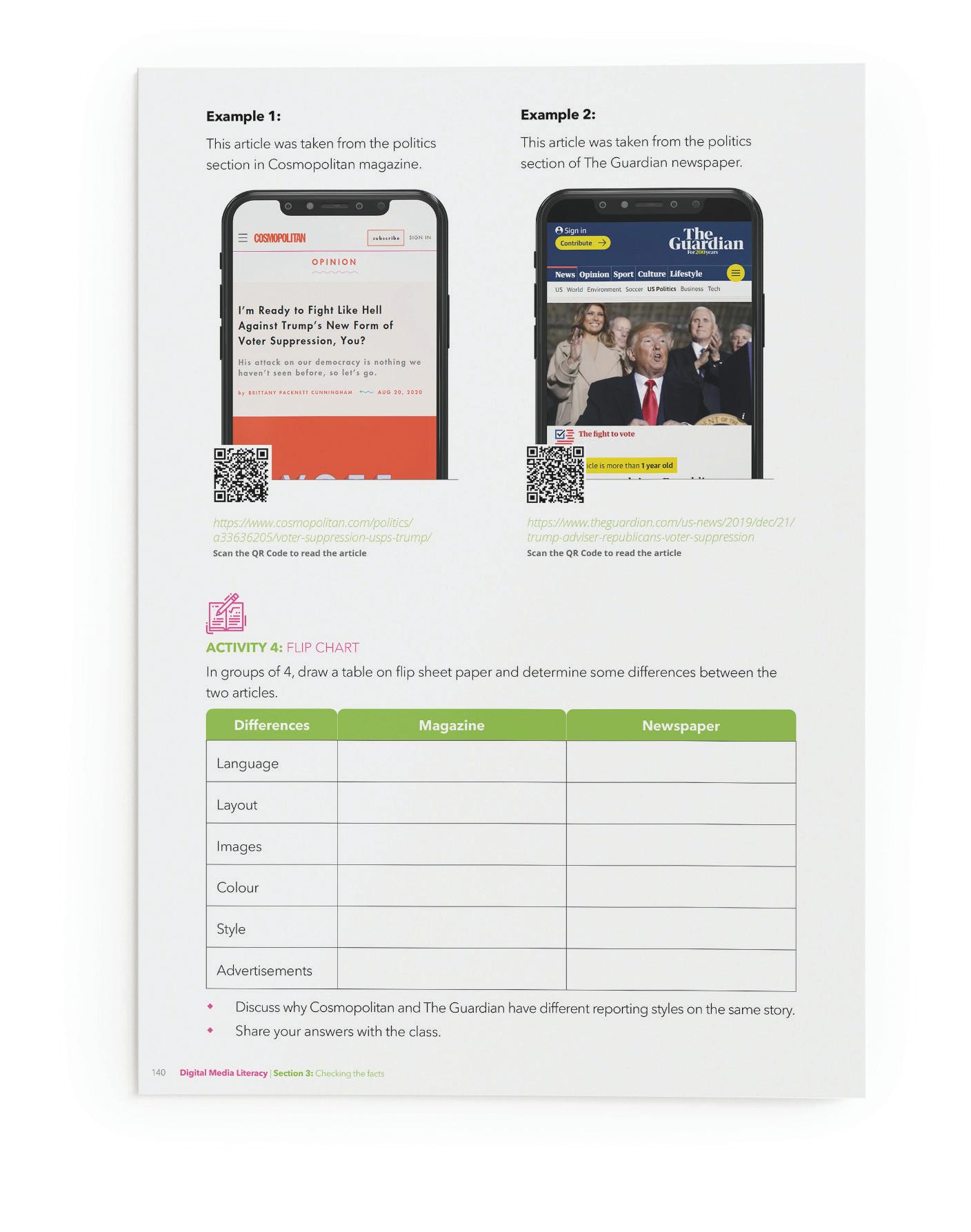
ACTIVITY 5: EXPLORATION Students will find examples online of different media formats that deal with the same topic. They can look at: Government websites Adverts and influencers Newspaper versus magazines PAUSE & REFLECT In your reflection journal describe: SAMPLE Three things you learned in this section Two things you already knew One thing you would like to learn more about











