





In the exciting world of technology, with robots and computers taking center stage, learning how to talk their language is super important! From doctors using AI to diagnose diseases to scientists using robots to explore space—computers are everywhere! To keep up with this amazing age, just knowing how to use a computer isn’t enough. The bustling world of technology thrives on innovation, and that’s where artificial intelligence (AI) comes in.
Upon request from some schools, Uolo introduces the Artificial Intelligence (AI) series for Grades 9 and 10. The objective of this special series is to expose learners to essential elements in AI and introduce common domains and applications of AI to them. The series also introduces the fundamentals of AI through engaging activities that can be done in a computer lab or on a computer at home. Thus, this book serves as a gateway to explore its fascinating depths. Get ready to embark on an intellectual adventure as you unravel the mysteries of AI and its potential impact on your future.
Each book comprises a defined set of chapters, which have detailed theoretical explanations. The explanations of concepts have been designed keeping the context of learners in mind, so that the topics are relatable, engaging and exciting. The in-chapter activities offer students practical experience to various AI concepts and domains, facilitating a deeper understanding.
To reinforce takeaways of each chapter, the chapter-end summary includes key pointers of all that has been covered. This also provides a comprehensive overview of the entire chapter at a single glance. Comprehensive exercises at the end of each chapter include various question types, like fill in the blanks, true or false, multiple-choice, short answer, long answer, and application-based questions. To further enhance student proficiency, these chapters end with an unsolved activity which provides additional practice of the AI concepts.
We hope this series ignites the learners’ curiosity and empowers them to become informed participants in the ever-evolving world of AI.
Types
What do you think of when you hear or read the word ‘intelligence’? Mostly, you may think of the smartness within humans. But, did you know, these days, even machines have a built-in form of smartness?
For example, you must have used Google Maps to find your way home or got recommendations on streaming platforms like Netflix or YouTube, based on your viewing history. Have you ever wondered where these technologies get their intelligence from? That’s where AI comes into the picture. AI enables machines to be smart, solve problems, and handle various tasks automatically.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a branch of computer science that deals with the study of the principles, concepts, and technology of building machines that enable them to think, act, and learn like humans.

AI has become an essential part of our daily life, making certain tasks more efficient, personalised, and entertaining. Let us explore some amazing applications of AI that we experience in our daily life.
Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Google Assistant are all examples of virtual assistants that use AI to understand and respond to our voice commands. They can set reminders, answer questions, play music, provide weather updates, and even control smart devices in our homes.

Streaming services like Netflix and music platforms like Spotify use AI algorithms to analyse our preferences. They recommend films, shows, or songs based on time spent watching certain content, frequently played songs, and feedback given through ratings, making content suggestions as per the user’s preferences.
The facial recognition technology on our smartphones is powered by AI. It makes use of computer vision to recognise our faces using the front camera, allowing us to unlock our phones with ease and security.



AI plays a significant role in the gaming industry. Many video games use AI to control the behaviour of the computer-controlled characters to make them act intelligently, and adjust to your strategy. AI can also create dynamic environments, improving the gaming experience.
AI is used in medical diagnostics, helping doctors analyse medical images like X-rays and MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) more precisely. It assists in the early detection of diseases and leads to more effective treatment procedures.
Autonomous vehicles are self-driven vehicles. The AI algorithms in them analyse data from their sensors and cameras to build an understanding of the vehicles’ surroundings. This helps in navigating and making real-time decisions on the road, ensuring safe and efficient transportation.


AI-powered translation apps, like Google Translate, are used to understand and translate text instantly, enabling us to communicate in different languages.
AI has seamlessly integrated into our everyday routines, improving various aspects of our lives. From entertainment and communication to healthcare and transportation, the applications of AI continue to evolve. This promises a future where technology plays an even more significant role in making our lives easier and more convenient.

AI does not do just one thing. It actually has different domains or areas where it can be used. The three main domains of AI are Data, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing (NLP). AI can help computers play games, recognise faces in photos, respond to our voice commands, etc.
Data is a collection of raw facts that can be transformed into useful information. It can be in the form of text, images, audio, or video.
AI learns from data, helping computers to improve themselves, thereby becoming smarter and more efficient. The more the data, the more intelligent the machine becomes. AI can process and analyse data, identify patterns and trends based on its goals. When you play games online, AI applies what it has learnt to make the game more enjoyable and challenging.
Let us perform the following experiment to understand how AI learns from data.
Objective: This is an interactive game based on data for AI where the machine tries to predict the next move of the participant. It is a digital translation of the basic rock, paper, and scissors game where the machine tries to win by learning from the participant’s previous moves.
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Visit the given link: https://next.rockpaperscissors.ai/
2. The following window appears.

3. Make a paper (palm), scissors (index and big fingers), and rock (fist) in front of the camera, as shown.

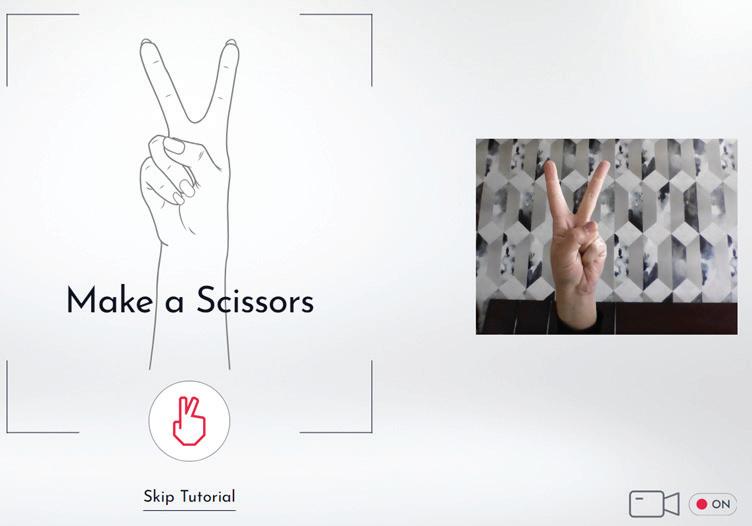

4. Now, start playing the AI game. Make your moves (rock, paper, or scissors) and see how the machine reacts if you make moves in a specific order or randomly.

Computer vision is how AI uses cameras to see and understand things.
Let us take an example of Google Lens, which is an image and text recognition app developed by Google. If you point your camera at a landmark, Google Lens might tell you interesting facts about it. You can also use the app to scan a QR code to display the digital menu of a restaurant or make a payment from your phone.

Let us perform the following experiment to understand how AI uses computer vision to see and understand things.
Objective: This is an interactive game based on computer vision for AI where the machine tries to guess your drawing. The more you play with it, the more it will learn.
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Visit the given link: https://quickdraw.withgoogle.com/

2. The following window appears.
3. Click on the Let’s Draw button to draw different things. Look at this example to see how the AI responds to the drawing of a tree.
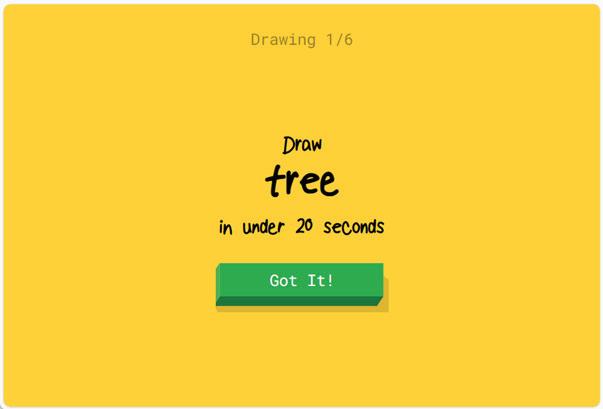
4. The AI makes use of computer vision to identify your drawing.

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a domain of AI that helps computers understand and respond to us when we talk to them. It allows computers to talk to us in a way that feels natural to us. Some of the popular examples of NLP applications include Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa, Google Translate, etc.

Let us perform the following experiment to understand how AI uses NLP to understand and respond to our commands.
Objective: This is an interactive word association game based on NLP for AI. A list of words is displayed on the screen. The player has to think of a word related to the displayed words. Each time you enter a clue, the AI looks at all the words that are in play and chooses the ones it thinks are the most related.
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Visit the following link: https://research.google.com/semantris/
2. The following window appears.

3. Click on the PLAY ARCADE button. It will direct you to a page as shown.

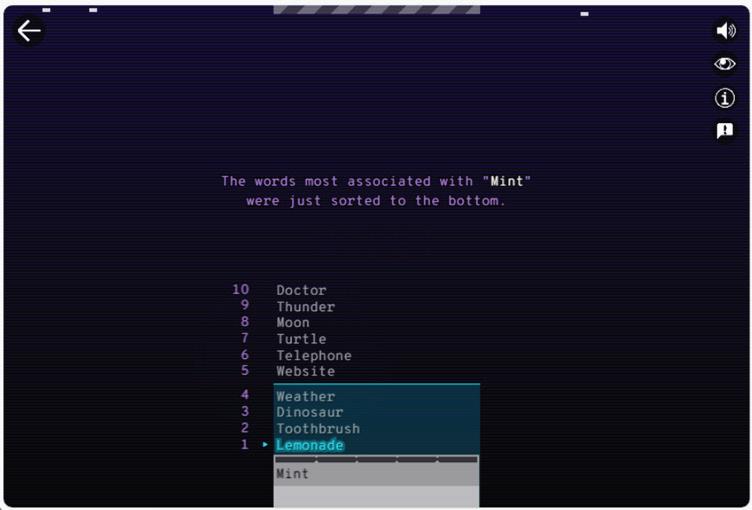
4. Here, the player has to type a word related to the highlighted word. In this example, the word “Lemonade” is highlighted. The player has to type a word related to “Lemonade”. For example, you can type “Mint”. When the AI sorts the list, the most related words are moved to the bottom. As you can observe, the word “Lemonade” shifts to the bottom of the list.
5. Keep on experimenting with different types of clues to learn how NLP works and earn scores.
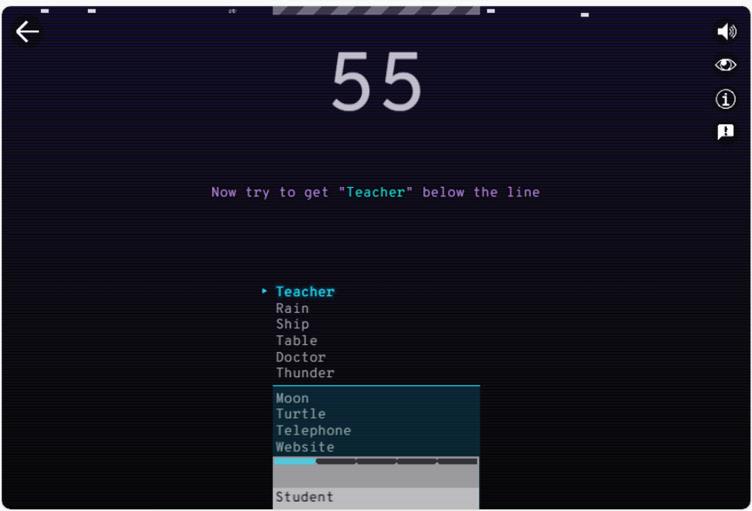
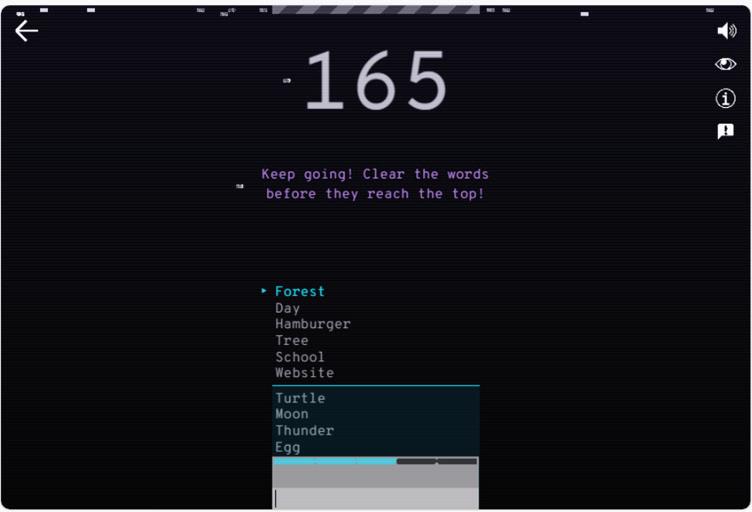
6. Now, you will see that the words pop-up one after the other on the top of the list. Type in the associated words before the stack of words fills in, and you lose the game.
Integrating data, computer vision, and NLP can result in highly efficient and beneficial applications. Data in the form of visuals is beneficial for computer vision, while data in the form of speech, audio, and music can help with NLP. When data is available in audio-visual form, both computer vision and NLP can be utilised for maximum benefit.

AI offers innumerable advantages across various fields and applications. Some of these advantages are:
1. Efficiency: AI can perform repetitive tasks without getting tired. It can also perform tasks much faster, improving efficiency and productivity.
2. Accuracy: AI systems do not experience fatigue or emotional factors that can cause errors. As such, the AI systems execute tasks with high precision and accuracy.
3. Data Analysis: AI can analyse vast amounts of data quickly. It can also identify patterns and trends that might be challenging for humans to recognise. This helps in better decision-making.
4. Automation: AI enables the automation of various processes using advanced algorithms, leading to cost savings and increased production in industries, such as manufacturing and customer service.
5. Medical Advances: AI plays a crucial role in medical research and diagnostics, helping in the early detection of diseases, personalised treatment plans, and drug discovery.
6. Assistive Technology: AI is used in developing assistive technologies, such as voice recognition systems or screen readers, to assist people with disabilities like language impairments or visual impairments in their daily lives.
AI offers innumerable advantages, but at the same time, it also offers a lot of disadvantages.
1. Lack of Creativity: AI lacks the ability to think creatively or understand emotions, unlike humans. Tasks requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, or empathy remain challenging for AI.
2. Dependency: Overdependence on AI systems makes humans trust more on AI recommendations than their own cognitive skills. This could be hazardous when AI systems fail or make errors.
3. Security Concerns: As AI becomes more prevalent and sophisticated, there are concerns about the potential misuse of this technology, including cyber-attacks or exploiting its weaknesses.
4. High Initial Costs: Using AI technologies can be expensive as it requires a lot of investments in infrastructure. This can make it challenging for smaller businesses or developing countries to use these advancements.
5. Ethical Concerns: The use of AI raises ethical questions, such as privacy issues, bias in algorithms, and handling AI decisions responsibly. For example, the use of AI in surveillance and monitoring can raise questions on individual’s privacy.
6. Inequality: AI technologies have the potential to widen existing digital divides and socio-economic disparities, favouring those with access to resources and expertise while marginalising others.
The AI project cycle is a step-by-step process to solve problems using proven scientific methods. It also helps us understand the problem statements better. It defines each step that every project should follow to be successful.
The 5 important steps involved in an AI project cycle are shown below:
Let us learn more about these steps involved in the AI project cycle:
This is the initial stage that defines the goals to be achieved and helps understand the problems that need to be addressed with the help of an AI system.
Theme, Topic, and Problem Statements
Theme: A theme is a broad term that covers all the relevant aspects that may lie in it.
Topic: A topic is a subject that you choose from a theme.
For example:
Theme: Health
Topics: Medicinal Aid, Mobile Medications, Spreading of Diseases, etc.
Problem Statements: Problem statements means making lists of the problems which come within our topic or those that we find in our daily-life scenarios.
For example:
Topic: Health
Problem Statements
High cost of treatments
Poor medical infrastructure
Nursing and Physician shortages
Personalised medicines, etc.
Thus, the process of defining our problem statements starts with identifying the theme on a very broad level, then choosing a relevant topic, and then listing multiple problem statements within it.
The 4Ws of Problem Scoping help us identify the key elements related to the problem-solving approach we need to take.
Why? Where? What? Who?
Let us go through each of the blocks one by one.
• Who refers to someone who is facing a problem and to the other people related to the problem.

• What refers to what the problem is and how you know about it.
• Where refers to the context, situation or location of the problem.
• Why refers to why we need to solve the problem and what benefits the people involved will receive after solving the problem.
Data refers to raw facts, figures, information, or statistics. The process of collecting data from various sources and making it more informative and meaningful for the AI model is called Data Acquisition. Acquiring and compiling the relevant data is used to train the AI system.
There can be several ways in which we can collect data. Some of them are:
• Surveys: Surveys are used to collect data from the target audience and gather insights into their preferences, opinions, choices, and feedback.
• Sensors: Sensors are devices that take live information and turn it into digital data, which can then be fed into a computer to analyse the data and turn it into information.
• Cameras: Devices such as surveillance cameras help capture a large number of video and photographic data points. For example, the collected data can be used to improve the management of parking spaces, police resources, traffic patterns, and so forth.
Exploring and interpreting the acquired data to derive useful information from it and then organising it uniformly in a proper format and layout for better understanding. For example, data can be arranged in the form of a table, plotting a chart or making a database. If anyone wants to make some sense out of the acquired data, they have to work on some patterns.
To analyse the data, we need to visualise it in a user-friendly format so that we can:
• Quickly get a sense of the trends, relationships, and patterns contained within the data.
• Define a strategy for which model to use at a later stage.
• Communicate the insights to others effectively.
AI Modelling refers to developing algorithms or programs, also called AI models which can be trained to get intelligent outputs and solve our problem statement.
In normal programming, we define the rules and give certain input, and based on those rules we get the expected output. So, rule-based AI modelling is where the relationships or patterns in data are defined by us in the program. The computer follows the rules or instructions and performs its task accordingly.
It is AI modelling where the relationships or patterns in the data are not defined by the developer. In this approach, random data is fed to the machine, and it is left on the machine to figure out patterns and trends. Generally, this approach is followed when the data is unlabelled and too random for a human to make sense of it. These are also termed Machine Learning models.
Evaluation is basically to check the performance of our AI model and collect and analyse information about its outcomes. Through evaluation, our purpose is to make judgements about a model, improve its effectiveness, make informed programming decisions, etc.
Evaluation is done by mainly two things: Predicting and Reality.
We will first search for some testing data with a resulting outcome that is 100% accurate.
Then we will feed the testing data to the AI model.
The correct outcome we have is termed Reality.
Then, when we get the predicted outcome from the AI model (Prediction).
We will compare the Prediction with the Reality. Through this, we will improve the efficiency and performance of our AI model.
1. AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a branch of computer science that deals with the study of the principles, concepts, and technology for building machines that enable them to think, act, and learn like humans.
2. Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Google Assistant are virtual assistants that use AI to understand and respond to our voice commands.
3. AI-powered translation apps, like Google Translate, are used to understand and translate text instantly.
4. Some common domains of AI are Data, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing (NLP).
5. Data is a collection of raw facts that can be transformed into useful information. It can be in the form of text, images, audio, and video.
6. Computer vision is how AI uses cameras to see and understand things.
7. NLP is a domain of AI that helps computers understand and respond to us when we talk to them.
8. AI project cycle is a step-by-step process to solve problems using proven scientific methods.

A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints: data AI project cycle learning-based NLP computer vision
1. AI makes use of to unlock our phones using facial recognition.
2. is a collection of raw facts that can be transformed into useful information.
3. is a step-by-step process to solve problems using proven scientific methods.
4. is a domain of AI that helps computers understand and respond when we talk to them.
5. AI models are also called machine learning models.
B. Select the Correct Option.
1. Which among the following is not an NLP application?
a. Google Translate
c. Siri
b. MRI
d. Google Assistant
2. Which of the following is an interactive game where the machine tries to guess your drawing?
a. Quick Draw
c. Semantris
b. Google Lens
d. Spotify
3. is an image and text recognition app developed by Google.
a. Google Assistant
c. Google Lens
b. Google Maps
d. None of these
4. is the full-form of NLP.
a. Natural Language Processing
c. Neural Language Programming
b. Natural Language Program
d. Natural Language Process
5. use AI algorithms to analyse our preferences.
a. Facial recognition
c. Streaming services
C. State True or False.
b. Autonomous vehicles
d. Translation apps
1. Virtual assistants can set reminders, answer questions, play music, etc.
2. AI does not have the capability to create dynamic environments while playing games.
3. Data can be only in the form of text.
4. In the Rock, Paper, Scissors AI game, the machine tries to win by learning from the participant’s previous moves.
5. AI algorithms analyse data from the sensors of autonomous vehicles to build an understanding of the vehicle’s surroundings.
D. Answer the Following.
1. Define AI.
2. Describe the advantages of AI.
3. What is AI project cycle? Name the steps involved in the AI project cycle.
4. What is Google Lens? For what purpose can this app be used?
5. Describe the different domains of AI.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Swati consistently receives film recommendations tailored to her preferences on Netflix. Help Swati know the reason.
2. Ananya notices that her smartphone’s facial recognition feature helps unlock her phone with a great ease. How is this possible?
3. Avyan is amazed by self-driving cars’ ability to navigate autonomously. He wants to know the specific domain of AI that enables this technology to operate safely and efficiently.
4. Sidhant, a doctor, is curious about AI’s impact on healthcare. How can AI support him in providing medical care to his patients?
5. Nisha holds a positive outlook on AI, recognising its potential for numerous advantages. However, what are some significant disadvantages that she should also consider in her assessment of AI’s future?
1. Visit the link: https://experiments.withgoogle.com/thing-translator and take a picture of something and discover how AI says it in a different language.
2. Visit the link: https://deepdreamgenerator.com/generate to generate personalised artistic images.
3. Visit the link: https://aidungeon.com/%EF%BC%89 to play an interactive text-based adventure game.

Have you ever wondered how your phone unlocks itself with your face or fingerprint, and how some apps suggest words while you type, or recommend TV shows that you might like? All of this is possible because of Machine Learning (ML). Let us learn more about machine learning in this chapter.
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that makes machines learn from large amounts of data. By identifying patterns in this data, machines can make predictions or decisions without needing explicitly programmed instructions. Machine learning enables a computer system to learn from this experience of using the provided data and making accurate algorithms for predictions or decisions from them.



To better understand how machines learn, let us take an example of fruits. Let us take an apple and a banana. How do we differentiate between them? When we look at an apple, we know it is spherical in shape and red in colour. However, when we look at a banana, we see that it is curved in shape and yellow in colour.
Just as we can differentiate the two fruits by looking at their shapes and colour, computers too can differentiate them from the data we provide, such as images of apples and bananas. We show the computer a lot of images of each fruit. The computer identifies
the patterns. It appears that all the images of apples follow a certain pattern (in terms of colour and shape), whereas the images of bananas follow a different pattern. We call these images of apples and bananas as training data as we use these images to train the computer to learn about the patterns of the fruits.

Once the computer has learnt to identify and understand the pattern, we use test data, which is any new image of an apple or a banana, and give it to the computer to identify the image based on its learning.

Machine learning involves showing a large volume of data to a machine so that it can learn and make predictions, find patterns, or classify data. The three types of machine learning are supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.

Supervised learning is a machine learning method that uses well-labelled datasets to train algorithms to predict outcomes and recognise patterns.
In supervised machine learning, we know the data really well. We provide this known data to the machine learning model, which then learns from the data. Here, the model refers to the algorithms or programs, which can be trained to give intelligent outputs and solve our problem statement. Once the model learns the relationship between the input and output data, it becomes capable of classifying new and unseen datasets as well as predicting outcomes.
The identification of apples and bananas as different fruits is a great example of supervised learning.
Since we knew the data really well, i.e., apples are spherical and red while bananas are curved and yellow, we ‘feed’ this data to the computer by providing a large number of images of both apples and bananas. This is then reasoned into the statements, “Given an image of an apple, we know it as an apple”, and “Given an image of a banana, we know it as a banana”.
Thus, the computer learns this information and applies it to new images, thereby starting to make predictions.

Its an apple!
These are apples.
As the name suggests, unsupervised learning is a machine learning technique in which models are not supervised using datasets. In unsupervised machine learning, machines do not know any patterns in the data. Instead, the model itself finds hidden patterns and insights from the given data.
Imagine showing a computer various picture of fruits—apples, bananas, and grapes. We do not tell the computer anything about these images, including which one belongs to which fruit. We simply display all the images on the computer. The computer automatically finds a pattern in these images.
For example, it understands that all the apple images have similar properties, like red colour and spherical shape. All the bananas have similar properties, like yellow colour and curved shape. Similarly, all the grapes have similar properties, like green colour and small and round shape.
Hence, it creates clusters (groups) and separates these images into three different groups.
Now, every time you give a new image of apple, banana, or grapes, the computer can ‘separate’ them into one of these three groups. This is an example of unsupervised learning.

I can see a pattern.
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to take actions in an environment to maximise a cumulative reward. The agent learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for good actions and penalties for bad ones. In our fruit recognition problem, the computer learns to recognise fruits by identifying images. When the computer correctly identifies a fruit, it receives a reward. However, if it guesses incorrectly, there is no reward. With each attempt and its corresponding feedback, the computer becomes ‘smarter’. It starts recognising the key features that distinguish different fruits. For example, it learns that apples are red and spherical, while bananas are curved and yellow. This process helps it understand which actions, like identifying specific features, are effective and which can be ignored.

The learning and accuracy of the machine learning model are dependent on various factors, like:
Quantity of Data: The more images of apples and bananas we feed to the computer, the better it will learn from this data and predict more accurately.
Quality of Data: Depending on how good the images of apples and bananas are, the accuracy of the model will vary.
Let us do the following experiment using the application Teachable Machine to understand how machine learning works.
Objective: Teachable Machine is a web-based tool that makes the creation of machine learning models fast, easy, and accessible to everyone. It helps train a computer to recognise images, sounds, and poses.
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Visit this link: https://teachablemachine.withgoogle.com/
2. The following window opens. Click on the Get Started button.

3. You will be directed to a web page, as shown. From the window that appears, you can use any of the following options to teach your machines:
• Images: To teach a model to classify images using files on your system or your webcam.
• Sounds: To teach a model to classify audio by recording short sound samples.
• Poses: To teach a model to classify body positions or poses using image files on your system or striking poses in your webcam.
•
4. Let us create a pose project. For this, click on the Pose Project option.
5. Collect images of random people’s sitting and standing poses, as shown. Here is the training data, in the form of images, of standing and sitting poses, for your reference.













6. Click on the Upload button to upload the images related to these poses.

7. The results of any machine learning model depend on the examples or the sample data you give it. So, if it’s not working as you had intended, then add more samples to the training data that was provided to your computer.
8. After uploading the training data, click on the Train Model button.
9. Now, test your machine learning model by posing in front of the webcam and see what Output (standing or sitting pose) it displays in the Preview window.


From self-driving cars to personalised recommendations, machine learning is transforming our daily lives. Here are some exciting applications of this technology.
Recommendation Systems: Imagine that you have been watching a lot of videos on YouTube that are on computer programming. The machine-learning algorithms of YouTube track your choices. By analysing this data, they can recommend programming videos that align with your interests.


Language Translation: Google Translate, a translation app, uses machine learning to understand and translate text instantly, enabling us to communicate in different languages. It learns from millions of translated texts to understand the patterns and meanings in different languages.
Customer Service Chatbots: Have you ever wondered how the chatbots seem to get smarter with every new conversation? It is because of machine learning! By analysing the questions that the customers ask, these chatbots learn to provide increasingly helpful and accurate answers.

Image Recognition: Applications like Snapchat or Instagram can add fun effects to your photos by analysing your facial features using machine-learning algorithms. Machine learning application looks at your face in the camera and figures out where your eyes, nose, and mouth are. Then, it puts the filter on the right spot to make it look like it is part of your face. For instance, Snapchat might overlay a dog’s nose and ears on your face or add funky glasses.


Self-driving Cars: Self-driving cars use both computer vision (to see the road, pedestrians, vehicles, etc.) and machine learning (to make decisions). A self-driving car learns from all the different situations it encounters on the road, like slowing down on detecting pedestrians, stopping at a red light, or navigating around other vehicles.


Banking: Machine learning makes banking safer, more personalised, and easier for everyone. It helps banks detect unusual activity that may be fraudulent. It also helps banks decide who can get loans by looking at their borrowing history and their likelihood of repaying them. Also, there are chatbots on banking apps that provide customer support by answering questions effectively.
Weather Prediction: Machine learning helps predict the weather by analysing historical weather data, like temperature, precipitation, wind, etc., to find patterns. It makes use of these patterns to make better guesses about what’s going to happen next.

Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning in which a machine is trained with vast amounts of data which help it to train itself around that data. Some practical applications of deep learning includes virtual assistants, computer vision for driverless cars, detection of money laundering, face recognition, and many more. It is an AI function that mimics the working of the human brain in processing data and uses it in detecting objects, recognising speech, translating languages, and making decisions.
Artificial Intelligence
Machine Learning
Deep Learning
•
Deep learning is the most advanced form of artificial intelligence. Then there is machine learning, which is intermediately intelligent, and artificial intelligence which covers all the concepts and algorithms that, in some way or other, mimic human intelligence.
1. Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI where the machine makes predictions and decisions based on the data that we provide it.
2. In supervised ML, we give data to the machine on which it is already trained and it learns from that data.
3. In unsupervised ML, we do not give any data that has patterns in them. Instead, the machine adapts itself to find the hidden patterns and insights from the given data.
4. In reinforcement learning, machines learn from the feedback on the predictions they made. They are rewarded for correct guesses. They learn about the nature of actions that are necessary or unnecessary.
5. Machine learning algorithms learn from your past choices or preferences and make recommendations for films, songs, articles, etc., tailored to your interests.
6. Google Translate, a translation app, makes use of machine learning to understand and translate texts instantly.
7. Machine learning helps chatbots to function more efficiently by making them learn from the different types of questions customers ask and get better at giving helpful answers.
8. Self-driving cars use both computer vision (to see the road, pedestrians, vehicles, etc.) and machine learning to make decisions.
9. Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning where a machine is trained with vast amounts of data which then help it to train itself around the data. It is the most advanced form of AI.

A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints: Google Translate test data supervised chatbot Machine Learning
1. is a branch of AI that uses large amounts of data to make predictions.
2. makes use of machine learning to help us communicate in different languages.
3. A interacts with you online to answer your queries or assist during online shopping.
4. In machine learning, we know the data really well.
5. Once the computer learns, we use or any new image, and the computer can identify these new images based on its learning.
B. Select the Correct Option.
1. In learning, a computer gets feedback on whether it is right or wrong.
a. Reinforcement
c. Unsupervised
b. Supervised
d. Superlative
2. How does machine learning help in banking?
a. It helps banks detect unusual activity.
b. It helps banks decide who can get loans by looking at their borrowing history.
c. It provides customer support on banking apps.
d. All of these.
3. Machine learning involves feeding a large volume of to a machine so that it can make predictions.
a. Outputs
c. Noise
b. Data
d. Algorithms
4. Which of the following is the most advanced form of AI?
a. Supervised Machine Learning
c. Deep Learning
b. Machine Learning
d. Unsupervised Machine Learning
5. In learning, the model can classify new datasets and predict outcomes after learning the relationship between input and output data.
a. Supervised
c. Reinforcement
b. Unsupervised
d. Recommendation
C. State True or False.
1. Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning.
2. Machine learning does not have the capability to predict the weather.
3. A self-driving car uses both computer vision and machine learning.
4. The accuracy of the machine learning model depends only on the quality of the data.
5. YouTube is an example of a recommendation system.
D. Answer the Following.
1. Define machine learning.
2. Differentiate between supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
3. Explain any three applications of machine learning.
4. What is deep learning?
5. Differentiate between training data and test data.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. When Neelam first heard about self-driving cars, she was curious about how she would manage to navigate on the road. Explain to Neelam how self-driving cars achieve this.
2. Yashika visits Germany but she cannot speak German. You have suggested using Google Translate to communicate effectively there. Explain to her how the app can help her communicate with ease.
3. Avartika and her grandmother like adding filters on the pictures they click using Snapchat. Curious, Avartika’s grandmother asks her how these filters work. What should Avartika tell her grandmother?
Visit the link: https://experiments.withgoogle.com/ai/ai-duet/view/ to see how AI responds to you when you play the piano.

Have you ever wondered how your smartphone understands your voice commands so easily? Or how search engines like Google understand your queries and help you find the information you need, with just a few keystrokes? Or how virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa respond to your inquiries? All of this is possible thanks to Natural Language Processing (NLP).
NLP is a domain of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with language-based interactions between machines and humans as well as between two machines. It equips computers with the ability to understand, interpret, and generate human language in an accurate and relevant way. NLP algorithms are trained on vast amounts of text data, learning patterns, structures, and the meaning of words and sentences. It also involves understanding the context, sentiment, and intent behind those words. This enables computers to perform a wide range of tasks, from recognising voice commands to translating languages and generating human-like responses in chatbots.
NLP is essentially an effective tool that helps us communicate with technology in a more efficient, intuitive, and natural way by bridging the gap between human language and computer understanding.

With its wide range of useful application, NLP transforms our day-to-day interaction with technology. Some of these are given as follows.

Virtual Assistants: This is one of the most common applications of NLP. A virtual assistant is an AI tool that understands and responds to voice commands or text inputs, such as questions and requests, or performs tasks for you. Virtual assistants come in the form of applications, or combinations of devices loaded with applications. Siri on the iPhone, Alexa on the Amazon Echo device, and Google Assistant on the Android phone are some of the popular virtual assistants. You can ask a virtual assistant to set alarms, check the weather, play your favourite songs, or even tell you jokes.
Search Engines: Search engines are websites and applications that help you find information on the internet. Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc., are some of the popular search engines. These search engines use NLP to understand the words you type into the search bar and then direct you to relevant web pages. NLP helps search engines comprehend the meaning and context of your search and help you find what you are looking for.


Sentiment Analysis: NLP can be used to analyse the sentiment or emotion expressed in the text. For example, businesses might use sentiment analysis to analyse customer feedback and preferences for their products and services across reviews on social media platforms and product remarks on online stores. This insightful data can help companies enhance their products, services, or customer experiences.
Spam Detection: NLP helps keep your email inbox free from unwanted mails, also known as spam. Spam-detecting algorithms employ NLP to identify patterns or characteristics common to spam emails, such as certain keywords or phrases, and then filter spam from reaching your inbox.


Autocorrect: Autocorrect is a handy tool featured on devices, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc., that allows users to automatically correct misspelt words as they type them. Autocorrect algorithms employ NLP to analyse the context of the text being typed and suggest corrections based on frequently used words and phrases. This is particularly useful when typing on small touchscreen devices.
Speech Recognition: NLP algorithms analyse audio input from speech and transcribe it into text, enabling hands-free interaction with devices, such as smartphones or voice-controlled appliances. Speech recognition technology is used in applications, like voice search, home automation, voice dictation, voice biometric, etc. The ‘Read Aloud’

feature in Microsoft Word makes use of NLP algorithms to read all or part of your document, highlighting each word as it is read. You may also dictate your documents in Word. Dictating within Microsoft Word automatically transcribes your spoken words into text.


Education: Chatbots and virtual assistants that are powered by NLP engage with students in natural conversations, providing guidance and support. NLP enables automated assessment of students’ work and provides them with instant feedback and assistance in identifying areas for improvement, saving educators’ time. ChatGPT, for example, offers personalised learning experiences by adapting to individual learning styles. NLP-powered tools like Grammarly analyse written text for grammatical errors or inappropriate word usage.
Language Translation: NLP facilitates the translation of text from one language to another. A popular example is Google Translate, which uses artificial intelligence to provide instant translations. NLP algorithms analyse the structure and meaning of text and capture the patterns and probabilities of word sequences. This allows them to provide suggestions for improving translations, detecting errors, or offering alternative translations.

Google Translate is an AI-powered translation app that allows users to translate text into different languages. It can translate texts entered by typing, handwritten text, spoken words, and text scanned through the camera or captured in images.
Let us perform the following experiment to understand how AI uses NLP to translate text from one language to another.
Objective: Experience real-time translation between different languages using the Google Translate app thereby leveraging the power of NLP.
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Download the Google Translate app from the Google Play Store in your smartphone or your device’s app store.
2. Open the Google Translate app. The following screen appears.

Camera Option
3. Click on the Camera option in the bottom-right corner.
4. Select your preferred language, for example, ‘Hindi’.


5. Take a picture of the words to translate using your smartphone’s camera.

6. The translated text appears as follows.

1. NLP is that domain of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with the language-based interactions between machines and humans as well as between two machines.
2. A virtual assistant is an AI tool that understands and responds to voice commands or text inputs, such as questions and requests, or performs tasks for you.
3. Search engines are websites and applications that help you find information on the internet.
4. Google Translate is an AI powered translation app that allows users to translate text into different languages.
5. NLP can be used to analyse the sentiment or emotion expressed in a text.
6. Autocorrect is a handy tool featured on devices, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc., that allows users to automatically correct misspelt words as they are being typed.

Hints: spam
Siri Autocorrect NLP Google Translate
1. is a handy tool featured on smartphones that allows users to automatically correct misspelt words as they are being typed.
2. on iPhones is a popular virtual assistant.
3. NLP helps keep your email inbox clean and clear from unwanted mails called
4. is an AI-powered language translation tool.
5. is the domain of AI that deals with the language-based interactions between a machine and a human as well as between two machines.
1. NLP helps comprehend the meaning and context of your search and find what you are looking for.
a. search engines
c. spams
b. home automation
d. sentiment analysis
2. Which of the following application uses speech recognition?
a. ChatGPT
c. Spam Detection
3. What is the full form of NLP?
a. Natural Language Processor
c. Natural Language Program
b. Grammarly
d. Read Aloud of Microsoft Word
b. Natural Language Processing
d. Neuro Language Processing
4. Which of the following is a potential application of sentiment analysis using NLP?
a. Chatbots tutoring students
b. Autocorrecting misspelt words
c. Assessing customer feedback on products
d. Asking a virtual assistant to check the weather
5. You can ask to play your favourite song.
a. Siri
c. Google Assistant
b. Alexa
d. All of these
C. State True or False.
1. ChatGPT is an NLP-powered tool.
2. NLP algorithms are trained on vast amounts of text data.
3. Virtual assistants come in the form of applications only.
4. E-commerce sites make use of sentiment analysis to know customer’s preferences.
5. NLP can be used to analyse written text for grammatical errors.
D. Answer the Following.
1. Define NLP.
2. What are virtual assistants?
3. How does NLP contribute to providing a personalised learning experience?
4. How can NLP help businesses know their customer preferences?
5. What role does NLP play in enabling search engines to understand user queries and deliver relevant search results?
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Sita’s friend Anita is visually impaired. Sita sees Anita working on MS Word and notices that the text written in that file was being read aloud to Anita. What will Anita’s answer be when Sita asks her about this interesting feature in MS Word?
2. Sneha notices that whenever she makes a spelling mistake while texting, the messaging app automatically corrects the word. Which application of NLP do you think is being used here?
3. Rohan is amazed to see how his friend uses Alexa to play his favourite songs with voice command. He asks what else can this virtual assistant do other than play his friend’s favourite songs. What do you think Rohan’s friend will tell him?
Visit the link: https://www.ibm.com/demos/live/natural-language-understanding/self-service and observe how NLP analyses your text.

The Artificial Intelligence (AI) series for grades 9 and 10 by Uolo aims to expose learners to essential elements in AI and introduce common domains and applications of AI to them. It also introduces the fundamentals of AI to the learners through engaging activities that can be done in a computer lab or on a computer at home. This series paves the way for students to become informed participants in the exciting future shaped by artificial intelligence.
• Engaging In-chapter Activities: Engaging activities within each chapter that offer students practical experience of various AI concepts and domains, thereby facilitating a deeper understanding.
• Let’s Revise: To reinforce takeaways of each chapter, these chapter-end summaries include key points that recaps everything that has been covered in the chapter.
• Chapter Checkup: Comprehensive exercises at the end of each chapter that have various question types, like fill in the blanks, true or false, multiple-choice, short answer, long answer, and application-based questions to provide students a thorough revision of the text.
• Activity Section: To further enhance student proficiency, all the chapters end with an unsolved activity which provides additional practice of the AI concepts.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 10,000 schools across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East. hello@uolo.com
