






Module-wise
MODULE 1 BASIC CONCEPTS CHAPTER

MODULE 2 FORMS OF MARKET
CHAPTER 2.1
2.2
MODULE 3 MONEY AND BANKING
CHAPTER 3.1
CHAPTER 3.2
3.3
MODULE 4 ECONOMIC AND BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER 4.1
CHAPTER 5.2
STEWARDSHIP THEORY & AGENCY THEORY OF MANAGEMENT
CHAPTER 5.3
PLANNING, ORGANIZING, STAFFING & LEADING
CHAPTER 5.4
COMMUNICATION, COORDINATION, COLLABORATION, MONITORING & CONTROL
CHAPTER 5.5
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE, RESPONSIBILITY, ACCOUNTABILITY & DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
CHAPTER 5.6 LEADERSHIP & MOTIVATION
5.7
Solved Paper: December 2024 (Suggested Answers)
Solved Paper: June 2025 (Suggested Answers)

CHAPTER 2.1
PRICING OF PRODUCT & SERVICES IN VARIOUS FORMS OF MARKET
Quick Revision of the chapter INTRODUCTION
Under perfect competition each firm takes the market price as given and adjusts the level of output in order to maximize profit. But perfect competition hardly exists in reality. Monopoly, monopolistic competition, discriminating monopoly and oligopoly are closer to the real world.
The business firms may have objectives other than profit maximization in mind, such as
Sales maximization: Penetration price strategy is followed to increase the sales and subsequently to maximize it.
Price stabilization: Frequent price fluctuations do not permit forward planning of turnover, stock, investment and finance hence price stabilization is necessary.
Increasing the market share: Size of the market is a symbol of prestige, hence increasing the market share is a coveted goal.
Target return on capital: The rate of return must be higher than the cost of capital – this is the basic consideration for fixing a target return on capital.
Thwarting competition: Through limit pricing policy, the existing firm prevents the entry of new firms, thus thwarting competition in the market.
Ethical pricing: When firms fix moderate prices, they set ethical prices to maintain a good public image.
PRICING STRATEGIES:
Cost-plus pricing: Cost-plus pricing is the simplest pricing method. The firm calculates the cost of producing the product and adds on a percentage (profit) to that price to give the selling price.
Limit pricing: A limit price is the price set by a monopolist to discourage economic entry into a market. The limit price is often lower than the
average cost of production of just low enough to make entering not profitable.
Penetration pricing:
Setting the price low in order to attract customers and gain market share. The price will be raised later once this market share is gained.
Price discrimination: Setting a different price for the same product in different segments to the market. For example, this can be for different classes, such as ages, or for different opening times.
Psychological pricing: Pricing designed to have a positive psychological impact. For example, selling a product at ` 3.95 or ` 3.99 rather than ` 4.
Dynamic pricing: A flexible pricing mechanism made possible by advances in information technology, and employed mostly by internet based companies.
Price leadership: An observation made of oligopolistic business behavior in which one company, usually the dominant competitor among several, leads the way in determining prices, the others go on following.
Target pricing: Pricing method where by the selling price of a product is calculated to produce a particular rate of return on investment for a specific volume of production. The target pricing method is used most often by public utilities, like electric and gas companies, and companies whose capital investment is high, like automobile manufactures.
Absorption pricing: It is a method of pricing in which all costs are recovered. The price of the product includes the variable cost of each item plus a proportionate amount of the fixed costs and is a form of cost-plus pricing.
High-low pricing: Method of pricing for an organization where the goods or services offered by the organization are regularly priced higher than competitors, but through promotions, advertisements, and coupons, lower prices are offered on key items.
Marginal cost pricing: In business, the practice of setting the price of a product to equal the extra cost of producing an extra unit of output is called marginal cost pricing.
MARKET
Market is a means by which exchange of goods and services takes place as a result of buyers and sellers being in contact with one another.
CLASSIFICATION OF MARKET
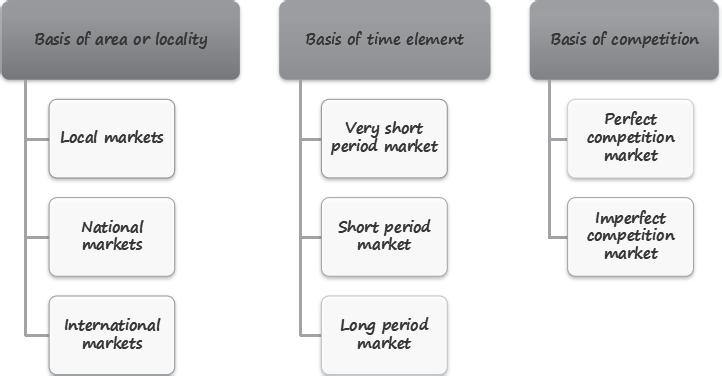
PERFECT MARKET
“The more nearly perfect market is the stronger tendency for the same price to be paid for the same thing in all parts of the market” – Alfred Marshall.
FEATURES OF PERFECT MARKET
Large number of sellers and buyers
Homogeneous commodities
Free entry and exit
Mobility of factors of production
Absence of transport cost
Perfect knowledge of market
TYPES OF EQUILIBRIUM
SHORT PERIOD EQUILIBRIUM
In the short period equilibrium the firm can get either abnormal profits or losses. Abnormal profit/supernormal profit: When the firm is in the short period equilibrium sometimes it can get abnormal profits.
Abnormal profits = TR – TC = Q × P (AR) – Q × AC = OM × OP – OM × OS = OPQM – OSRM = PQRS
Normal profit
Losses: When the firm is in the short equilibrium sometimes it may get losses.
Losses = TC – TR = Q × AC – Q × P (AR) = OM × OP – OM × OS = OPRM – OSQM = PRQS
LONG PERIOD EQUILIBRIUM
When the firm is in the long period equilibrium it gets only normal profits. In the above diagram output is shown on OX-axis Costs, Revenue, Price is shown on OY-axis. In the diagram LMR is the long run Marginal Revenue curve. LMC is the long run Marginal Cost Curve. It intersects the LMR from below at point Q. So the equilibrium output is determined as OM at this level of output the price (AR) is OP. The average (AC) is also OP. Here AR = AC. It means the total revenue (OPQM) is equal to total cost (OPQM). So the firm will get only normal profits. Point Q is called Break Even Point or revenue and cost equalizing point.
IMPERFECT MARKET
IMPERFECT MARKET
MONOPOLY
The word Monopoly is derived from two words ‘Mono’ and ‘Poly’. Mono means Single and Poly means seller. In the market where there is only one seller or one producer or one firm it is said to be monopoly market. The single seller supplies the commodity to the entire market.
FEATURES OF MONOPOLY
Single firm
No close substitute
Strong barriers to entry
Firm and Industry are same
Price maker
Nature of AR & MR curves
Price discrimination
Maximum profits
PRICE AND OUTPUT DETERMINATION:
In monopoly market as there is a single producer, he can control either the price of the commodity or supply of the commodity. But he can’t control both at the same time. He can increase the price by decreasing the output or he can sell more output by decreasing the price. Maximization of profits is the sole objective of the monopolist. This can be shown by the following diagram.
In the below diagram output is shown on OX-axis. Cost, Revenue and Price are shown on OY-axis. In the diagram MR is the Marginal Revenue Curve and MC is Marginal Cost Curve. It intersects the MR curve at point E so the equilibrium level of output is determined as OM at this level of output the average revenue is at point Q. So the price is determined as OP the average cost is OS. Here AR > AC as the monopoly is to earn maximum profits.
Abnormal or super normal profits
= TR – TC
= O × AR – Q × AC
= OM × OP – OM × OS
= OPQM – OSRM = PQRS
DUOPOLY MARKET
Where there are two sellers or two producers or two firms it is said to be duopoly market. It is also one of the forms of oligopoly markets.
OLIGOPOLY MARKET
The word oligopoly is derived from two Greek words oligo and pollien, oligo means “A few”, Pollien means seller. Where there are a few firms or few producers or few sellers, it is said to be oligopoly market.
A market with a small number of producers is called oligopoly. The product may be homogeneous or there may be differences. Since producers are a few each firm produces a large portion of the output. It is a market with competition among the few. This market exists in automobiles, electrical and cigarettes etc.
FEATURES OF OLIGOPOLY MARKET:
Less number of firms
Interdependence
Selling costs
Uncertainty
Rigid price
Price and output determination under Oligopoly Market:
Cournot’s Duopoly Model:
According to Cournot each duopolist believes that regardless of his actions and the effect upon the market of the product the other firm will go on producing the same commodity.
Cournot output is 2/3rd of the competitive output & the price is 2/3rd of most profitable i.e. monopoly price.
Stackleberg Duopoly Model:
The producer under duopoly structure incorporates the decision level of his rival. It then incorporates in its own profit function and thereby maximizes profit. Non-collusion is practiced at large. Leader-follower relation emerges.
Bertrand Duopoly Model:
In the Bertrand model, the assumptions/conjectures of the model are similar to the Cournot model but the former is based upon price as the strategy variable. According to this model each producer can always lower the price until price is equal to cost of production.
Edgeworth Model:
Each duopolist believes that his rival will continue to charge the same price as he is just doing irrespective of what price he himself sets in. No determinate equilibrium can exist under duopoly.
Collusive Oligopoly:
According to this model a cartel is formed when firms jointly fix the price and output with a view to maximize joint profit. For example: OPEC countries form a cartel.
MONOPOLISTIC MARKET
The concept of monopolistic competition was introduced by Prof. Chamberlin. It is a market with many sellers for a product but the products are different in certain respects. The features of monopoly and competition are combined in this market. Hence, it is called monopolistic competition. Example: Cosmetics, Soaps etc.
FEATURES OF MONOPOLISTIC MARKET
A considerable number of producers
Product differentiation
Entry and exit
Selling costs
Imperfect knowledge
Price decision
PRICE AND OUTPUT DETERMINATION UNDER MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION MARKET
Perceived demand curve:
This demand curve shows the different combinations between quantity demand and price such that neither of the firms has any further initiative to deviate from their decisions.
SECTION A : FUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ECONOMICS
Proportional demand curve
This demand curve captures the impact of the all firms simultaneously changing the same price and hence it takes into accounts the effects of the actions of the rivals.
When the perceived demand curve (dd) and proportional demand curve (DD) intersect, then the price is determined in monopolistic competition market.
Equilibrium condition under monopolistic competition
Marginal cost = marginal revenue (MC = MR).
MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
TR = Q × P(P (AR) TC – Q × AC = OQ × OP – OQ × OC = OPaQ – OcbQ
Abnormal profit = Pabc
LONG-RUN EQUILIBRIUM UNDER MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
Excess profits earned by each firm during the short-run would attract new firms into this market. As there is no barrier on the entry into the market, new firms can easily enter into the market in the long-run. As a result, the actual market-share of each firm will be less than before. So, the actual market-share demand curve shifts in the leftward direction. At that situation, each firm may think that, with a fall in
their product price, more quantity can be sold following its perceived demand curve. Thus, in an attempt to increase the profit, a firm wants to lower the price. It expects to sell more along its perceived demand curve. A situation of price competition would arise when each firm tries to do the same thing independently. The equilibrium point is E where the Long-run Marginal Cost (LMC) curve of the firm cuts the Marginal Revenue (MR) curve from below. So, the long-run equilibrium output is 0Q0 and the equilibrium price is 0P0. At this output level, the actual market-share is equal to the perceived sale (i.e., P0F = 0Q0). It is important to note that this profit maximizing level output has been derived by equating the perceived MR and the LMC. So, in this case the perceived profit is maximized not the actual profit. This situation is similar to that of perfect competition; but unlike the longrun equilibrium condition of a firm under perfect competition, the long run equilibrium of a firm under monopolistic competition shows equilibrium production with excess capacity.
SELLING COSTS AND MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
The recognition of product differentiation provides the rationale for the selling expenses (particularly expenses for advertisement) incurred by any firm under monopolistic competition. The firm desires to accentuate the differences between its own brand and other brands of the product available, through its advertising and other selling activities. Thus, selling expenses have a definite role in strengthening the preferences of the consumers for the advertised product, and making the demand for the product relatively inelastic. Chamberlin argues that there are both economies and diseconomies of advertising with changes in the level of output. At the initial stage, expansion in sale will not require an equi-proportionate increase in selling expenses; and this causes a decline in spend more per unit of output to attract buyers of other varieties, and the average selling costs will rise. So, the average selling costs curve becomes U-shaped and the vertical summation of the U-shaped Average Cost (AC) curve and the average selling cost curve, would result in the true AC curve. It operates less than its full utilization level. This calls for the emergence of the excess capacity in the market.
According to the above diagram the difference between Qmc and Qpc captures the extent of excess capacity.
PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
Q.1. Monopolists:
(
a) Are guaranteed at least a zero economic profit
(b) Are guaranteed more than a normal profit
(
c) Are guaranteed an economic profit
(d) None of the above is correct [Sep. 2014]
Q.2. For the perfectly competitive firm, the profit maximising level of output is where:
(
(
a) Marginal revenue equals price
b) Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
(
c) Price equals average variable cost
(d) Price equals average total cost [Sep. 2014]
Q.3. A decrease in demand that results in economic losses in a perfectly competitive industry will:
(
a) Encourage entry into the industry
(b) Encourage exit from the industry
(c) Induce new, more efficient, firms to enter the industry
(d) Cause existing firms in the industry to expand the scale of their operation [Sep. 2014]
Q.4. A market is defined as perfectly contestable if:
(
(
a) Entry to it costly, but exit from it is costless
b) Entry to it & exit from it are both costly
(
c) Entry to it & exit from it are both costless
(d) Entry to it is costless, but exit from it is costly [Sep. 2014]
Q.5. The monopolist demand curve is:
(
a) Identical with industry or market demand curve
(b) Non-existent
(c) Perfectly elastic
(d) Perfectly inelastic [Dec. 2014]
Q.6. A firm that makes profit in excess of normal profit is earning:
(
a) Economic profit
(b) Costing profit
(c) Normal profit
(d) Super normal profit [Dec. 2014, June 2023]
Q.7. The ideal level of operation for a pure monopoly firm is the level where:
(a) TR and STC curve are parallel to each other
(b) TR = TC
(c) TR = Total variable cost
(d) TR is less than STC [Mar. 2015, Dec. 2022]
Q.8. A competitive firm maximizes its total profit when
(a) Average cost equal average realization
(b) Marginal cost equals price
(c) Total revenue is the maximum
(d) MR = AR [Mar. 2015, June 2015]
Q.9. Which of the following is/are the characteristic of a monopolistically competitive market?
(a) No restriction on exit and entry
(b) Many sellers
(
c) Product differentiation
(d) All the three [June 2015]

