






A ‘fresh’ look at modern gemmology



PD Dr.Michael S. Krzemnicki, Swiss Gemmological Institute SSEF www.ssef.ch
Photos © M.S. Krzemnickiand SSEF, except where indicated otherwise







From Geology to Gemmology
Metamorphic rocks (mainly marbles and gneisses) closely in contact with magmatic rocks (mainly granite and syenite).


SimplifiedgeologicalmapfromKhinZaw et al. 2014
Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 4



From Geology to Gemmology



Inclusionsuitein rubyfromMogok
Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 5

Inclusion studies
What microscopically looks as one inclusion is quite often a mixture (intergrowth) of several mineral phases.


of Na, Mg, F

Tiny baddeleyite(ZrO2) as accessory inclusions indicate magmatic contribution to gemstone formation in metamorphic marbles.
Raman spectrum of baddeleyite ZrO2




Inclusion studies
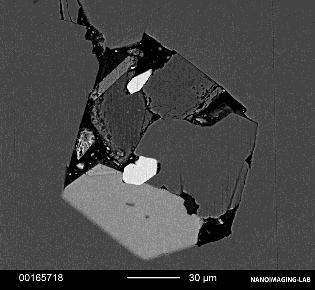
Zircon ZrSiO4



SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 8
GemTOF

Zircon inclusions (at the surface) enable us to carry out U-Pbage dating of gemstones, using the GemTOF(LA-ICP-TOF-MS).
30th June 2017 | Page 9


Zircon at girdle of sapphire
Granitoidzircon (zoned) Figure (modified) from Chew et al. 2017
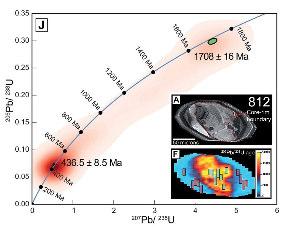

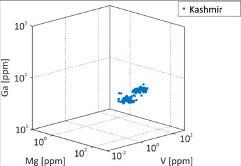
WH1 A new figure is attached, including two analyses of Zircons on SriLanka and kasmir sapphires. Wang, Hao; 25.09.2017
Inclusion studies
4
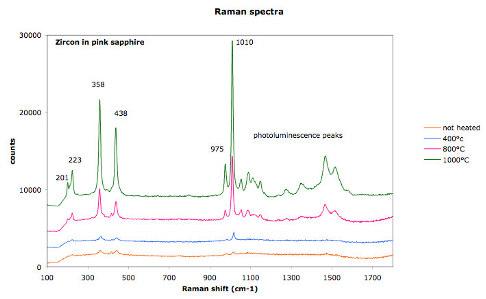
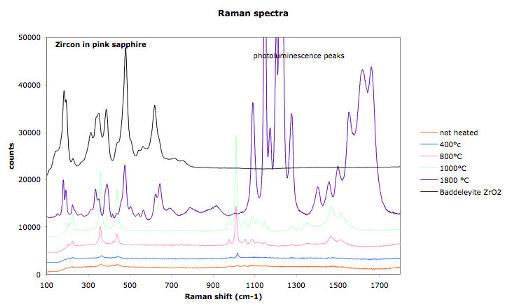
Zircon in pink sapphire from Ilakaka, Madagascar
1000°C
800°C
400°C



Raman spectra show the effect of heat treatment on the cristallinity of zircon inclusions in pink sapphires (from Ilakaka, Madagascar).
SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 10

Inclusion studies
ZrSiO4
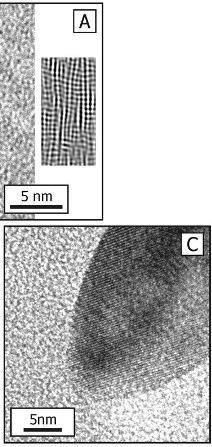
High-temperature heating results in melting of zircon and precipitation of baddeleyite in silica glass matrix
Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 11
reference baddeleyiteZrO2 heated 1800°


dendritic baddeleyiteZrO2 precipitates within silica glass matrix (amorphous) on the surface of beryllium diffusion treated corundum.
Inclusion studies



prismatic zircon inclusions in Kashmir sapphires, often slightly corroded.



tiny prismatic zircon inclusions in sapphires from Bemaintynear Ambatondrazaka (Madagascar), visually quite similar to zircons in Kashmir sapphire

Inclusion studies

Kashmir

non-metamictzirconinclusions
Ambatondrazaka Madagascar metamictzirconinclusions
‚Kashmir-like‘ sapphires of excellent quality from new deposit at Bemaintynear Ambatondrazaka, Madagascar.
Raman spectra of zircon inclusions
SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 14
Inclusion studies
Zircon ZrSiO4
Analysis of Raman spectra (position and peak width of 1008 cm-1 peak) of zircon inclusions of corundum (ruby/sapphire) specimens from different origins.
Mogok, Burma
Madagascar
Sri Lanka
Umba, Tanzania
Kashmir
Mercaderes, Colombia
Raman peak at ~ 1008 cm-1, anti-symmetric ν3 (SiO4) stretching:
SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 15


increase in metamictisation

New instrument



SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 16




SGG Zermatt 30th June 2017 | Page 17





New instrument
Time ofFlight : GemTOF
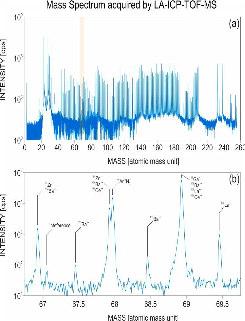
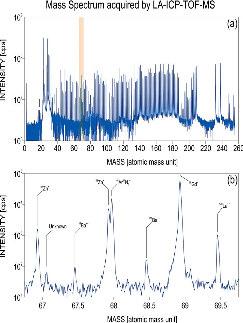



New Instrument
Time ofFlight : GemTOF





Inclusion studies



The
soldatSotheby‘s Geneva forUS$ 8.35 mio.



Pargasite(amphibole) in sapphire from Kashmir


FromGeologyto Gemmology



FromGeologyto Gemmology
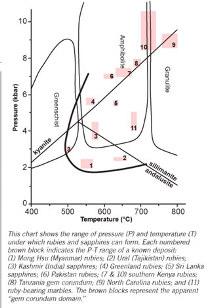
Rubies from amphibolite (metamorphic rock) are characterised by a distinct iron concentration, thus contributing to their colour and UV fluorescence reaction.
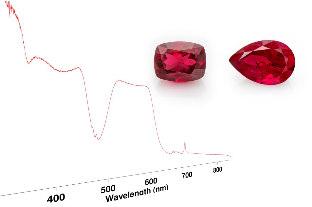



Inclusion studies
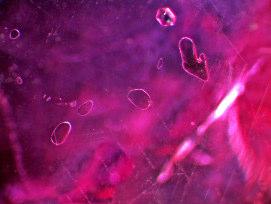





Inclusion studies



Inclusion studies

1


local change of the Ti4+ -Fe2+ intervalencecharge transfer (IVCT) presumably caused by a reaction with the amphibole inclusion results in spericalcolour „hole“ around these amphiboles.

Inclusion studies
Emerald sample –LABc_1144 Sandawana(Zimbabwe)
actinolite-tremoliteneedles Raman spectrum

X-rayµ-tomographysection

Inclusion studies
3D visualisation of inclusions and organic fillers in emeralds Project in collaboration with the Laboratory forNeutron ScatteringandImaging atPSI




Inclusion studies
Neutronµ-tomographyX-rayµ-tomography


Neutronµ-tomographysectionX-rayµ-tomographysection White=±notseen=cavityfilling(epoxy)
Grey=white=pyrite
Black=black=cavity
Weakgreyishlines=notseen=fissurefilling(epoxy) ±notseen=grey=calcite


Inclusions in gemstones are highly important clues for a better understanding of (coloured) gemstones.
They reveal important information about formation processes, geological setting, and treatments.
The analysis of gemstones and their inclusions is based on a large range of methods from basic microscopy to advanced methods using laser light, X-rays, electrons and neutrons.
The aim is to characterize their chemical, isotopic, and structural state as far as possible.
Until today, meticulous microscopic examination of gemstones and their inclusions remains crucial, as it not only unveils their beauty, but also provides a wealth of information to gemmologists.

Thankyoufor yourattention









swiss-image.ch_AndreasGerth
