
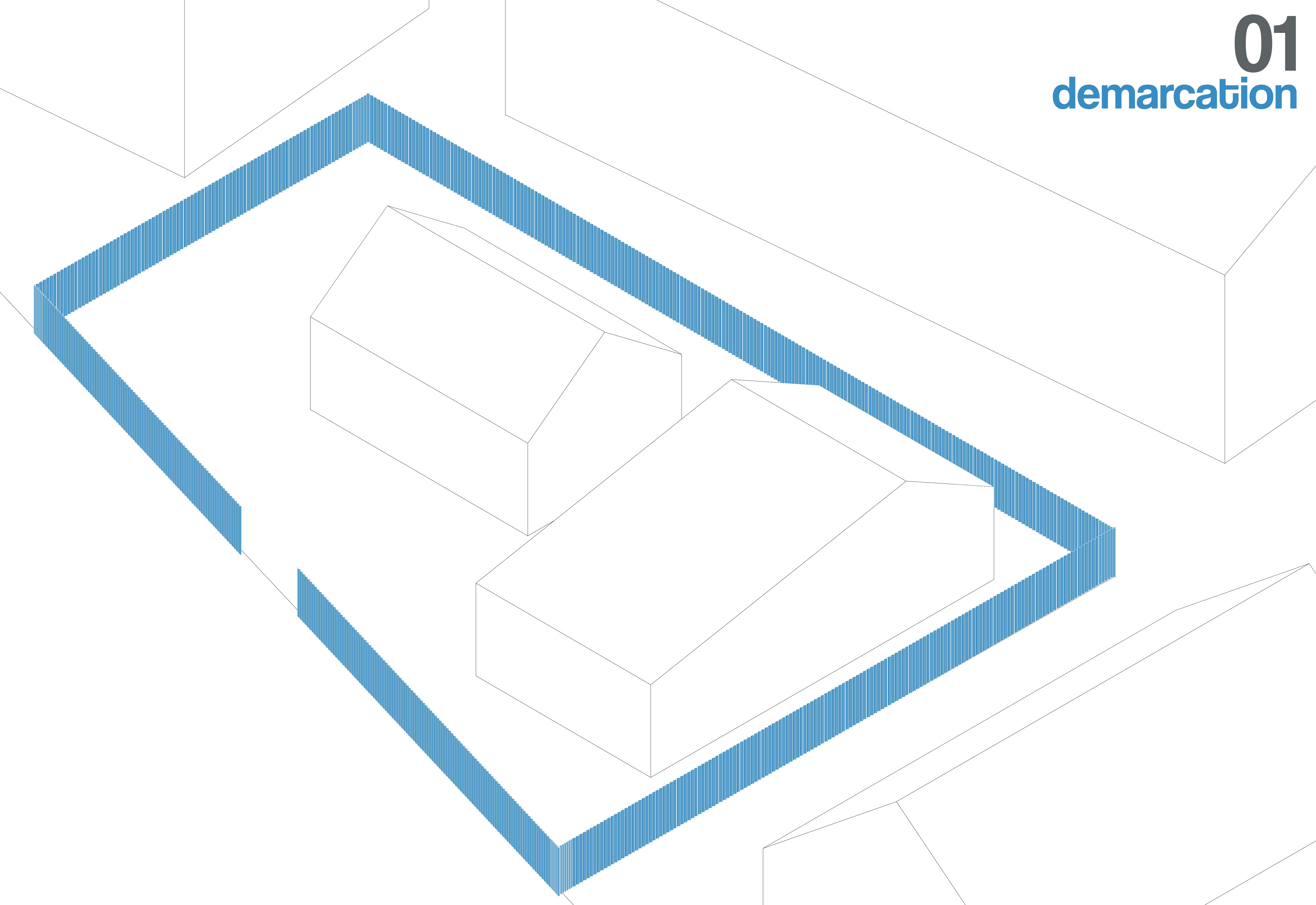
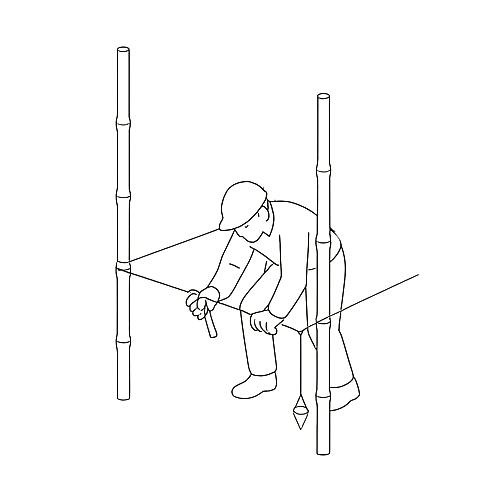
The site is measured and marked using stakes and string lines based on the construction drawings. Reference points for key structural elements, such as walls and foundations, are established to guide excavation and alignment. drawings. Reference points for key structural elements, such as walls and foundations, are established to guide excavation and alignment.


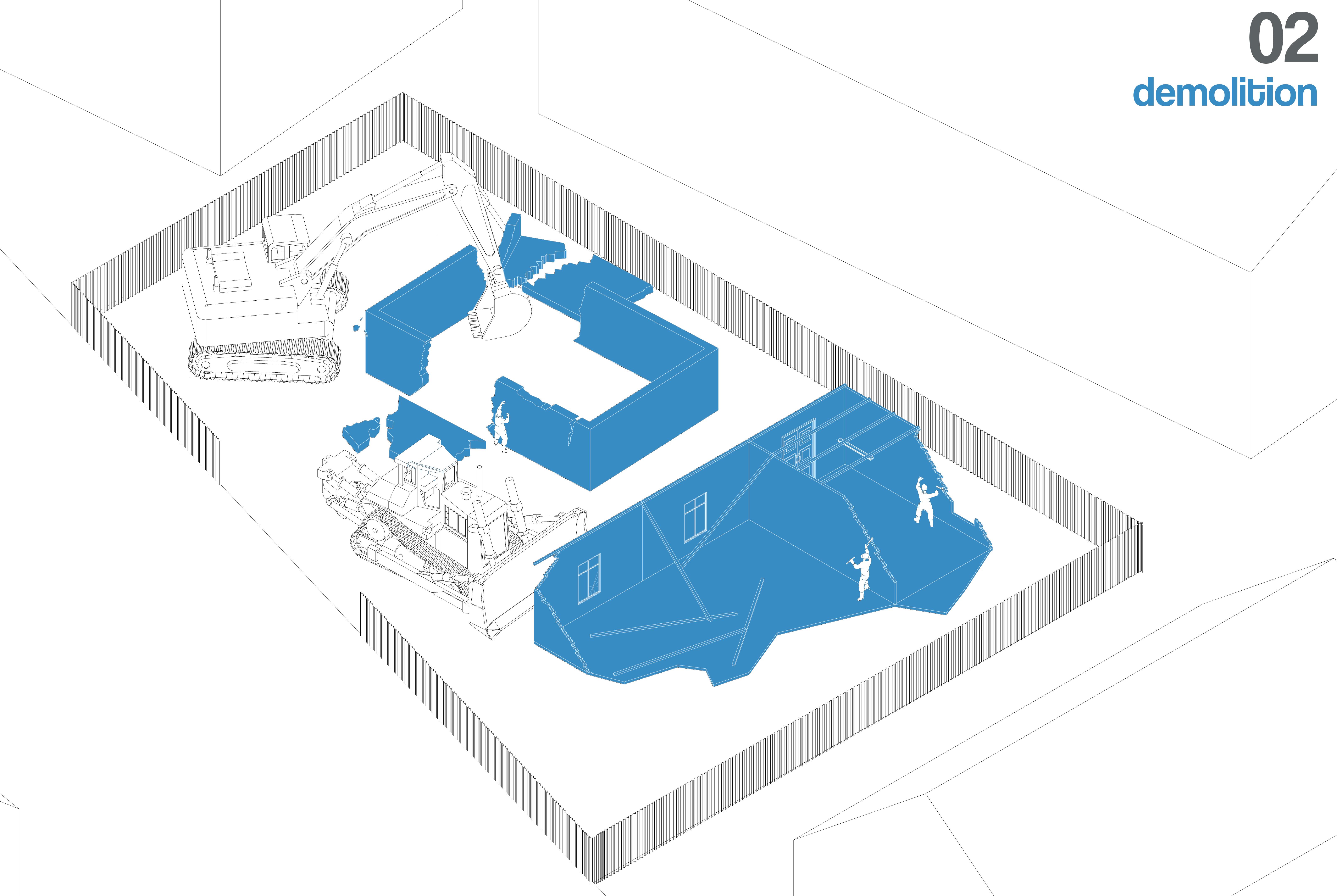
The area is cleared of vegetation, debris, and obstructions. The ground is leveled, and necessary soil compaction is performed to prevent settlement. If necessary, temporary drainage systems are installed to prevent water accumulation.
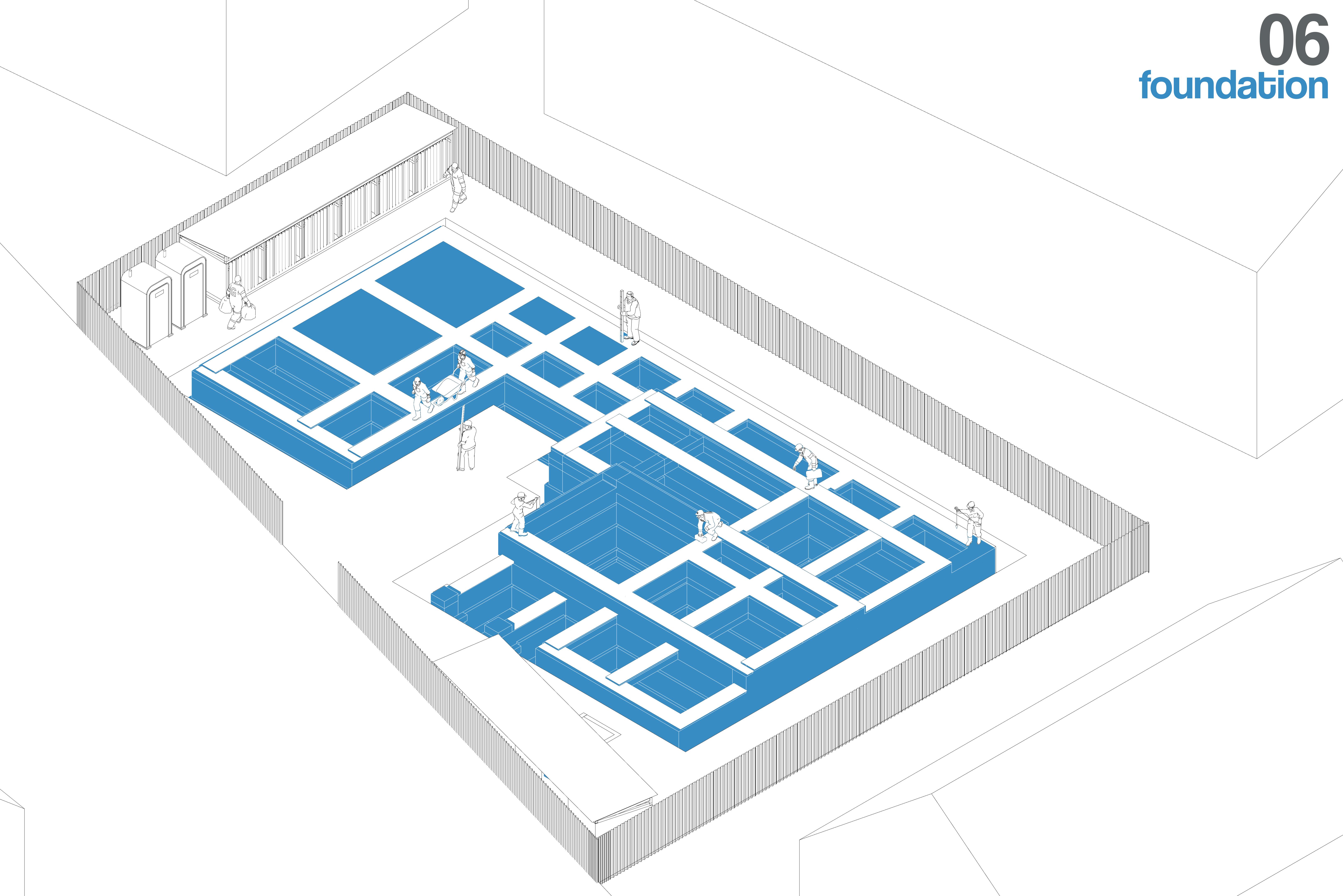
The foundation layout is marked precisely on the ground using chalk, string, or lime powder. This ensures that excavation follows the correct dimensions and alignment. Corner posts or batter boards are placed to maintain reference points.
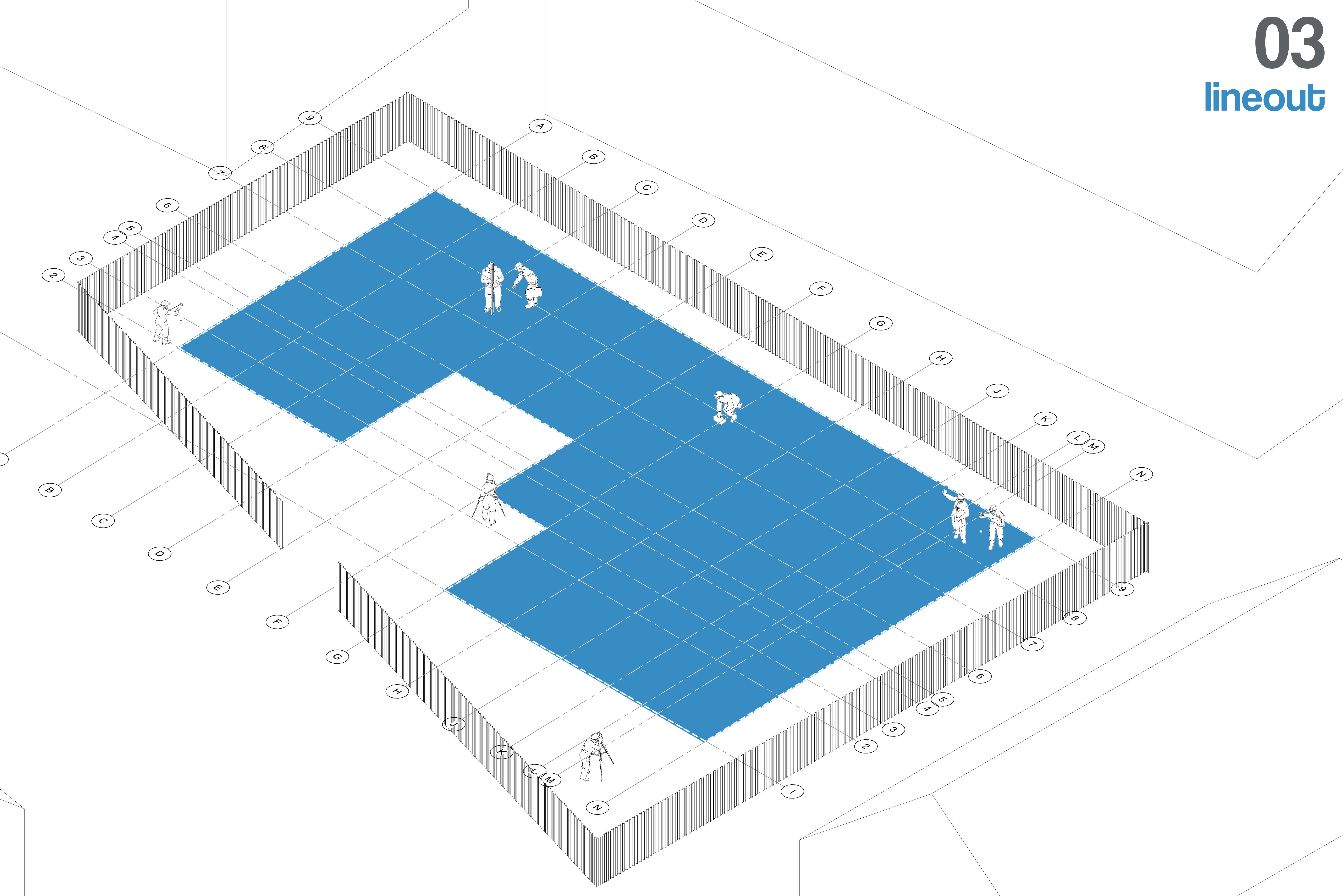
Trenches for the stone strip foundation are excavated to the required depth based on soil conditions and structural load requirements. The trench bottom is leveled, compacted, and prepared for foundation work.
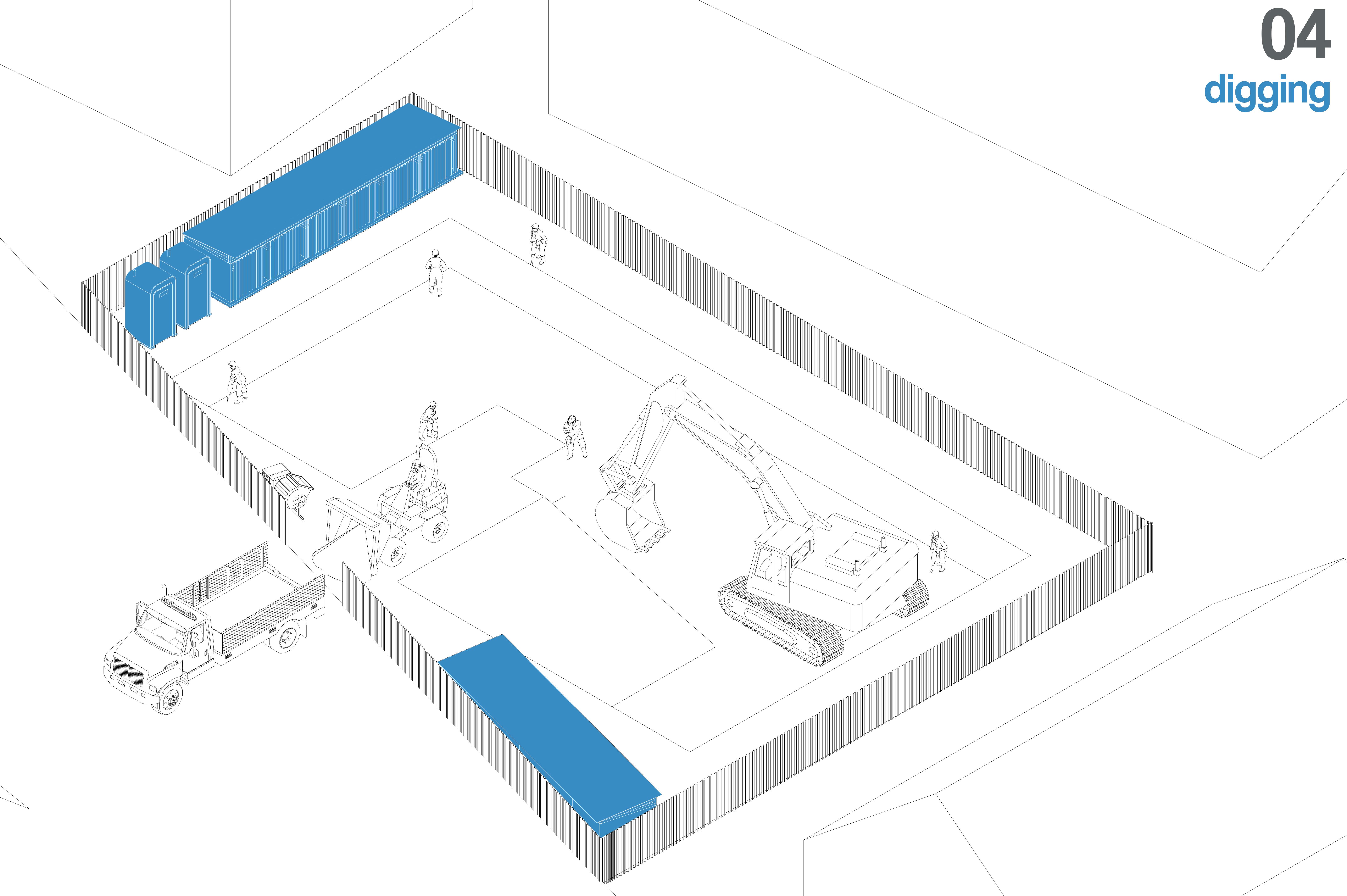
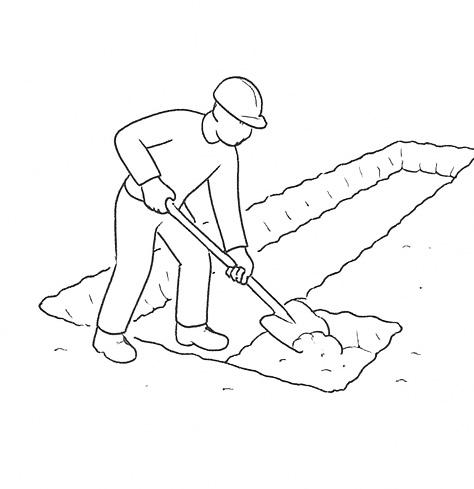

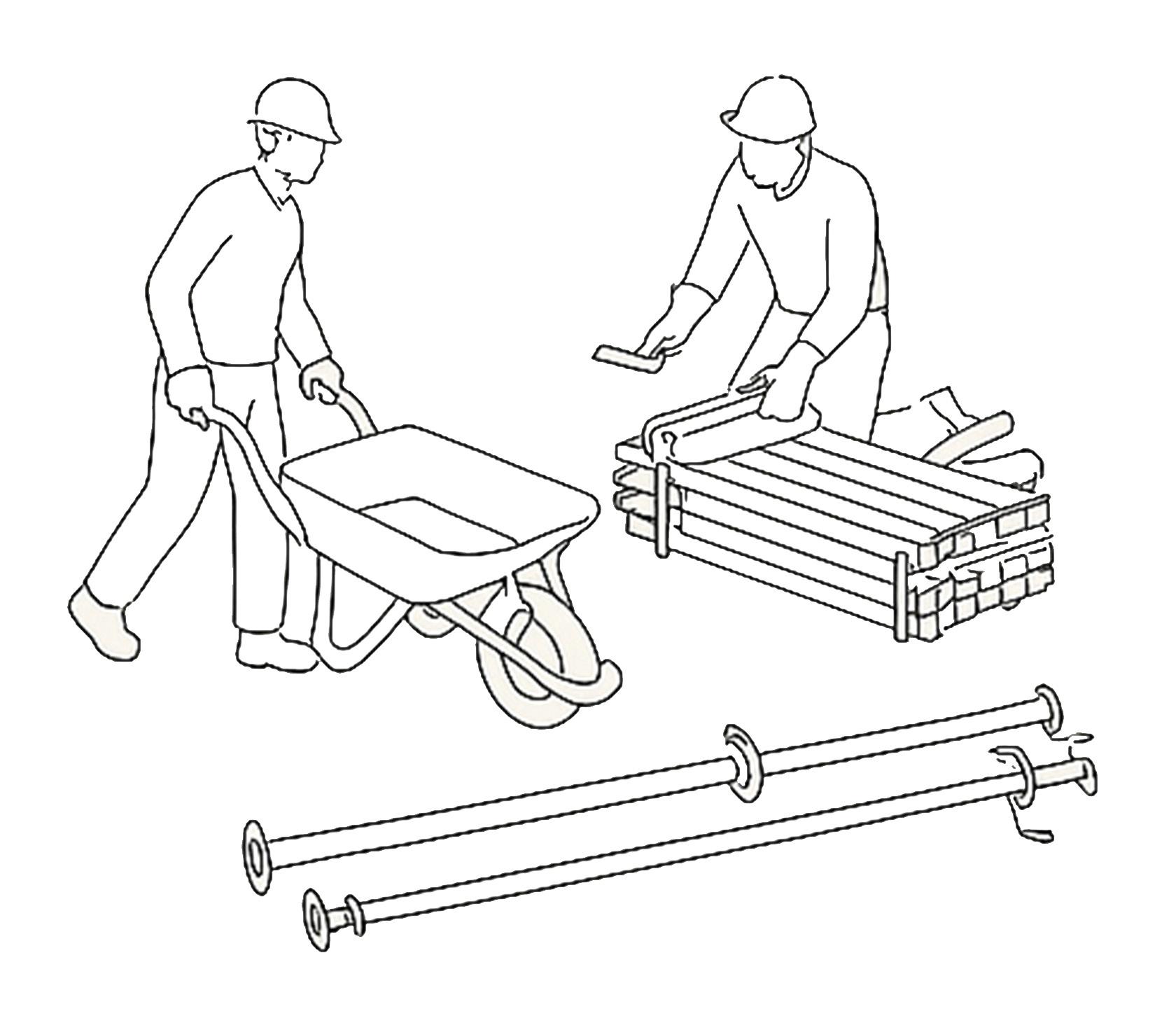
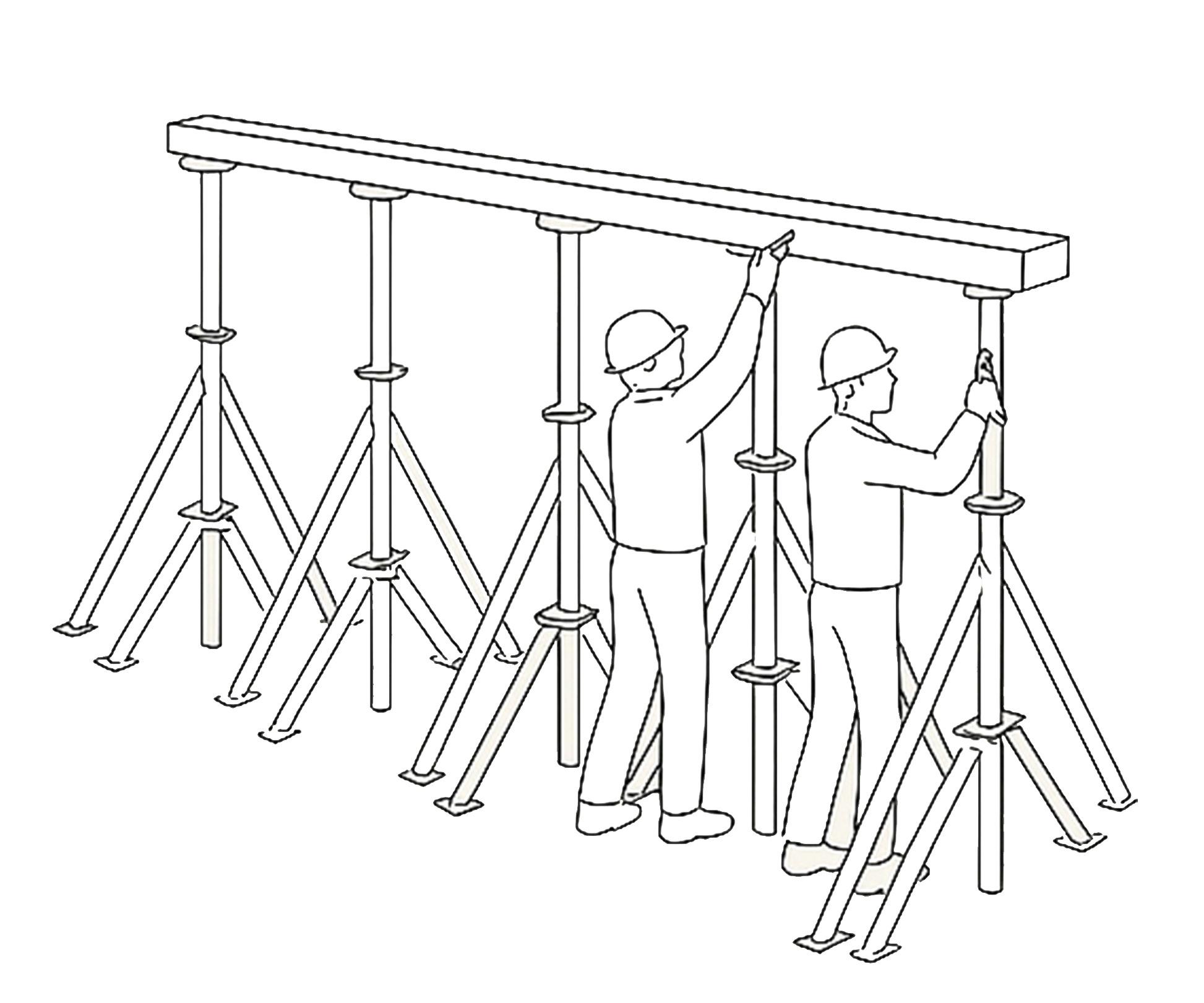
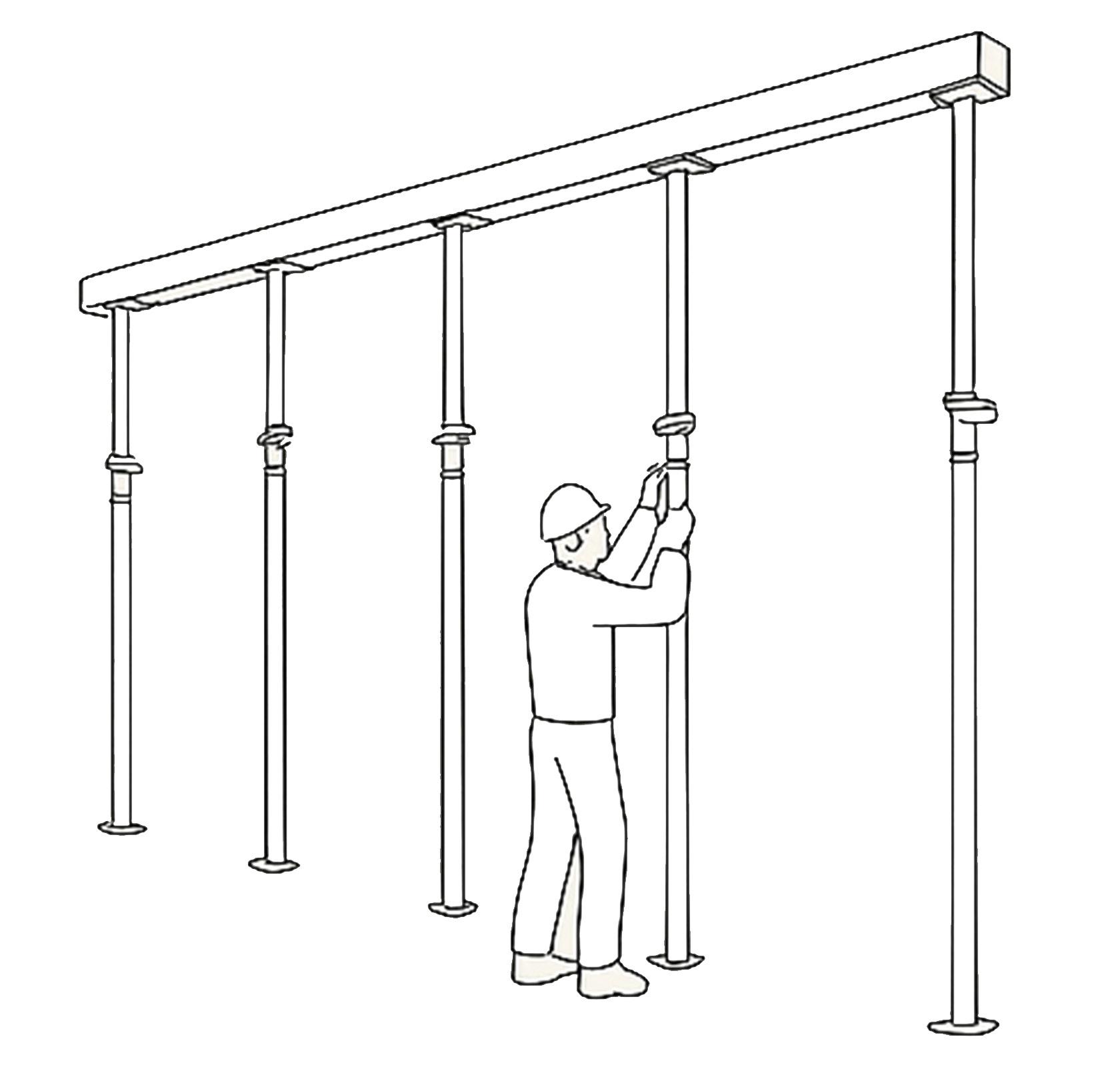
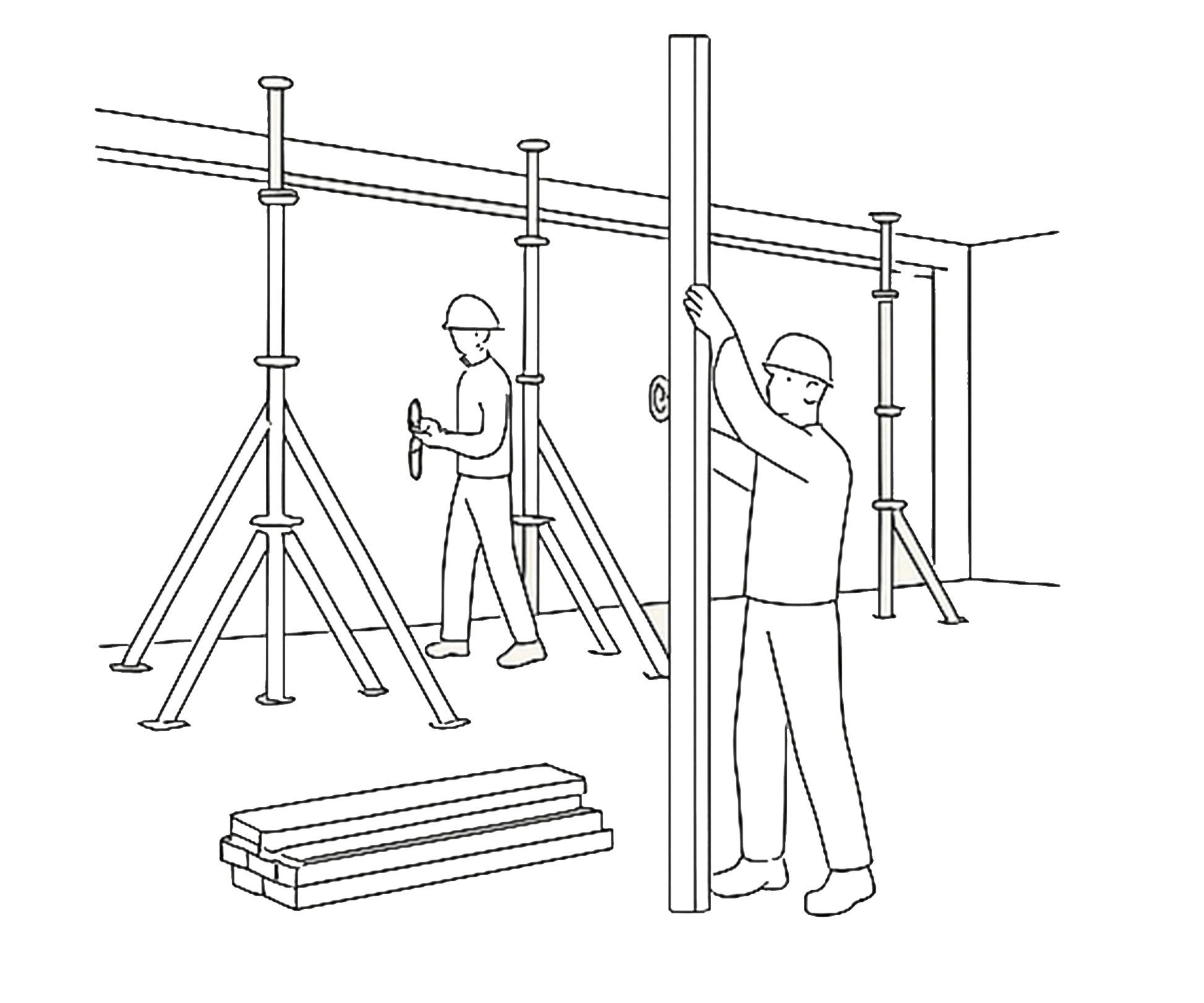
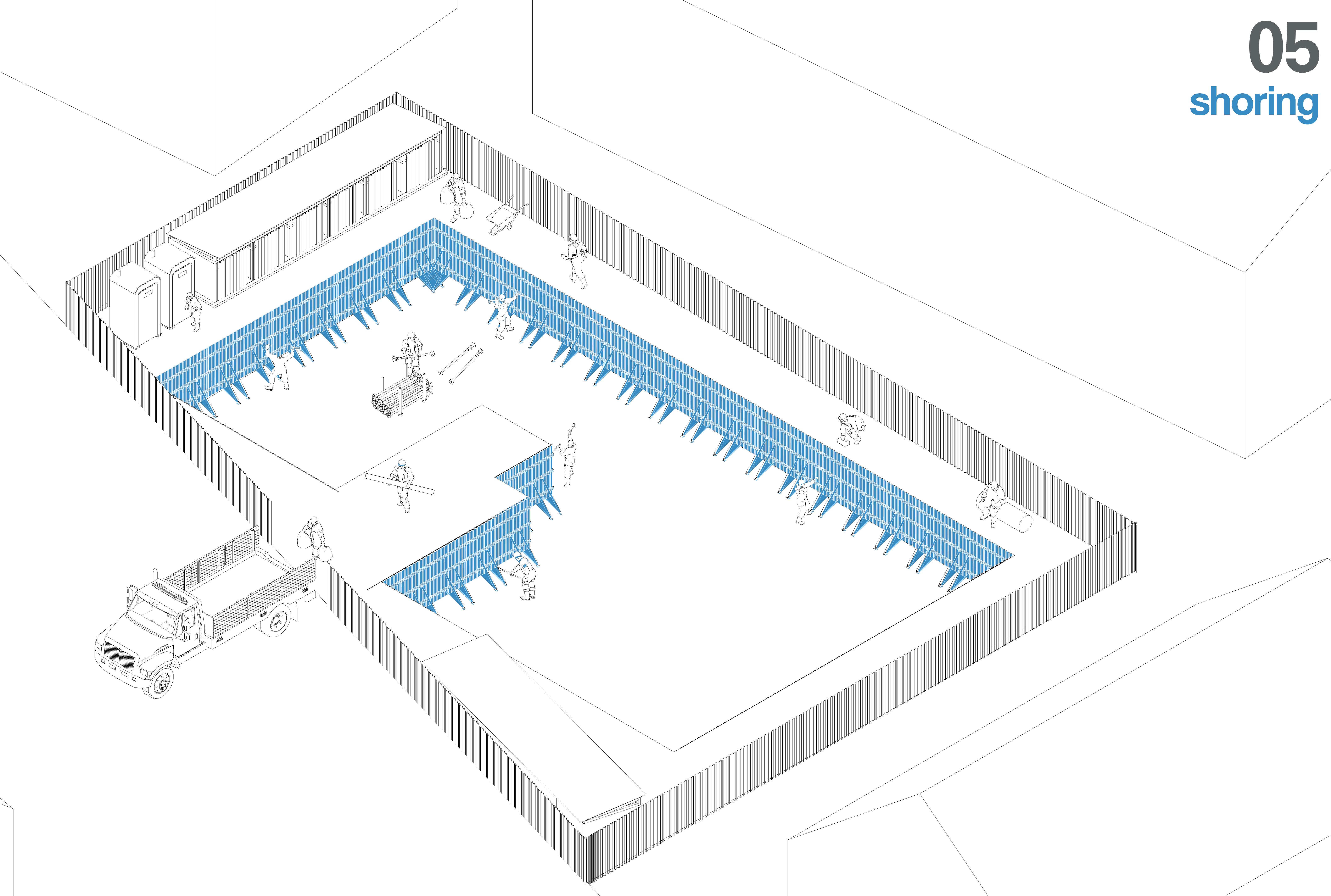
If the excavation depth is significant or the soil is loose, temporary wooden or bamboo shoring is installed to support the trench walls and prevent soil collapse, ensuring worker safety.


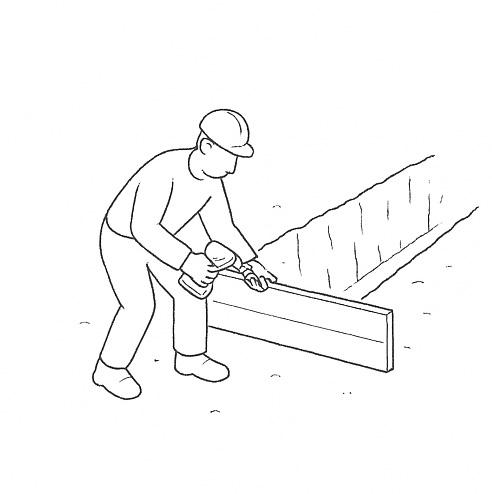
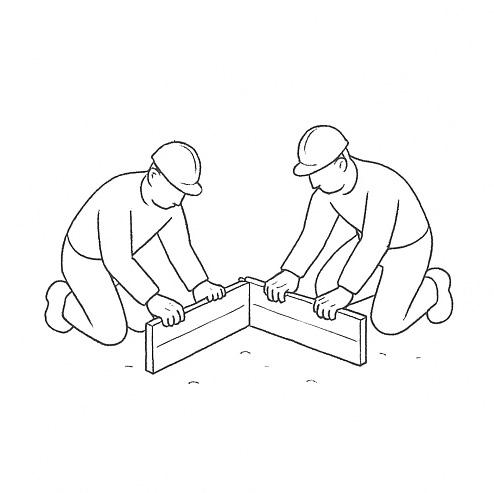
Formwork is set up using wooden or bamboo boards to shape the stone strip foundation. A base layer of compacted gravel is laid for drainage, and the first layer of stones is placed with lime or cement mortar for binding. The foundation is built up to the plinth level with properly staggered joints for strength.
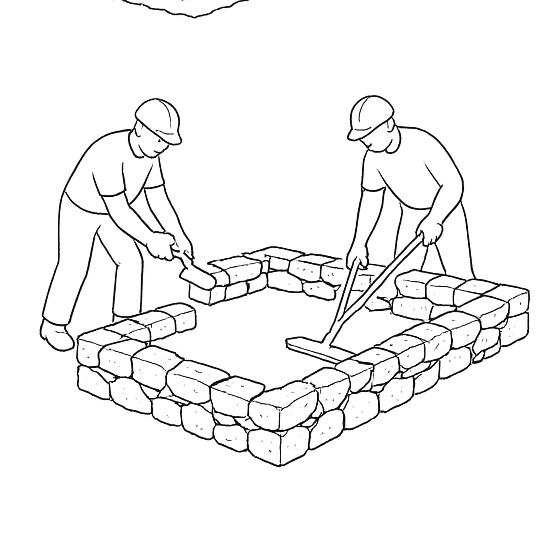
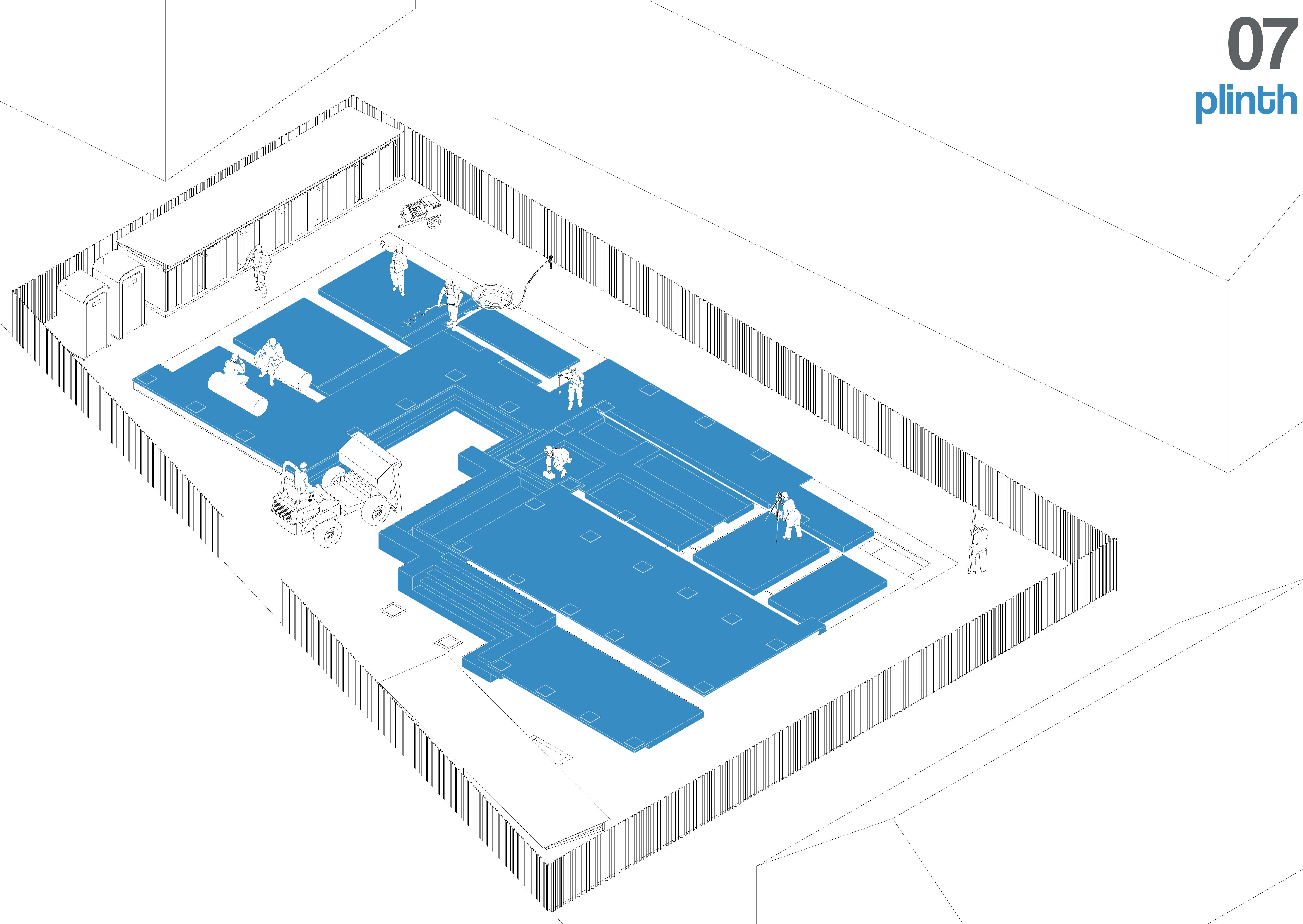
After the foundation sets, the plinth is constructed using IPS stone, providing a solid, moisture-resistant base for the walls. The plinth is finished with a smooth, polished surface and allowed to cure.
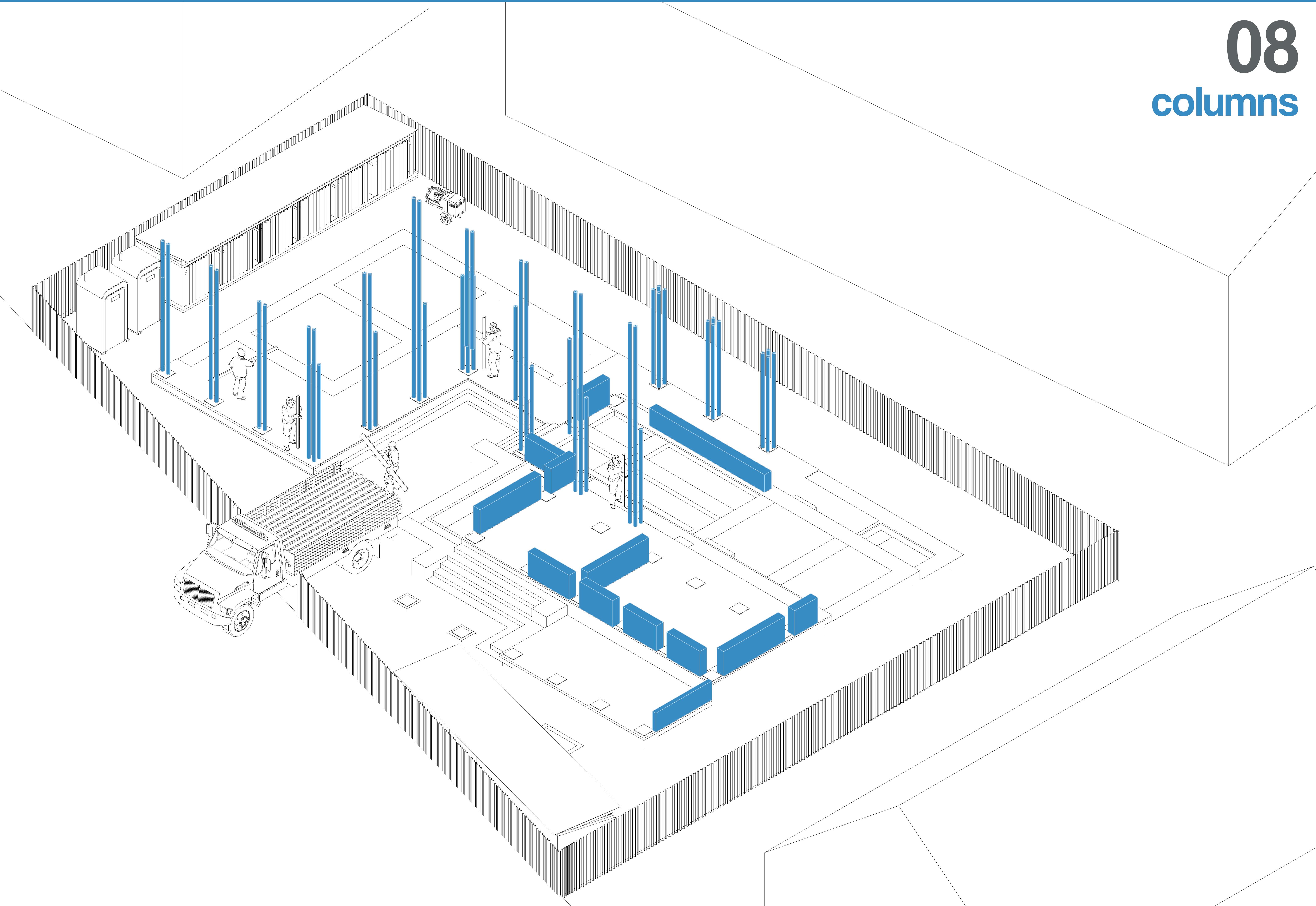
Bamboo columns are erected in framed sections, anchored securely to the plinth beam. Parapet walls are constructed in designated areas using earth to ensure safety and wind resistance on the upper level.
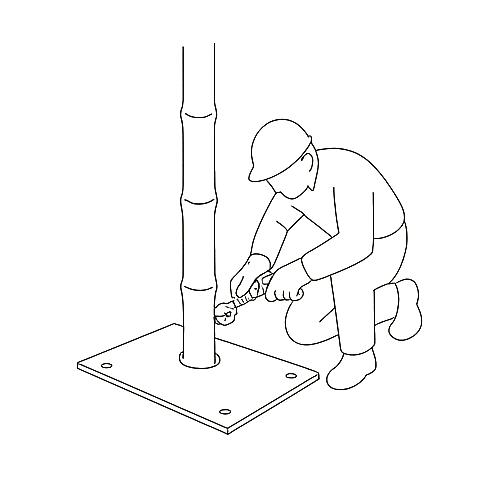
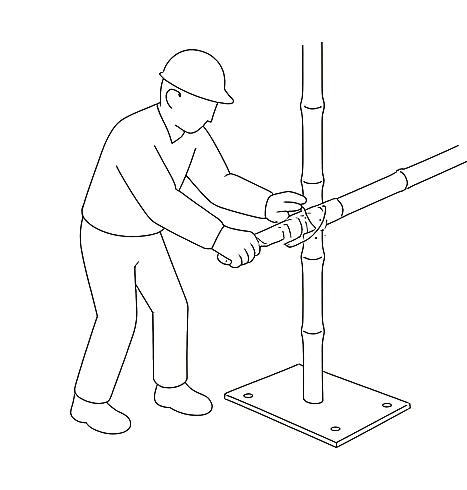
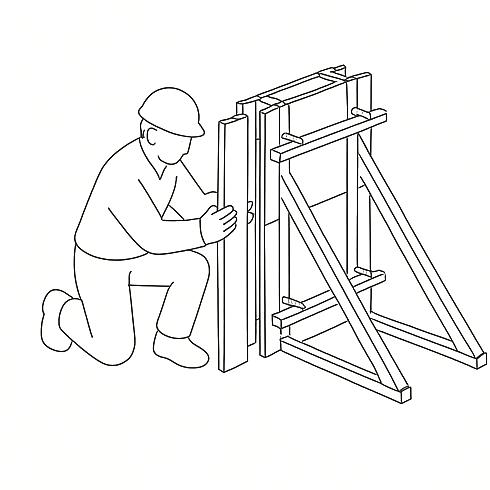
Rammed earth walls are constructed using temporary formwork. Earth is poured in layers, compacted using rammers, and the formwork is progressively moved upward. Door and window frames are embedded during construction to ensure a secure fit.
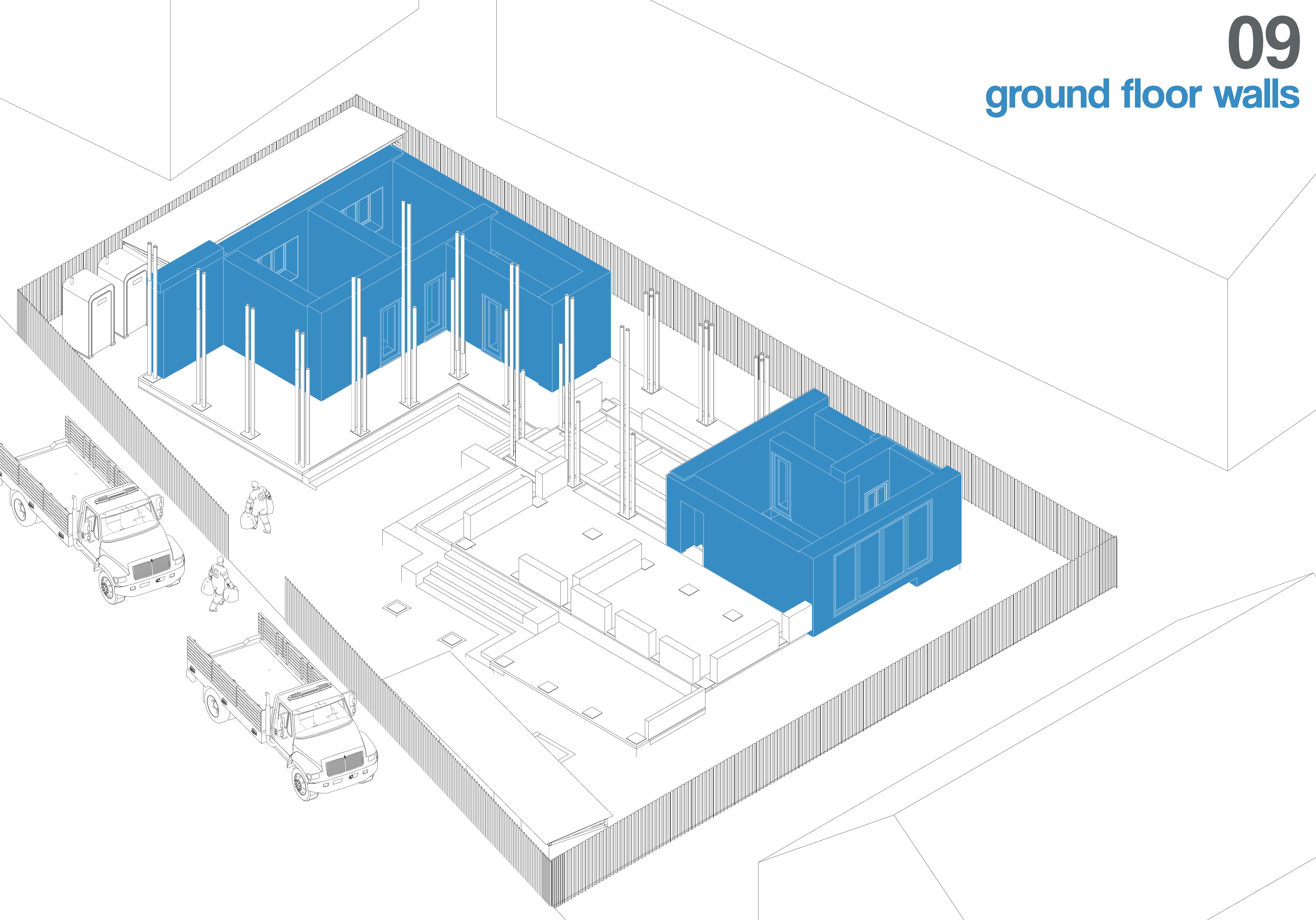
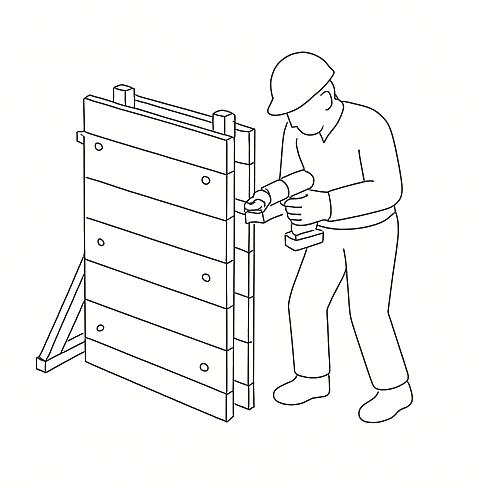
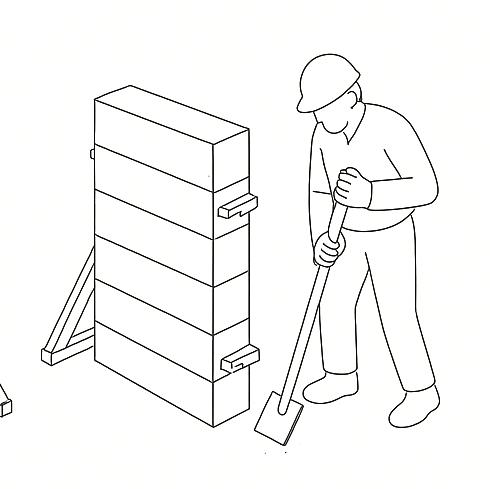

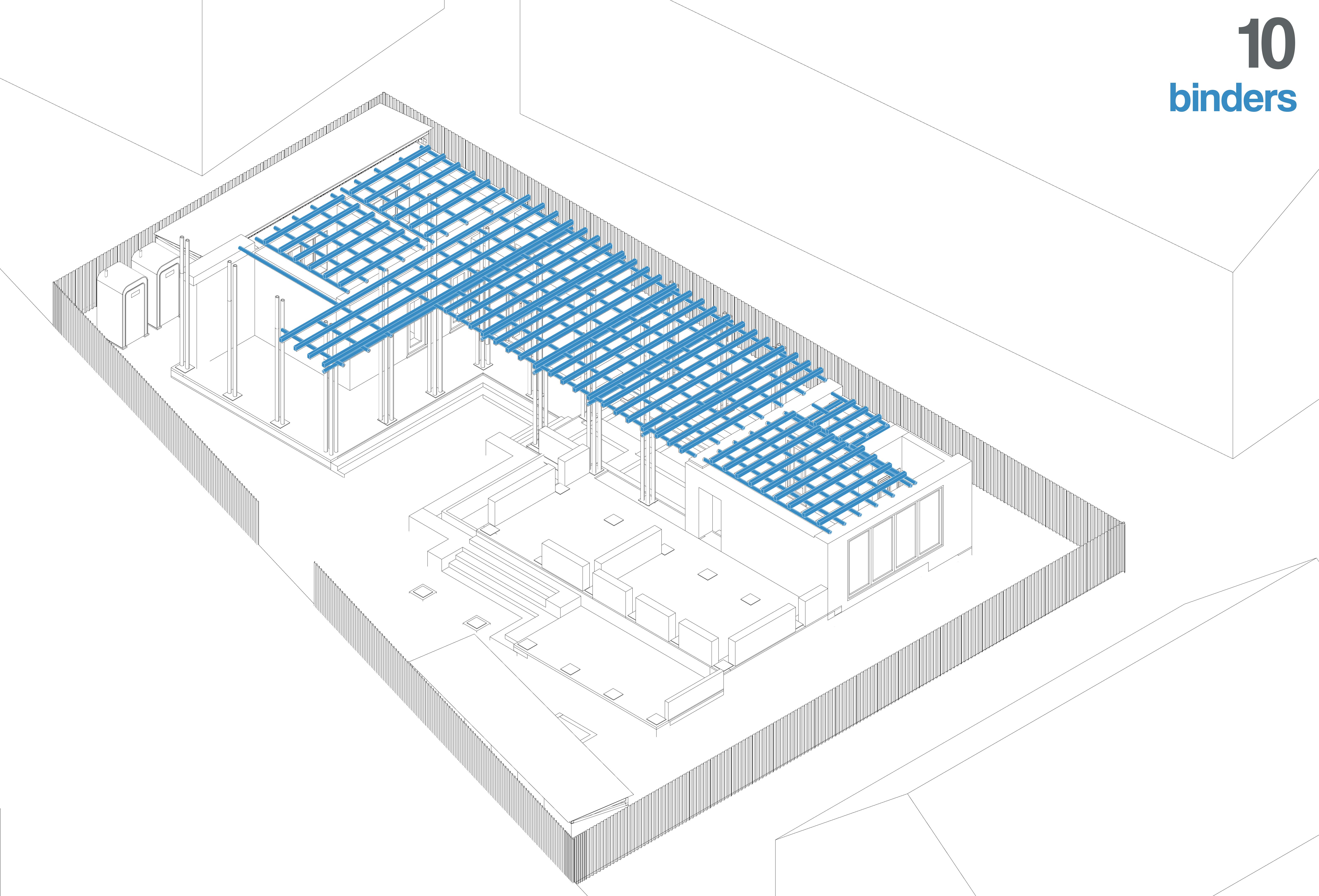
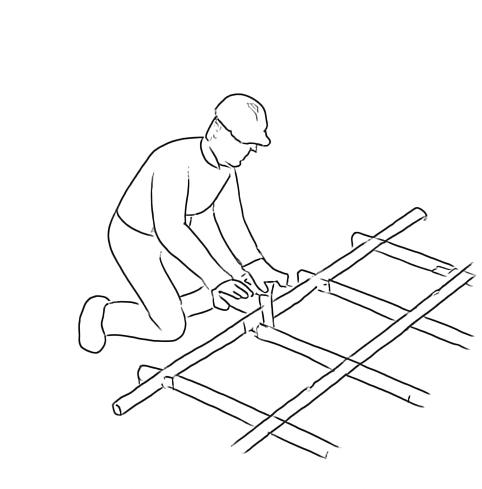
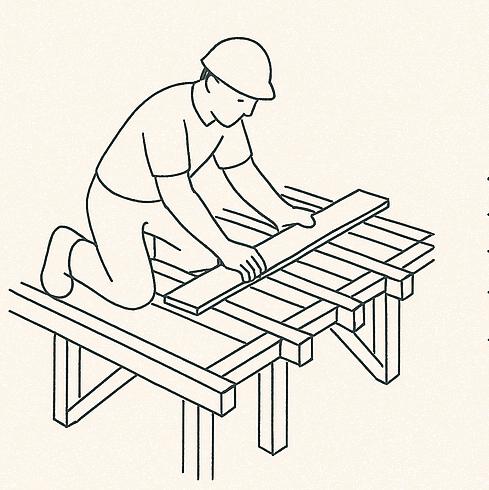
Horizontal bamboo binders are installed to connect the walls and distribute structural loads. Timber joists are placed on the binders, spaced appropriately, to support the first-floor timber decking.
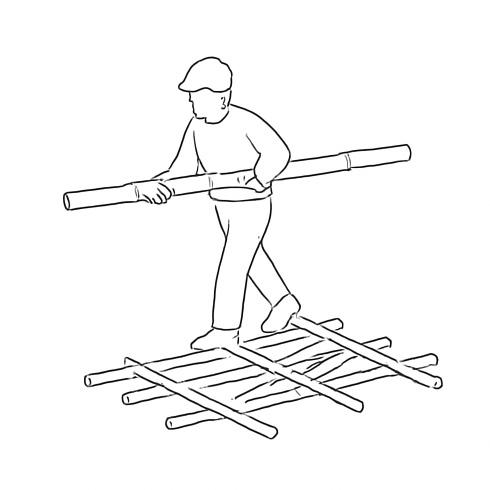
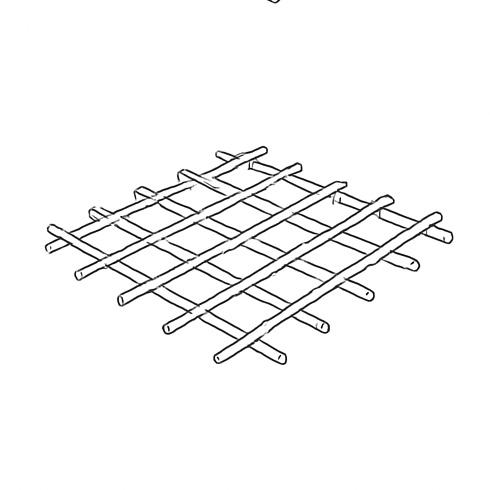
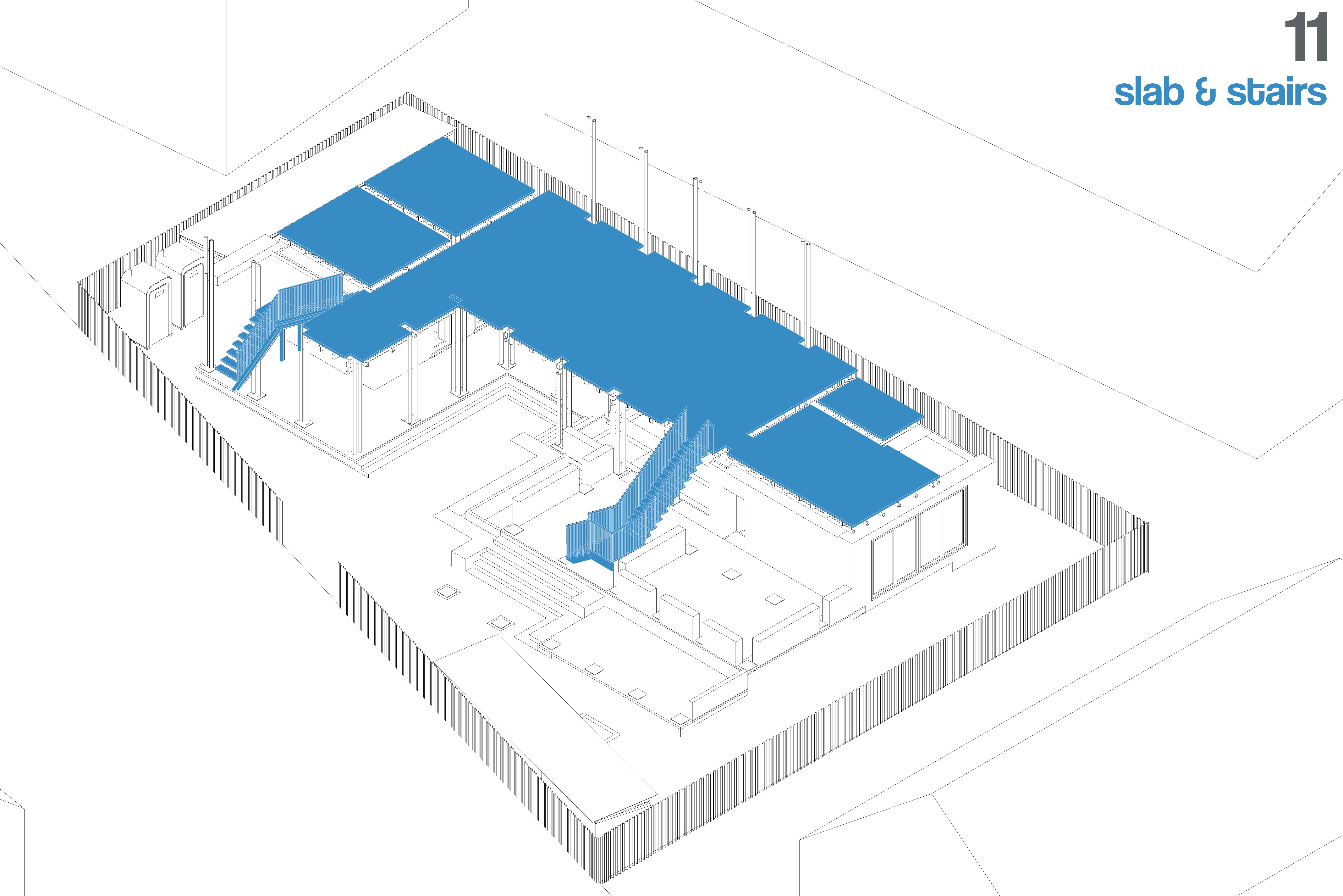
A timber staircase is installed for access to the first floor. The first-floor timber planks are laid over the joists, fastened securely, and treated to prevent moisture damage and termite infestation.
The second level of rammed earth walls is constructed similarly to the ground floor, with the integration of window and door frames. Adequate curing time is given for structural stability.
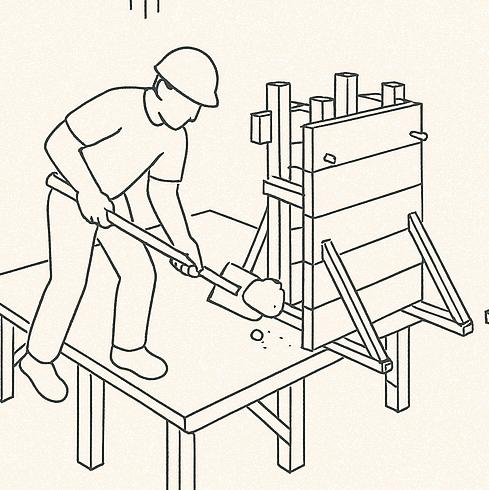
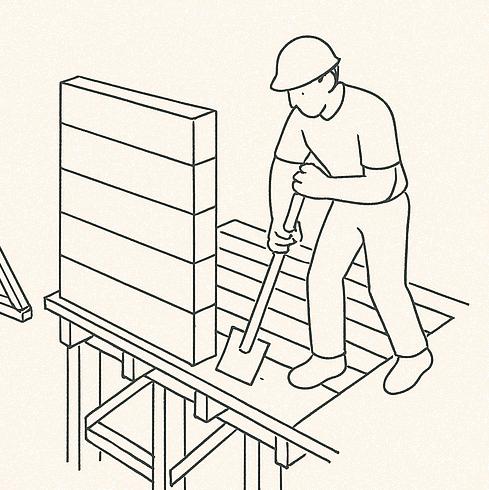
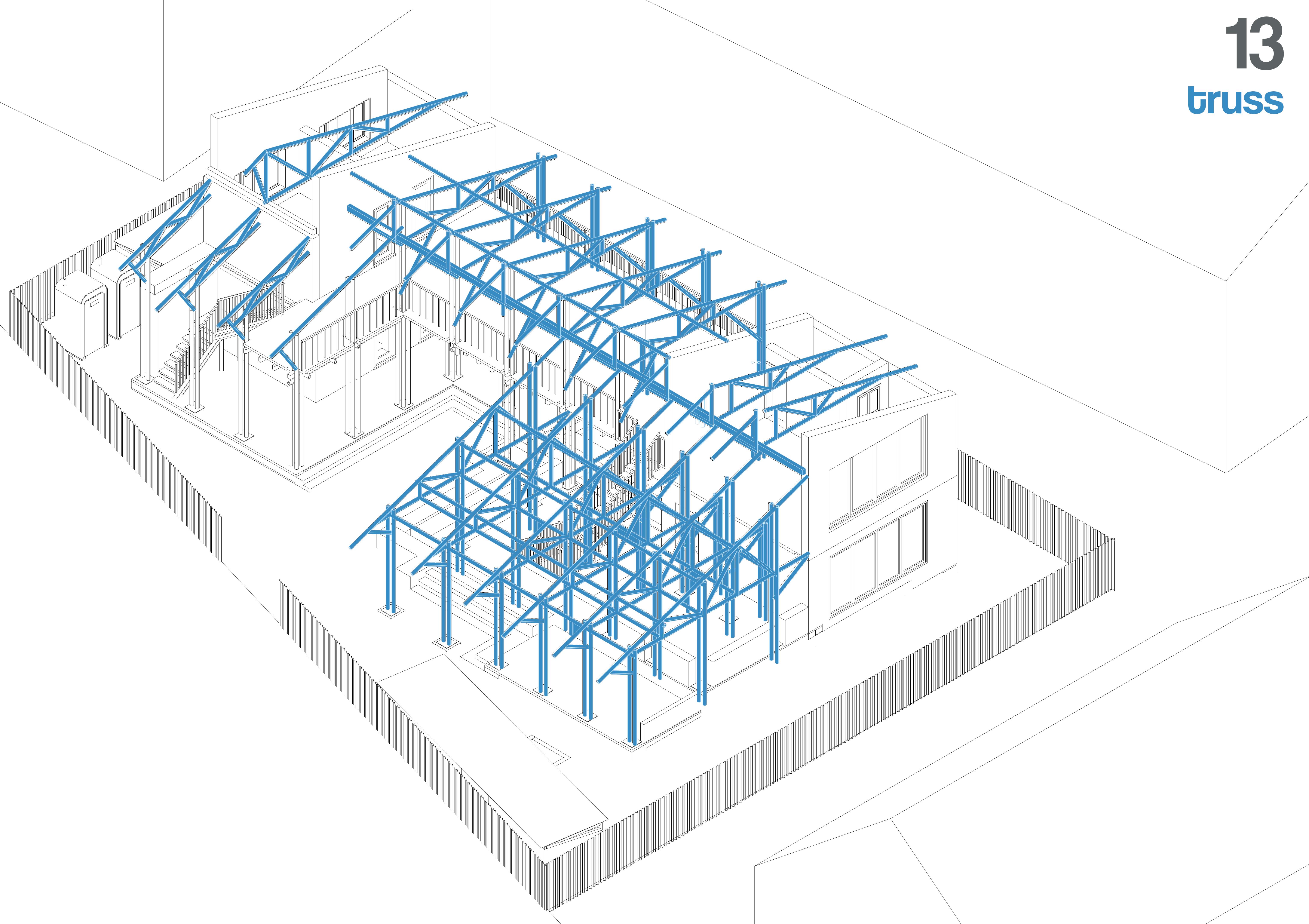
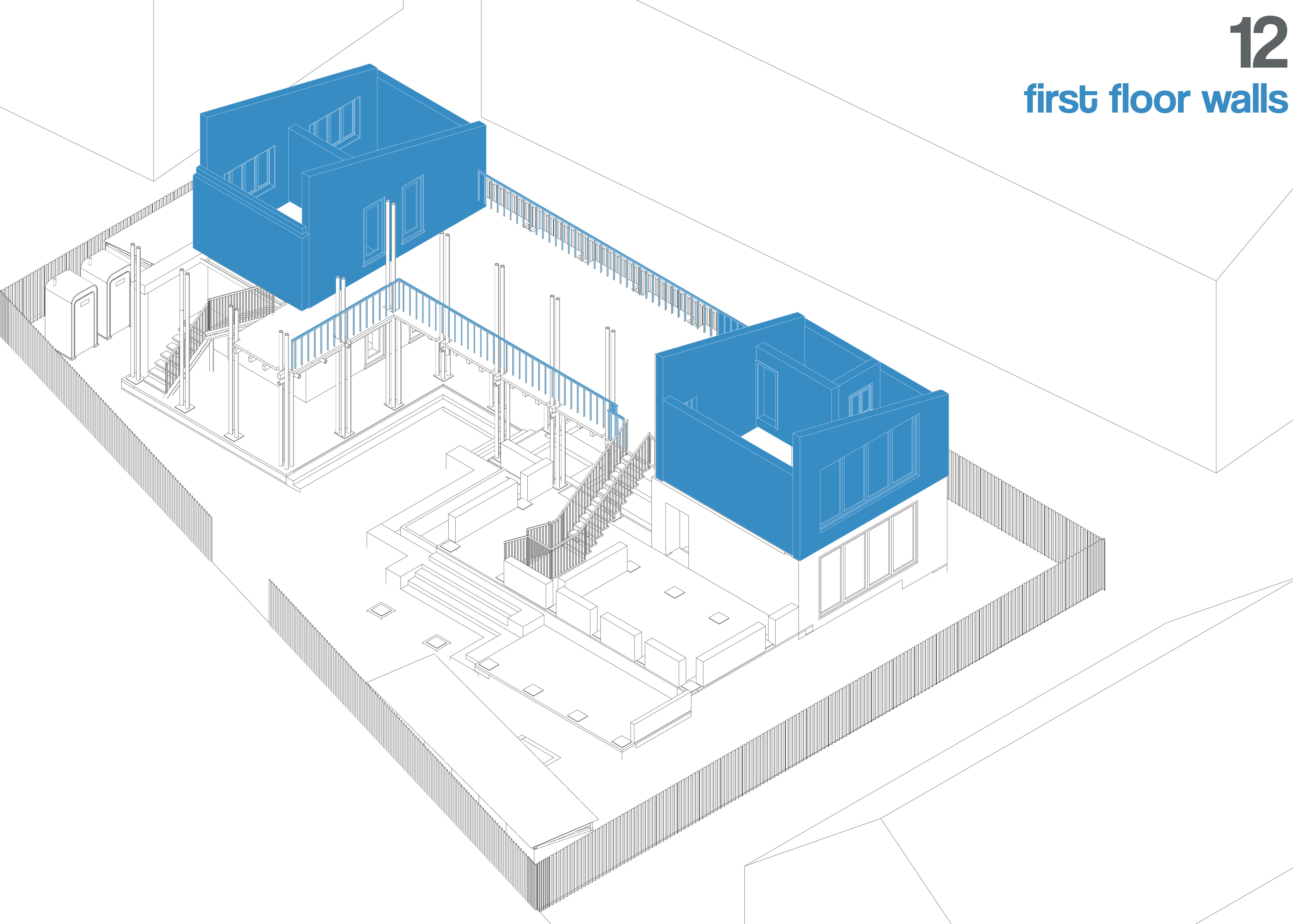
The roof structure is framed using bamboo trusses, designed for efficient load distribution. The trusses are secured using traditional joinery techniques, bolts, or lashings to ensure stability.


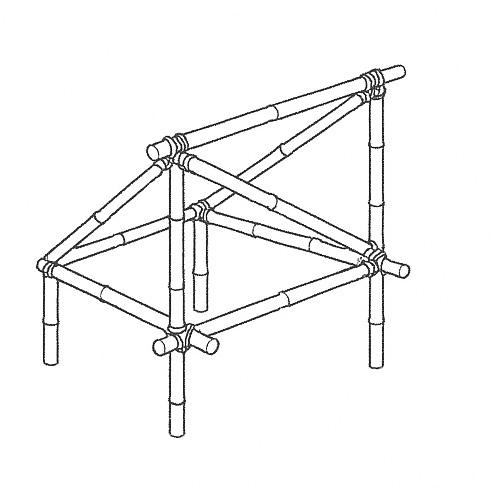
Additional bamboo joists are placed across the trusses to provide intermediate support for the roof covering, improving load-bearing capacity and resilience against wind loads

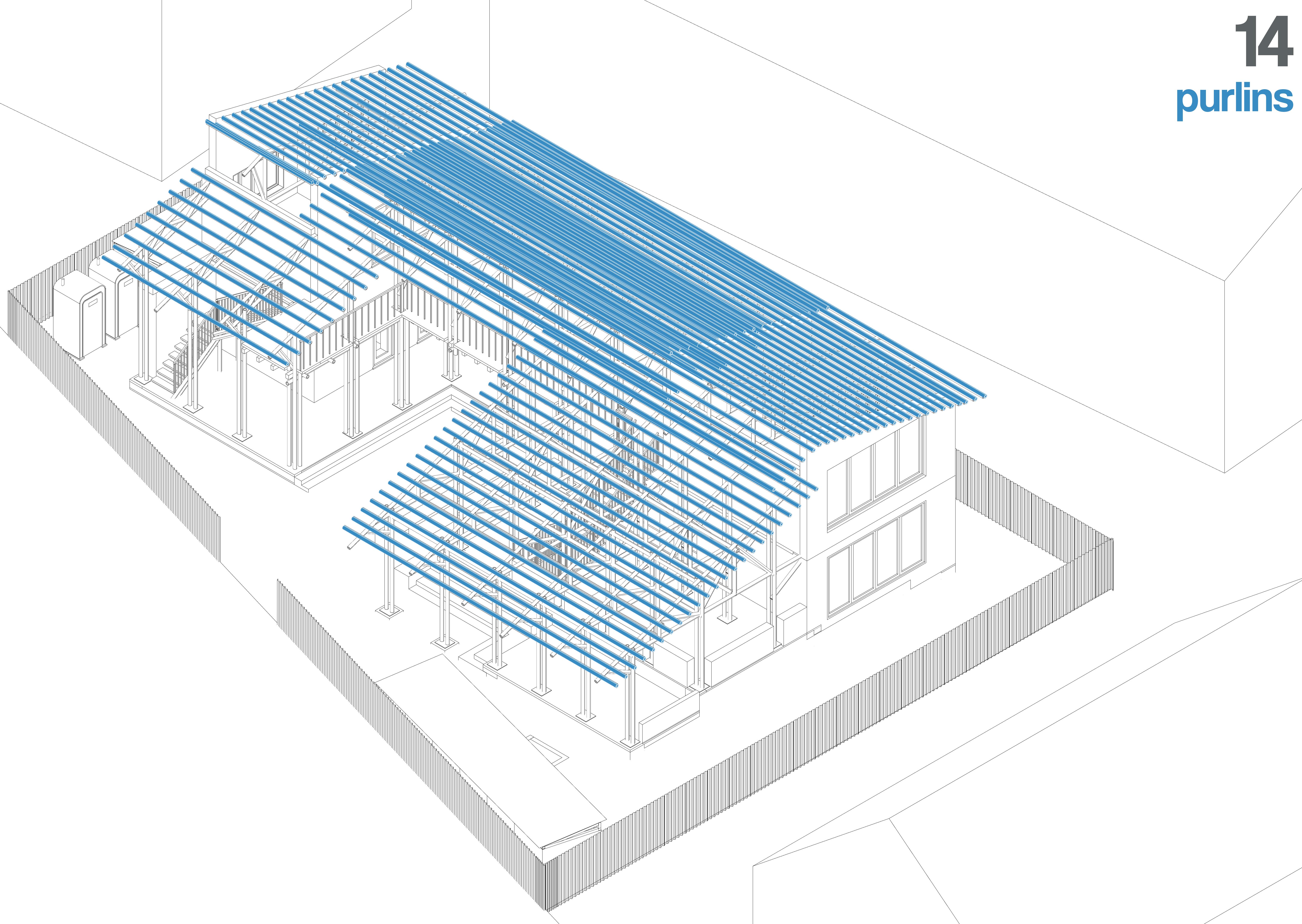
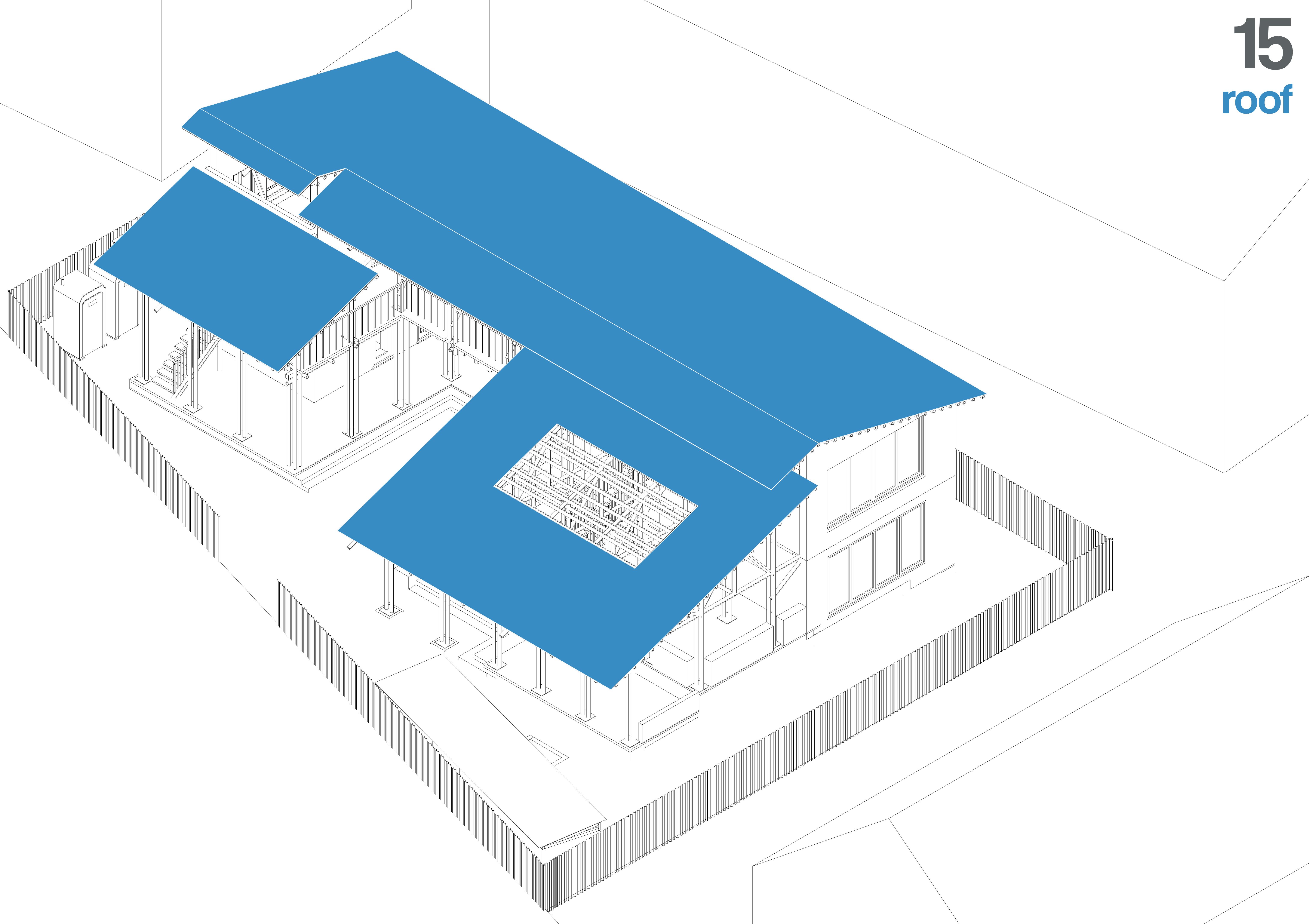
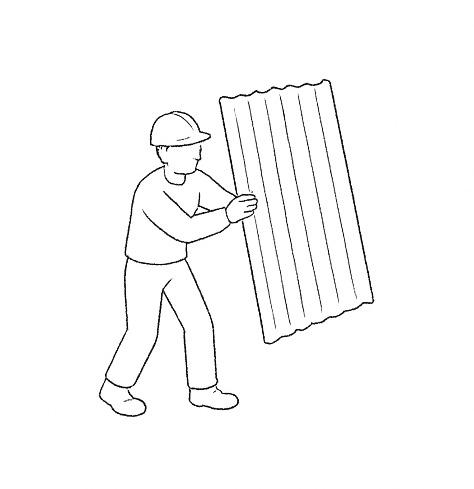
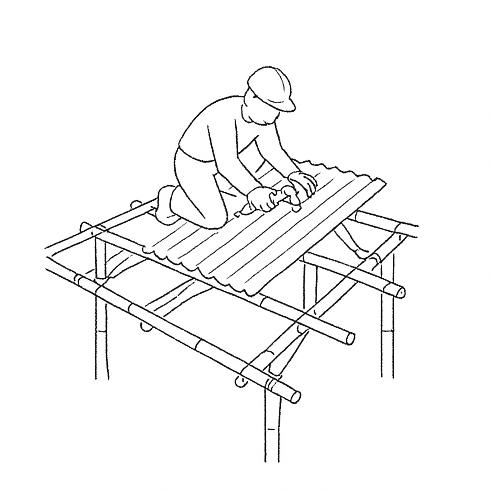
Corrugated GI tin sheets are installed over the bamboo framework. The sheets are fastened with screws and washers, ensuring proper overlap to prevent leaks. Adequate overhangs are provided for water runoff, and ventilation openings are incorporated to regulate indoor temperature.
2024-25_6_BATCH A22_BUILDING MAKING COURSE
SCHOOL OF ENVIRONMENT AND ARCHITECTURE





