








- Arafin Mallick
In recent years, global supply chains have undergone significant transformations. One of the most noteworthy trends is the shift from global to regional manufacturing hubs, commonly referred to as reshoring and nearshoring. These strategies have gained traction as companies reevaluate their supply chain models in response to rising costs, geopolitical tensions, and thedisruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. In this article, we will explore what reshoring and nearshoring mean, the cost-benefit analysis of these strategies, and real-world examples of companies that have embraced them.

Reshoring refers to the practice of bringing manufacturing and production activities back to the company's home country. For example, a U.S.-based company might relocate its manufacturing operations from China back to theUnitedStates Ontheotherhand,nearshoring involves moving production closer to the home market but not necessarily within the same country. For instance, a U.S. company might relocate its production to Mexico or Canada instead of Asia.
Both strategies aim to reduce the complexities and risks associated with long-distance global supply chains while improving responsiveness to market demands.

Source: Censuswide, 2023
Globalization dominated supply chain strategies for decades, as companies sought to capitalize on low labor costs in countries like China, Vietnam, and India. However, several factors have prompted a reevaluation of this approach:
1. Rising Labor Costs: Labor costs in traditionally low-cost countries have been increasing steadily. For example, wages in China have risen significantly over the past decade, reducing its cost advantage.

Source: Greater Pacific
2. Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains. Lockdowns, port closures, and transportation delays caused significant disruptions, prompting companies to reconsider reliance on distant suppliers
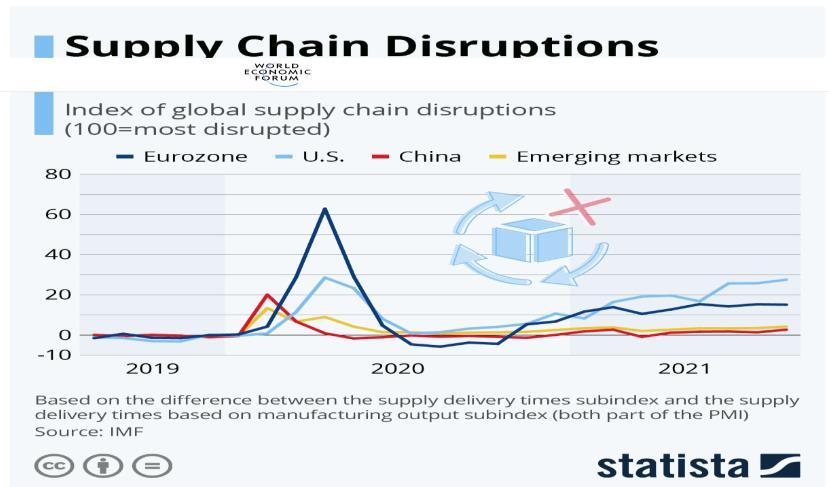
Source: World Economic Forum
3. Geopolitical Tensions: Trade wars, tariffs, and sanctions have made it more challenging and expensive to maintain global supply chains. The U.S.-China trade war, for instance, led many companies to explore alternative sourcing options.
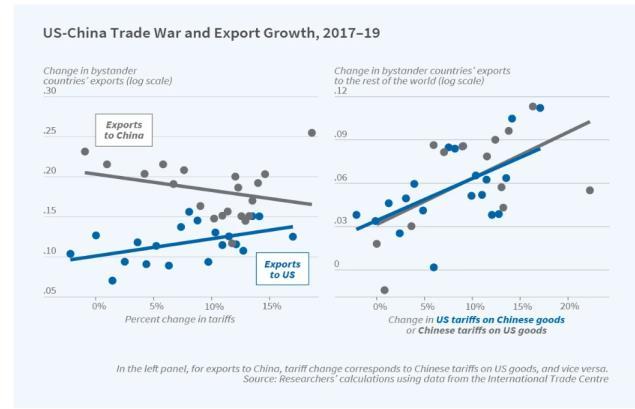
4. Consumer Expectations: Customers today demand faster delivery times. By relocating production closer to the end market,companiescanreduceleadtimes and improve service levels

Cost-Benefit Analysis of Reshoring and Nearshoring
1. Reduced Transportation Costs: By manufacturing closer to the end market, companies can save on shipping costs and reduce their carbon footprint.
2. Improved Supply Chain Resilience: Shorter supply chains are less susceptible to disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics.
3. Faster Time-to-Market: Nearshoring allows companies to respond quickly to changes in customerdemand,improvingcompetitiveness.
4. Quality Control: Relocating production closer to home often ensures better oversight and quality control, which can reduce defect rates and enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Producing in regionswithstringentlaborandenvironmental standards can enhance a company’s reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
1. Higher Labor Costs: One of the primary reasons companies offshored production was to benefit from lower wages. Reshoring and nearshoring often involve higher labor costs, which can impact profitability
2. Initial Investment: Relocating production
facilities requires significant capital investment,includingnewinfrastructure, training, and technology.
3. Supply Chain Ecosystem: Many companies rely on an established network of suppliers in traditional manufacturing hubs. Rebuilding this ecosystem in a new location can be challenging and time-consuming.
4. Limited Expertise: Some regions may lack the specialized skills or technology required for specific manufacturing processes.
Applehasbeengraduallydiversifyingitssupply chain to reduce dependence on China. The company has started manufacturing some of its products,liketheMacBook,intheUnitedStates. Additionally, Apple has expanded production in countries like India and Vietnam as part of its nearshoring strategy.

General Motors has reshored several production activities to the U.S. to meet the growing demandforelectricvehicles(EVs).Byinvesting in American manufacturing plants, GM aims to streamline its supply chain and ensure faster delivery of EV components.
establishing “Speedfactories” in Germany and the U.S. These automated factories allow the company to produce shoes closer to its key markets, reducing lead times and enhancing customization.

Walmart has committed to reshoring initiatives by investing $350 billion in U.S.-made products over a 10-year period. This strategy not only supports local manufacturing but also helps Walmart reduce transportation costs and improve inventory management.

Reshoring and nearshoring are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Companies must carefully evaluate their supply chain strategies based on their industry, customer needs, and financial goals.
Adidas adopted a nearshoring approach by
Inthecomingyears,wecanexpectmorecompaniesto adopt these strategies as they seek to balance cost efficiency with supply chain stability. Advanced technologies like robotics, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing will also play a crucial role in enabling successful reshoring and nearshoring initiatives.
Reshoring and nearshoring represent a paradigm shift in supply chain management. As companies navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain global environment, these strategies offer a way to mitigate risks,improveresponsiveness,andalignwithevolving consumer expectations. By embracing regional manufacturing hubs, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in a dynamic world.
Reshoring Initiative. (2022). The State of Reshoring in the U.S. Retrieved from reshorenow.org Deloitte. (2023). Global Supply Chain Trends. Retrieved from deloitte.com Financial Times. (2023). Apple's Diversification of Supply Chain. Retrieved from ft.com Reuters. (2022). General Motors and Electric Vehicle Manufacturing. Retrieved from reuters.com Harvard Business Review. (2021). Adidas and the Future of Reshoring. Retrieved from hbr.org McKinsey & Company. (2023). Supply Chain Regionalization: Opportunities and Challenges. Retrieved from mckinsey.com


Arafin Mallick is an MBA Finance student at XAVIER BUSINESS SCHOOL under SAINT XAVIER’S UNIVERSITY aspiring to excel in equity research with a focus on the jewelry industry with a keen interest in Operations field. With a passionforfinance,macroeconomictrends,anduncoveringindustryinsights,heis dedicated to becoming a leader while sharing valuable perspectives in the real world.
- Mohan Kumar Mishra
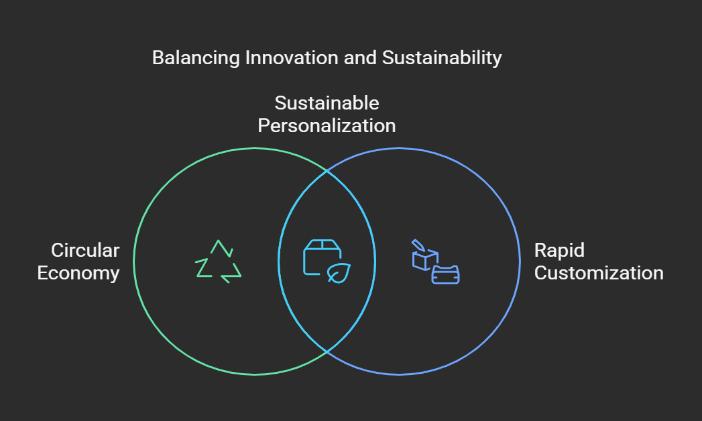
After considerable time in manufacturing and operations and now diving deeper into business studies I've been reflecting on something that feels like a paradox – the relationship between Circular Economy and Rapid Customization. A circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development designed to benefit businesses, society, and the environment.
In my 13+ years of working in manufacturing and operations I have seen the incredible ways industries have developed to meet consumer demands. As soon I started going deeper into Business studies and sustainability, I find myself wrestling with a question that feels personal and urgent: Is it possible for us to balance the requirement for rapid customization with the principles of a circular economy? Will we be sending one at the expense of the other?
"It shouldn’t be an option, a question, or even a passing thought; it is a reflection." It is a reflection shaped by years of experience and learning in the industry and a growing awareness of our, sustainability, climate change, balance sore card, planet’s limits.
The idea of the Circular Economy gives us hope: a worldwherewemakeproductsthatlast,reusewhat we already have, and minimize waste. Yet, the increasing consumer appetite for personalized and quick turnarounds makes me wonder: Are we designingforthefuture,orarewetrappedinacycle of short-term gains that add long-term costs?
Mahatma Gandhi once said, "The world has enough foreveryone's needs, but not enough for everyone's greed," has a profound impact on me. The focus is not on stopping innovation or dispensing with customization; rather, it's about rethinking our approach. Is it feasible to embrace innovation without harming our environmental responsibilities?? Is it possible to offer personalized products without increasing waste?
Are we truly balancing the scales?
The effects of these issues are being felt by individuals, professionals, and global citizens, not just industries. My core objective of writing this article is to initiate a dialogue that is based on my own experiences and my belief that questioning these trends, we have the potential to improve our understanding of them. Sustainability and customization can coexist in a future that we can design
PurposeofCircularEconomy'sconsistofdesigning products that durable and long product life cycle, reducing wastes, and embracing reuse. The main objective is to guarantee sustainability by ensuring that products are Designed that last longer, reducing waste, repairable, and recyclable & reusable without many impacts on environment. It’s true that this is a fantastic plan and will take considerable time.

On the other hand, there is a rise in the Rapid Customization race. Consumers want unique and tailored products, and companies are racing to deliver personalized products. Even though this is changing the market, I am curious about the environmentalcostofcustomizedproducts,shorter life cycles, more resources consumed, increased energy usage, and more waste are frequently observed.
Is this the approach we should take to achieve sustainability objectives? Like "Greenwashing or care washing" circular economy concept also going to become just an immersive topic for discussion?
I’mnotsayingthatcustomizationisgood/bad"I’m not criticizing customization”, few great world leader and industries are already using recycled materials in their custom products, and there are amazing innovations happening in upcycling and sustainability. Some industries like IKEA working to incorporate recycled materials or waste into customized products, which is fantastic. But as customization continues to rise and demand for personalized products grows even faster like anything, I wonder: Can the speed of customization keep up with our ability to turn waste into value in a sustainable way?
MyconclusionisthatIdon'twanttoarguewhether customization is good or bad, but my concern is whether we are truly balancing the rising trend of rapid customisation with the need for sustainable practices, or are we moving too quickly in one direction and leaving the other behind?
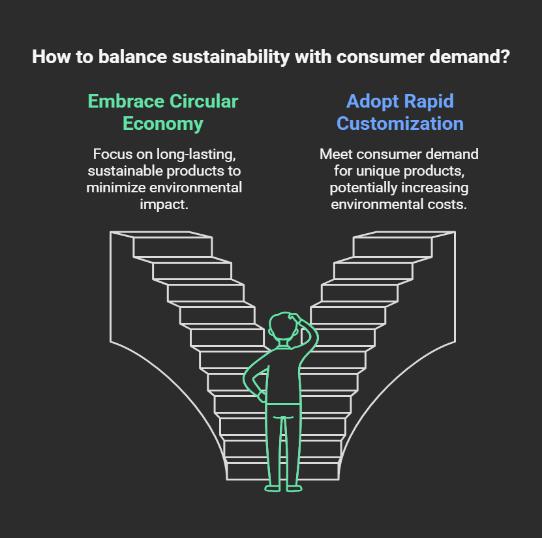
As someone who has worked at the intersection of manufacturing and sustainability, I don’t have all the answers. But I believe these are the kinds of conversations we need to have. The choices we make today will define whether we can reconcile the demand for customization with the need for long-term sustainability.
I conclude by asking if we are designing for the
planet as much as we are designing for individual preferences? What actions can we take today to ensure that personalization and sustainability can coexist without compromising the sustainability of the planet?

References:
1. Resource for Image creation: Napkin Ai
2. Book for reference: Embedding sustainability
3. Online certification: Reliance Foundation Academy, UNCC, CII
4. Classroom study: Supply chain management




A seasoned professional with a distinguished career in supply chain manufacturing, specializing in Manufacturing Operations, Quality Management Systems, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Capacity Enhancement, and Operational Excellence. Skilled in implementing world-class methodologies and auditing compliance across in-house and collaborative manufacturing sites. Currently pursuing General Management at IMI Delhi to enhance leadership capabilities and drive impactful strategic initiatives
- Piyush Goyal
Abstract
Digitaltransformationisredefiningtheprinciples of operations and supply chain management by integratingadvancedtechnologiessuchasIoT,AI, blockchain, robotics, and big data analytics. This article explores the roleof these technologies in enhancing efficiency, improving visibility, and fosteringsustainability.Additionally,itaddresses thechallengesofimplementation,futuretrends, and actionable recommendations for businesses aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly digitalera.
. Introduction
The rapid advancement of digital technologies has ushered in a new era for businesses worldwide, transforming how operations and supply chain management are conducted. With increasing globalization, competition, and consumer demand for faster and more personalized services, businesses must adapt to stay relevant. Digital transformation allows companies to innovate, streamline processes, andmakedata-drivendecisions.
Supply chains, which form the backbone of industries, benefit immensely from these advancements.TechnologiessuchastheInternet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and blockchain ensure seamless operations, better communication, and greater efficiency. This article aims to analyze the scope, benefits, challenges, and potential of digital transformation in operations and supply chain management.

IoT is a cornerstone of digital transformation, enabling interconnected systems to communicate seamlessly. IoT sensors allow realtimetrackingofshipments,inventorylevels,and equipmentconditions.
Applications
• Asset tracking: Monitor shipment locations and conditions (e.g., temperature,humidity).
• Predictive maintenance: Anticipate machinefailurestominimizedowntime.
• Example:LogisticscompanieslikeFedEx and DHL use IoT to optimize delivery routesandmonitorpackages.

2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML empower companies to analyze vast amounts of data, pattern recognition, make informed decisions, and automate repetitive tasks.
Applications in Operations:
• Demand forecasting: Predict customer needs to optimize inventory.
• Process automation: Automate repetitive tasks like invoice processing.
• Warehouse optimization: Use robotics and algorithms to streamline operations.
• Example: Alibaba uses AI to predict demand during shopping festivals, ensuring optimal stock levels.

Blockchain ensures secure and transparent data sharing across the supply chain. Its decentralized nature minimizes fraud, enhances traceability, and builds trust among stakeholders.
Applications in Supply Chain:
● Traceability: Track raw materials to finished goods.
● Fraud prevention: Ensure authenticity in product sourcing.
● Smart contracts: Automate payment processes based on predefined conditions.
● Example: IBM and Walmart’s blockchain-based food safety system
reduces the time to trace contaminated products from seven days to 2.2 seconds.

Big data analytics helps organizations gain insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and operational inefficiencies.
Applications in SCM:
● Risk management: Identify potential disruptions in supply chains.
● Customer behavior analysis: Personalize offerings based on preferences.
● Route optimization: Reduce transportation costs and delivery times.
● Example: Coca-Colaleverages big datato optimize its supply chain operations globally.

Robotics increases operational efficiency and accuracy in repetitive tasks. Combined with AI, robotics brings precision and scalability to SCM.
Applications in Operations:
● Automated picking and packing in warehouses.
● Autonomous vehicles for transportation.
● Example: Amazon Robotics (formerly Kiva Systems) automates warehouse operations, significantly reducing order fulfillment times.

6. Cloud Computing:
Cloud-based platforms enable real-time collaboration and data sharing across global supply chains.
Applications:
● Centralized data management for supply chain stakeholders.
● Improved scalability and flexibility in operations.
● Example:Unileverusescloudsolutionsto enhance supply chain collaboration and visibility.

1. Operational Efficiency:
• Automation of repetitive tasks reduces manual errors and improves process efficiency.
• Companies can achieve faster production cycles, streamlined logistics, and reduced costs.
2. Supply Chain Visibility:
• Technologies like IoT and blockchain enable real-time monitoring, helping businesses track goods from origin to destination. This visibility builds customer trust and ensures compliance with regulations.
• Reduces theft, fraud, and product loss.
3. Cost Reduction:
• Predictive analytics reduces maintenance costs and optimizes resource allocation.
• Automation lowers labor costs and improves accuracy.
4. Agility and Resilience:
• Digital transformation enhances the ability to respond quickly to disruptions such as natural disasters, pandemics, or geopolitical events.
• Facilitates demand-driven production models.
• Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with digital supply chains adapted more effectively to demand fluctuations.
5. Customer Satisfaction:
• Faster deliveries and personalized services improve customer experiences.
6. Sustainability:
• Optimizedresourceusereduceswasteand carbon footprints.
• Encourages ethical sourcing and ecofriendly practices.

Challenges in Implementation
1. Integration with Legacy Systems:
• Integrating new technologies with outdated infrastructure is challenging.
• Upgrading systems requires substantial investment.
2. Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
• Digital systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches.
• Ensuring data security is critical for trust and compliance like GDPR are critical.
3. Change Management:
• Resistance to change from employees and stakeholders can slow adoption.
• Requires strong leadership and communication.
4. Skill Gaps:
• Lack of technical expertise among employees can hinder implementation.
• Continuous training and development are essential.
5. Cost Barriers:
• High initial investment in technology and infrastructure.
• SMEs face greater financial constraints.

Case Study:
1. Starbucks implemented a digital supply chain system integrating AI, IoT, and blockchain technologies.
Results:
• Enhanced visibility into coffee bean sourcing.
• Improved demand forecasting to minimize wastage.
• Real-time inventory management across outlets.
2. A global manufacturing firm implemented IoT sensors across its facilities to monitor machinery performance. By analyzing data from these sensors,thecompanyidentifiedinefficienciesand predicted equipment failures.
Results:
• 30% reduction in downtime.
• 25% decrease in maintenance costs.
• Increased production capacity and profitability.
1. 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance IoT applications by enablingfasterdatatransmissionandrealtime analytics.
2. Advanced Robotics and Automation: Robotics integrated with AI will lead to smarter automation, especially in warehouses and production lines.
3. Augmented Reality (AR): AR can revolutionize training, equipment maintenance, and assembly processes by providing real-time visual guidance.
4. Digital Twins: Digital twins virtual replicas ofphysical systems will allow companies to simulate operations, predict outcomes, and optimize performance.
5. Sustainability Initiatives: Businesses will increasingly adopt digital technologies to track carbon footprints and ensure sustainable practices.
References:

Conclusion
Digital transformation is no longer a choice but a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s competitive environment. By adopting technologies like IoT, AI, blockchain, and big dataanalytics,businessescan achieveoperational excellence, enhance customer satisfaction, and build resilient supply chains.
However, success in digital transformation requiresaddressingchallengessuchasintegration issues, cybersecurity risks, and workforce skill gaps. Organizations that invest strategically in technology and human capital will be better positioned to leverage the benefits of digital transformation, ensuring long-term growth and sustainability.
1. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11020941/
2. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/joom.1271
3. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/15/13/10107
4. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/21582440241281616
5. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/18479790241234986
6. https://ajemb.us/index.php/gp/article/view/57
7. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360168315_A_Review_of_Digital_Transformation_on_ Supply_Chain_Process_Management_Using_Text_Mining
8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376594743_Digital_Transformation_in_Business_Opera tions_Management
9. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/377324508_Digital_Supply_Chain_Management
10. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4512167
11. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13675567.2024.2332123
12. https://nawalaeducation.com/index.php/MJ/article/view/774
13. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/dts-09-2023-0087/full/html
1. https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevebanker/2023/04/09/digital-transformation-in-supply-chainmanagement/
2. https://www.intuz.com/guide-on-top-iot-sensor-types
3. https://www.jagannath.org/blog/ai-ml/
4. https://www.cyberbahnit.com/blockchain/
5. https://kakacrm.com/big-data-analysis/
6. https://www.e-spincorp.com/what-is-robotic-process-automation/
7. https://stock.adobe.com/search?k=cloud+computing
8. https://c-link.com/blog/digital-transformation-in-supply-chain-management/
9. https://kissflow.com/digital-transformation/digital-transformation-challenges/?hs_amp=true
10. https://www.clariontech.com/blog/digital-transformation-trends?hs_amp=true


I am a second year Bachelor of Management Studies student at Aryabhatta College, Delhi University, passionate about leadership, teamwork, and fostering innovation. With experience as the CR and PR Head at The Startup Club and the External Relations Head at AIC, I have honed my communication, negotiation, and management skills. My background includes organizing large-scale events, handling sponsorships, and building strategic partnerships. Proficient in financial accounting software like Tally, Busy, and Marg, along with advanced Excel and MySQL,Iaimtoleveragemyexpertisetocreateimpactfulopportunitiesanddrive success in dynamic environments.




Contact us at:



https://www.instagram.com/opscentrix_iimrohtak?igsh=cm8xM2NuODR4cDUy https://www.linkedin.com/in/opscentrix-iimrohtak/ operationsclub@iimrohtak.ac.in