2 minute read
PASSIVE SOLAR COOLING
ii) roof radiation trap
Isolated gain
Advertisement
- solarium - sunroom
PASSIVE SOLAR COOLING
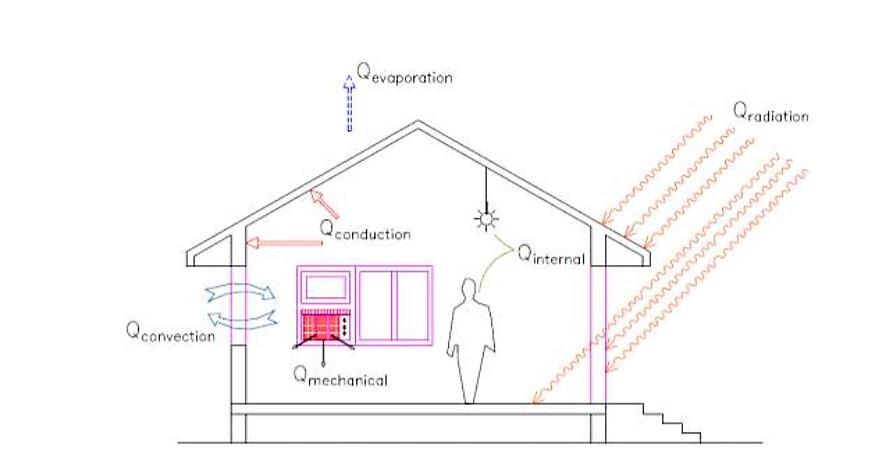
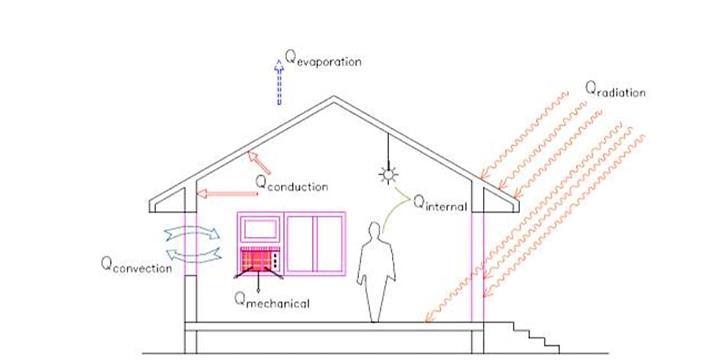
A passive cooling system uses elements of the building to store and distribute energy and when prevailing conditions are favourable to discharge heat to the cooler parts of the environment the sky, atmosphere and ground. Since the collection, discharge, storage and distribution of energy is generally accomplished by the architectural elements and textures of the building the passive cooling system components are not easily distinguishable from the remainder of the structure.
PASSIVE COOLING DESIGN STRATIGIES
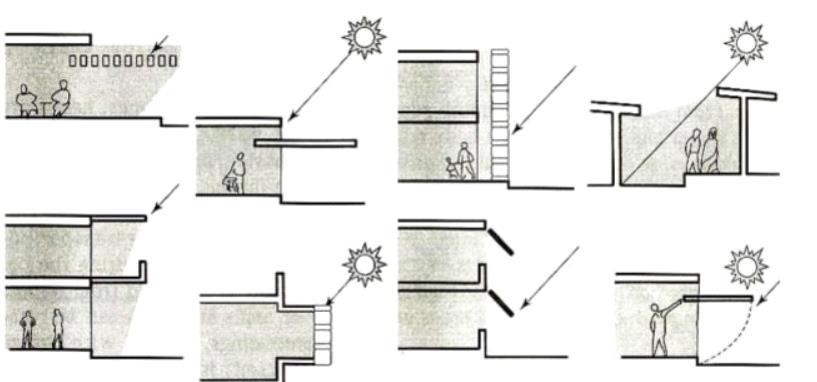
Solar control through: -
- Form and orientation of building
- Shading by neighbouring building
- Shading by vegetation - Shelter against hot winds
- Shading by louvers, overhangs and textured façade.
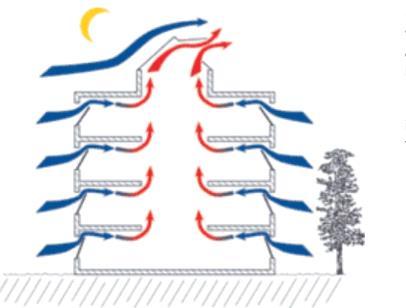
• VENTILATION COOLING - Cross ventilation - Wind tower - Induced ventilation • EVAPORATIVE COOLING • Passive Solar Energy Conclusion • Passive Downdraft Evaporative Cooling (PDEC) • Roof Surface Evaporative Cooling
BENEFITS –
As we know, the present climate changes are directly linked to the human activities and also the concerns regarding exploitation of the fossil fuel have reached a level where the negative effect are having impact on the life of a common man. This resource intensive development model posed problems for a developing country like rising of costs, loss of productivity and disruption of economic activity etc. With the advancement of technology, the consumption of energy has increased and thus even technology is seen as a factor of environmental degradation. As we are aware that there is a limit to the natural resources
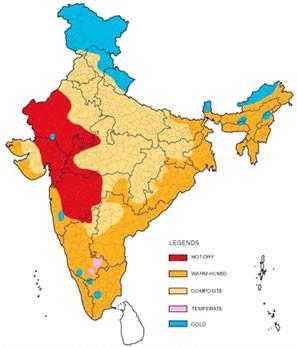
available on earth, we need to conserve these by judicially utilizing these. In the case of India reducing the consumption of energy may be linked to slowing down the development rate which surely may not be appreciated by many. It is need of the hour therefore to look into the aspects and methods which shall help to reduce the consumption of energy without hampering the development rate. It is therefore taken up in top priority by the Indian Government, although sustainable development in India is often misunderstood that such type (sustainable or energy efficient) construction is luxury and considered to be costly but the fact is not true as it is necessary to address this issue before it is too late and the costs of reversing the tends rise beyond control. The results are significant as this issue is of particular relevance for developing countries such as India that are in the process of industrializing but are yet to confront the high costs of development. Both urbanization and suburban growth take a heavy toll on the environment and the lack of appropriate technologies and sustainable framework suggests that the architectural profession has failed to recognize the critical need for developing socially appropriate sustainable architectural practices for India. There is an increasing demand for higher quality office buildings in India. Occupants and developers of the office building ask for a healthy and stimulating working environment. They also demand the buildings that create less environmental damage. The need for energy conservation and sustainable design in buildings is the main reason for this study. The commercial sector posted the highest economic growth rate and accounts for larger share of energy consumption in India. Double skin façades are getting ever-greater importance in building practice in modern building practice in the developed countries of the world. Providing comfortable environment to the building occupant is a major challenge for building designer in Hot and Dry regions.