2 minute read
MATERIAL DIFFERENTIATION
from AEOLIAN - AADRL
by Salim Hilles


Advertisement
AGENT TO STRUCTURE
Agents have the ability to recognize the structure based on the difference in properties between sand and glass (fused sand). Three significant characteristics, colour, reflection, and temperature provide the information for agents to interact with the glass structure.




Colour
Reflection
Temperature

Sensing
FOLLOWING GLASS STRUCTURE
The better performance was archived with IR sensors by sensing the reflection of the surface. The agent can recognise and follow the glass structure by employing the ability to seance the difference in reflection between sand and the glass.



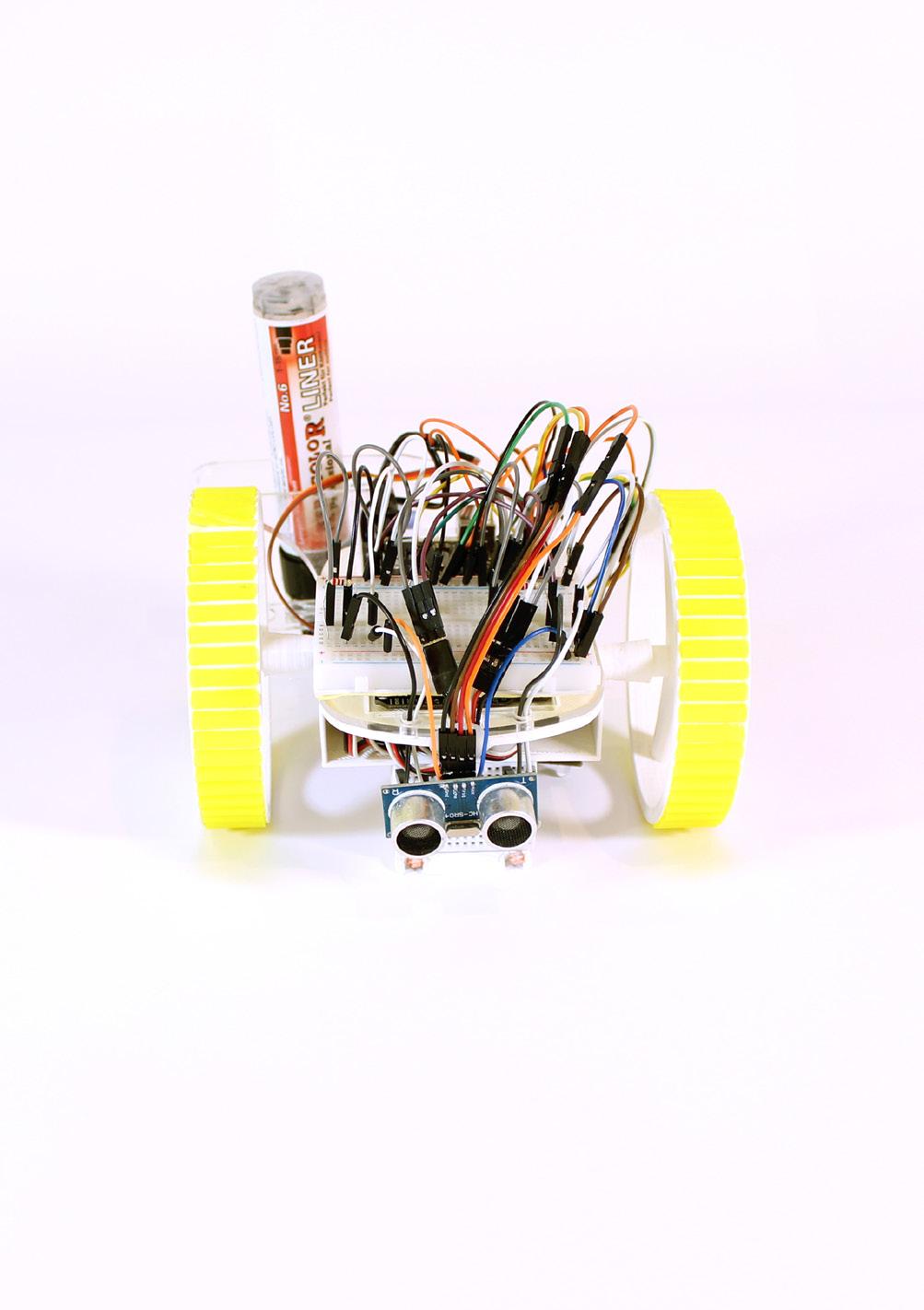
FOLLOWING LINE FOLLOWING | ITERATION 1
The agent in the experiment has a photoresistor that detects the difference in light reflection between different materials. In the experiment, the robot was programmed to avoid crossing the black line by sensing the difference in the reflection between black and white paper.
LINE FOLLOWING | ITERATION 2
The robot has two photoresistors in the front which allow it to follow the black line in between them. If both sensors sense the bright area, the robot moves forward. If one of the sensors senses dark, the robot turn left or right to adjust its path.
DRAWING PRINTING | ITERATION 1
Leading agents leave a trace that others can recognize and follow. In the prototype, the agent holds the red marker, which leaves the trail. The trail pattern is influenced by the agent’s movement, avoiding obstacles.
PRINTING | ITERATION 2
The second iteration of the drawing experiment aimed to combine two distinct behaviours, particularly linefollowing and line-drawing at the same time. The agent is able to recognise the line and offset it with a new line while moving.
DRAWING COMMUNICATION | ITERATION 1
Agent communicate with each other through the structure (line) and distance sensor to avoid collision. The agent’s prototype has a distance sensor and a servo motor, which allow testing the distance and avoid hitting obstacles.
COMMUNICATION | ITERATION 2
The following experiment was conducted in order to develop strategies for interaction between robots. In the prototype, the agent senses another one with an obstacle sensor in the front. When one of them senses another, it stops moving without bumping it until it passes through.
DRAWING COMMUNICATION | ITERATION 1
The leading agent in the centre draws a red-line trajectory for other agents to follow the path and simultaneously avoid the surrounding obstacles. Followers are supposed to move along the path. Implemented DC motors do not have enough power which caused unstable movement patterns.
COMMUNICATION | ITERATION 2
Agents leave a trace or line, other agents should recognise and follow the line which represents the black line. Implemented system allows agents not only to sense and follow the trail from the leading agent but also to leave the new trail for other agents to follow, demonstrating the stigmergy behaviour among robots.




Drawing

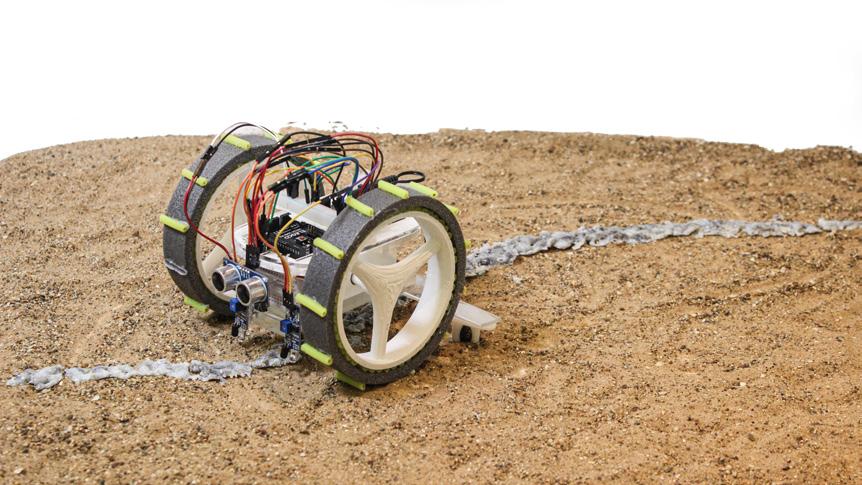
COMMUNICATION | ITERATION 2 | LARGE SCALE
The robots collaboration test was conducted on a larger scale in an outdoor setting. The robots were launched from various locations to evaluate their behaviour and reactions to the lines drawn by other robots. This test serves as a demonstration of collective behaviour resulting in stigmergic pattens, in which the robots coordinate their actions through the modification of their environment.
COLOUR DATA COLOUR SENSING | ITERATION 1
During this experiment, the agent follows the blue light and turns in that direction by using the colour sensor located in front.
COLOUR MAP ANALYSIS | ITERATION 2
The agent reacts to the colour map which represents the landscape. When the colour sensor senses blue or green, the robot shifts the maker down and draws the line. If it’s red, it lifts the marker and no line is drawn. The strategy lets the agents to decide where they need to draw a line based on the landscape analysis.
Colour Data
COLOUR MAP ANALYSIS | ITERATION 2 | LARGE SCALE
The printing paper is a representation of the landscape. When the robot is moving on top of the red area, it draws the line. If it’s on a green colour, the robot elevates the marker and does not draw.











