
1 minute read
MORPHOLOGY AGENT FLOCKING BEHAVIOUR
from AEOLIAN - AADRL
by Salim Hilles
Implementation
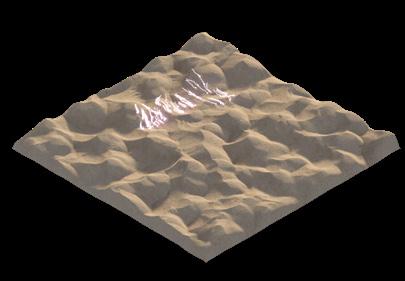
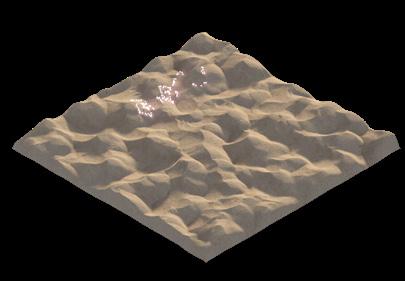
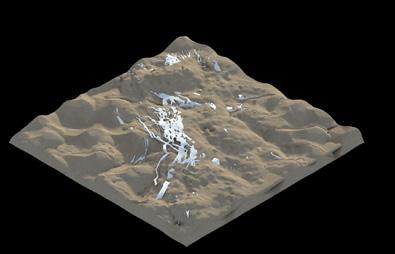
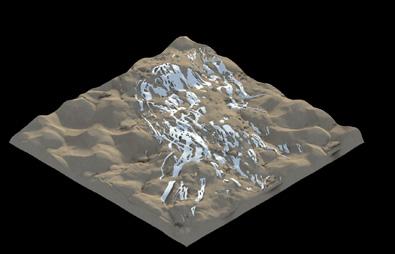
The system used a range of behaviours in order to construct the structure for deflecting sand particles. This included a global overview, in which the system examined the area to be surrounded by the structure and created a boundary from it; an intermediary overview, in which it used data on the dynamic properties of the landscape; and a local overview, in which the agents responded to analyses of the physical state of the dunes, such as their height, curvature, and slope. These studies were then layered to develop strategies for the density and thickness of the structure. The frame-by-frame diagrams below show how particles are responding to the implemented strategies in real-time.
Advertisement
























Morphology
Results
During each iteration, the agent-based system undergoes a cybernetic process in which the landscape is analysed at three different levels (global, intermediary, and local). Based on this analysis, the agents use cohesion and repulsion values that are influenced by mapped data to make decisions about where to deposit sand and where not to. The resulting structure is then tested by subjecting it to sand particles over time. If the structure is not able to fully repel the sand particles, the process is repeated until it is able to do so.






The simulations presented in the previous pages illustrate this cybernetic process as iteration after iteration the overall system reacts to changes in the environment. The structure gets larger and multilayered after the simulations are repeated. The more iterations are conducted, the more efficient the structure becomes in re-directing sand particles away from the designated site, creating a proof-ofconcept for the hypothesis of this research.
PARTICLE SIMULATION - 01
PARTICLE SIMULATION - 02
PARTICLE SIMULATION - 03
PARTICLE SIMULATION - 04










