PUBERTY A Boys Overview









is the time when your body changes from being a child to a
Your body is preparing itself to be able to reproduce (have a baby).
◼ Puberty starts when extra amounts of chemicals called hormones start to be produced in the body.
◼ The body produces the sex hormones OESTROGEN, PROGESTOGEN and TESTOSTORONE which are responsible for many different changes in the body.
◼ The brain and pituitary gland release the sex hormones that regulate the reproductive organs.

Physical changes happen because the body starts to produce chemicals called sex hormones; oestrogen, progesterone and testosterone.
Puberty happens anywhere between 8 and 18 years of age.
The female body mainly produces progesterone and oestrogen which start the changes of puberty. Usually starts between 8-13 years.
The male body mainly produces testosterone which start the changes of puberty. Usually starts between 10-15 years.
◼ Grow taller and heavier
◼ Bones grow bigger and heavier
◼ Nose and jaw get bigger and face gets longer
◼ Get more muscles
◼ Hair and skin can become oily and you may get spots
◼ Body sweats more
◼ Hair grows on the face, under the armpits, around the genitals (pubic hair).
◼ May get more hair on arms, legs and chest.
◼ Voice gets deeper
◼ Penis and testicles grow bigger and longer
◼ May have mood swings, sexual thoughts and feelings
It is not just your body that changes during puberty–your mind and feelings change too.
Sometimes:
- You may feel lonely and confused. -
- You may have mood swings (including irritability, tearfulness, overwhelming happiness and confusion).- You may want more independence. -
- You may also become argumentative and bad tempered.
❖ Homework
❖ Clothes
❖ Games consoles (i.e. Wii, X-Box, Playstation)
❖ Internet usage
❖ Music choices and volume
❖ Friends
❖ Bedroom
❖ Choice of leisure activities
❖Keep them involved, tell them how you are feeling about things.
❖Ask their advice, listen and if you disagree tell them why.
❖Accept that they have the right to lay down some rules, be willing to meet them halfway.
❖Try not to lose your temper, if you show them you can accept when they say no, may be they will be willing to say yes in the future.
❖When going out, tell them where and with who, agree a time when you will return and ALWAYS let them know if you are going to be late.
❖Help more around the house, without waiting to be asked!
❖ Other friendships, new friends.
❖ Misunderstandings, arguments.
❖ Girlfriends or boyfriends.
❖ Choice of things to do together.
❖ The way they talk to you, making you feel bad about yourself.
❖ They do not listen to you, they only talk about themselves.
❖ Jealousy.
❖Try to not demand too much support and attention without giving some in return, they will feel resentful and used.
❖Show mutual respect.
❖Be honest with them.
❖If you let a friend tell you how to behave and what to do, then you are not being fair
yourself or to them.
to

◼ Your penis and testicles will grow bigger and longer. Sometimes one testicle grows faster than the other, and it is natural for one to hang lower than the other.
◼ Pubic hair, will also start to grow at the base of the penis. As you get older, this hair will grow thicker and courser.
◼ Penises come in all shapes and sizes and all are very different. Your penis also doesn’t stop growing until you reach the ages of 18 to 21.

This diagram is only a representation. All boys’ bodies look different and penises come in many different shapes and sizes.
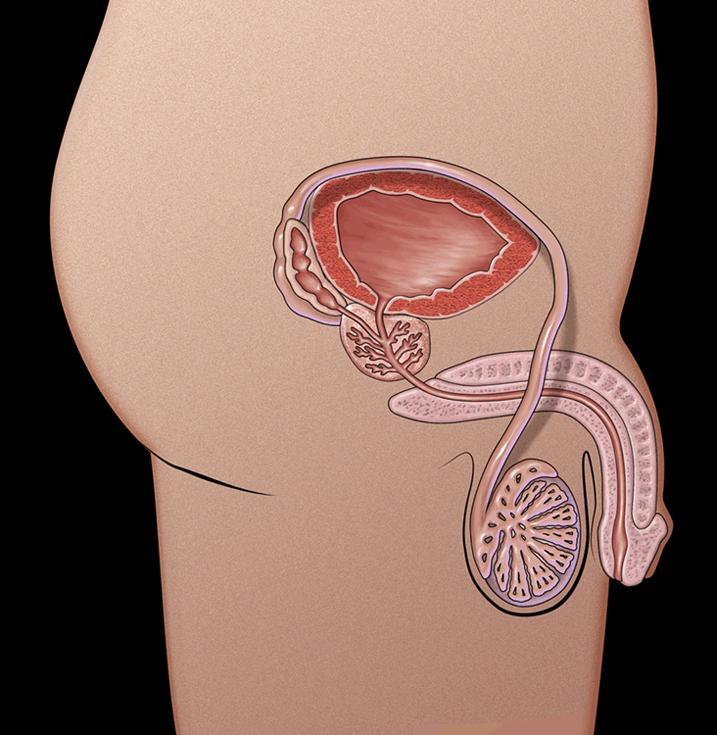
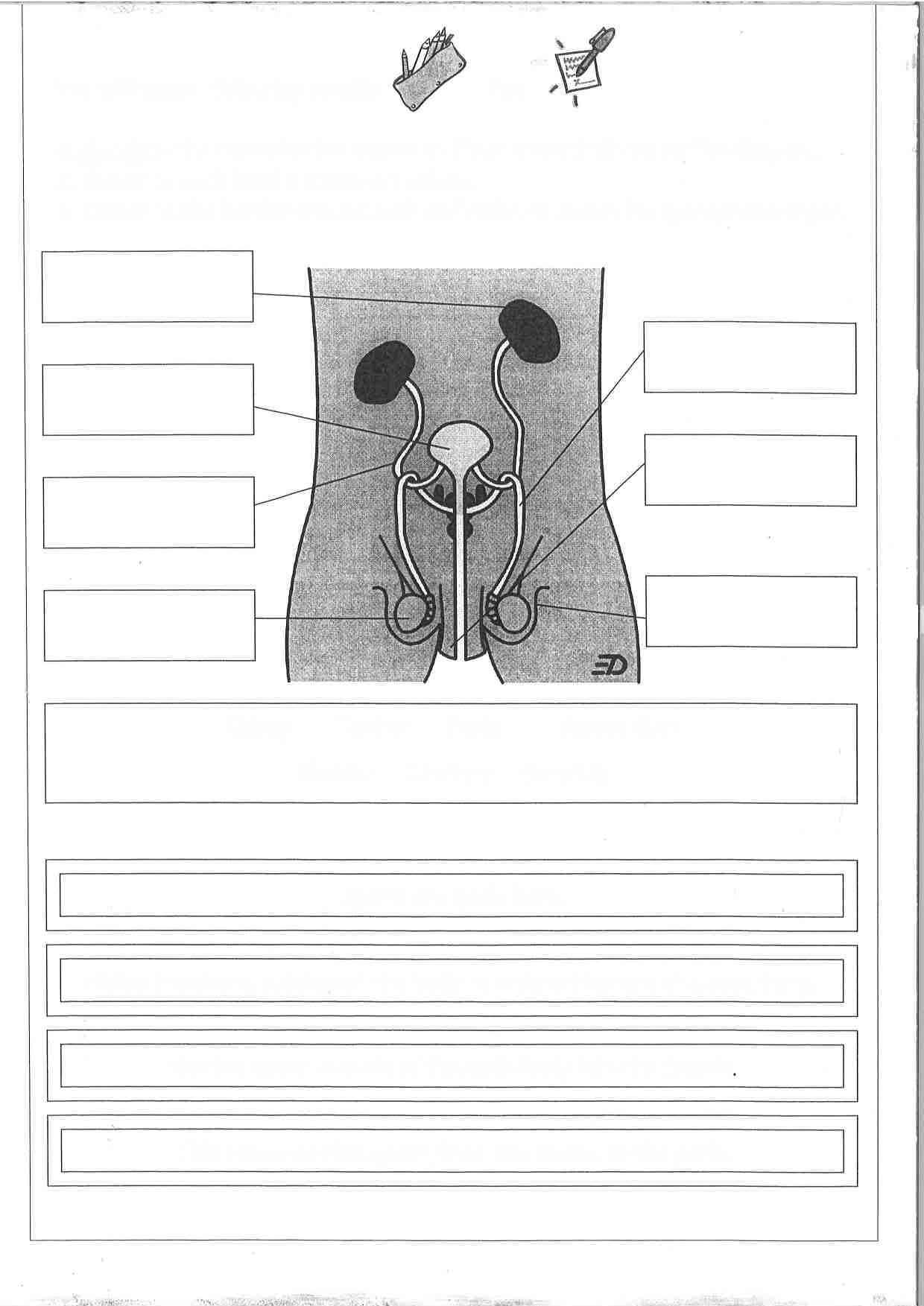
Urethra
- The tube through which urine and semen leaves the boy’s body
Penis
- Tube-like organ that hangs outside the body
- Come in all sizes and shapes, determined by our genes
Testicles or testes
- Usually two, one hangs lower
- Sometimes called balls or nuts
- Where sperm are made
Scrotum
- Bag of skin that holds testicles
- Keeps them at right temperature to make sperm, slightly cooler than body’s temperature
- Gets bigger and baggier and turns a darker colour
◼ An erection happens when extra blood flows to the penis. This causes the penis to harden and lengthen.
◼ Most erections are not straight, and tend to either curve upwards or to either side.
◼ Erections can happen at any time: - When you touch it - Have exciting/sexual thoughts - See someone attractive - Or for no reason at all!

◼ Sometimes semen (sperm and fluids) spurts out of the penis.
◼ This is called an ejaculation. It happens when muscles at the base of the penis start to expand and contract (tighten).
◼ This pushes the semen through the urethra and out through the tip of the penis.
◼ But this won’t happen every time you have an erection.
◼ Sometimes you can ejaculate when you are asleep.
◼ This is called a nocturnal emission, more commonly known as a “wet dream.”
◼ It happens without you knowing about it, and it’s not necessarily because you are dreaming about sex.
◼ You may notice that your pyjamas or sheets feel wet or sticky when you wake up.
◼ Most males experience wet dreams between the ages of 12 to 18.
◼ IT IS NORMAL!
◼ You will experience wet dreams less frequently as you grow older, you will have more control over your body.
• Get taller and heavier
• Bones grow bigger and heavier
• Hips get wider and more curvy
• Face changes shape
• Voice gets a little deeper
• Hair grows under the armpits, around the genitals (pubic hair)
• Hair on arms and legs grows darker
• Breasts and nipples get larger
• Body sweats more
• Internal and external sex organs grow
• May have mood swings, sexual thoughts and feelings
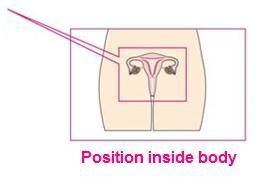
Periods (menstruation) happen due to the hormones changing in your body.
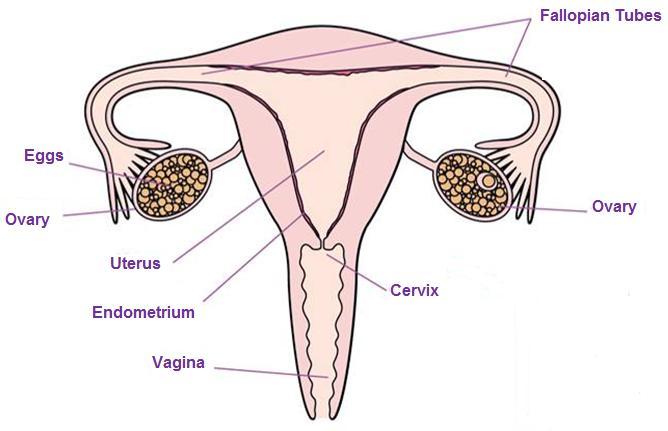
Even before birth, a girl has 1-2 million tiny eggs (Ovum) in her ovaries. When puberty is reached usually an egg is released each month from her ovaries.
The egg moves from the ovary and along the fallopian tube and down into the (womb) uterus.
If the egg is fertilised by sperm then a pregnancy will occur.
If the egg is not fertilised then the lining of the womb and the egg leave the body through the vagina; this is called a period.
Bleeding can last between 3 and 8 days.
The average blood loss is only around 80ml (roughly 3 tablespoons).
Periods happen once a month but a girls body takes time do get into a routine so for the first year or so the time between each period may vary.


◼ Sweat is your body’s natural way of helping you to cool down.
◼ Sweat can also some times become smelly when the chemicals it contains mixes with bacteria that live naturally on your skin.
◼ It is very important to keep ourselves clean and fresh. Adults use deodorants, anti-perspirants and roll-ons to stop the smell of sweat








Before we start the topic on puberty itself, we need to


Pantosaurus is a really important friend to have and is great to help us to talk about PANTS





the time when your body changes from being a child to a young adult.
Your body is preparing itself to be able to reproduce (have a baby).
Why does it happen?
• Puberty starts when extra amounts of chemicals called hormones start to be produced in the body.
• The body produces the sex hormones OESTROGEN, PROGESTOGEN and TESTOSTORONE which are responsible for many different changes in the body.
• The brain and pituitary gland release the sex hormones that regulate the reproductive organs.

Physical changes happen because the body starts to produce chemicals called sex hormones; oestrogen, progesterone and testosterone.
Puberty can happen anywhere between 8 and 18 years of age.
The female body mainly produces progesterone and oestrogen which start the changes of puberty. Usually starts between 8-13 years.
The male body mainly produces testosterone which start the changes of puberty. Usually stars between 10-15 years.
• Get taller and heavier
• Bones grow bigger and heavier
• Hips get wider and more curvy
• Face changes shape
• Voice gets a little deeper
• Hair grows under the armpits, around the genitals (pubic hair)
• Hair on arms and legs grows darker
• Breasts and nipples get larger
• Body sweats more
• Internal and external sex organs grow
• May have mood swings, sexual thoughts and feelings
Your mind and feelings change too.
- You may feel lonely and confused.
- You may have mood swings (including irritability, tearfulness, overwhelming happiness and confusion).
- You may want more independence.
- You may also become argumentative and bad tempered.
- You may love your friends or family at times and not want to have anything to do with them at other times.
- Sometimes you may feel like a grown-up, other times like a kid.
- Sexual thoughts and feelings.
❖ Homework
❖ Clothes
❖ Games consoles (i.e. Wii,
❖ Internet usage
❖ Music choices and volume
❖ Friends
❖ Bedroom
❖ Choice of leisure activities
❖Keep them involved, tell them how you are feeling about things.
❖Ask their advice, listen and if you disagree tell them why.
❖Accept that they have the right to lay down some rules, be willing to meet them halfway.
❖Try not to lose your temper, if you show them you can accept when they say no, may be they will be willing to say yes in the future.
❖When going out, tell them where and with who, agree a time when you will return and ALWAYS let them know if you are going to be late.
❖Help more around the house, without waiting to be asked!
❖ Other friendships, new friends.
❖ Misunderstandings, arguments.
❖ Girlfriends or boyfriends.
❖ Choice of things to do together.
❖ The way they talk to you, making you feel bad about yourself.
❖ They do not listen to you, they only talk about themselves.
❖Jealousy.
❖Try to not demand too much support and attention without giving some in return, they will feel resentful and used.
❖Show mutual respect.
❖Be honest with them.
❖If
you let a friend tell you how to behave and what to do, then you are not being fair to yourself or to them.


Usually when you are between 10 - 16 years but you could be anything from 8 to 18 years.

Your periods will start when your body is ready. You can’t make them start or stop them from starting.
Periods are caused by hormone levels changing within your body.
It is nature’s way of preparing your body for having a baby.
Periods are part of the female reproductive cycle.
Bleeding can last between 3 and 8 days.
Blood flow may be heavier in the first few days.
The average blood loss is only around 80ml (roughly 3 tablespoons).
Periods happen once a month but your body takes time to get into a routine so for the first year or so the time between each period may vary.
Many girls will feel PMS (premenstrual syndrome), symptoms can include:
- Tender breasts - Headaches - Mood swings - Stomach cramps - Feeling bloated - Tiredness - Spots - Food cravings - Difficulty concentrating
• Some girls may experience pain.

• Tell your parent/big sister and ask advice.
• You can take pain relief to help, but carry on as normal.
• Remember to tell your teacher as well.
• If pain continues or is really painful then see a doctor who will help.
• Have a warm bath
• Massage your stomach
• Have a nice warm drink
• Use a hot water bottle or use a heat pad.
• Eat a well balanced diet.
• Exercise
There are three types of protection you can use during your period to absorb your period to stop it getting on to your clothes/underwear.
The choice is a personal choice and different for each girl.
1. Pantiliners
2. Sanitary Towels
3. Tampons

• Worn outside your body, in your underwear
• Can be used:
- When your period is light - As tampon backup - To help keep you fresh every day

• Worn outside your body, in your underwear.
• Many different absorbencies.
• Wings provide extra protection.
• Change frequently to keep fresh and dry (generally every 4-6 hours, more often when your period is heavy).
• They will start to leak if you don’t change them!
1. Pull off paper strip or wrapper.
2. Attach sticky part securely to centre of underwear.
3. For wings, peel off paper strips and wrap around sides of underwear.


• Worn inside your body in your vagina to absorb menstrual flow. Normally used from your late teens, but remember many women prefer not to use them.
• Different range of absorbencies.
• Good for swimming and gymnastics.
• Should be changed regularly (every 4-8 hours, more often when your period is heavy).
• Mark on a calendar the date of your first period.

• Count 28 days from the day of your FIRST blood show, this will give you a rough idea of when your next period will be.
• Always carry some spare knickers and sanitary towels in your bag. However, Sister Beatrice has some for emergencies.
REMEMBER periods will not have a set pattern in the beginning, they will eventually settle into their own pattern.
• Your genes determine the size and shape of breasts.
• The first thing you may notice is a bump behind the nipple.
• Then there will be swelling underneath
• The nipple area gets darker.
• Breasts grow slowly and one side may be bigger for awhile.
• They may feel sore at times while they are developing.
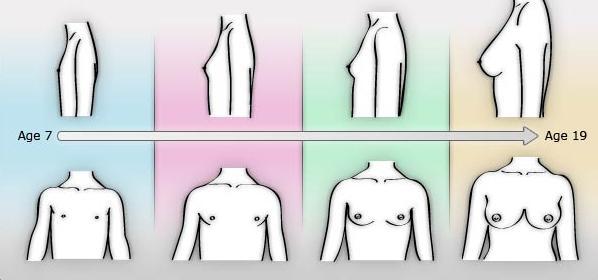
This diagram is only a representation. All girls’ bodies look different and breasts come in many different shapes and sizes.
• Grow taller and heavier
• Bones grow bigger and heavier
• Nose and jaw get bigger and face gets longer
• Get more muscles
• Hair and skin can become oily and you may get spots
• Body sweats more
• Hair grows on the face, under the armpits, around the genitals (pubic hair).
• May get more hair on arms, legs and chest.
• Voice gets deeper
• Penis and testicles grow bigger and longer
• May have mood swings, sexual thoughts and feelings

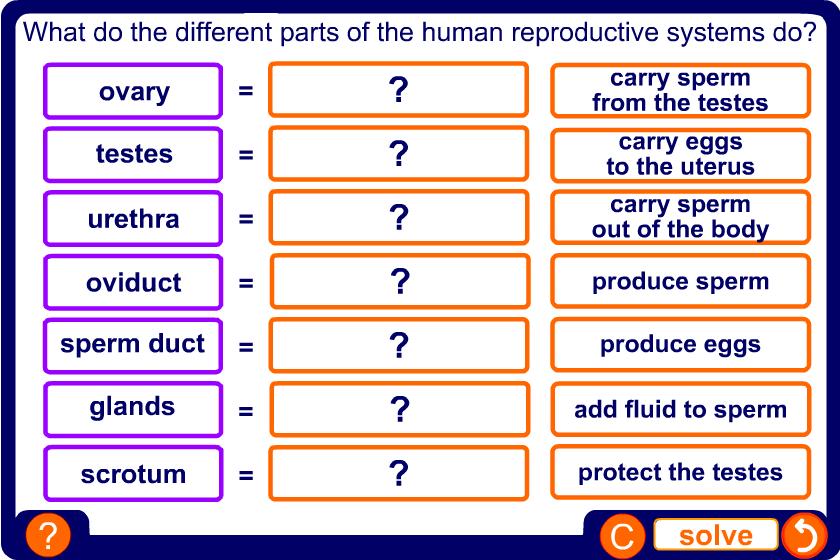
The reason boys have a reproductive system is because it provides the sperm needed to fertilize a female’s egg, which can then develop into a baby.
During puberty the levels of the hormone testosterone in your body begin to rise. This causes the penis and testicles to get bigger and the testicles to produce sperm.
The testicles cannot make sperm before puberty.
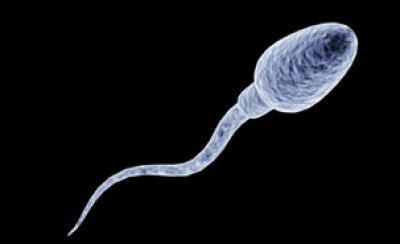
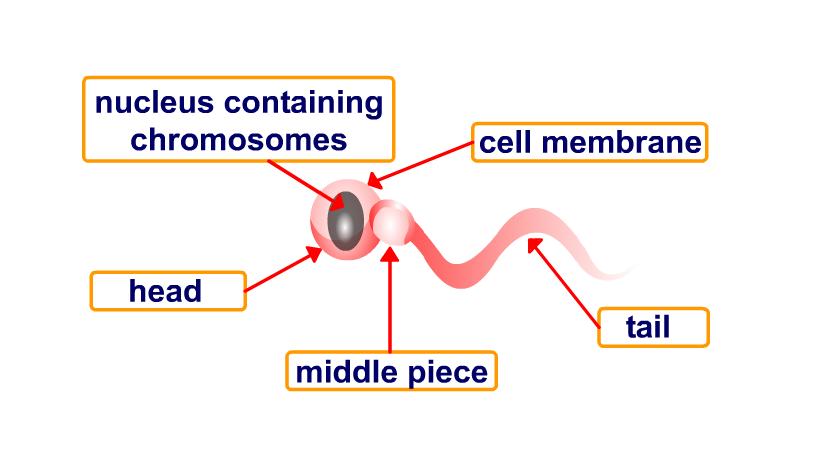
Sperm look like tadpoles, with what appear to be a head and a tail.





• Sweat is your body’s natural way of helping you to cool down.
• Sweat can also some times become smelly when the chemicals it contains mixes with bacteria that live naturally on your skin.
• It is very important to keep ourselves clean and fresh. Adults use deodorants, anti-perspirants and roll-ons to stop the smell of sweat


























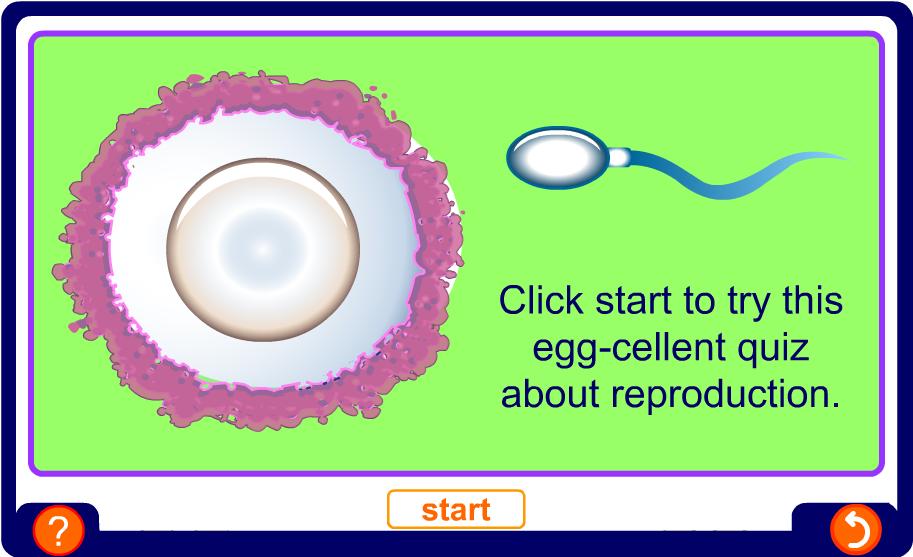
Reproduction is one of the seven life processes. All living things reproduce.
Humans use sexual reproduction to produce their young.
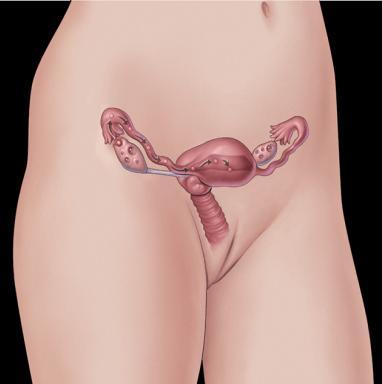
In order to do this, the two parents (male and female) have different reproductive systems and organs that produce different sex cells.










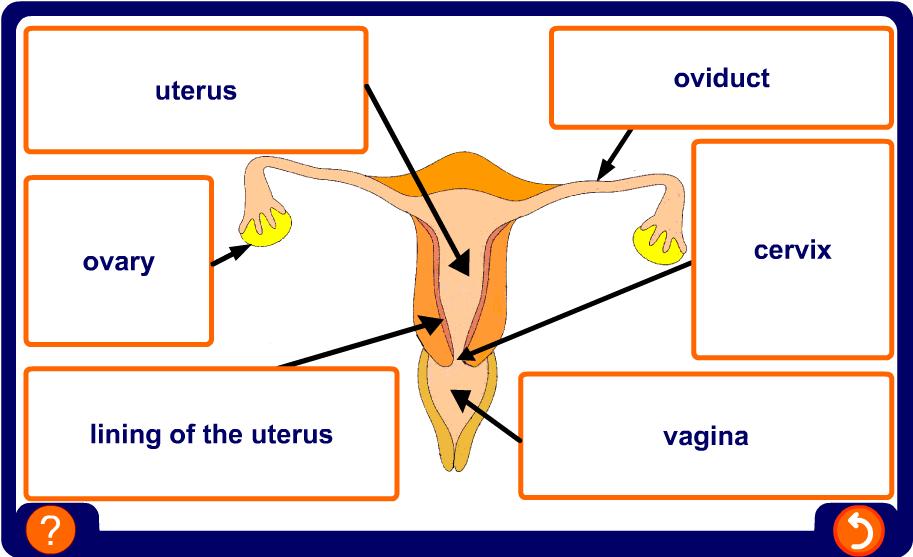




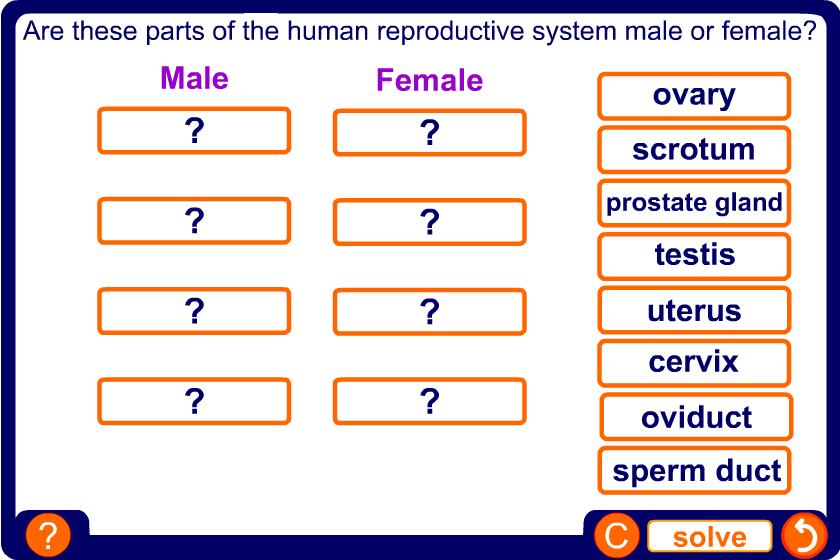










In females, the sex cells are called eggs. Eggs are produced in sex organs called ovaries.

membrane
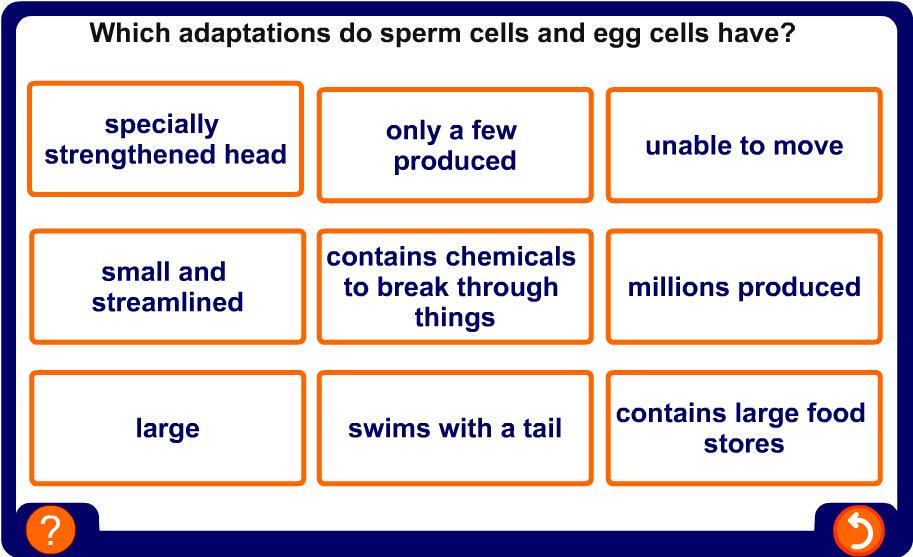
An egg is so big that this is how small a sperm looks next to it.











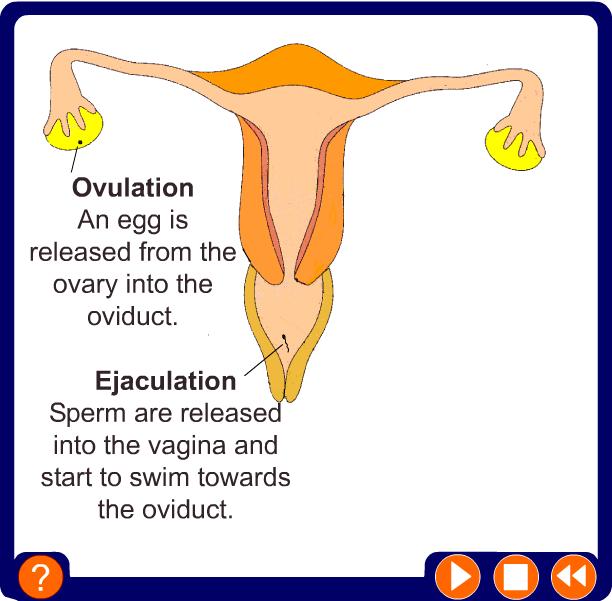
In the female, one of the ovaries produces an egg every 28 days. This is called ovulation.
During sexual intercourse millions of sperm are ejaculated into the vagina. If a sperm meets the egg, the sperm’s nucleus can join with the egg’s nucleus.
This fusing of the nuclei is called fertilisation.

















placenta
How does an embryo get food and oxygen and how does it get rid of waste?
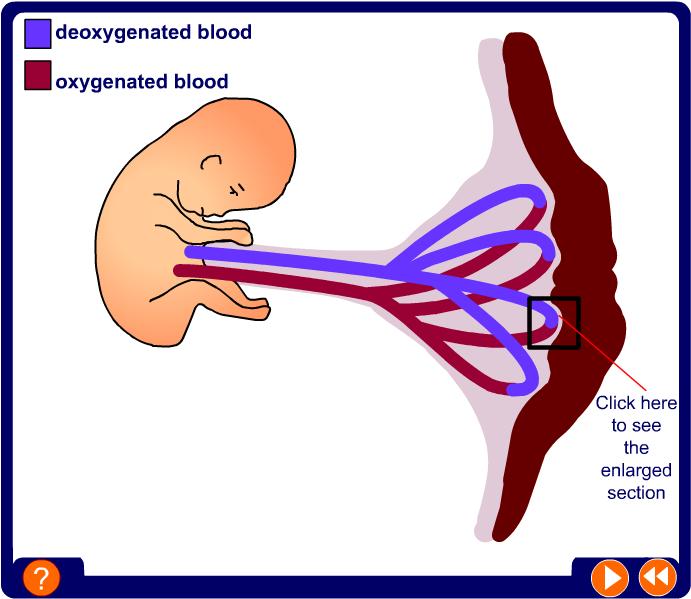
An embryo forms a plate-like structure called the placenta.
The umbilical cord joins the fetus to the placenta.
In the placenta, food and oxygen diffuse from the mother’s blood into the blood of the fetus.
Carbon dioxide and waste products diffuse from the blood of the fetus to the mother’s blood.







In the earliest stages of development, a human baby is called an embryo.
After the first eight weeks of pregnancy, a human embryo is then called a fetus.
At this stage the fetus has all the main human features.

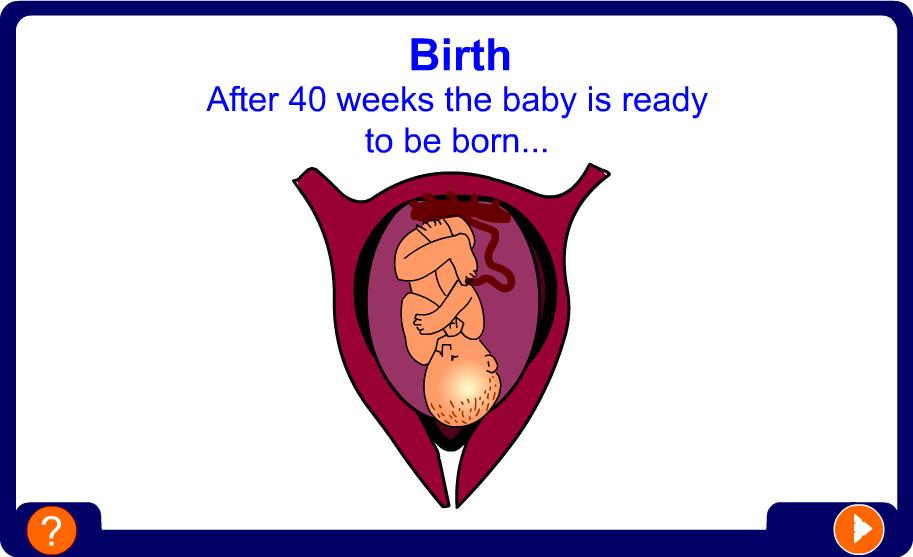
The fetus continues to develop and grow inside its mothers’ uterus for a total of 40 weeks.
What happens next?

















Puberty



Human children are born with a complete set of sex organs. However, they do not become active until between the ages of 10 and 18.
In males, the testes start to make sperm in boys and in females, the ovaries start to release eggs.
This stage of development is called puberty.
During this important period, many changes take place in the bodies of young men and women.













An important part of puberty for girls is the beginning of their monthly cycle. This is known as the menstrual cycle.
The menstrual cycle involves the preparation of the uterus lining so that it is able to receive a fertilized egg.
If an egg is fertilized, it can implant itself in the prepared uterus lining.
If it is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus breaks down and is lost from the body. This is called menstruation or a period.








Puberty



Glossary
⚫ egg - The female sex cell.
⚫ embryo - The first two months of development of a baby.
⚫ fertilisation - When the egg and sperm nuclei fuse.
⚫ menstruation - The monthly cycle in females.
⚫ ovary - The part of the female reproductive system that produces eggs.
⚫ ovulation - The release of an eggs from the ovary.
⚫ placenta - The structure made by an embryo to obtain food and oxygen from its mother.
⚫ puberty - The time when sex organs begin to work.
⚫ sperm - The male sex cell.
⚫ testis - The part of the male reproductive system that produces sperm.