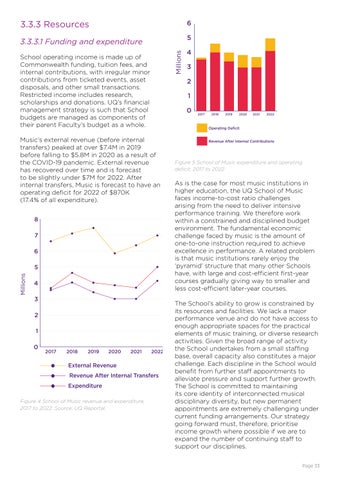
6
3.3.3.1 Funding and expenditure
5 Millions
3.3.3 Resources
School operating income is made up of Commonwealth funding, tuition fees, and internal contributions, with irregular minor contributions from ticketed events, asset disposals, and other small transactions. Restricted income includes research, scholarships and donations. UQ’s financial management strategy is such that School budgets are managed as components of their parent Faculty’s budget as a whole.
1 0
7 6
Millions
5 4 3 2 1 2018
2019
2020
2021
2022
External Revenue Revenue After Internal Transfers Expenditure Figure 4 School of Music revenue and expenditure, 2017 to 2022. Source: UQ Reportal.
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
2022
Operating Deficit
8
2017
3 2
Music’s external revenue (before internal transfers) peaked at over $7.4M in 2019 before falling to $5.8M in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. External revenue has recovered over time and is forecast to be slightly under $7M for 2022. After internal transfers, Music is forecast to have an operating deficit for 2022 of $870K (17.4% of all expenditure).
0
4
Revenue After Internal Contributions
Figure 5 School of Music expenditure and operating deficit, 2017 to 2022
As is the case for most music institutions in higher education, the UQ School of Music faces income-to-cost ratio challenges arising from the need to deliver intensive performance training. We therefore work within a constrained and disciplined budget environment. The fundamental economic challenge faced by music is the amount of one-to-one instruction required to achieve excellence in performance. A related problem is that music institutions rarely enjoy the ‘pyramid’ structure that many other Schools have, with large and cost-efficient first-year courses gradually giving way to smaller and less cost-efficient later-year courses. The School’s ability to grow is constrained by its resources and facilities. We lack a major performance venue and do not have access to enough appropriate spaces for the practical elements of music training, or diverse research activities. Given the broad range of activity the School undertakes from a small staffing base, overall capacity also constitutes a major challenge. Each discipline in the School would benefit from further staff appointments to alleviate pressure and support further growth. The School is committed to maintaining its core identity of interconnected musical disciplinary diversity, but new permanent appointments are extremely challenging under current funding arrangements. Our strategy going forward must, therefore, prioritise income growth where possible if we are to expand the number of continuing staff to support our disciplines. Page 33