
8 minute read
Protective barriers from low to high˚C
Romuald Machac, Hutchinson, South Korea, details the importance of insulation and barriers for the LNG market to ensure safety and longevity.
In a context of energy transition initiated by many countries and companies, LNG is set to play a leading role with rapid growth over the next 20 years.
Hutchinson designs and manufactures solutions that are designed to guarantee safety and energy performance in the most demanding markets: automotive, aerospace, energy, rail, and various other industries. Hutchinson Precision Sealing Systems, with its Foam & Converting Division (FCD), produces some protection and insulation solutions, in addition to foam and sealing components, for structures in contact with LNG.
Hutchinson’s expertise contributes to the development of LNG by providing solutions for its transport and storage at cryogenic temperature.
This source of energy represents real challenges in terms of customer demands such as deadlines and quality standards, which are becoming increasingly strict.
After being extracted, natural gas is liquefied to reduce its volume. This makes it possible to transport up to 600 times more energy for the same volume. To convert natural gas into LNG, it must be cooled down to the cryogenic temperature of -162˚C.
Fully customised solutions
Hutchinson, a subsidiary of TotalEnergies, is a global company with 40 000 employees spread across 25 countries. The company, with its know-how and experience of more than 30 years in the LNG industry, has developed solutions capable of coping with the constraints of extreme temperatures. At the cryogenic temperature of -162˚C, safety is fundamental, particularly in the transport of LNG by LNG carriers.
Today’s large capacity LNG tankers, consisting of four tanks with a total transport volume of approximately 175 000 m3 of LNG, require perfect insulation and sealing of the two containment barriers.
Hutchinson, with its development strength and its material expertise, can meet technical constraints of
demanding markets. Its solutions are also certified by all the classification societies, thus guaranteeing their merit. The company works in close collaboration with its customers to provide each of them with a fully customised solution.
The secondary cryogenic barrier
For more than 30 years, Hutchinson has been the major supplier of the secondary barrier on Mark III LNG tanks designed by the French company GTT. To date, Hutchinson has more than 240 references of Triplex® consisting of onshore storage tanks, fuel tanks, bunkering vessels, FLNG, FSRUs, and mainly LNG carriers. The Triplex product is designed to ensure the perfect sealing of the secondary barrier, securing the LNG tanks of more than a third of the world’s LNG carriers.
Triplex is a composite membrane that is LNG-tight at -170˚C. It is created to be flexible, not only during normal operation, which is approximately -100˚C, but also in the event of a problem on the primary barrier when it will be at -162˚C and in direct contact with the LNG. This flexibility allows it to absorb the thermal contractions of the LNG tanks as well as the deformations at sea of the vessel’s structure.
Hutchinson supports its customers and partners in new developments. The company has supplied Triplex on the first FLNG (Prelude), on the first fuel tank, on the first gravitybased structure (GBS) for Arctic LNG 2, and more. Hutchinson has also supplied Triplex for the argon tank for Cern and for the arctic cruise ship Le Commandant Charcot by PONANT.
Although the market is historically located in South Korea, it is expanding rapidly in other geographical areas including Europe, China, and Russia. To meet this growing global demand, Hutchinson is starting to distribute the Triplex in these new countries, especially in China, which will soon become the largest LNG importer.

Figure 1. LNG carrier SK Audace equipped with GTT Mark III flex containment system and Hutchinson Triplex®. Image courtesy of CHO Seongjoon - Capa - TotalEnergies.
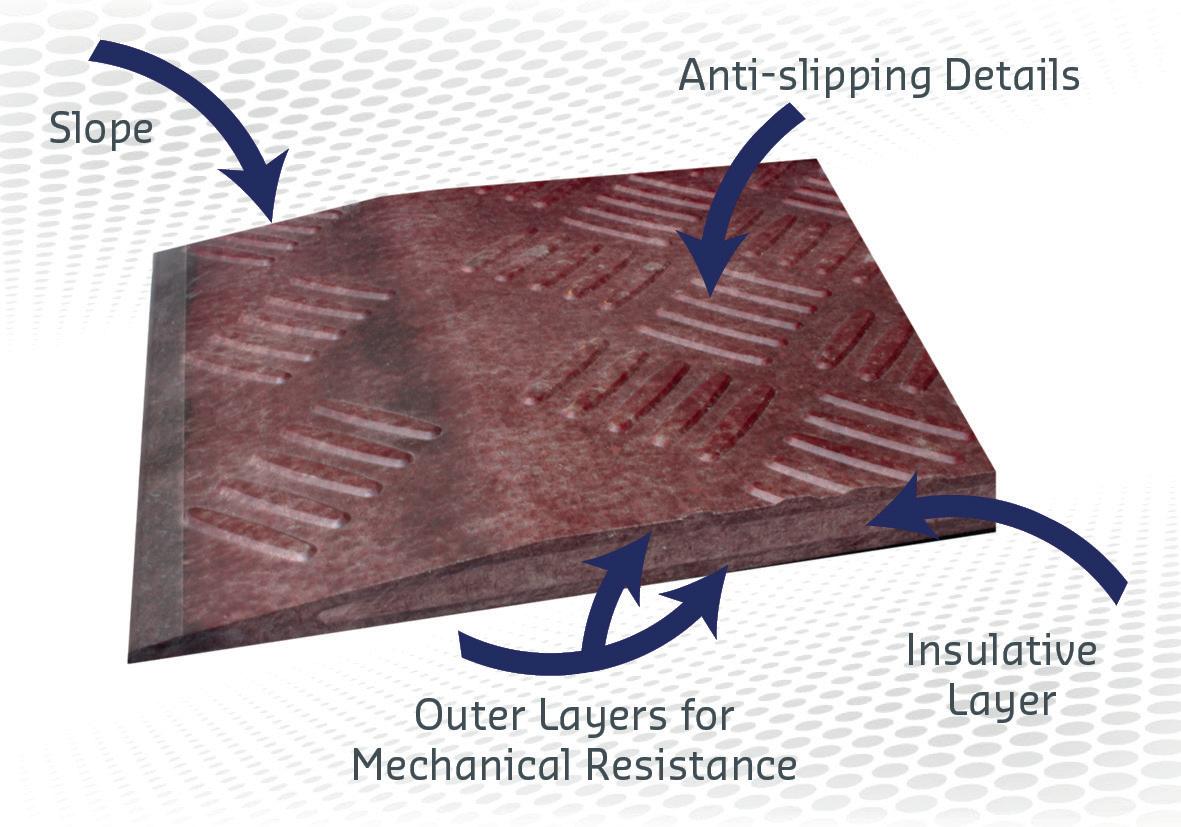
Figure 2. Zaltex® : Two hours of cryogenic spillage protection (CSP) and passive fire protection (PFP), with low thickness (21 mm) and density (18 kg/m3).
Addressing new problems in the LNG market
In 2008, and after strong experience with Triplex, Hutchinson wanted to open up to a new market by addressing new issues related to the evolution of the LNG market.
At that time, companies such as TotalEnergies and TechnipEnergies were in the midst of developing new LNG plants and FLNG projects that required enhanced protection against the risks of LNG leaks.
As a result of its expertise in cryogenics and materials, Hutchinson was able to offer an innovative product and solution in terms of protection materials.
In parallel to this development, and due to a lack of experience and standards on the validation of materials at cryogenic temperature, in 2011 Hutchinson joined a group of companies, led by TechnipEnergies, whose mission was to define precisely how to characterise the protective solutions for LNG liquefaction plants in a representative way. This group of end users, contractors, and suppliers jointly drafted the ISO 20088 standard, which will eventually include three parts: � Part 1: Nitrogen cryo pool test. � Part 2: Nitrogen liquid and vapour test. � Part 3: Nitrogen jet cryo test.
Hutchinson continues to actively participate in the development and the fine-tuning of the test methods for the three parts of this new standard.
The company has successfully passed the part one, which is the reference, allowing the validation of the Zaltex® as an effective protection against the spills of cryogenic fluids, combining mechanical resistance and speed of installation.
A new CSP and PFP solution
Zaltex is an innovative composite foam panel designed for cryogenic spillage protection (CSP) and passive fire protection (PFP).
This panel is made for cryogenic protection of onshore and offshore structures against accidental LNG spills, requiring high mechanical strength and insulation. Fully customisable, Zaltex can be used in LNG plants, chemical equipment, drilling/production facilities, storage, or transportation. Advantages of this composite foam panel include: � Ease of assembly under any weather conditions. � High mechanical resistance. � Resistant to multiple cryogenic shocks. � Fire resistant.
� Can be designed to meet specific requirements such as the duration of protection or the mechanical stress. � The lightest and thinnest technology on the market.
Example: withstanding the most severe cold and fire tests for two hours with a thickness of only 21 mm and a density of 18 kg/m3 .
As part of a strategy of continuous improvement and simultaneous engineering, Zaltex has successfully obtained several certifications that confirm its ability to fully meet the requirements of the LNG market.
Certification: Cryogenic pool test – ISO 20088-1
Zaltex has been successfully tested to achieve the ISO standard target of 2 hrs at -40˚C.
Another sample designed for the Yamal projects withstood a 1 hr cryogenic pool test at -196˚C, retaining its integrity and remaining intact. It prevented the steel from reaching the critical temperature of -50˚C after 1 hr.
Certification: Jet cryo – ISO 20088-3
To attest to its CSP performance, Zaltex was certified to ISO 20088-3 in March 2021 by DNV Spadeadam under the supervision of Lloyd’s Register. This solution withstood a 2 hr jet release at -196˚C while maintaining its integrity and remaining intact. It also prevented the structural steel from reaching the critical temperature of -44˚C after 2 hrs.
Certification: Jet fire – ISO 22899-1
The fire resistance of Zaltex, via the jet fire test, was also certified by Lloyd’s Register to ISO 22899-1 in December 2020 after withstanding a 2 hr test. Zaltex’s fire panels protect the primary steel structures of LNG facilities from fire hazards and prevent the critical temperature of 400˚C from being reached.
As part of the project to develop a fire version of Zaltex, Hutchinson’s development team has published a paper on jet fire testing with the UMET - ISP laboratory and EFECTIS FRANCE. It deals with the development of a bench scale test (jet fire lab) reproducing the fire exposure of the jet fire installation on a large scale according to the ISO 22899-1 standard. The Lloyd’s Register-approved Zaltex passive fire protection was used to demonstrate the value of such a bench for the development and improvement of PFP solutions for oil and gas installations.
Table 1. Cryogenic spill ISO 20088-1
Density (kg/m3) 400 700
Thickness (mm) 17+3 3+9+3
Temperature after 1 hr (˚C) -15 -47
Temperature after 2 hr (˚C) -38 -60
Further validation
To meet customer requests and strict project specifications, extensive tests of multiple Zaltex designs have been carried out. This has allowed a solid database to be created to quickly design a solution that is fully adapted to customer constraints.
The Yamal LNG site in Russia
One example of the application of Zaltex is when Hutchinson equipped the Yamal LNG site in Russia to protect the structures of the three MCHE modules of the LNG trains in the extreme conditions of Arctic Siberia. This protection is designed to ensure the structural integrity of the modules in the event of an accidental spill of LNG, whether it would be temporary or prolonged.
Zaltex can also be used as the main material for boxes or supports combining insulation, thermal protection, and mechanical structure.
Certified for both cryogenic applications and fire resistance, Zaltex is becoming a solution with many advantages and capable of being installed on all LNG structures in the future.
The challenges of the future
Hutchinson’s objective is to provide infrastructures with thermal insulation, protection against fire and/or cold, rapid installation in all conditions, and solid mechanical properties.
With state-of-the-art products offering thermal protection, mechanical resistance, and safety, Hutchinson effectively meets the ever-growing needs of the LNG market and contributes to its development as a greener, safer, and more economical energy source. Its technical solutions used for LNG bring the company closer to the use of other innovative energy sources such as hydrogen or liquid ammonia.


Providing clean, floating marine infrastructure technology for smarter unloading, re-loading and bunkering. Efficient plug and play solutions for:










