90
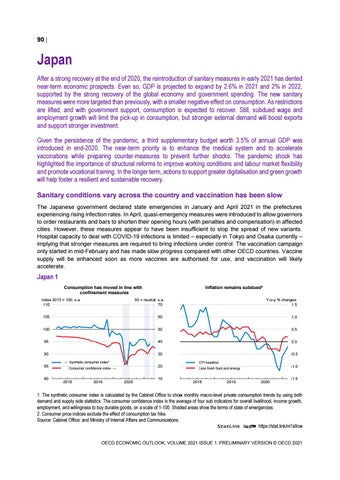
Japan After a strong recovery at the end of 2020, the reintroduction of sanitary measures in early 2021 has dented near-term economic prospects. Even so, GDP is projected to expand by 2.6% in 2021 and 2% in 2022, supported by the strong recovery of the global economy and government spending. The new sanitary measures were more targeted than previously, with a smaller negative effect on consumption. As restrictions are lifted, and with government support, consumption is expected to recover. Still, subdued wage and employment growth will limit the pick-up in consumption, but stronger external demand will boost exports and support stronger investment. Given the persistence of the pandemic, a third supplementary budget worth 3.5% of annual GDP was introduced in end-2020. The near-term priority is to enhance the medical system and to accelerate vaccinations while preparing counter-measures to prevent further shocks. The pandemic shock has highlighted the importance of structural reforms to improve working conditions and labour market flexibility and promote vocational training. In the longer term, actions to support greater digitalisation and green growth will help foster a resilient and sustainable recovery. Sanitary conditions vary across the country and vaccination has been slow The Japanese government declared state emergencies in January and April 2021 in the prefectures experiencing rising infection rates. In April, quasi-emergency measures were introduced to allow governors to order restaurants and bars to shorten their opening hours (with penalties and compensation) in affected cities. However, these measures appear to have been insufficient to stop the spread of new variants. Hospital capacity to deal with COVID-19 infections is limited – especially in Tokyo and Osaka currently – implying that stronger measures are required to bring infections under control. The vaccination campaign only started in mid-February and has made slow progress compared with other OECD countries. Vaccine supply will be enhanced soon as more vaccines are authorised for use, and vaccination will likely accelerate.
Japan 1 Inflation remains subdued²
Consumption has moved in line with confinement measures Index 2015 = 100, s.a. 110
50 = neutral, s.a. 70
Y-o-y % changes 1.5
105
60
1.0
100
50
0.5
95
40
0.0
90
30
-0.5
← Synthetic consumer index¹
85 80
CPI headline
20
Consumer confidence index →
2018
2019
2020
10
-1.0
Less fresh food and energy
0
2018
2019
2020
-1.5
1. The synthetic consumer index is calculated by the Cabinet Office to show monthly macro-level private consumption trends by using both demand and supply side statistics. The consumer confidence index is the average of four sub indicators for overall livelihood, income growth, employment, and willingness to buy durable goods, on a scale of 1-100. Shaded areas show the terms of state of emergencies. 2. Consumer price indices exclude the effect of consumption tax hike. Source: Cabinet Office; and Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/m7a9cw OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2021 ISSUE 1: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2021