199
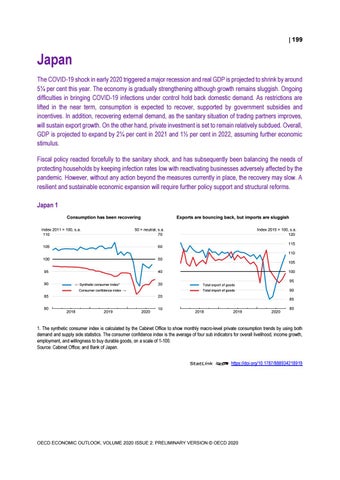
Japan The COVID-19 shock in early 2020 triggered a major recession and real GDP is projected to shrink by around 5¼ per cent this year. The economy is gradually strengthening although growth remains sluggish. Ongoing difficulties in bringing COVID-19 infections under control hold back domestic demand. As restrictions are lifted in the near term, consumption is expected to recover, supported by government subsidies and incentives. In addition, recovering external demand, as the sanitary situation of trading partners improves, will sustain export growth. On the other hand, private investment is set to remain relatively subdued. Overall, GDP is projected to expand by 2¼ per cent in 2021 and 1½ per cent in 2022, assuming further economic stimulus. Fiscal policy reacted forcefully to the sanitary shock, and has subsequently been balancing the needs of protecting households by keeping infection rates low with reactivating businesses adversely affected by the pandemic. However, without any action beyond the measures currently in place, the recovery may slow. A resilient and sustainable economic expansion will require further policy support and structural reforms. Japan 1 Consumption has been recovering Index 2011 = 100, s.a. 110
Exports are bouncing back, but imports are sluggish
50 = neutral, s.a. 70
105
60
100
50
95
40
Index 2015 = 100, s.a. 120 115 110
90
105 100 95
30
← Synthetic consumer index¹
Total export of goods
Consumer confidence index →
80
90
Total import of goods
85
20
2018
2019
2020
10
85 0
2018
2019
2020
80
1. The synthetic consumer index is calculated by the Cabinet Office to show monthly macro-level private consumption trends by using both demand and supply side statistics. The consumer confidence index is the average of four sub indicators for overall livelihood, income growth, employment, and willingness to buy durable goods, on a scale of 1-100. Source: Cabinet Office; and Bank of Japan. StatLink 2 https://doi.org/10.1787/888934218919
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2020 ISSUE 2: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2020