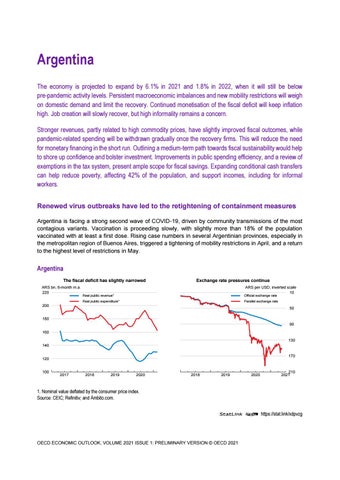
Argentina The economy is projected to expand by 6.1% in 2021 and 1.8% in 2022, when it will still be below pre-pandemic activity levels. Persistent macroeconomic imbalances and new mobility restrictions will weigh on domestic demand and limit the recovery. Continued monetisation of the fiscal deficit will keep inflation high. Job creation will slowly recover, but high informality remains a concern. Stronger revenues, partly related to high commodity prices, have slightly improved fiscal outcomes, while pandemic-related spending will be withdrawn gradually once the recovery firms. This will reduce the need for monetary financing in the short run. Outlining a medium-term path towards fiscal sustainability would help to shore up confidence and bolster investment. Improvements in public spending efficiency, and a review of exemptions in the tax system, present ample scope for fiscal savings. Expanding conditional cash transfers can help reduce poverty, affecting 42% of the population, and support incomes, including for informal workers. Renewed virus outbreaks have led to the retightening of containment measures Argentina is facing a strong second wave of COVID-19, driven by community transmissions of the most contagious variants. Vaccination is proceeding slowly, with slightly more than 18% of the population vaccinated with at least a first dose. Rising case numbers in several Argentinian provinces, especially in the metropolitan region of Buenos Aires, triggered a tightening of mobility restrictions in April, and a return to the highest level of restrictions in May.
Argentina The fiscal deficit has slightly narrowed ARS bn, 6-month m.a. 220
Exchange rate pressures continue ARS per USD, inverted scale 10
Real public revenue¹
Official exchange rate
Real public expenditure¹
Parallel exchange rate
200
50
180 90 160 130 140 170
120 100
2017
2018
2019
2020
0
0
2018
2019
2020
210 2021
1. Nominal value deflated by the consumer price index. Source: CEIC; Refinitiv; and Ámbito.com. StatLink 2 https://stat.link/xdpvzg
OECD ECONOMIC OUTLOOK, VOLUME 2021 ISSUE 1: PRELIMINARY VERSION © OECD 2021