











Course name: Design. Location:
Project Involvement: analysis studying Tollerance and Movement, Building physics,Assembly sequencing,Fire safety,EIA and Structual performance of the facade.
Year/semester: semester of MSc.
School: Email adderss of studio head: betel.biruk@eiabc.edu.et
Project type: The Muse.





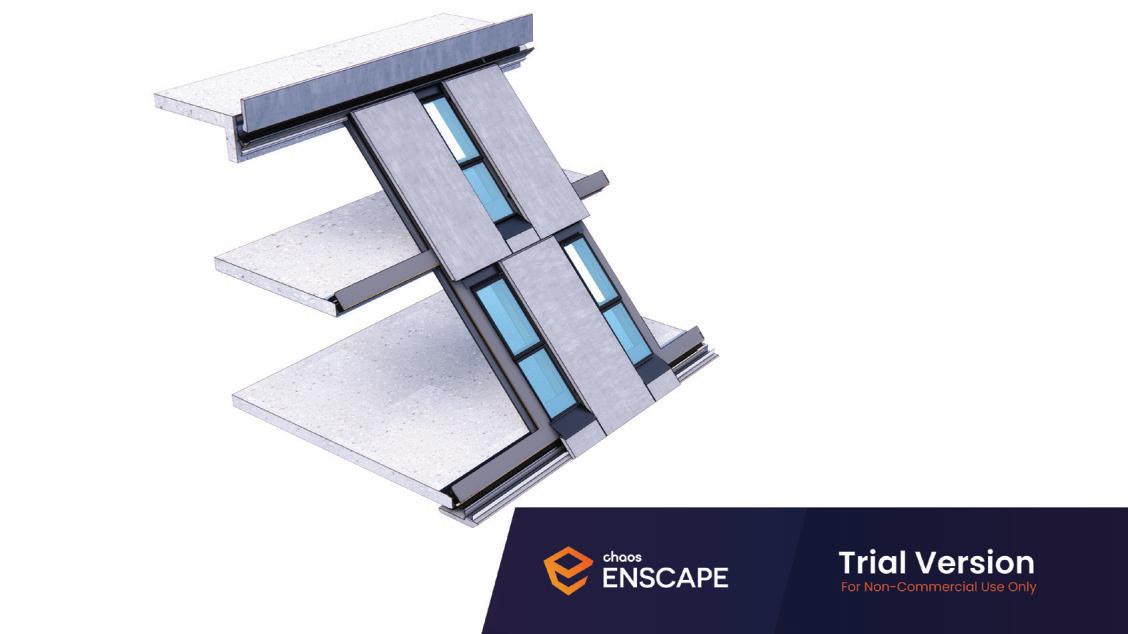



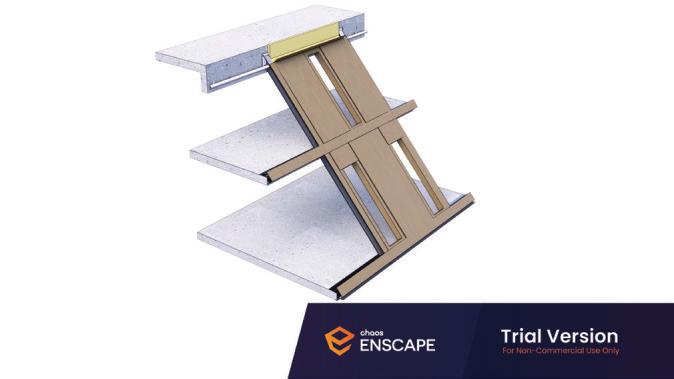
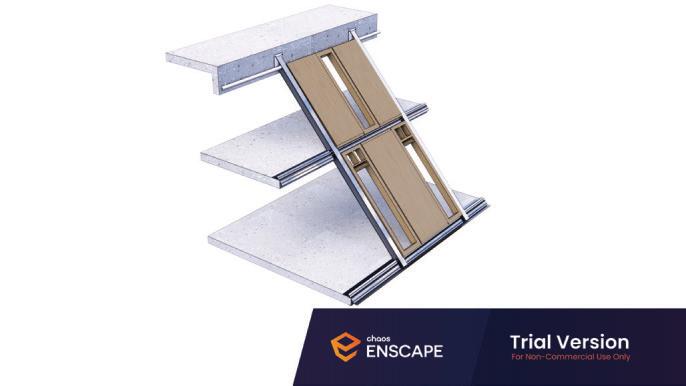
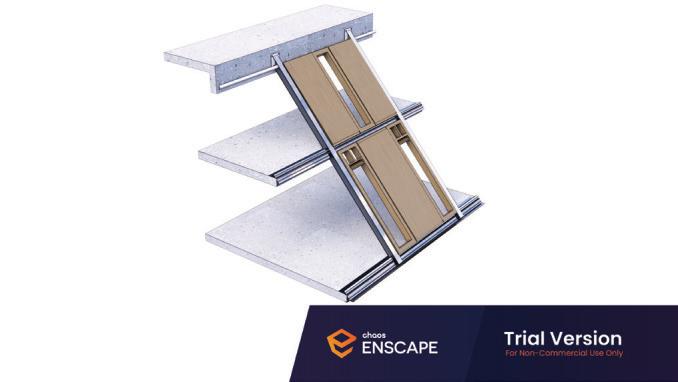
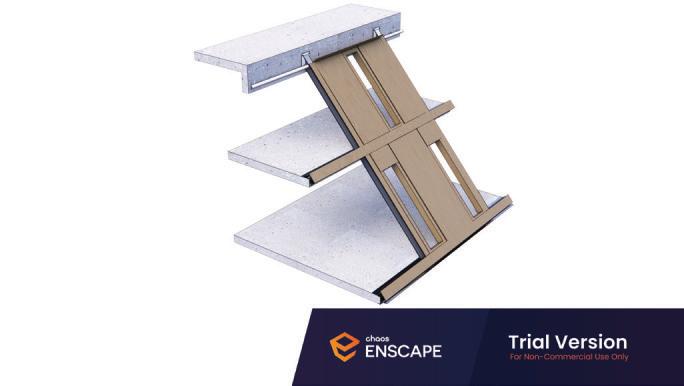
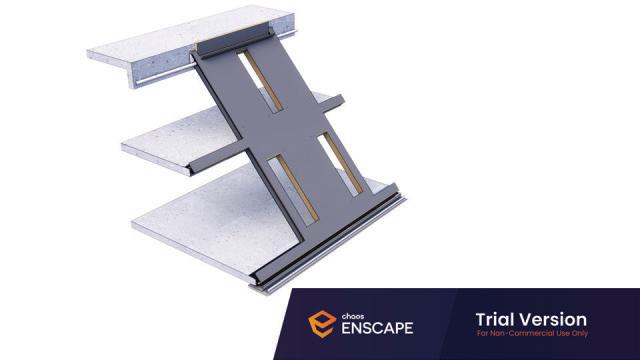
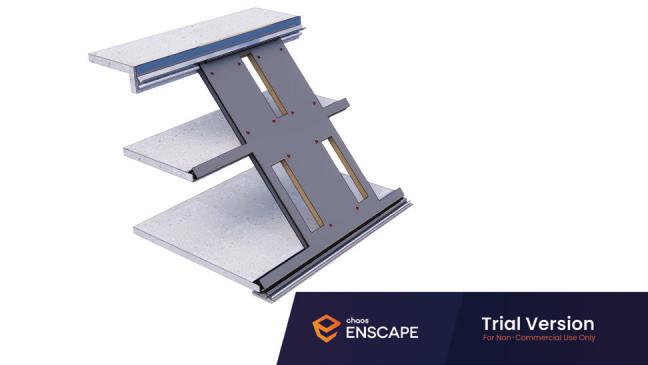
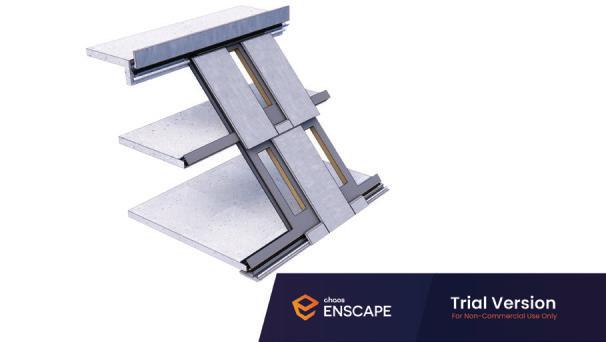
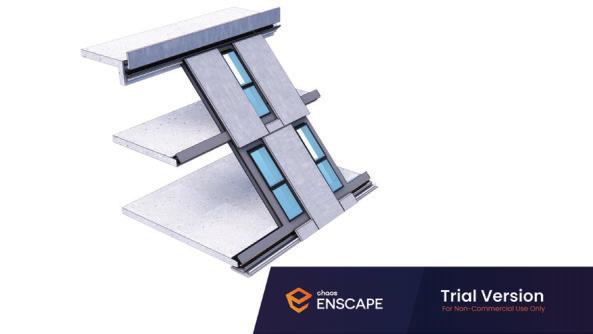
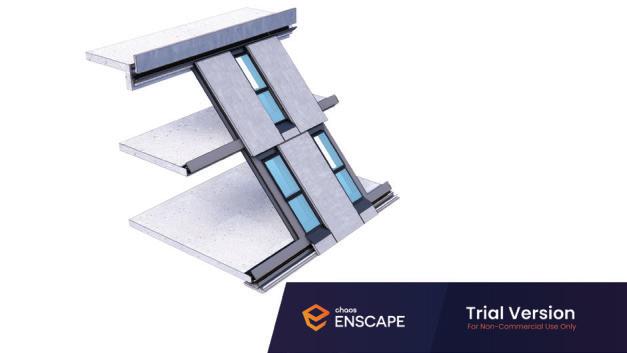
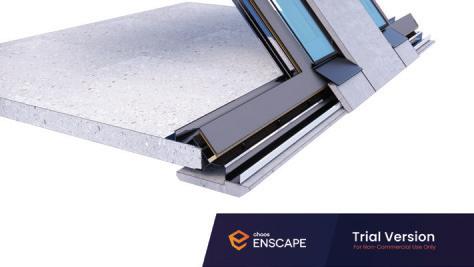
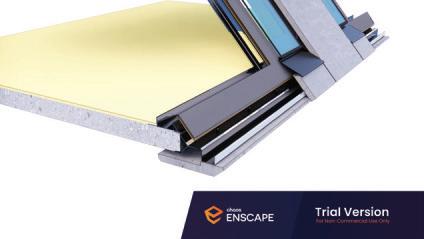
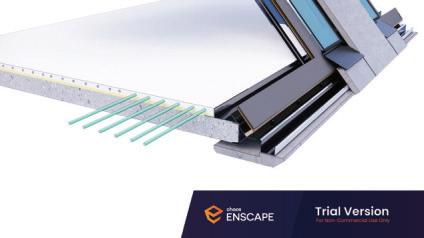
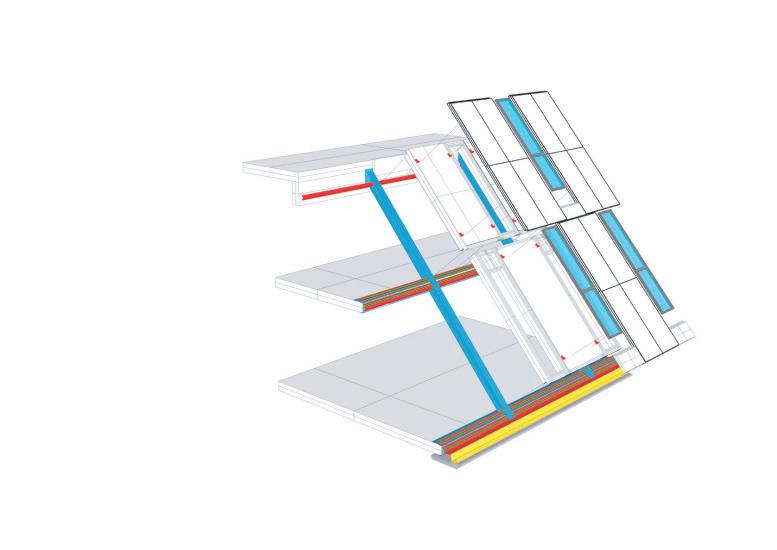
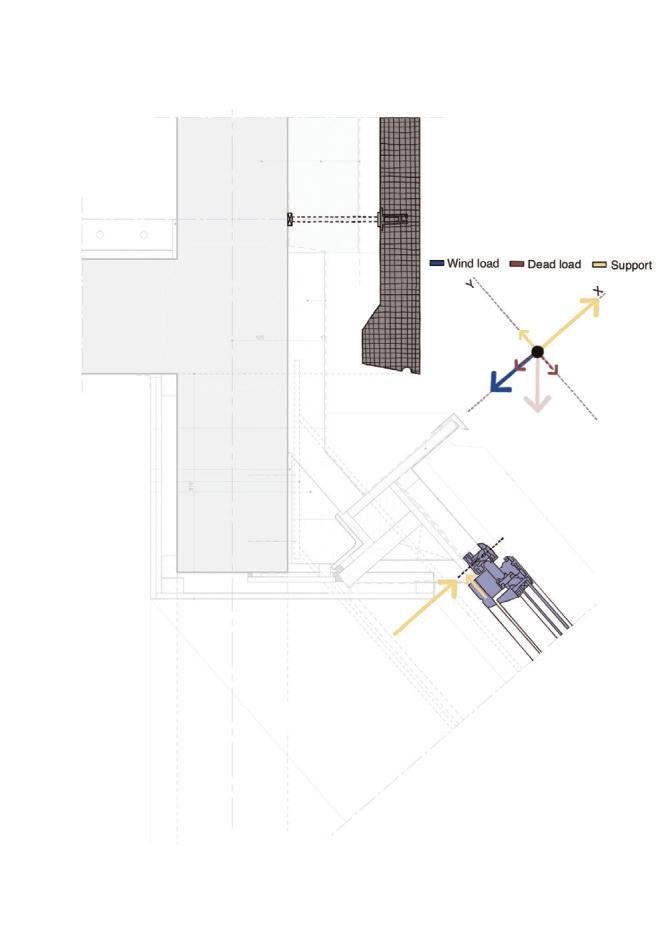
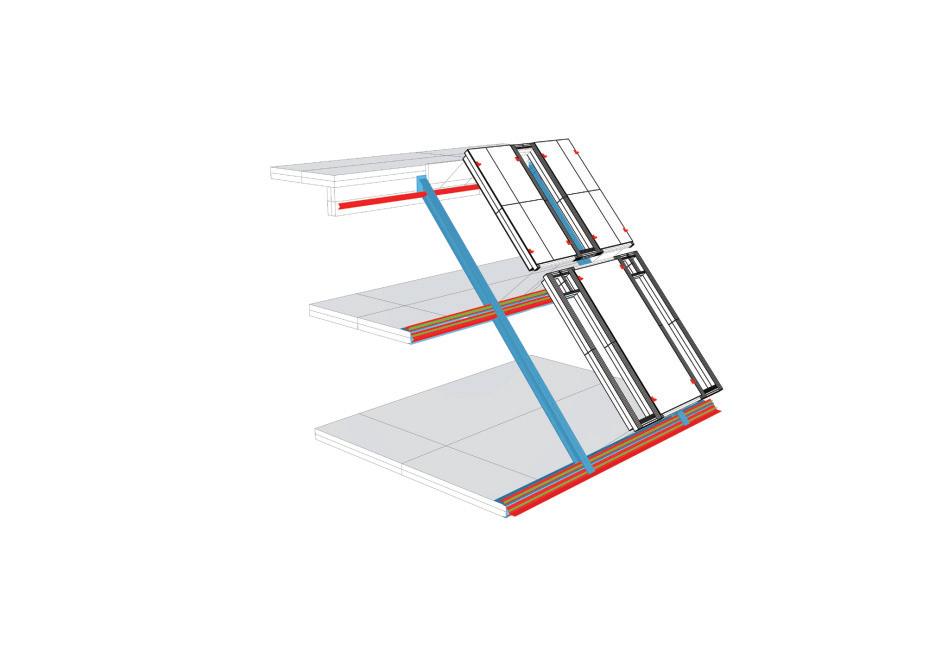
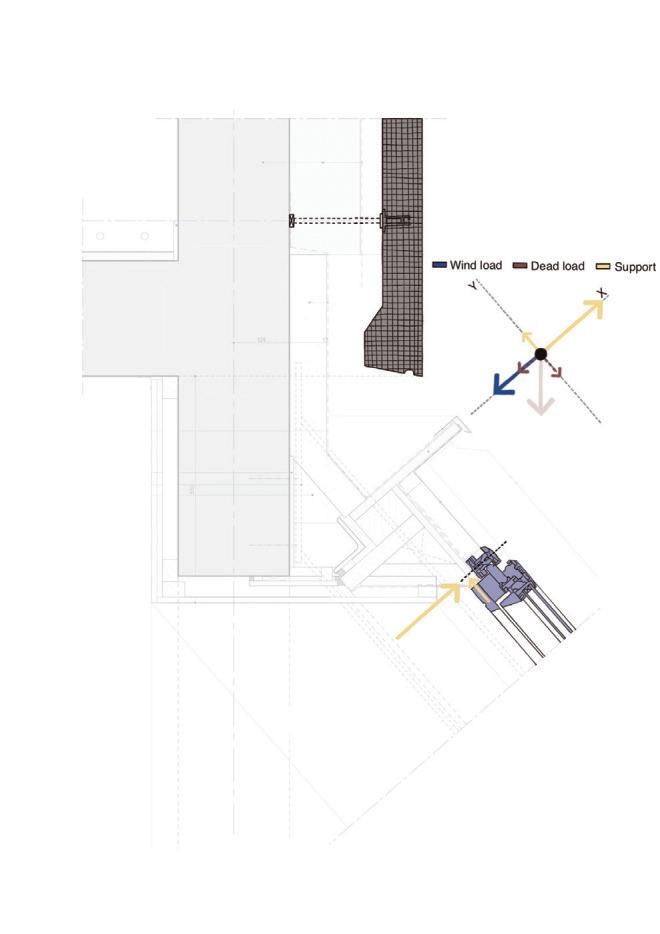
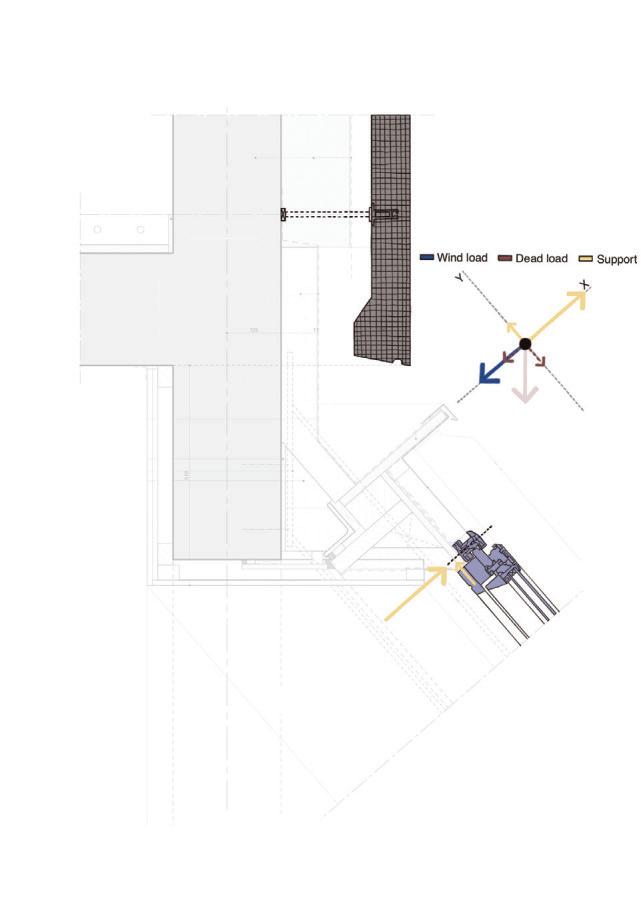
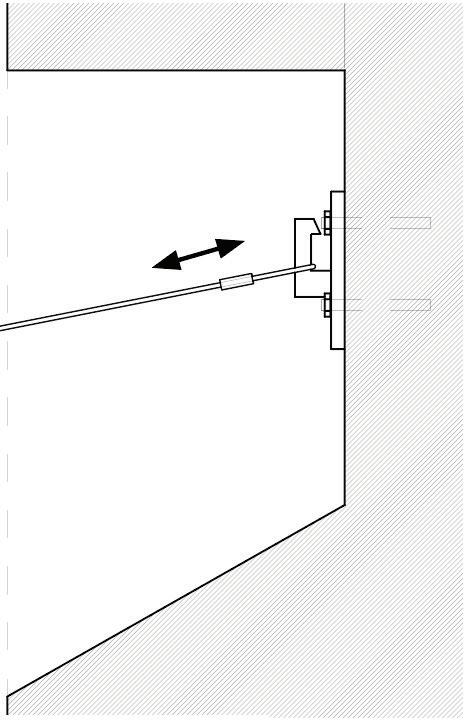
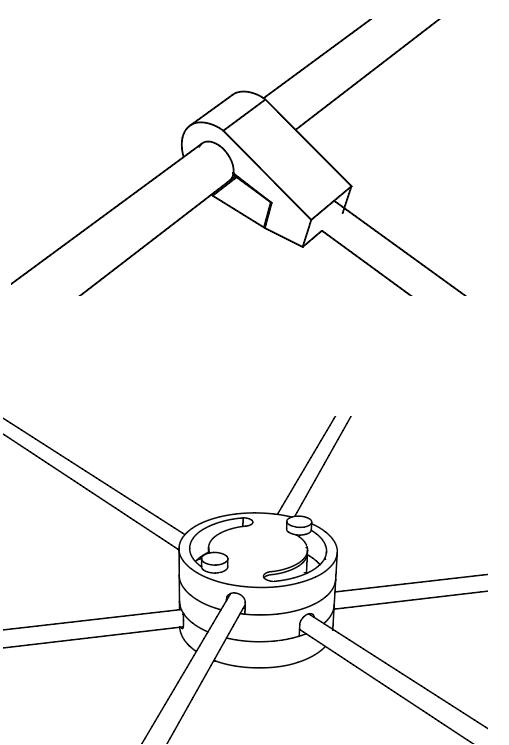
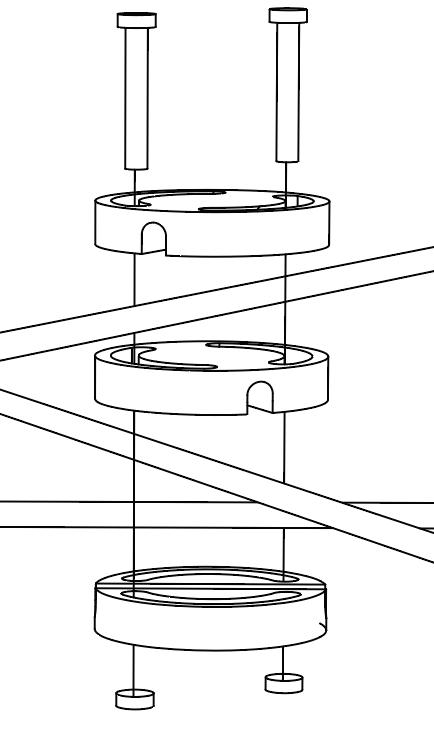
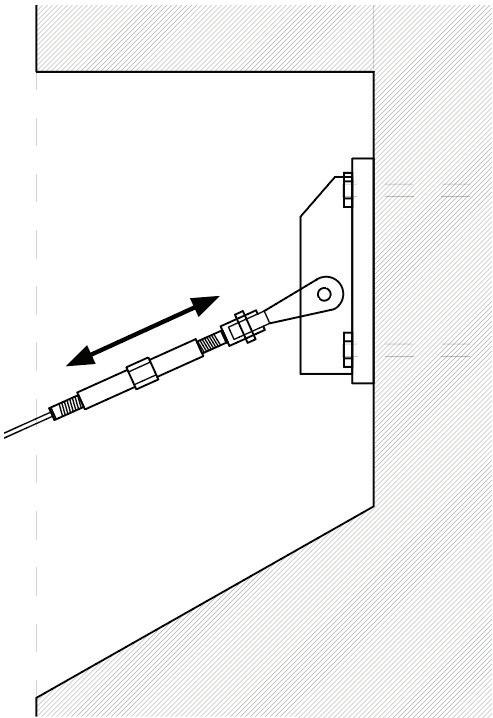
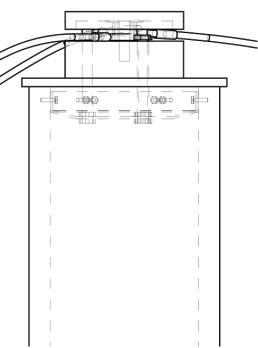
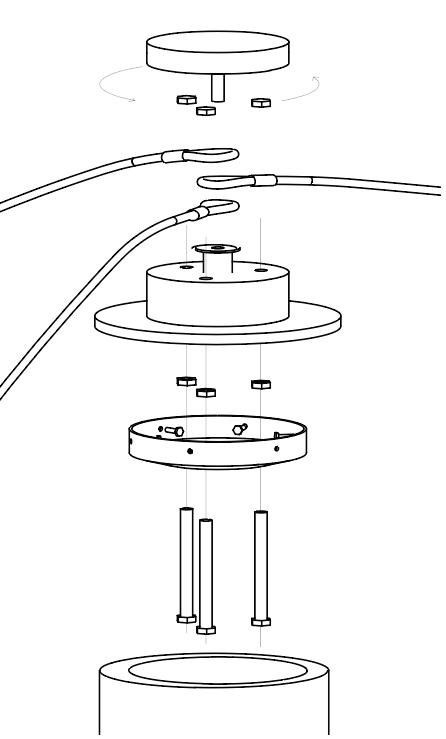
Diagonal HEA 220 column hangs the floor at the bottom(an in-situ connection) and is anchored to the top floor using a J bolt.
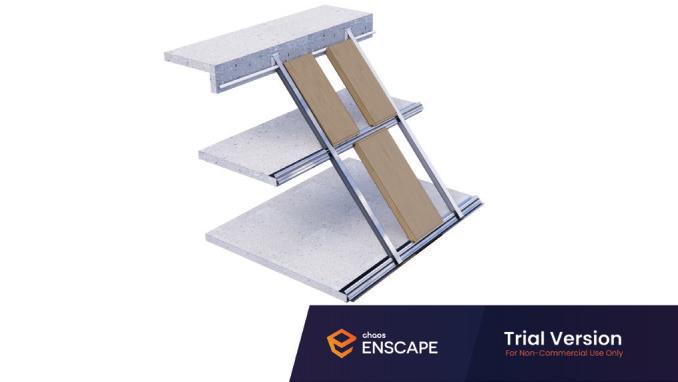
An assembly of L profiles are welded to the HEA at Point A (see figure above). At point B(see fig. above) the L-profiles are welded to a base plate and attached to the floor and welded to the HEA side.





































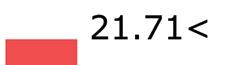

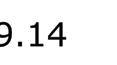

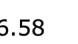

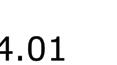









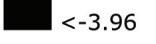


























































Course name: Structural Design+ Computational Intelligence
Project type:Academic
Location:Egypt,Giza
Project Involvement:8 weeks of design exercise with a group of 4,involved in conceptual design, structural design and computational approach to rationalizing the floor structure.
Year/semester:2023,1st year 2nd Semester MS.
School: Delft University of Technology.
Email address of studio head: J.D.OCallaghan@tudelft.nl
Temple of the Rising Sun.
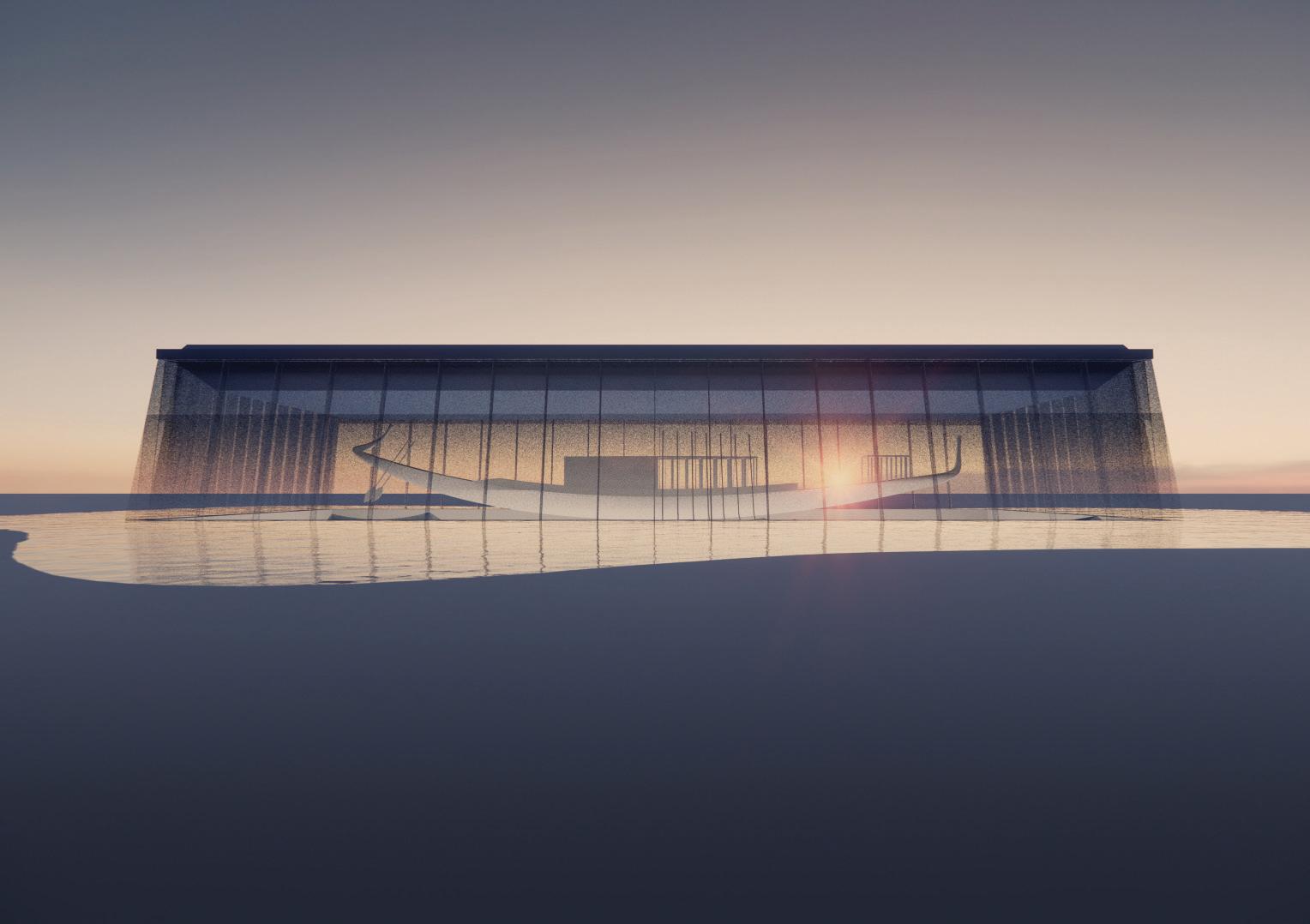
Glass floor design iteration: Aesthetics, structure, and standardized panels were considered


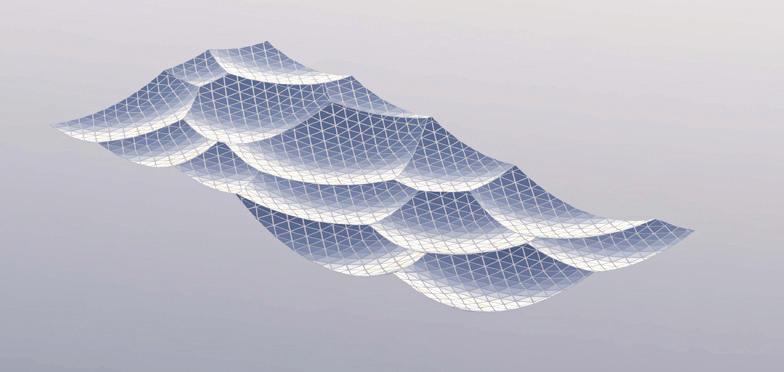
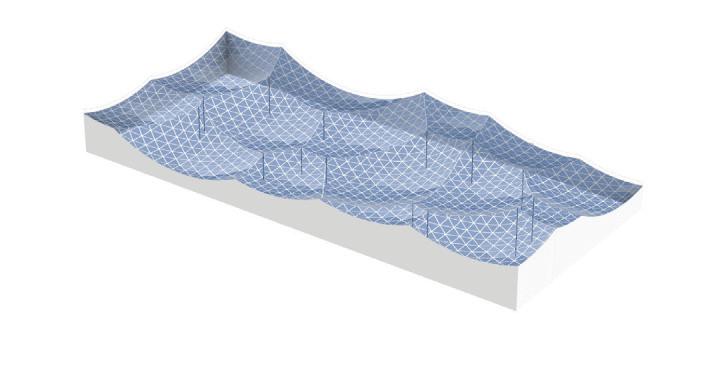
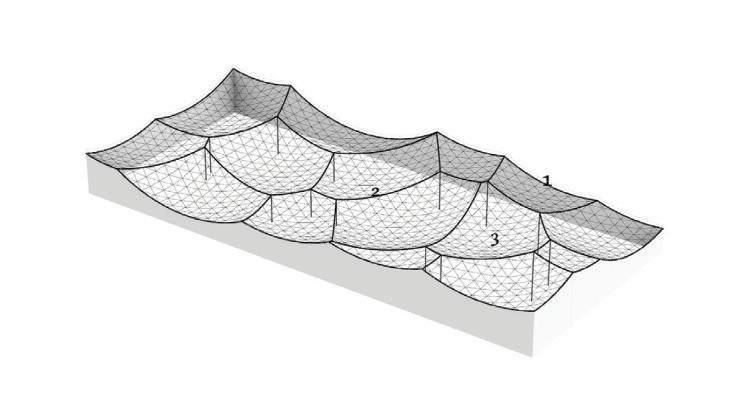
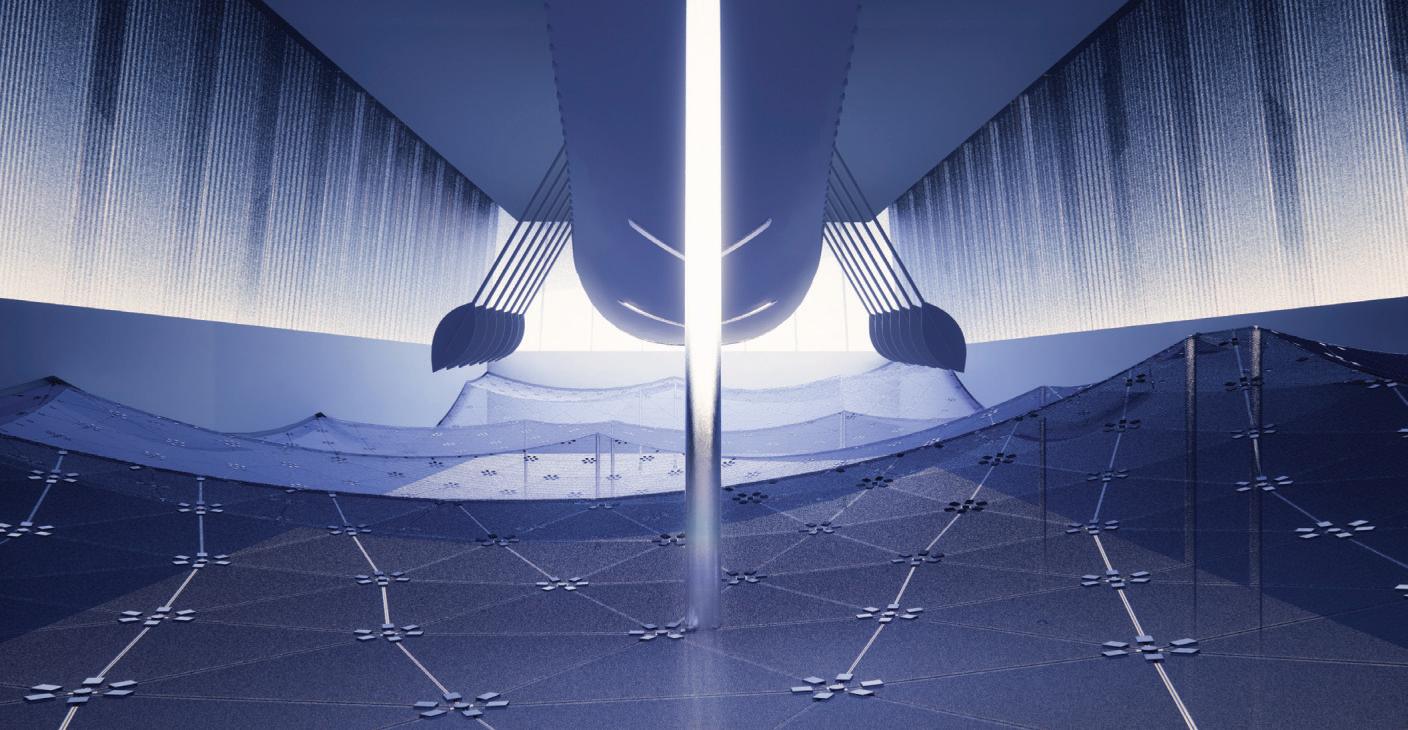

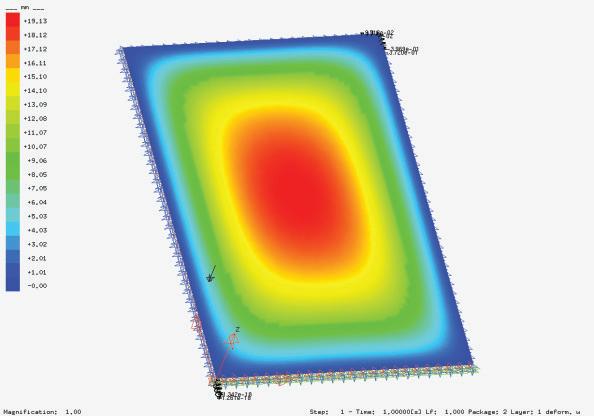
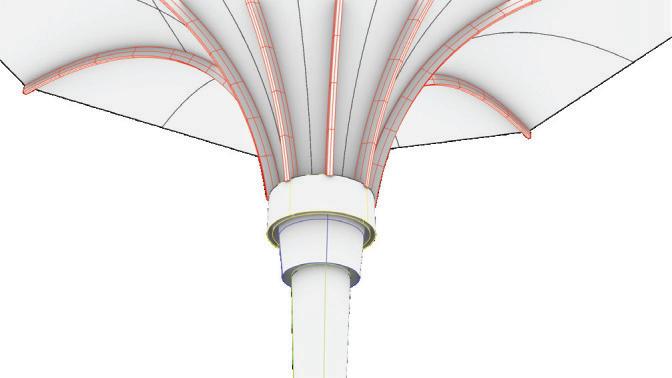
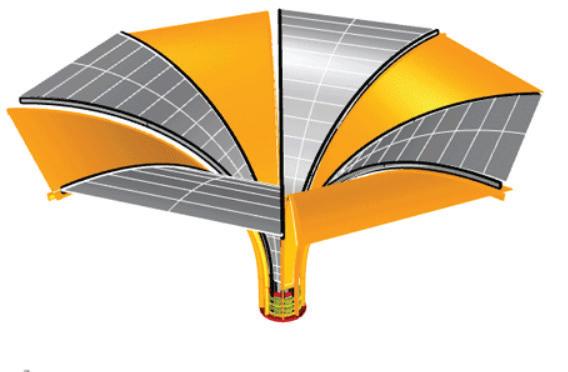
Using hand calculations the glass walls sizings were calculated and Karamba was used to confirm the structural analysis. The glass diaphragm wall is made up of two 9*3.125 m laminated glass panels and used for the internal and external pane of glass. This size fits the maximum width possible for lamination of glass which is 3.2 m. The karamba model consists of a pinned connected roof space frame, loaded by point loads that simulate the dead load of roof decking and cladding. Th roof is pinned connected to a beam attached to glass facade boxes that are clamped from the top and bottom. A wind load of 1kN/m2 is applied to the facade, and no maintenance loads are in place. Th resulting utilization factor for stresses resulting from bending does not exceed 10%. Maximum deflection occurs in the corner glass boxes, which bear the highest wind load due to their location and larger size compared to the rest of the boxes. The utilization factor for stresses is within the acceptable range, and the deflection is lower than expected.
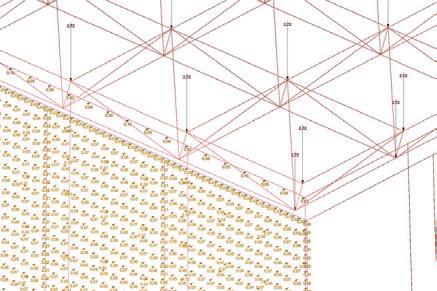





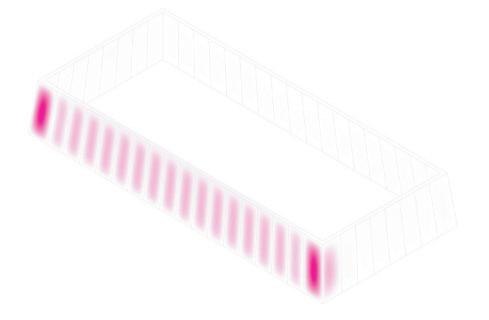
The roof space frame has been optimized in terms of circular hollow section (CHS) size, using members made of 7020 aluminum alloy. Th maximum allowable deflection was set at 8cm at the center of the roof, which was loaded by wind loads and dead loads from the roof cladding and decking. To ensure ease of assembly and production, the number of allowable member ties was limited to three. Th Karamba component “optimize cross-section” was used to perform the optimization. Th resulting section dimensions are as follows: CHS 33.7 / 3.2, CHS 60.3 / 3.2, and CHS 60.3 / 3.2. Th use of a limited number of member ties facilitates ease of assembly and simplifies production processes
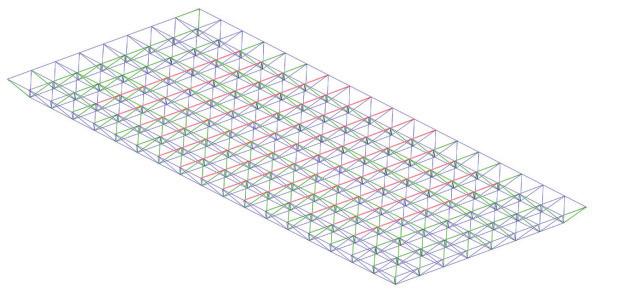
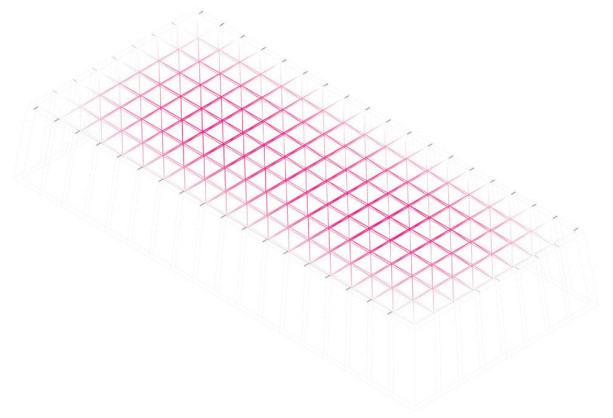
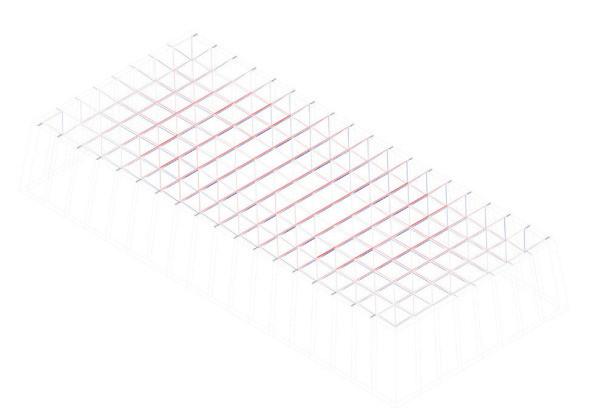
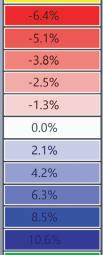
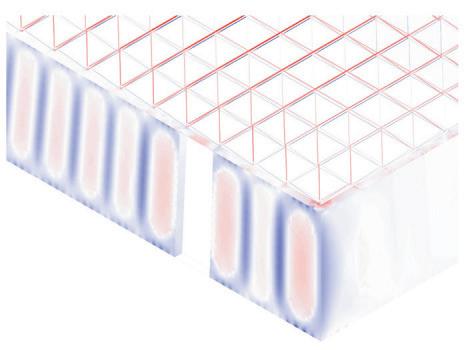
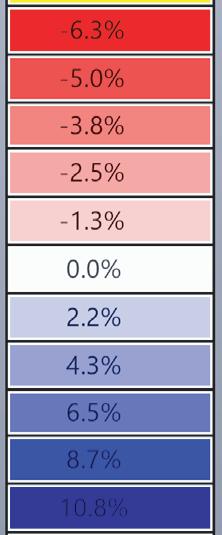
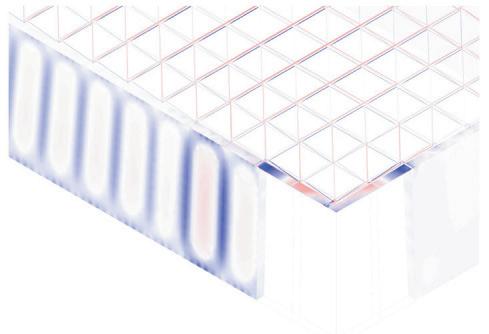
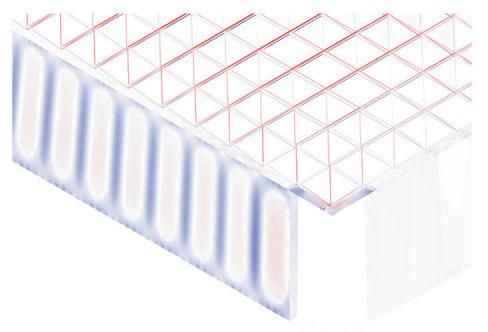
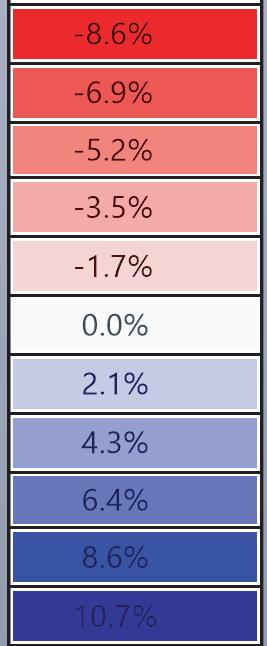
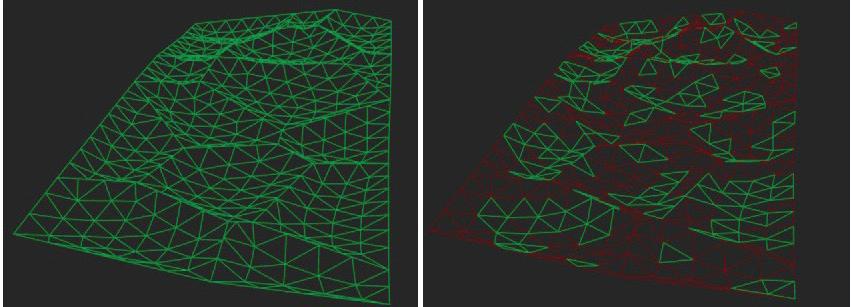
The structural safety analysis performed in Karamba on the façade structure with dead loads and a the wind load applied yielded positive results. The analysis showed that the building was able to maintain its structural integrity under different loading scenarios, even when several glass boxes were missing. Even in the third case where four corner boxes were missing, the building remained structurally sound and did not collapse or suffer any structural failure.
The stress distribution analysis conducted alongside the structural safety analysis revealed that the higher stresses could be observed in the areas adjacent to the missing boxes. Additionally, the beam connecting the roof to the façade underwent strong stresses and deflections resulting from the load of the space-frame. However, the overall stress levels remained within the acceptable range for the materials(Glass and steel).
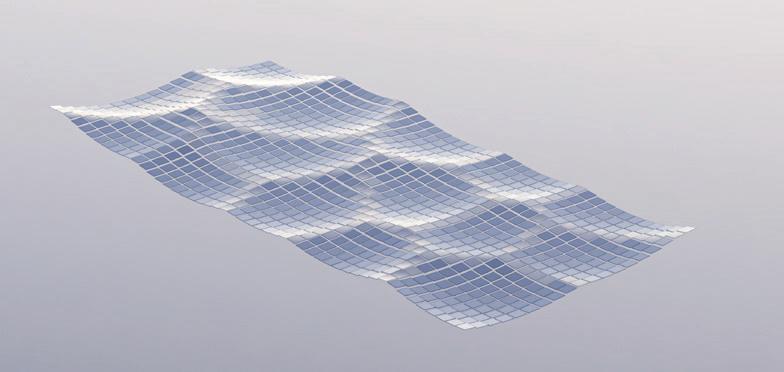
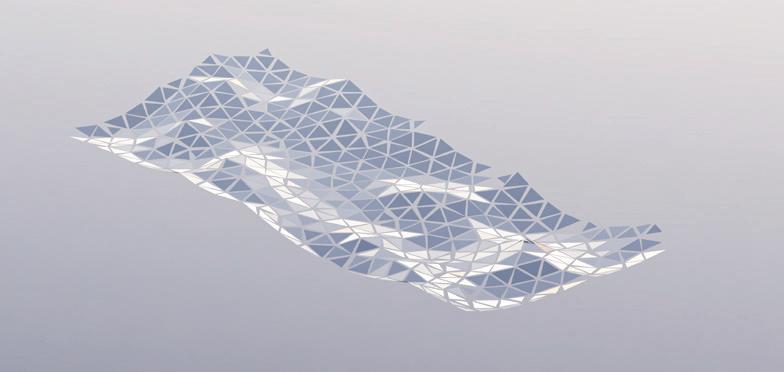
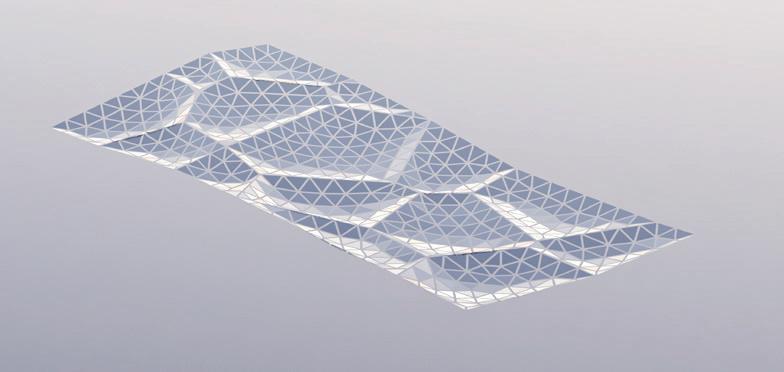
Glass Floor Panelization: clustering and offsetting the average


Clustering
Steps:



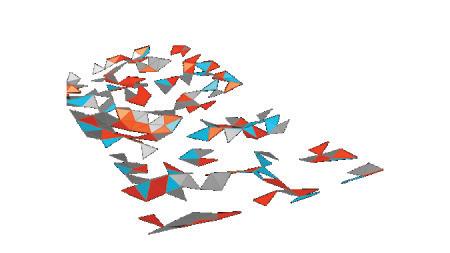

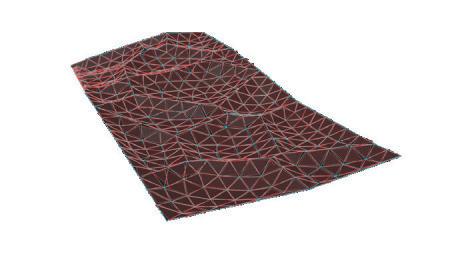

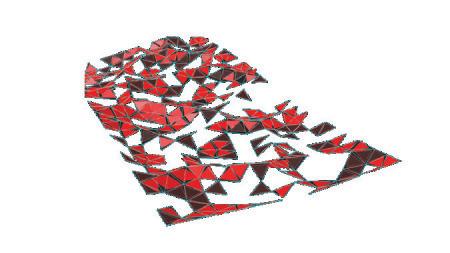



Final result of 4 different Gaussian Mixtures represented in 4 Different colors.
Course name: MS. Thesis - Facade and structural engineering
Project type:Academic
Location:Delft, Netherlands
Project Involvement:8 months of Research , conference pretension and journal publication.
Year/semester:2024,2nd year MS.
Email address of advisor: A.LunaNavarro@tudelft.nl
Industry partner: AGC School: Delft University of Technology.

Research project description.
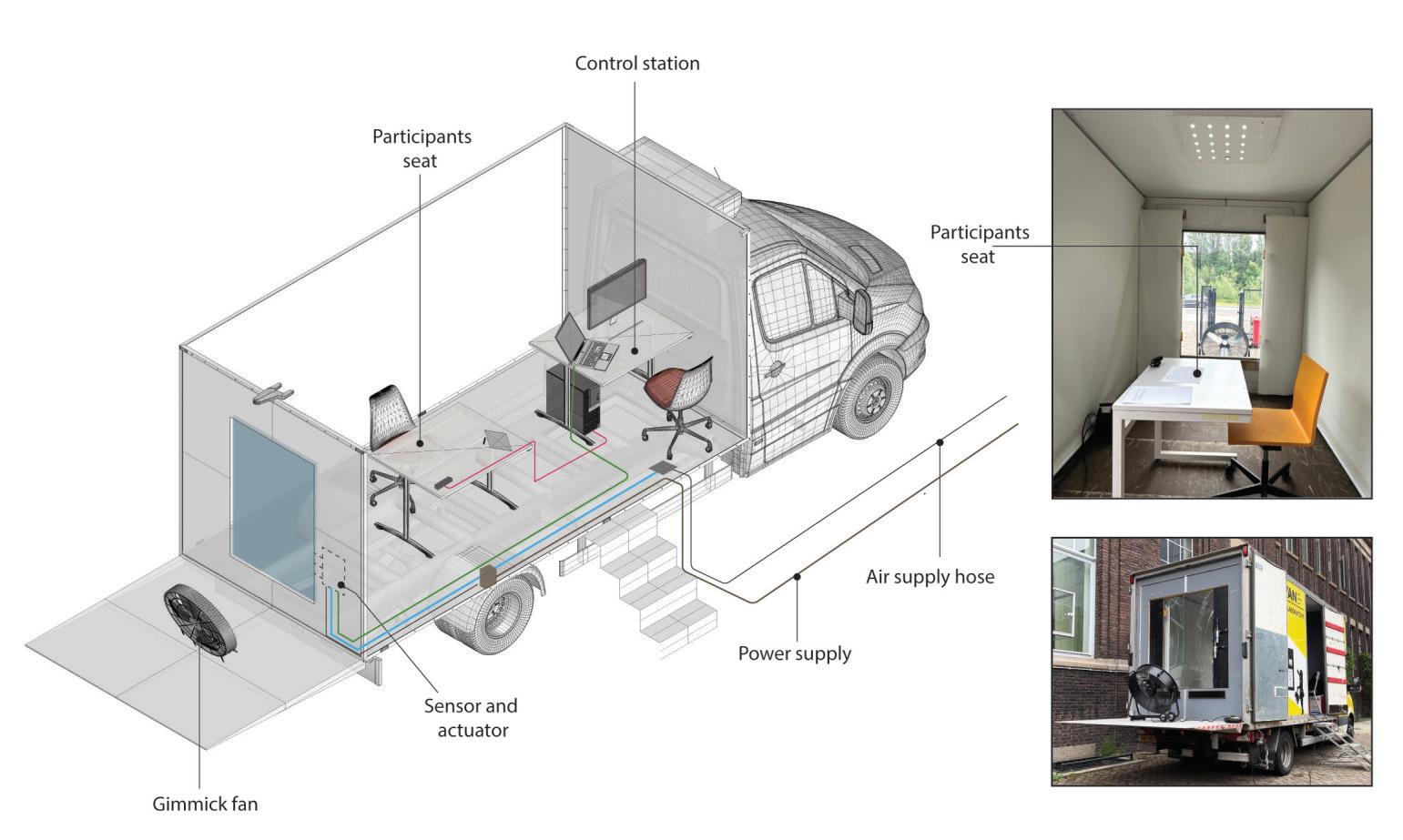
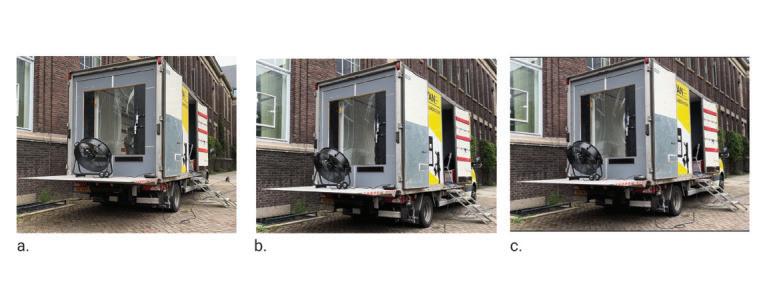
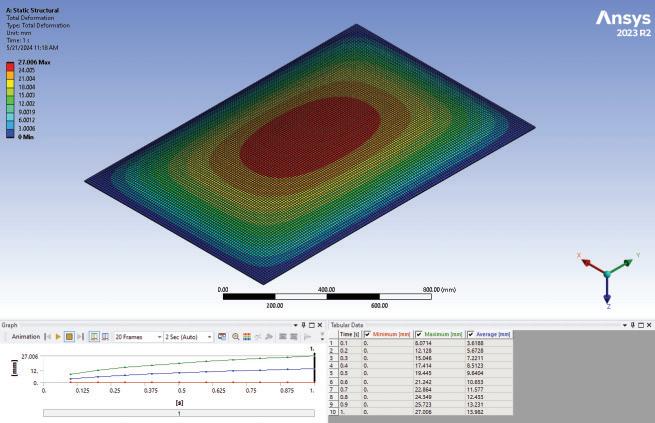
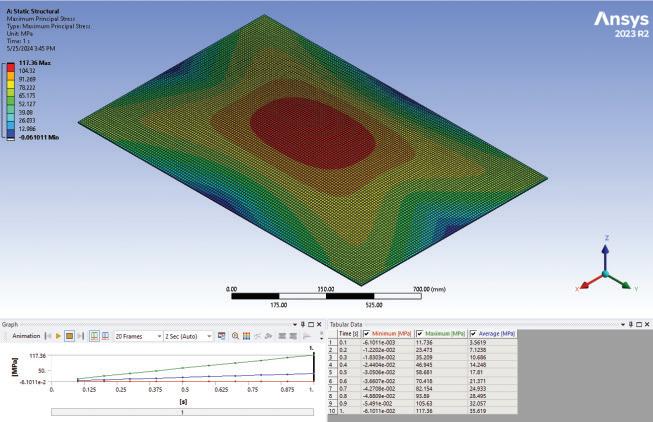
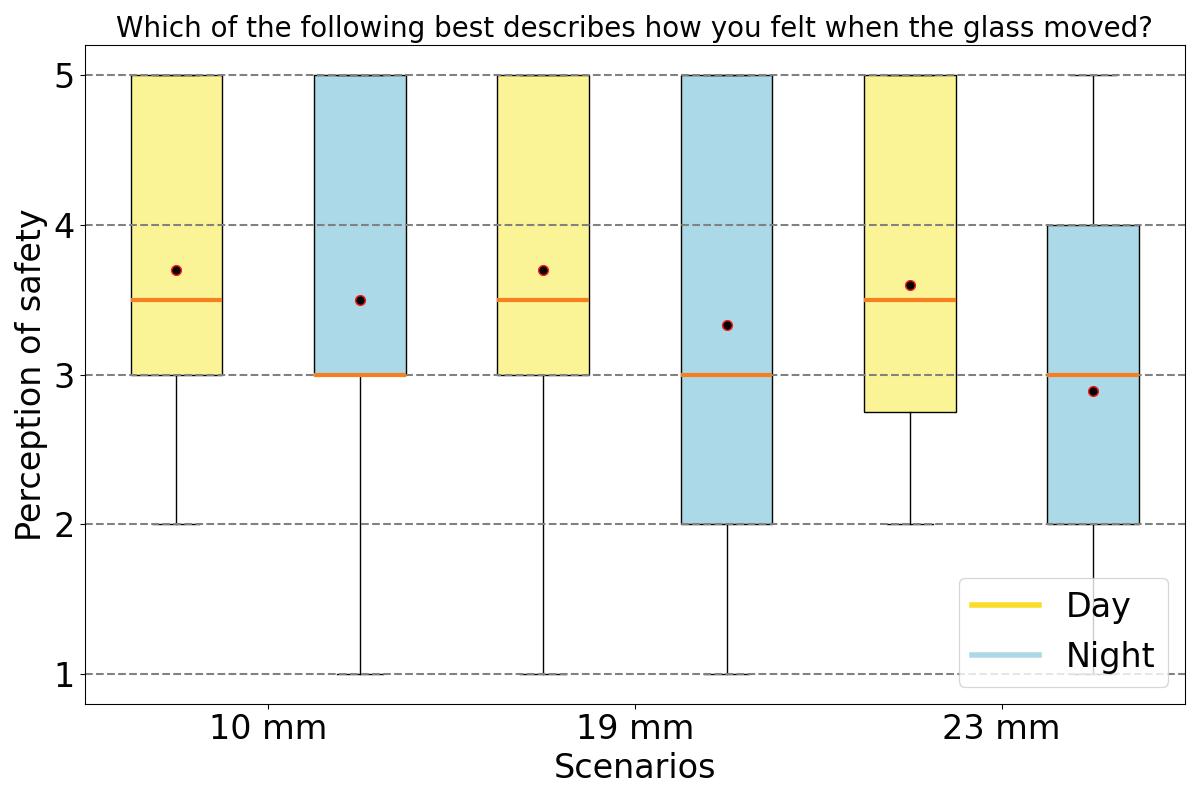
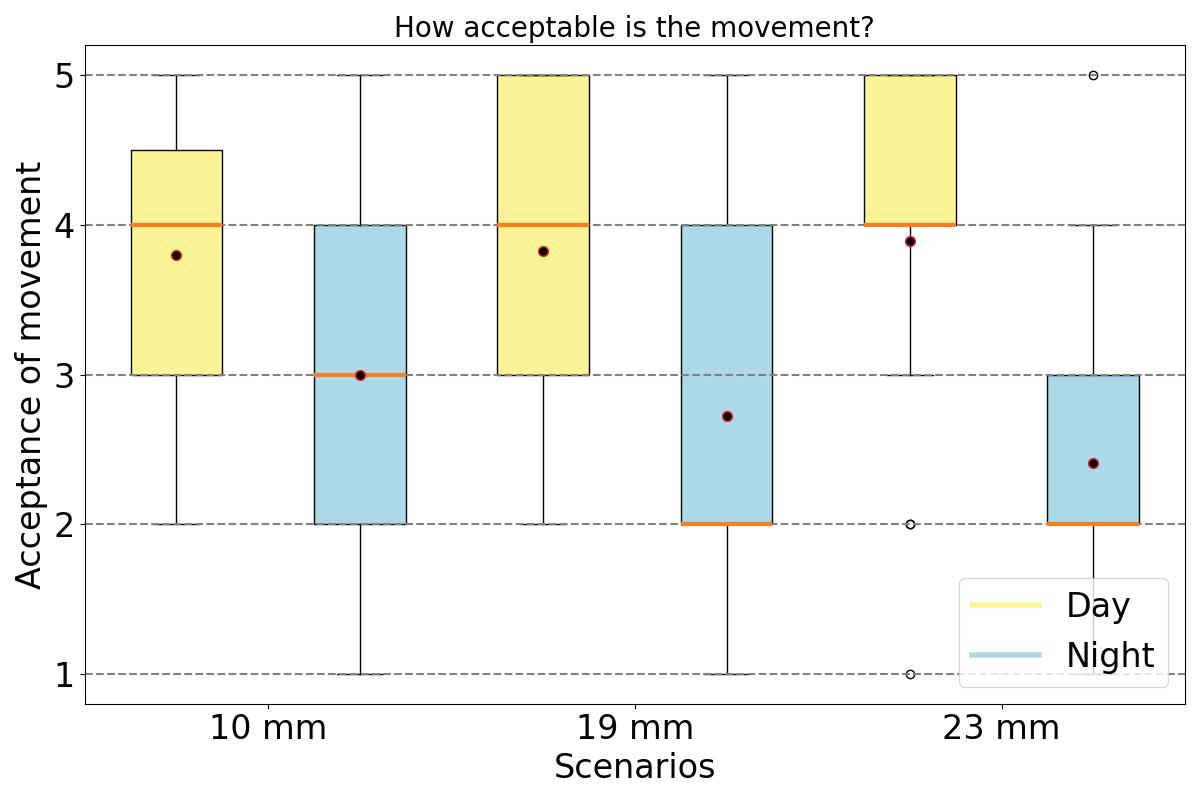
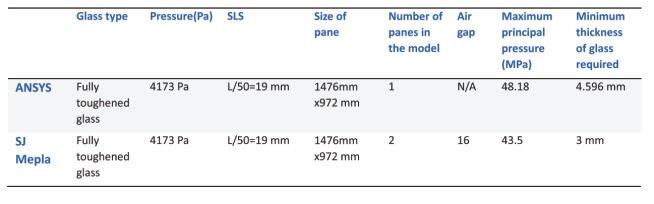
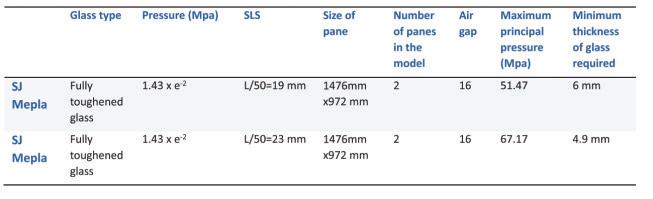
The study involves a novel experimental campaign to assess volunteers’ levels of perception and acceptance of various glass deformations. The glass was deformed using a bespoke electro-pneumatic system at levels corresponding to below, above, and at the current serviceability limit. To insure safety of experiment , a break test was performed using similar IGU (1470x950) and the data collected was compared with FEA in Ansys to set a safety threshold for the experiment. The Electro-pneumatic system was able to deflect the IGU in a cyclic motion mimicking movement during a wind load.
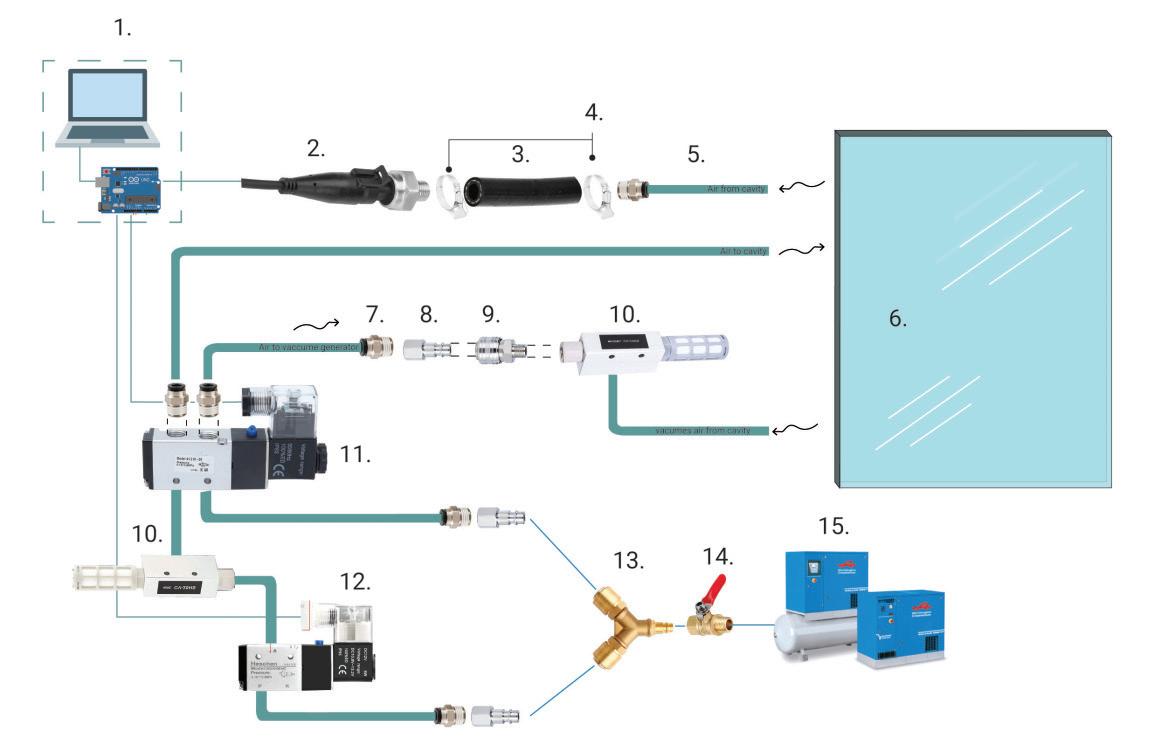
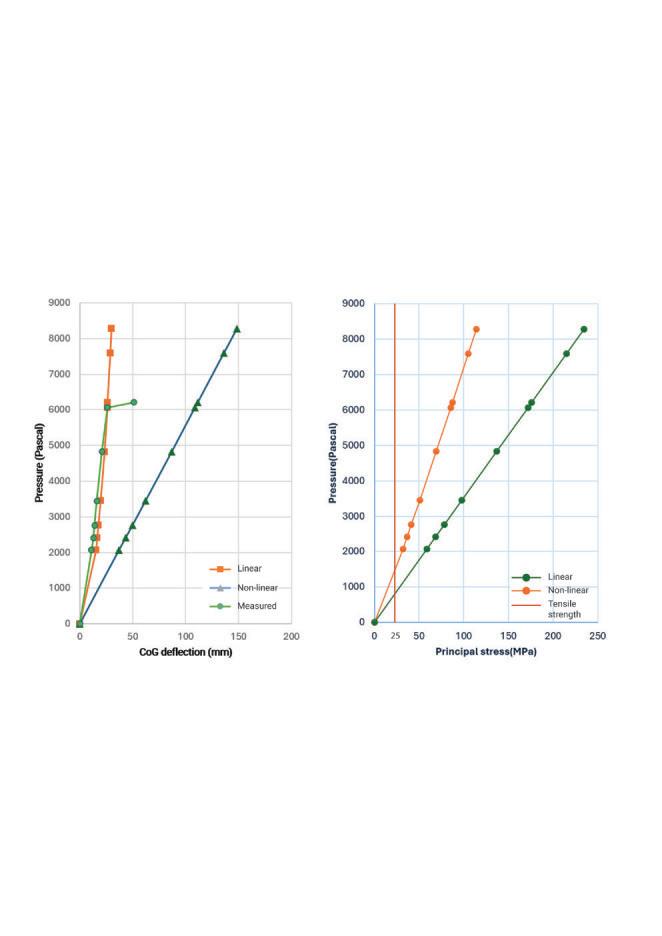
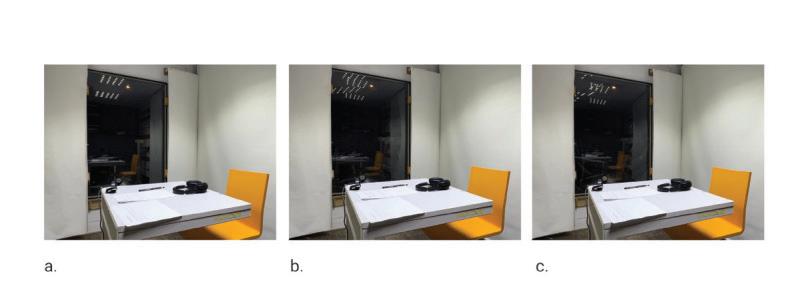
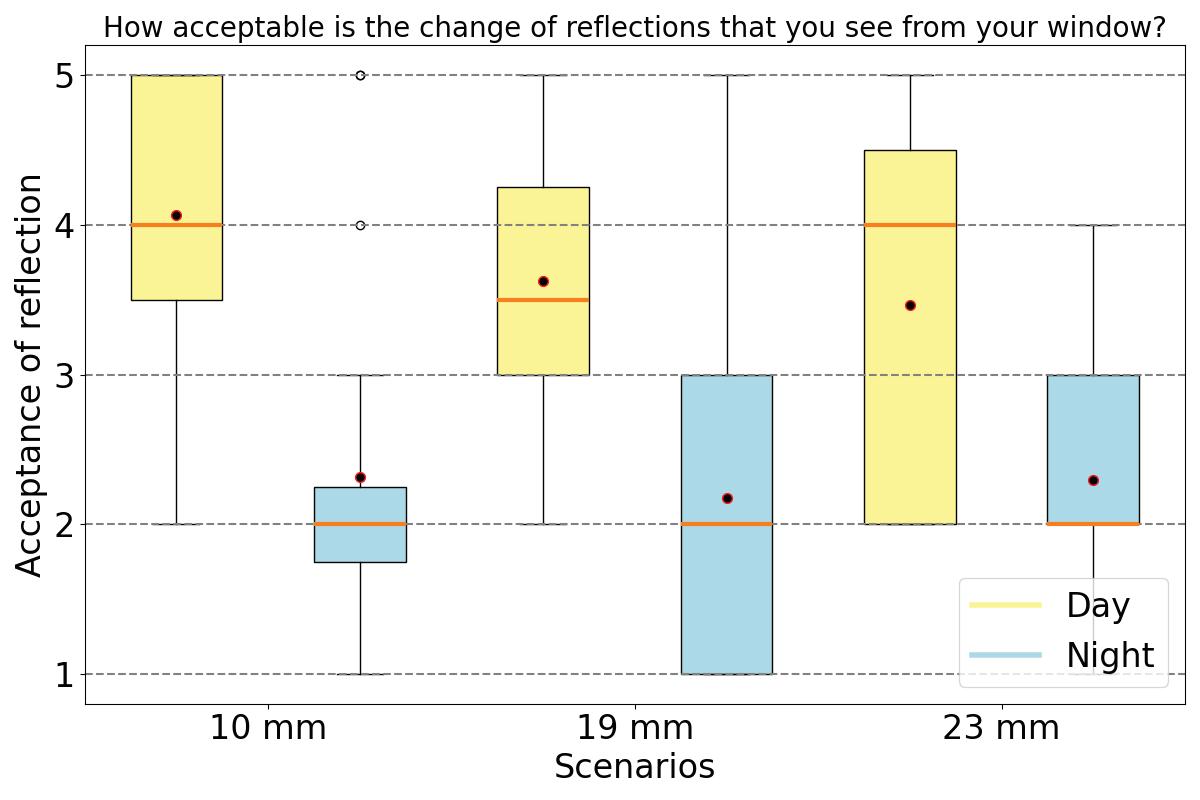
During the experiment participants response was recorded using questionnaires. The results demonstrate the feasibility of measuring human responses to deformations in the glazing and provide essential data for setting serviceability limits. The experiments and corresponding user satisfaction feedback indicate that the current serviceability limit of L/50, may be relaxed, thereby presenting opportunities for material efficiency, such as the adoption of thinner glass in facades. The methodology effectively captures human responses, revealing that changes in reflection were the primary reason for the perception of movement, leading to a higher perception of glazing movement and a lower acceptance at night. Overall, participants felt safe regardless of their prior knowledge on glass properties, and providing this information to participants did not improve acceptance, which was already sufficiently high. The findings from this research fill an important knowledge gap in understanding user acceptance of glass deformations, crucial for comprehensive user satisfaction assessments and evidence-based reductions in glazing thickness.

Course name: Introduction to Computational Design
Project type:Academic
Location: The Netherlands , Delft
Project Involvement:8 weeks of Design with a team of 3.Taskes involved include design formulation , strategizing computational approach and scripting in grashopper.
Year/semester: 2022, 1st year ,1st semester.
School: Delft University of Technology.
Email adderss of studio head: S.Asut@tudelft.nl
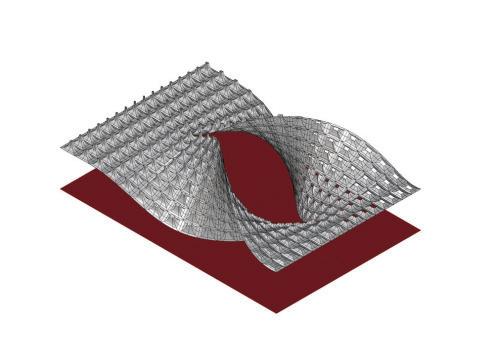
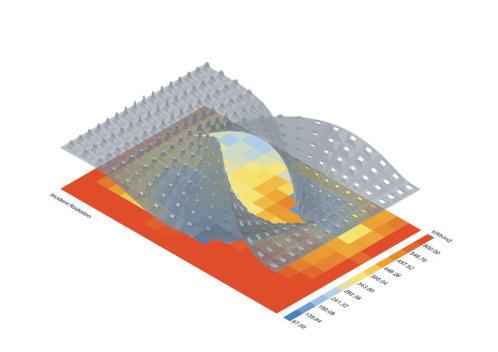
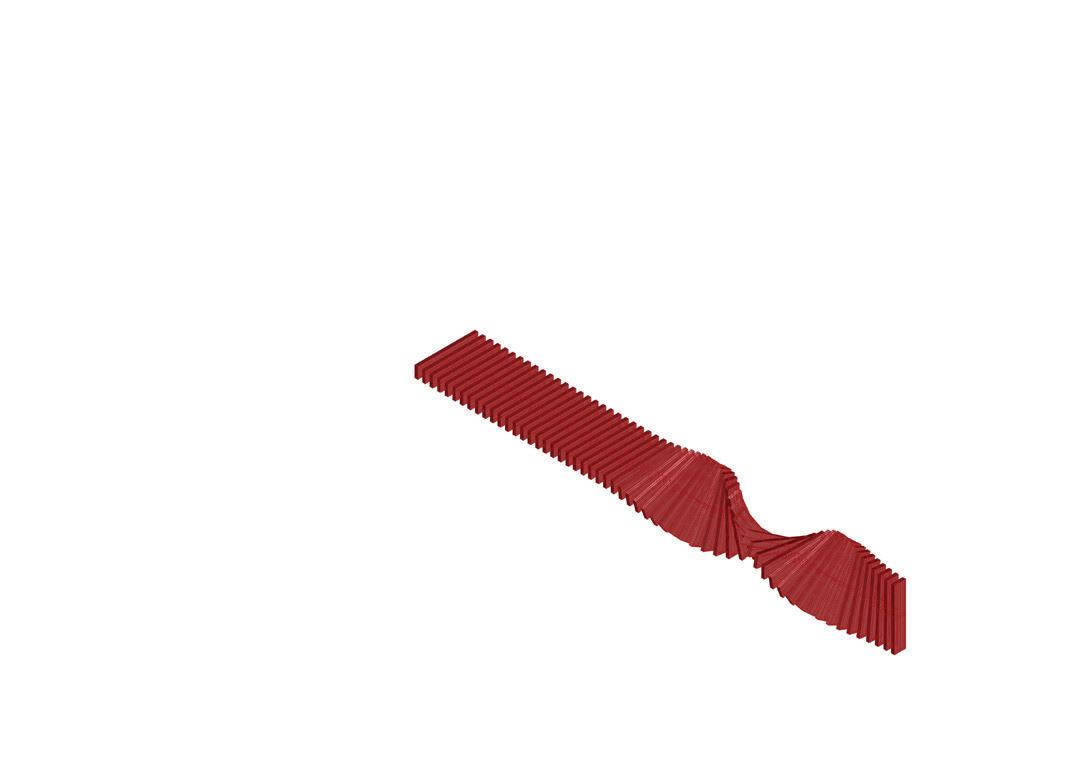
Wave and Shade.
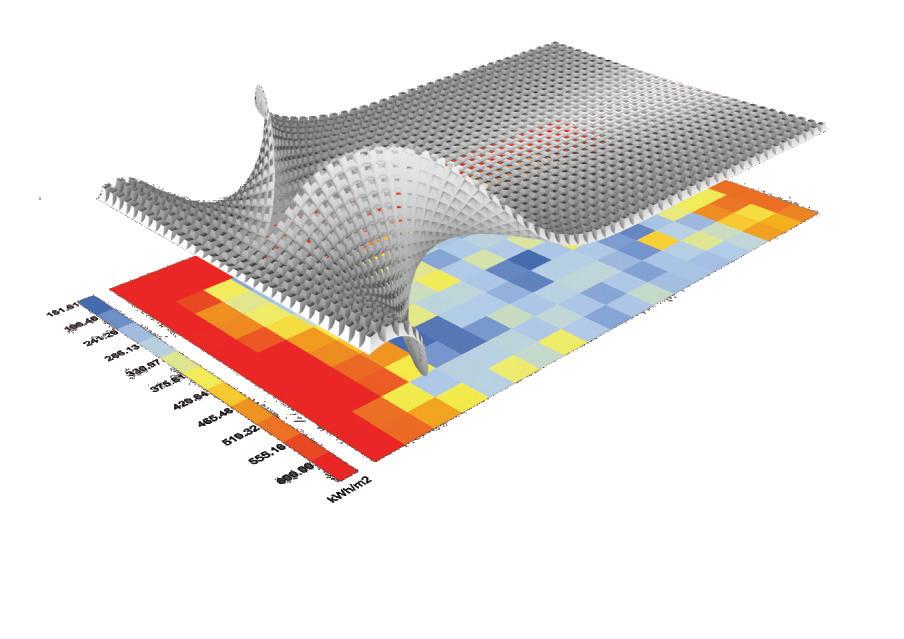
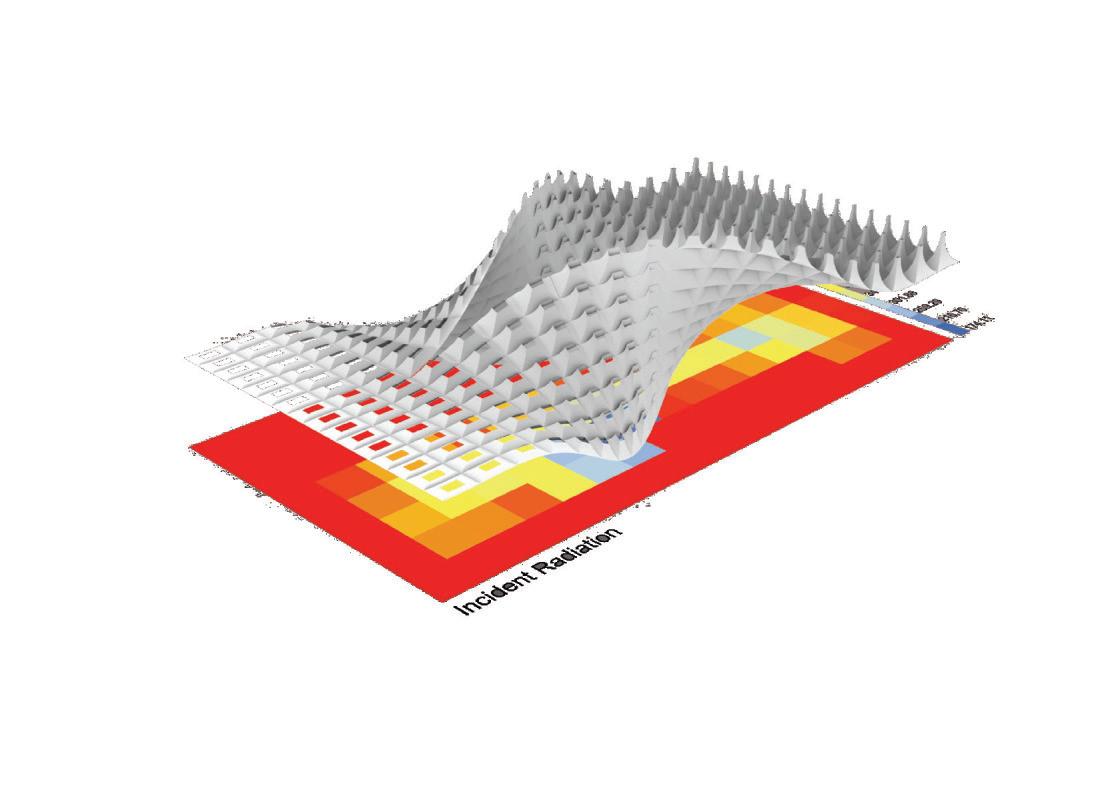
The Flowchart - Creating twisted curve
The Flowchart - Panneling the surface The Flowchart - Lofting, extruding, and mirroring
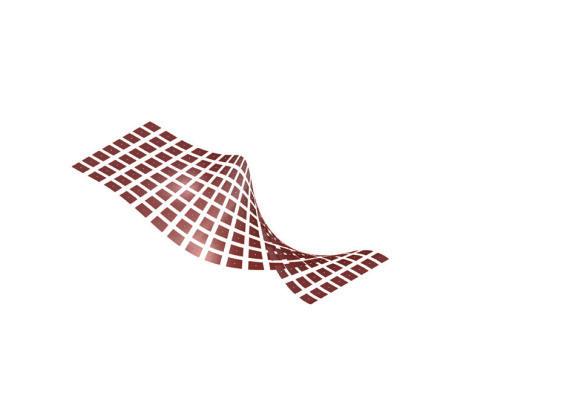
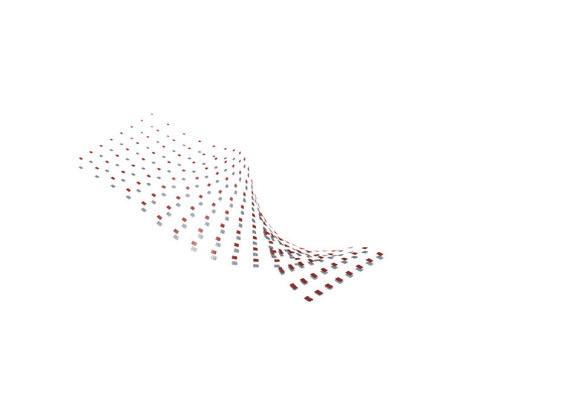
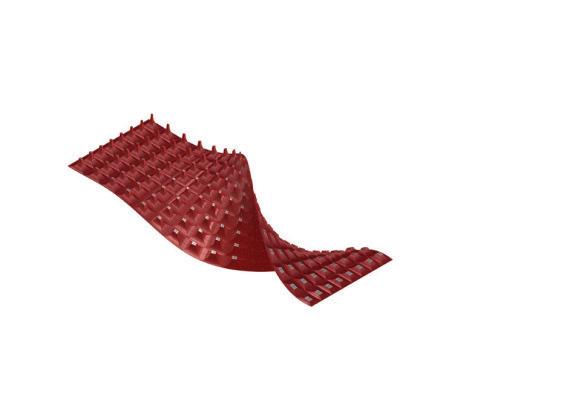
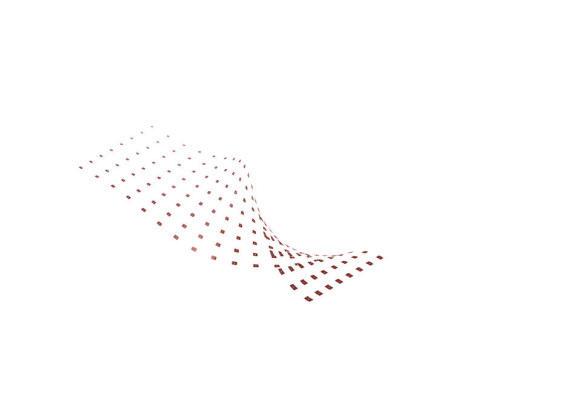
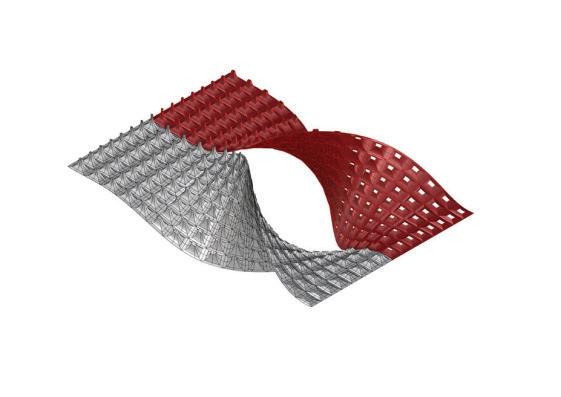

Course name: Bucky Lab
Project type:Academic
Location:Spain,Granada
Project Involvement:16 weeks of design. Working in a team of 4. The project involved design , proof of concept experiment, 1:1 detailing and a 2 weeks long prototyping in a woodworkshop,building a 1:1 prototype of the critical section of the design.
School: Delft University of Technology.
Year/semester:2022 1st year 1st semester MSc.
Email adderss of studio head: m.bilow@tudelft.nl
PClima-shade.
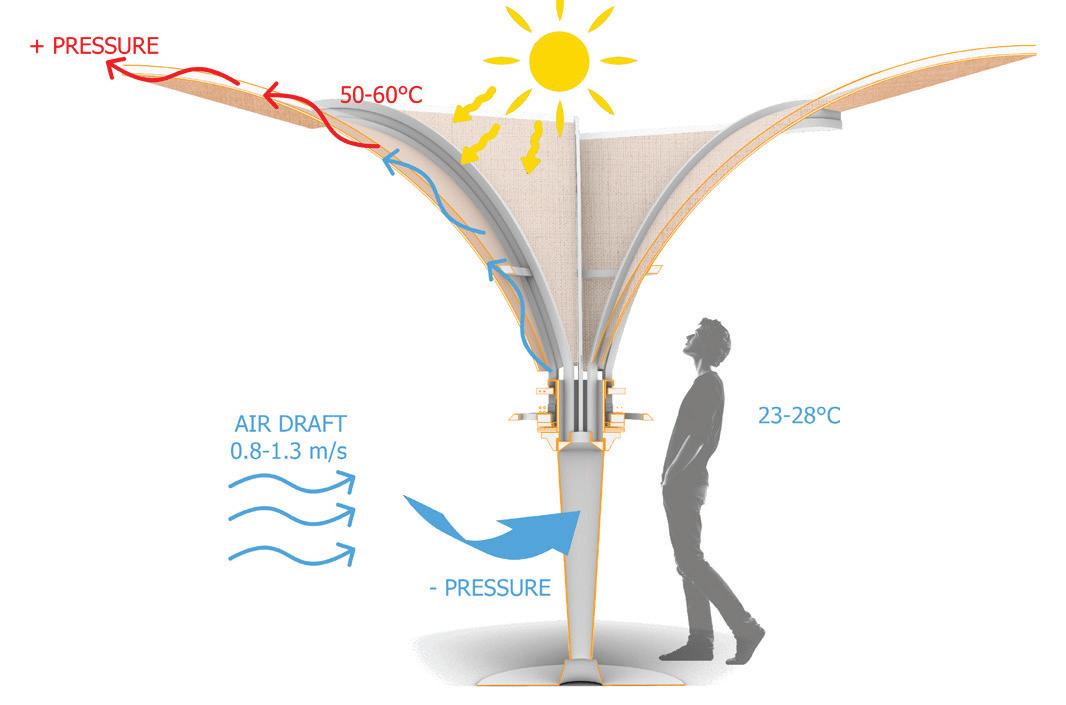



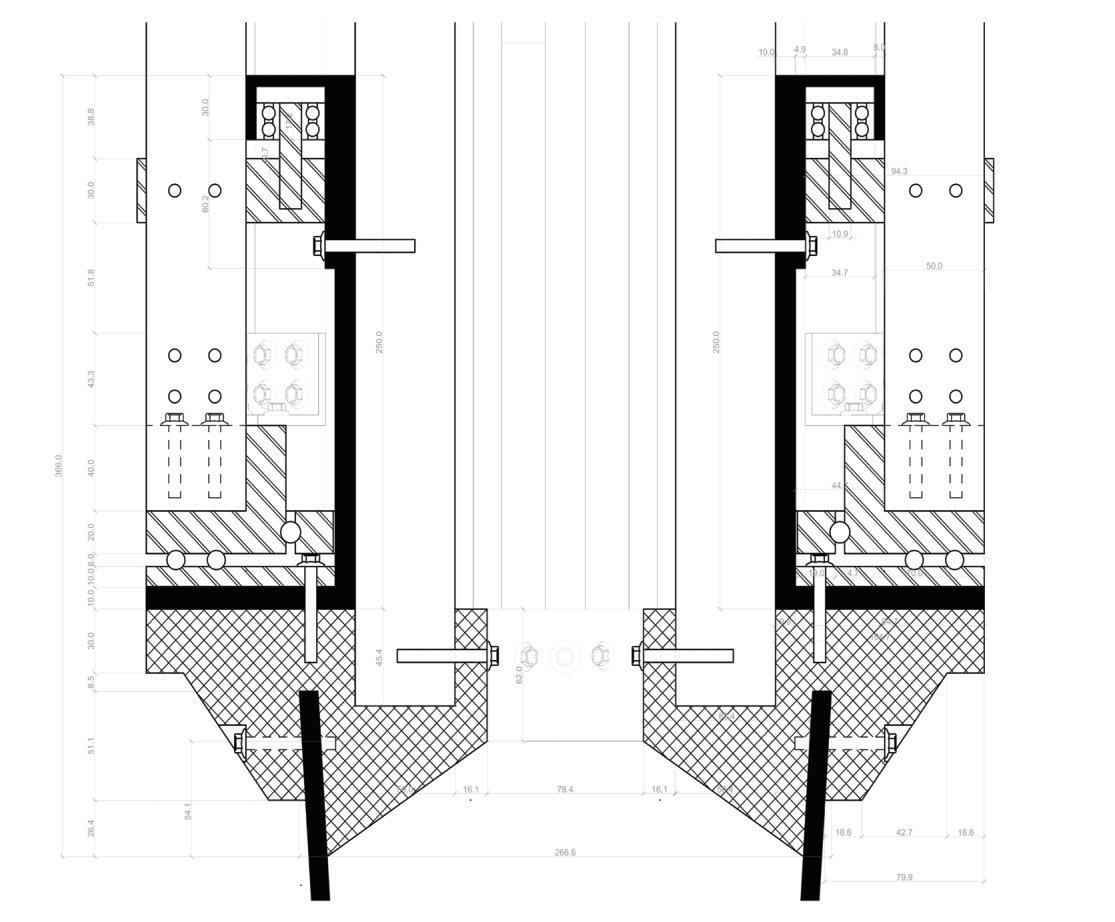
Clima-shade Proof of Concept.









INTERNAL BRACING
MOVABLE PANEL (ROTATION)
FIXED PANEL
ROTATION MECHANISM (SEE SECTION)
CYLINDRICAL
STEEL TUBE
FIXED TO THE GROUND
EXPLODED AXONOMETRIC NOT TO SCALE
FIXED PANEL ASSEMBLY BOLTED ONTO STEEL BRACKET
MOVEABLE PANEL ASSEMBLY FIXED ON CIRCULAR STEEL BASE
WHEEL MOUNTED ON STEEL BRACKET ATTACHED TO THE MOVABLE PANEL ASSEMBLY
4-BOLTED STEEL BRACKET ON MOVABLE PANEL ASSEMBLY
STEEL “U” PROFILE HOUSING WHEEL FOR MECHANIZED PANEL MOTION
CIRCULAR TUBE
FIXED PANEL LATERAL SUPPORT
BEARING MOUNTED ON U PROFILE UNDERNEATH
STEEL PROFILE MOUNTED ON CIRCULAR STEEL TUBE
BOTTOM HEAVY BASE CONCRETE
EXPLODED 1:1 PROTOTYPE NOT TO SCALE
ROTATING MECHANISM DETAIL NOT TO SCALE


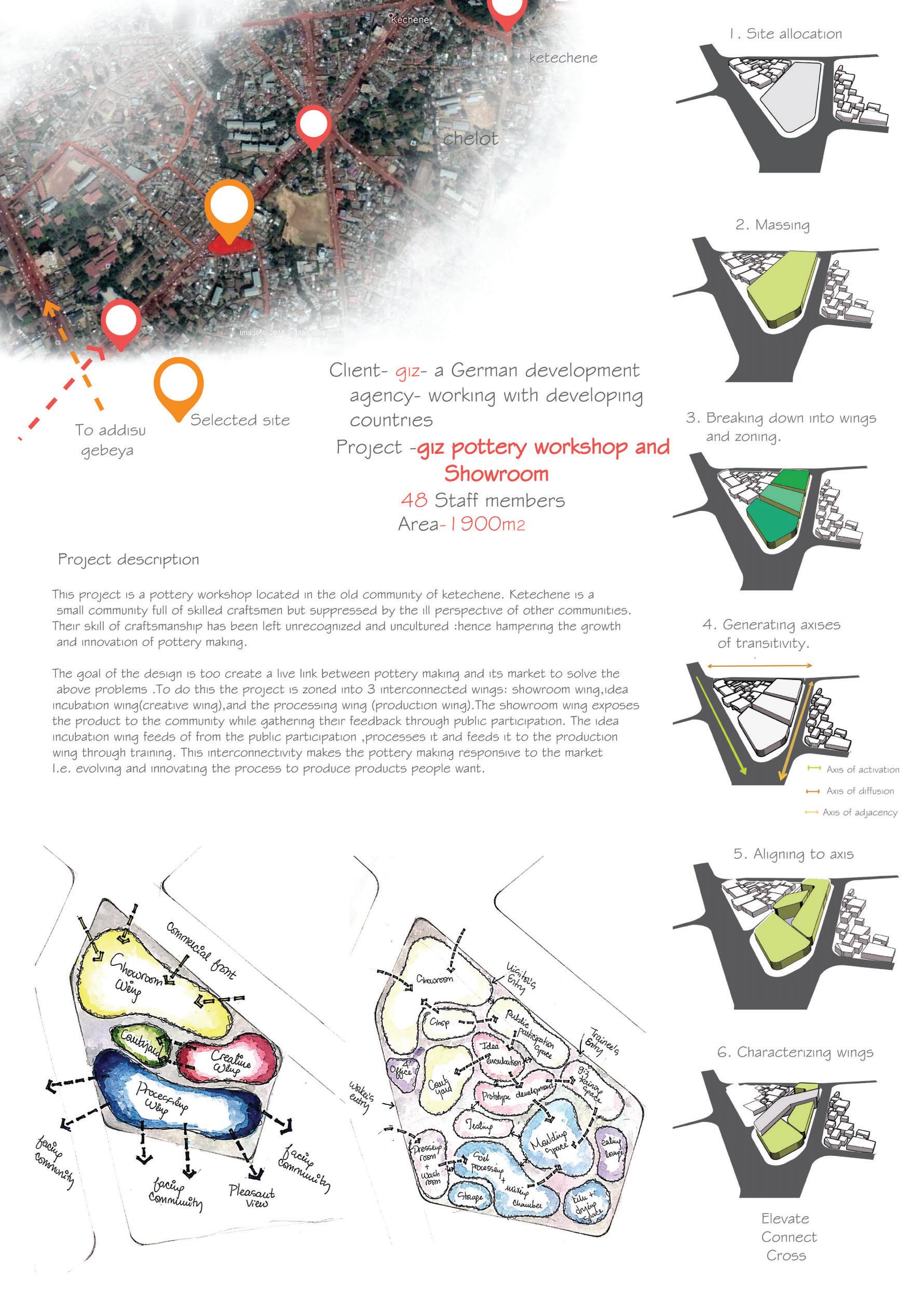
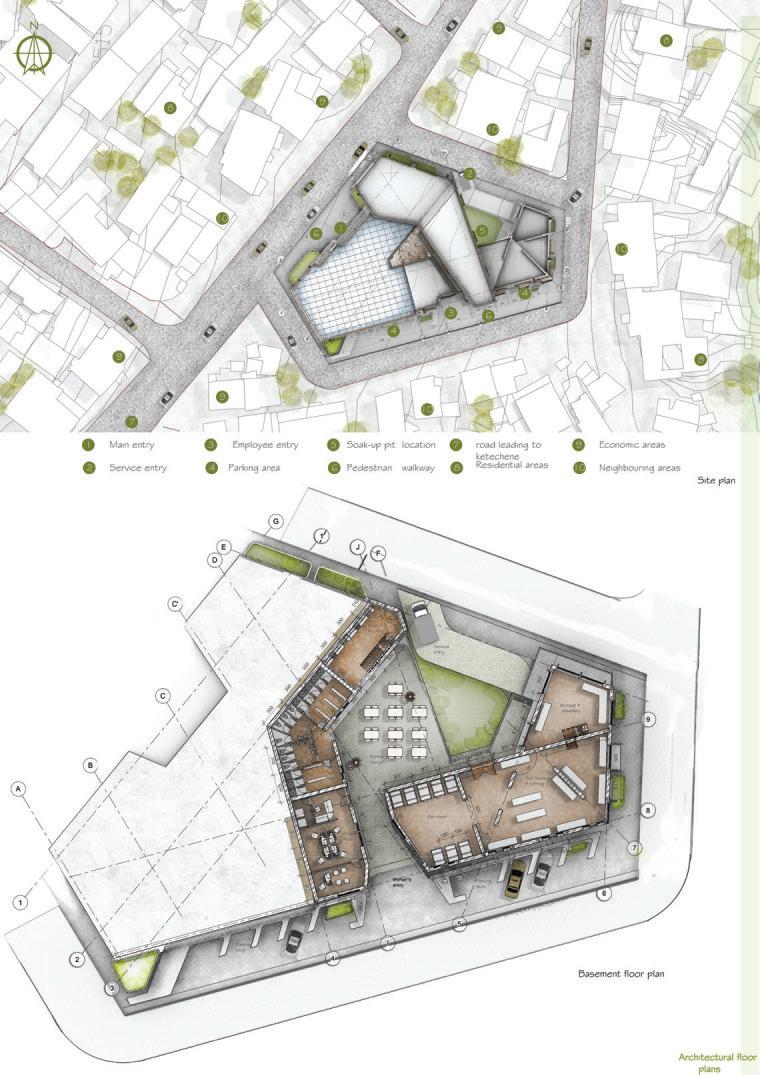
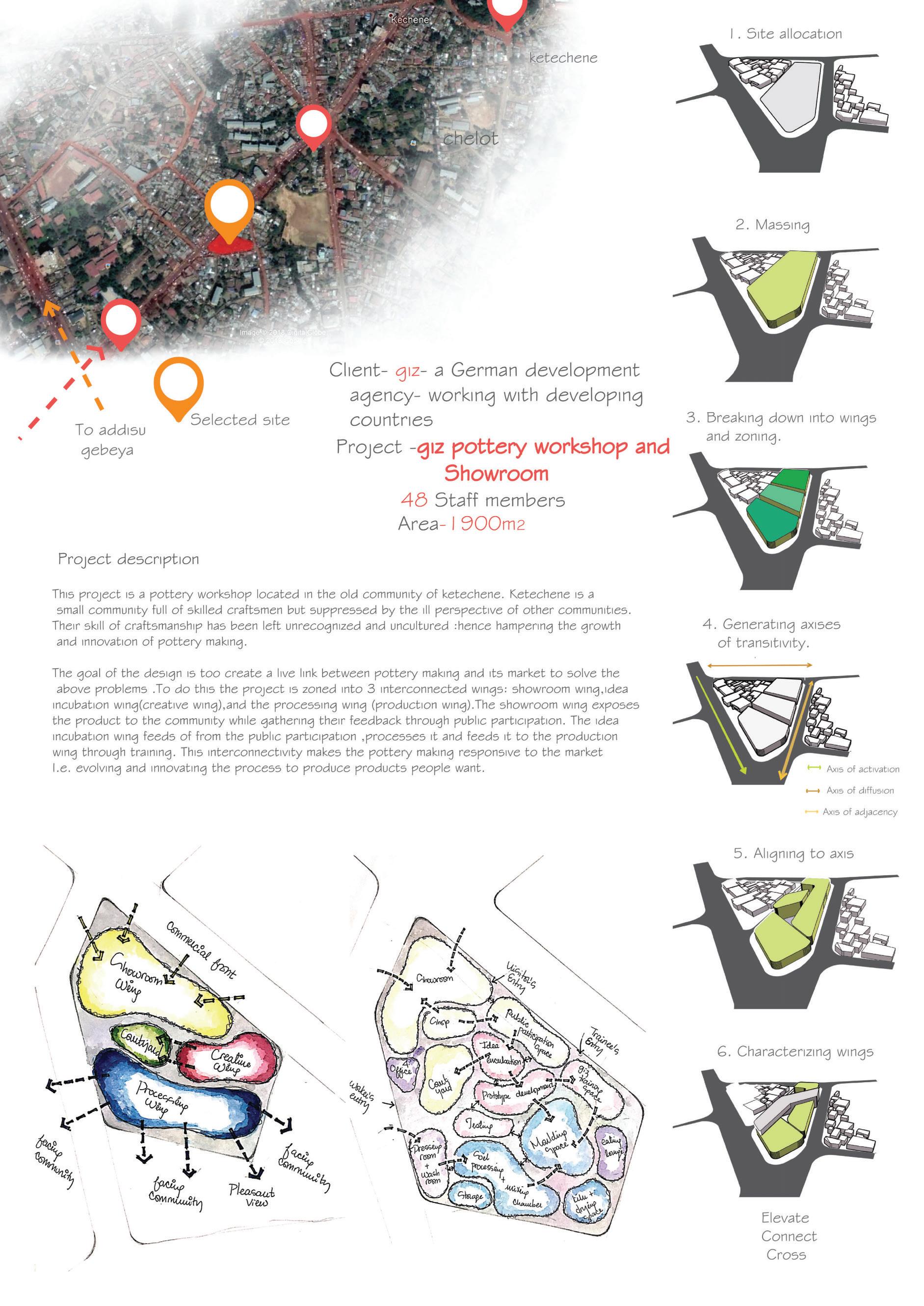
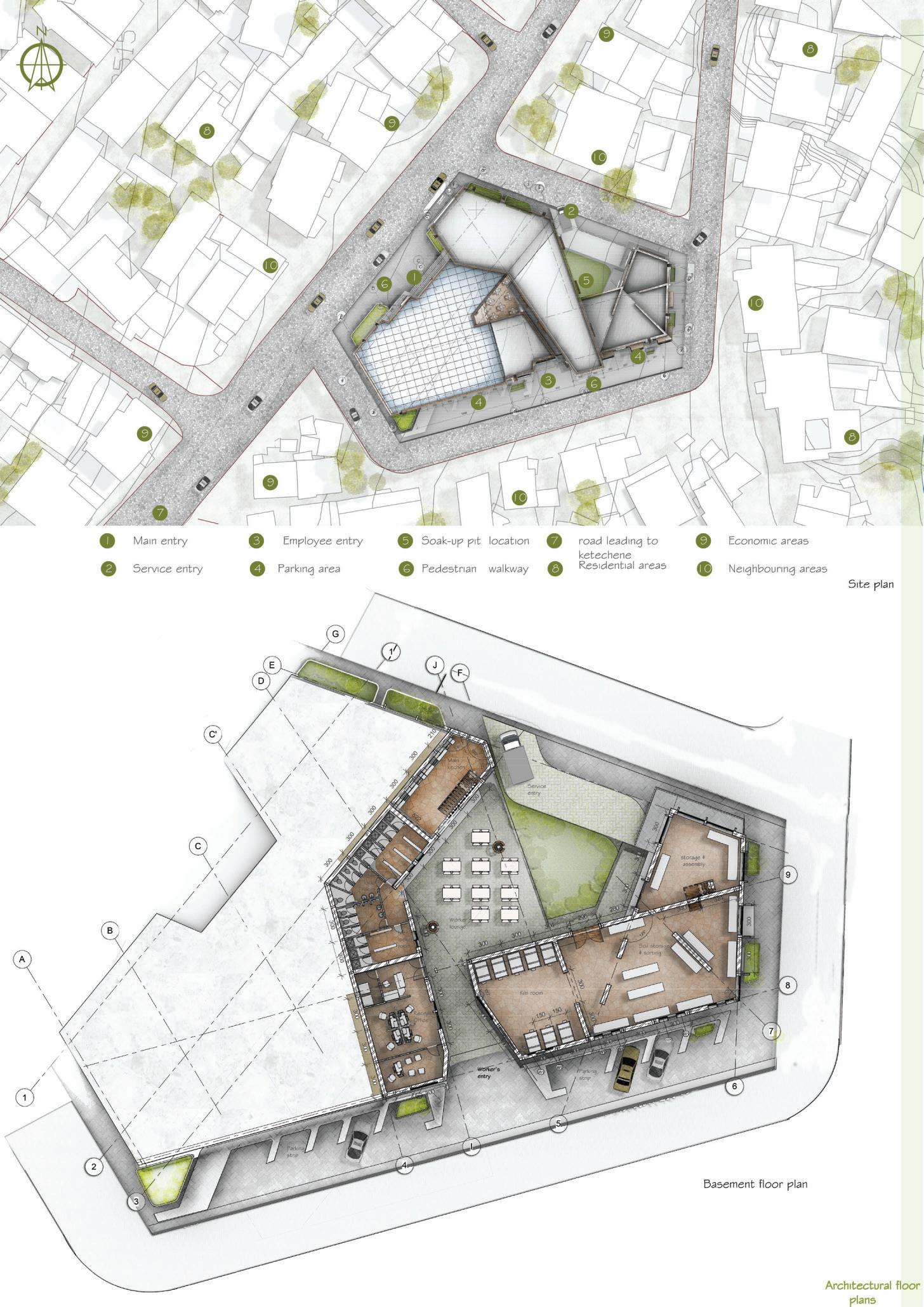
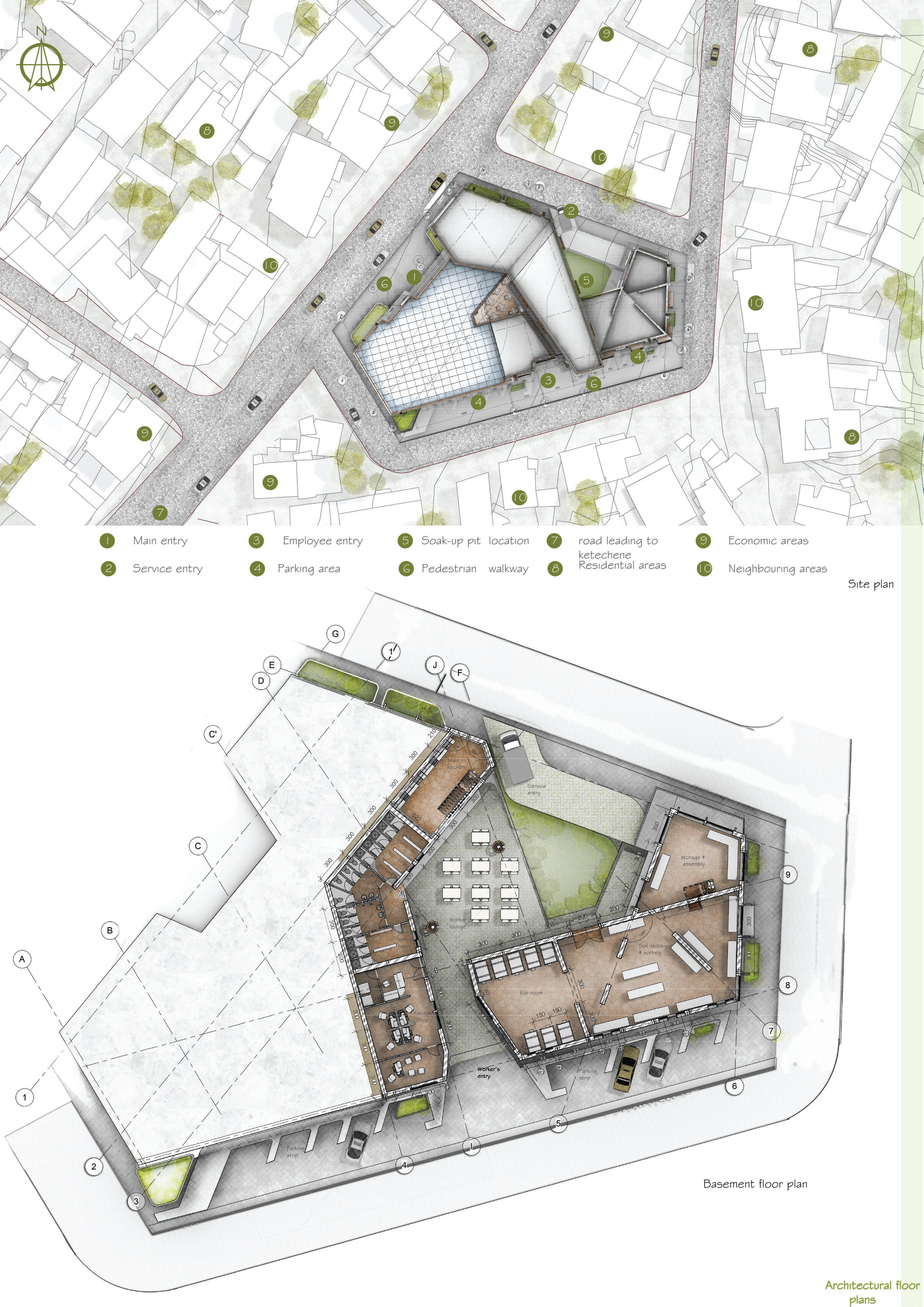
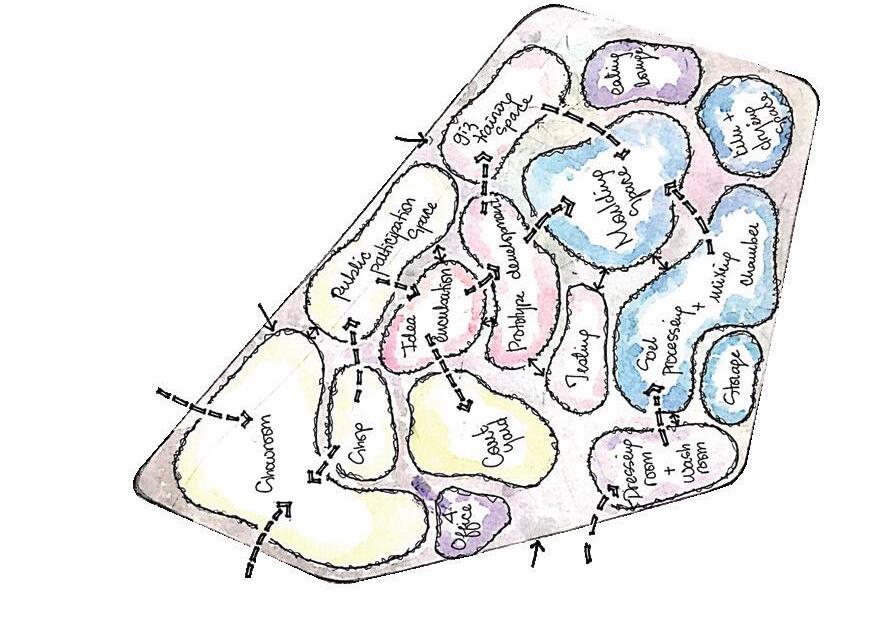
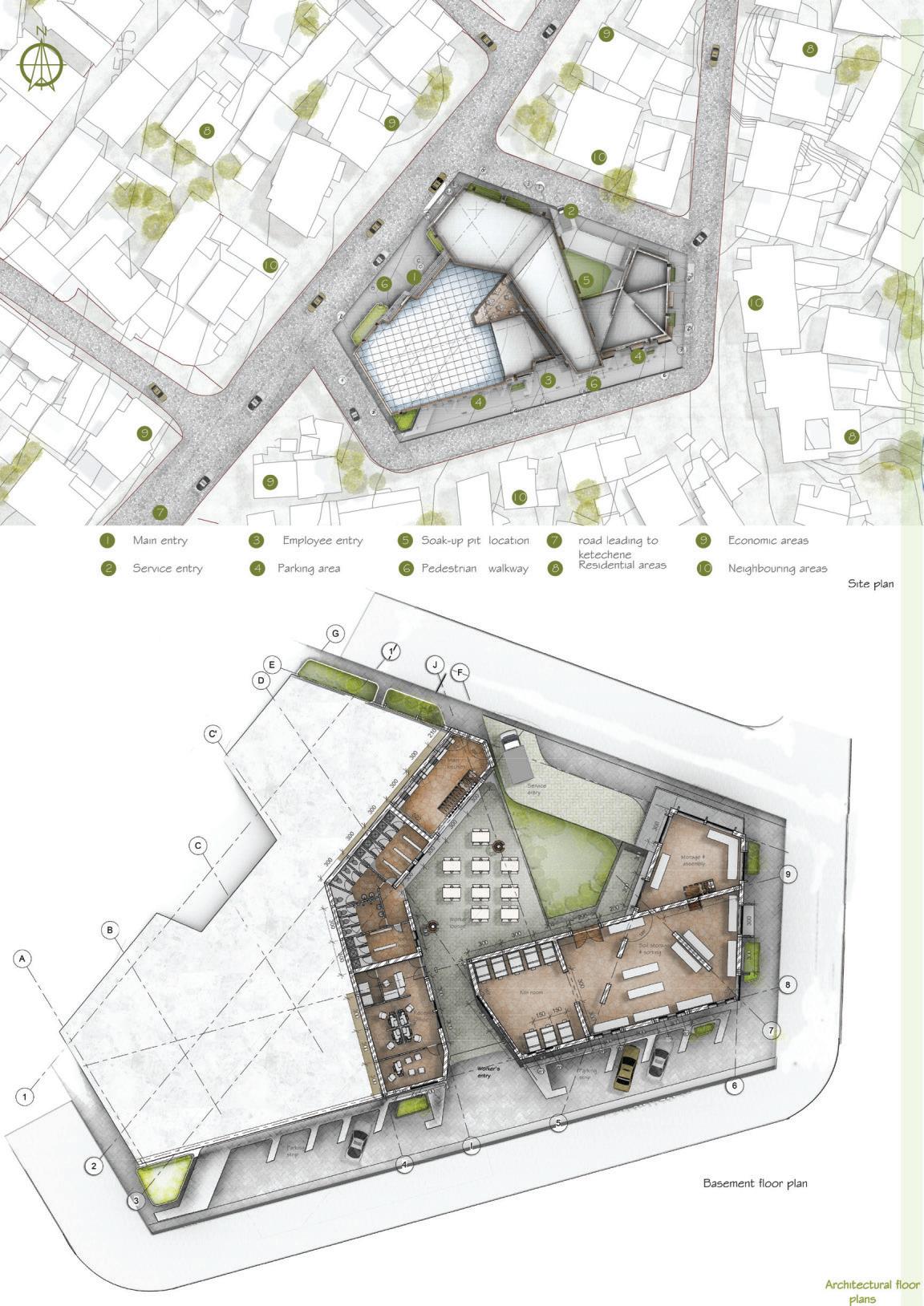
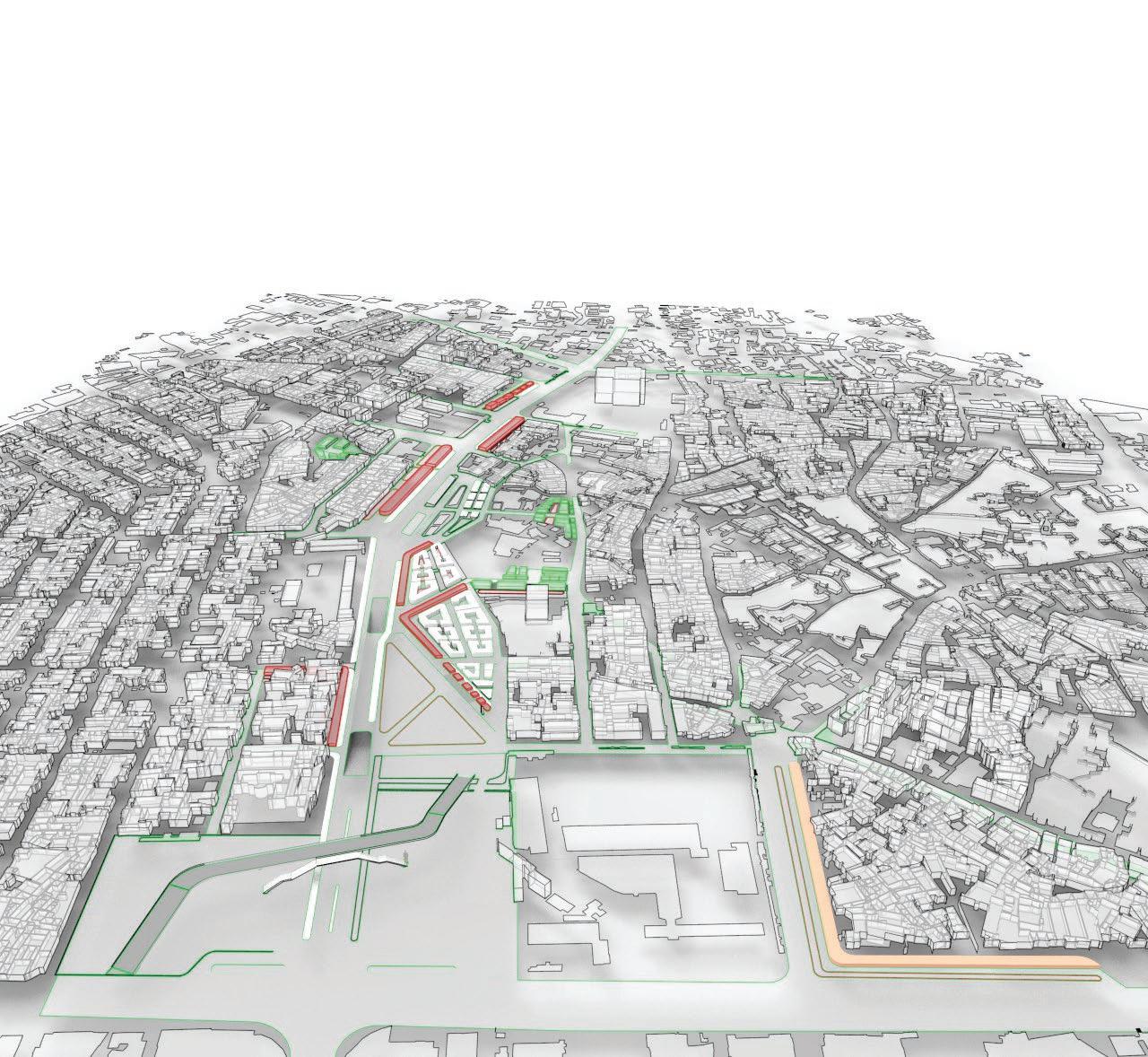
Course name: Integrated design Project III.
Location:Ketchene /Addis Ababa.
Project Involvement:14 weeks of design studio.I worked in a group of 2 with my partner Tinsae Tsegahun.I was involved in all steps of the project design and documentation.
Year/semester:2017/2018,3rd year 2nd semester.
Email address of Studio Head: Samuelafewerk@eiabc.et













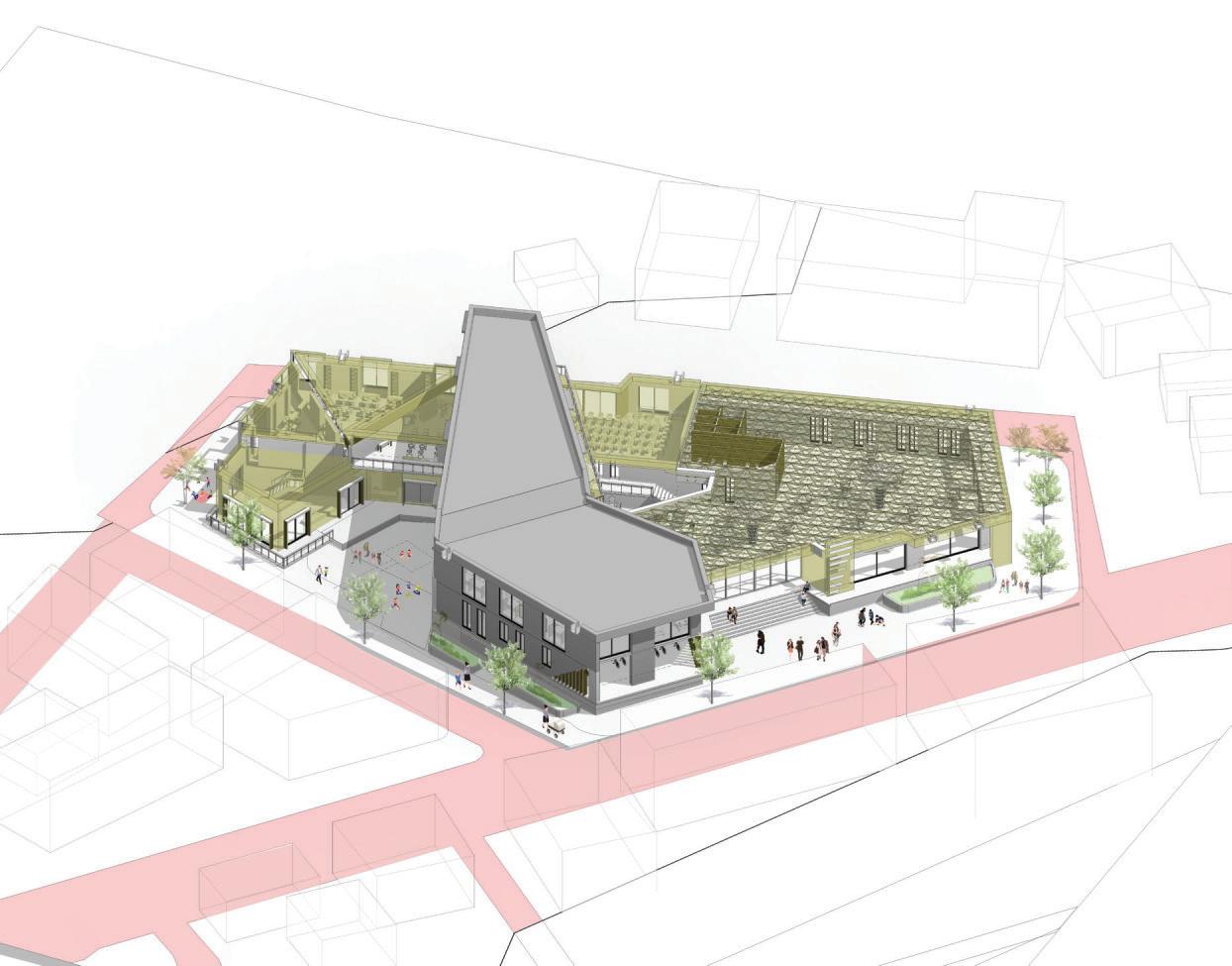
3D impression (Birds eye view)
Structural exploded
Glulam Column Detail

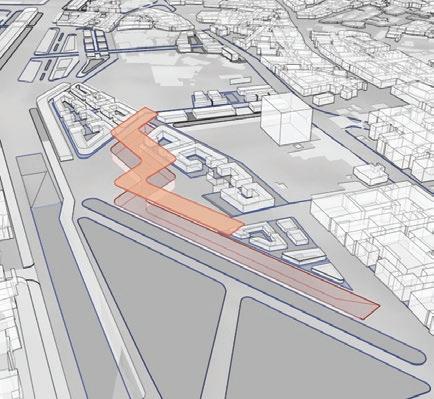
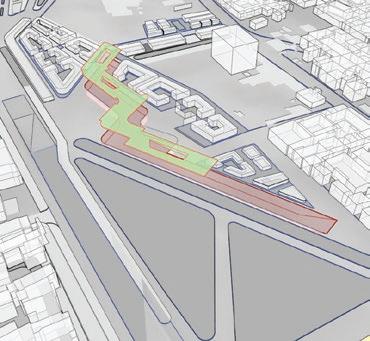
Course name:Architecture for social change (Building science and building construction)
Location:Autobistera /Addis Ababa.
Project Involvement:14 weeks of design studio.I worked in a group of 4 for the first 4 weeks of design and the rest 10 weeks I worked on an architectural scale with my design partner Abenezer degu.I was involved in all steps of design and document preparation.
Year/semester:2018/2019,4th year 2nd semester.
Project type:Academic Email address of studio head:habtamu.nekatibeb @eiabc.edu.et





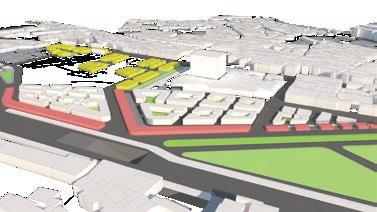
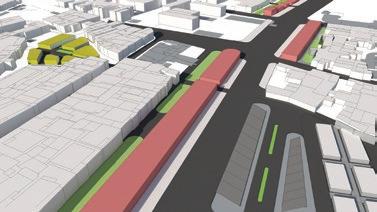
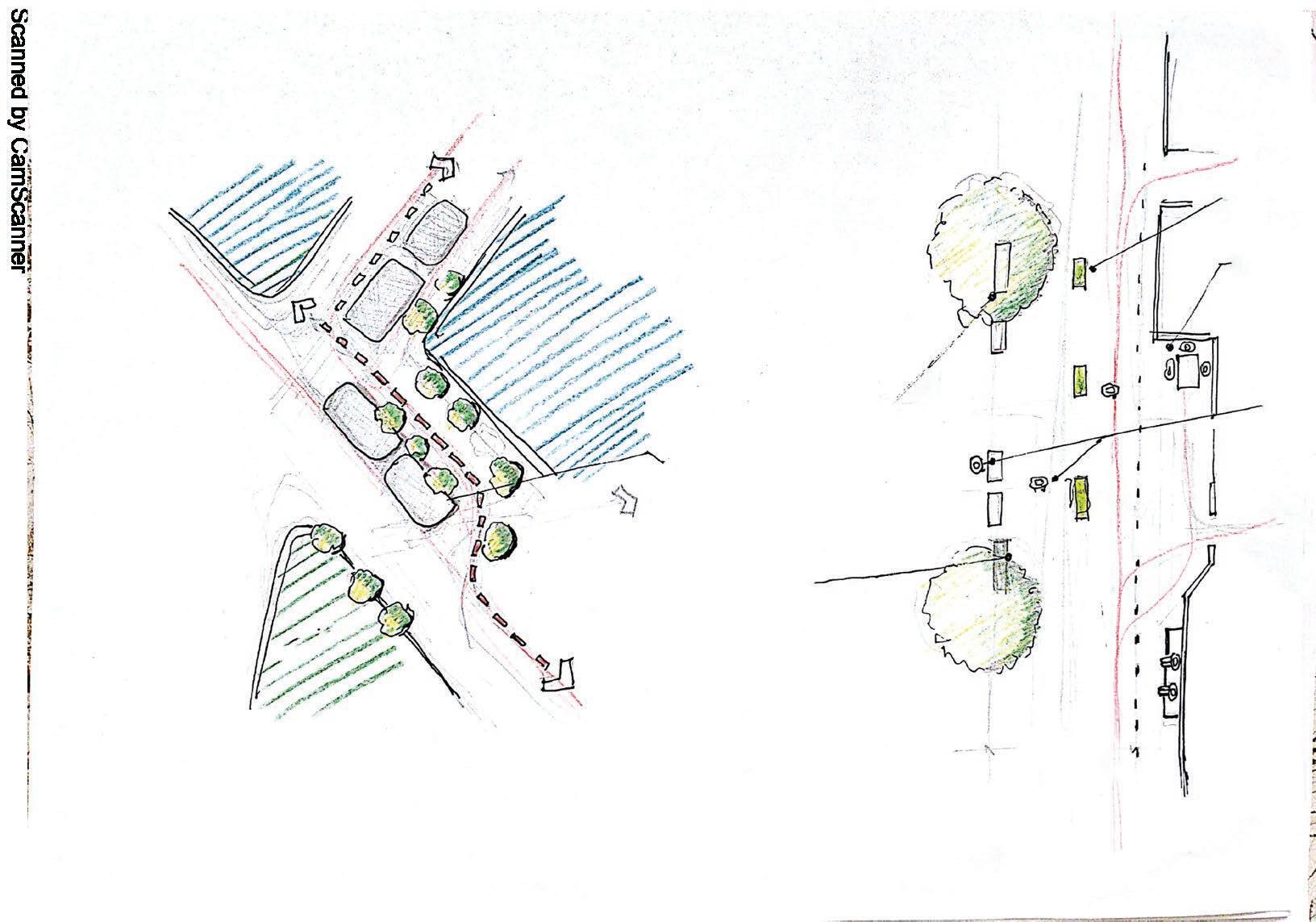
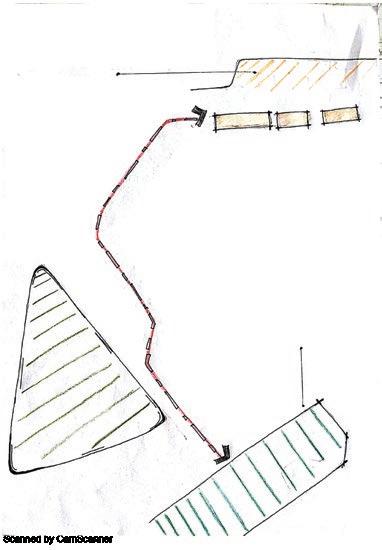
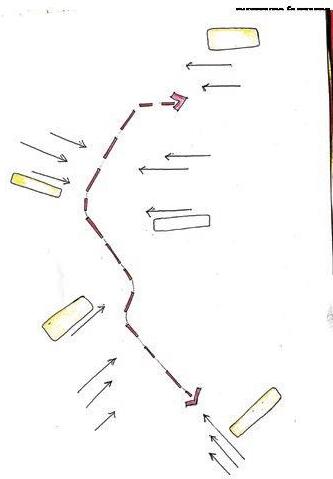
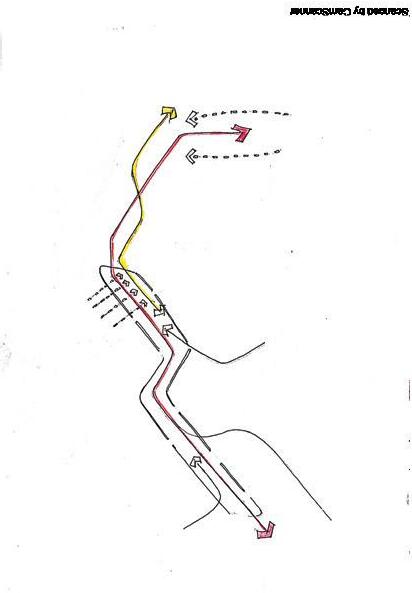
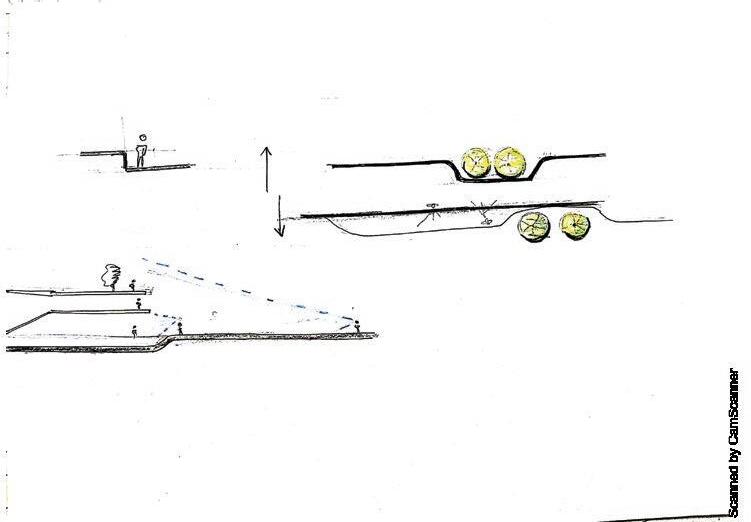
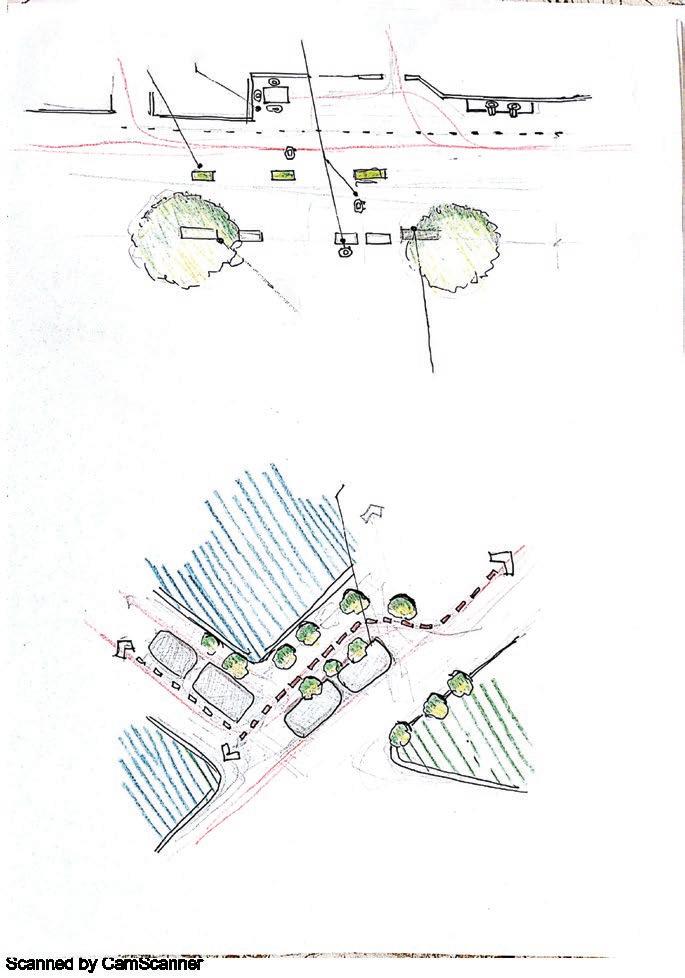
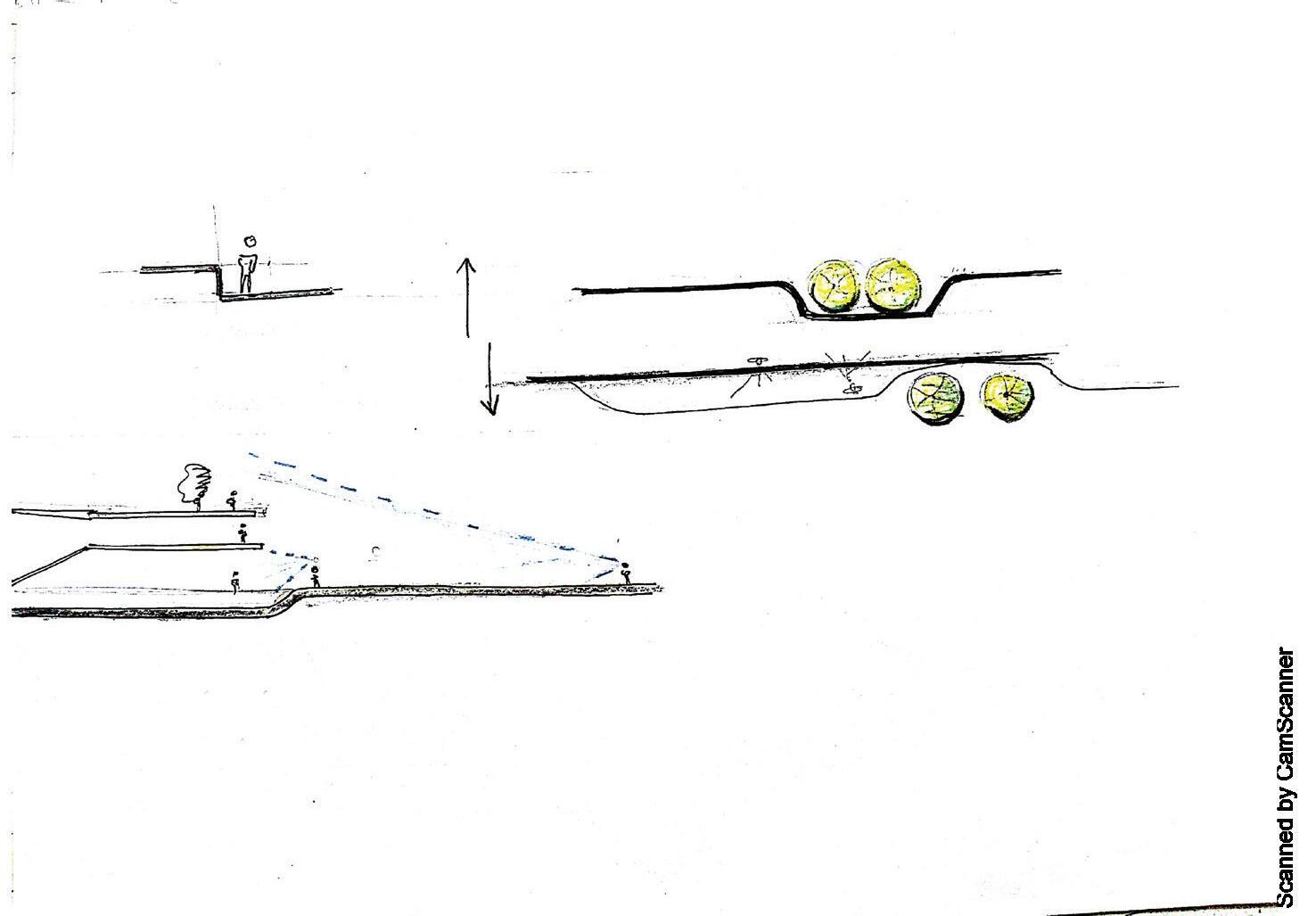
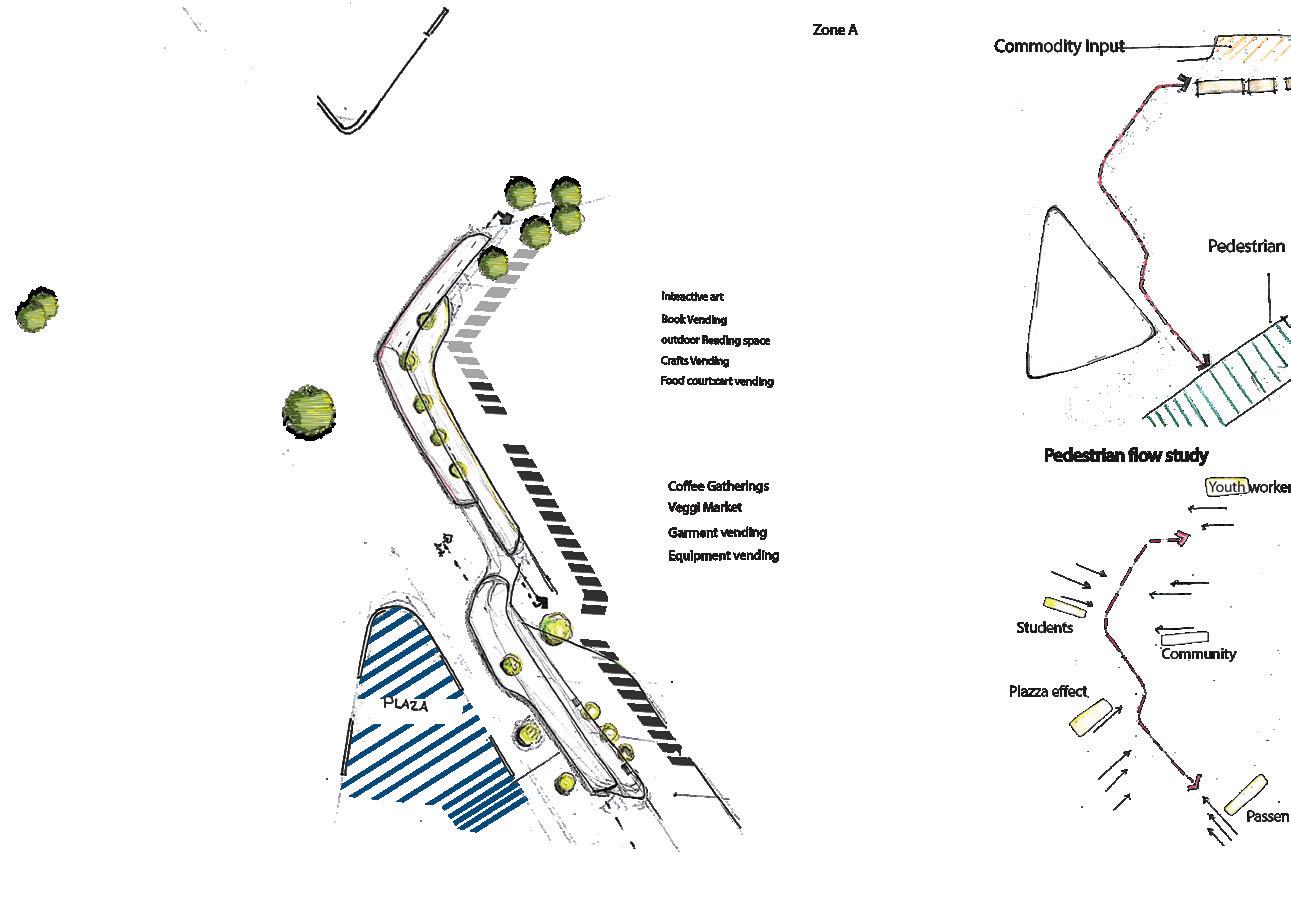
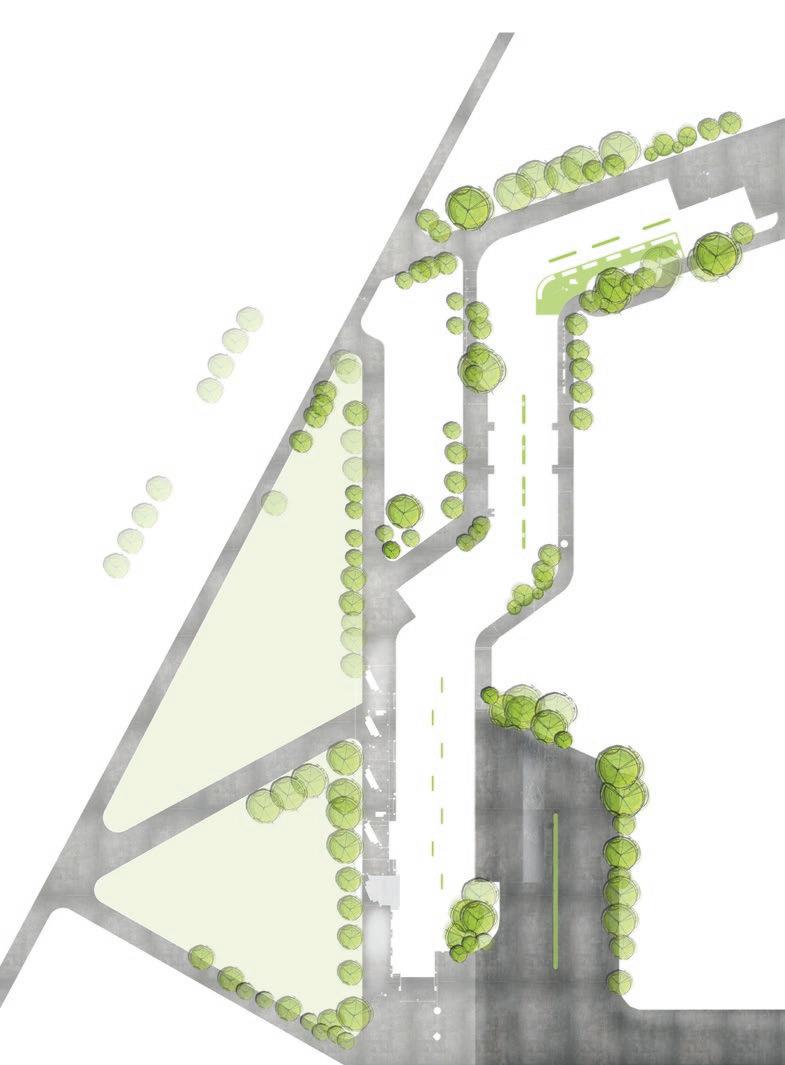
Pedestrian flow study



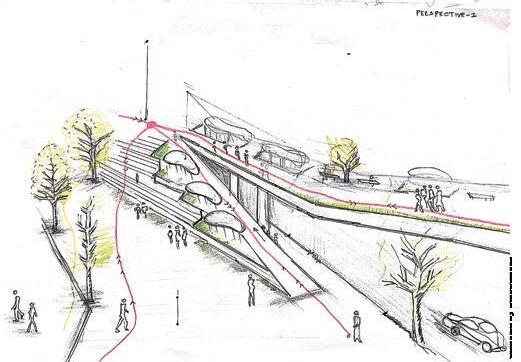




3D Impressions.








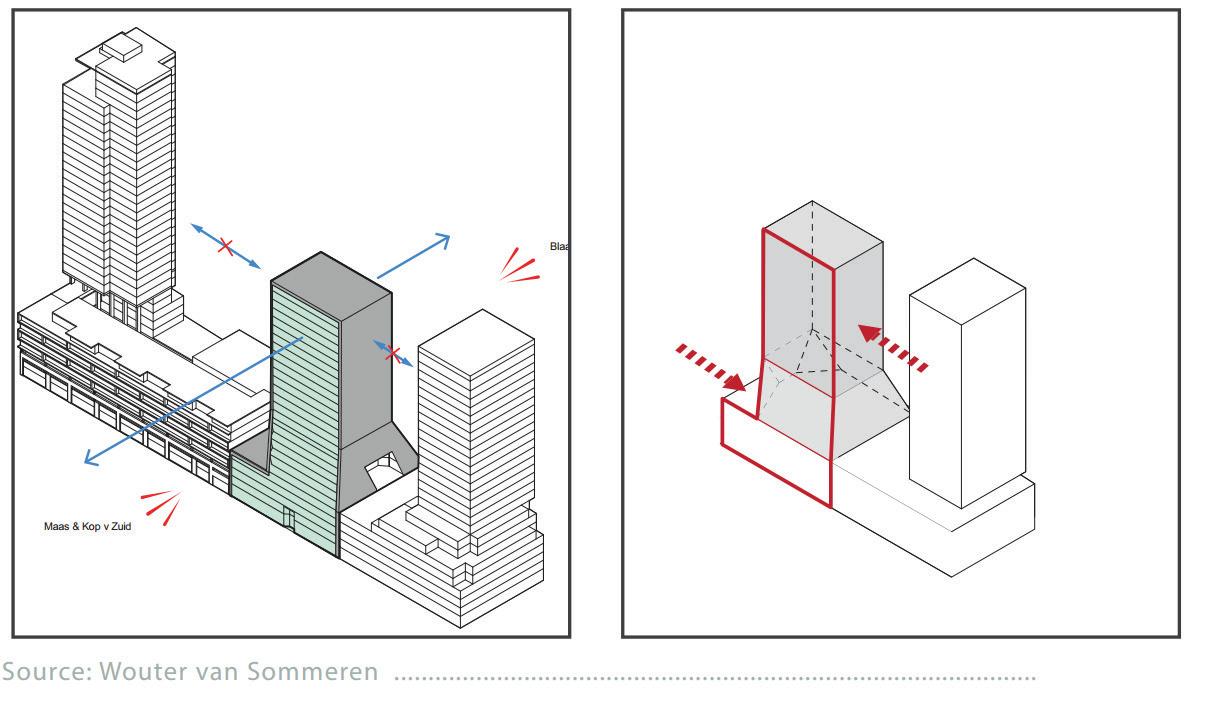
Project: Cooperative Bank of Oromia Transitional HQ:
Design Studio:Makers Lab(Design Studio). Location:Addis Ababa.
Project Involvement: Interior design develoment and construction supervisoion for a 2100 m2 office space.I have been involved in conceptualization stage,design development aswell as construction drawing preparation of the project.
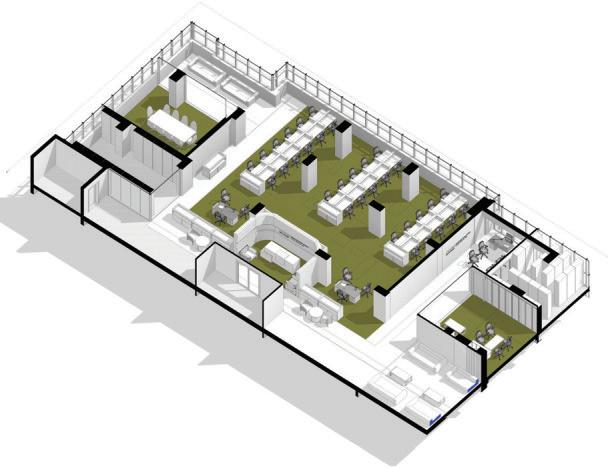
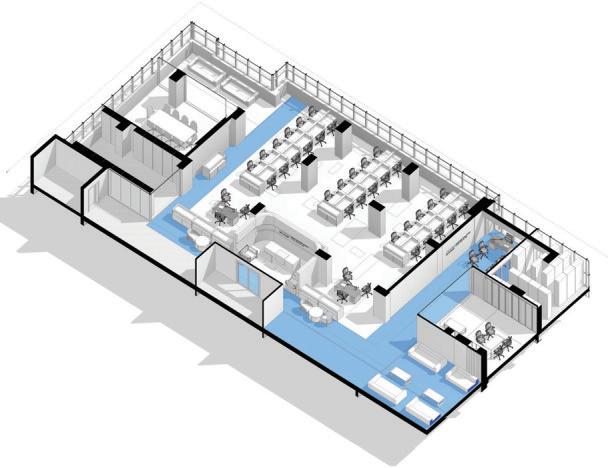
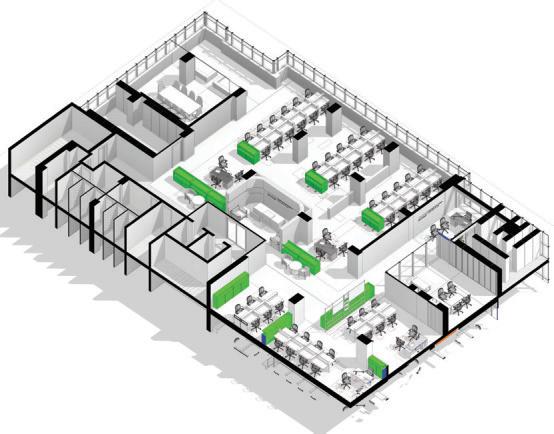
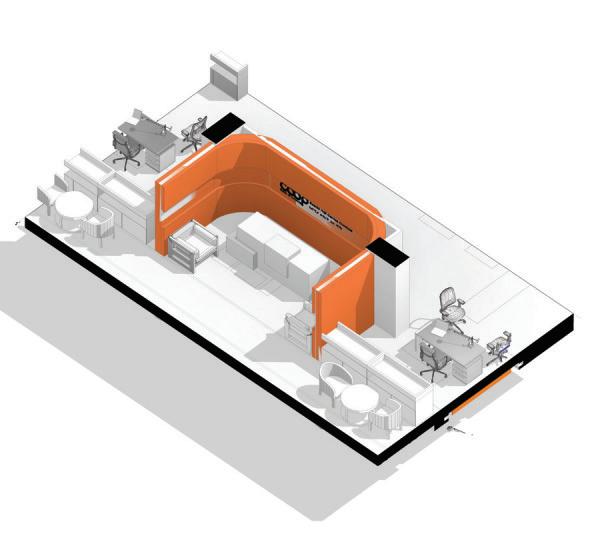
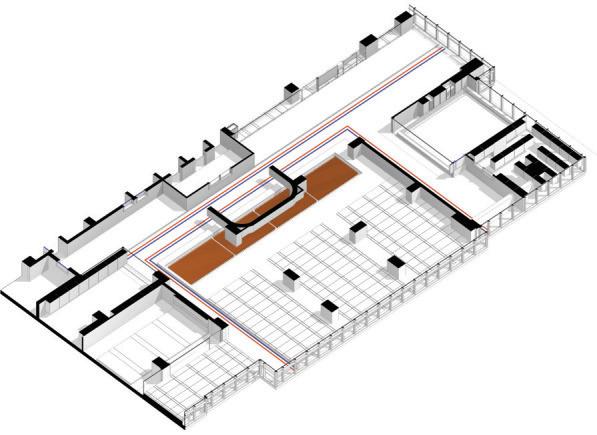


Project: Intergovernmental Authority for Development HQ
Design Studio:Makers Lab(Design Studio).
Project Location:Djibouti.
Project Involvement:
The schematic design was done by MEZZ DESIGN BUREAU(Italy).I was involved in the preliminary and final design development which included floor plan modification, interior design,modeling,rendering and a preliminary proposal to a sustainable approach to the facade already done in preliminary stage.
A development of the interior of the IGAD HQ to reflect the cultural elements of the East African region and a modest approach to making a comfortable space with a functional layout and orientation.Involved in designing ,rendering and drawing preparation.
As the daily heat and humidity of Djibouti makes it difficult for opening a window for ventilation,MEZZ DESIGN BUREAU have proposed an exterior shade and an active artificial ventilation. This approach plummeted the energy consumption as the full glazing of the building increases the temperature load on the AC system.
During the preliminary phase ,we have proposed for a double facade system which optimizes the underground aquifer to cool air and circulate around the building. An approach to decrease the energy consumption of the building and a provide a sustainable ventilation system.




Optionering