Ibero-American University Panama

Licenciature in preschool education
Teacher: María Miranda
Subject:Elements of didactics
Student: Marleni jimenez
Yenixel Camarena
Group 3
School year 2024


Ibero-American University Panama

Licenciature in preschool education
Teacher: María Miranda
Subject:Elements of didactics
Student: Marleni jimenez
Yenixel Camarena
Group 3
School year 2024


• In this work you will have the opportunity to analyze and understand everything related to the concept of didactics, its importance in the teaching and learning process, the various elements that support didactics and the various methods and techniques that can be developed within and outside the classroom; that help to carry out quality pedagogical practice. It is important to consider that all these elements need to be programmed, in the sense that to address them it is necessary to set objectives and content, design development and evaluation activities, and provide the necessary resources.

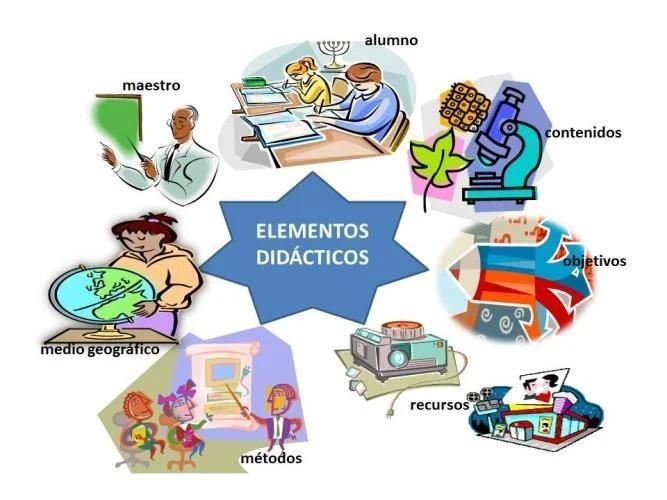

Didactics maintains elements that could not be developed as such without them, which is why it is of utmost impártanse to monitor them and provide them with good support, making them work in a synchronized manner as they pass.
Students and teachers constitute the personal elements of the process, a crucial aspect being the interest and dedication of teachers and students in teaching-learning activities.


Didactics has to consider six fundamental elements that are with reference to its field of activities:




• refers to the learner, for whom the instruction is prepared or directed, which must be appropriate to their level of cognitive and emotional maturation, age, individual differences, learning pace, abilities and skills, among others. The elements of didactics that are applied to the student can be divided into three categories:


• Motivation: Motivation is a key element in learning. A motivated student will be more willing to learn and will work harder to achieve their goals.
• Interest: Interest is a factor that drives the student to learn. When a student is interested in a topic.
• Attention:Attention is the ability to concentrate on a specific stimulus. An attentive student will be able to better process the information presented to them.
• Memory: Memory is the ability to store information and retrieve it when necessary. A student with a good memory will have an easier time learning and remembering what they have learned.

• Prior knowledge: A student's prior knowledge of a topic influences his or her ability to learn new information. If a student has solid knowledge of a topic, it will be easier for him or her to learn new information related to that topic.
• Learning strategies: Learning strategies are the tools that a student uses to learn.
• Comprehension: Comprehension is the ability to process and understand the information that is received. A student who understands the information they are learning will have an easier time remembering and applying it.
• Reasoning: Reasoning is the ability to think critically and solve problems. A student who reasons well will be able to apply the information they have learned to new situations.


• Self-esteem: Self-esteem is the assessment that a student has of himself. A student with high self-esteem will be more willing to learn and will work harder to achieve his goals.
• Social relationships: The social relationships that a student has with his classmates and teachers influence his learning.
• Emotions: Emotions play an important role in learning. A student who is excited to learn will retain information better.




• It is the mediator of learning, the same one that must be a source of stimuli that leads the student to react so that the learning process is completed. The teacher's duty is to try to understand the student to direct him to learning.


• The teacher is a fundamental actor in the teachinglearning process, and his role goes beyond the simple transmission of knowledge. To achieve effective learning, the teacher must master a series of didactic elements that allow him to guide and facilitate learning. of their students.These elements can be classified into three categories:


• Mastery of the subject: The teacher must have a deep knowledge of the subject he teaches. This will allow him to explain the concepts clearly and precisely, answer students' questions and adapt his teaching to the needs of each one.
• Knowledge of the curriculum: The teacher must know the official curriculum of the subject he teaches, as well as the learning objectives expected of his students.
• Knowledge of learning theories: The teacher must know the different learning theories to be able to adapt his teaching to the needs of his students.
• Knowledge of new technologies: The teacher must be familiar with new technologies to be able to use them effectively in their classes.


• Communication skills: The teacher must have good communication skills to be able to explain concepts in a clear, concise and attractive way. They must also be able to listen to their students and answer their questions effectively.
• Planning skills: The teacher must be able to plan his or her classes effectively, including the selection of content, the organization of activities and the evaluation of learning.
• Classroom management skills: The teacher must be able to manage the classroom effectively, creating a positive and productive learning environment. This includes establishing clear rules, managing student behavior and resolving conflicts.
• Assessment skills: The teacher must be able to assess student learning fairly and effectively. This includes selecting appropriate assessment instrumentes, applying assessment criteria, and communicating results to students.

• Positive attitude towards learning:The teacher must have a positive attitude towards learning, as this will be transmitted to his students.
• Responsibility: Teachers must be responsible for their work and the results of their students. This means planning their classes carefully, evaluating their students' learning fairly, and working to improve their teaching practice.
• Empathy: The teacher must be able to put himself in his students' shoes and understand their needs.
• Flexibility: The teacher must be flexible and be willing to adapt his teaching to the needs of his students and new situations.
• Reflection: The teacher must be able to reflect on his or her teaching practice and look for ways to improve it.




• Every didactic action involves objectives, which guide the educational process. In this sense, there are general objectives that can be of the educational system, of the institution, of a level, of a course or of a subject. At the same time, there are others that are specific in nature, that is, those that are intended to be achieved in the short term, such as those proposed to be achieved in one class hour. They are planned to lead the student towards achieving certain behaviors. Some of these objectives may be:
• Carry out the purposes of what is conceptualized as education
• Make teaching, and therefore learning, more effective
• Adapt teaching to the possibilities and needs of the student
• Guide the organization of school tasks to avoid wasting time

key elements of didactics and their relationship with the objective:
• Starting point: Every educational process starts with the clear definition of the objectives to be achieved. These objectives must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and timed.
• Guide to action: The objectives serve as a compass for the teacher, guiding the selection of strategies, resources and activities.
• Learning evaluation: The objectives are also fundamental to evaluate the success of the educational process, allowing us to determine whether the expected results have been achieved.




• Knowledge to be transmitted: The contents are the set of knowledge, skills and attitudes that students are intended to acquire.
• Selection and organization: The teacher must select and organize the contents in a coherent and meaningful way, adapting them to the level and needs of the students.
• Updating: It is important that the content is relevant and constantly updated to reflect advances in knowledge.




• The teaching method is a set of strategies and techniques used by educators to transmit knowledge, skills and values to students. These methods are designed with the objective of facilitating the learning and comprehensive development of students.


The elements of didactics related to the teaching method are the fundamental components that make up the pedagogical strategy used to facilitate student learning. These elements include:
•1. Teaching objectives: Specific educational goals that are intended to be achieved through instruction. Teaching objectives guide the design of the teaching method and determine what students are expected to learn.
•2. Curricular content: The set of knowledge, skills and concepts taught in the classroom. The teaching method must be designed to effectively address and convey this content.
•3. Teaching strategies: Approaches and techniques used by teachers to deliver educational content and promote student learning. This may include methods such as expository teaching, project-based learning, cooperative learning, among others.
•4. Educational resources: Materials and tools used to support teaching and learning. These may include textbooks, multimedia resources, practical activities, online tools, among others.
•5. Learning Assessment: Process of collecting and analyzing information to evaluate student progress and determine achievement of instructional objectives.



A teaching technique is a specific method used by educators to impart information, facilitate learning, and promote skill development in students. These techniques are practical tools that are applied within a broader teaching strategy. Each teaching technique is designed to achieve specific learning objectives and may vary based on content, objectives, instructor preferences, and student needs.
• 1. Learning objectives: Establish clear and specific goals that you want to achieve at the end of the teaching process. Learning objectives guide content selection, instructional activities, and assessments.
• 2. Curricular content: It is the material that is taught in the classroom. Content selection should be relevant, meaningful, and appropriate for students, as well as aligned with learning objectives.
• 3. Teaching and techniques: These are the strategies used to deliver the content and promote student learning. This may include lectures, debates, practical activities, research projects, among others.

• 4. Educational resources: These are the materials and tools used to support teaching and learning. This may include textbooks, online resources, audiovisual materials, laboratory equipment, among others.
• 5. Assessment of learning: It is the process of collecting information on the progress and achievement of students in relation to learning objectives. Assessment can be formative (during the teaching process to provide feedback) or summative (at completion to determine level of achievement).
• 6. Adaptation and flexibility: The ability to adjust teaching based on individual student needs, assessment results, and the educational context.
• 7. Educational context: Considers the environment in which teaching takes place, including factors such as class size, availability of resources, level of students, school culture, among others.

• In conclusion, we can say that the elements of didactics are fundamental parts that relate dynamically to facilitate an effective and meaningful educational process. Didactics seeks to promote active, reflective and student-centered learning, where students acquire not only knowledge and skills, but also the ability to apply them critically and creatively in various contexts of life. Didactics allows the teacher to strategically plan the teaching-learning processes. These processes ensure that the student assimilates the content provided more quickly. Didactics are particular resources that the teacher uses to carry out the purposes planned from the strategies, and the strategies are procedures or sets of methods, techniques, activities by which teachers and students organize actions consciously to achieve and build planned and unforeseen goals in the teaching-learning process, adapting to the needs of the participants in a significant way, the teaching resources provide information to the students, are a guide for their learning and are a key element for their motivation and interest.

• Promote teachers' participation in professional development programs that allow them to improve their skills in the design and implementation of effective teaching strategies.
• It recommends that teachers use pedagogical approaches that encourage active student participation in the learning process, such as project-based learning, cooperative learning, and experiential learning.
• It suggests that teachers incorporate activities that promote reflection on the learning process and the development of metacognitive skills, such as selfassessment and strategic study planning.

• https://books.google.com/books?
id=vQ2tDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA7&lpg=PA7&dq=elementos+ de+la+did
%C3%A1ctica+en+el+alumno&source=bl&ots=05vYj6u K81&sig=ACfU3U31sYqT5yX_18bQ2zV_87o80yL4y0Q&h l=es* **Factores que influyen en el aprendizaje:**
https://www.redalyc.org/jatsRepo/274/27457765008/ht ml/index.html***Estilos de aprendizaje:**
• https://books.google.com/books?
id=vQ2tDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA7&lpg=PA7&dq=elementos+ de+la+did
%C3%A1ctica+en+el+docente&source=bl&ots=05vYj6 uK81&sig=ACfU3U31sYqT5yX_18bQ2zV_87o80yL4y0Q&