



Unlocking circularity Liveworkstudio.com | London Rotterdam Sao Paulo | Livework Studio © 2023 A Livework quick-read
Is this quick-read for me?
1. Intro: The case for circularity
2. The Circularity Challenge
How to move at different levels at once?
3. The 4 circularity strategies out there
And corresponding challenges
4. Unlocking circularity at scale
Start with the customer, translate to organisation & value chain
5. Examples from practice
6. Get in touch
quick-read
● You work for a manufacturer
● You work in a innovation/design team or as a sustainability professional
● Circularity is a growing priority
About Livework
We are a company founded to change the world, filled with people whose passion it is to make life better for everyone. The clue is in the name: Livework. We improve the way people live and work. We do this by designing services that are better for the people who use and deliver them.
2
..an
P.3 P.4 A Livework
P.5 P.8 P.10 P.7
Contents
Scaling Circularity — Introduction
What can enable business to go circular at scale?
Reimagining the way we live, work and do business

There is an enormous desire to change our economy to stop polluting our planet. Circular business models are widely recognized as the right direction of travel and will be mandated by fast approaching legislation.
So why isn’t it happening on the scale required?
What is preventing businesses from rolling this out beyond small-scale initiatives?
This quick-read provides a simple overview of the challenges of going circular and a strategy to overcome them, helping consumer product manufacturers pursue their circular ambitions.
Linear business models
Future proof business models are circular

..an
p R e u r p so e Take Make Dispose Resources Waste Use
Scaling Circularity
A circular ecosystem
Thechallenge
Circular principles must be considered across four levels of business.
Unlike other innovations, new circular solutions don’t automatically fit into the fabric of our value chains, organisations, economy or even our lives, as these are tightly knit to fit a linear system that benefitted decades of adoption and optimisation.
The only road to success is thinking through circular needs at each level.
Organising and partnering to reduce the impact of value chain and operationalise reverse logistics.
A circular business
Mapping the route to a desired circular business model addressing customer, financial and operational needs in various probable futures. Grow capabilities to operationalise a production process that has circular principles applied across and a (digital) infrastructure for circularity — tracking, reverse logistics, new ownership models and financial + legal implications.
Circular services & experiences
Creating services and experiences to engage customers to participate — maintain, repair, upgrade, share, return.
Circular products
Applying circular principles to products and packaging design with entire product lifecycle in mind — production, logistics, (re)use, return and regeneration.
4
Scaling Circularity
The four circularity strategies
And corresponding challenges
Talking to manufacturers across industries we see organisations approach their transition in 4 different ways, each with its own challenges
Reverse logistics first Particular challenges
Find ecosystem partners for setting up the reversed value chain or built and set up the internal capabilities. Set up to manage large variety of linearly produced products coming back Built decision-making capabilities to make impact trade offs: are refurbished/ updated old products better/worse than producing new product?
Circular product first
Circular service first
All-round effort
Particular challenges
Re-imagine & design product, production and product use Partner to set up the infrastructure for product tracking, reverse logistics and redistribution and underlying infrastructure (digital/legal/ accounting)
Particular challenges
(Re-)imagine & design a circular service — the desired customer experience, delivery and business model. Redesign the financial model and the way a business captures value, changing from a one-off sales transaction to recurring revenue (requires adapted accounting procedures and financial instruments)
Particular challenges
Manage multiple changes at the same timemaintain momentum and manage interdependencies whilst some parts move faster than others
5
..an
Strategy agnostic challenges (1/2)
Bring customers along
Imagine and test circular offers
Internal or external set-up
Shared challenges for every business trying to scale circularity
Understand what customers need to buy into circular offers and make the behavioural change attached to that. Using product, operations and business model design to facilitating customers to take care of products and help closing the loop.
Understand which (small) steps from linear to circular can be made given the path dependencies of customer expectations, the organisational-, and value chain set-up. Test circular concepts' desirability, feasibility, viability and sustainability to understand the minimal viable set-up for circular success and de-risk roll-out.
Trade off: organise circular operation internally or outsource it (temporarily)? Depending on:
● Internal availability of capabilities
● Strength and availability of local partners
● Local legal requirements for repairing, refurbishing or recycling
6 ..an
Scaling Circularity
Scaling Circularity
Strategy agnostic challenges (2/2)
Scale circularity
Scale the circular processes (e.g. circular accounting and distribution) and business models across:
● Product lines
● Geographies
● (legal) contexts
Embed circularity in org
Embed circularity in organisation across:
● Business functions; Translating to reality of finance, R&D production, marketing, digital technology etc.
● Structures & set-up; e.g. new (carbon) accounting structures, information flows, KPI’s
● Activities & routines;
● Mindsets; Shifting from sales- to a life cycle focus and from pure delivery to co-creation and experimentation
Measure impact
Built capabilities and setup for continuous measurement of environmental and social impact
7 ..an
Scaling Circularity
Unlocking circularity at scale

Don’t lose your customers — Start with them, design great circular experiences, and and use this to inform the other levels.
We need to engage customers to be part of the journey to circular as we are still (and will remain for a while) in a consumption based economy. What does a circular proposition look like? What will the customer buy into and how does that fit into their lives?
A service perspective is needed. Services are the connective tissue between the full circular offer to the customer and what is needed to deliver it operationally.
By understanding customer barriers, motivations, needs and triggers to maintain, repair, upgrade, reuse or return we can imagine and create service concepts that make sense. Prototyping these —testing both desirability and feasibility across product, operation and value chain— uncovers the requirements to enable circularity and de-risks roll out.
Scaling Circularity


Examples from practice
A global leader in household appliances
Gucci wanted to improve the longevity of its products by improving its repair services. Together we set out to reinvent them to live up to the expectations of a high-quality luxury brand.


We did in-depth customer research and a series of internal co-creation workshops involving teams across the organisation. This allowed us to map out the customer's and the product's repair journey and create an overview of the underlying operational infrastructures (logistics, digital, customer service, legal considerations, etc.).





Together we designed a series of interventions in the repair services. We de-risked these by prototyping and piloting them across markets before international roll-out.
Design for maintenance | The secret to the elevator industry’s whopping margins is maintenance. People hate getting stuck in lifts. So they pay $2,000 - 5,000 a year to keep each one running smoothly. Kone saw that margins on maintenance services were 25-35%, compared with 10% for new equipment and decided to get properly set up for a business model based on repair and maintenance rather than machine sales.
We helped kone redesign their offer (to include these services), streamline the back office, and provided agents with the tools to have quality conversations with customers. This enabled them to create flexible, personalised offers, delivered at higher efficiency. A


Design for circular customer behaviour | A global leader in household appliances boldly decided to embrace a circularity but soon realized users play a key role in prolonging product life and closing product/material loops. We partnered to find opportunities to stimulate circular behaviour.
We observed and spoke at length with people across markets and captured the insights in two models: a relationship lifecycle and a loop model. These allowed us to profoundly understand the human-product relationship from start to end and get insight into what drives or prevents people to maintain, repair, share or recycle their products.


9
A holistic approach Some key tools & methods
We are deeply rooted in a linear set-up. That set-up needs reconfiguration to close loops and connect value streams. Service design embraces systems thinking to reimagine how material, people, communication and activities are coordinated across infrastructure or value chain. That provides the creative confidence to redesign an organisation and the world around it. Some key tools used:
System map
Transitioning industries, value chains or complex stakeholder collaborations to a new circular pathway requires a deep understanding of how different ecosystem parts interact. System mapping is a deep-diving exercise into the actors involved to understand how they relate, interact and what value they exchange.



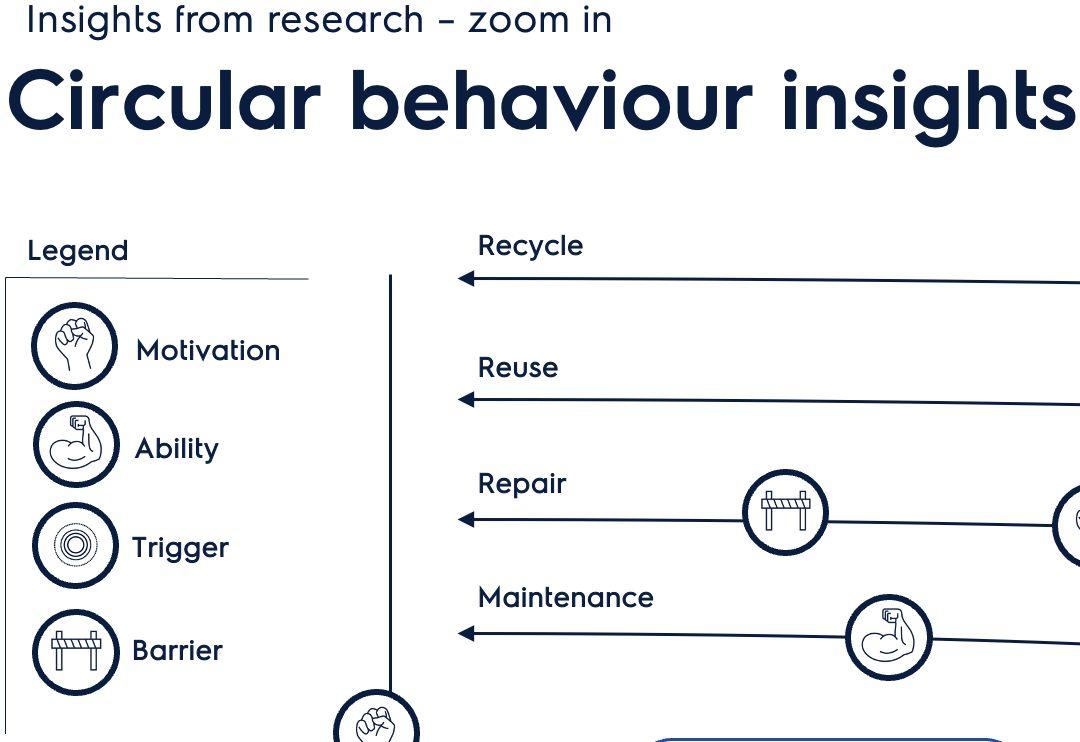
If customers don’t buy into or participate in circular propositions they will fail. The circular behaviour model is a framework to understand the motivations, abilities, triggers and barriers influencing circular behaviour. This framework situates customer insights from research on each loop to facilitates an understanding of what needs to be (re)designed to close them.
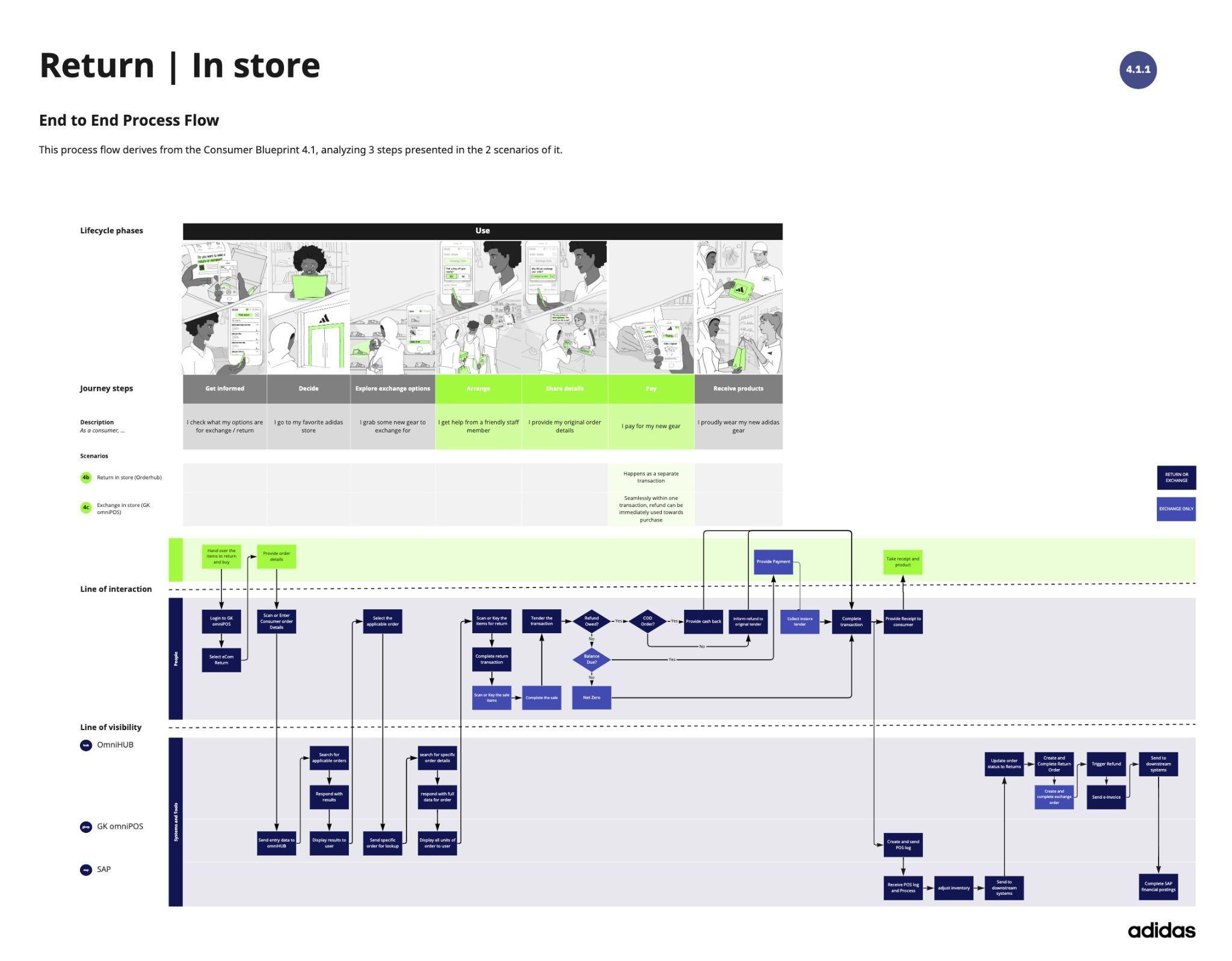




Circular offers require the coordination of activities spanning infrastructure, communication, people, and material components. A target state blueprint provides a holistic view that connects the circular offer to the customer to what is needed to deliver it operationally - from roles and behaviors to touchpoints, tools and processes.

10
Circular behaviour model
Target state blueprinting
“Unlocking circularity: A multilevel approach to scaling circularity” presents Livework’s understanding of the challenges of transitioning to a circular economy to inform discussions on the approach for steps forward. The document is intended to develop a vocabulary and framework to help us identify the often intangible barriers to change and find approaches to address them.
Anna van der Togt
Lead Design & Sustainability

anna@liveworkstudio.com
Ben Reason Founder & Managing Director
ben@liveworkstudio.com

in touch
Get




























