
MANUFACTURING PRODUCTION END OF YEAR REVIEW EDITION 2022 ENGINEERING MANUFACTURING PRODUCTION ELECTRIC VEHICLES ELECTRIFYING AUTOMOTIVE TREND PREDICTIONS FOR 2023 TECHNOLOGY WE NEED A MODERN TOOLBOX FOR MACHINE VISION DATA CHALLENGES



A PREMIUM CHAIN SOLUTION FOR HIGH DEMAND DRIVES A new Chain for the UK market offering a premium solution with three times the performance for wear resistance, fatigue resistance and high speed performance of comparable Roller Chain. Designed with unique pin coating, optimised plate geometry and high precision stamping, the X³ Roller Chain delivers significantly reduced maintenance downtime and longer service life. Available from Approved Product Partners and Stockists. donghua.co.uk/X3-chain 1 6 2 5 3 4 Optimised plate shape 1 High press fit to guarantee maximum fatigue strength 3 Special heat treatment and surface-coated pins give exceptional wear life 4 Seamless bushings & rollers throughout 5 High performance pre-lubrication 6 Calibrated pin and bushing holes 2 DOWNLOAD THE NEW X³ CATALOGUE Tube Tel: 01902 866200 Donghua Limited Sidings Close Wednesfield Way Wolverhampton West Midlands WV11 3DR
Sustainability: The close relationship between sustainability and supply chain planning

Automotive Electric Vehicles: Electrifying Automotive Trend Predictions for 2023




Robotics: Reaping the robotics rewards in the manufacturing sector Technology: We need a modern toolbox for machine vision data challenges
Welcome to the Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine End of Year Review.

2022 has been a testing year all round for industry, attempting to recover to pre-pandemic levels and having to cope with Global pressures affecting both supply and demand.
In this issue we wrap up the year with the usual mix of news and features including a review of the LiftEx 2022 event.
We look at a Survey on manufacturing systems design & analysis in industry written by Dr April Bryan from the University of Manchester, who discovered that many companies use bespoke in-house designs for their processes and procedures. We also feature a piece with Nick Hughes, Sales Manager at independent systems integrator, Invar Group, who gives us an insight into what to key factors are shaping the future of Warehouse Automation.
We hope you enjoy this issue and as always, if you have any news that you would like to feature within our first edition of 2023, please email details to editor@mpemagazine.co.uk. We wish all our readers, subscribers and contributors a happy and peaceful Christmas and New Year.
Every effort is made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of material published in Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine however, the publishers accept no responsibility for the claims or opinions made by advertisers, manufactures or contributors. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, mechanical, electronic (including photocopying) or stored in any information retrieval system without the prior consent of the publisher.
03 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine CONTENTS
Editor Paul Attwood editor@mpemagazine.co.uk Senior Editorial Assistant Francesca Amato editorial@mpemagazine.co.uk Features Editor Harry Peters editorial@mpemagazine.co.uk Production/Design Laura Whitehead laura@lapthornmedia.co.uk Sales Manager Charlotte Chapman charlotte@mpemagazine.co.uk Sales Executive Felicity Hamilton sales@mpemagazine.co.uk Accounts Richard Lapthorn accounts@mpemagazine.co.uk Circulation Manager Leo Phillips subs@mpemagazine.co.uk Publishing Director Maria Lapthorn maria@lapthornmedia.co.uk Lapthorn Media Ltd 5-7 Ozengell Place, Eurokent Business Park, Ramsgate, Kent, CT12 6PB Tel: 01843 808 117 10 22 36 38 44 Overcoming Today’s Manufacturing Challenges for Tomorrow’s Workplace
10 44 36 22 38
Editors Note
@mpemaguk mpemagazine.co.uk
Paul Attwood Editor
PTC delivers cloud-native simulation in Onshape
PTC has announced the availability of cloud-native simulation as part of its Onshape® product development platform.
Onshape Simulation enables designers and engineers to perform finite element analysis (FEA) in a fast and simple way and to make informed design decisions with structural analysis throughout the product development process.
It is the only computer-aided design (CAD) and product data management (PDM) tool to offer simulation that is interwoven with the core design and assembly environment, which helps reduce the time, effort, and workflows required to set up and calculate structural analysis.
Features and benefits of Onshape Simulation include:
• Designers receive accurate mechanical guidance, such as strength and rigidity, without ever leaving the design environment. The CAD model and the simulation model are the same definition, which dramatically simplifies the assembly set-up for simulation
• Onshape uses the existing assembly mates in the definition of the part-to-part interactions, eliminating the need to defeature, simplify, or set up connections for their models before running simulations
• Explore design variations quickly by simultaneously designing and analysing assemblies with no preprocessing or meshing required. Simulation results are automatically refreshed when changes are made to Onshape models
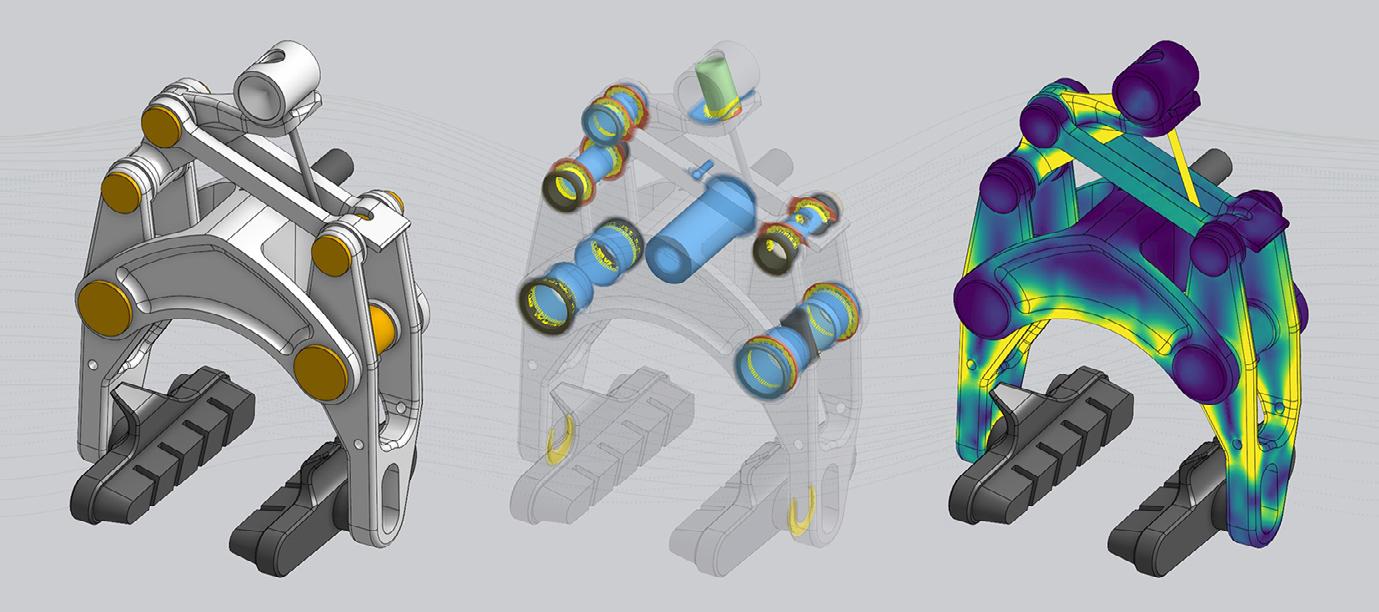
• As part of an Onshape document, simulations are version-controlled with built-in PDM – including simulations for all design variations – and can be shared instantly with other users for simple collaboration and decision making
• Cloud computing allows simulations to be conducted fast and interactively, with no need for specialised local hardware.
• Simulation is available now for
EMV Capital leads £2.5m financing package in domestic heat efficiency champion Ventive
Launch of Exhaust Air-source Heat Pumps programme enabled by innovative financing package.
EMV Capital, the deeptech and venture capital specialist, a wholly owned subsidiary of NetScientific plc, the international life sciences and sustainable technology investment and commercialisation group, is delighted to announce that it has led a £2.5m financing package in the domestic heat efficiency specialist, Ventive.
The new funding will allow Ventive to deliver its modular heat pump production facility in Hartlebury, Worcestershire. Ventive’s modular exhaust air heat pumps are targeted at both new build and retrofit applications and will provide significant cost and carbon dioxide emissions reductions across their installation, operation, and production.
The deal syndicated by EMV Capital is an investment package which includes an initial equity and debt investment of £600,000 from new investors. EMV Capital has taken a c.16% direct stake in the business, in partial settlement of fees. The package also includes the restructuring of c. £1m of historical debt. The fresh cash enables the launch of a Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS) matched funding grant of £1.5m, in line with EMV Capital’s capital light investment approach.
Ventive has partnered with QM Systems, a subsidiary of AIM-quoted PipeHawk PLC, to setup and scaleup its production to meet growing market demands. QM Systems offers multi-disciplinary production design, automation and high value manufacturing services backed by years of engineering experience.

Ventive Home Heat Pumps are demand responsive, fully integrated Indoor Environment Control systems which provide integrated ventilation, renewable heating, and hot water with free summer cooling. The Heat Pump will arrive pre-plumbed and pre-configured with monitoring and energy storage to enable quick and simple installation.
The investment in Ventive fits well with EMV Capital (and NetScientific’s) strategy for proactive investment management, trans-Atlantic growth, and a focus on transformative technology companies in high impact sectors. EMV Capital excels at helping innovative companies to raise money, and to take a stake as a principal, thereby committing to its portfolio companies.
Onshape Enterprise users, with availability for Onshape Professional users to follow shortly.
For more information, please visit our simulation page on Onshape.com
Company News 04 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
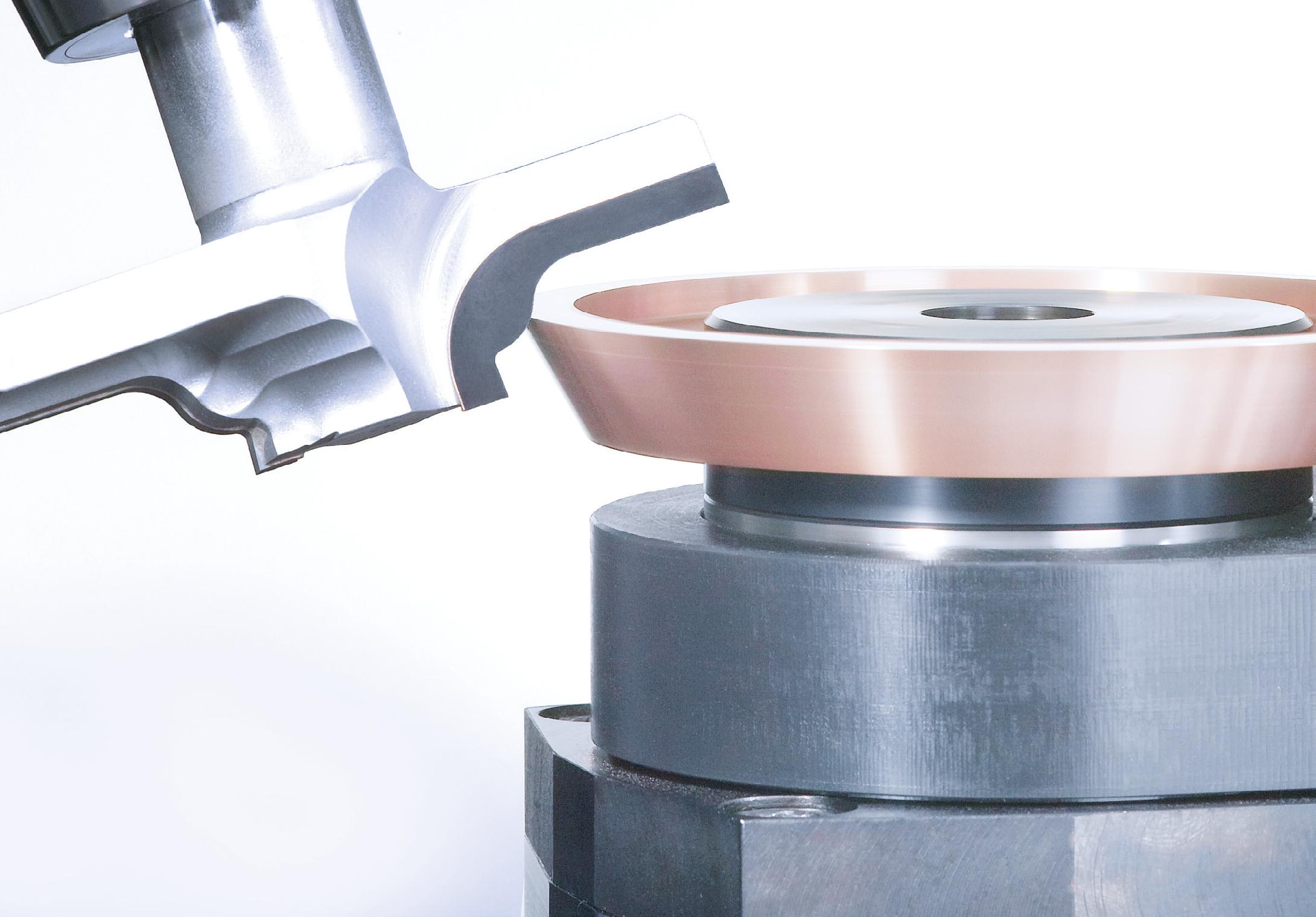
Into the future with more precision
–
Micro-Epsilon
Messtechnik opens new competence centre for micromechatronics
Precision sensor manufacturer Micro-Epsilon Messtechnik has opened a new production centre for micromechatronics at its headquarters in Ortenburg, Germany. Miniaturised mechatronic systems for semiconductor machine construction and aerospace applications are manufactured there. As a result, the growing demand for high-tech products from these key industries can continue to be met.
On an area of 36 x 36 m, the competence centre for
micromechatronics offers optimal conditions for the demanding production of miniaturised mechatronic systems, including sensors and systems for the latest generation of semiconductor lithography machines, as well as sensors for use in aircraft and space applications. Micro-Epsilon sensors contribute to the highest accuracy in the production of future chip generations. In order to manufacture such high-tech sensors, a clean room is required that offers optimal environmental conditions. In addition to the high demands on cleanliness, humidity and temperature must also be kept constant.
Satellites and reflector telescopes
Sensor-actuator solutions for laserbased satellite communication are also manufactured in the new production centre. Fast tilting mirrors enable precise positioning of the laser beam to the nearest satellite at a distance of several hundred kilometres, thus enabling a global satellite-based Internet of the future.
Another application is high precision sensors for the world’s largest reflector telescope. The large-scale project comprises several thousand inductive position measuring systems. In the telescope, these sensors are used for the exact positioning of the 798 individual mirror segments.
The competence centre is also considered an important milestone for the sustainable safeguarding and expansion of the company’s business development and as a clear commitment to the Ortenburg location. The company focuses on the four business areas of industrial sensor technology, 3D sensor technology, micromechatronics, as well as measurement and inspection systems.
With the completion of the construction work, the company now has 3,800 additional square metres on three levels at its disposal. The investment in buildings, technology and equipment amounts to a total of 10 million euros. The company area at the Ortenburg site is thus growing to around 15,000 square metres. The competence centre for micromechatronics alone offers space for over 100 employees. Micro-Epsilon currently employs around 450 people in Ortenburg and has more than 1,400 employees worldwide at 24 locations within the Group.

For more information, please visit www.micro-epsilon.co.uk
VW Group shows faith in FANUC with order for 1,300 robots
The Volkswagen Group has placed an order with FANUC for 1,300 robots, demonstrating the strength of its relationship with the leading industrial automation specialist. Throughout 2022 and 2023, FANUC will supply four VW plants across Europe with a variety of robotic solutions to support production of both Audi and VW models.
The majority of the robots will be installed at Volkswagen’s manufacturing facility in Bratislava, Slovakia. “We are delighted that we can now extend our longstanding and trusted cooperation with Volkswagen to the Bratislava plant,” says Ralf Winkelmann, Managing Director of FANUC Deutschland GmbH.
As well as the Bratislava facility, the main VW plant in Wolfsburg will also receive a significant percentage of the 1,300 newly ordered robots. Volkswagen’s all-electric ID.3 is due
to roll off the Wolfsburg production line from 2023, and FANUC robots will be integral in assisting with body construction.

Further contributing to the expansion of e-mobility, the new FANUC robots will also be installed at Audi’s battery assembly plant in Ingolstadt. The fourth facility benefitting from the contract is the Audi plant in Györ, Hungary.
With a 40-year history of automating production lines, a portfolio comprising over 100 models, and a monthly production capacity of around 10,000 robots, FANUC is ideally placed to supply major automotive projects on time and on budget, despite the ongoing global supply chain crisis.
The company’s offering includes SCARA robots, which are in high demand for electric vehicle battery production due to their payload and proven reliability, as well as a newly
launched model capable of handling loads of up to 1,000 kg, making FANUC the go-to automation partner for automotive manufacturers.
BELOW: FANUC robots working at the Audi plant in Györ, Hungary; one of four VW sites that will benefit from the order of 1,300 new FANUC robots (© Audi)
05 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Company News
Duke Street acquires Suir Engineering

Duke Street, a European midmarket private equity group, announces that it has agreed to acquire Suir Engineering a provider of innovative mechanical, electrical and instrumentation engineering solutions across Europe. Headquartered in Waterford, Ireland, Suir is currently owned by EDF Energy Services, a joint venture between the French energy group EDF and Dalkia, an energy services and facilities management subsidiary. EDF Energy Services acquired Suir in 2017. The completion of the transaction remains subject to obtaining applicable regulatory approvals.
Suir has close to four decades of engineering expertise in its core sectors of life sciences, renewable power and technology, and employs more than 1,200 people. With offices in Dublin, Waterford, Stockholm, Copenhagen and Frankfurt, the company has a superb track record of delivery in core project focus and an excellent safety history. The business supports 320 apprentices at any one time and has a strong track record for retaining staff, which is testament to its continued investment in professional development.
Paul Adams, Partner at Duke Street, commented: “We are delighted to acquire Suir Engineering, a market-leading business that is a great fit for our investment program and an exciting opportunity for Duke Street and our investors. The Duke Street investment team has previous successful experience in industrial services as well as Suir’s underlying sectors.
“Equipped with a skilled workforce, cuttingedge technology and a healthy pipeline of projects, Suir has significant growth potential

News 06 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Enclosures from the smallest to the largest. Rittal_ The System_ 2022_ EN_MPE_Oct 2022.indd 1
in Europe across all of its highly attractive end sectors. We have been impressed with Suir’s growth strategy and we look forward to actively supporting the existing management team in delivering their ambitious plans.”
Michael Kennedy, Managing Director, Suir Engineering, said “We at Suir are looking forward to partnering with Duke Street who share our vision, values and ambition. Together, we will accelerate Suir’s growth by expanding the business proposition to include more international work in key client sectors such as technology, renewables and life sciences facilities. We believe this will consolidate our position as a leader in the provision of mechanical, electrical and instrumentation engineering services that are expertly delivered by our very experienced team.”
The Suir acquisition represents another key deal milestone for Duke Street. Earlier this year Duke Street sold Medi-Globe Technologies GmbH to DCC Healthcare, a leading healthcare business listed on the FTSE 100, for an EV of approximately €245m. In January it announced the sale of Voyage Care, a sectorleading provider with over 30 years’ experience of specialist care and support, to Wren House, the London-based global infrastructure investment manager. It has also added two incremental acquisitions to COMPO, continental Europe’s leading gardening care company acquired in August 2021.
£5m funding open to businesses to help the UK PEMD industry scale up
Manufacturing businesses in the UK are being invited to benefit from a share of £5M funding, to help improve power electronics machines and drives (PEMD) manufacturing supply chains throughout the UK.
The ‘PEMD scale-up competition’ has been launched by Innovate UK and is part of the Driving the Electric Revolution challenge, and aims to support and highlight the need to invest in PEMD manufacturing in the UK.
Funding is broken down into two different strands, creating opportunity for a variation of projects within PEMD manufacturing in the UK, as well as supporting the UK supply chain to enable technologies critical to help to achieve the government’s net zero goals.
Driving the Electric Revolution challenge director, Professor Will Drury, said: “Drivers such as climate change, supply chain resilience and the cost of energy mean that there is a growing need to invest in UK manufacturing, particularly across the PEMD value chain.
“This new funding allows us to bring in manufacturers from outside the PEMD industry to help us develop
a strong, cross-sector, UK supply chain for these technologies vital for reaching net zero.”
There are two strands of funding that can be applied for:
• ‘Adopting manufacturing best practice’ (strand one) aims to fund feasibility studies supporting the transfer of knowledge, solutions, technologies and best practice from other manufacturing sectors, that demonstrate the impact of these innovations on the PEMD supply chain.
• ‘Manufacturing process development’ (strand two) aims to fund innovative process development projects that impact manufacturing costs, capability and efficiency to grow resilient manufacturing PEMD supply chains.
UK businesses of any size in the PEMD supply chain can apply to access the funding and are invited to explore the Driving the Electric Revolution Industrialisation Centre (DER-IC) partner network which has openaccess design, manufacturing and testing facilities which demonstrate the world-class technology and innovations that could be accessed by winning applicants.
www.rittal.co.uk

07 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine News
31-Oct-22 4:00:01 PM
CGTech appoints a direct Sales Engineer for Swedish Growth
To support ambitious plans for growth within overseas markets, CGTech has appointed a direct Sales Engineer in Sweden.
Svante Eriksson joined the company on October 10th, 2022 and will be tasked with growing the VERICUT user base, and supporting existing customers, in the Swedish market. Based in Trollhattan Svante will be perfectly positioned to deliver the exceptional levels of customer support that CGTech is renowned for.
Gavin Powell, CGTech Ltd. Managing Director, commented: “This is the first time CGTech Ltd. has employed a Sales Engineer within the Swedish territory and it is a testament to the positive growth plans for the company.”
Having previously used VERICUT CNC simulation, verification and optimisation software for more than 15 years in his previous role, Svante has hands on knowledge and experience of the software that will be invaluable in his new role.
Svante commented: “This is an exciting challenge for me. I am well aware of the benefits of VERICUT and I am looking forward to helping existing and prospective customers realise it’s power and potential.”
Rainford Expands Team
As part of its continued growth strategy, Rainford Precision has now expanded its team with the addition of a new Technical Sales & Applications Engineer. The appointment of Jaison Toon is a welcome extension to the Rainford Precision business, as the company continues to increase its sales, service and customer support.
Jaison will be responsible for sales and customer support in the Midlands and Northern regions of the UK, promoting the extensive portfolio of Rainford Precision products and services. Serving an apprenticeship in the mid-1980s as a machinist and rapidly progressing to manage machine shops before entering sales and application engineering in the late 1990’s, Jaison has more than 30 years of expertise in the manufacturing sector. During this period, Jaison has worked as a technical sales engineer with some of the world’s leading machine tool and cutting tool brands, supporting a variety of customers from small subcontract machine shops to OEM’s in all manufacturing sectors.
Rainford Precision is recognised as the UK’s outright experts in micro and small part machining with a portfolio of products that encompasses everything from micro abrasive waterjet cutting and lasers, high precision end mills, coolant drills, boring bars, taps, threadmills and reamers through to machine tools with precision and repeatability to a micron.
Altus Brings in New Operations Director
Altus Group, a leading distributor of capital equipment in the UK and Ireland, has announced the appointment of Jiri Kucera as Operations Director, strengthening its after sales and delivery department.
Jiri joins Altus as an experienced professional in engineering and operations development and will take the newly created role to support the company’s growth as the business
Commenting upon Jaison joining Rainford Precision, Managing Director, Miles Evans says: “We are delighted to have Jaison join us at Rainford. I have personally known Jaison since the 1990s and he is an excellent engineer with an outstanding depth of knowledge. During his career, Jaison has proven extremely successful in the sales of both machine tools and cutting tools, which makes this appointment a perfect fit for us. By welcoming Jaison to our team, we are demonstrating our commitment to enhancing service and customer support for our growing customer base.”

continues its rapid expansion and solidifies its management team for future growth.

He brings a wealth of experience and in-depth industry knowledge, having worked with several of Altus’s key customers in his career, and having worked closely with Altus as a business consultant, where he advised on processes and management of the customer ecosystem. This enabled the company to offer its customers and suppliers even more value over the last 18 months.
Jiri will oversee all after-sales operational elements of the business’s strategy and help to lead Altus on its impressive growth trajectory.
Most recently, Jiri was Head of Engineering for STI Ltd and has held similar top tier management roles as Operation Director at Fabrinet.
People On The Move 08 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Have you changed the way you work?
Have you changed the way you work?
Have you changed your materials?
materials?
existing product?
impact you?
Have you adapted an existing product? Do


Do you do R&D?
new products?
Do you ever develop
Have you developed or adapted an IT system? Have you
IP? Were you
outcome? Did you complete a claim? Have you discussed R&D tax credits with a specialist? 97% of eligible businesses don’t make a claim Call MCS Corporate Strategies for a no obligation R&D tax credits consultation 01926 512 475 You could benefit from Patent Box Tax Relief Speak to us today to discuss your eligibility 01926 512 475 R&D can show up in the most unexpected places but it can take an expert to spot it Call us now to find out more 01926 512 475 Is R&D buried in your business? It’s all about asking the right questions... Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N Y Y Y Do you do R&D?
you
new
customers use you to provide knowledge or expertise? Do regulations or accreditation
developed
happy with the
Do
ever develop
products?
Have you developed or adapted an IT system? Have you developed IP? Were you happy with the outcome? Did you complete a claim? Have you discussed R&D tax credits with a specialist? 97% of eligible businesses don’t make a claim Call MCS Corporate Strategies for a no obligation R&D tax credits consultation 01926 512 475 You could benefit from Patent Box Tax Relief Speak to us today to discuss your eligibility 01926 512 475 R&D can show up in the most unexpected places but it can take an expert to spot it Call us now to find out more 01926 512 475 Is R&D buried in your business? It’s all about asking the right questions... Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N Y Y Y
Have you changed your
Have you adapted an
Do customers use you to provide knowledge or expertise? Do regulations or accreditation impact you?
Overcoming Today’s Manufacturing Challenges for Tomorrow’s Workplace

10
Feature
The manufacturing industry has suffered significant challenges over the past few years. Supply chain vulnerabilities, labour shortages, pressures of COVID-19, and ongoing global political upheavals have created a very challenging and uncertain economic outlook.
Despite this, global production is growing at a steady pace. In September 2022, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization reported a 3.1% year-on-year increase in global manufacturing output, with end-ofyear figures likely to surpass pre-pandemic levels.
to pre-plan production runs, and help ensure the right amount of inventory and consumables to keep production lines running smoothly.
Staff shortages
Businesses in all industries are currently facing a shortage of workers – but the manufacturing sector has been hit particularly hard. In a recent report, Deloitte estimated that the US manufacturing skills shortages could reach a shortfall of 2.1 million skilled jobs by 2030.
With this in mind, Eddie Storan, Director of Global Service, Domino Printing Sciences, explores the biggest challenges facing manufacturers today and discusses the steps to take and the technology to use to transform these pain points into growth opportunities.

Supply chain turbulence
Supply chain turbulence is one of the greatest challenges facing manufacturers. From COVID-19 and the Suez Canal blockage to the energy crisis and the Ukraine conflict – the last few years have seen a series of unprecedented events that have wreaked havoc in supply chains with very little resiliency. In the UK, the ONS reported that between February 2021 and February 2022, 16% of businesses reported global supply chain disruption. Such disruptions can negatively impact manufacturing operations and cause knock-on effects on consumers via increased prices and extended lead times. Smart systems and automation are ways to mitigate some of these causalities.
Using automation can increase both control and agility by creating trusted, repeatable production processes that improve efficiency and reduce the risk of expensive errors. Automated coding solutions, for example, are a way of achieving this by limiting the risk of coding errors and associated downtime. When used to integrate and connect production machinery, automated coding can also provide manufacturers with options for increased data sharing and visibility of what is happening in real-time on a production line.
Storan
These factors combine to fuel more efficient manufacturing operations.
These solutions can also provide critical business insight that can help manufacturers cope with changes in demand or disruptions in supply. Data gleaned from automated coding, including the number of items coded per day, provides the insight needed
Automation, augmented reality, and cloud computing can provide a way of mitigating this risk to business productivity. When used effectively, these technologies can help manufacturers to overcome issues and maintain or improve production line efficiency.
Manufacturers can automate systems to work with limited operator intervention and take care of routine, manual tasks so that systems can continue to operate despite a reduced number of workers. It’s not about replacing manual workers – but ensuring that the existing manufacturing company workforce is put to the best use rather than carrying out mundane tasks which can easily be automated.
Companies can also look to their equipment suppliers to lend a hand in keeping machines running smoothly without significant operator intervention. During the pandemic, innovative suppliers developed ways of providing remote support applications, using augmented reality to allow engineers to interact with production line staff and resolve issues with machinery in real time or, on matters necessitating a site visit, to arrive onsite with everything needed to fix the issue. The use of augmented reality can also help to lessen customer training needs.
Remote monitoring via the cloud can also help to keep production running smoothly with a reduced workforce. Machines equipped with cloud connectivity can provide data on overall throughput, monitor performance, and use alerts and emails to notify of any changes which could signify – or, if not addressed, result in – an item of machinery not operating correctly.
Continued >>> 11 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Ensuring high levels of quality in everything from manufactured goods to product packaging and final coding and labelling is a high priority in any manufacturing environment.
Feature
Eddie
However, the one thing we can’t do is be complacent. To prepare for success, businesses must take steps to address today’s top manufacturing challenges.
This helps to avoid unnecessary downtime and keep production lines running at full capacity.
Quality control
Ensuring high levels of quality in everything from manufactured goods to product packaging and final coding and labelling is a high priority in any manufacturing environment. Consumer, retailer, and regulatory requirements and concerns around product safety and quality are higher than ever – and the pressure is on manufacturers to ensure that any product that leaves the factory is produced to the required standard.
Any manufacturing line needs rigorous quality and control processes, including product inspection. Automating inspection via intelligent machine vision systems is the most effective way to facilitate this. In coding and marking, such systems allow manufacturers to ensure that their products are adequately coded and can also help to identify where other issues on the line could be leading to coding issues. For example, a problem with box assembly results in incorrect code placement.
Vision inspection systems can be set up to provide automated alerts or automatic line stops when a specified error threshold is reached. This allows production workers to verify where on the production line an issue may be arising and take preventative action to rectify the problem. The risk of a sub-optimal product leaving the
factory unnoticed is reduced as is the production of waste.
Production (in)efficiency
Growth and competitiveness go hand in hand with production efficiency – or mitigating inefficiency. No matter how large or small a manufacturing plant is, efficiency and productivity will always be vital in maintaining a competitive edge.
The most effective means to facilitate this is data collection and analysis via cloud computing. Cloud dashboards allow manufacturers to track performance across production lines and understand how processes work effectively. This helps to keep things running smoothly and to identify areas for improvement, including opportunities to reduce waste and increase productivity.
Production managers can use cloud data to observe how a machine functions in real-time and identify changes in output that may signify a problem. The same technology will also accumulate a wealth of historical production data when utilised over time, which can be used for scenario planning and simulation to provide insight into additional value-added services that maximise overall equipment effectiveness.
Over time, data analysis and collaborative action between manufacturers and equipment providers can be used to develop the optimal conditions for production, with minimal downtime, reduced waste, and consistently high-quality products.
Sustainability
Though perhaps compounded in recent years, these four challenges
are not necessarily anything new to manufacturers. Arguably, they pale in comparison to the question of how best to achieve a sustainable production line and the goal of net zero.
The good news is that many of the tools and systems available to help manufacturers overcome the more common production challenges and remain competitive can also lend a hand regarding sustainability, efficiency, and waste reduction.
Whether through augmented reality support to reduce road miles needed to facilitate a machine fix; vision inspection to identify and rectify causes of production waste; or remote monitoring and data collection via the cloud to help identify and maintain consistently high quality across production lines, automation and smart solutions provide an excellent backbone for sustainable production.
Manufacturers who optimise their production via these systems and processes will be better placed to meet net zero targets and better manage suppliers and costs – by ensuring that all materials and energy are used to create high-quality, consumer-ready products rather than waste.
Conclusion
The most prominent challenges facing manufacturers today can be addressed through automation and intelligent use of data, but it is not easy to do this alone. Partnering with a trusted, reliable partner with experience working with smart systems, their relevant stages of application, and how these apply to individual sectors can play a key role in overcoming today’s manufacturing challenges and preparing for the workplace of tomorrow.
12 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Feature
Any manufacturing line needs rigorous quality and control processes, including product inspection. Automating inspection via intelligent machine vision systems is the most effective way to facilitate this. In coding and marking, such systems allow manufacturers to ensure that their products are adequately coded and can also help to identify where other issues on the line could be leading to coding issues.
Eddie Storan
The most prominent challenges facing manufacturers today can be addressed through automation and intelligent use of data, but it is not easy to do this alone.
Eddie Storan
Over 600 national and international suppliers come together to exhibit at Farnborough International Exhibition and Conference Centre this February for Southern Manufacturing and Electronics (inc AutoAero) 2023. Meet the power behind UK manufacturing industry and see live demonstrations and new product launches of machine tools & tooling, electronics, factory & process automation, packaging & handling, labelling & marking, 3D print technology, test & measurement, materials, composites & adhesives, rapid prototyping, ICT, drives & controls and laboratory equipment.
Free industry seminar programme online @ www.industrysouth.co.uk


The exhibition is free to attend, free to park and easy to get to. Doors open at 9.30am on Tuesday 7th February.
www.industrysouth.co.uk
7th | 8th | 9th FEBRUARY FARNBOROUGH | Hants | GU14 6TQ 9.30am - 4.30pm (3.30pm close Thurs) FREE SEMINARS FREE PARKING AUTOMATION DEFENCE ELECTRONICS AUTOSPORT MARINE AEROSPACE TRANSPORTATION PACKAGING ELECTRICAL & MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING LOGISTICS FOOD & DRINK ENERGY SMART MANUFACTURING SPACE ENGINEERING R&D MEDICAL COMPOSITES CONSTRUCTION Where Industry and Innovation converge
PRE-REGISTER TODAY for your Fast Track Entry Badge, Preview Magazine and Event Catalogue at
SOUTHERN MANUFACTURING & ELECTRONICS is an ETES event organised by European Trade & Exhibition Services Ltd Tel
· email philv@etes.co.uk
01784 880890
UK government awards grant




Machines & Machinery
Global
and electric powertrain systems supplier Danfoss
Solutions
to
Skills
which
• Danfoss plans to make electric offroad vehicles cheaper to own and run than diesel equivalents • New Danfoss Power Solutions facility in U.K. will be a global technology center and manufacturing site
hydraulics
Power
has secured a grant worth £407,112 from the U.K. government
accelerate the electrification of construction machinery. The U.K. Department for Business Energy and
awarded the grant through its Red Diesel Replacement competition,
seeks to accelerate the transition to electric off-road vehicles such as excavators and wheel loaders.
to Danfoss Power
decarbonize construction
PART OF THE MORVERN GROUP Great Western Business Park, Worcester WR4 9GN Tel: +44 (0)330 363 8484 www.altarasinternational.com With its state-of-the-art tooling and machining facilities based in Worcester UK, we are working with the leading engine manufactures across the world, supplying wax pattern dies, and complex ceramic core dies through to post cast 5 axis detailed machining.
Solutions to
machinery




15 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Machines & Machinery Morvern House, Ormonde Drive, Denby Hall Business Park, Denby, Derbyshire, DE5 8LE Tel: +44 (0)330 363 8484 www.morverngroup.com Leading independent supplier group of pre and post cast services to the investment casting industry. We supply tooling, wax injection and ready to cast assemblies and post cast 5 axis detailed machining. These funds will be used to accelerate the work we’re doing to develop nextgeneration, climate-friendly technologies in hydraulics, digitalization, and electrification.
Leif Bruhn
Floyd is a Star With New Alesa Line
For the precision cutting of components and slots, Floyd Automatic Tooling has now introduced the new Nutex Star Mini system that complements the existing line of Nutex saws. The latest addition to the popular Nutex system now incorporates a powerful interface with small shank diameters that helps to extend the application possibilities.
Available with a complete range of saw blade diameters and widths with a comprehensive selection of toolholders,
the Nutex Star Mini system is ideal for all machine shops. Precision cutting is assured with an innovative design that delivers precision, repeatability, ease of use and uncompromising tool life, regardless of the material being cut.

Precision cutting is derived from the saw and holder having an identically ground seven-cam interface. This makes the mounting of blades a self-centring proposition that is backlash-free. Furthermore, the saws can be hollow ground or in the known ‘Plus’ design with
a side relief angle. The mounting process is rapidly conducted with precision credit to a central screw system that enables fast and easy fitting on the long solid carbide holders. The seven-cam design also ensures that cutting forces are transmitted evenly and tangentially. This enables significantly higher cutting forces to be transmitted through the system, especially when compared with rival systems that offer 2, 3 or 4 driving cams. The benefit for the end-user is twofold with improved precision and process reliability, especially when cutting challenging materials such as aerospace or medical-grade alloys that demand increased torque.
To enhance swarf removal and prolong tool life, Alesa has developed the Nutex Star Mini system with through coolant supply. The internal coolant supply delivers coolant directly to the saw surface via internal cooling channels in the tool shanks. The tool shanks are manufactured from steel or optionally solid carbide to enhance rigidity, performance, vibration dampening and tool life, they are also cylindrically ground to h6 with the option of a Weldon design.
Website: floydautomatic.co.uk
New potentiometric sensor raises the bar for level measurement
Sensor specialists BAUMER continue to develop their award winning IO-Link sensors the latest example being the CombiLevel PLP70 level sensor. This new sensor will excel in applications with high grade diversity and frequent media changes such as those occurring in the beverage, brewing and other similar liquid handling processes.
The key benefits of this innovative potentiometric sensor make continuous level measurement easier and more flexible including the ability to automatically adapt to a wide range of media. Typical applications include precise monitoring of process levels in feeding containers, storage and buffer tanks and fast changing levels in filling lines.
One of the most important features of the PLP70 sensor is its ability to measure very low minimum conductivity media. For example, previous sensors were able to measure media with a conductivity starting at 50 microsiemens/cm whereas
this new option will detect extremely low conducting media starting at 5 microsiemens/cm. This pushes the conventional limits of these sensors and allows for use in media such as process water.
Thanks to its media-independent measuring principles, the PLP70 sensor ensures ultra-high precision and repeatability even in the most demanding applications which involve low-conducting, pasty, adhering or
foaming media which are difficult to measure with less advanced sensors. The sensor also provides short response times of less than 100 milliseconds and this, combined with ultra-high precision, helps to maximise process efficiency.
Operators will also appreciate the easy monitoring and control of the sensor via the proven Baumer display which includes a background changing colour and effectively provides all the required information at a single glance, even from longer distances. Functions of the touch display include temperature, pressure and conductivity enabling quick and convenient operator intervention directly at the sensor display.
The new PLP70 CombiLevel sensor with standard digital IO-Link interface and analog output is the latest example of how Baumer can improve your engineering processes, saving you time and money.
More at: https://www. baumer.com/gb/en/ product-overview/processsensors/level-sensors/ potentiometric-levelsensors/c/35486

Latest Product Launches 16 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
World Leaders in Selective Soldering
PILOT
Entry-level, benchtop, single point selective soldering system


JADE MKII
Elementary, exible, single point selective soldering system
ORISSA FUSION


High speed, in-line, multi-platform selective soldering system
SYNCHRODEX PRO LINE
Enhanced, exible, in-line, modular selective soldering system
Pillarhouse International Ltd.

Rodney Way, Widford, Chelmsford, Essex CM1 3BY UK
www.pillarhouse.co.uk



Tel: +44 (0) 1245 491333 Email: sales@pillarhouse.co.uk
Pillarhouse USA, Inc. www.pillarhouseusa.com
201 Lively Blvd, Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 USA
Tel: +1 847 593 9080 Email: sales@pillarhouseusa.com
Pillarhouse (Suzhou) Soldering Systems Co., Ltd. www.pillarhouse.cn
105 Weixi Road, Suzhou Industrial Park, China 215127 Tel: +86 512 6586 0460 Email: sales@pillarhouse.cn
20 years precision engineering at A&M
A&M EDM, precision engineers in Smethwick, West Midlands celebrated 20 years in business with an anniversary event for customers and business partners and a report on the company’s economic impact.


A&M was set up by Arthur Watts and Mark Wingfield in rented space with one wire eroder in October 2002. In October 2022, the award-winning business now
owns two factories close to each other, with 76 employees and record sales of £7 million in the year to September 2022.
The Black Country Economic Intelligence Unit has produced an independent report on A&M’s economic impact over 20 years. This report provides a detailed analysis of the growth of A&M as a manufacturing SME and its impact as a local “anchor organisation” creating long term jobs and relationships with customers and suppliers.
the future. Over 20 years, the company has driven strong economic value as well as cultivating a committed, skilled workforce at the heart of the local community. A&M EDM truly is a leading light of manufacturing in the West Midlands, particularly highlighting the excellence of the region’s many SME, supply chain firms.”
Delma Dwight
TTI Europe Supports Future Industrial Trends at Electronica
2022
Discover advanced technologies from TTI’s trusted manufacturing partners.
TTI, Inc. – Europe, a leading specialty distributor of electronic components, will be exhibiting the latest technologies to support future industrial trends at Electronica in Munich, Germany, on stand C3.578, 15th – 18th November 2022. Visitors to the stand will be able to learn about the newest
Professor Delma Dwight, Director of Black Country Economic Intelligence Unit said: “Manufacturing is a critically important industry in the Black Country and West Midlands, providing high levels of good employment and added value to the economy. As this impact report shows, A&M EDM is a great example of the entrepreneurship, growth and resilience of manufacturing, ready to take on the challenges and opportunities of
Mark Wingfield, Managing Director of A&M EDM said: “In 2002 our ambition was to become a sustainable sub-contractor offering EDM (electronic discharge machining) services to West Midlands manufacturing. The reduction of the Midlands toolmaking and automotive industries created opportunities to grow the business into other sectors such as aerospace. My advice to anyone starting today is to find ways to add value to every customer and continuously reinvest in equipment and developing apprentices and employee skills.”
technologies such as passives, sensors, connectors and power solutions, from TTI Europe’s valued manufacturing partners as well as understanding how they are advancing industry.
“Within the industry, there are several important areas of development, such as the digitalization and automation of machinery and production, the integration of robotic and autonomous platforms, and energy,” said Markus Lorenz, Director Industry Marketing – Industrial at TTI Europe.
“We will be showcasing electronic components from our global partners that are pushing the boundaries in all these areas.”
Energy is a particularly important focus as industry looks to operate in a more sustainable and cost-effective way. Engineers are increasingly having to consider energy efficiency as a priority in the design of their systems
as energy costs continue to rise, and state-of-the-art electronic technologies are proving vital here.
Additionally, there is an increased focus on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar as companies and consumers look to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. The latest electronic components will be critical for next generation energy battery storage systems, which are central to a successful energy transition, and heat pumps which are becoming an important sustainable technology.
Visitors will have the opportunity to learn about innovative technologies from TTI Europe’s manufacturing partners including sensing systems from Honeywell and Amphenol Sensors, passive and discrete electric components from Vishay, Yageo or Littelfuse as well as interconnect solutions from 3M, Amphenol, Molex and TE Connectivity.
18 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
A&M EDM truly is a leading light of manufacturing in the West Midlands.
Events & Awards News
Astley Hire is one of the first industrial equipment hire companies to achieve carbonneutral status, which has recently been verified by the NQA and recognised with a gold medal award from EcoVadis.



Before 2020 Astley Hire had achieved an environmental standard under ISO 14001, which the company had held for many years, but this achievement has since been replaced with their successful efforts to become a carbon-neutral company under the successor framework of PAS 2060. This goal was inspired by the UK’s Net Zero initiative to create a carbonneutral economy by the year 2050.
Astley Hire engaged with
consultancy service Charis Ventures Ltd to assist with the project. By working together to form and implement a comprehensive carbon scheme, Astley Hire and Charis Ventures were able to reduce a potential carbon footprint of 485.21 tons down to a residual value of 476.95 2 tons, which has been offset via the government-approved Carbon Footprint scheme.


The culmination of a 12-month environmental program between 2020 and 2021 was the announcement of Astley Hire’s carbon-neutral status which has since been externally verified by the NQA (National Quality Assurance) as well as the online organisation, EcoVadis.

19 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
West Industrial Hire Firm Awarded Gold EcoVadis Medal Events & Awards News WATER JETTING TRAINING FOR MANUFACTURING AND ENGINEERING info@waterjetting.org.uk +44 (0) 208 320 1090 www.waterjetting.org.uk Contact us for details of WJA-Approved Instructors in your area Water Jetting Association - The Engine House, Veridion Way, Erith, Kent, DA18 4AL, UK JOIN THE WATER JETTING ASSOCIATION Find out about the many benefits of being a WJA member Key Benefits City & Guilds Accredited WJA-Approved Instructors New Recruits & Refresher Written Compliance Test Certificate & Photo ID Card Courses Offered Safety Awareness Pressure Washing Tube & Pipe Cleaning Surface Preparation Hydrodemolition Drain & Sewer Cleaning ARE YOUR WATER JETTERS AND PRESSURE WASH OPERATIVES WJA QUALIFIED? Level 2 Water Jetting Technician Certificate UK’s first competency qualification for water jetting Accredited by ABBE / Ofqual Qualifies holder for CSCS card 40/60 skills learning and assessment Enhances productivity and safety Supports succession planning and retention
North
Alchemy guarantees accurate metals testing

To maximise the value of your scrap metals accurate metals testing is essential – the team at Alchemy use the latest handheld Niton Thermo Scientific XRF analysers and spectrometers to confirm the exact grade of your materials.

A great example of this is Stainless Steel – grades 304 and 316 are widely used across a range of industries however if you mix these materials as scrap then you may well only be receiving the price for the lowest grade 304. They will provide containers for you to segregate these waste streams yourself or if this is not practical then they will segregate them on your behalf using Niton technology.


With mixed swarf Alchemy will arrange for this to be analysed meaning that you can receive a rebate for the average contents of the load rather than the lowest value material in the load.

It is common within the scrap metal industry to receive a ‘mixed metals’ price for your metal scrap, this is generally much lower than when your materials are segregated for you, or alternatively appropriate containment is provided for you to segregate on site.
Either way the team at Alchemy will help increase your financial returns.
www.alchemymetals.com
20 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Spend less while your machines do more Start saving today. Call ROCOL Customer Care Team on: +44 (0)113 232 2600 for information and suppliers Longer-lasting generating 15,200 litres of cutting fluid per barrel with 1% top up Cost-effective making the equivalent of 3 barrels of our competitor’s product* Economical with a single product to support your cutting and grinding operations * Based on lab testing at ROCOL laboratories ULTRACUT 370 EP keeps your CNC machine tools working harder for longer, for less money. with ROCOL® ULTRACUT 370 EP high performance semi-synthetic fluid ULTRACUT 370 EP is Our extreme pressure additive ensures a greater surface finish and improved tool life for your machinery. And that’s not all.

Sustainability
The close relationship between sustainability and supply chain planning
By Jim Bralsford, Senior Director, Industry Solutions, Kinaxis
While many manufacturers are taking steps to ensure sustainability in their own operations, it’s in fact the end-to-end supply chain surrounding them that is responsible for the vast majority of social and environmental costs.
McKinsey figures estimate that the supply chain accounts for as much as 80% of greenhouse gas emissions. It’s proof to manufacturers that success in sustainability will depend much more on supply chain planning than previously thought.
Incorporating scope 3
Before action is taken, exploring the types of emissions created by the supply chain is critical to understanding where planners can make the difference. The Scope of Emissions model highlights the three different types of emissions associated with organisations. Business leaders are much more likely to be aware and taking action in regard to scopes 1 and 2, which covers aspects such as fuel combustion, company vehicles and purchased electricity, heat and steam.
Jim Bralsford
In today’s world, supply chain planning should be at the front-and-centre of green initiatives, with strategies needing to be in place to ensure that money isn’t simply thrown at decarbonisation of the supply chain and daily planning decisions reverse the impact. What steps can planners take to make an immediate mark?
Transportations and distribution, employee commuting and business travel are some of the aspects that come under scope 3 emissions, In many cases however, these can go unnoticed, and this is particularly damaging for the manufacturing sector. Scope 3 emissions in this sector are higher on average than in the food, electronics and textile, apparel and shoes sectors.

In this sector especially, they form the bulk of the emissions iceberg and must be addressed if we are to positively impact our planet. Considering that some of the aspects of scope 3 are very much based around the supply chain as a whole, planners have an important role to play. Sustainability doesn’t just stop at the factory gates. It continues all the way through to delivery of a product or services to a consumer. Focusing on these scope 3 emissions helps clear the path to ultimately meeting sustainability goals.
Increasing knowledge
For planners to make their mark on increasing supply chain sustainability, knowledge of the issue is vital.
The first step to achieving this is to attain transparency of the whole network. It’s only through this visibility that planners can understand how to make better decisions. It’s time to think beyond just carbon emissions and consider water usage, rare raw material consumption, renewable energy and materials across the whole chain.
As another measure, corporate sustainability strategy needs to move up the company hierarchy.
22 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Transportations and distribution, employee commuting and business travel are some of the aspects that come under scope 3 emissions, In many cases however, these can go unnoticed, and this is particularly damaging for the manufacturing sector.
Planners need a seat at the boardroom table, informing directors and working directly with the Chief Sustainability Officer (or the C-level executive charged with delivering the sustainability strategy) to ensure that sustainability initiatives are not falling foul of bad planning. It’s only with this input at the highest level that tangible change can then be delivered.
Tangible actions
Already, a number of organisations are making progress in supply chain sustainability. In the manufacturing space, Mars is reducing the number of palm oil manufacturers it works with in order to better manage its impact on deforestation. Schneider Electric has committed to convert its 14,000 fleet vehicles to electric by 2030, and Cisco enables circularity with a significant reverse supply chain.
The supply chain planner will be essential to any initiative of this kind. The enabler to make these initiatives happen? Technology. Individual functional excellence has been a primary focus of organisations, but modern supply chain solutions should consider a holistic approach. Warehouse operations can be made as efficient as possible, but sustainability will ultimately suffer if, for example, transportation is not considered.
With technology to hand, supply chain planners have complete end-to-end

visibility, enabling them to take action to enhance efficiency, whether it’s by saving employees time, reducing fuel costs or using fewer raw materials. Costly stockouts and wasteful overstocks can be eliminated thanks to the ability to more precisely predict and balance supply and demand. Additionally, the most efficient route and delivery options for both forward and reverse logistics with realtime scenario planning can be identified. Leveraging these solutions also helps to ensure that the wider supply chain meets environmental regulations such as the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) for sourcing, clean air and emissions.
Looking beyond internal operations
Sustainable supply chains are not just a nice-to-have in today’s manufacturing environment. Boardrooms are now sitting up and taking notice of environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) in their organisation, with tangible action in addition to corporate statements. At the consumer end, more are placing sustainability at the forefront of purchasing decisions. In fact, almost ninein-ten (90%) Generation X consumers are happy to spend an extra 10% on a sustainable product. Businesses must therefore implement strategies to win over the hearts of green-focused consumers and gain the attention of suppliers and manufacturers.
With technology by their side, supply chain planners can be empowered to maintain a more mature, efficient and sustainable supply chain. Now, they need to be positioned across the table from key decision makers to inform them on the best measures to be incorporated. By melding sustainability and supply chain planning, manufacturers are best placed to reduce carbon emissions and ensure greener initiatives in the product journey, from manufacturing floor to consumer.
Sustainability
With technology to hand, supply chain planners have complete end-to-end visibility, enabling them to take action to enhance efficiency, whether it’s by saving employees time, reducing fuel costs or using fewer raw materials.
23 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Jim Bralsford
Survey on manufacturing systems design & analysis in industry
Written by Dr. April Bryan, Ph.D. CEng MIMechE Department of Mechanical, Aerospace, and Civil Engineering
Manufacturing systems affect the speed and cost of the delivery of a product to market. Therefore, their design and analysis are of significant importance. Whether it is a component to be machined, or a device to be assembled, the manufacture of a product at significant volume necessitates the use of a manufacturing system. As a result, for many years researchers have pondered about and developed methods through which manufacturing systems can be designed, analysed, and optimized. However, the extent of adoption of these techniques by industrial practitioners is unknown.
In a survey that was conducted at the Manufacturing and Engineering Week in England, manufacturers were asked about the methods most commonly used in the engineering of manufacturing
systems. The results were quite surprising. It was discovered that the majority of organizations did not use formal approaches to design or analyse manufacturing systems. Instead, the manufacturers relied on intuition and experience to develop and optimize the performances of their manufacturing systems. Furthermore, it was discovered that the type of software most commonly used for manufacturing systems design and analysis was computer aided design (CAD).
Types of Manufacturing Systems
Manufacturing systems are typically utilized when products are too complex, and the volumes of products to be produced are too high, to be completed within a single operation. Given that operational steps are therefore required, the manufacture of a product is typically completed on a series of workstations,
design
Dr. April Bryan, Ph.D. CEng
which are either manual, automated or a combination of both. As shown in Fig. 1, manufacturing systems can be classified by the variety of products to be produced, and the volume of products per variant required to satisfy market needs. This results in three main types of manufacturing systems, job shops, cellular manufacturing systems (CMS), and flow lines¹. Flow line manufacturing systems, are further classified as dedicated manufacturing systems (DMS), flexible manufacturing systems (FMS), and reconfigurable manufacturing systems (RMS).
About the Manufacturing Systems Survey
At the 2022 Manufacturing and Engineering Week Conference and Exhibition, nineteen (19) UK manufacturers took part in a survey that was aimed at determining the methods most commonly used to design and analyse manufacturing systems.
Left: Figure 1 Types of Manufacturing Systems

24 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Feature
To accomplish the
and analysis of the manufacturing systems, the software packages with the highest response rates were SolidWorks, followed by another version of CAD software.
MIMechE
The University of Manchester
The majority of companies that completed the survey were original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), 10. Seven of the companies were small to medium enterprises (SMEs), and two were macro, non-OEM, enterprises. None of the companies were micro enterprises or cottage industries. As the survey was anonymous, the names of the companies cannot be revealed.
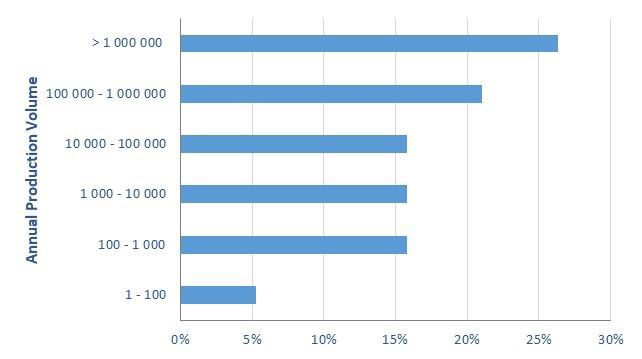
The companies represented a range of industries engaged in the manufacture of discrete products. This included manufacturers who manufactured products for the transportation, industrial equipment, electronics and home appliance sectors. The majority of companies manufactured products for only one sector, 53%, while there was one company that manufactured products for as many as 15 sectors. As shown in Fig. 2, the volume of products produced by the respondents also varied widely, with one company producing fewer than 100’s of products, and 26% of the companies producing more than 1 000 000 products annually.
Seventy-nine percent of the respondents engaged in assembly, while 32% in fabrication, 26% in electronics processing, and smaller percentages in machining and other types of operations. Of these, 58% used only one type of manufacturing process, 26% two types, and 11% three types of processes. The most popular combination of processes observed in the survey was assembly and fabrication. This was followed by assembly and electronics processing.
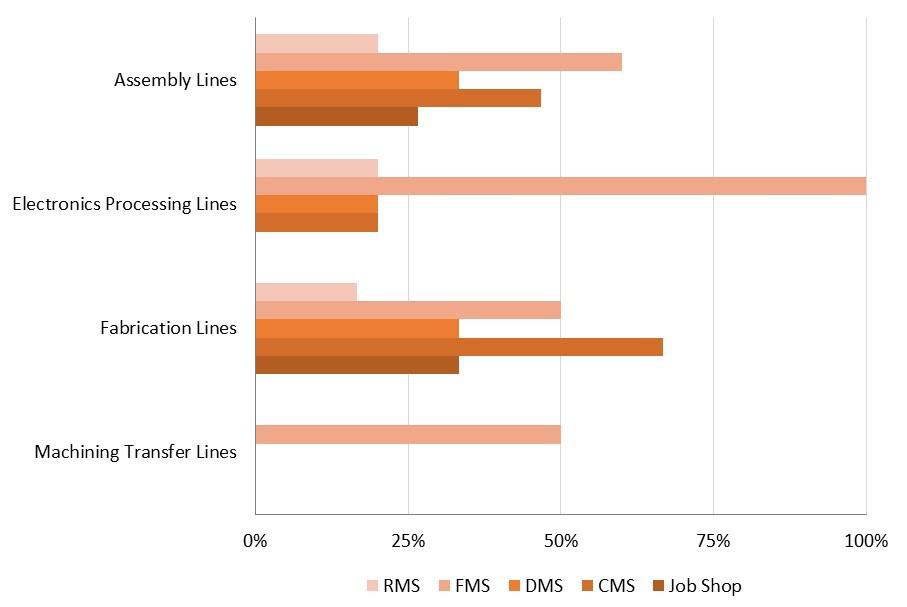
Of those companies that engaged in assembly, 60% reported use of the FMS type of manufacturing system, 47% CMS, and 33% DMS. Interestingly, 100% of the companies producing electronics reported use of flexible
manufacturing systems, and none, job shops. Figure 3 gives the results of the type of manufacturing system that was adopted for various types of processing operations. The most popular type of manufacturing system used among manufacturers was the CMS, which was used by 47% of the companies surveyed. An equal number of companies reported use of the DMS and FMS types of manufacturing systems, 37%. Reconfigurable manufacturing systems had the lowest usage among the types of manufacturing systems investigated. A few manufacturers reported the use of Lean Manufacturing, approximately ¼ of the companies surveyed. The both companies that used machining transfer lines also reported use of Lean Manufacturing.
Manufacturing Systems Design and Analysis Methods
When it came to the design and analysis of manufacturing systems, it was discovered that 89% of the companies completed the design of manufacturing systems in-house. Eighty-four percent (84 %) also indicated that the analysis of the manufacturing systems was performed within their organizations. Just three companies indicated that the design of manufacturing systems was outsourced, or completed with the support of outside consultants. Similar results were obtained for the analysis of manufacturing systems. Of the three companies that reported that the engineering of the manufacturing systems was outsourced, two were the macro enterprises that took part in the survey. All of the SMEs indicated that manufacturing systems were designed and analysed in-house, and just one SME indicated the design was completed with the assistance of an outside consultant. The picture is similar for the
Left: Figure 2
Volumes of Products Produced Annually
by Survey Respondents
OEMs. Just two OEMs reported that the design or analysis of their manufacturing systems were completely outsourced, and another two OEMs indicated that the analysis was performed with the support of outside consultants.
Of the companies surveyed, the both macro enterprises reported that they were most likely to use mathematical or algorithmic approaches to accomplish the design and analysis of their manufacturing systems. Seventypercent (70%) of the OEMs also reported the use of mathematical or algorithmic approaches. The approaches used in order of frequency was some form of FMS design strategy, operational process planning, line balancing, and buffer sizing. None of the manufacturers reported the use of Group technology and Markov chains. It was also observed that none of the SMEs reported the use of mathematical or algorithmic approaches. Instead, all the SMEs indicated that qualitative or experiential methods were used to accomplish the design and analysis of their manufacturing systems.
Qualitative and experiential design methods were also reportedly adopted by the both macro enterprises, and 80% of the OEMs surveyed. Lean Manufacturing was one of the qualitative approaches used. One SME, both macro enterprises, and 20% of the OEMs surveyed reported use of Lean Manufacturing. A few companies indicated that simple trial and error methods were used for manufacturing systems design and analysis. Some of the companies also indicated that the design and analysis of manufacturing systems was accomplished through the use of the knowledge and experience of expert practitioners.
Much fewer companies reported use of simulation. Of the companies surveyed, only 11% of the companies indicated that simulation was used for manufacturing system design or analysis. These companies were OEMs, and the simulation approach that was adopted was Discrete Event Simulation. None of the companies indicated the use of Monte Carlo Simulation, or any of the other specialized simulation methods, in the engineering of their manufacturing systems.
Continued >>> 25 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Feature
To accomplish the design and analysis of the manufacturing systems, the software packages with the highest response rates were SolidWorks, followed by another version of CAD software. Sixtyseven percent (67%) of companies that reported the use of algorithmic approaches, and 60% of companies that reported the use qualitative approaches, which responded to the question, reported the use of SolidWorks, as shown in Fig. 4. Altogether, 87% of the companies that responded to the question used some type of CAD software, either SolidWorks, AutoDesk, or another CAD package to accomplish manufacturing systems design and analysis. The SMEs and OEMs were most likely to use CAD software, with approximately 70% of each type of organization using CAD. Furthermore,
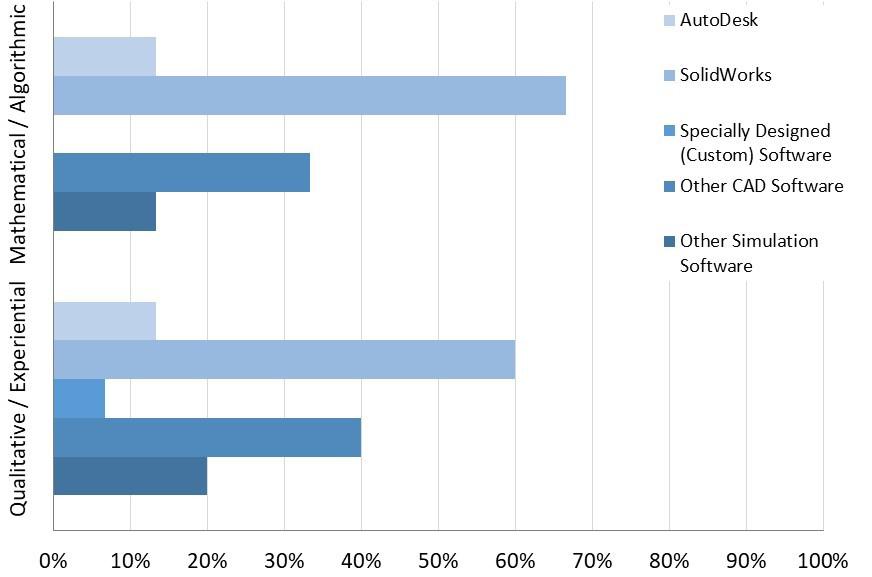
Below: Figure 4
Software Most Commonly Used
the only software mentioned to accomplish techniques such as FMS design and line balancing was CAD.
Approximately 20% of the companies did not provide a response to the question on the type of software that was used in the engineering of their manufacturing systems. Understandably only one OEM reported the use of simulation software. Lastly, only one company, a macroenterprise, reported the use of software that was specially designed in-house to design and analyse manufacturing systems.
Conclusion
This survey provided insight into the methods used by UK manufacturers in
Above: Figure 3
Types of Manufacturing Systems Used for Various Processes
the design and analysis of manufacturing systems. While the survey size was not large, as a result of the survey location, and the types of companies which took part, the results of the survey give a reliable indication of the practices most commonly used to accomplish the design and analysis of manufacturing systems in industry. As a reminder, the survey was performed at the Manufacturing Week Conference and Exposition, one of the biggest annual manufacturing conferences in the UK.
As indicated by the survey’s results, manufacturers seemed to have a preference for engineering their manufacturing systems in-house using the knowledge of experienced manufacturing engineers. When designing and analysing the manufacturing systems, the FMS design strategy, followed by operational process planning were the most commonly reported strategies. The most popular software reportedly adopted by manufacturers was CAD based, with SolidWorks having the greatest popularity.
1. Groover, M. P., 2008, Automation, Production Systems and Computer Aided Manufacturing Ed. 3, Pearson International.
26 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Feature
As indicated by the survey’s results, manufacturers seemed to have a preference for engineering their manufacturing systems in-house using the knowledge of experienced manufacturing engineers.
Dr. April Bryan, Ph.D. CEng MIMechE

Science Minister unveils
£15m satellite technology fund
Science Minister Nusrat Ghani has unveiled a new £15 million fund to support UK space businesses for the development of satellite communications technology.
The fund takes the form of a competition, running until spring 2023, encouraging businesses to develop and share satellite communications technologies. The competition is designed to spark further investment and growth in the UK space sector.
Nadeem Gabbani, Founder of Exobotics, commented: “It is great to see the new science minister unveiling investment and support for the science and space sectors, which will play a vital role in boosting the UK economy. Demonstrating support for space businesses is hugely encouraging for new start-ups and SMEs who will have the confidence to expand and innovate, whilst providing new high skilled science jobs within their businesses.
“All eyes are on the UK space sector at the moment, so it is vital that we demonstrate the growth and strength of the industry through upcoming launches, economic growth and widespread job creation in order to establish the UK as a major player in the global space market.”
“The support and investment provided by the new minister should be used to make space accessible for everyone by breaking down the barriers to entry for companies outside of the space industry.”
The fund comes alongside a new report which revealed that every £1 invested in the European Space Agency provides an £11.80 return for the UK economy.
Science Minister Nusrat Ghani said: “I am proud to be representing the UK space sector as we discuss our ambitions ahead of the ESA Council of Ministers next months. There are a series of important programmes on the table, and I want to harness opportunities in space to grow the UK economy, create jobs and inspire young people into STEM careers.”
Thousands of jobs up for grabs as rail sector looks for injection of ‘girl power’


One of the UK’s leading providers of rail related training has made a rallying call for more women to get involved in a sector that has thousands of immediate jobs available.
Davie Carns, Managing Director of National Infrastructure Solution (NIS), believes the industry needs to work harder to create more opportunities to ensure female talent can succeed.
The former Royal Marine is working with City of Wolverhampton College and the West Midlands Combined Authority (WMCA) to help change perceptions and to highlight the vast array of roles available across the rail industry.
As well as many positions available on worksites across the country, there is also a diverse range of ‘off track’ careers, such as office roles, project management, health and safety and digital marketing,
Part of the recruitment drive is providing flexible training courses with start and end times that fit around paternal activities and educating employers on creating work conditions and shift times that are more accessible to women.
“With major infrastructure projects, including HS2 and the Midland Metro Extension well underway, there has never been a better time for a more inclusive workforce,” explained Davie, who started NIS in 2020.
“If you take the total rail workforce
in the UK, only 14% are women…a stunning stat that we need to change, “It’s not just about digging holes on track, there’s so many different opportunities for women looking for a career change or those entering or reentering the workplace.”
He continued: “There’s thousands of jobs immediately available and, with our strategic partners, we can offer the training to help get them into the sector or, for those already plying their trade across the network, the opportunity to upskill and support progression.
“Rates of pay are good and individuals with the right aptitude can progress quickly into team leader and senior roles.
“It’s our job to equip learners with the right skills and to work with key employers across the industry to create employment opportunities at the end of their course.
“A perfect example of this is how we currently work with Vital Rail, who have donated equipment and resource to support our training centre.”
The partnership between City of Wolverhampton College and National Infrastructure Solutions is into its third year and offers a pioneering approach to academic/industry training.
Sector-specific and designed with employment at the forefront of the learner journey, the tailored courses are offered at different levels depending on the experience of the individual.
Supported by the West Midlands Combined Authority, the relationship also benefits from a dedicated rail training centre at the college’s Wellington Road Campus in Bilston. This is equipped with installation and maintenance equipment and a standard rail track to support courses on conventional, high speed and light rail lines.
The facility is also the first in the UK to offer training on slab track systems used in the construction of high-speed rail lines, such as HS2.
For further information, please visit www.nisgroup.co.uk or follow NIS on its social channels.
Latest News 28 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Figures Soar in

RTITB, the leading accrediting body for workplace transport training, has reported a surge in registrations of new Lift Truck Instructors so far this year.
Between January and August 2022, 508 trained Lift Truck Instructors have already joined the RTITB Register of International Instructors. This is a steep rise from 2021, where 580 Instructors registered across the whole year.
UK Instructor numbers have steadily grown year on year. With the exception of 2020, where COVID-19 restrictions prevented Instructors from completing training. As a result, 50% fewer Lift Truck Instructor examinations took place compared to the previous year.

“A lot of training fell behind in the pandemic. This led to massive bottlenecks for Lift Truck Instructor training,” explains Laura Nelson, Managing Director for RTITB. “Our latest figures indicate that businesses are now prioritising clearing their Instructor training backlogs.”
She continues “COVID-19 delayed operator training too. There is also increased pressure on the supply chain. This means that the industry now urgently needs to train more Lift Truck operators to meet demand.”

There are currently 13,162 ‘Forklift Operator’ roles currently advertised by organisations across the UK. However, many businesses suggest that filling Instructor roles with existing qualified candidates is challenging.
To fill these Instructor vacancies, some organisations are therefore looking to upskill existing employees. RTITB suggests that lift truck operators, warehouse operatives, or supervisors may all be keen to develop their career as Instructors. This could help close the skills gap.
“Your existing employees come with an understanding of your business and operations. This can prove incredibly helpful when they become an Instructor,” says Laura. “Plus, this upskilling approach demonstrates a

clear career progression path within your business. New opportunities can boost morale, ensure your team uses their skills to the fullest, and can help retain valuable talent. Career development can also make you an attractive employer in a competitive recruitment market,” continues Laura.
To train skilled and safety-focused Lift Truck Instructors, businesses can book courses with the nationwide network of RTITB Accredited Instructor Centres.
These providers must all achieve and uphold specific standards to be RTITB Accredited for Instructor training. This gives businesses peace of mind that they are delivering exceptional quality training. As a result, you benefit from highly skilled and safety-focused Lift Truck Instructors to train your team in-house.

To find an RTITB Accredited Instructor Centre for Lift Truck Instructor training, visit www.rtitb. com and view the Course Locator.

29 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Latest News
Lift
2022 COMPLEX FORMS NEED STRAIGHTFORWARD SOLUTIONS: VOLLMER www.vollmer-group.com To shape the future you will need forward-looking PCD tools – and intelligent solutions for their production, processing and maintenance. VOLLMER supports you: with innovative PCD sharpening and eroding machines, economical automation options and strong services. For the highest flexibility, efficiency and quality. The future takes shape: with VOLLMER. VOLLMER UK LTD. // Nottingham NG10 5BP // +44 115 9491040 // info-uk@vollmer-group.com VGrind 360 VPulse 500
Registered
Truck Instructor
Reflecting on LiftEx 2022 and looking forward to LiftEx 2023
LiftEx, the flagship event of the Lifting Equipment Engineers Association (LEEA), was held over two days (5-6 October 2022) at P&J Live in the major Oil and Gas centre of Aberdeen, celebrating the successes and triumphs of the inspiring and fantastic Lifting Industry. The event provided a one-stop shop to find services, products as well as to gain the latest lifting related knowledge and insights no matter what the sector. P&J Live also played host to the fourth annual LEEA Awards Ceremony – otherwise known as the ‘party of the year’ on the evening of 5 October 2022.
LEEA CEO Ross Moloney said: “The responses we have received have been overwhelmingly positive. I would like to express my gratitude to the exhibitors, sponsors RRS Group and Royal Van Beest, the LEEA Board, our speakers, the hard working LEEA team for bringing the entire event together and all the visitors who attended for making LiftEx 2022 in Aberdeen such a success. Together, we represent a truly astounding global industry that wins the battle with gravity on a daily basis.”
LiftEx 2022 was the Association’s 17th exhibition and the first after the pandemic lockdowns. The exhibition floor was packed with major lifting suppliers


One of the most positive and rewarding aspects of this year’s event was the LiftEx Industry Careers Day on 6 October 2022, organised with TechFest, a local specialist in the promotion of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) subjects, and Developing the Young Workforce (DYW), and
Ross Moloney
organisation that makes it easier for employers to connect with students in schools and colleges across Scotland. Senior pupils aged 16-18, and their teachers, with an interest in learning more about the huge range of opportunities available to them in the lifting industry gathered at LiftEx and engaged with the industry professionals, global companies and organisations present at the event. They were able to gain career information, advice and guidance session for the students. Speakers from industry and partners from universities and the military introduced the students to learning opportunities and career routes. And after trying the interactive experiments, which are part of LEEA’s Think Lifting programme, the students explored the show hall to meet the exhibitors.
LiftEx 2023
LEEA is pleased to announce that LiftEx 2023 and the 5th Annual LEEA Awards will take place on the 21 & 22 of November at the Exhibition Centre Liverpool.
Sponsorship and Exhibition opportunities are now available. Requests will be dealt with on a first-come, first-served basis, so please contact Leah Phelps on +44 20 3488 2865 or at enquiries@L2Events.com to secure a sponsorship package or a prime position on the exhibition floor.

30 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Post-Show Summary
It was great to see attendees from multiple markets meeting LEEA members to discuss ways they can help achieve best lifting practice, as well as gaining vital lifting related knowledge and insights from our programme of speaker sessions, delivered by the LEEA team and industry experts.



Nuclear Science and Technology Designed to create a generation of nuclear engineers and scientists with the skills to secure a sustainable and safe future for nuclear energy. MSc - 1 year full time MSc - 2 or 3 year part time PG Diploma • PG Certificate Short Courses for CPD info.ntec@manchester.ac.uk or visit www.ntec.ac.uk Register at: Course delivered by: The University of Birmingham • University of Central Lancashire • The University of Leeds • The University of Liverpool The University of Manchester • The University of Sheffield • The Nuclear Department of the Defence Academy Key features: Demand-driven • Breadth of learning • Delivered by experts • Flexibility • Short-course format Science and Technology generation of nuclear engineers skills to secure a sustainable nuclear energy. time part time Certificate for CPD For more information: email: info.ntec@manchester.ac.uk or visit www.ntec.ac.uk Register at: Central Lancashire • The University of Leeds • The University of Liverpool University of Sheffield • The Nuclear Department of the Defence Academy Breadth of learning • Delivered by experts • Flexibility • Short-course format Designed to create a generation of nuclear engineers and scientists with the skills to secure a sustainable and safe future for nuclear energy. MSc - 1 year full time MSc - 2 or 3 year part time (Taught and Distance Learning) PG Diploma • PG Certificate Short Courses for CPD For more information: email: info.ntec@manchester.ac.uk or visit www.ntec.ac.uk Key features: • Demand-driven •Breadth of learning •Delivered by experts •Flexibility •Short-course format Courses delivered by: University of Birmingham • University of Central Lancashire • University of Leeds • The University of Liverpool • The University of Manchester • The University of Sheffield • The Nuclear Department, Navy Command
Four key factors shaping the future of warehouse automation
Available and emerging, high-performance warehouse technology will determine the future productivity of fulfilment operations. Nick Hughes, Sales Manager at independent systems integrator, Invar Group, shares his insights into the key influences and technologies shaping the modern warehouse.

1. What’s driving warehousing strategies?
Ultimately, it’s customer service levels. Customers have ever-higher expectations regarding service levels and this is driving huge change in the warehouse. Along with the rapid growth of ecommerce, there is a strong desire to develop faster fulfilment strategies and importantly, equally efficient returns processes.
A key SLA for any ecommerce business keen on growing and retaining a healthy customer base is the speed with which customers are credited back on returned items – and that requires fast processing of returns. Likewise, multi-channel
businesses will need to progress to develop slick omni-channel operations capable of offering the diversity of service options that customers now demand. And a key enabler will be automation.
A lack of available labour is another factor influencing thinking within the four walls of the warehouse. But it’s not just a shortage of labour per se, the key thing is there’s far more volume going through piece picking warehouses in the last few years, so the number of people required is not able to keep pace with the increased demand. It’s stretching the labour pool that is there, and this, combined with a growing requirement for increased capacity, is a big driver for automation.
2. What technologies are emerging?
With the cost of labour rising and availability falling, businesses will have little option but to adopt higher levels of automation, and in many instances that means robotics. Their low-cost, excellent flexibility and great scalability makes them the ‘must have’ warehouse technology of today.
However, with robots gaining critical momentum within the warehouse, protocols supporting them will need to become more standardised, so that various types of robots can be deployed to perform different tasks under one controller. Customers will demand flexibility to use the best robots suited to individual tasks and the industry will need to move in this direction. This will significantly simplify the deployment of robots.
Augmented Reality (AR) is also likely to start appearing in warehouses in the near future. Trials are in progress at the moment for AR glasses that can be used to guide an individual to picking locations. In a way, it’s like a SatNav for the warehouse, but offering a head-up display with information, so no need for a handheld terminal. The issue at present is cost, but hopefully, prices will come down as the technology takes off.
32 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Automation
Customers will demand flexibility to use the best robots suited to individual tasks and the industry will need to move in this direction.
Nick Hughes
Cobots too will soon become more commonplace, working alongside pickers and warehouse staff. And once the technology around grippers is improved, they will be seen travelling around doing the picking too. The vision systems and AI are there, it really just needs a breakthrough in gripper design to offer the dexterity needed for a broad product portfolio.
3. What technologies and applications are currently seeing most interest?
At the moment there is huge interest in flexible tote handling systems using Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs). When combined with pick-to-light technology, phenomenal pick-rates can be achieved with exceptionally high levels of accuracy.
Importantly, SMEs have a great opportunity to steal a march on larger retailers that may have committed to inflexible, fixed automated systems.
By adopting intelligent software and advanced mobile robot technology, SMEs can leverage the flexibility, speed and performance of goods-to-person automation as a low-CapEx project.
AMRs offer tremendous flexibility and, importantly, scalability in traditional labour-intensive tasks such as order picking and put-away. AMR systems
combined with pick-to-light technology can boost order picking performance from under 100 units per hour using traditional methods, to up to 600 picks per hour, with an ROI that can be as little as 12 months.

4. A new approach to automation from 3PLS.
Interestingly, 3pls are beginning to explore a new approach to winning business. They are looking at putting automation in first and then approaching customers with a solution in place. The driving factor is, end customers want to see sites that offer automation as a ready-to-go solution.
This emerging trend requires service providers to speculatively invest in
automation on the assumption that appropriate customers can be found. Their task will be to target industries that have a profile that matches the automation on site.
Robotic systems are becoming easier to deploy and can be simply expanded as required. A low-level, high SKU or high volume storage system may be adopted with a few robots and added to as more customers come on-stream – perfect for a multi-user facility.
Importantly, the modus operandi of logistics service providers will need to change from acquiring a customer and running a manual operation for a few months, before taking in robots, to adopting automation in advance and then finding appropriate customers. At present, a number of 3pls are investigating this approach.
With all the productivity gains that can be achieved through the judicious application of robotics and AI, the future of warehouse automation looks bright.
Further independent advice on the latest technologies transforming operational performance in the warehouse can be found at: www.Invargroup.com
33 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Automation
Robotic systems are becoming easier to deploy and can be simply expanded as required.
Nick Hughes
Automation Helping UK manufacturers climb the automation ladder
It’s no secret that despite its position as a top 10 manufacturing economy, the UK lags well behind its global counterparts when it comes to our use of industrial robots. According to the 2021 IRF World Robot Report, the UK ranks just 24th in the world robot density league with 101 units per 10,000 employees, far outpaced by countries such as China, Japan, Korea, the US, Germany, Italy and France. Globally, however, it is a promising picture – the average figure of 126 robots per 10,000 employees is nearly double what it was in 2015. This makes the UK’s continued reluctance to automate all the more surprising. Here, Oliver Selby, Robotics Business Development Manager at industrial robot specialist FANUC UK, shares his thoughts on what could be holding the UK back, how companies like FANUC are helping to drive a change in mindset, and the surprising positives to come out of the pandemic…
we need more robotics users to come forward and say so. Most plants find that investment in robotics actually leads to productivity gains, company growth and, subsequently, the need to employ more people.
industries, such as food, but this has been the exception rather than the rule – it’s always ‘next year’ with UK companies. Manufacturing and process plants here tend to dip their toe in the water regarding investment in automation, unlike their counterparts in mainland Europe who are more inclined to throw themselves in. That being said, things are steadily beginning to change, with more companies across all industries now waking up to the benefits of automation. Enquiry levels are holding steady in the UK and we predict that sales of FANUC robots will be reasonable this year.
What part does education have to play in changing the UK mindset around automation?
There’s a long-standing misconception that automated solutions including robots take the place of production workers. In actual fact, this is not the case but
Labour shortages post-Brexit and the much-debated ‘Great Resignation’ following the pandemic have prompted some recent investment activity in certain
I believe that educating young people on the benefits of robotics and automation can hugely help to alter our national perception that robots are the ‘enemy’. Robot arms can now be found in schools, colleges, universities and training centres up and down the country. At FANUC we’ve had cost-effective educational cell packages available for the past seven years, with increasing uptake, thanks in part to our role as a sponsor partner of WorldSkills, a global vocational skills championship that helps prepare young people for a career in robotics. We sell around 25 educational cells into the UK every year, with the latest package featuring a FANUC CRX-10iA collaborative robot.
In general, UK companies have trouble relating to the added value that connected or smart technology brings. However, we are talking to some UK plants about adopting higher levels of digitalisation via our open-platform FIELD system, which stands for FANUC Intelligent Edge Link and Drive. The FIELD system can connect robots and machine tools of different generations from all manufacturers and with FIELD system apps, companies can monitor, measure and analyse data to improve production efficiencies.

34 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Why do you believe some UK manufacturers are still reluctant to automate?
Do you believe that UK manufacturers are fully aware of the benefits of digitalisation?
Q&A with Oliver Selby, Robotics Business Development Manager, FANUC UK
I believe that educating young people on the benefits of robotics and automation can hugely help to alter our national perception that robots are the ‘enemy’.
Oliver Selby
The automotive industry’s transition to electric vehicles is high on our agenda. Hopefully, we are seen as the market leader for both battery and EV manufacture, particularly as FANUC is at the heart of all Tesla’s automated production in the US and Germany. The UK is planning to build a number of gigafactories for battery manufacture, but if these gigafactories are looking at space and buildings, they should also be looking at the associated automation infrastructure – particularly given the current global supply chain issues.

There is certainly a growing appetite for digital transformation among UK manufacturers, particularly in key growth markets such as food processing and packaging, making it an exciting time to be involved in the automation industry.
Oliver Selby
If people commit, we will work with them commercially to ensure we manage any risks effectively.
Despite its challenges, one of the positives to come out of the pandemic was the fact that it accelerated digitalisation. Businesses that had already embraced automation were shielded from some of the immediate operational challenges caused by lockdowns and social distancing. This has prompted a shift in tone towards the benefits of automation rather than barriers to implementation.
Of course, there’s still a lot of work to be done to bring us in line with our international peers, but I do feel as though the tide is beginning to turn.
Readypower Group switches to the Toyota Corolla Commercial
Specialist rail and infrastructure services provider Readypower Group is replacing its fleet of diesel vehicles with 45 hybrid electric Toyota Corolla Commercial vans. The new vehicles will be in service from October, used by the company’s engineers to support clients across the country.


Readypower Group is a market-leading asset hire business with a specialist civil engineering division. Operating out of six principal hubs and additional satellite facilities across the UK, it supports customers in a wide range of sectors, including rail, power, highways and regulated infrastructure.

Tony Buckland, Transport Manager from Readypower Group said: “We have been running diesel vans and were keen to address the issue of our vehicle emissions. We looked at diesel models available on the market, but by choosing Corolla Commercial hybrids we have been able to reduce our average fleet CO2 emissions. There is a further positive as we are supporting British industry with the vans being built here in the UK.”
There is certainly a growing appetite for digital transformation among UK manufacturers, particularly in key growth markets such as food processing and packaging, making it an exciting time to be involved in the automation industry.
Neil Broad, General Manager One Toyota Fleet Services said: “Our Corolla Commercial enjoys a unique position, being the only full petrol hybrid electric van available in the UK market. Its efficient hybrid system is self-charging, so businesses do not have to factor in vehicle downtime for recharging. This makes it a practical and attractive proposition for customers who are not yet in a position to adopt fully electric vehicles.”
Corolla Commercial is built at Toyota UK’s manufacturing plant in Derby and is derived from the Corolla Touring Sports passenger car. Available in a single equipment grade, its high standard specification includes the full complement of Toyota Safety Sense active safety and driver assistance features.
Do you feel we are on the cusp of an electric vehicle revolution here in the UK?
Are you optimistic about the future for UK automation?
35 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Automation
Electrifying Automotive Trend Predictions for 2023
As the world turns its focus to sustainability and clean power, rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is restoring confidence in this sector in the post-pandemic world.
Fuelled by battery-powered electric motors instead of the internal combustion engines (ICE) found in traditional petrol and diesel vehicles, these cars have the potential to generate significant energy savings worldwide.
As automakers navigate supply chain issues and ramp up the development of EVs and organisations continue to advocate for low-carbon mobility, these once seemingly futuristic vehicles will soon shift from a novelty to the norm on our roads.
However, as the cost of electricity rises sharply alongside the price of motor fuel, car manufacturers have new challenges ahead to ensure motorists have access to high-quality, economical EVs before the 2030 ban on new petrol and diesel car sales in the UK.
So, what is driving development within the EV market, and what can consumers expect to see in the coming years?
The background of electric vehicle development

The benefits of EVs compared to traditional petrol and diesel cars have been widely reported, contributing to the growing demand in this industry.

Pure-electric cars or battery-powered electric vehicles (BEVs) are run solely on electric motor power and typically have an average range of approximately 100 to 350 miles. These models do not have exhaust pipes and create no emissions, making them the most environmentally friendly choice.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) run on electricity from a small battery and petrol or diesel fuel. Their maximum range is usually between 15 and 30 miles, after which the car will switch to fuel power until the vehicle recharges.
Alternatively, hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) do not have a plug but use kinetic energy from regenerative braking to recharge their batteries on the move.
This developing branch of the automotive industry produces cars that are quieter, more cost-efficient to run and have better resale value. Due to their many advantages for drivers, roads and the planet, there are several governmentbacked incentives to owning an electric car, such as not paying congestion charges, financial grants and free parking in some places.
36 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Automotive Electric Vehicles
Phil Simmonds, CEO of global electronics manufacturing services provider EC Electronics, outlines developments and trends within the electric car market.
As a result, 2022 is predicted to be another record year for the EV sector, with online marketplace heycar recording a 17.7% increase in new EV registrations in May 2022. Demand for used electric cars is also growing, increasing by 119.2% last year as new models enter the market and national charging infrastructure expands.

With OEMs and start-ups constantly churning out innovative new EV designs, the electric car market is forecast to continue this upward trajectory in 2023 and beyond. But could the current supply chain issues presented by the fuel crisis and war in Ukraine prevent the automotive industry from reaching its full potential?
Driving toward a greener future
We have reached a tipping point for electric car adoption as consumers grow more receptive to the many advantages of EV technology.
Consequently, electric car manufacturer Tesla has set ambitious targets, forecasting production that could see the company end 2023 with sales of over 2.1 million EVs. Top automakers like Audi, BMW and Chevrolet are also preparing to launch a wave of new electric cars next year to suit a broader range of applications.
However, the automotive and electronics manufacturing industries still face obstacles to developing new products. Shortages of semiconductors and other digital components continue, and the price of materials, labour and energy will keep rising alongside inflation.
Following COVID-19 and the Ukraine war, the cost of charging an electric vehicle has climbed steeply — as much as 42% in four months, according to the RAC —
Consequently, electric car manufacturer Tesla has set ambitious targets, forecasting production that could see the company end 2023 with sales of over 2.1 million EVs. Top automakers like Audi, BMW and Chevrolet are also preparing to launch a wave of new electric cars next year to suit a broader range of applications.
Phil Simmonds
Automotive Electric Vehicles
More affordable EVs are on the horizon. BloombergNEF research predicted that BEV prices will reach parity with ICE vehicles in all European light vehicle segments between 2025 and 2027, thanks to rapidly evolving battery technology and manufacturing capabilities, making EV production less expensive.
The UK government has also invested £20 million for the 2022–2023 financial year to develop suitable charging point infrastructure to help overcome the socalled ‘range anxiety’ that deters many people from opting for an EV. Range, efficiency and fast-charging capability will become key differentiators between models moving forward.
making EVs more of a luxury purchase than an accessible alternative to ICE vehicles. Still, this is a symptom of the economic turmoil plaguing almost every sector — one that will ease in the long term.
With efficient supply chain management and investment in local manufacturing, automotive developers can mitigate the impact of ongoing disruptions on largescale EV production and make dreams of a net-zero future a reality.
Following COVID-19 and the Ukraine war, the cost of charging an electric vehicle has climbed steeply — as much as 42% in four months, according to the RAC — making EVs more of a luxury purchase than an accessible alternative to ICE vehicles.
Phil Simmonds
Robotics
Reaping the robotics rewards in the manufacturing sector
 By Mikko Urho, CEO, Visual Components
By Mikko Urho, CEO, Visual Components
In previous decades, the idea of man and machine co-existing together was more the work of fiction than reality. Now, robots are increasingly becoming a part of our daily lives, whether it’s via virtual means or on the factory floor. Recent statistics show that there are an estimated 2.7 million industrial robots in use across the globe, and almost nine-in-ten (88%) organisations plan to invest in robotics. As adoption continues to grow, what do manufacturers need to consider when aiming to get the best out of the technology?

The role of robotics in Industry 5.0
There are a number of benefits provided by robotics in the manufacturing space. They can automate repetitive, menial tasks such as assembly or material handling, freeing up time for employees to apply their skills elsewhere. While humans can be prone to error in these situations, robotics enables tasks to be completed more quickly and with greater accuracy and repeatability. It’s these capabilities which place focus on robots acting as a collaborative partner to human resource, and aligns closely to the core concept of Industry 5.0.
While Industry 4.0 has largely centred on uptake of internet connectivity and artificial intelligence to bring smart manufacturing systems to fruition, 5.0 brings with it the aim of enabling professionals to work hand-in-hand with these innovations. Robots are therefore a key cog in the 5.0 machine, but they must be implemented effectively for manufacturers to derive full value.
Mikko Urho
Take for example a robot with insufficient reach to be able to effectively interact with objects in its work cell. A poor design process before deployment can create a costly defect that requires immediate rectification. The key to avoiding this and any unwanted costs or downtime is ensuring that robots are programmed correctly from the get-go.
Robot offline programming

Robot offline programming (OLP) capabilities give manufacturers the ability to program robots independently from the cell, before being uploaded to the real robot for execution. Visualising this cell in a 3D simulation can enable organisations
to refine specific movements, actions and logic. It’s these abilities that have recently been integrated into Visual Components’ product offering with its acquisition of Delfoi, a pioneer company in OLP solutions worldwide.
Alongside layout design, feasibility and control logics, programs and processes validation, the inclusion of OLP into the Visual Components portfolio will essentially make a onestop-shop for digital transformation of production systems a reality. This enables manufacturers to significantly reduce instances of downtime and improve the accuracy of robotic programming processes. With the role of humans core to Industry 5.0 progress, access to a number of disciplines from just one solution will enable manufacturers to upskill workers at a time of widespread shortages in the technology industry.
Ramping up robotic capabilities
The use of robotics in the manufacturing industry only looks set to achieve wider uptake in the era of Industry 5.0, from automotive applications to component builds. This will only escalate as manufacturers look to meet evolving customisation requirements from consumers, uphold sustainable practices and meet the increased need to upskill the current workforce. As manufacturers bring robotics technology onto the factory floor, ensuring that it provides full value and a sufficient ROI is critical to success. Manufacturers can access a range of solutions, underpinned by the trial-anderror approach offered by easy-to-use 3D simulation software, to take their next steps in digital transformation.
38 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
There are a number of benefits provided by robotics in the manufacturing space.
Tackling the threat of Fluid Injection Injuries
The British Fluid Power Association (BFPA) promotes the highest working standards in fluid power through training and education and aims to support fluid injury accident management with its essential booklet Fluid Injection Injury Booklet “THE FACTS”.
BFPA’s Fluid Injection Injury – The Facts Booklet
This handy top-pocket sized booklet is available from the BFPA, covering the background, symptoms and treatment of fluid injection injuries –identifying people who are most at risk and how such an injury should be treated. Every booklet now comes with a wallet sized plastic card detailing the emergency action steps to take immediately after an injury.
Fluid Injection Injuries have been known to occur at pressures as low as 6.9 bar (100 psi) which means the people most at risk are not just limited to those who work within the mobile replacement hose business, but anyone who works with equipment under pressure which uses oil (hydraulic) or air (pneumatic) as the medium, or even bystanders in the wrong place at the wrong time.
The Fluid Injection Injury Emergency Fact Book covers the following:

ACCIDENT MANAGEMENT
• How to Treat a Fluid Injection Injury
• Treatment and timeline
• Guidelines for optimal treatment (for the medical professional)
• Site of Injection
• Injection Injury Patient Information Sheet
• What to look out for: Step by step progression of high-pressure injections
RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
• Abstract
• The People Most at Risk
• Material injected
• Identifying the symptoms
• Outcomes
To order your copy of the BFPA Fluid injection Injury booklet, visit the BFPA’s website www.bfpa.co.uk/ publications or call us on 01608 647900


NOT KNOWING IS NOT AN OPTION





INDUSTRY RECOGNISED COURSES FROM THE BFPA
The BFPA have for many years been passionate about raising standards within the fluid power market and industry as a whole, with this objective in mind we have created a suite of valuable training courses now available.

FOUNDATION
SAFETY COURSE
This course has been developed to provide an introduction into hose, connectors and the safe assembly of these components for industry use. During the day the attendee will gain a knowledge and understanding of safe hose assembly and if applied will only enhance the safety within the hydraulic industry and the attendee.
HOSE ASSEMBLY SKILLS COURSE
The skills course will take the candidate through the many techniques and considerations essential for the safe production of a quality hose assembly and ultimately leading to installation. This two day course involves both the theoretical and practical elements in working with hose and connectors.

SMALL BORE TUBING
INTEGRITY COURSE
Delegates are offered a valuable understanding of the complexity surrounding small bore tubing and compression fittings. The course covers generic manufacturers twin ferrule compression fittings, thread awareness, tube and pipe differences and the preparation process, tube manipulation (bending) principles, common installation and routing techniques.
HOSE INTEGRITY, INSPECTION & MANAGEMENT
The key themes covered during the one-day course include: hose life expectancy; risk analysis; competence by way of a robust competence assurance system; identify, inspect & record; hose register –recording of a hose assembly prior to it going into service; and visual hose assembly (installation) inspection check list.

HYDROSTATIC PROOF PRESSURE TESTING
The course will help give the delegate a greater understanding of the dangers associated with pressure testing. During the one day course the delegate will learn how to safely test hose and connector assemblies by taking into account a safe system of work best practice procedure (HSE GS4 document) along with relevant pressure test standards commonly used within industry.
39 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Health & Safety
Courses can be delivered face to face or online for more information or to check availability please visit: www.bfpa.co.uk/training Please call 01608 647900 or email enquiries@bfpa.co.uk 17923 TA_Half_Page_Ads_AW.qxp_Layout 1 04/01/2021 13:25 Page 1
Powering research and discovery Motors
In May 2021, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft left its study asteroid Bennu to return back to Earth. Scientists will use the rubble it brings back to learn more about how the planets formed and how life arose on Earth. This is just one example where a technological feat is aiding research. Here Stewart Goulding, managing director of precision drive system supplier, EMS, explores how and where advanced micromotor technology is facilitating investigation and experimentation projects.
While new ideas, creative leaps and pure chance can all play a role in new scientific discoveries, technological advances provide the supporting resources to make new concepts a reality. Due to their ability to complete tasks independently and at a faster rate, automated equipment has accelerated research in a number of industries.
Laboratory labour
One area where automation has made waves is in laboratories. Previously, testing samples was a tedious process, filled with manual mixing, transporting and handling of samples. Now, motorised equipment takes on many of the simpler laboratory tasks, allowing staff to have more time to focus on innovation.
For instance, a motorised conveyer belt can transport samples around the laboratory to its designated station. There, a robot can pick up the sample and scan its barcode using an onboard camera to identify it and decipher what type of analysis is required.

Using its motorised arm, the robot then places the sample into the appropriate piece of laboratory equipment, such as a centrifuge or a spectrophotometer. Motors are also found in these pieces of equipment, helping to power the spinning force in centrifuges, and positioning the sample mounts in spectrophotometers.
Laboratory automation can aid medical research, such as in the analysis of samples from patients in a clinical trial, and also speed up drug discovery by enabling high throughput screening of potential new medicines against a compound library.
Shoot for the stars
The benefits of micromotors in research aren’t solely confined to the four walls of a laboratory. There are projects where micromotors are traveling hundreds of millions of kilometres away from the ground as part of explorative space missions.
Rovers allow us to explore planets and other celestial bodies without sending humans into space. After landing on a surface, the rover can travel across it while taking photos and collecting samples.
A rover can have up to 20 cameras onboard, which can be used for navigating during landing and traversing the surface, and for sending images back to scientists on Earth for study. The pan and tilt functions of the cameras, along with the lens filters, are controlled by micromotors, and allow panoramic photographs to be taken.
Along with capturing images of the study environment, rovers are tasked with collecting rock samples. Here, micromotors power the drills that excavate the rock, and the robotic arms that place the samples in a safe chamber. Once transported back to a laboratory on Earth, the rock pieces can be used to discover the biological and geological history of the body.
Meeting high requirements
Precision is vital in scientific research to achieve accurate and reliable results. Therefore, it’s important to build automated equipment using dependable and high quality components.
EMS is the sole UK supplier of FAULHABER motors, which are all made in a finely controlled manufacturing process that ensures they perform with reliability and repeatability. They also deliver high power in a small space envelope, helping to keep research equipment compact, which is beneficial when trying to fit between other laboratory equipment or transporting into space, for example.
Technology is an integral part of research, providing the support required to study the unexplored and test out scientists’ hypotheses. With the help of precision micromotors, automated equipment can act as research assistants, performing tasks independently from the depths of the oceans to outer space.
40 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Micromotors play a key role in scientific study and experimentation
Precision is vital in scientific research to achieve accurate and reliable results.
Mikko Urho














THE NORTON RAPID RANGE www.nortonabrasives.com sga-uk@saint-gobain.com STRIPPING & CLEANING BLENDING & CONDITIONING FINISHING & REFINING SCAN FOR VIDEO SCAN FOR VIDEO SCAN FOR VIDEO
Finding Alternative Motors Motors
By John Walters, Technical Engineer at maxon
maxon’s DC motors operate with higher torque and speed at smaller sizes due to the revolutionary maxon technologies developed in the company’s 60-year life span. Due to the constant update in both winding and magnet technologies, motors can go into NRND (Not Recommended for New Designs) status and become obsolete. It is a standard process to replace older motors with more modern options, perhaps for a more compact design or for competing lead times or pricing.
Technology updates result in improvements in efficiency and torque, and speed output; whilst this is highly beneficial for placing newer and smaller motors in tighter applications, it can cause problems for integration into legacy designs. In most cases, finding a close match with previous maxon products is possible.
A range of parameters should be considered when replacing DC or BLDC motors. These are:
Motor Behaviour: Speed-torque gradient, speed constant, and torque constant are critical values, as these
John Walters

directly correspond to how the motor responds to current and voltage. These values are characteristic of the motors’ behaviour and must be compared to the previous product to ensure they behave similarly.
Power Limitations: Maximum speed, peak torque, continuous/nominal torque and available power supply voltage and current are essential to ensure that the power supply can achieve the required operation points to match the prior motor.
Motor Type – DC (Direct Current):
maxon’s DC motors are typically used between 4000 and 9000 rpm and have no magnetic cogging, simple operation and high acceleration. Graphite brushes or precious metal brushes with CLL (Capacitor Long Life) are important as these determine how the mechanical commutation through the brushes occurs. Graphite brushes are typically used in larger motors with high load currents, in start/stop and reverse operations and with PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) power stages. Precious metal brushes are typically used in smaller motors in continuous operation with smaller loads and battery operations. CLL is also important as this reduces spark generation in precious metal commutation.

Motor Type - BLDC/EC (Brushless Direct Current/Electronic Commutation): maxon’s EC motors have speeds of up to 120,000 rpm and long service life, and reach high torques and speeds. Variables for EC motors include sensored or sensorless, commutation electronics and inclusion of integrated electronics. Sensored EC motors commutate using information from hall sensors, while sensorless motors use back EMF at high speeds using a speed-dependent pause. Some maxon EC motors, the EC flat range for example, have integrated electronics such as encoders.
Electrical Interfaces: Electrical interfaces to motors directly affect how the motor is powered and how communication takes place. The electrical interfaces have numerous variations, such as the terminals and cabling type, length and their respective connectors. Different
42 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Precious metal brushes are typically used in smaller motors in continuous operation with smaller loads and battery operations.
brands may use different cabling and terminals so adapter wiring harnesses may be required.
Mechanical Interfaces: Mechanical interfaces are the way the motor connects to the external components. These include flange geometry, shaft geometry, maximum diameter/length and bearing types. Flange and shaft geometry varies from motor to motor and company to company, so this is a common area for problems when specifying new motors. Bearing types come in two categories, sintered sleeve and ball bearings. Sintered sleeve bearings are suitable for continuous operation at a lower cost, whilst ball bearings are suitable for all operating modes at up to 100,000rpm and with higher experienced loads.
Combinations: For maxon’s mechatronics systems, hundreds of thousands of combinations are available. The options include the motors and their respective windings and modifications, gearboxes and their respective ratios, encoders and their respective resolutions, screw drives, brakes and controllers. It is important to match these combinations closely in specification with previous motors to achieve similar performance.

Commercial Aspects: maxon’s motors can be significantly modified, which can cause complications when bringing older modifications into newer specification
motors. Another consideration is the quantity, product availability and delivery dates.
The following factors may also be relevant depending on the operation and scenario of the previous specification motor:
Operation: If the previous specification motor was being used with extreme environmental conditions such as high temperature, high vacuum or intense vibration, an off-the-shelf solution might not be appropriate as a replacement, and further customisation may be required.
Duty Cycle: Motors work outside of a “continuous operating zone”, but only for a duration limited by the thermal time constant of the winding. Sometimes in cases that experience either increased torque or speed, the motor operates outside of this zone and to prevent damage and overheating, the motor is required to work intermittently. It is essential whilst specifying motors to consider the motor’s duty cycle, and if it is intermittent, to know both the on-time and the off-time of its operation.
Motion Profile: The motion profile can be essential to determine the motor’s root mean square (RMS) torque to know if the motor is operating outside its continuous operating zone. There is a range of different profiles; these are “General”, “Symmetrical”, “3/3 Trapezoidal”, and
“Triangular”. Symmetrical profiles are used to travel over long distances at a limited velocity, 3/3 Trapezoidal for minimal power useable and thermal improvements, and triangular for a limited acceleration of force and a lower time requirement.
Once the qualified engineers know these parameters at maxon, a set of the previously stated factors can be calculated. These values correspond to a range of compatible motors to decide the most appropriate. It is worth noting that the flange, shaft design, and electronic solutions are likely to be the main restrictor. In cases where the design is restricted, the motor parameters will likely be slightly different and require slightly different power supply voltages and current values.
43 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine Motors
Technology
We need a modern toolbox for machine vision data challenges
The interest, innovation, and buzz around various types of artificial intelligence (AI) — machine learning, neural networks, and computer vision (CV) is well recognised. What is less recognised is the renewed interest and application of modern machine vision (MV) systems by warehousing operators and manufacturers.
MV and CV are both intelligence-based systems used for image capture, processing, and analysis. However, the speed and level at which this intelligence is gathered, distributed, and applied is one of the most distinguishing factors between the two types of technologies.
MV systems tend to be self-contained, meaning the image capture and analysis occur right there on the line — data does not have to be sent to a back-office system for processing.
On the other hand, CV is often used as a back-end processing platform for frontline image capture technologies. Though CV elicits fast decision-making and action, the lead time tends to be longer, given the depth and breadth of data being processed through the system.
Jim Witherspoon
Every company looking to implement MV systems today must decide how to share and manage image datasets and how to use them to deliver quality, actionable results on a consistent basis — data has become as important as code. However, while there are industrial practices for code management, progress needs to be made for managing image data.
One of the biggest challenges we face today, whether as MV specialists or businesses looking to implement MV systems, is the correct capture and annotation of data. However, there are now new solutions to help industrial imaging professionals to think and act like data scientists.
For that to happen, engineers need modern software tools that make working with today’s machine vision systems easier and accessible within minutes of set-up.

A three-step approach to data tools
One way to conceptualise today’s need for engineers to think and act like data scientists is to set the groundwork by breaking down the process into three parts.
Stage one we could call ‘Capture,’ with a focus on setting-up the exposure, lighting, and triggering. The second stage, ‘Build,’ would aim to make is easier to add and configure MV/FIS tools. And third, ‘Connect,’ makes it painless to get
44 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
image
Jim Witherspoon, Product Manager, Machine Vision, Zebra Technologies
MV and CV are both intelligence-based systems used for image capture, processing, and analysis. However, the speed and level at which this intelligence is gathered, distributed, and applied is one of the most distinguishing factors between the two types of technologies.
data from the MV/FIS camera to the host system. With each stage, users need modern software that will augment their experience and help them get faster ROI.
For example, with ‘Capture,’ engineers could utilise a software that would allow them to capture a number of images in one go, but with each having perfect lighting. This would create a ‘perfect’ library of images. Often, parts are not evenly lit or have inspections at different depths and focus, necessitating changes to exposure settings.
With such a tool, an engineer could quickly adjust image settings, link the tool they need for the inspection to the ‘perfect’ library they’ve created, and get a pass/fail response with a single trigger pull. By eliminating the need for multiple job changes or tracking, hours are saving when deploying a system.
When it comes to ‘Build,’ how about software with the ability to draw vision tools directly onto the image? Such an approach would eliminate unnecessary clicks and drags when adding a tool to a solution. That may not sound like much, but as solutions get more sophisticated, the time savings can really add up.
And being able to capture images at the time of set-up is highly desirable—it’s when the system works best. Now, imagine being able to capture and save time-of-set-up images in perpetuity. If an issue causes the system to malfunction, the user can simply click on the image captured at the time of set-up and get a side-by-side view next to the new image.
If the camera was bumped, or a light is no longer working, or if key settings were
changed, the software would help a user quickly identify the problem and get the system back up and running immediately. Such an approach would help eliminate downtime should something happen to the camera or setup.
A powerful toolbox for a range of users
Progress is being made when it comes to dataset management, which is vital for newer machine vision systems and those who use them. Engineers need a software toolbox if they’re to become more like data scientists: no one relies on just one screwdriver to complete a complex construction job, so why rely on just one vision tool when it comes to the complexities of data capture and processing?
Another example: getting optical character recognition (OCR) inspection right can be challenging. A variety of factors including stylised fonts, blurred, distorted or obscured characters, reflective surfaces and complex, nonuniform backgrounds can make it impossible to achieve stable results using traditional OCR techniques.
However, there’s new industrial-quality deep learning OCR tools that makes reading text quick and easy. They come with ready-to-use neural networks that are pre-trained using thousands of different image samples. Such a tool can deliver high accuracy straight out of the box, even when dealing with very difficult cases. Users can create robust OCR applications in just a few simple steps—all without the need for machine vision expertise.
Even things like user interfaces can and are being improved, to reduce excessive mouse clicks and scroll bars.
Jim Witherspoon
That might sound small but the time savings add-up and the user experience feels more like working with a photo editor. Similarly, the navigation process should be intuitive for MV inspection and barcode scanning specialists as well as for novice users.


The goal is to give users—experienced experts and non-specialists alike—the best and most appropriate solutions to address their business needs, and that starts with getting to grips with better data tools.
To discuss how industrial imaging professionals can overcomes today’s data challenges, get in touch with Jim Witherspoon here
45 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
Engineers need a software toolbox if they’re to become more like data scientists: no one relies on just one screwdriver to complete a complex construction job, so why rely on just one vision tool when it comes to the complexities of data capture and processing?
Technology
New wire insert range of taps & threadformers from ITC
Following the publication of its latest threading and tapping catalogue, Industrial Tooling Corporation (ITC) is now delighted to announce the arrival of a raft of new threading products that include the new series of EG Metric Wire Insert Taps & Thread Formers.
With wire inserts or helicoils increasingly used in industry in instances where vibration can generate excessive thread wear, ITC has now launched its new wire insert thread formers to support manufacturers. In the transport industry where excessive vibration can disrupt the integrity of a thread in high-value components, such as aerospace engine casings, train and rail components – manufacturers are increasingly applying wire inserts in favour of re-manufacturing costly components. This is where the ITC thread formers serve manufacturers.
Included in the ITC range of Wire Insert Taps are the new EG Metric HSSE-PM Spiral Flute and Spiral Point taps which are manufactured from HSS powdered metal HSSE-PM, to

increase performance and longevity whilst delivering a perfect thread form. The new HSSE-PM Wire Insert Spiral Flute and Spiral Point taps are manufactured to a 6HX tolerance and the dimensions are in accordance with DIN 371/376. The Spiral flute series is available from M2 through to M20 with an overall length from 50 to 160mm depending upon the selected thread. The new Issue 7 of the ITC tapping and threading catalogue has details of all Spiral Point, Spiral Flute and the Wire Insert Thread Formers.
In the impressive new threading catalogue, ITC has also identified the respective drill required for each thread. Simplifying the selection process for the end-user, the new publication has the appropriate drill diameter in both 3XD and 5XD with corresponding catalogue pricing. So, if you want to produce threaded holes in preparation for wire inserts, you can download the new catalogue from the ITC website at https://www.itc-ltd. co.uk/products/ or you can speak to an ITC representative for more information on the extensive product lines that are available.
Walter TC130 Supreme tap with improved quality and tool life
With the new TC130 HSS-E Supreme tap, Walter is launching a premium tool for blind-hole tapping that combines many different benefits. Taking tapping to a new level, the new TC130 Supreme tap incorporates straight grooves to produce short chips, resulting in high process reliability.
The special geometry of the taps produces an exceptionally high surface quality on the threads, which improves tool life by maintaining the quality of the thread. The last thread in the chamfer section of the tool is designed to ‘finish’ the thread, this results in an excellent thread surface. The high thread quality results in improved tool life.

Walter is offering the TC130 Supreme tap for thread depths up to 3.5 x DN with a wide product range including larger thread sizes. This includes M4 to M42 (metric coarse), M10 x 1 to M33 x 2 (metric fine) and UNC ¼ to UNC 1. As well as the impressive geometry, the two coating options, TiN coating (WY80AA) and the HiPIMS coating (WY80EH) further improve the wear resistance and thread quality.
The TC130 Supreme HSS-E taps feature axial internal coolant and have a tolerance of 6HX. As the taps can be used for ISO materials P and K, users benefit in particular from the competitive advantage offered by the innovative new patentpending geometry. Preferred application areas include interference contours, deep threads, large batch sizes and series production.
Latest Product Launches 46 Manufacturing & Production Engineering Magazine
EXPERTS IN PUMP TECHNOLOGY
Our progressive cavity pumps, macerators and control systems are used across all industry sectors wherever thin to highly viscous, shear-sensitive, aggressive or abrasive media must be conveyed at low pulsation rates.

SEEPEX’s portfolio also includes digital solutions, consulting, spare parts and after sales services.
“SEEPEX stands for technological leadership, excellent management and outstanding product and application expertise. Focusing on our core competencies and know-how enables us to take the best, most forward-looking course of action for each part of our business. We identify innovative approaches that bring about positive changes for the entire industry.”
PETER MCGARIAN MANAGING DIRECTOR, SEEPEX UK LTD.
SEEPEX UK Ltd. | sales.uk@seepex.com | www.seepex.com






















































































 By Mikko Urho, CEO, Visual Components
By Mikko Urho, CEO, Visual Components


































