Foundations oF direct support: a national training program For direct support practitioners trainer’s manual Edition 2 September-November 2023 phase ii Keystone institute india B-6/22, First Floor, Safdarjung Enclave New Delhi – 110029 Tel: 011 49053451/52 | www.keystonehumanservices.org training For trainers
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners iii Table of contents i. Welcome Letter v ii. schedule vi iii. Module structure 3 iV. Modules Module 6: Promoting Health and Wellbeing 5 Module 7: Positive Approaches to Challenging Behaviour 123 Module 8: Community Membership 135 Module 9: Family Collaboration 159 Module 10: Legal Framework 175 Module 11: Advocacy & Activism 183 Module 12: Sexual Wellbeing 195 Module 13: Promoting Competency 231
Welcome to Phase 2 of the Foundations of Direct Support: A National Training for Direct Support Practitioners, Training of Trainers.
On behalf of Keystone Institute India, we would like to thank you for setting aside significant time and commitment to become master trainers of this rich and new development course to promote the competence of direct support practitioners across India. We realize that time away from typical responsibilities is a major investment of your time and energy, and we are glad that both you and your organization have committed to learning about and teaching Foundations of Direct Support for a new and respected profession within India, all working towards rich, full lives for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities.
This second phase of the Training for Trainers of the National Training for Direct Support Practitioners is a deep dive into critical subject areas that are key to person-centered support and empowerment of people with disabilities.
YOU belong to the second cadre of Master Trainers taking this high-quality, value based training to develop highly competent and sensitive Direct Support Practitioners who can support and empower people with disabilities to lead rich, valued, and meaningful lives.
We are privileged to have excellent faculty who bring with them decades of experience both on the ground and in training for this course. Many of our faculty are content experts and leaders in this space and are passionate about implementing and training in best practices.
We are also happy and honored that you have taken the time to invest in this rigorous and demanding training course, and we hope that you will leave this event with a passion and commitment to teach others and learn more. We are excited to partner with you and support your endeavours in enhancing the lives of the people you serve.
Elizabeth Neuville and Leela Raj eneuville@khs.org
 Keystone Institute India lraj@khs.org
Keystone Institute India lraj@khs.org

B-6/22, First Floor, Safdarjung Enclave
New Delhi – 110029
Tel: 011 49053451/52
SCHEDULE
PHASE 2 Trainer Preparation
Until meeting next day
• Participants to review any or all of the prerecorded presentation videos of Module 6, Section 1 & 2:
– Health & Wellbeing – Assessing Healthcare Needs
– Health & Wellbeing – Assisting with Activities of Daily Living
Until meeting next day
• Live online presentation of Module 6, Section 3:
– Health & Wellbeing – Common Health Problems & Interventions
• Participants to review the prerecorded presentation video of Module 6, Section 4:
– Health & Wellbeing – Health & Safety
• Live online presentation of Module 6, Section 5:
– Health & Wellbeing – Health & Wellness
Until meeting next day
• Participants to review the prerecorded presentation video of Module 6, Section 6:
– Health & Wellbeing – Mental Health Wellness
vi Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
1: SEPTEmbEr 4-8,
Day Time Activity Day 1: 4 Sept, 2023 04.00 PM – 05.00 PM
WEEK
2023
• Welcome & Opening of Phase 2
Day 2: 5 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 05.30 PM
House
• Open
Day 3: 6 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 05.30 PM
• Open House
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners vii Day Time Activity Day 4: 7 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 5.30 PM • Open House • Live online presentation of Module 7 –Positive Approaches to Challenging Behaviours Day 5: 8 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 6.00 PM • Live online presentation of Module 8 –Community Membership • Wrap up Phase 2, Week 1 WEEK 2: SEPTEmbEr 11-16, 2023 Day 1: 11 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 06.00 PM • Welcome to Phase 2, Week 2 • Live online presentation of Module 9Family Collaboration (Part 1) Day 2: 12 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 06.00 PM • Live online presentation of Module 9Family Collaboration (Part 2) Until next meeting
to review prerecorded presentation video of Module 10 –Legal Framework Day 3: 13 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 05.00 PM • Open House
online presentation of Module 11 –Advocacy & Activism Day 4: 14 Sept, 2023 02.00 PM – 06.15 PM • Live online presentation of Module 12 –Sexual Wellbeing Day 5: 15 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 06.00 PM • Live online presentation of Module 13 –Promoting Competency (Part 1) Day 6: 16 Sept, 2023 03.00 PM – 06.00 PM • Live online presentation of Module 13 –Promoting Competency (Part 2)
16-17 November 2023
Team Presentations
Finale
• Participants
• Live
PrACTICUm (In-Person New Delhi)
• Welcome • Pre-assigned
• Grand
Demonstration Videos for Trainer Preparation
VIDEO DEmO NAmE DEmO PrESENTEr LENGTH OF VIDEO LINK 1. Module 6: Section 1Assessing Healthcare Needs Dr. Neelam Sodhi 53 minutes https://youtu.be/4tXGijscjBA 2. Module 6: Section 2Assisting with Activities of Daily Living Dr. Neelam Sodhi 30 minutes https://youtu.be/OZ3YF78Rvlc 3. Module 6: Section 3Common Health Problems & Interventions Dr. Neelam Sodhi 2 hours, 20 minutes https://youtu.be/auVMzJv7snE 4. Module 6: Section 4Health & Safety Dr. Neelam Sodhi 30 minutes https://youtu.be/cGPdVtNVndM 5. Module 6: Section 5Health and Wellness Dr. Neelam Sodhi 1 hour 44 minutes https://youtu.be/5QEypx7UZ8U 6. Module 6: Section 6Mental Health Wellness Leela Raj 1 hour 3 minutes https://youtu.be/ux_lmGYUcb4 7. Module 7: Positive Approaches to Challenging Behaviour Aparna Das 44 minutes https://youtu.be/k0YzQ55yibE 8. Module 8: Community Membership Leela Raj & Betsy Neuville 1 hour 16 minutes https://youtu.be/JcpMsu-PP2Q 9. Module 9: Family Collaboration Session 1 Module 9: Family Collaboration Session 2 Ranjana Chakraborty, Liz Albuquerque, Chitra Paul & Geeta Mondol – do –1 hour 57 minutes 1 hour 54 minutes https://youtu.be/DJ6mQqNSoR0 https://youtu.be/Ve9j_36vhqQ 10. Module 10: Legal Framework Shampa Sengupta 12 minutes https://youtu.be/SmqZB2hDvkQ
...People learn very quickly when they have a need for the skills and information. If it will change their lives, if it will help them accomplish what is important to them, everyone can become a good learner. We learn complex competencies and knowledge in a matter of weeks, not months or years. And people learn best in community, when they are engaged with one another, when everyone is both student and teacher, expert and apprentice, in a rich exchange of experiences and learnings.
- Margaret Wheatley
phase 2: module structure
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 3
modules, Sections and Approximate Duration PHASE 2 mODULE SECTION DUrATION (Hrs) 6. Promoting Health and Wellbeing 1. Assessing Health Care Needs 2. Assisting with Activities of Daily Living 3. Common Health Problems & Interventions 4. Health & Safety 5. Health & Wellness 6. Mental Health Wellness 1.5 1.0 2.5 1.5 2.0 1.5 7. Positive Approaches to Challenging Behaviour 2.5 8. Community Membership 2.5 9. Family Collaboration 6.0 10. Legal Framework 1.0 11. Advocacy & Activism 2.0 12. Sexual Wellbeing 4.0 13. Promoting Competency 6.0
Take care of yourself, be healthy, and always believe you can be successful in anything you truly want.
module 6: promoting health & Wellbeing
- Alessandra Amrosio
Health and Wellbeing











Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 7
Something isn’t right …
Agenda
• Health Outcomes for People with Disabilities

• Assessing Health Needs
• Behavior as an Indicator of Illness
• Vital Signs
• Accuracy in Assessing Vital Signs
• Special Considerations for People with Disabilities
SECTION 1: Assessing Health Care Needs of People with Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities
8 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Health Outcomes for People with Disabilities

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 9
Assessing Health Needs

A young woman with a mild level of intellectual disability developed an earache. Her mum took her to a general physician who prescribed antibiotics for her. However, the pain continued and got worse.
Her mum then took her to the emergency department. They had to wait over five hours to be seen, and as time progressed, the pain worsened. The young woman found it difficult to cope with her pain and expressed this by sitting on the floor, rocking, making sounds, and holding her head. When the doctor came the mum tried to explain, but she was dismissed. And the doctor wrote in her chart that the woman was having a temper tantrum.
The young woman and her mum were asked to leave and return after she ‘settled down’. She died six hours later in her mum’s arms. An investigation into the cause of death identified that she had died as a result of undiagnosed meningitis.
10 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Something isn’t right…
SIGNS


SYMPTOMS





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 11
Signs on eyes/ears/nose
Changes in eating habits
Urinary changes

Signs specific to men
Signs on skin
Signs in breathing/respiration
Change in bowel habits
Signs specific to women
12 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Observe and Respond
Baseline
Medical History
Daily Life
Communication Ability
Interpreting Internal Cues
Documentation
Regular Health Checkups
Behavior as an Indicator of Illness

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 13
General Activity Level
Quiet
Restless
Drowsy
Alert
Nervous Calm
Overactive
Specific Behaviour
Refusing to eat
Crying
Holding stomach
Rubbing elbow
Jerky movements
Limping
Hitting face/head

Body Positioning
Outstretched
Twisted
Bent over
Cramped
Foetal position
Aggression or any self-injurious behaviour

Be mindful of…
Behaviour changes and trigger points for same
Changes in energy levels or losing interest in activities

Changes in sleep habits, moods or appetite


14 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
What should you do now?
What should you do first?
What should you say to John and the doctor?
∙ Tell John not to talk
∙ Talk to John about going for a blood test
• Take John immediately to the hospital
• Talk to John’s family
∙ Call John’s doctor immediately and schedule a test
• Review John’s medical history

∙ Make sure he understands what the doctor is saying, and let the doctor know he is confused by this
∙ Don’t say anything
∙ Don’t do anything, it’s John’s choice if he wants to take the test
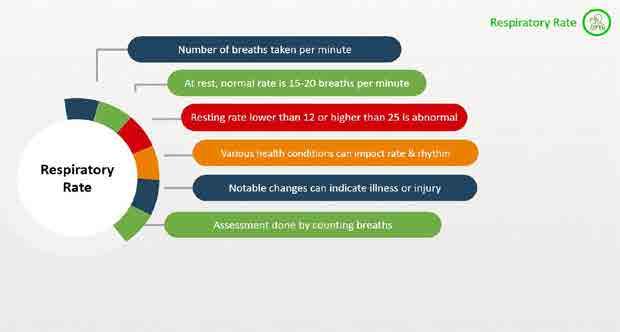
Vital Signs
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 15
Factors








16 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Age Illness Weather Medication History Infection Time of Day Exercise Emotions
Affecting Temperature Temperature












Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 17
to Assess Orally Temple Touch Tympanic Axillary Temperature Readings Hand hygiene Device hygiene Gloves Remember Temperature
Ways
Ways to Measure





18 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Radial Brachial
Pulse
Factors Affecting BP

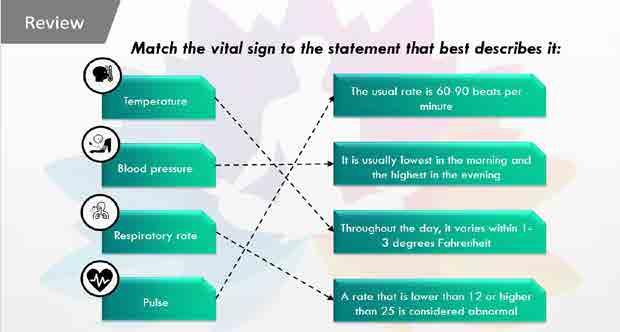
Age & Gender Medications
Weight Disease conditions
Emotions
Heredity
Viscosity of Blood
Conditions of Blood Vessels
Blood Pressure
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 19
Accuracy in Assessing Vital Signs
Gayatri has autism. During a routine check-up, the nurse briskly walked into the room and immediately placed the blood pressure cuff onto Gayatri’s arm.
This frightened her (who did not understand what the doctor was doing), which elevated her BP during the assessment. In turn, the doctor incorrectly diagnosed Gayatri with hypertension.
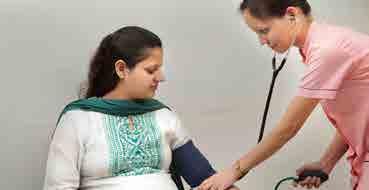
20 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Points to Note
1 2 3 4
Person’s appearance and behavior





Skin appearance and temperature
Timing of medication just before assessment
What’s “Normal” for the person

Factors Affecting Accuracy of Vital Signs

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 21
Special Considerations for People with Disabilities




22
Health
and Wellbeing

SECTION

2:
Assisting with Activities of Daily Living

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 23
AGENDA
▪ What are Activities of Daily Living


▪ Assisting with Eating
▪ Assisting with Personal Care
▪ Bathing
▪ Dental Care
▪ Hair Care
▪ Toileting
▪ Nail Care
▪ Menstrual Care
▪ Clothing
ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIVING
24 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
▪ What are activities of daily living (ADL)?
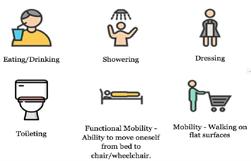
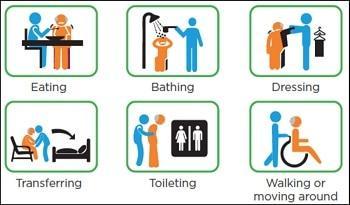
▪ Eating
▪ Dressing
▪ Hygiene
▪ Mobility
▪ What are instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) ?





ADL and Support
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 25
Potential Needs of People with IDD
Need for consistency
Assistance in making changes

Assisting with Eating
Reminders of how to perform tasks

Reminders to perform personal care tasks
Encouragement or acceptance
26 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 27
Positioning
1 Maintain good body alignment


2 Provide comfort
3 Inhibit unhelpful reflex patterns




Positioning Essentials
Ensure body as upright as possible
Ensure chair fits the individual
Ensure individual is relaxed


4 Decrease respiratory problems





Alert individuals before positioning







Prevent head from tipping back
Ensure feet are supported Reposition if required
Ensure upright position post eating
28 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Personal Care

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 29
Important Considerations
Review
Precautions
✔ Allow as much independence as possible
✔ Familiarise yourself with person-centred plan

✔ Consider use of special equipment
✔ Check water temperature
✔ Poor bathing habits increase chances of bed sores/infections
✔ Examine skin for injuries/indications
✔ Honour personal choice
✔ Wash your own hands
✔ Inadequate drying after the bath can cause fungal infections
You are helping Kantha get ready for her evening bathing routine. She requires assistance transferring from her walker to the shower chair, but otherwise performs all her own bathing activities. In the past, Kantha had slipped on the bathroom floor because the floor was wet. What should you do before assisting Kantha to the shower chair to ensure she does not slip this time?
✔ Demonstrate correct bathing procedure
✔ Close windows to prevent drafts
✔ Be wary of scrubbing the body too hard or using products that may irritate the skin
A. Remove the shower curtain
B. Spread a small towel across the floor
✔ Ensure privacy - draw curtains, close doors
C. Place the bathmat on the shower floor
✔ Gather all supplies beforehand
✔ Encourage use of toilet before bathing
✔ Guard against spreading bacterial infection from one body part to another
✔ Place a mat/towel on bathroom floor
✔ Ensure use of after-bath products to keep skin healthy
✔ Follow top-to-bottom approach
✔ Watch out for any skin irritations; report if any
✔ When finished, wash hands and straighten bath area

Guidelines
✔ Wash your hands before and after physically assisting the individual
✔ Place the head of the toothbrush alongside the teeth with the bristles at 45º angle

✔ Use a back and forth ‘vibrating’ / up and down / circular motion


✔ Brush the outer side of each tooth with this technique
✔ Repeat this technique on the inside surfaces
✔ For the inside surfaces of the front teeth, tilt the brush vertically and brush up and down using the front part of the brush head
✔ Brush the tops of the teeth using a back and forth motion
✔ Brush the tongue
✔ Don’t brush too hard
✔ Best remedy for bleeding gums is to keep brushing gently
30 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
ORAL
BATHING
CARE HAIR CARE
Even individuals who do not have any teeth or dentures need mouth care. This would include at least a daily, gentle brushing and rinsing of the gums, tongue and roof of the mouth.
TOILETING NAIL
MENSTRUAL
DENTAL
CARE
CARE BATHING
CARE
HAIR
TOILETING NAIL CARE MENSTRUAL CARE
CARE
Guidelines


✔ Teach and assist with drying hair and applying hair products
✔ Section long hair to avoid pulling and tugging
✔ Teach and assist the individual to comb or brush hair from scalp to ends
✔ Special care while handling curly hair
✔ Gentle touch
✔ Ensure cleanliness of comb/hair brush
✔ Ensure safety and dignity always
✔ Promote independence
✔ Never leave the person served out of hearing range
✔ Familiarise yourself with adaptive equipment used


✔ Follow hygiene practices


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 31 BATHING ORAL CARE HAIR
CARE TOILETING NAIL CARE MENSTRUAL CARE
BATHING ORAL CARE HAIR
CARE TOILETING
NAIL
MENSTRUAL
CARE
CARE
Keep in mind Guidelines
✔ Ensure use of product as per directions on packing

✔ Female staff only
✔ Nail care important for overall health

✔ Medications
✔ People with diabetes may require help of health professional
✔ Consent and clear communication
✔ Period flow
✔ Advisable to trim nails every fortnight
✔ Mark the date
✔ Pads – Used externally; many varieties and brands available; depends upon specific features – high absorbency, with wings, thin, etc
✔ Skipped cycles
✔ Pre-menstrual symptoms
✔ Not changing products timely can cause deadly infections

✔ Report unusual conditions

CLOTHING

32 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
BATHING ORAL CARE HAIR CARE TOILETING NAIL CARE
Health and Wellbeing



SECTION 4:
Common Health Problems and Interventions


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 33
Agenda
• The Crucial Four
• Aspiration
• Dehydration
• Seizures
• Constipation
• Other Common Health Issues
• Incontinence and UTI
• Pressure Injuries
• Allergies and Asthma
• Diabetes
The Crucial Four
34 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 35 Dehydration Constipation Seizures Aspiration 1 Aspiration 2 Dehydration 3 Constipation 4 Seizures
36 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Aspiration Dehydration Choking Dysphagia Aspiration Constipation Seizures Aspiration Dehydration Seizures Constipation
Aspiration Dehydration
Choking
Dysphagia
Aspiration
Signs
Constipation
Seizures
Aspiration Dehydration
Choking
Dysphagia
Aspiration
Indications
Constipation Seizures
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 37
38 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Dehydration Aspiration Constipation Seizures Aspiration Dehydration Choking Dysphagia Aspiration Behavior Other Signs Interventions Risk factors Common foods Case Study Constipation Seizures
Signs
Risk Factors Causes Prevention & Interventions
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 39 Dehydration Aspiration Constipation Seizures Dehydration Aspiration
Constipation Seizures
Aspiration
Dehydration
Constipation
General Signs
Specific Signs
Factors
Factors
Seizures
Aspiration
Dehydration
Constipation Example
Seizures
Risks
Causes
Triggers
Signs
Treatment
Response
Seeking Medical Help
Helping Manage
Reporting and Documenting
40 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Risk
Alerts Influencing
Prevention Treatment Example Review
Choking - Signs
Dysphagia
Pain while swallowing
Choking/coughing
Indications of Dysphagia
Food getting stuck
Chest pain/pressure
Heartburn/acid reflux
Unexpected weight loss
Food remaining in the mouth
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 41 Dehydration
Aspiration Gurgling sounds Constipation Seizures Unable to talk Look panicked Loose consciousness Cough Forcefully Clutch their chest Skin turning bluish Wheeze 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 Signs of Choking Dehydration
Aspiration Constipation Seizures
Sarla has cerebral palsy Sarla loves cup cakes

She has trouble swallowing and her food is pureed
She longs for ‘real’ food and has a history of grabbing food
Neighbour brings cupcakes for a birthday party
Sarla grabs one when you are not looking Sarla looks agitated and soon becomes unconscious.
You give CPR and call for help, but .it’s too late!
42 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Dehydration 02 Coughing or choking during meals 04 Coughing/clearing the throat before/after swallowing 05 Food and fluid falling out the person’s mouth 10 A gurgling voice during or after eating or drinking 09 Runny nose, sneezing or persistent coughing during or after meals 08 Difficulty swallowing or chewing 07 Getting tired during a meal 06 Feeling something stuck in throat 01 Watering eyes Behavioural Indications Aspiration Constipation Seizures 03 Irregular breathing, turning blue, wheezing or rapid respiration Dehydration Example Aspiration Constipation Seizures
Risk Factors
Risk Factor - Foods









Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 43 Aspiration Dehydration Grapes 01 Peanut butter 02 Sandwiches 03 Whole, raw vegetables 06 Dry, crumbly food 04 Hard nuts 09 Dry meat 05 Candy with nuts 08 Whole hard fruits 07
Constipation Seizures Aspiration Dehydration Acid reflux Having decreased muscle tone or coordination Inadequately trained staff Weak/absent coughing/gagging reflexes Poor chewing/swallowing skills 05 01 02 03 04 Poor self-eating skills or habits Inappropriate fluid consistency and/or food textures Medication side effects 08 0 7 06 Epileptic seizures Impaired mobility Difficulty holding head up/sitting up straight Problems with oral or dental health 09 10 11 12
Constipation Seizures












44 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Dehydration 01 02 03 04 Identification and planning Prevention is critical Observation Intervention and Supervision
Aspiration Constipation Seizures Aspiration Dehydration Awareness & Training Diet modification Alteration of Body Position Interventions Constipation Seizures
Important to Remember
Based on your knowledge of swallowing problems, what could have gone wrong?
- Dhoni should have been hospitalized when he got a chest cold


- The thickened orange juice Dhoni drank did not allow him to swallow pills effectively
- Dhoni should not have had his medication in a tablet form

- Dhoni should have had medications before his breakfast

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 45 Aspiration Dehydration
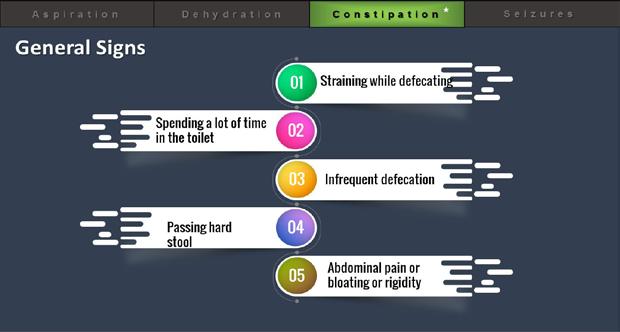
Review Constipation Seizures Aspiration Dehydration Constipation Seizures
Signs
Causes and Risk Factors
46 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Aspiration Access difficulties 01 Assistance needs 02 Dyspha gia 03 Drooling 04 Suppression of thirst mechanisms 06 Refusal of food and fluids 05 Communication difficulty 07 Medical conditions 08 Fluid loss from other conditions 09 Effects of medication 10
Dehydration Constipation Seizures Aspiration 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 Dry, hard stools Constipation Dark colored urine Decreased urinary output Fever Dry skin or chapped lips Extreme thirst Lethargy or decreased alertness
Dehydration Constipation Seizures
Aspiration
Prevention
Regularly offer water throughout the day Understand the person’s communication style
Be aware of other medical conditions
Interventions
Pay attention to any weather changes
Urine or stool pattern changes
Medications
Offer fluids if the person is alert and can drink safely Else contact healthcare professional for intravenous fluids
Example
Wilson – 24 year old with moderate intellectual disability
Lives with 4 roommates; attends a day program
Works with Mukesh – a DSP at the day program
Mukesh notices Wilson spending a long time in bathroom
Wilson’s behavioural outbursts
Mukesh’s concern

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 47 Dehydration Aspiration Seizures Constipation
Constipation
Dehydration
Seizures

48 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 49 Dehydration Aspiration Prevention Diet 01 Physical activity 02 Medication side effects 03 Seizures Constipation Risk Factors Neuromuscular degenerative disorders 01 Spinal cord injuries or birth defects 02 Muscle weakness 03 Diets poor in fiber/fluids 04 Swallowing skills 05 Access to bathroom 06 Immobility and poor body alignment 07 Toilet routine and privacy 08 Medications 09 Hemorrhoids 10 Frequent laxative use 11 Psychiatric issues 12 Dehydration Aspiration Seizures Constipation
At the suggestion of Wilson’s physician, Mukesh helps him track his food and fluids for two weeks. Mukesh shows Wilson that he is eating balanced meals but is not drinking enough fluids. Mukesh encourages Wilson to drink more water throughout the day. Wilson’s physician also prescribed him a laxative that he could take as needed. Because of Wilson’s depression, he was not getting as much physical activity as he needs. Mukesh helped Wilson choose activities that he enjoyed and could practice every day, including taking walks around his neighborhood.


50 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Dehydration Aspiration Review Seizures Constipation
Aspiration
Dehydration
Treatment Medication Manual Modalities Seizures Constipation
Meet Meena and Richard
Richard - a 35-year old man with a mild intellectual disability who lives in the community.
Meena - a new DSP working with him
Meena’s been told Richard has seizure disorder; limited details given by her supervisor
Richard’s seizure during grocery shopping
Dazed look
Lip smacking
Loss of bladder control
Meena is clueless and helpless
Meena realizes there’s a lot she needs to learn
Seizures
• Epilepsy is another name for seizure disorder
• More prevalent for people with developmental disability

• May impact daily living skills
• Is a spectrum condition

• Seizures vs Convulsions

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 51
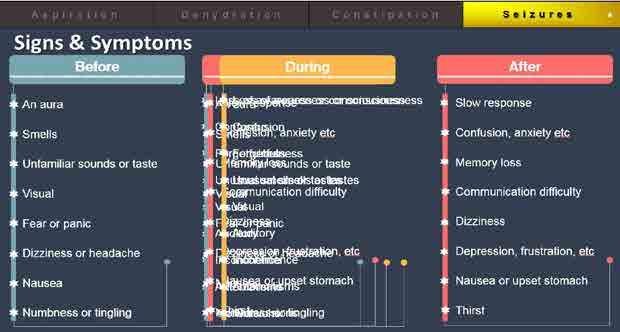
Dehydration Aspiration
Constipation Seizures








52 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Dehydration Aspiration Congenital issues Electrolyte imbalance Low blood sugar Stroke Head injuries Infections Medication non-compliance 01 02 03 04 05 06 07
Constipation Seizures Dehydration Aspiration Risks Constipation Seizures Loss of consciousness Cognitive damage SUDEP 1 2 3
Causes









Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 53 Dehydration Aspiration Triggers Stress Poor nutrition Missed medication Flickering lights Skipping meals Illness/ allergies Lack of sleep Emotions Heat/ humidity Constipation Seizures





54 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Response to seizure Stay with the individual until the seizure is over Call for medical help if seizure lasts for more than 5 minutes Keep the individual comfortable and safe from injury If in public, keep onlookers away Don’t hold the person down or put anything in their mouth Don’t give any pills/water/food until the individual is fully alert Stay calm and supportive Dehydration Aspiration Constipation Seizures Dehydration Aspiration Treatment Surgery 02 Medication 01 Dietary therapy 03 Constipation Seizures
When to call for medical help

Multiple seizures happen one after the other without the person regaining consciousness between seizure episodes
Seizures happen closer together than usual for that person
If the individual appears to be choking or having trouble breathing
The seizure happens in a body of water, such as a pool or bathtub
The person injures themselves during a seizure
This is the first seizure the person has ever experienced Seizures that last for five minutes or longer
Helping to Manage

Information
Community
Empowerment

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 55 Dehydration Aspiration
Constipation
Seizures
Dehydration Aspiration Constipation Seizures
Aspiration
Dehydration
Reporting and Documenting
Constipation
Seizures
Be aware of likely triggers

Provide appropriate assistance
Record conditions and description
Aspiration
What to document
Dehydration
Constipation
Seizures
Time of the seizure
Any drug or alcohol use

Parts of the body affected
Types of movement
Antecedent conditions
Impairment in consciousness

Changes in skin colour
Any resulting injuries
Condition after the seizure
Any difficulty with recall
Who the seizure was reported to

56 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Other Common Health Issues
Urinary / Faecal Incontinence

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 57








58 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Drinking adequate water 01 Drinking other fluids 02 Correct cleaning 03 Prevention and Treatment Urinary Tract Infection Strong and persistent urge to urinate 01 03 Frequent, small amounts of urine 04 Urine that is cloudy/pink/red 05 Rectal pain in men and pelvic pain in women 06 Strong smelling urine Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Signs and Symptoms Burning sensation while urinating 02
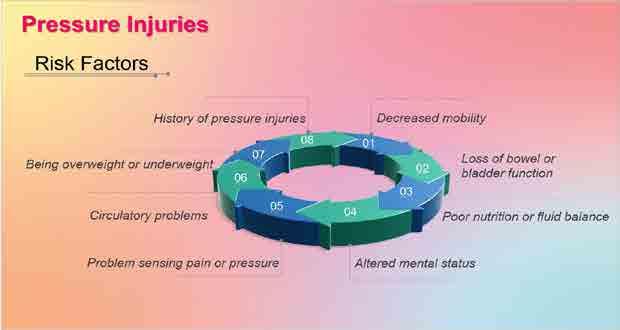
Pressure Injuries
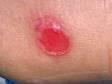





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 59
Breakage in area of skin Sore or intact skin
areas
Common













60 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Allergies Symptoms Anaphylaxis Prevention Pressure injuries Prevention 03 Emergency medical care 02 Seek medical help 01 Wash sore 02 Keep pressure off 03 Follow good hygiene 01 Change positions frequently Treatment
Asthma


Cause Symptoms
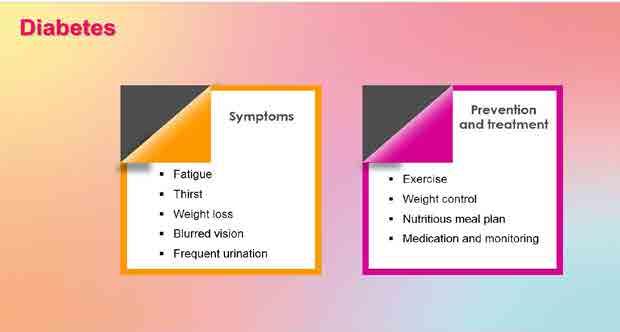
Prevention and Treatment



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 61
SECTION 4: Health and Safety

Health and Wellbeing




62 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
• Safety
• Privacy
• Dignity
• Communication
• Independence
• Infection Control

• Fire safety
• First Aid
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 63
Agenda
Safety
- Preventing Falls
- Preventing Shocks and Electrocution
- Preventing Burns and Scalds
- Preventing Poisoning or Chemical Accidents
- Preventing other Household Injuries

64 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners







Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 65 Assist people who might fall Preventing Falls














66 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Pick up things dropped on floor Clean up floor spills
Remove potential tripping hazards













Unplug

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 67
electricals when not in use














68 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
in bathrooms
use of extension chords
Place rubber mats
Limit
Install grab rails

Straighten carpets/rugs/throws












Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 69
Clear entrances and passages








Ensure good lighting






70 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners













Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 71 Use walkers/canes for support Exercise/physiotherapy can help







72 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Preventing Shocks and Electrocution Use special equipment for emergency alert
Preventing Burns and Scalds


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 73
Preventing other Household Injuries
Teach Safety
- Modelling
- Using every teachable opportunity
- Providing positive reinforcement
74 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
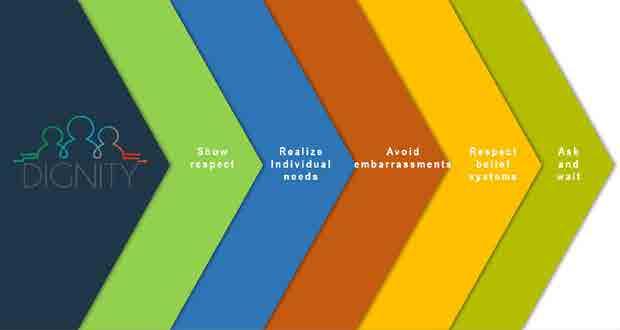
Respect
Do not discuss personal issues

Respect confidentiality






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 75
Close door before assisting
personal space and belongings Knock and wait
Dignity
76 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Communicatio n
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 77
78 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
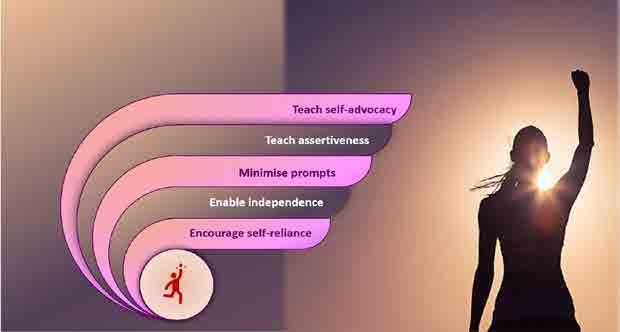
Independence
Infection Control






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 79
Controlling spread of germs
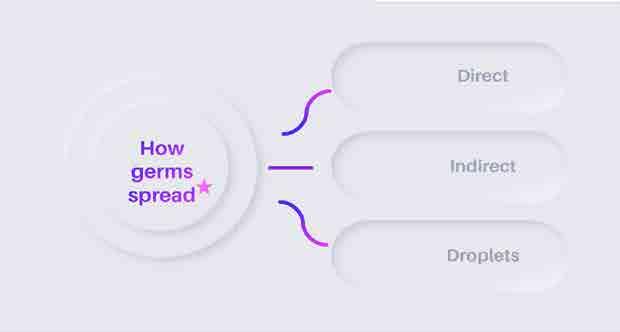
• Hand washing

• Choice of soap
•Remove any protective equipment
•Moisturizing

80 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 81


82 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Fire Safety



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 83
Response to Fire
Remember to RACEE
If you smell smoke or discover a fire at your site, you must do the following in the order outlined:

• Remove/Rescue
• Alert (contact)
• Contain (control)
• Extinguish (put out)
• Evacuate (leave)
In the Event of a Fire

84 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 85 Thank you! www.youtube.com/c/powerupwithpowerpoint First Aid
Health and Wellness

Health and Wellbeing





86 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Wellness and Healthy Lifestyle



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 87
A healthy lifestyle
Nutrition & Weight Management


Health care management

Exercise
Diet











Exercise

Health Checkups

Infection control

Sleep
Stress management



Hygiene & Grooming

88 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
In your opinion, are Shashi’s decisions helpful or not?

▪ Shashi baked a cake to celebrate Devi’s first night at the home.
▪ Shashi told Devi that “lights out” was at 10.00 and he must comply.
▪ Shashi told Devi he could not watch television in his bedroom.
▪ Shashi decided that she should get Devi’s bath ready for her.
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 89
Dis(ability)


Good Nutrition

90 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 91









92 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 93








94 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners General Tips 01 02 03 04 05 Drink water instead of sugary drinks Make at least half of your grains whole grains Make half your plate fruits and vegetables Avoid oversized portions Enjoy your food, but eat less


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 95
Preparation





Method

96 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 97 Setting up for success Water within reach 4 Fruits, cut vegetables on table 3 Junk once in a while 2 Healthy snacks easily reachable 1 Portion packaged food 5
Smaller plates





Smaller serving utensils
Condiments from bowls
Portion large items
Extra food out of sight
98 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 99



100 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 03 Exercise: For a healthy body & mind
Aerobic activity
Muscle strengthening activity




Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 101
Balance and Flexibility





102 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Other Strategies





Exercise


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 103
A B C D E Start Small Join In Get it Right Recognize Small Efforts Be Encouraging
Think of one person you support who would benefit from increased exercise – Come up with one exercise idea to try with that person that is new to them.
Supporting healthy lifestyles






104 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Model Healthy Choices Support Choices Learn and Educate Build Routine Know the person’s wants/needs
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 105
Health and Wellbeing




Mental Health
Wellness

106 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
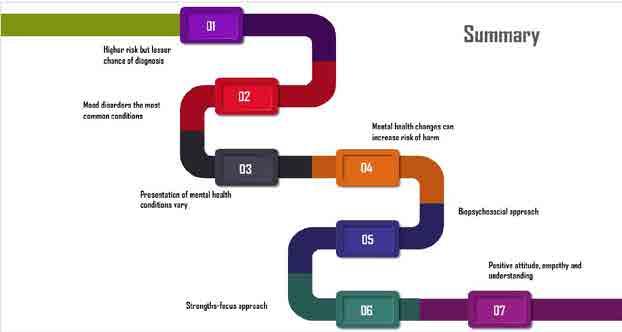
Can take many forms
What are mental health conditions?



Conditions that impact a person’s thinking, feeling or mood

Diagnosis requires clinical judgement
When a person has both a developmental disability and a mental health condition, the person is said to have a “co-occurring diagnosis of a mental health condition”.
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 107
Biopsychosocial Approach

Biological Aspects


Psychological Aspects



Social Aspects


Genetic, biological component


aspects
Family history
Psychological challenges
Social connections
Physical illness
Verbal communication challenges
Opportunity to contribute
Communication
Functional challenges
Recreation
Role of DSP
Stressful life events
Challenges with control and regulation
Behaviour
Healthy habits
108 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
A 35 year old woman, Lakshmi, has moved into an apartment in the community, sharing the apartment with two other women in their 30s. It’s been a couple of months since Lakshmi moved here from an institution where she lived since she was 10. The women are supported by direct support staff.
Lakshmi is mostly withdrawn, aloof, and cries frequently. One day she screams at her roommate and throws things around the room for no apparent reason. Another day she seemed disoriented when they were getting down to having lunch around 2 pm.
Lakshmi has intellectual disability. She has diabetes for which she takes medication. At the institution, she was used to having lunch at 12 and followed a strict routine around food. She had a couple of good friends at the institution.
Please share your thoughts using the biopsychosocial approach.

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 109


110 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
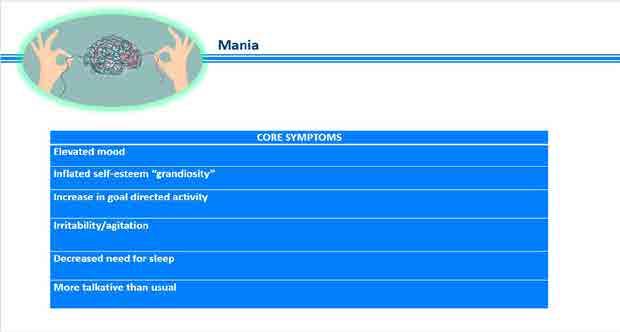
Specific Mental Health
Conditions

Mania Anxiety Disorder



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 111
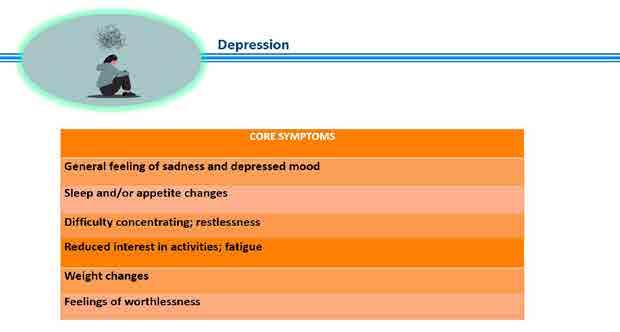
Depression
s

112 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 113 Be creative Focus on one topic at a time Plan positive activities Use positive thinking 01 02 03 04
Depression – Support Strategies




114 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Changes in sleep, eating patterns and overall activity levels What is realistic Mania Behavior changes 01 02 03






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 115 Jamal has recently been giggling a lot, talking non-stop and pacing; he also made several remarks toward female DSPs, which is not usual for him. He offered to take Anita, his DSP, to Mauritius on his jet. As his DSP, and from you just learned what would be best to do? Mania - Review Reduce simulation 01 Brief conversations 02 Encourage sleep 03 Recognize emotion 04 Use grounding strategies 05 Mania – Support Strategies

116 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Various Terms Concerned Worried Apprehensive Afraid Scared Restless Stressed Panicked Nervous
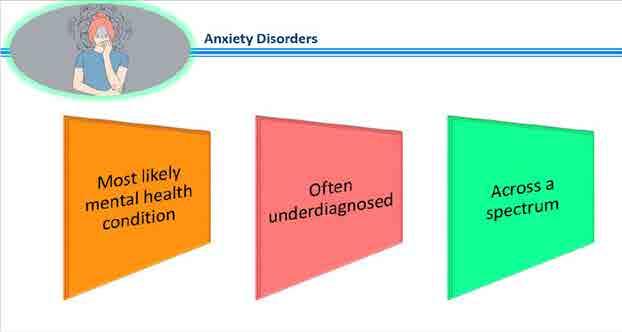
Anxiety Disorders

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 117









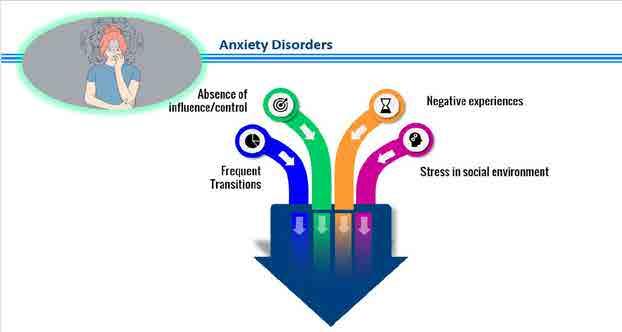
118 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Empathy 01 Consistency 02 Prevention 03 Autonomy 04 Anxiety Disorders – Other Strategies Reduce anxiety and stress 01 Minimize change 02 Environment management 03 Anxiety Disorders – Support Strategies

























Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 119 02 01 03 04 Power Genuineness Trust Modeling Relationship
• Which of the following are common mental health conditions among people with IDD?

o Depression
o Anxiety
o Bipolar disorder
o All of the above
• Shanti gets easily stressed and hits others when she is asked to do household chores. Shanti has many interests and strengths, one of which is drawing. How might you best support Shanti if she shows signs of becoming agitated?
o Offer Shanti opportunities to draw, but when she shows signs that she is becoming stressed, take the drawing materials away
o Let Shanti know that if she does not hit others, she can have the drawing materials after she does her chores
o Allow Shanti the opportunity to draw when she starts to become stressed and at other times during the day when she isn’t doing chores
o Don’t let Shanti have drawing materials until she shows that she will not hit others for one week
120 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
QUIZ
• True or False: Intellectual disabilities are typically present at birth or appear during the developmental period.
• When someone has both an IDD and a mental health condition, this is commonly referred to as
o Double diagnosis
o Multiple medical challenges
o Simultaneous conditions
o Co-occurring conditions
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 121
- Robert M.
module 7: positive approaches to challenging Behaviour
There is no greater disability in society than the inability to see a person as more.
Hensel

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 125
Defining Behaviour
Examples of “behaviors”
Explain Clearly

126 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
B
REMEMBER:
Behaviour = Communication
Interferes with learning
Also think…
Interferes with participation in the community
Hurts self or others
Affects the emotional health of the family
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 127
Factors that affect behaviour
External Environment (including socio-emotional factors)
• Distractions
• Are you rewarding a behaviour without meaning to? (Giving something to make her quiet and easier)
• Can you change the setting that bothers the individual? –heat/cold/noisy
• Are your expectations matched with his ability?
• Core factors of the disability
• Past learning
• Family issues
• Unmet needs
• Abuse
Internal Environment
Factors that affect behaviour
• Pain
• Hormones
• Effect of medication
• Sensory Issues
• Health – allergies/seizures
• Mental Health
128 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Wrong Patterns
Difficult behaviors get faster results So

Difficult behaviours occur again and again

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 129
But – No assumptions please

Most Important Factors:
1. Relationship
2. Relationship
3. Relationship
What we have to put
▪ Increase involvement
▪ Decrease confusion and unnecessary distractions
▪ Allow easy access to materials

▪ Address transitions
▪ Consistency
▪ Notice
▪ Daily schedule
130 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
The Importance of Choice


Teaching Functional Skills
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 131
Supportive Interactions
Sometimes, a crisis occurs despite our best efforts


132 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
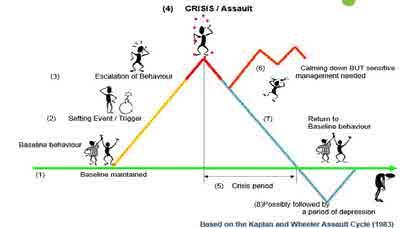
Stages of Behaviour
• Can you think of what behaviours you might see at each stage?
• Discuss in your group.
AGITATION SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE RAGE SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE
1.Withdrawal (physical or emotional)
2. Power struggle
3. Protest (person or situation)
4. Fidgeting, tensing
1. Recognize signs of stress
2. Remain calm
3. Use quiet voice
4. Slow down speech
5. Take a deep breath
6. Use fewer words, less emotion
1.Screaming
2. Emotional to explosive
3. Biting, hitting, and/or kicking
4. Self-injury
5.Destroying property
1. Ensure safety of others
2. Control fight-or-fligh t tendency
3. Do not posture or arrange yourself
RECOVERY SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE
1. Fragile
2. Sleeping
3. Withdrawal into fantasy
4. Apologizing
1. Remain calm and quiet
2. Reassure student
3. Do not debrief or reexamine Incident with student
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 133
AGITATION SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE

5. Rocking, foot tapping
6. Loud voice, name calling, verbal threats
7. Tears
7. Avoid power struggle
8. Be flexible—the child cannot
9. Do not trap student in corner
RAGE SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE
6. Physical escape; “fight or flight”
7. Abusive insults to staff and peers
4.Remember that less is more
5. Remain calm and quiet
6. Do not lecture 7. Disengage emotionally
8. Preserve student dignity
RECOVERY SIGNS YOUR RESPONSE
5. May not remember or deny episode occurred
6. Expressions of relief
7. May show gratitude
4. Do not moralize or preach
5. Take time for yourself to regroup by taking a break
6. Preserve confidentialit y!
7. Do not share “war stories”
70%
20%
10%
134 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Some people think they are in community, but they are only in proximity. True community requires commitment and openness. It is a willingness to extend yourself to encounter and know the other.
- David Spangler
module 8: community membership
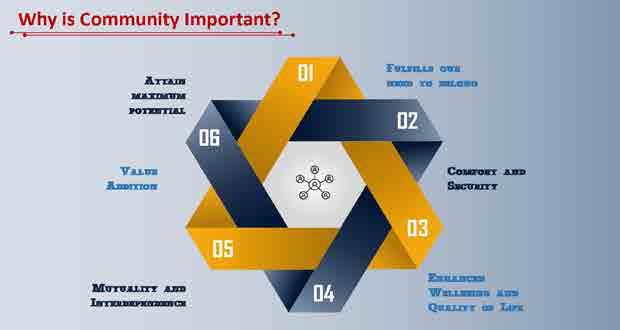
Community is a group of people who come together for a common reason.


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 137
Everyone needs Community. Community needs everyone.

138 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
A community that excludes even one of its members is no community at all – Dan Wilkins
Community involvement
History
Role of Human Service Client

Services
Especially important to people with disabilities
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 139
• Aditya lives in a group home with nine other adults who have disabilities. On some days he attends a day centrewith 20 other people also with disabilities. His support worker is encouraging him to research training programs that could eventually lead to employment. The program provides computers where he can conduct his research. On weekends, his family sometimes picks him up to spend time at their house.





140 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
In (but not of) the Community -
Physical integration does not necessarily lead to social integration –Lemay, 2006
• Prabha lives in an apartment with a roommate in a program that provides support services. She is currently unemployed and is looking for either a part time job or an interesting volunteer opportunity. Because she doesn’t have a computer, she goes to the cyber café a few days a weekto search for jobs and work on her resume and surf the internet for areas that interest her. She has gotten to know one of the staff there and they often take a break together for coffee or just a walk. On weekends, Prabha and her roommate often host potluck dinners for friends and/or family.

Being part of a Community

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 141
C o m m u n i t y P r e s e n c e
C o m m u n i t y P a r t i c i p a t i o n
C o m m u n i t y I n c l u s i o n
Family Roles


What Does Community Inclusion Encompass?
Leisure & Recreation
Education




Friendships
Work & Career
Civic Life
Spirituality


142 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Elements of Community Inclusion

Barriers to Community Engagement
People with disabilities segregated, congregated, distanced
Mindsets, attitudes, stigmatization and discrimination




Autonomy, self-determination and expectations
Accessibility and other barriers
Other
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 143
-(Hastabackaet
al., 2016)
Active participation Choice Responsibility Acceptance
Natural supports Valued roles
Roles
Connections with Community



Relationships
Places

144 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
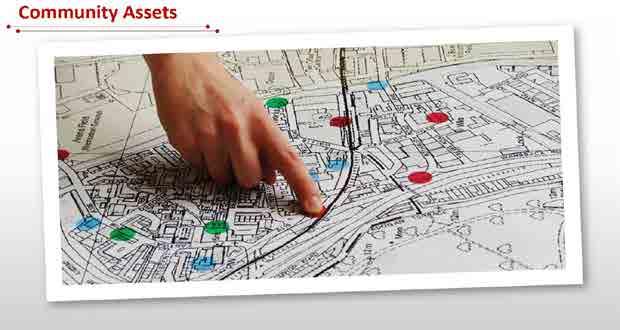
Community Mapping helps figure out what talents, gifts, skills, and capacities lie within a community, and find ways that the community can strengthen itself by “bringing” out those gifts and using the capacities that already exist.


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 145


146 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 147
Town of Herbertpur


Located on the bank of river Asan.

As of 2011India Census, Herbertpur had a population of 9,782.
Languages spokenHindi, Punjabi,English,Garhwali and Tibetan.
Self sufficient town
Here you find diversity in religious beliefs
148 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners









Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 149
Community
Gathering Celebrations happen here !!
Bakery
150 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Café | Restaurants
What do people do for a living ?
Major Local Businesses



Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 151
Domestic Connectivity






152 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
??
Passing time
Where do people study ?


Fitness & Lifestyle Services







Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 153
Healthcare Services

























154 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Digital Seva Kendra & Postal Services
Standard of Living






Financial Services





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 155
Educational Institutions
Farm Area/ unoccupied Space
Residential Area
Religious places
Medical Stores/Clinics/Individual practitioners
Banks and ATMs
Departmental Stores
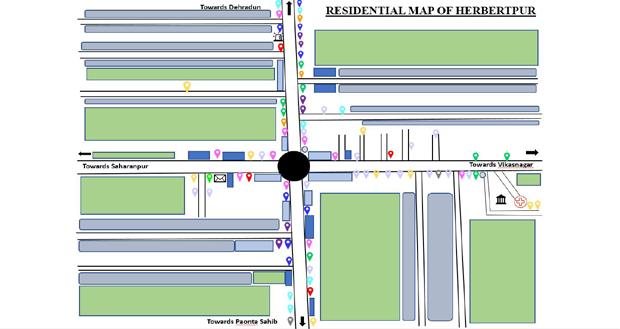
Eateries, bakeries and confectionary stores
Selfcare and Beauty Services
Celebration Hall
Other Small Business Shops (Electrical, furniture &Plywood, marble work, iron work, etc.)
Small Shops
Police Station
Post office Hospital, Local Court
Bus Stand
156 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Final Thoughts
Authentic inclusion is not likely to happen when people with disability “visit community” in large groups.

It IS likely to happen if people with disability are introduced to people, places, and activities which are a good fit for them…individually, one person at a time. Just because this is a challenge does not mean it is not true.

So…get out there, see what’s around, see who’s around and your life will get richer and more included as well!

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 157
Before you start to judge me, step into my shoes, walk the life I’m living and if you get as far as I am, just maybe you will see how strong I really am.
module 9: Family collaboration
- Anonymous
INTRODUCTION
Family Collaboration
 Developed by Darcy Elks
Developed by Darcy Elks
Purpose Goal Structure

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 161
For Keystone Institute India
► The importance of collaborative relationships with families


► The importance of understanding the kinds of hurtful experiences families may have had
► What families want from direct support staff
► Some possible challenges you may encounter when collaborating with families
► Some guidelines to foster collaboration between staff and families
What You Will Learn:
Part
1: Creating the Context
Focus on Family: a Mindset
► The importance/value of family relationships for all people, especially vulnerable people

► Vision for collaborative staff family relationships
► Understanding Family Experiences
► Reflecting on our role and responsibility in the life of the person with a disability
162 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Part 2: Fostering Collaborative Relationships
► Brief review of key ideas in part 1
► Some possible challenges that could impact staff/family relationships
► General guidelines to help develop collaborative relationships
► Family and staff presentations of positive examples
► Working through some situations
► Conclusion

Part 1: Creating the Context
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 163
Focus on Family: a Mindset
► The importance/value of family relationships for all people, especially vulnerable people
Reflection Questions:
1. Think about the importance of family in your own life.
2. What would your life be without your family?
Write down your thoughts and we will have a brief sharing afterwards.
A Family Is……
❖ A Changing Life Mobile
❖ A Balanced Environment
❖ A Birthplace of Creativity
❖ A Formation Center of Human Relationships
❖ A Shelter in the Time of Storm
❖ An Education Center
❖ A Museum of Memories
❖ A Mutual Admiration Society
164 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
From Edith Schaffer
VISION FOR COLLABORATIVE FAMILY/STAFF RELATIONSHIPS: PARTNERSHIP

Partner = someone associated with another in a common undertaking, partnership implies relationship
Being in partnership means:


► Working together for good of person with disability
Working Together
► Being open, willing to listen to each other
► Having a shared vision
► Having a sense of one another’s vulnerabilities, pressures, etc.
► Willingness to accept challenges from one another
► Willingness to try to understand one another ’s point of view
► Others you can think of:
IT IS IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER THAT:
While some families may contribute to hurtful life experiences of a person with a disability, for example:
• Rejection
• Participating in segregation
• Denial of autonomy
• Contributing to life-wasting
• Conveying to person that he/she stresses the family
A family also has tremendous potential to:
• Protect from some wounding
• Share the suffering which comes from wounding life experiences
• Offset some of the negative effects of wounding
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 165
SOME TYPICAL DIFFICULT EXPERIENCES OF FAMILIES WHO HAVE A MEMBER WITH A DISABILITY
Dealing with the “differentness” of your family member
Experiencing negative attitudes towards your family member from others
Experiencing value crisis and disagreements
Needs of family member may be hard to meet at times
Getting a reputation as “difficult”
Living with the impact on the whole family that even a small negative experience can generate
Having to ask for help
SOME TYPICAL DIFFICULT EXPERIENCES OF FAMILIES WHO HAVE A MEMBER WITH A DISABILITY (cont. ’d)
Having to see your family member be wounded
Having your vision for your family member dampened or even scoffed at
Being let down by the very services that say they are there to help
Being humiliated by service professionals
Having to endure the self righteousness of others (e.g., professionals, other family members, friends)
166 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
SOME TYPICAL DIFFICULT EXPERIENCES OF FAMILIES WHO HAVE A MEMBER WITH A DISABILITY (cont. ’d)
Experiencing some of the same wounds your family members with a disability experience (e.g., rejection, cast into negative roles, etc.)

Feeling guilt/inadequate
Coping with the vulnerability of your family member with a disability
Being judged by others
Being fearful of
•The future
The effects of advocacy
•Placing the life of your family member in someone else’s hands
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 167
WHAT FAMILIES WANT FROM STAFF

168 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Respect – for family and traditions, spiritual preferences A belief in the worth and value of their family members See the whole person not just the disability True appreciation and acceptance of their family members An honest interest in getting to know their family members Genuine concern that their family member be loved and have a full, meaningful life Openness and willingness to learn from the family Honesty – even if painful Expertise Patience Humility


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 169
Role Confusion (role of staff/family) e.g., staff as cleaner

Supporting the person with a disability when there is a difference of opinion between the person and family
When there is a difference of opinion between what you think is best and what the family thinks is best
Honoring a family’s traditions and spirituality if they are different (maybe in conflict) with yours
There is poor communication between you and the family
170 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
SOME POSSIBLE CHALLENGES THAT COULD IMPACT STAFF/FAMILY RELATIONSHIPS
Some Possible Challenges That Could Impact Staff/Family Relationships
The person you work with shares a confidence with you and you think that the family should have the information, but the person does not want you to share it.
The family is committed to traditional ways of doing things and is not willing to let their family member try to do things differently

You do not know much about the past experiences of the person you are supporting
Sharing of Two Stories About Collaboration Between Staff and
Family Staff/family share story #1
What did I learn from this story?
Staff/Family share story #2
What did I learn from this story?
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 171
Some Ideas To Help Develop Collaborative Staff Family Relationships
► Really listen to what family members (e.g., parents, siblings, grandparents) are saying
► Try to put yourself in the shoes of family member(s) and the person you are supporting
► Be respectful and patient
► Remember the importance of your role in the life of the person with a disability
► Don’t jump to conclusions
Some Ideas To Help Develop Collaborative Staff Family Relationships
► Be open to suggestions of family members
► Let the past be the past
► Be interested in learning from the family
► Encourage family members
► Be positive
172 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
► How are family members responding to the situation?
► Why might the family be responding in this way?
► How can you respond in a way that is respectful of the family and the family member with a disability?
► Is there a way that you can respond which will build trust with the family?
► Is there a way that you can respond which will affirm and strengthen your relationship with the family and the person with a disability?
► Is the person with a disability and a vision of a full meaningful life at the heart of the conversation?
► What can staff and family do on a regular basis to nurture and build a collaborative relationship?
Questions To Guide Our Actions When Thinking About A Specific Challenging Situation

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 173
Concluding Thought


Alone
THANK YOU!
174 Foundations
direct support: a national training
for direct support practitioners
oF
program
we can do so little. Together we can do so much.
…Hellen Keller
The marvelous richness of human experience would lose something of rewarding joy if there were no limitations to overcome. The hilltop hour would not be half so wonderful if there were no dark valleys to traverse.
- Helen Keller
module 10: legal Framework
Legal Provisions Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act

Historical Background
No Specific Law till 1995
Ratification of UNCRPD by India
In 2010, Government agrees to bring new Disability Law
Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act passed in 2016
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 177
Salient features








Definition of disability changed from medical model of disability to rights based model
Focus on barriers
21 categories of disabilities named
Clauses on Rehabilitation, Health, Education
Separate Clauses on Women/Children
Punishment Clause

178 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
RPD mentions :
• Equality and non-discrimination
• Protection from cruelty and inhuman treatment
• Accessibility in voting
• Time-limit for compliance with some of its substantive provisions


Education
Free Education for children with Disabilities aged 6-18


Choice to select Special Education or Inclusive Education

5% reservations in Higher Education

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 179
4% reservation in employment
Reservation category includes autism, intellectual disabilities


Chief Commissioner of Disabilities
State commissioner of Disabilities
Special Courts
180 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Mechanisms
Complaint
Employment
Case Study I
Amar’sparentswantedhimtostudyina nearbyschooltosavetimeincommuting. However,whentheyapproachedoneof thelocalschoolstoknowaboutadmission procedure,theyweretoldtheschooldoes nothaveaSpecialEducator;theschoolis notreadytoadmithimashewillneed specializededucation.


What steps can be taken?
Case Study II
Roshenarahascompletedhergraduation degreeandislookingforajob.Asshe scanstheadvertisements,shefoundthat theRailwaysislookingforstaff–butin theadvertisements,thereisnomention ofreservationforpersonswithautism. Shewantstoapplyforthisjobandavail reservationgiventopersonswith autism.
What steps can she take?
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 181
Case Study III
Kavitawasveryhappythatshewillbevoting forthefirsttime.ShereceivedherVoterCard recently.However,whenelectionswere announced,shelearntthatherboothison thefirstfloorofanearbyschool.Shefindsit difficulttoclimbthestairs.Shealsoheard thatsupportpersonsarenotallowedduring elections.Shefeltverysad.
What steps can be taken so that Kavita can cast her vote?

182 Foundations oF direct
training
for direct
support: a national
program
support practitioners
So many of our dreams at first seem impossible, then they seem improbable, and then, when we summon the will, they soon become inevitable.
- Christopher Reeve
module 11: advocacy & activism


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 185

186 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
All persons with intellectual disabilities can be selfadvocates.

I've got a voice and even without a voice I can communicate in other ways.

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 187
Persons with intellectual disabilities can work and earn money. Obviously they will take decisions of their lives in such a scenario.
DevanshiJoshi, a young woman with Downs Syndrome, said in a video interview that she thinks earning money is an important part of her life. We are seeing groups of self-advocates with different developmental disabilities in India these days.
People must listen to me.
I can go to the shop with support and if required, can take help from others.

I can think for myself
I am not incapable and take decisions of my own
188 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners E x c e r p t s : W h y i t i s i m p o r t a n t f o r P e o p l e w i t h I n t e l l e c t u a l D i s a b i l i t i e s t o h a ve a v o i c e o f t h e i r o w n . - K a t h e r i n e O w e n ( U K ) a n d Ja c k i e D o w n e r ( U K )
I can take a risk, have a relationship
As care-givers, we sometimes think we need to take decisions on behalf of persons with intellectual disabilities.
Sometimes, we treat them as “children” even when they are adults.
We need to change our mindset and understand everyone has equal legal capacity i.e. right to be an adult individual with personal choices and thoughts.

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 189
According to our law, a person with any kind of disability can take action if his/her rights are violated.
Care-givers can also lodge similar complaint if they see any violation.
This can be done after discussing the same with the person violated.
Care-givers can support the person with intellectual disabilities to become a self-advocate in such cases.
190 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Case Study I
A popular TV serial shows a character with intellectual disabilities as a very incompetent/childish person. Everyone talks to her in the serial as if she is a baby although she is an adult. The other characters use the term “mentally retarded” when they talk about her.
What activities can self-advocates do after watching this serial?

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 191
Case Study II
Private buses do not stop at a particular bus-stop even though many passengers wait there. The conductor of the bus says that since this is the time when a special school nearby closes, most of the passengers at the bus-stop are disabled. Disabled students have bus-passes and do not need to buy tickets. So, if many of them take the private bus, they will run at a loss.
How can one find a solution to this problem?
Case Study III
The corporation office of a metro city decides to make a list of vulnerable people so that they can be given preference at the time of a medical emergency like Covid-19. They have enlisted the elderly and transgenders but left out those with disabilities. They are starting the survey in seven days time.

How can self-advocates act as change agents in this kind of scenario?

192 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 193
Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Wellbeing
- Martin Luther King, Jr.
module 12: sexual
Sexual Wellbeing


Part 1: Awareness and Understanding

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 197
Let’s get to know each other ☺
Stand by your opinion
People with developmental disabilities do not feel the desire to have sex.
People with developmental and physical disabilities are asexual, childlike, sexually innocent.
People with developmental disabilities are sexually impulsive, aggressive men & women promiscuous.
People with developmental disabilities will not marry or have children so they have no need to learn about sexuality.
It is not really necessary to broach the subject of intercourse since people with developmental disabilities are simply not capable of a close relationship, let alone a sexual encounter.

198 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Stand by your opinion
They will be accompanied all their life by a support worker, so there is practically no chance that they will have sex.
People with developmental disabilities who are intellectually much behind their age or are very young, do not need to know about sex or sexuality. This type of information can be given to them much later - five years or even later.

Persons with disabilities should not be allowed to masturbate because it can become a habit.
It is not natural for women to be sexually attracted to women or men to be sexually attracted to men.
Self awareness and introspection

Self awareness and Introspection related to sexuality and sharing

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 199









200 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners Dress Friendship Warmth Social outlets Affection Approval How is it for the people we support? Let us contemplate on our sharing in relation to adults with disabilities
Possibility of physical relationships



















What do they feel about themselves?
Self image
Gender identification

Sharing with others
How is their body experience?
Openness towards self-pleasure/ sexual relationship

Opportunities for physical contact

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 201
- Understanding puberty


- In relation with people with disabilities

202 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
What is Puberty?
Puberty is the time in life when a young person starts to become sexually mature.
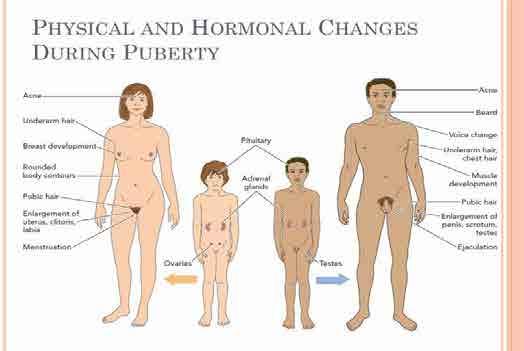

- Final stages of development
- Menstrual cycle and ovulation have begun
- Pubic hair growth
- Breast growth continues
- Vagina enlarging


- Produces discharge
- Breast growth
- Height & weight gain
Usually begins
Nearing adult appearance
Development continues
-Penis begins to grow in length
-Changes in hair, height and voice

Testicles and scrotum begin enlarging
Usually begins
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 203 8 11 13 15 12 14 16 9
Menstrual Cycle
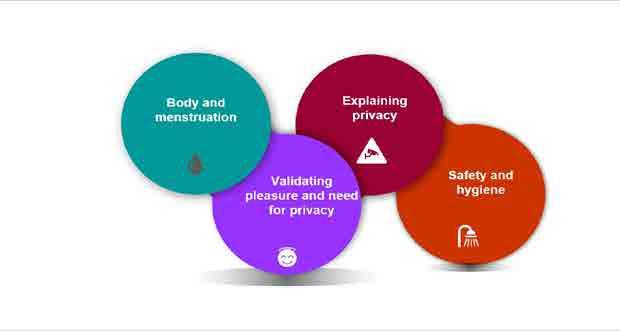
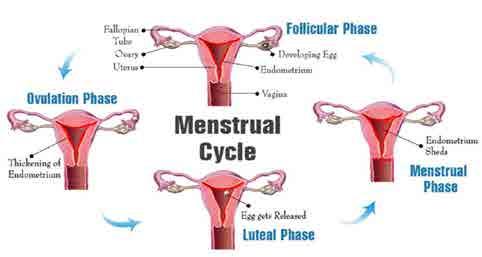
204 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Masturbation
A perfectly normal stage of a child’s development.
Self-pleasure
•Masturbation should only be considered a problem if it is:
•Done in public places
•Excessive (causing pain, interfering with other daily activities such as school, therapy, training and work )
•Causing other behavioral issues
•Upsetting for the child.
Wet Dreams/Nocturnal Emissions
Nocturnal means
emission





Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 205
A wet dream is also known as a nocturnal emission.
“at night” and
means “discharge.”
Puberty: social and emotional development


Changes in social interactions during adolescence


Every child’s social and emotional development differs

Unique combination of genes, brain development, environment, social experiences, community and culture
Puberty issues
• Have difficulties monitoring and expressing emotions



• Difficulties balancing emotions and behavior
• Moodiness, has more arguments with you

• Sees things differently from you
• Difficulties with peer and social relationships
• Might have difficulties making and keeping friends
• Antisocial behavior and risk-taking behavior
• Wants to spend less time with family

206 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Biological Emotional & Social Cognitive


Adolescent development
Without disabilities
-Puberty development the same
With disabilities
-Puberty development the same
-Mood swings
-Social-sexual changes
- A variety of ways to express feelings
- May understand more complex language
-Mood swings
-Social-sexual changes
- More challenging to express feelings
-Need more concrete language
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 207
Snippets 2



208 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
NEXT
Impulsive
Poor self-esteem
Depression
Part 2
Harmful effects of repressing of sexual expression
Emotional instability
Anger
Child Abuse
Aggression
Criminal behaviour
Inferiority complex
Isolation
Related physical problems

Frustration, confusion
Misconduct
At-risk behaviour

Poor decision making
Loneliness
Anxiety
Physical discomfort
Mental health issues
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 209
Scenarios
Ajay is a young man who is exploring his sexuality. This leads to frequent self pleasuring, which is often done in socially inappropriate situations e.g., in the garden when taking a walk.

An attempt was made to stop his behavior by calling in a policeman who threatened Ajay with prison and beatings if he was found doing this again. Ajay is now terrified of being caught.

210 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Bhagyashree is a young lady who has been constantly stopped and scolded for self pleasuring at home.


As a result, she had taken to pleasuring herself in the shower cubicle of the swimming pool she visited, with a hanger.
At an overnight picnic from a school, Chanda, a very sociable and talkative person was caught fondling with her room mate by mutual consent, at night after lights out. The room mate was also a young lady. Her parents were called and she was shamed in front of the whole class and parents. She carried the humiliation for years.
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 211
Dheeraj and Ekam are very fond of each other and are colleagues. They only meet at work. On one occasion, when the sheltered workshop had gone on a picnic, the two were seen being cozy with each other. Dheeraj was sitting on a garden bench and Ekam was lying down with his head in her lap. The staff immediately broke them up and scolded them for their behavior. They experienced guilt and became very secretive.
Firuza used a wheelchair. She had a crush on a boy at her college and wanted to look special for him on a particular day. She needed help bathing so that day, she asked her mother to shampoo her hair. Her mother, who needed to drive Firuza to college before reporting to her work, scolded Firuza for asking for a shampoo on Wednesday when she knew that Sunday was shampoo day. Firuza felt dejected and angry at her mother.


212 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Gurpreet, a middle aged woman was very terrified of any workers in her home. She would become very agitated and it was very difficult for her family to get any repair or renovation work done. This was directly the result of a childhood experience when her building was being renovated and a worker had climbed into her room from the scaffolding and molested her.
Need for social-sexual education


A Decreases the Likelihood of Abuse


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 213
Need for social-sexual education
B


Combats myths and misinformation
Need for social-sexual education
C



Promotes personhood, pleasure, etc.

214 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Need for social-sexual education
D







Reduces fear, anxiety, worry, etc.
Need for social-sexual education
E
Increase self-awareness, gender comfort
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 215
Need for social-sexual education


Allows for mature and healthy relationships
Difficulty learning
Challenges

Communication problems

Mistrust of own body
Diminished gender role expectations from society
216 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
F
Part 3

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 217
TEA BREAK
Exploring the body and bodily needs
Exploring the body and bodily needs
218 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
What are the aspects to be aware of


Body parts Self touch
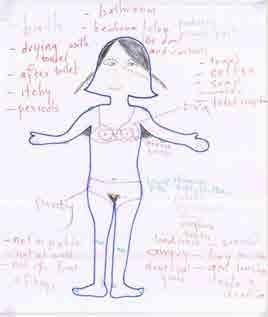
Private vs. Public Circle of trust Boundaries
Good/bad touch
Hidden social etiquette
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 219





























220 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 01 02 03 04 Significance of understanding complex emotions Emotions as a tool for self awareness for the child/adult, explored as connected to sexuality Simple Complex How can we support/educate SadHappy AngryScared GuiltyAshamedConfused FrustratedExcited
How this could be communicated to the adults with disabilities






Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 221 bad touch Trust framework Circleoftrust Empowerment Self-care Games Sharing Socialstories OtherMeans
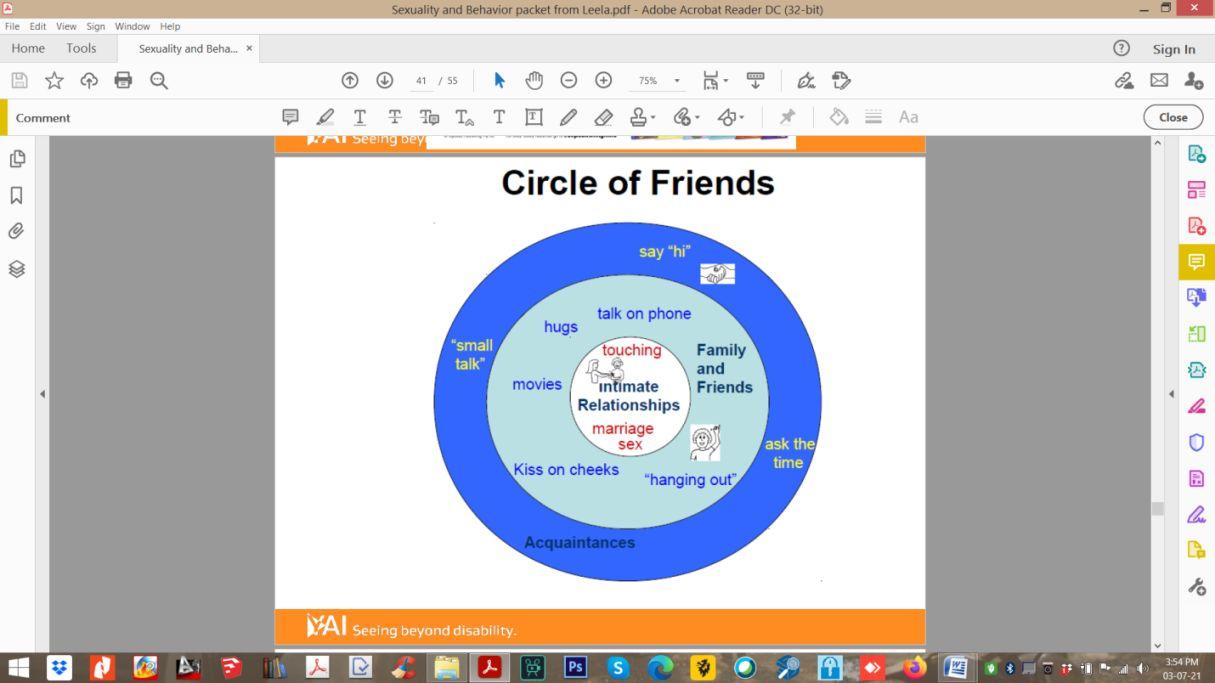




222 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Nidhi – make it
Empowerment
angry when someone touches me like this
happy when someone touches me like this
Where does the possibility of these arise?
scared when someone touches me like this
Important points
• Normalize the discussion of sexuality!
• Use concrete language at their cognitive level & pictures

• Making it taboo encourages secrecy and increases vulnerability


• You may need to initiate the conversation
• Be honest and give correct information
• Respond to all sexual issues non-judgmentally
Be proactive not reactive Addressing situations without creating guilt or shame
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 223
"I am the boss of my body"
RESPONDING TO SITUATIONS
Gia, is a 35-year-old lady, who is in the practice of self pleasuring in the afternoons in her bedroom. She does not shut the bedroom door or draw the curtains.
On one such afternoon, you walk in on her.
Do you see an issue here?

How would you address it?

224 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Hiren, a young, adolescent lad has not been able to sleep well, and it has been disturbing his daily routine. You notice that he has been using up all his underwear, shorts, pajamas, pants through the night and putting them in the washer.
He has been saying “toilet” all day and going in, changing clothes and coming out without using the toilet.
He does not appear to have a stomach upset or a urinary tract infection.
Do you see an issue here? How would you address it?
Further examination tells you that he has been having nightfall and his sensory issues make it difficult for him to sleep with even slightly damp clothes.
What would you do? to explain what is happening and to restore his sleep needs
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 225
Yogesh, inappropriately puts his nose into the blouse fronts of women who might be using perfumes he likes.
This has led to him being called an “attacker” and women avoid him.
Do you see an issue here?
How would you address the situation?
Joginder, a 50-year-old man likes to surf YouTube videos on his cell phone and watch raunchy numbers.
His surfing often takes him to pornographic sites, which too he enjoys watching in the privacy of his room and by himself.
However, when he wants to maneuver his way back to where he started from, he finds that he cannot do it without assistance and lands up approaching his care giver for help.
Do you see an issue here?
How would you address it?
226 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Karthik, a middle aged man has been in a relationship with the liftman of their building. It has been going on for several years.
Recently, this young man decided to confide in you and tell you that the two of them meet often and that he likes this person’s company and the relationship.
Do you see an issue here? How would you address it?
One day, while going about your daily chores, you notice that Lalit, the person in your care is making physical and sexual advances towards you.
When you ask or observe closely, you are certain that you are not mistaken.
Do you see an issue here? How would you address it?
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 227
Mehtab, a man in your care, confides in you that he dearly loves a lady at his workplace and wants to marry her, hold her hand and kiss her.
But she is very firm that she only wants to be his friend. This is disturbing M a lot and he wants your help.
Do you see an issue here? How would you address it?
You come to know that Noel, a man in your care, follows a girl who travels on the same public bus with him and gets off at his stop, everyday, right up to her home.
This is unsettling to the girl, who has complained to you about Noel’s behavior.
Do you see an issue here? How would you address it?
228 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
A relook at our opinions
Stand by your opinion
People with developmental disabilities do not feel the desire to have sex.
People with developmental and physical disabilities are asexual, childlike, sexually innocent.
People with developmental disabilities are sexually impulsive, aggressive men & women promiscuous.
People with developmental disabilities will not marry or have children so they have no need to learn about sexuality.
It is not really necessary to broach the subject of intercourse since people with developmental disabilities are simply not capable of a close relationship, let alone a sexual encounter.


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 229 70
Stand by your opinion
They will be accompanied all their life by a support worker, so there is practically no chance that they will have sex.
People with developmental disabilities who are intellectually much behind their age or are very young, do not need to know about sex or sexuality. This type of information can be given to them much later - five years or even later.

Persons with disabilities should not be allowed to masturbate because it can become a habit.
It is not natural for women to be sexually attracted to women or men to be sexually attracted to men.
Closing Questions
230 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Your present circumstances don’t determine where you can go; they merely determine where you start.
- Nido Qubein
module 13: promoting competency

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 233


234 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
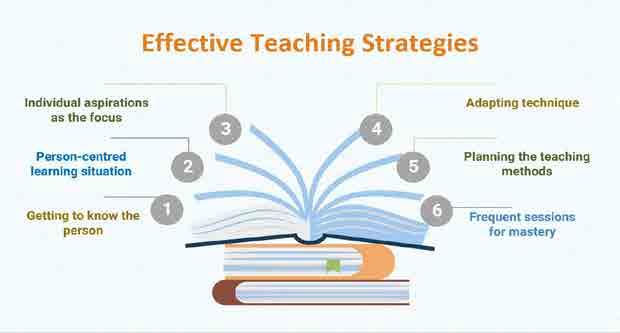

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 235


236 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 237


238 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
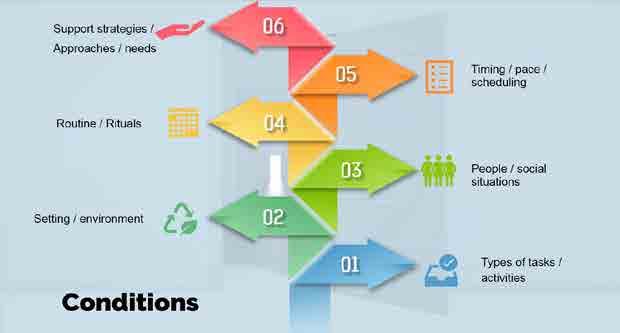

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 239

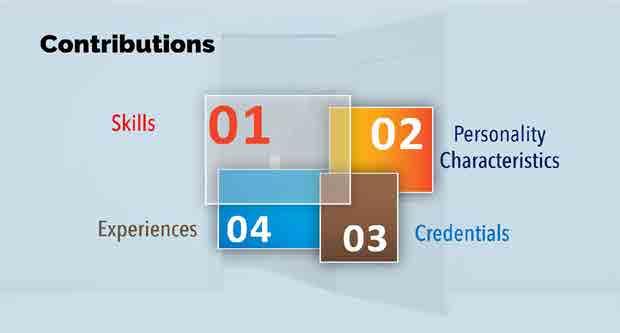
240 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners

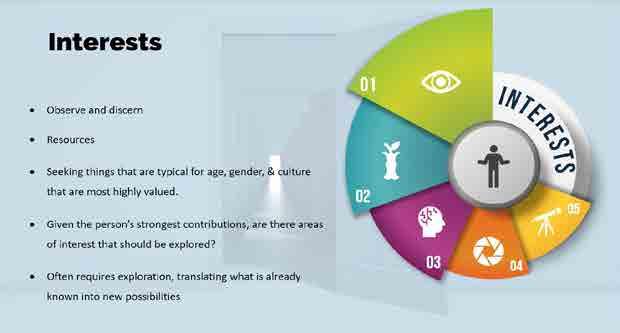
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 241

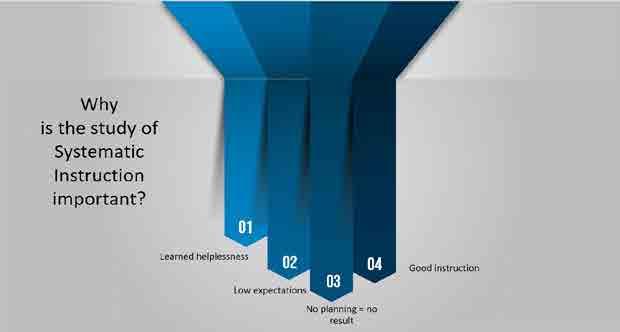
242 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 243


244 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 245


246 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 247


248 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 249


250 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 251


252 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 253


254 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 255


256 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 257

258 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners


Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 259

260 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners

Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 261


262 Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners
Foundations oF direct support: a national training program for direct support practitioners 263
 Keystone Institute India lraj@khs.org
Keystone Institute India lraj@khs.org






































































































































































































































































































































































































































 Developed by Darcy Elks
Developed by Darcy Elks
















































































































































































