6 minute read
PRIMARY CASE STUDY – AURANGABAD AIRPORT
Overview
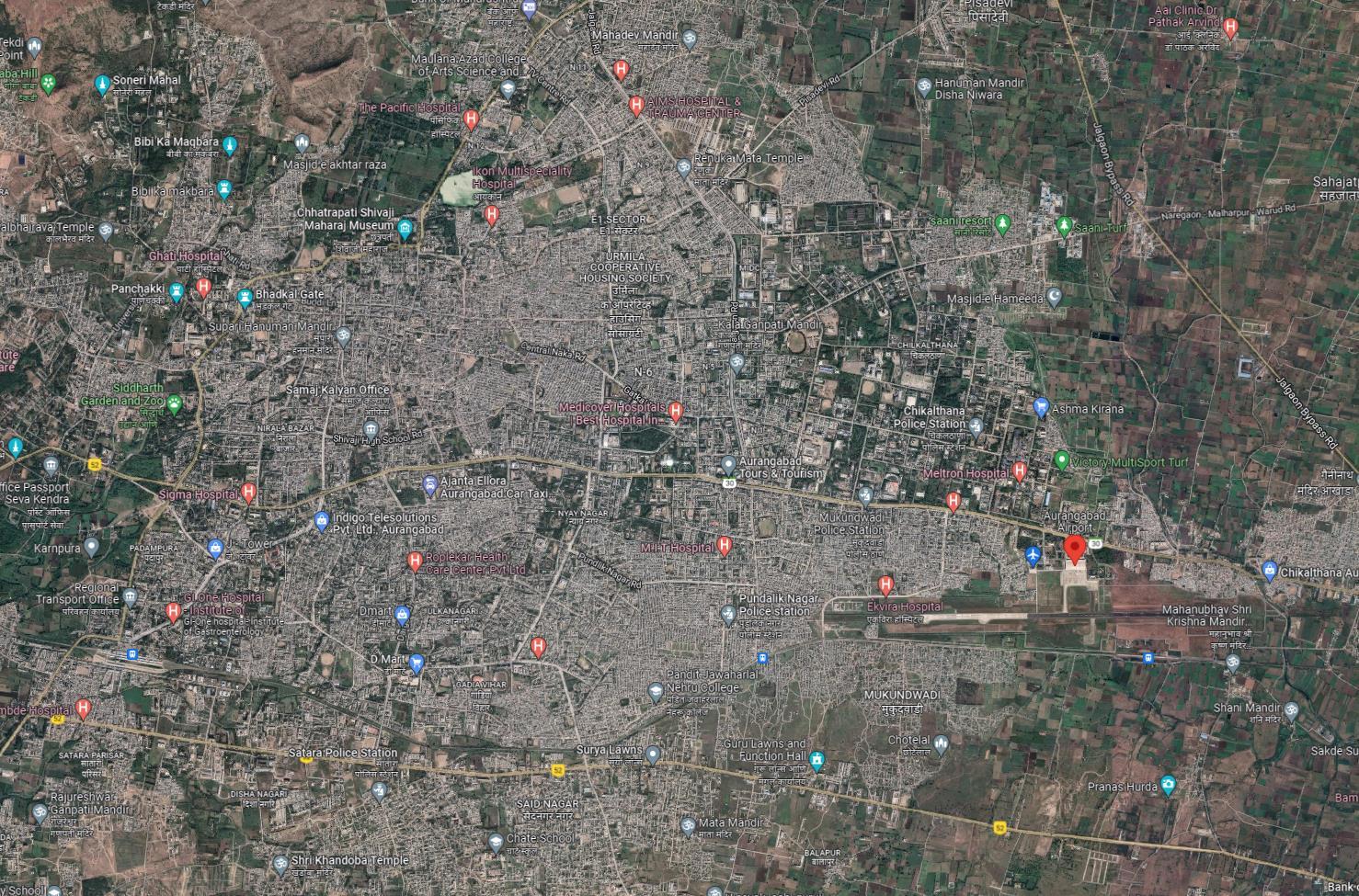
• Aurangabad airport is a public airport located in Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India.
Advertisement

• It is located about 5 5km east of the city center
• The airport is owned and operated by the Airports Authority of India with one passenger terminal with a 190000 Sqft floor area.
• The airport ordinally only has domestic destinations.
• However its operators seasonally run Haj services using makeshift immigration and custom counters.
Climate Analysis
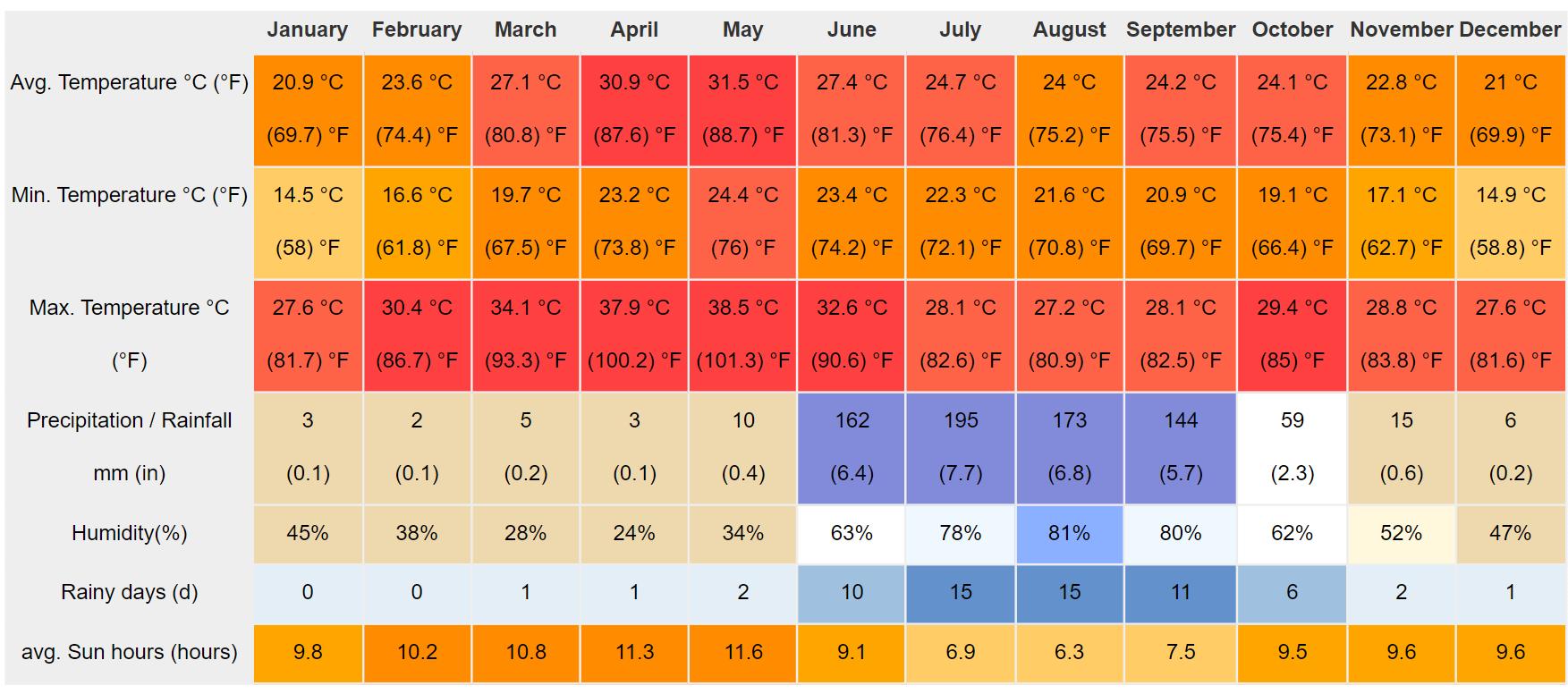
• Aurangabad is influenced by the local steppe climate.
• The temperature here averages 25.2 °C | 77.3 °F. The annual rainfall is 777 mm | 30.6 inch.
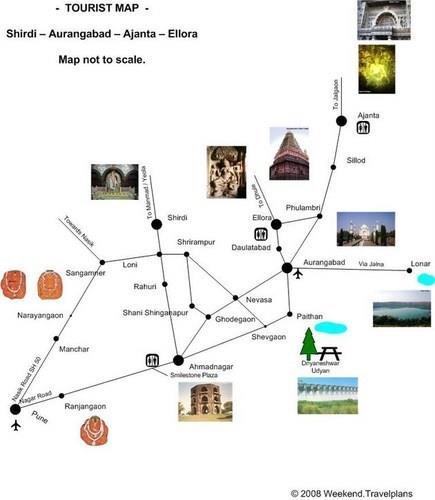
Tourism Map
Airport Details
• LOCATION
• ELEVATION
• ARCHITECT & ENGINEERS
• SITE AREA
• NUMBER OF RUNWAYS
• ORIENTATION
• RUNWAY DIMENSIONS
• SURFACE
• RUNWAY CONFIGURATION
• TYPE OF AIRCRAFT
• NO OF AIRCRAFTS ARRIVING/DEPARTING PER DAY
• APRON LENGTH
• APRON DIMENSIONS
• APRON CAPACITY
• NO OF HANGARS
• TERMINAL AREA
• PASSENGER CAPACITY
• NO OF FLOORS
• BUILDING MATERIALS
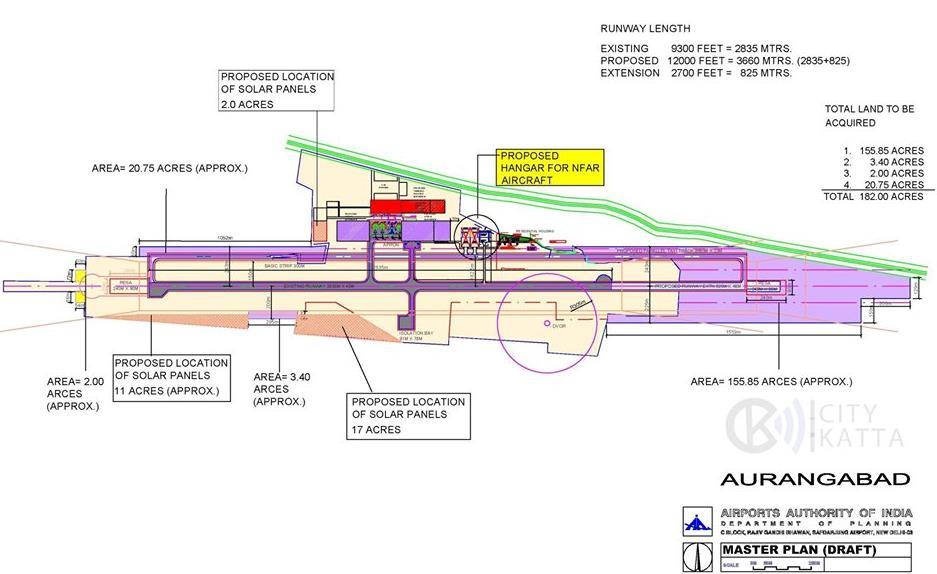
EXISTING SITE PLAN
Aurangabad, India
582m above sea level
Punj Lloyd Group
557.55 acres 01 09/27 2835 x 45M ASPHALT SINGLE
A320, B-737, B767, ATR72 31/day 116M 220x145M A320, B-737, B767, ATR72
22964.35 sqm 700
Ground + 1 RCC + steel structure. Aluminium composite sheet used for external cladding.
Pie Chart Showing Site Area
PROPOSED SITE PLAN W PROPOSED TAXIWAY SITE PLAN
• The airport is directly connected to Jalna Aurangabad highway. Currently there is an existing single runway with turnarounds.

• But a new taxiway is being proposed.
• The old terminal at the site is being used as a cargo hangar.
ALLANA COLLEGE OF ARCHITECTURE

Area Analysis
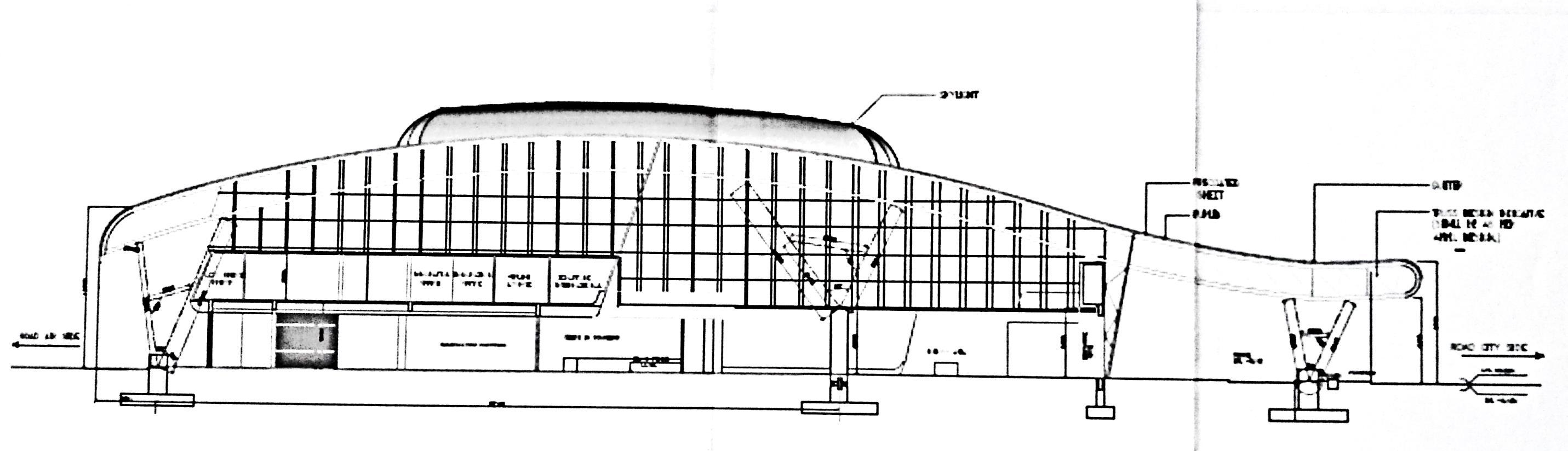
Structural System
Project History
• In the early 1990s, the Government of Maharashtra attempted to develop tourism in Aurangabad district (Ajanta, Ellora, Daulatabad, Bibi Ka Magara in Aurangabad city) but the project failed to take off.

• Late in the decade the government awarded it to JBIC (Japan Bank for International Cooperation), which planned, financed and implemented the project. JBIC was to assist in several ways - monument conservation, airport expansion, upgrading roads to the monuments, improving water quality, expanding electrical service and implementing a visitormanagement system
• Funds required for the fist phase were =817.1 million, of which = 694.8 million was allocated by JBIC.
• This phase concentrated on the basic infrastructure and necessary amenities in and around Aurangabad.
• The second phase (costing € 3.60 billion) received about 3 billion from JBIC, with the remainder
• RCC columns have been used as primary structural member
• Steel pipe sections have been connected to these columns using pin joints.
• These pipe sections connect to the truss members which support the sheet roofing.
Architectural Features
Sustainability
• The roof projection at the entrance is an 'open style' modern artistic design.
• Robust pillars depict the local architecture of Ajanta and Ellora caves and brings its resonance to the spaces inside the terminal
Views
• The large glass openings and roof lighting has been designed to reduce the use of energy and maximize natural sources of light and ventilation

• In the new proposed site plan, a total combined area of 30 acres has been provided for installation of solar panels in order to reduce energy consumption.
Overall Analysis
• A systematic approach is used for planning in terms of arrangement of spaces.
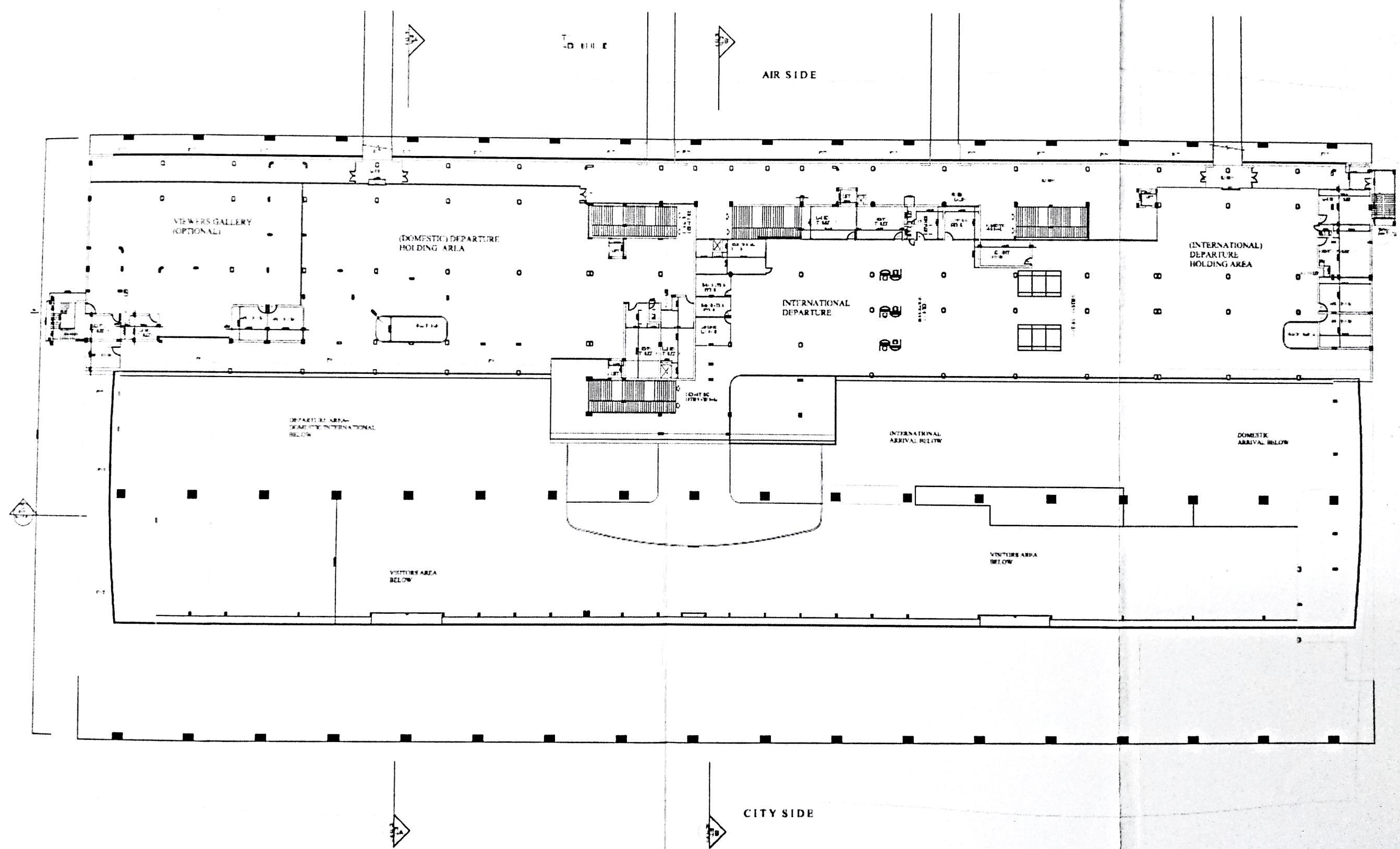
• ATC is located such that it gets an overall view of the entire runway and apron area.

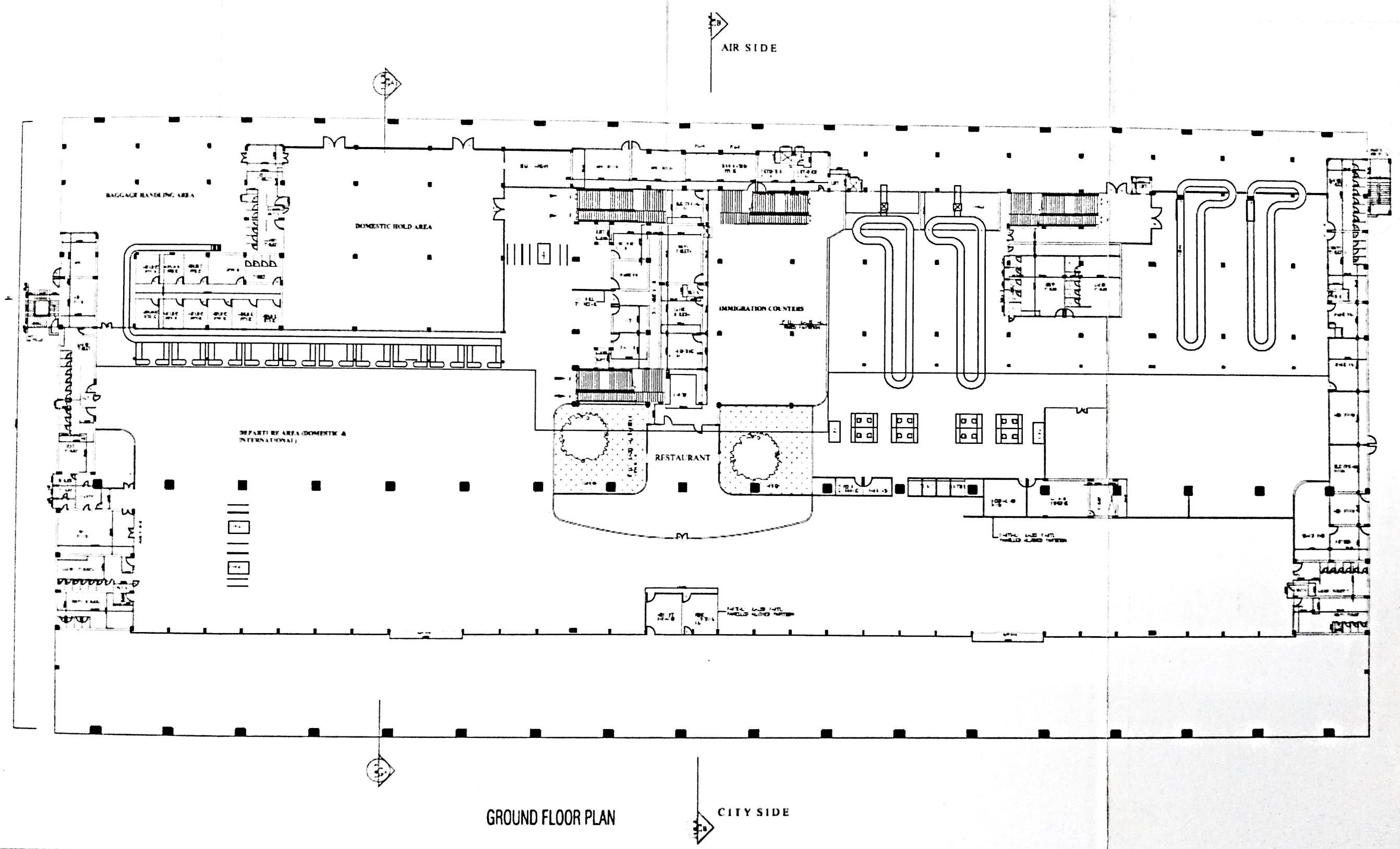
• Segregation is done for departure hall and arrival hall in order or avoid chaos between passenger circulation


• Large openings are used to reduce energy and maximize natural light and ventilation
• Columns speak about the architecture of Aurangabad

Airport Details
• LOCATION
• ELEVATION
• ARCHITECT & ENGINEERS
• SITE AREA
• NUMBER OF RUNWAYS
• ORIENTATION
• RUNWAY DIMENSIONS
• SURFACE
• RUNWAY CONFIGURATION
• TYPE OF AIRCRAFT
• NO OF AIRCRAFTS ARRIVING/DEPARTING PER DAY
• APRON DIMENSIONS
• APRON CAPACITY
• NO OF HANGARS
• TERMINAL AREA
• PASSENGER CAPACITY
• NO OF FLOORS
• BUILDING MATERIALS
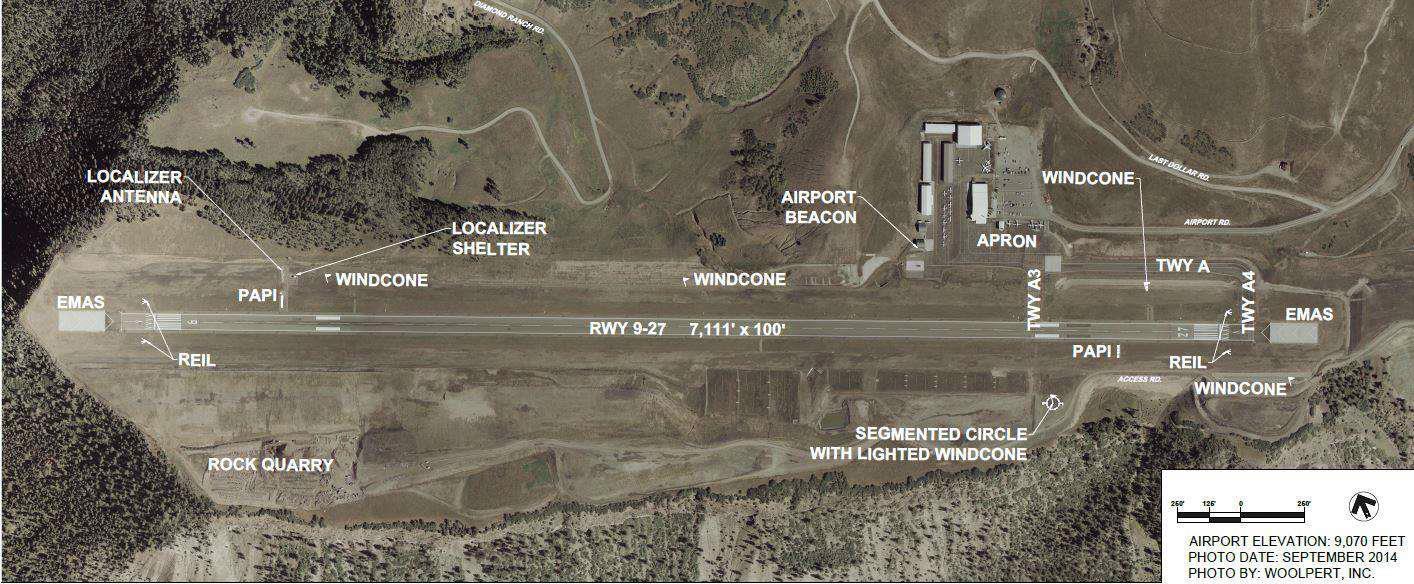
Runway Design
Telluride, Colorado, USA
2767m above sea level Reynolds, Smith and Hills, Inc
542 acres
01 9/27
2167 x 30m
Asphalt/grooved Single
F50, A119, B463, BE99 Avg 26/day
170x60M
B463x4nos, BE99x6nos
5 1714 sqm 75-100 during peak hours
Ground + 1 Steel structure. Aluminium composite sheet used for external cladding.
Overview
• The Telluride Regional Airport is a public airport located in southwest Colorado, approximately four miles west of the Town of Telluride.

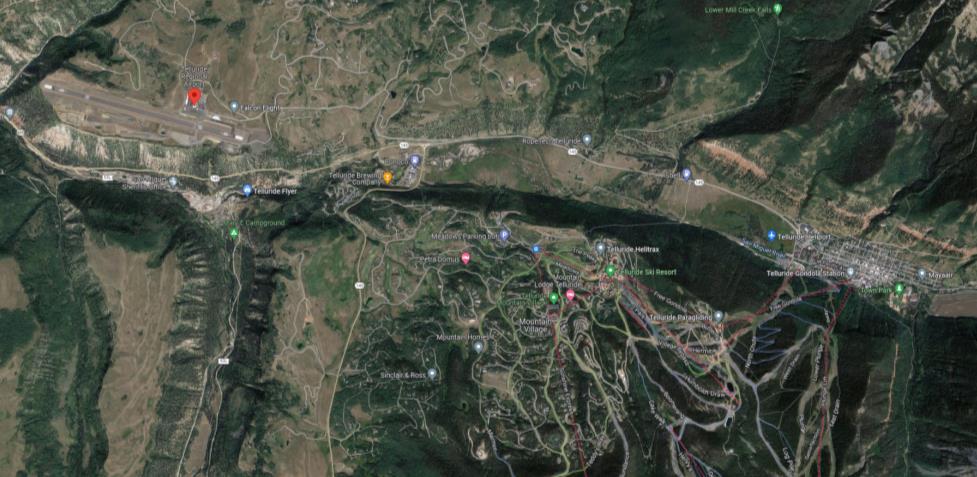
• Built in 1980, The Airport is a critical asset for the Telluride resort community which is driven economically by tourism.

• This objective was partially intended to help ward off increased vehicle usage, and subsequent needs such as parking, in effort to maintain the area’s rich historic culture
• Due to increased tourism in the region, there was a need to redevelop parts of the airport, provide a new strategic plan to support the Airport’s need for the next 20 years.
Location
Climate Analysis
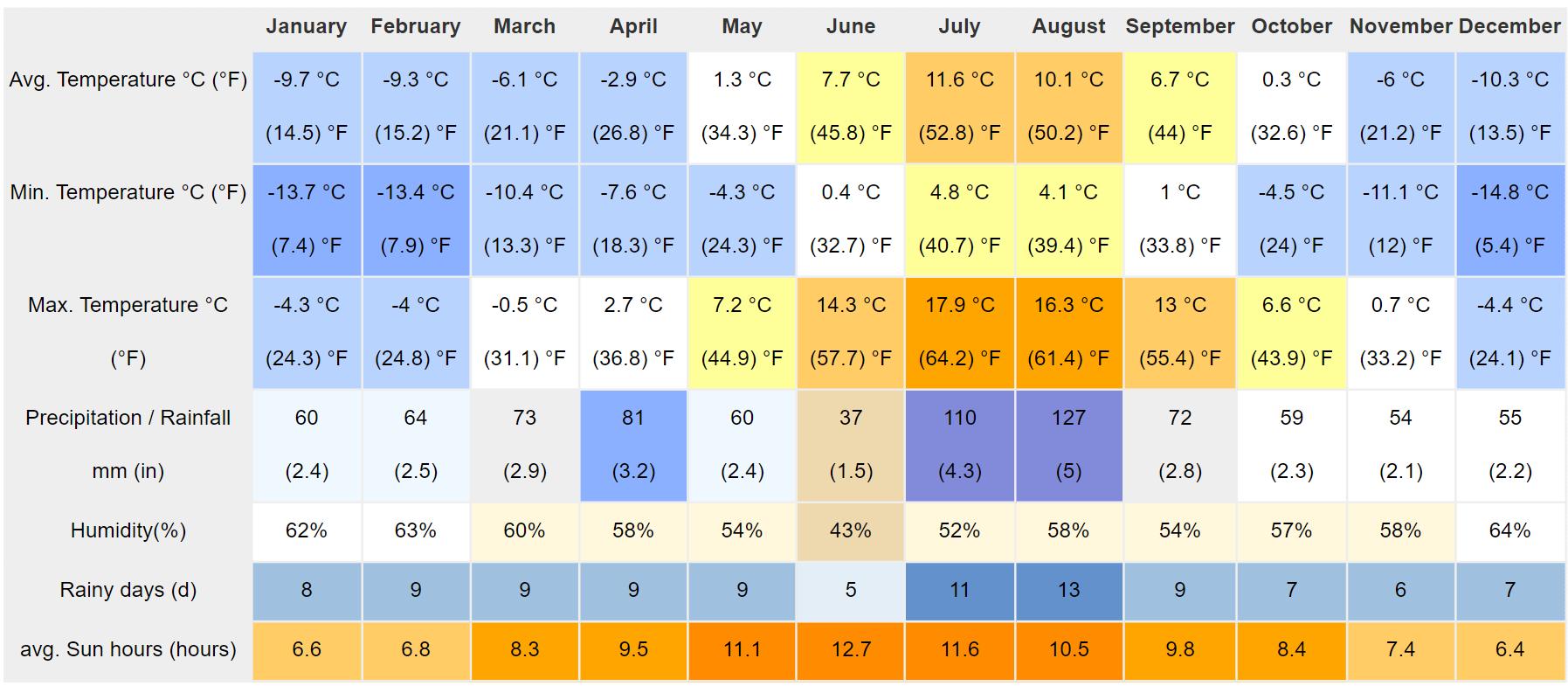
• Runway faces an open valley at 90 degree and 270 degree such that planes taking off or landing do not collide with a mountain cliff
• Due to site restrictions, a turn-around taxiways is provided instead of a parallel taxiway.

PROPOSED SITE PLAN OPTIONS
• In Alternative 1 the snow removal and maintenance area has been relocated, allowing more floor area for the terminal, while in Alternative 2, entire terminal block has been shifted giving more space for the apron area
• Parking in Alternative 2 has been shifted to north creating a better distinction between landside and airside
• Taxiways have been improved and additional parking space has been provided for aircraft parking.
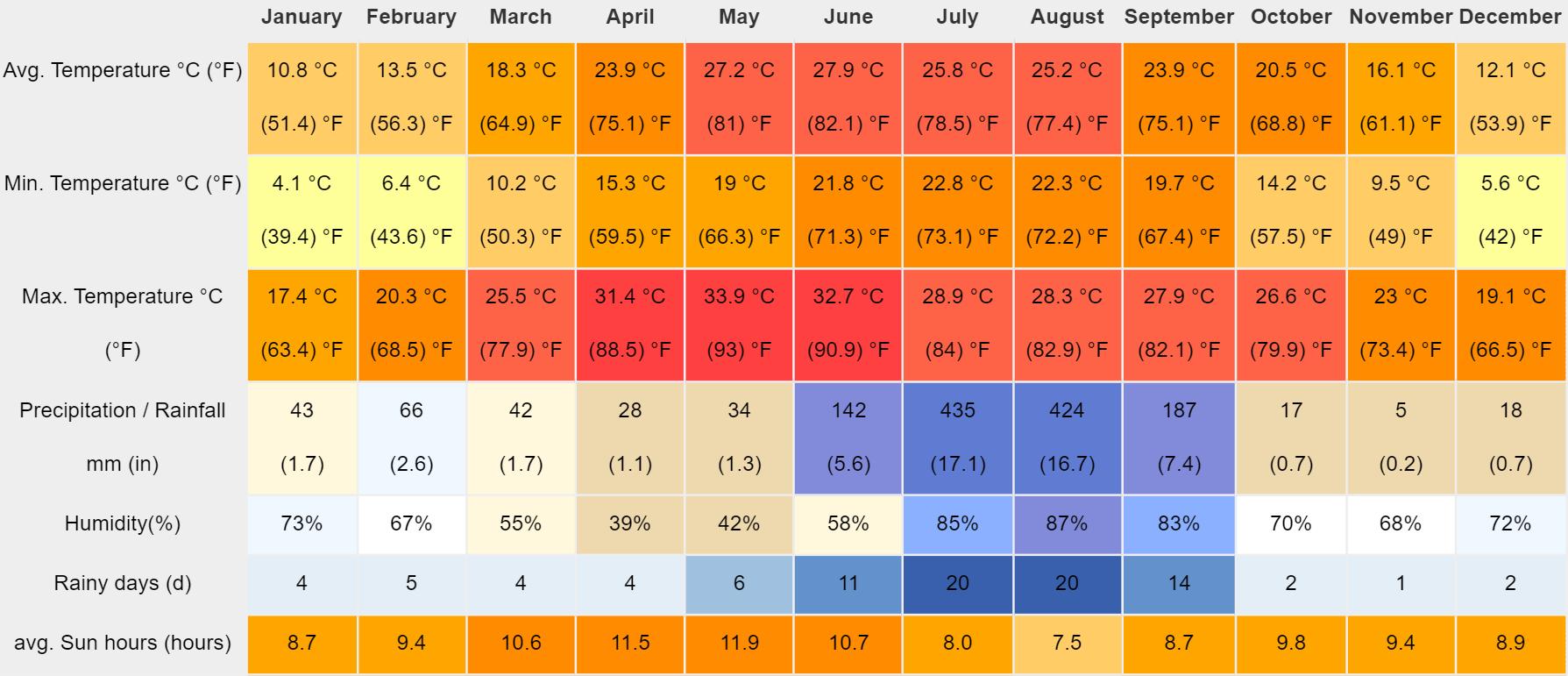
• It is cold and temperate in Telluride. The climate here is classified as Dfb by the KöppenGeiger system. The average temperature in Telluride is -0.6 °C | 31.0 °F. Precipitation here is about 852 mm | 33.5 inch per year.
Sustainability
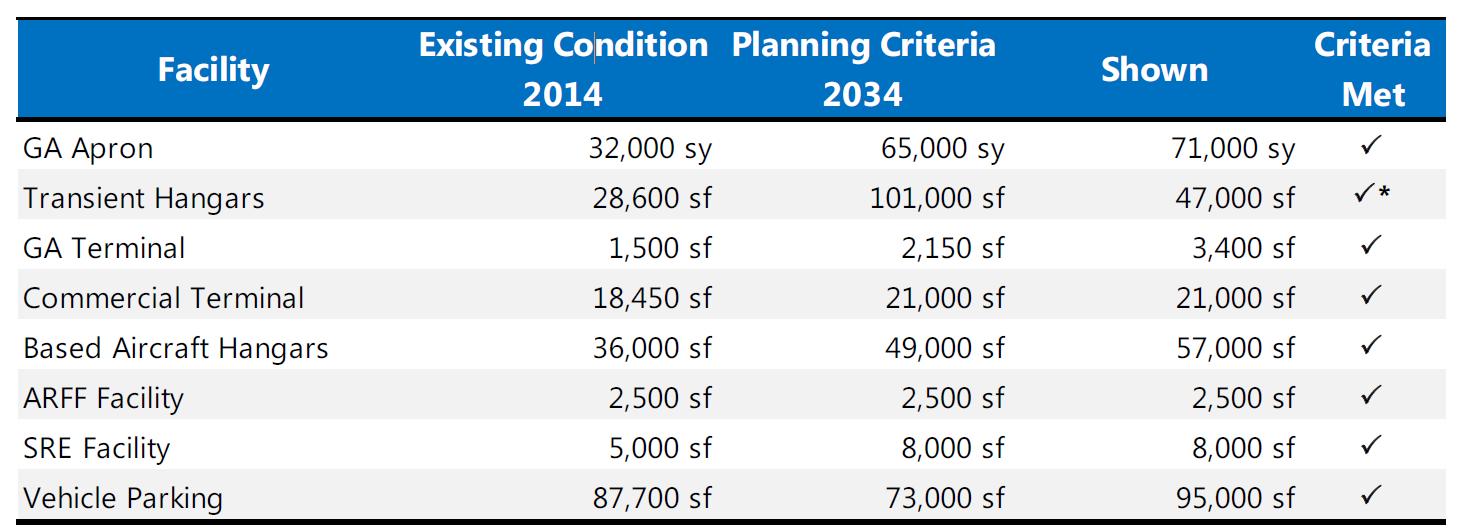
Planning Criteria
• Low cost, locally available materials have been used for construction
• Large opens provided to allow maximum amount of sunlight as it is in a cold region.
Overall Analysis
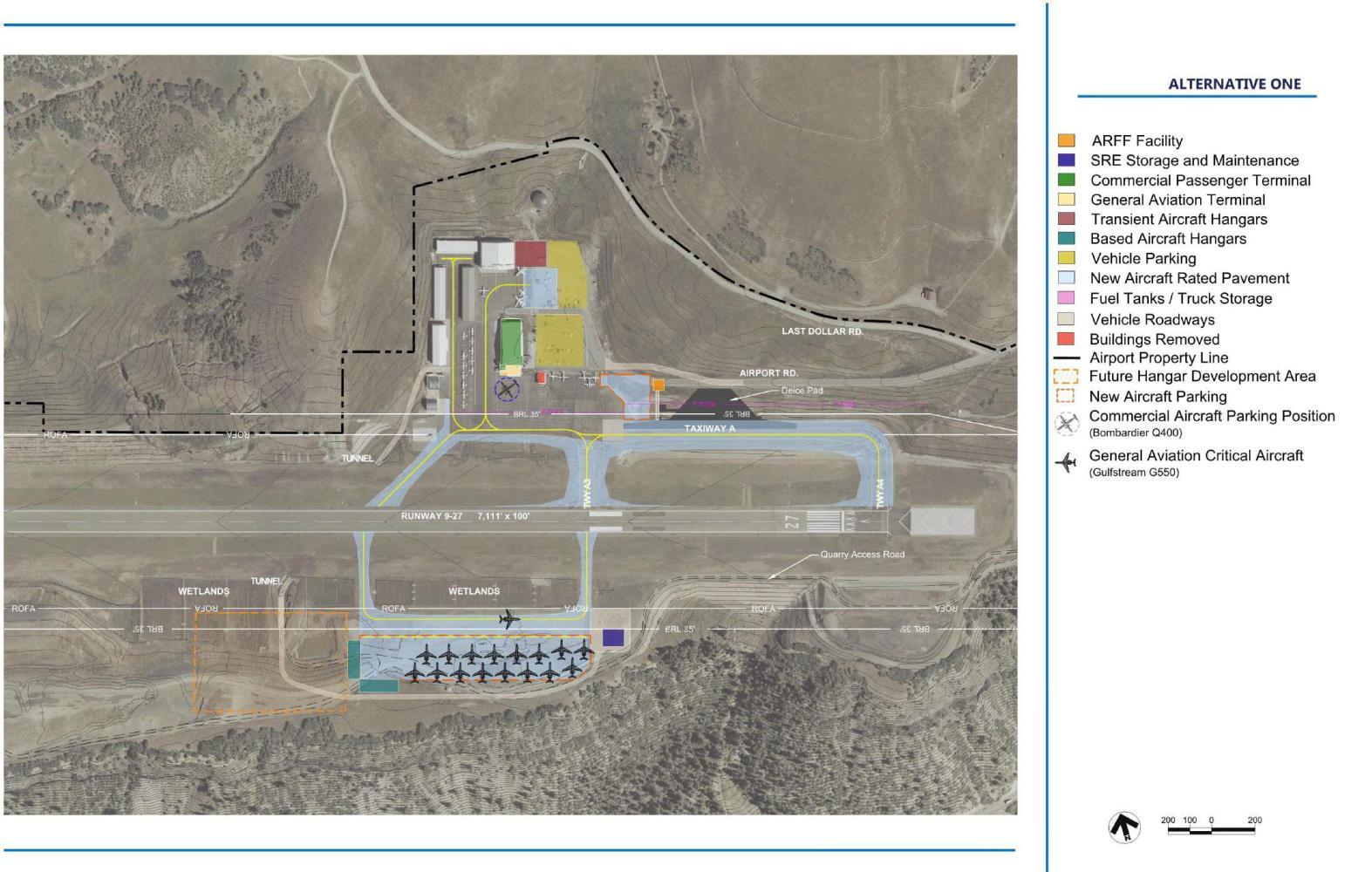
• Initially, as the requirement was less, a hangar itself was used as a terminal which had very less floor area
• With the increased need, modifications were made to the overall master plan including relocation of terminal in order to handle more amount of passengers and aircraft flow.
• Small to medium size aircrafts are operated from here due to the surrounding terrain and runway restrictions
• Runway is oriented towards a valley in order to avoid collision into a cliff during takeoff.


• Due to site limitations, a turn-around taxiway is provided instead of a parallel taxiway.
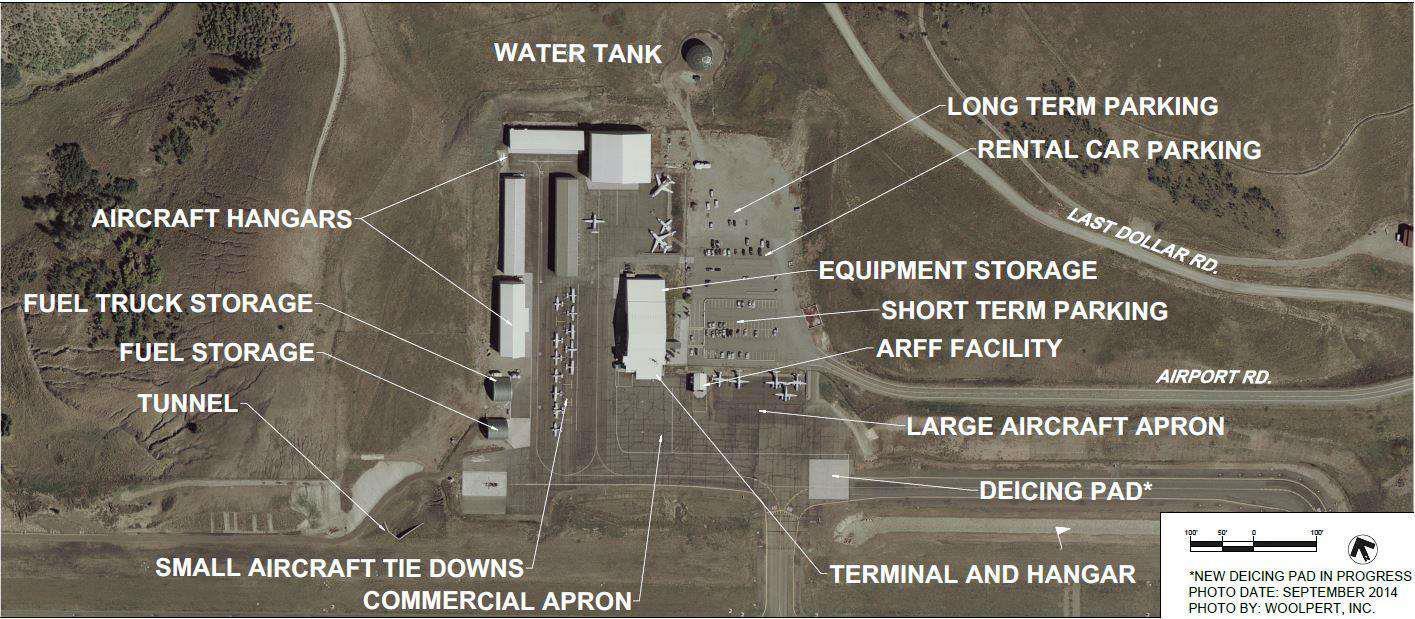
EXISTING SITE PLAN
PLAN
Overview
• The state of Uttarakhand depends on tourism – the backbone of its economy Dehradun Airport, also known as Jolly Grant Airport, is a domestic airport located 25 km south-east of Dehradun.
• As many airports in Uttarakhand come under unserved airports and are not in much use, hence this airport is a major connectivity hub in the state.





• The airport was built in 1974 and initially use to only handle small size Dornier aircraft but over time, it has had several expansions and can now handles many large size aircrafts
• With increase in passengers a new international terminal was constructed at a site adjacent to the existing terminal.



Airport Details
• LOCATION
• ELEVATION
• ARCHITECT & ENGINEERS
• SITE AREA
• NUMBER OF RUNWAYS
• ORIENTATION
• RUNWAY DIMENSIONS
• SURFACE
• RUNWAY CONFIGURATION
• TYPE OF AIRCRAFT
• NO OF AIRCRAFTS ARRIVING/DEPARTING PER DAY
• APRON DIMENSIONS
• APRON CAPACITY
• NO OF HANGARS
• TERMINAL AREA
• PASSENGER CAPACITY
• NO OF CHECKIN COUNTERS
• NO OF FLOORS
• BUILDING MATERIALS
Jauligrant, Uttarakhand
566m above sea level
Harpal Singh (AAI)
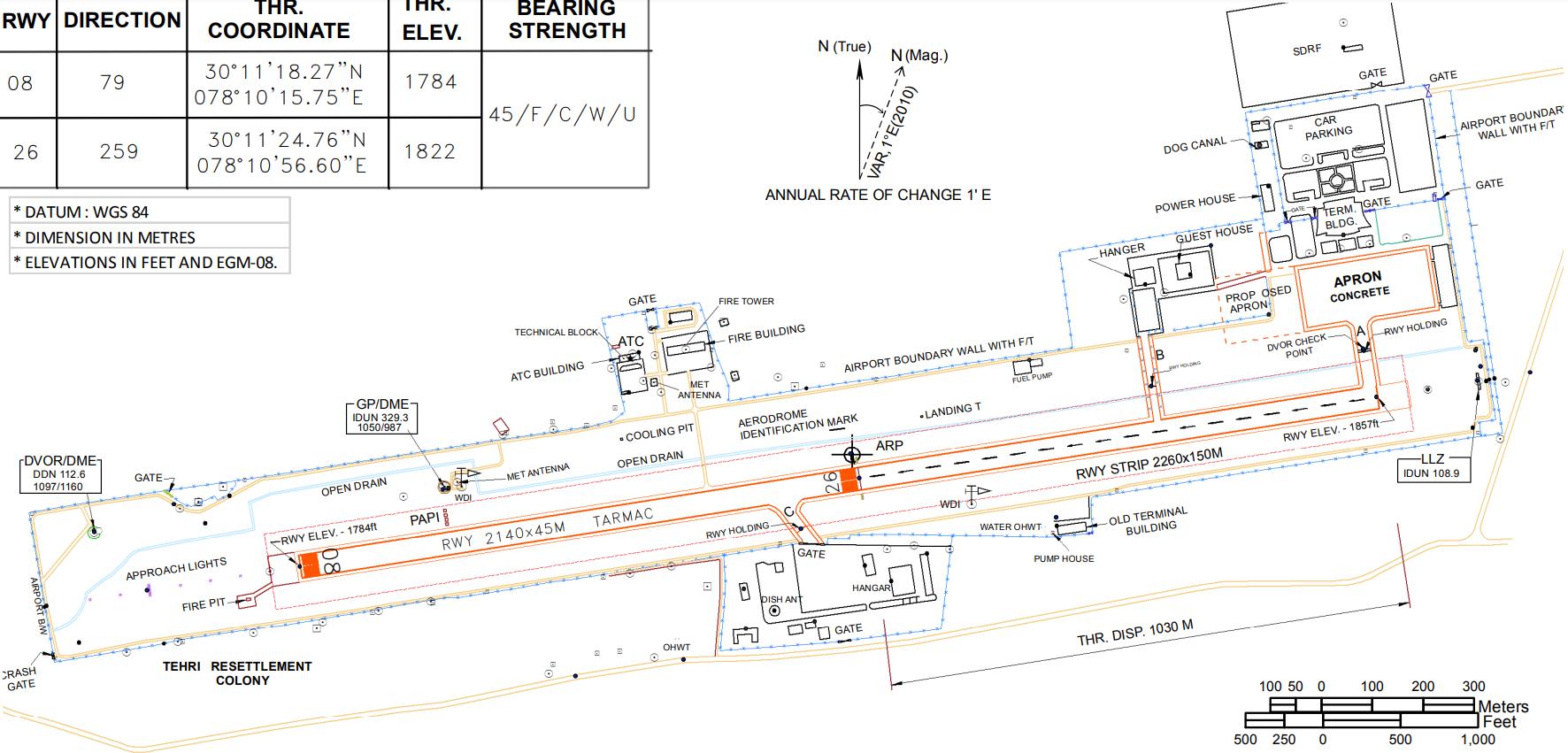
326 acres 01 08/26
2140x45M Asphalt Single
B747, AB300, B737, ATR72 Approx 30-50/day
253.5m x 115m
B747x8nos, ATR 72x4nos
2nos
Old- 4200, New- 42766sqm 1800 during peak hours 11
Ground + 1
Concrete + steel. Aluminium composite sheet used for external cladding.
Location
Climate Analysis
DEHRADUN
Old Terminal Features
• The climate here is warm and temperate. This climate is considered to be Cwa according to the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. In Dehradun, the average annual temperature is 20 4 °C | 68 8 °F About 1441 mm | 56 7 inch of precipitation falls annually
Sustainability
• Large glass opens and skylights are provided to allow heat to enter the building as it is in a cold region.
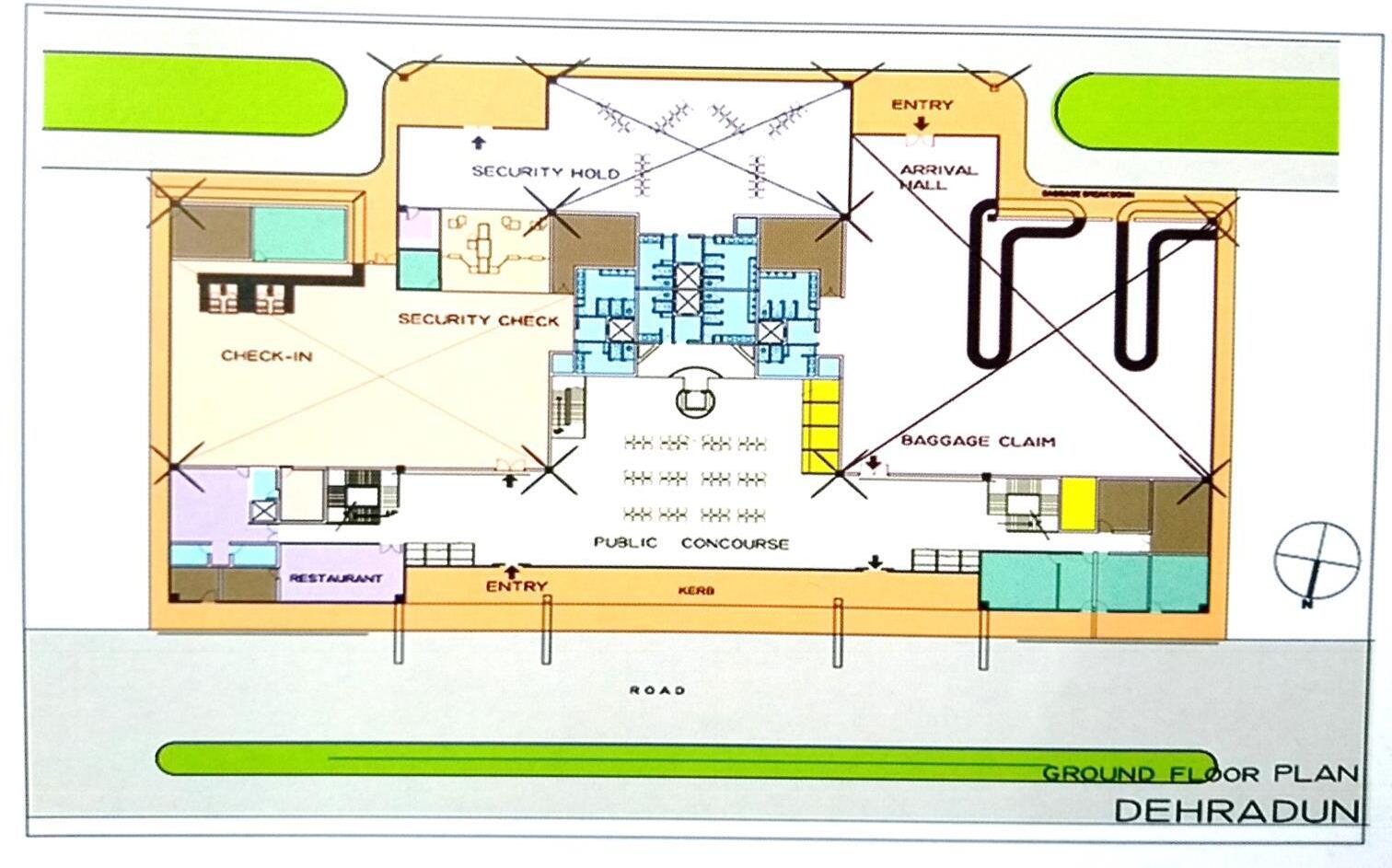
Old Terminal Layout
• A clear segregation is done between arrival and departure zones in order to avoid chaos between passengers in the terminal
• First floor consists of restaurants, lounge areas etc.
New Terminal Features
• The new terminal handles 1800 passengers during peak hours

• The design of the columns are inspired by the shape of the state flower of Uttarakhand

• Large paintings are done in the interiors which depict the culture of Kedarnath and Badrinath.
Overall Analysis
• In terms of site plan, there is proper segregation between airside and landside activities

• Pawan Hans touring facility is located away from main terminal to avoid collision between different activities.
• Due to space restrictions, turn around taxiway is provided instead of a parallel taxiway.
• The airport handles large aircrafts arriving from metro cities, but also handles a large number of ATR 72 which are used for connectivity in remote locations.
• Clear segregation between arrival and departure is done in the terminal in order to avoid chaos between passengers.






