
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Yashashree Hanumant Khanolkar
Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Science, Sant Rawool Maharaj Mahavidyalaya, Kudal, Maharashtra, India
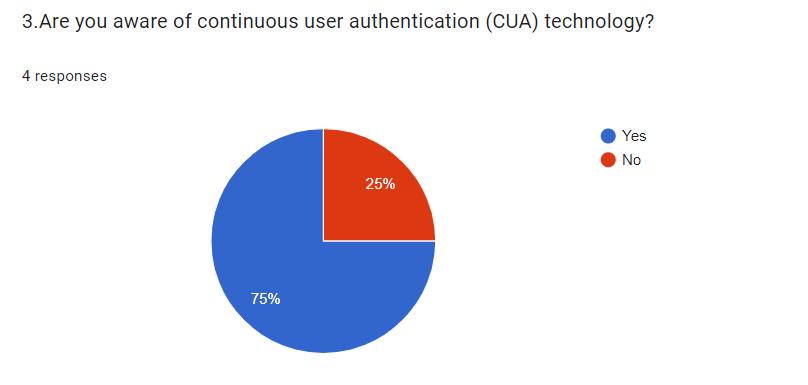
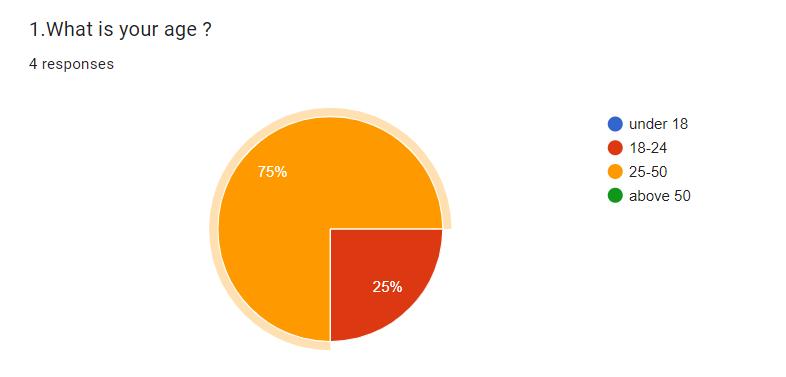
Abstract - In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobile technology, ensuring the security of personal and sensitive information is paramount. Continuous user authentication represents a significant advancement in mobile security, offeringongoingverificationofuseridentitybeyondtheinitial login. This paper explores the importance, methods, benefits, and challenges of continuous user authentication on mobile devices. It provides a comprehensive review of current technologies and research, highlighting the critical role continuous authentication plays in enhancing security and user experience in mobile ecosystems.
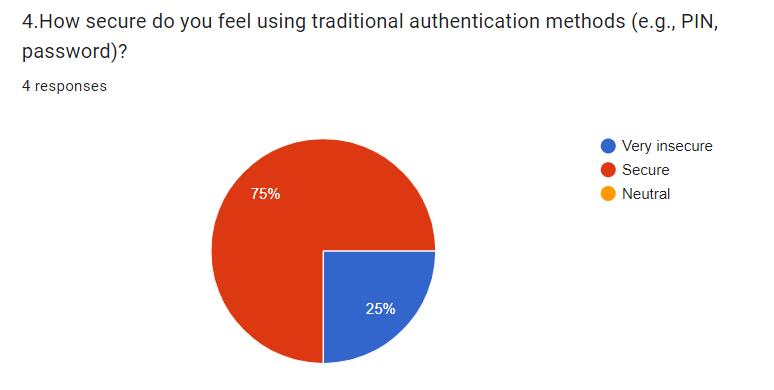
With the increasing reliance on mobile devices for a wide range of activities, from communication to banking, the security of these devices has become a major concern. Traditionalauthenticationmethods,suchaspasswordsand PINs, provide a one-time verification that can be easily compromised.Continuoususerauthentication(CUA)offersa dynamic and persistent security solution by continuously monitoringandverifyingtheuser'sidentitythroughoutthe device's usage session. This paper delves into the significance of CUA, examining its potential to mitigate securityrisksandenhanceuserconvenience.
Behavioral biometrics are an advanced method of continuous user authentication that relies on analyzing unique patterns in a user's behavior. This approach leverages the inherent uniqueness in how individuals interactwithdevicesandsystems,providinga robustand continuousverificationmechanism.Here’sanin-depthlook atvariousaspectsofbehavioralbiometrics:
1.1.1
Description: Keystroke dynamics analyze the rhythm and patterns of typing on a keyboard. This method captures various typing characteristics that are unique to each individual.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Typing Speed:Overalltypingspeedmeasuredincharacters perminute.
Dwell Time:Durationeachkeyispressed.
Flight Time:Timetakentomovefromonekeytoanother. Error Patterns:Commonmistakesandcorrectionpatterns.
Pressure: Amount of pressure applied to each key (in deviceswithpressure-sensitivekeyboards).
Applications:
Secureaccesstosystems.
Detectionofunauthorizedaccessduringactivesessions.
Challenges:
Variabilityintypingduetofatigue,injury,ormood.
Difficultyincapturingaccuratedataonmobiledevices.
Description:Mousedynamicsinvolvetrackingandanalyzing the way a user interacts with a mouse. This includes movementpatterns,clickbehaviors,andscrollinghabits.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Movement Patterns: Speed,acceleration,anddirectionof mousemovements.
Click Patterns: Timingandfrequencyofmouseclicks. Drag and Drop Actions: Mannerofperformingdrag-anddropoperations.
Scroll Behavior: Speedandfrequencyofscrollingactions.
Applications:
Continuousauthenticationindesktopenvironments.
Detectionofanomalousbehaviorindicatingpotentialfraud.
Challenges:
Limitedapplicabilitytotouchscreendevices.
Environmental factors (e.g., surface texture) can affect mousebehavior.
Description:Touchdynamicsanalyzeuserinteractionswith touchscreens. This includes swiping, tapping, and multitouchgestures.
Characteristics Analyzed: Swipe Patterns: Speed, length, and direction of swipe gestures.
Tap Behavior: Pressureanddurationoftaps. Multi-touch Gestures: Use of pinch, zoom, and rotation gestures.
Typing Patterns: Analysis of on-screen keyboard usage similartokeystrokedynamics.
Applications:
Secureaccesstomobiledevices.
Continuoususerverificationinappsandmobilebrowsers.
Challenges:
Variability in touch behavior due to different device sizes andtouchinterfaces.
Sensitivitytoenvironmentalfactorslikehumidityandscreen cleanliness.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Description:Gaitanalysisstudiestheuniquewayaperson walks. This can be captured using sensors in wearable devicesorsmartphones.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Step Length: Distancecoveredineachstep.
Body Movements: Hip,knee,andanklemovementsduring walking.
Rhythm and Symmetry:Consistencyinwalkingpatterns.
Applications:
Continuousauthenticationforwearabledevices.
Securityinapplicationsthatrequiremovementtracking.
Challenges:
Variabilityduetoinjuries,changesinfootwear,orwalking surfaces.
Limitedaccuracyincrowdedenvironmentswherewalking patternscanbedisrupted.
Description: Voice recognition in behavioral biometrics involvesanalyzingthecharacteristicsofauser’svoiceand speechpatterns.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Pitch and Tone: Frequencycharacteristicsofthevoice.
Rhythm and Pace:Speedandtimingofspeech. Accent and Pronunciation: Uniquespeechcharacteristics influencedbybackgroundandregion.
Voice Modulation: Variationsintoneandvolume.
Applications:
Secureaccesstovoice-controlledsystemsanddevices. Continuous verification during phone calls or voice interactions.
Challenges:
Backgroundnoisecanaffectaccuracy.
Variabilityduetohealthissues(e.g.,coldorsorethroat).
Description:Signaturedynamicsfocusontheuniquewaya person signs their name. This can be analyzed on digital platformsusingstylusortouchinputs.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Stroke Order and Direction: Sequenceanddirectionofpen strokes.
Pressure: Variationsinpressureduringthesigningprocess. Speed and Timing: Howquicklyandsmoothlythesignature iscompleted.
Size and Shape: Overall size and geometric shape of the signature.
Applications:
Documentverificationandauthorization. Continuous monitoring in applications requiring frequent signatures.
Challenges:
Variability in signatures due to different devices or surfaces.Potentialforintentionalalterationsbytheuser.
Description: Behavioral profiling involves building a comprehensive profile of a user's typical behavior within digitalenvironments.
Characteristics Analyzed:
Application Usage Patterns: Frequency and duration of usingspecificapplications.
Navigation Paths: Typicalpathstakenthroughwebsitesor applications.
Interaction Sequences: Commonsequencesofactionsor commands.
Time of Use: Typicaltimeswhentheuserisactive.
Applications:
Detection of unusual activity patterns indicating potential securitythreats.
Personalizeduserexperiencesbasedonbehavior.
Challenges:
Privacyconcernsrelatedtocontinuousmonitoring. Potentialforfalsepositivesduetochangesinuserbehavior overtime.
Non-Intrusive: Does not require explicit user actions beyondnormalbehavior.
Difficult to Forge: Unique patterns are hard to replicate accurately.
Continuous Authentication: Providesongoingverification, reducingtheriskofsessionhijacking.
Variability in Behavior: Factors like stress, injury, or changinghabitscanaffectaccuracy.
Privacy Concerns: Continuous monitoring raises privacy issues; careful data handling and clear user consent are essential.
Environmental Factors:Changesintheenvironment,such as different devices or settings, can impact behavior and authenticationaccuracy
Implementation Complexity: Integrating behavioral biometrics into existing systems can be complex and resource-intensive.
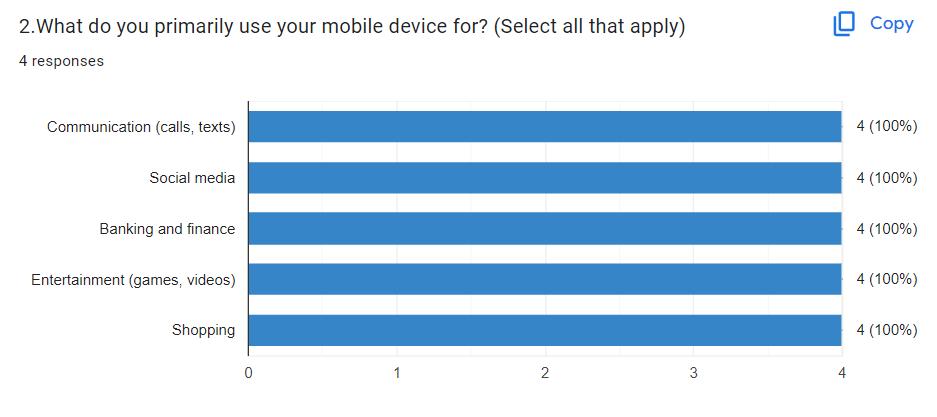
Banking and Finance: Enhancing security for online bankingandfinancialtransactions.
Healthcare: Securing access to sensitive medical records andsystems.
Enterprise Security: Ensuringsecureaccesstocorporate networksandapplications.
Consumer Electronics: Providing secure and seamless authenticationforsmartphones,tablets,andcomputers.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

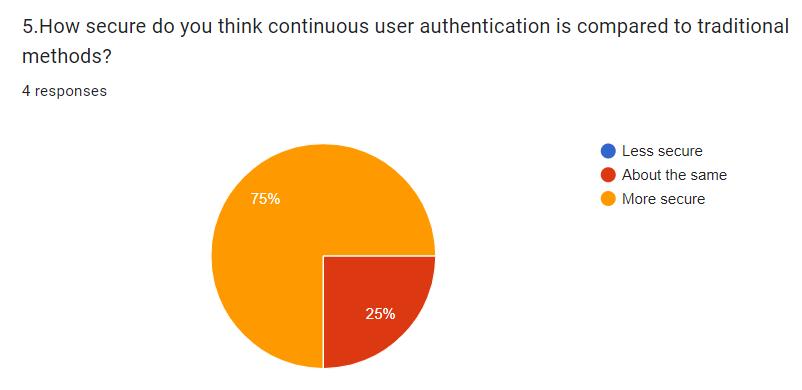
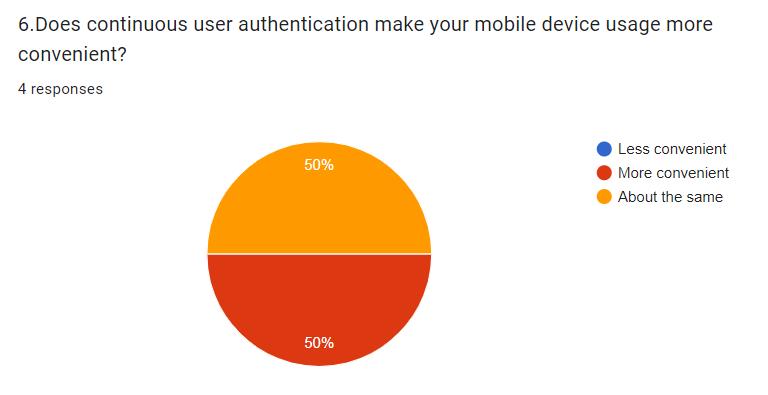
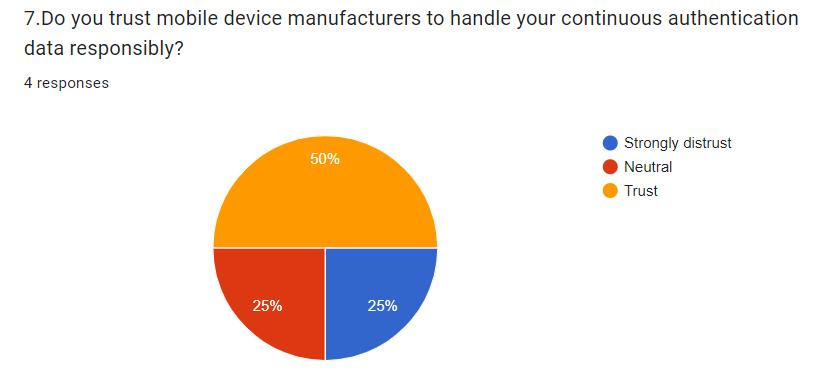
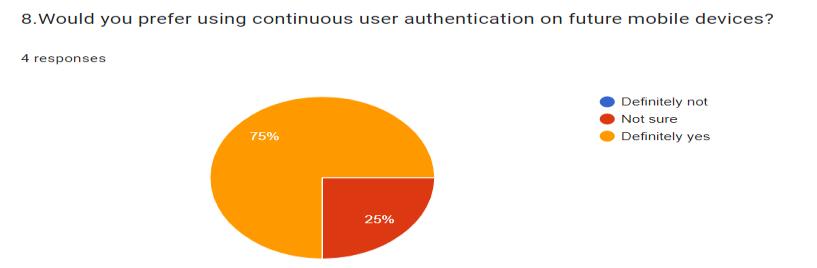
Privacy Concerns
Continuousmonitoringraisessignificantprivacyissues.The collectionandstorageofbiometricandbehavioraldatamust behandledwithutmostcaretoprotectuserprivacy.
Accuracy and Reliability
CUAsystemsmustbalancesecurityandusability.Highfalse positiveorfalsenegativeratescaneitherinconveniencethe userorfailtopreventunauthorizedaccess.
Resource Consumption
Continuous authentication can be resource-intensive, impacting battery life and device performance. Efficient algorithms and hardware optimizations are essential to mitigatethisissue.
4. CURRENT RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENTS
Recent studies focus on enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of CUA methods. Research into multimodal authentication, which combines various biometric and contextualdata,showspromiseinimprovingreliabilityand reducingfalsepositives/negatives.
4.1 Future Directions
The future of continuous user authentication lies in the integrationofadvancedAIandmachinelearningtechniques. Thesetechnologiescanenhancethepredictivecapabilitiesof CUAsystems,makingthemmoreadaptiveandresponsiveto theuser'sneedsandbehaviors.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, continuous authentication will play a crucial role in securing interconnected devices. Ensuring seamless and secure interactionsbetweenmobilegadgetsandIoTdeviceswillbe essential.
Continuous user authentication represents a vital advancement in the field of mobile security, providing significant benefits by enhancing both security and user experience.Thistechnologyaddressesthegrowingneedfor robustsecuritymeasuresinaworldwheremobiledevices are ubiquitous and integral to personal, professional, and financialactivities.Byleveraginguniquebehavioralpatterns and continuous monitoring, continuous authentication ensuresthatonlyauthorizedusershaveaccesstosensitive informationandservices,therebymitigatingrisksassociated withunauthorizedaccess,fraud,andidentitytheft.
While the promise of continuous user authentication is substantial,itisnotwithoutchallenges.Variabilityinuser behaviorduetofactorssuchasstress,healthconditions,or changesinhabitscanaffecttheaccuracyofthesesystems. Additionally,therearelegitimateconcernsregardingprivacy and data security, as continuous monitoring requires the collection and analysis of personal behavioral data. The implementation complexity and the need for seamless integration into existing systems also present significant hurdles.
However,thelandscapeofcontinuoususerauthenticationis rapidly evolving. Ongoing research and technological advancements are poised to address these issues. Innovations in machine learning and artificial intelligence are enhancing the accuracy and reliability of behavioral biometrics, while advances in data encryption and anonymization are addressing privacy concerns. These developmentsarepavingthewayformorerobust,secure, anduser-friendlyauthenticationsystemsthatcanadaptto thedynamicnatureofhumanbehavior.
Asmobiledevicesbecomeincreasinglyintegraltodailylife, from online banking and shopping to healthcare and communication, the importance of continuous authentication will only grow. It is expected to become a cornerstone of mobile security strategies, ensuring that users can trust their devices to protect their personal informationandprovidesecureaccesstocriticalservices.In this context, continuous user authentication not only representsasignificanttechnologicaladvancementbutalso anecessaryevolutioninthequestforcomprehensivemobile security.
By fostering a secure and seamless user experience, continuousauthenticationstandstosignificantlyimpacthow weinteractwithourdevices,providingpeaceofmindanda higherlevelofsecurityinanincreasinglyconnectedworld. Aswecontinuetorelymoreheavilyonmobiletechnology, theadoptionandrefinementofcontinuousauthentication methodswillbecrucialinsafeguardingourdigitallives.
Bojkovic,Z.,&Bakmaz,B.(2018).Continuousauthentication in mobile environments: A survey. Journal of Information SecurityandApplications,42,53-64.
GoogleATAP.(2016).ProjectAbacus:Thenextevolutionof userauthentication.RetrievedfromGoogleATAP
Jain,A.K.,Ross,A.,&Nandakumar,K.(2011).Introductionto Biometrics.Springer.
Angulo,J.,&Wästlund,E.(2015).ContinuousAuthentication Using Touchscreen Gestures on Mobile Devices. IEEE TransactionsonInformationForensicsandSecurity,10(8), 1792-1801.
Khan,H.,Atwater,A.,&Hengartner,U.(2014).It'snotabout size, it's about timing: Methods for continuous authenticationofsmartphoneusers.Proceedingsofthe2014 ACMSIGSACConferenceonComputerandCommunications Security(CCS),145-156.
Frank,M.,Biedert,R.,Ma,E.,Martinovic,I.,&Song,D.(2013). Touchalytics:OntheApplicabilityofTouchscreenInputasa Behavioral Biometric for Continuous Authentication. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 8(1), 136-148.
Bo, C., Zhang, L., Li, X.-Y., Huang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2013). SilentSense:SilentUserIdentificationviaDynamicsofTouch and Movement Behavioral Biometrics. Proceedings of the 19thAnnualInternationalConferenceonMobileComputing &Networking(MobiCom),187-190.
Shi,N.(2010).MobileandUbiquitousCommerce:Advanced E-BusinessMethods.IGIGlobal.
Jiang, R., Al-maadeed, S., Bouridane, A., Crookes, D., & Beghdadi,A.(Eds.).(2017).BiometricSecurityandPrivacy: Opportunities&ChallengesinTheBigDataEra.Springer.

YashashreeHanumantKhanolkar M.ScInformationTechnology SantRawoolMaharaj Mahavidyalaya,Kudal