
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dipesh D. Sambare1 , Trupti Narkhede2 , P. J. Salunke3
1PG Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Mahatma Gandhi Mission's College of Engineering and Technology (MGMCET), Kamothe, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Mahatma Gandhi Mission's College of Engineering and Technology (MGMCET), Kamothe, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3Head of Department, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Mahatma Gandhi Mission's College of Engineering and Technology (MGMCET), Kamothe, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - Theseismicperformanceofhigh-risereinforced concrete(RC)buildingswithverticalgeometricirregularities is a critical aspect of structural engineering. This study evaluatestheimpactofP-DeltaeffectsonaG+50RCbuilding with T-shape, L-shape, and Step-back irregularities under Nonlinear Time History Analysis (NLTHA) using Bhuj earthquakedata.AmodelwasanalyzedinETABS,considering variations in structural configuration and the presence or absence of P-Delta effects. The results indicate that displacement, story drift, and shear forces increase significantlywhenP-Deltaeffectsareincluded,particularlyin upper stories. Among the irregular configurations, L-shape structures exhibited the highest displacement and drift, indicating increased vulnerability. Step-back configurations demonstrated better stability, reducing excessive lateral deformations due to their inherent mass and stiffness distribution.
Key Words: P-Delta, Time History Analysis, Shear Wall, SeismicPerformance,VerticalGeometricIrregularities,highriseRCBuildings.
Theseismicperformanceofhigh-risereinforcedconcrete (RC)buildingsisacriticalaspectofstructuralengineering, particularly in regions prone to earthquake activity. Buildings with vertical geometric irregularities such as Tshape,L-shape,andStep-backconfigurationsposeadditional challengesinensuringstability.Theseirregularitiesdisrupt theuniformdistributionof massandstiffness,influencing the overall seismic response. To accurately assess the behavior of such structures, Time History Analysis is a widely adopted method. This method provides detailed insightsintothedynamicresponseofbuildingsunderreal earthquake conditions, making it particularly suitable for evaluatinghigh-risestructures.
A G+50 RCbuilding ismodeled inETABS,incorporating threetypesofverticalgeometricirregularities:
L-shapeirregularity
InvertedTirregularity
Step-backconfiguration
Table -1: ModeldatainETABSforparentmodel
Description
Materialproperty
Datavalues
Concretegrade M40
Steelgrade Fe550
Buildingdata
Story G+50
Buildingheight 150m
Storyheight 3m
Beamsize 300x600mm
Wallthickness 230mm
Columnsize
Shearwalls
Baseto20th=1000x550mm
21thto35th=900x450mm
36thto50th=800x450mm
Baseto20th=450mm
21thto50th=400mm
Slabthickness 150mm
Solitype II
Seismiczone V
Importancefactor 1.5
Responsereductionfactor 5
Loadingdata
DeadLoad
LiveLoad
Self-Weight
3KN/Sq.m
FloorFinishload 1.2KN/Sq.m
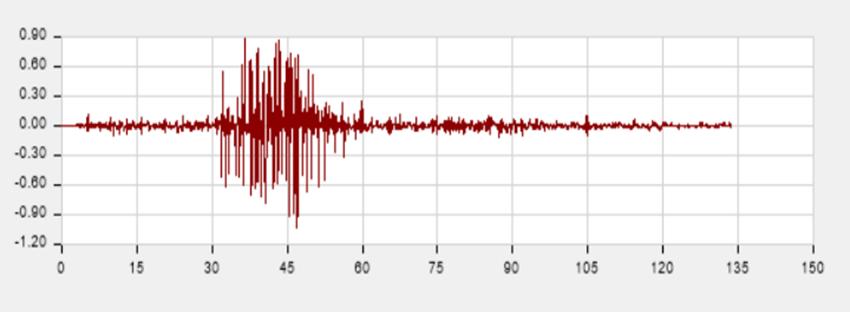
TimeHistoryData Bhuj

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Table 2. Variousmodelsconsideredintheproject
TypeofIrregularity
Model1
Irregularityonbothsides
Model2
Multiplesetback irregularity
Model3
Irregularityononeside
ModelName
For20%Setback[T-20]
For40%Setback[T-40]
For60%Setback[T-60]
For80%Setback[T-80]
For20%Setback[S-20]
For40%Setback[S-40]
For60%Setback[S-60]
For80%Setback[S-80]
For20%Setback[L-20]
For40%Setback[L-40]
For60%Setback[L-60]
For80%Setback[L-80]
TimeHistoryAnalysis(THA)isadynamicanalysismethod usedtodeterminethestructuralresponseunderaspecified earthquake ground motion. Unlike static methods, THA capturesthereal-timevariationofforces,displacements,and accelerationsthroughoutthebuildingduringseismicevents.
For this study, the Bhuj earthquake data was scaled appropriatelytomatchthesite-specificseismicparameters. Time history analysis allows precise evaluation of displacement, drift, shear forces, and other critical parameters,whichareessentialinidentifyingtheinfluenceof P-Deltaeffectsontallbuildings.
Thisstudyinvestigatestheimpact ofP-Delta effectsona G+50 RC building with various vertical geometric irregularities. Models were developed to analyze the combined influence of irregularities, structural configurations,andthepresenceorabsenceofP-Deltaeffects.



International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Chart -1:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongXdirection withP-DeltaforT
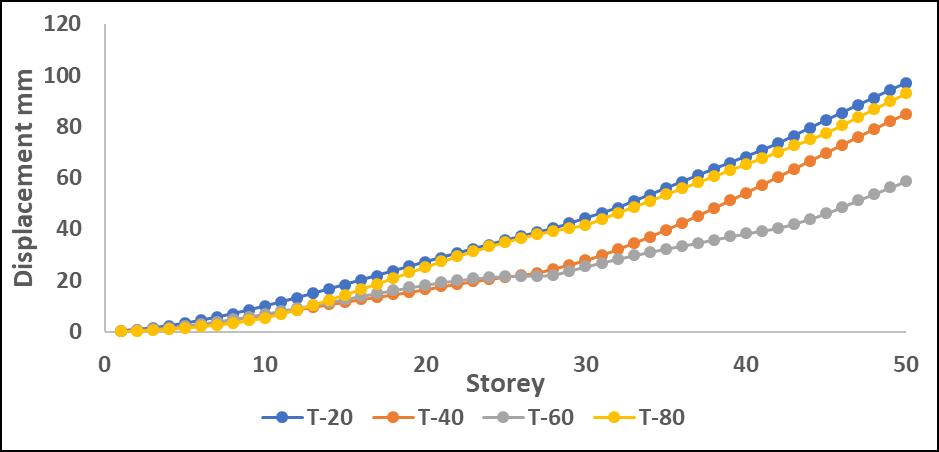
Chart -2:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongXdirection withoutP-DeltaforT
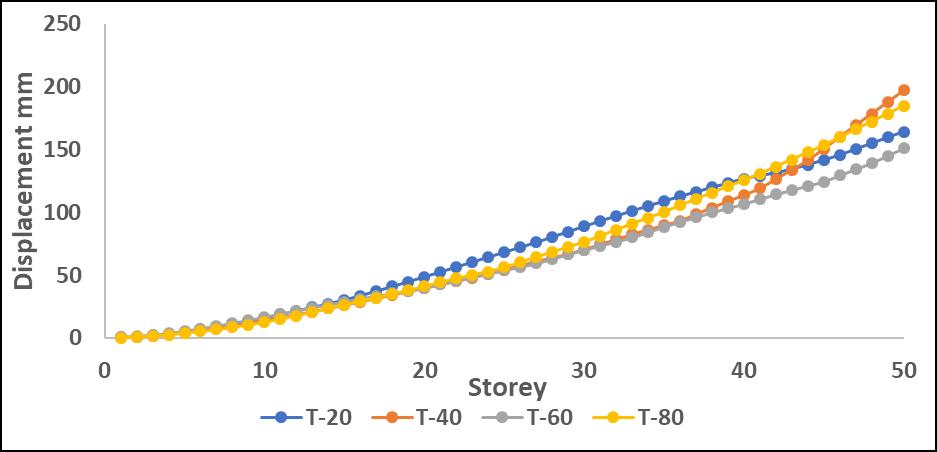
Chart -3:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongYdirection withP-DeltaforT
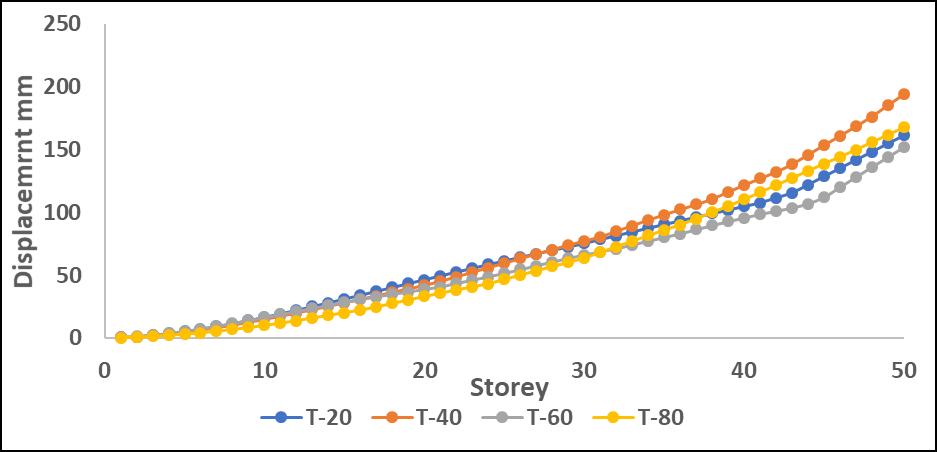
Chart -4:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongYdirection withoutP-DeltaforT
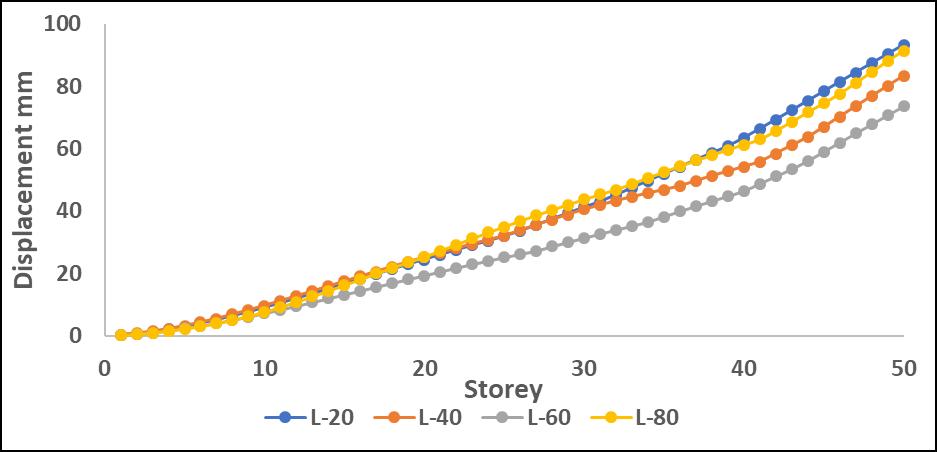
Chart -5:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongXdirection withP-DeltaforL
DisplacementObservations:
DisplacementvaluesincreasedwhentheP-Deltaeffectwas considered, with greater differences observed in upper stories.Amongtheanalyzedirregularities,L-shapestructures

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
exhibited the most significant displacement increase, indicating higher instability due to asymmetry. Step-back models showed better control over displacement due to improvedstiffnessdistribution.
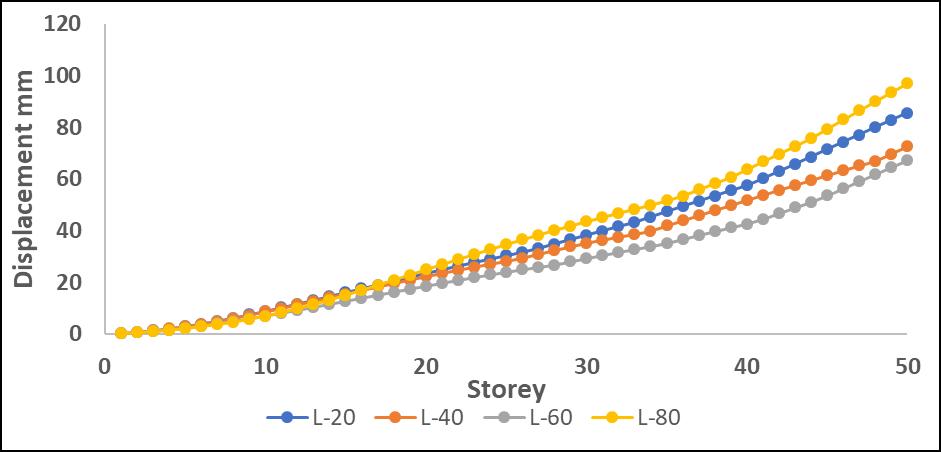
-6:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongXdirection withoutP-DeltaforL
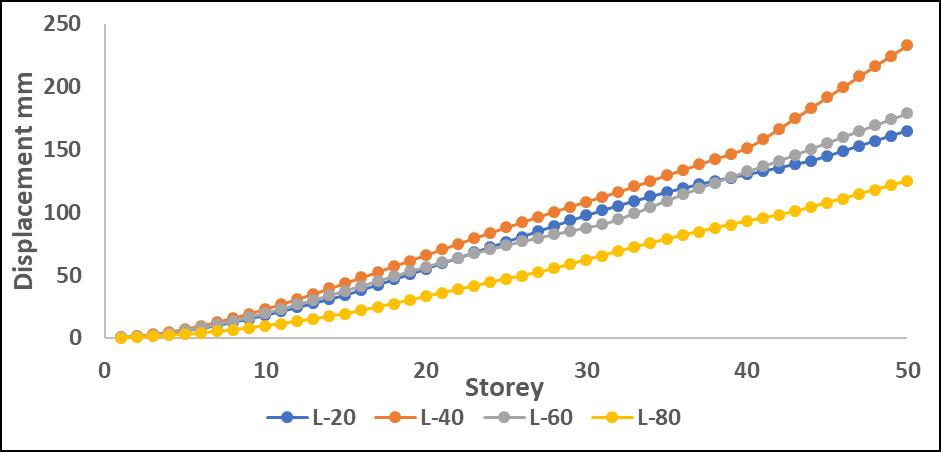
Chart -7:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongYdirection withP-DeltaforL
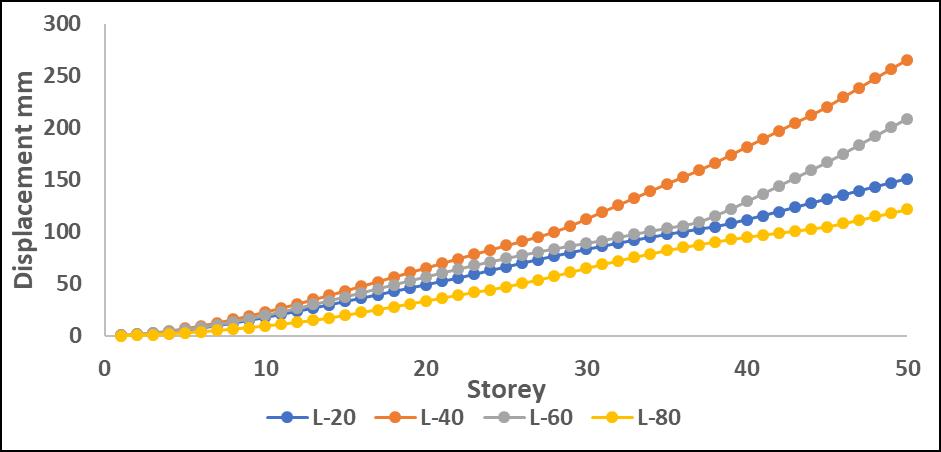
Chart -8:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongYdirection withoutP-DeltaforL
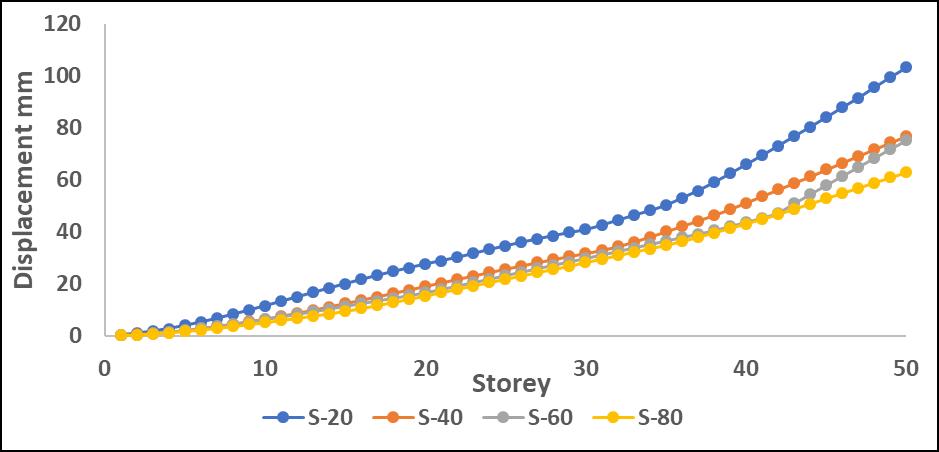
Chart -9:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongXdirection withP-DeltaforS
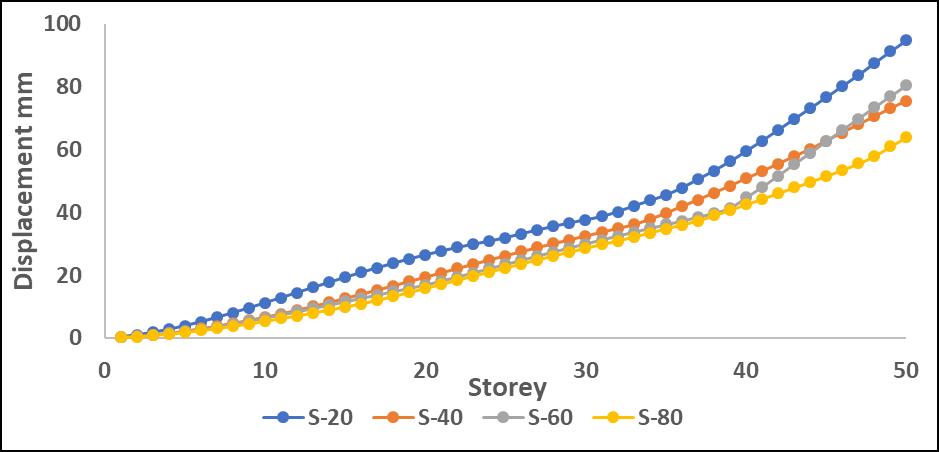
Chart -10:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongX directionwithoutP-DeltaforS
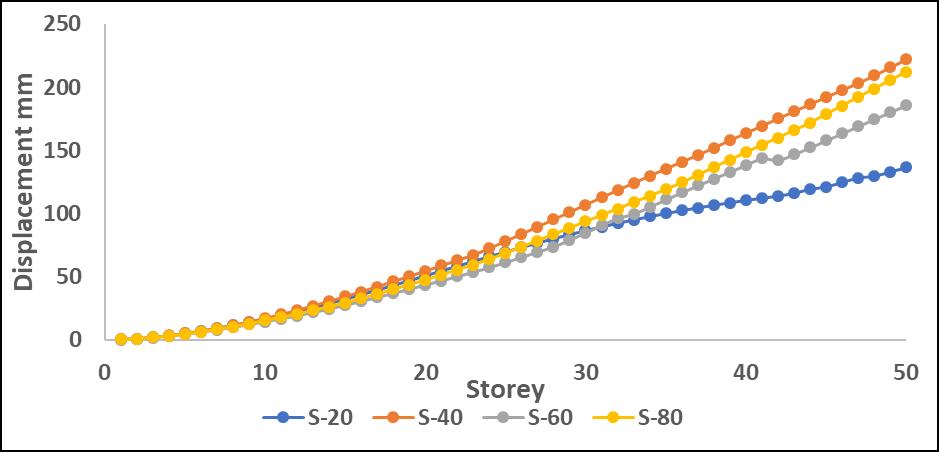
Chart -11:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongY directionwithP-DeltaforS
TheinclusionofP-Deltaeffectsledtoanoverallincreasein displacement,withthemostsignificantvariationsobserved intheupperstories.
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
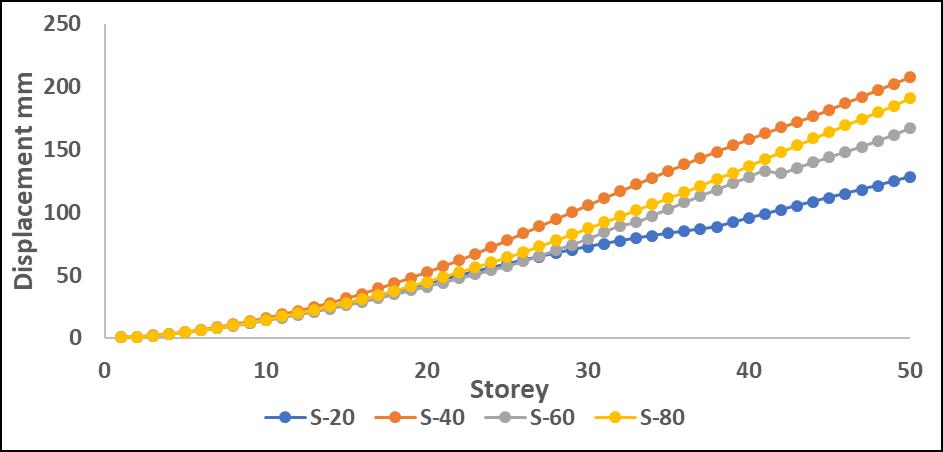
-12:MaximumStoreydisplacementalongY directionwithoutP-DeltaforS
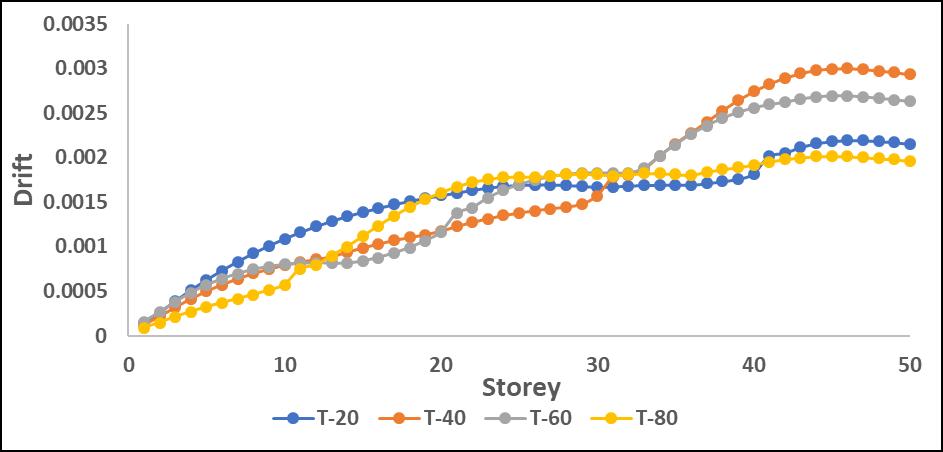
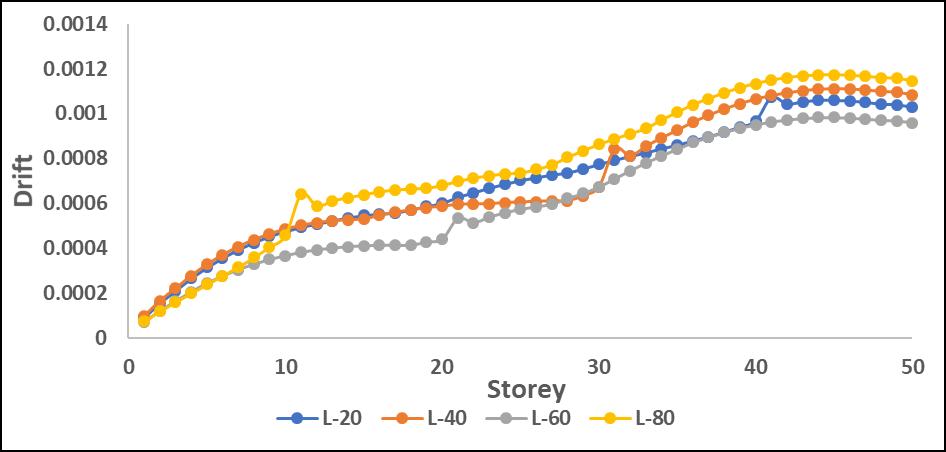
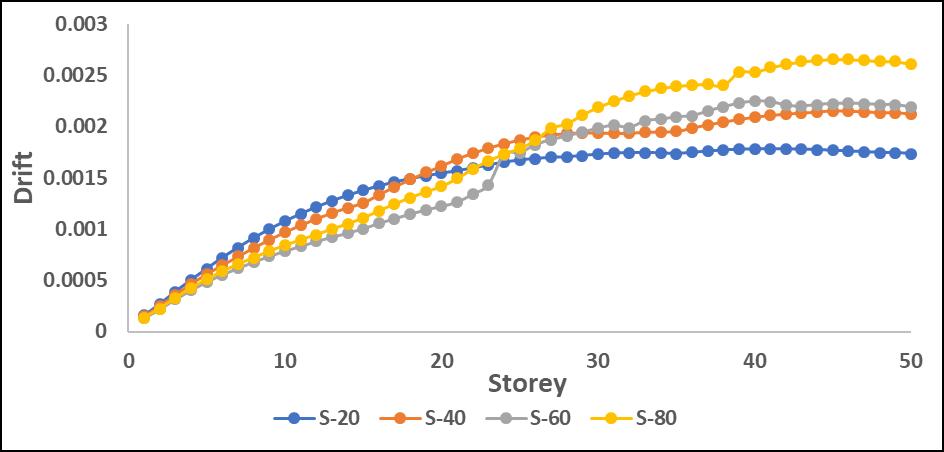
Drifts:Results:
The drift values increased significantly in mid-to-upper storeys when the P-Delta effect was considered. L-shape configurations experienced the highest drift amplification, particularlyinthedirectionoftheirasymmetricgeometry.
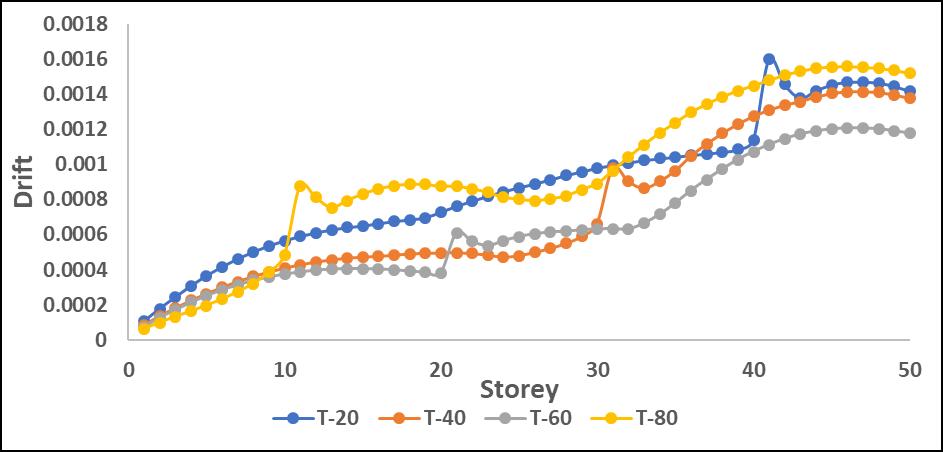
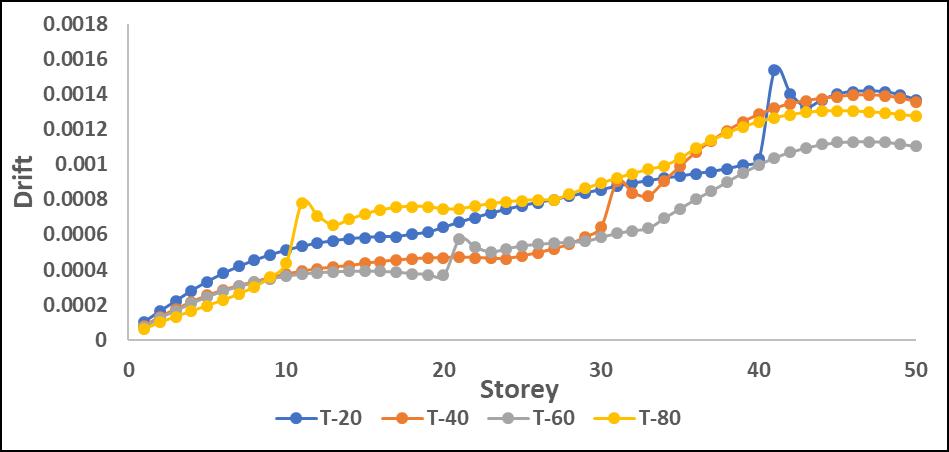
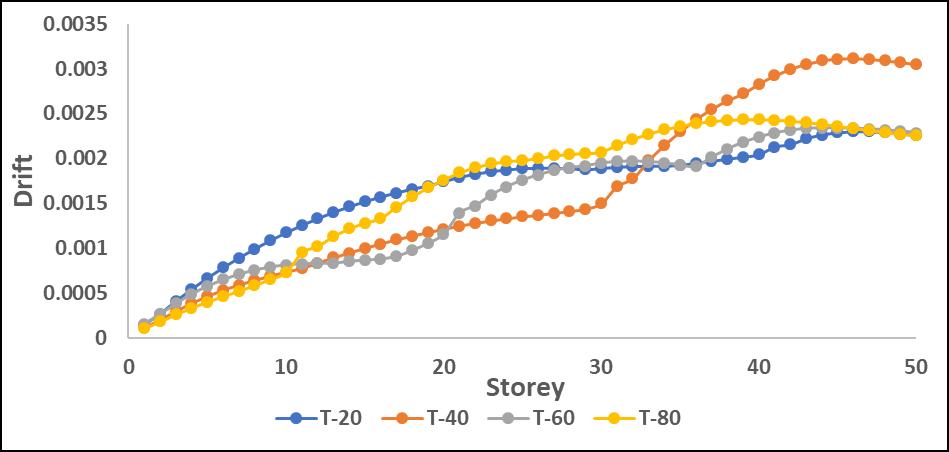
-17:StoreyDriftinXdirectionwithP-DeltaforL
Driftvaluesincreasedsignificantlyinmid-to-upperstories when P-Delta effects were considered, leading to higher structural instability. L-shape configurations showed the highestdriftduetotheirasymmetricstiffnessdistribution, resultinginunevenlateraldeformations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
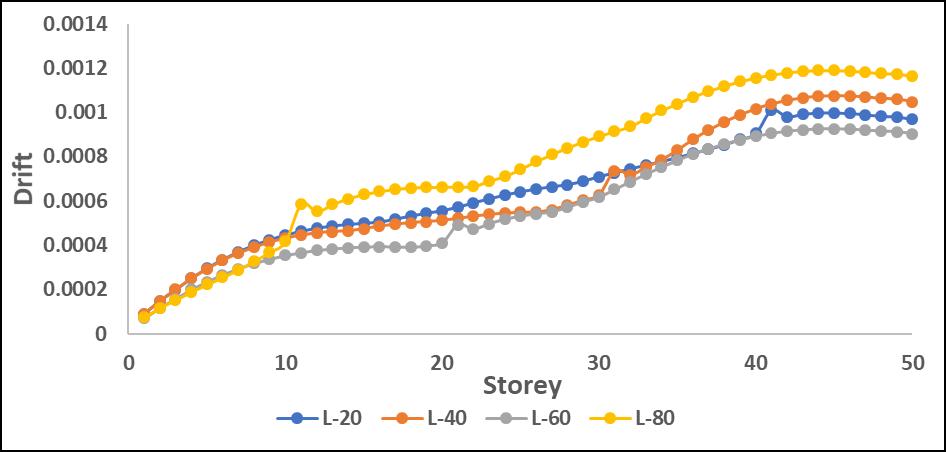
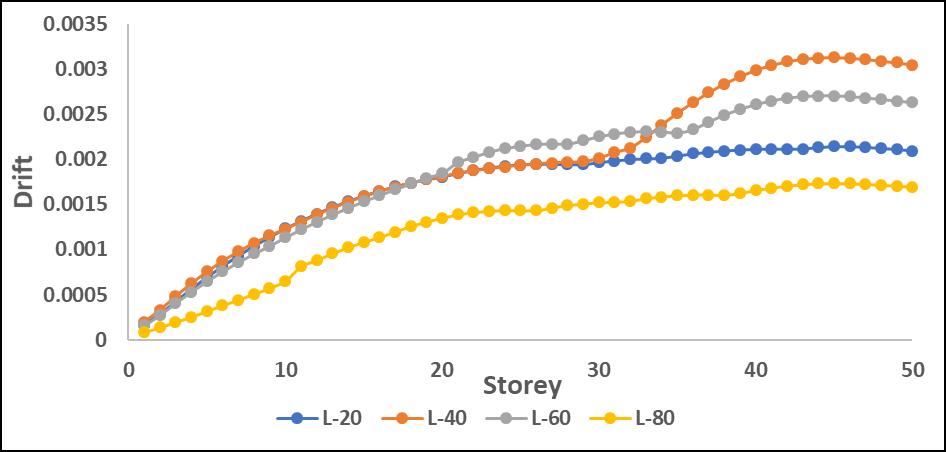
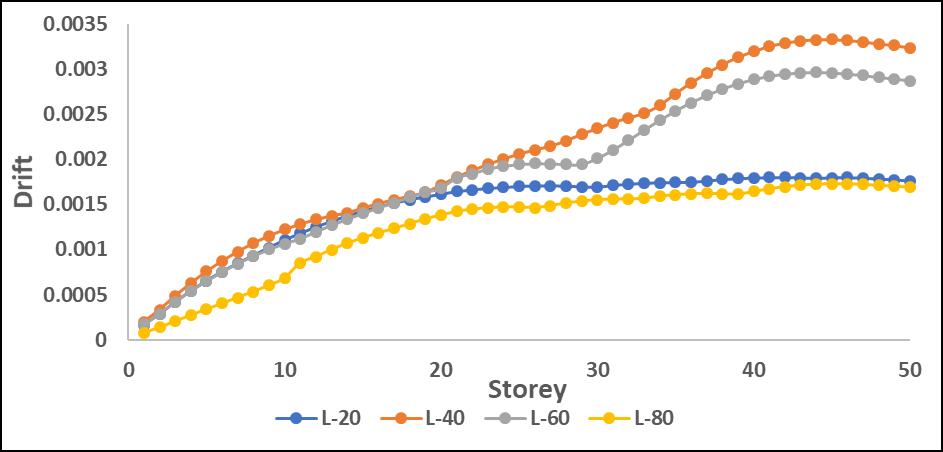
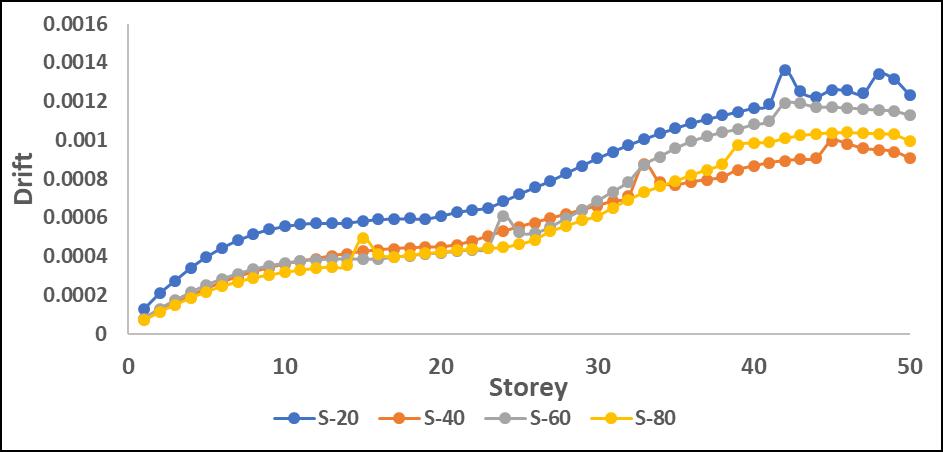
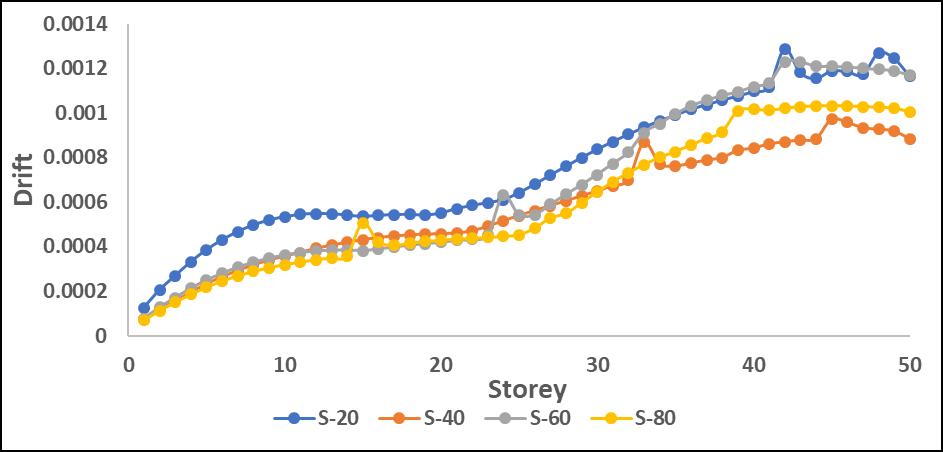
Step-back models exhibited better drift control, as the staggered geometry helped in distributing seismic forces moreefficiently.Maximumdriftwasobservedaroundmidheightlevels,whereP-Deltaeffectscoupledwithstructural irregularitiesledtogreaterlateralmovement.
StructuralEfficiency:Buildingswithoptimizedshearwall placements and additional bracing showed lower drift increments, demonstrating the effectiveness of lateral stiffnessenhancement
Higher drift values corresponded to increased seismic loading intensity, reinforcing the need for advanced mitigationstrategiesinhigh-riseirregularstructures.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
While significant progress has been made in understandingtheseismicbehaviourofhigh-risebuildings, therearestillseveralgaps:
The study reveals that P-Delta effects have a considerableimpactonthe seismicresponseofhighriseRCbuildingswithverticalgeometricirregularities.
L-shape buildings demonstrated the most significant displacement, drift, and shear force increases, indicatinghighervulnerabilitytoseismicloads.
Step-back structures proved to be the most stable configuration,showingimprovedperformanceunderPDeltaeffectsduetotheirstaggeredmassandstiffness distribution.
Incorporating advanced stability measures such as outriggersystems,bracedframes,andoptimizedshear wall placementscaneffectivelymitigate these effects andenhancetheseismicperformanceofirregularhighrisebuildings.
ThepresenceofP-Deltaeffectssignificantlyinfluenced theseismicbehaviorofhigh-risebuildingswithvertical geometricirregularities,increasingdisplacement,drift, andshearforces.
Further research can expand on the following areas to improveunderstandinganddesignstrategies:
Investigating the combined effects of soil-structure interaction with P-Delta effects for buildings on soft soils.
Exploring the influence of material nonlinearity in combinationwithgeometricirregularitiesforimproved accuracy.
Examiningalternativedampingsystemssuchastuned massdampers(TMDs)toreducedynamicresponsesin high-risestructures.
Extending the study to include wind load effects in combination with seismic forces for comprehensive designstrategies.
[1] T.B.Rao,M.Janardhan,andM.V.Narasaiah,“Study of P-Delta Effect in High- Rise Buildings with and withoutShearWall,”vol.9,no.4,pp.201–209,2022.
[2] S.BhavanishankarandP.Rita,“P-DELTAANALYSIS OF MULTISTOREY BUILDING USING ETABS SOFTWARE,”no.05,pp.3600–3613,2021.
[3] D. Naxine and A. Nag, “Strength and durability of concretebypartialreplacementofsandbyCopper SlagandcementbyEggShellPowder:AReview,” IOP
Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci.,vol.1084,no.1,2022, doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1084/1/012019.
[4] A.Bhandare,“Comparativestudyofconventionaland
outriggerstructureforp-deltaanalysis,”vol.9,no.1, pp.1–4,2021.
[5] I. Journal, O. F. Advance, and E. Trends, “AND ENGINEERING TRENDS SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF VERTICALIRREGULARBUILDING,”vol.5,no.12,pp. 234–238,2020.
[6] D.R.NaxineandS.Ghodmare,“Experimentalstudy of Compressive Strength of Concrete by Partial ReplacementofCementwithEggShellPowderand Fine Aggregate with Copper Slag,” IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 1326, no. 1, pp. 1–8, 2024, doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1326/1/012077.
[7] S.SardarandA.Hama,“Evaluationofp-deltaeffectin structural seismic response,” vol. 04019, pp. 1–10, 2018.
[8] S. Ghodmare, “Polymer & Composites Enhancing Mechanical and Durability Performance of Composite Material Using Egg Shell Powder and CopperSlag,”vol.2810,no.6,pp.1–7,2024.
[9] N.Mangukiya,“Studyof‘P-Delta’AnalysisforR.C. Structure,”no.March2016,2018.
[10] S.AliandA.Singh,“InternationalJournalofResearch PublicationandReviewsAnalysisofMultistoryRCC Structures Using P-Delta,” vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1190–1207,2023.
[11] Y.KatareandP.A.Rai,“‘ComparativeAnalysisofRC Multi -Storey Building Framed Structure With and WithoutConsideringP-DeltaEffect,’”pp.179–185, 2023.
[12] A. Shapoval and V. Courtillot, “Influence of the Pdelta Effect and Stiffness Irregularity on the StructuralBehaviorofReinforcedConcreteBuildings Influence of the P-delta Effect and Stiffness IrregularityontheStructuralBehaviorofReinforced Concrete Buildings,” doi: 10.1088/17426596/2287/1/012047.