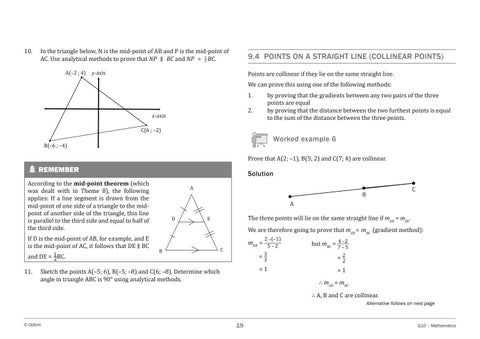
10.
In the triangle below, N is the mid-point of AB and P is the mid-point of AC. Use analytical methods to prove that NP ∥ BCand NP = _12 BC. A(–2 ; 4)
9.4 POINTS ON A STRAIGHT LINE (COLLINEAR POINTS)
y-axis
Points are collinear if they lie on the same straight line. We can prove this using one of the following methods: 1. 2.
𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥
B(–6 ; –4)
C(6 ; –2)
Worked example 6
Prove that A(2; –1), B(5; 2) and C(7; 4) are collinear.
REMEMBER
Solution
According to the mid-point theorem (which was dealt with in Theme 8), the following applies: If a line segment is drawn from the mid-point of one side of a triangle to the midpoint of another side of the triangle, this line is parallel to the third side and equal to half of the third side. If D is the mid-point of AB, for e𝑥ample, and E is the mid-point of AC, it follows that DE ∥ BC and DE = 12_ BC.
11.
by proving that the gradients between any two pairs of the three points are equal by proving that the distance between the two furthest points is equal to the sum of the distance between the three points.
A
D
A
The three points will lie on the same straight line if mAB = mBC.
E
B
C
B
We are therefore going to prove that mAB = mBC (gradient method): 2 –(–1)
mAB = _ 5 – 2
C
= _ 33 =1
Sketch the points A(–5; 6), B(–5; –8) and C(6; –8). Determine which angle in triangle ABC is 90° using analytical methods.
4 –2 but mBC = _ 7 – 5
=_ 22 =1
∴ mAB = mBC
∴ A, B and C are collinear.
Alternative follows on next page
© Optimi
19
G10 – Mathematics