

UNIVERSIDAD AUTÓNOMA DE COAHUILA
INSTITUTO DE ENSEÑANZA ABIERTA
UNIDAD SALTILLO


INGLESII

Módulo 12
Plan 980
Autores:
M.C. JUANA MARÍA MARTÍNEZ CÁRDENAS
ING. ERNESTO MEDINA RAMÍREZ
SALTILLO, COAHUILA JUNIO 2022.







Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

PRESENTACIÓN DELMÓDULO.
Bienvenido a la materia de Inglés II, Módulo12. Te presentamosellibro elcual refiereal manejo de estructuras básicas del idioma, que te permitirán comunicarte de una manera oral yescritaenuna segundalengua.ParanuestroInstituto,porperteneceraun sistema abierto, es importante que cuentes con un apoyo para que puedas concluir con éxito tu materia de Inglés.
El libro tiene como objetivo ser una herramienta didáctica para que desarrolles los aprendizajes esperados contenidos en el programa 980, para la adquisición de una segunda lengua. Este módulo propone una serie de estrategias, que van desde las lúdicas hasta las cognoscitivas, mismas que impulsan las actividades de aprendizaje desde los niveles de aplicación hasta la creación.
El presente texto de Ingles II, Módulo 12, que hoy servirá de apoyo para tu aprendizaje, estábasadoenelModeloEducativodelBachilleratodelaUAdeCqueasumecomoparte de sus principios filosóficos el Humanismo y el Constructivismo, el primero considera al estudiante como el centro de su razón de ser, que se forma y se transforma respetando

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

los valores y la dignidad humana (Guadarrama, 1977) y el segundo, considera el aprendizajesignificativopordescubrimientodondeserelacionalainformaciónnuevacon la ya existente en interacción con el medio. Bajo estos principios se asume un enfoque educativo centrado en el aprendizaje y en la formación integral de los estudiantes que retoma los cuatro pilares de la educación propuestos por la UNESCO (Delors, 1997):
AprenderaConocer,AprenderaHacer,AprenderaVivirJuntosyAprenderaSer;mismas que son la base para que con el sustento pedagógico apropiado permitirán el desarrollo de las Habilidades y Competencias del siglo XXI (Binkley, 2012): Maneras de Pensar (creatividad e innovación, pensamiento crítico, resolución de problemas, toma de decisión, aprender a aprender, metacognición), Herramientas para Trabajar (alfabetizacióndigital,alfabetizacióninformacional),ManerasdeTrabajar(comunicación, colaboración) y Maneras de Vivir en el Mundo (ciudadanía local y global, vida y carrera, responsabilidad social y personal).
ELPROPÓSITO DELMÓDULO
El estudiante utiliza la gramática del tiempo Pasado Simple, pasado del verbo To Be, el futuroconWillyGoingto,adjetivoscomparativosysuperlativosmodalesylosimperativos paracomunicarsedemaneraoralyescritaenunlenguajebásicoendiferentescontextos de la vida cotidiana.
Estructura de la asignatura

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Describingand Comparing UNIDADI

InglésII
TalkingAboutthe PastUsingRegular Verbs UNIDADII

MÓDULO12
Instructions,Rules, andMore UNIDADIII

Plansand Predictions UNIDADIV
La materia de Inglés II está formada por cuatro unidades, cada unidad contiene la explicación de los puntos gramaticales incluidos en el texto, en español, además se presentan los aprendizajes esperados. En ésta encontrarás también los proyectos a desarrollar, los cuales son requisito para la presentación de cada uno de los exámenes
Se te presenta además una autoevaluación al final de cada unidad, para que practiques antes de presentar tu examen. Además, en cada unidad se te presentan los ejercicios que tendrás que incluir en el portafolio de evidencias, mismo que tendrás que entregar a tu asesor para su evaluación y después en el Departamento de Evaluación antes de presentar tu examen.
¿Cómo será mi evaluación?
La evaluación totalde tu aprendizaje estará determinada por los siguientes elementos: 1. Evaluación de habilidades, la cual se llevará a cabo a partir del Portafolio de evidencias, conformado por las actividades de aprendizaje que se te solicitan en

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

el texto y que demuestran tus logros alcanzados; será revisado y calificado por tu asesor. Incluirá una portada, buena presentación, ortografía y limpieza y tendrá que estar completo. Valor máximo:16 puntos
2. Evaluación de actitudes y valores: Es el puntaje asignado por el asesor ante las actitudes y valores que has mostrado como: respeto y responsabilidad al planearyorganizartusactividades,asícomolaortografíaylimpiezaalrealizarlas. Valor máximo: 4 puntos
3. Evaluación de conocimientos: Corresponde al puntaje obtenido al presentar cadaunodelosdosexámenesdelMódulo,elcualsepresentaeneldepartamento de Evaluación y se realizará de la siguiente manera:
1. Primer examen: Comprende los contenidos de las Unidades 1 y 2.
Valor máximo: 20 puntos.
2. Segundo examen: Comprende los contenidos de las Unidades 3 y 4.
Valor máximo: 20 puntos
4. Examen Institucional: El cual tendrás que presentar al terminar tu examen de la segunda parte, para poder acreditar tu materia de INGLÉS II, sin este examen no podrás aprobar la materia. El valor de este examen institucional es de 20 puntos.
UNIDAD I DESCRIBINGAND COMPARING

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
UNIDAD I DESCRIBING AND COMPARING
Propósitodelaunidad:



Ulizarlosadjevoscomparavosysuperlavosparadescribiry compararobjetos,personasylugares,asícomoacvidadesde empolibre.


APRENDIZAJES ESPERADOS
Elestudiante:
1.Muestrauncomportamientoquereflejalapráccadelosvalores instucionalesyenlainteracciónconsumaestroysusparesalrealizarlas diferentesacvidadesdelaunidad.
2.Ulizaadjevosdeordenparadescribirycompararobjetos,personasylugares, asícomotambién,elvocabulariorelacionadoconlapersonalidadylaapariencia sica.


3.Ulizaadjevoscomparavosparadescribirycontrastarobjetos,personasy

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
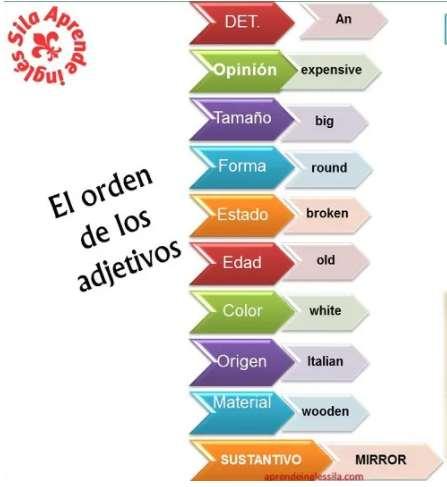
1.Adjective order

Enmuchosidiomas,losadje vosseu lizanenunordenespecífico,enelcasodelingléselorden eselsiguiente:
1.Can dadonúmero 2.Calidaduopinión (generaloespecífica) 3.Tamaño 4.Edad
5.Forma 6.Color 7.Adje vopropio (nacionalidad,lugarde origenomaterial)
8.Propósitoocualidad
Ejemplos:
Ilovethat really big old green an que carthatalwaysparkedattheendofthestreet.
Mysisteradopteda beau ful big white bulldog.
Cuandohaydosomásadje vosdelmismogruposeu lizalaconjunción and
Weliveinthebig green, white and red houseattheendofthestreet.
Myfriendlosta red, black and white watch.
Noseu lizacomaentreunadje voyunsustan vo.
Determiner Quantity Or number
Or opinion

h ps://acortar.link/JEUBBe
or
A beautiful old Italian sports car
The three beautiful little gold plates
An amazing heartshaped red and white sofa
Escribe el orden en el que están los adje vos en las siguientes oraciones:
1.A wonderful old Italian clock.
2.A big square blue box.
3.A disgus ng pink plas c ornament.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
4.Some slim new French trousers.
5.An amazing new American movie.
6.Iboughtapairof black leather shoes.
7.One beau ful old brick house.
8.A small black dog.
9.A new wool bu on-down sweater.
10.A small white ball.
Escribe los adje vos en paréntesis en el orden correcto:

h ps://acortar.link/3kZoTW
1.A_________________________________________woman.(Spanish/nice/old)
2.A_________________________________________table.(square/big/wooden)
3.A_________________________________________carpet.(Russian/yellow/rectangular)
4.A_________________________________________beach.(beau ful/quiet/long)
5.A_________________________________________car.(Italian/fast/red)
6.An_________________________________________girl.(cheerful/young/a rac ve)
7.A_________________________________________pain ng.(Spanish/modern/marvelous)
8.An_________________________________________book.(old/interes ng/German)
9.An_________________________________________watch.(golden/old/Swiss)
10.A_________________________________________diamond.(hexagonal/expensive/big)
1.1 Personality adjectives
Losadje vosnosayudanadescribirsituaciones.Sonpalabrasquedescriben Ycalificancosas,personaos,animales,lugares,entreotras.Losadje vosde personalidadeningléshablandesuscualidadespersonales,nosvanaservir endiferentescontextos,yaseanpersonalesoprofesionales;tambiénpodemos describiralaspersonasennuestroentorno,aspectosnecesariosenla comunicación.

h ps://acortar.link/wQ3Msn

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Ejemplos:
Heis serious.Hedoesn´ttalkmuch. Wearebad-tempered.
Myparentsarehumble.Theyalwaysthankpeople. Iamambi ous.Iwanttoberich.
Heissoforge ul.Hesome mesevenforgetshisownname.
Aquítepresentamosalgunosadje vosdepersonalidadmásu lizadoseninglés.
Traduce los adje vos que se te presentan en el siguiente cuadro:
Self-centered spoiled perfec onist reliable imagina ve aggressive perfec onist confronta onal confident reliable adventurous quiet introverted adaptable friendly irresponsible fun-loving sociable lazy enthusias c funny smart joyful cool polite gentle aggressive boring dull dishonest brave serious helpful loving shy trustworthy
Completa las siguientes oraciones con los adje vos del cuadro:
Talka ve outgoing brave helpful popular clever
nervous generous s ngy sincere reserved
1.PeoplethinkIam________________.ButIamnot.
2.Don´tbeso__________________.Peoplemaythinkyouarecri cizingthem.
3.Mysisterisa_______________person.
4.Iusedtobe__________________.ButnowIam________________.
5.Myniceis_________________.Shewillhelpmethecleaningtonight.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
6.Charlyisafireman.Heisvery______________.Hisjobistofightfire.

7.Javierhasthebestscoreinthegame.He’svery_____________________.
8.Mygrandparentsarevery_________________.Theyarealwaysgivingmepresents.
9.Someonewhois______________can´tgoonstageandsing.Itrequireshavingself-control.
10.Ididn´thavemanyfriendsinhighschool.Iwasnot______________atall.
Completa las siguientes oraciones con las palabras en el cuadro:
Honest brave kind dy anxious bad-tempered crea ve cheerful generous stubborn mean though ul 1
Ishareeverything thatIhavebecause Ibelievethat sharingiscaring.

Inevergive presents. Idon’tlike spendingmoney

IamtruthfulandI don’tcheatorsteal

Iworryfartoomuch aboutthings.



Iamnotafraidof Danger.
Igetangryalot Ineverchangemymind orconsideranyone else’sreasonspr

Icarefullythinkabout otherpeopleandhowto helpthem.

Ialwaysmakepeople feelhappybecauseI’m pleasantandenjoyable.
Ihavealotofimagina on andnewideas.


Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Ialwaysbehaveina caringwaytowards people.



I’mveryneatandwell organized.

1.Linda’sa______________________person. 2.Amy’san______________________person.
3.Billy’sa______________________person. 4.Robert’sa______________________ person.
5.Jack’sa______________________person. 6.Lety’sa______________________person.
7.George’san______________________ person. 8.Sue’sa______________________person.
9.Paul’sa______________________person. 10.Jim’sa______________________person.
11.Kate’sa______________________person. 12.Tina’sa______________________person.
1.2Appearance adjectives
Losadje vosdeaparienciasepuedenclasificardelasiguientemanera:
Body General appearance Face Hair curvy handsome Freckles Blond
overweight ugly,una rac ve Doublechin Gingerorred flabby Pre y,beau ful,gorgeousCrow’sfeet Brune e(mujeres) Brown(hombres)
muscular Good-looking spot Grey chubby,plump mole Dyed Darkhair Dark slim wrinkles highlights skinny,thin Turnedupnose Straight strong Pointednose Wavy
Age Height Oval Curly

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Young Verytall Rounded Frizzy
Middleaged Pre ytall Square Spiky
elderly Médiumheight Long fringe

old short sideburns
Adult Fairlyshort pigtails
Teenager dwarfs
Tall
Eyes bun
Hazel plait
Blue Ponytail Green dreadlocks
Brown long short
Bald Rasta
Parapreguntarycontestarporlaaparienciadeunapersonapodemosdecir:
Apariencia general
Como luce:Whatdoeshelooklike?
Heisahandsomeboy. Heistallwithbrownhair. He´sthin.
Color:Whatcolorishishair?
Hehaslightbrownhair. Hishairislightbrown.
Cabello
Largo:Howlongishishair?
Howlongishishair? It’smediumlength. It’sshortblackhair.
Que usa: Doeshewearjeans? Yes,hedoes. Doeshewearglasses? No,hedoesn’t.
Tipo de Cabello:
Doeshehavestraighthair? Yes,hedoes. Doeshehavecurlyhair? No,hedoesn’t.
Edad Altura
Howoldishe? Heisabout25.
Howtallishe? He’sImeter82.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Heisinhertwen es. Heismiddleage. Heisyoung.

He`s6feet2. He´s182cen meters. Heisfivefeetandtwoinches. He’squitetall.
Escribe los datos de cada persona en la imagen de acuerdo con lo que se te pide:
Name Laura Name Alex



Age Age
Height
Body
Hair
Eyes
General appearance

Height
Body
Face Face
Eyes
General appearance
Name Mary Name Paul
Age Age
Height
Body
Hair
Eyes
General appearance

Height
Body
Face Face
Eyes
General appearance
Name Alice Name Bob
Age Age
Height

Height

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Escribelaletraquecorrespondealadescripcióndelassiguientespersonas:


Shehasgotlonghair. Herhairiscurly. Shehasgotblue eyes. a

Shehasgotlongblack hair.Herhairisstraight. Shehasgotblackeyes. Sheisthin. b


Hehasgotblueeyes. Hehasgotblonde. hair
Hehasgotagrey moustacheandbeard. Heisbald.
Heisyoung. c Hehasgotblueeyes. Hehasgotgingerhair. hasgotglasses. d
e
Hehasgotglasses.
Escribe una F si la descripción de la persona es falsa o una V si es verdadera de acuerdo con su imagen:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.



Hehasgotblueeyes.
Hehasgotgingerhair.
Heisfat.
Hishairisshort

ShehasgotBrowneyes.
Shehasgotlongbrownhair.
Shehasgotglasses.

Hehasgotblackeyes.
Hehasgotbrownhair.
Hehasn’tgotglasses.
Hishairisshort.


Shehasgotblondehair. Shehasgotblackeyes. Sheisshortandfat.
Hehasgotshortcurly hair.
Hehasgotmustache andbeard.
Hehasgotglasses.
Hehasshorthblackhair. Hegotgreeneyes. Heisslim.
Hehasn´tgotglasses.
Observa la imagen y completa las oraciones de acuerdo con el nombre correcto según su descripción.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.


1._________________hasgotmediumlengthhair.She´swearingadarkblueschooluniform.
2._________________isfat.Hehasgotbrowneyes.Hehasgotglasses.Heiswearingastriped T-shirt.
3._________________hasgotlongstraightbrownhair.Sheiswearingaflowerydressand brownshoes.
4._________________hasgotcurlydarkhair.Heiswearingjeansandredtrainers.
5._________________hasgotgreyhairandgreeneyes.Heiswearinggreencardiganand browntrousers.
6._________________isold.Shehasgotblueeyes.Shehasgotglasses.Sheiswearingablack shirt.
7._________________isshort.Shehasgotshortbrownhair.Sheiswearingapinkdress.
8._________________istallandthin.Heiswearingadarkbluecapandanorangejacket.
9._________________hasgotdarkskinandwavydarkhair.Sheiswearingapurpletop.
10._________________hasgotspikyredhair.Hehasgotfreckles.Heiswearingacheckedshirt andshorts.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

11._________________isbald.Hehasgotbrowneyes.Heiswearingawhiteshirtlightblue sweaterandbrownshoes.
12._________________hasgotcurlyblondhair.Shehasgotblueeyes.Sheiswearingaspo ed topandredshorts.
1.3 Descriptive adjectives
Losadje vosdescrip vosseusanparadescribirsustan vosypronombres.Ejemplos:beau ful, silly,tall,annoying,loud,nice.
Algunosadje vosdescrip vosson: large modern green enormous beau ful impressive wealthy busy noisy congested wonderful good fantas c young Tradi onal experimental
Escribe una oración con el adje vo descrip vo que se te proporciona:
1.Wonderful.
2.Good.
3.Beau ful.
4.Wealthy.
5.Impressive.
6.Young.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

7.Noisy.
8.Fantas c.
9.Large.
10.Busy.
2. Comparative adjectives
En inglés se u lizan los adje vos compara vos cuando se comparan dos personas o cosas. Es importanteconocerlasreglasquesesiguenparaformarlos.
Reglasparaformarcompara voseninglés
1) Adje vos cortos.
Para la mayoría de los adje vos con una sílaba (adje vos cortos), añadimos la terminación “er” formarsucompara vo:
Ejemplos:
Excepciones:
Regla:
Ejemplos:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
a) Para adje vos cortos que terminan en “-e”, soloagregar “r”
Wide–wider Nice–nicer
Safe-safer
b) Para adje vos cortos que terminan en consonante + vocal + consonante, duplicar la úl maconsonanteyagregar “er”
Fat–fa er Thin–thinner big-bigger
c) Para adje vos cortos que terminan en “-y”, cambiarla “y” por “i” yagregarterminación “er”
Dry–drier Heavy–heavier Happy-happier

Ejemplos:
Thatskirtislongerthanthisone. Myhouseisbiggerthanhis. Theirdogbarkslouder.
Yourchildissmarterthanotherkids. Carrotsarecheaperthanbeetroots.
2) Adje vos largos
Paramuchosadje voscon2omássilabas,usamoslapalabra“more”máseladje vooriginal:
more + adjec ve
Ejemplos: Expensive - moreexpensive Beau ful - morebeau ful Generous - moregenerous
Thisparkisn´tmorebeau fulthanGoldenGatePark. Sheismorea rac ve
Youaremoreintelligentthanotherstudents. Theyellowcarismoreexpensivethantheblueone.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
3) Adje vos con compara vo especial

Algunosadje vos enenunaformacompara vaespecialoirregular: Adje voengradoposi voAdje vocompara vo Good Be er
Ejemplos: Myshoesare be er thanyours. Thesitua onis worse thanitlooks.
Escribe el compara vo de los siguientes adje vos:
difficult big boring cheap Old late short Interes ng nice busy Bad enjoyable beau ful good heavy Far serious thin cold famous dark
Escribe oraciones con adje vos compara vos con las palabras proporcionadas:
1. Karla / tal / Annie
2. Patricia / beau ful / Andrea

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

3. A / train / fast / a bicycle
4. I / happy / you
5. New cars / good / old cars
6. Colombia / large / Costa Rica
7. Rainy days / bad / sunny days
8. Elephants / big / dogs
9. Art / interes ng / fashion
10. Carl / funny / Andrew
Completa las oraciones con compara vos con el adje vo proporcionado.
1.Moscowis_________________________________Madrid.(cold)
2.Carsare___________________________________bicyckes.(cheap)
3.Catsare____________________________mice.(fast)
4.Skydivingis________________________________mostsports.(dangerous)
5.Saladsare_______________________________friedfood.(healthy)
6.Agoodadvicecouldbe_________________________________money.(useful)
7.Anneis____________________________________________Mary.(young)
8.Mycaris_____________________________________yours.(cheap)
9.Adogis______________________________________acat.(heavy)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

10.Pamis_______________________________________Jennifer.(pre y)
2.1 Comparisions: as (adjective) as…
Siseconsideraquedossustan vossonequivalentesensuscaracterís casseu lizalaestructura:
As+adje voengradoposi vo+as(tan…como)
Ejemplos: Ithinkzebrasareasfastashorses. Thim is as intelligent as Mary.
IranasfastasIcouldwhenIsawthemouseinthekitchen.
Mydogisasintelligentasmycat.
Loscompara vosdeigualdadlospodemosusarenformanega va: not +as+adje voengradoposi vo+as(noestan…como)
Peteris not as funny asRoberto
George is not as fast asLuisa
Selecciona un adje vo del cuadro para cada oración y u liza as… as
Bright tall yellow old heavy fast big
1.Thatclockis_________________________________mygrandmother.
2.Theelephantis_________________________________thattruck.
3.Bananasare_________________________________corn.
4.Thelightshines_________________________________asthesun.
5.Theschoolbusis_________________________________arock.
6.Thecheetahruns_________________________________theimpala.
7.Robertois_________________________________John.
Construye oraciones compara vas de igualdad u lizando las palabras proporcionadas:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

1. My bedroom is / big / yours_____________________________________________________________
2. You / work / not / you should
3. I have / brothers / Mary
4. She has been pa ent for / long / she can
5. He doesn’t listen / music / I do
6. My father / reads / books / my mother
7. Are you / Young / me?
8. This restaurant is / good / any in the world
9. He isn’t / smart / people think
10. I found / informa on / I needed in this book
Completa las oraciones con adje vos compara vos de igualdad con la información proporcionada:
1.Johnis1meter80cmstall.Daveis1meter80cmstall.(is/tall)
John_____________________________________________Dave.
2.Sevilleis40ºCinsummer.Cordovais40ºCinsummer.(is/hot)
Seville_____________________________________________Cordova.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
3.Johnisnotveryclever.Maryiscleverer.(is/clever)
John_____________________________________________Mary.

4.Thebluecarisnotexpensive.Theredcarismoreexpensive.(is/expensive)
Thebluecar_____________________________________________theredcar.
5.Mrs.Jonestalksveryquietly.Mrs.Smithtalksmoreloudly.(talk/loudly)
Mrs.Jones_____________________________________________ Mrs.Smith.
6.Thebrownhouseis100yearsold.Thegreenhouseis100yearsold.(is/old)
Thebrownhouse_____________________________________________thegreenhouse.
7.StevedidnotdowellintheEnglishtest.Melissadidbe erintheEnglishtest.(do/well)
Steve_____________________________________________Melissa.
8.Theimpalaruns90kmperhour.Thecheetahruns120kmperhour.(run/fast)
Theimpala_____________________________________________thecheetah.
9.Thefirstexamwasdifficult.Thesecondexamwasdifficulttoo.(was/difficult)
Thefirstexam_____________________________________________thesecondexam.
10.CiudadRealisnotverybeau ful.Sevilleismorebeau ful.(is/beau ful)
CiudadReal_____________________________________________Seville.
3. SuperlativeAdjectives
El obje vo de las oraciones con adje vos superla vos es expresar cuando algo ene una caracterís ca insuperable y que lo hace destacar del resto. Expresa un grado de superioridad entremásdedossustan vosqueseencuentranenelmismoenunciado.
1) Adje vos cortos
Paraconstruiradje vossuperla voscortosseañadeelsufijo “-est”:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Long–longest high–highest nice–nicest
Ejemplo: TheTeideis the highest mountaininthecountry.

Enelcasodelossuperla vos,siempredebemosponerelar culo “the” delantedeladje vo.
Thelongest thehighest thenicest
Cuandoeladje voescortoyterminaenunaconsonanteprecedidaporunavocal,laconsonante seduplica(silaconsonanteyaesdoblenosecambia).
Hot–ho est tal–tallest big–biggest
Ejemplo: Itwas the ho est topicatthemee ng.
Enadje voscortosacabadosen“y”,elfinaldelapalabrasetransformaen“iest”
Funny–funniest ny– niest
Ejemplo:SantaClausisknownas the merriest person.
2) Adje vos largos
Paralosadje voslargosañadimos “the most” delantedeladje voenformasimple:
Beau ful – the most beau ful expensive – the most expensive uncomfortable – the most uncomfortable
Ejemplo: Itwas the most beau ful dayofmylife,
3) Adje vos especiales
Como en los adje vos compara vos en los superla vos también algunos adje vos enen una formasuperla vaespecialoirregular:
voengradoposi voAdje vosuperla vo

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Far
Furthest/farthest

Ejemplos: Thatwas the best gameofall. ThedayIgotfiredfrommyjobwas the worst dayever.
Thisis the least expensiveperfumeinthestore.
Claire’shousewas the farthest fromthesite.
Para dis nguir el uso del compara vo y superla vo necesitamos saber que:
1. Usamos adje vos posi vos,cuandohablamosodescribimos un sustan vo (unapersona,cosa,acciónogrupoconotrapersona,cosa)etc.
2. Usamos compara vos, cuandocomparamos entre dos sustan vos (unapersona,cosa, acciónogrupoconotrapersona,cosa)etc.
3. Usamos superla vos, paracomparar entre más de dos sustan vos (unapersona,cosa, etc.conelgrupoenteroalqueél,ella,unacosaoanimal,pertenece)
Completa con los adje vos en su forma superla va:
1.TheAmazonis__________________________________riverintheworld. (long)
2.MountEverestis________________________________mountainintheworld. (high)
3.Marsis__________________________________planetfromEarth. (close)
4.Whatisthe__________________________________planetfromEarth? (distant)
5.IsCanada____________________________countryintheworld? (big)
6.Englishis________________________________languageintheworld. (interna onal)
7.Whatis__________________________________routefromEnglandtoIndia? (easy)
8.Brazilis_____________________________________countryinSouthAmerica.(large)
9.Hawaiiis________________________________________islandintheworld(beau ful)
10.TheVa canis___________________________________countryintheworld.(small)
11.__________________________volcanoinMexicoisThePopocatepetl(high)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
12.__________________________cityinMexicoisAcapulco(hot)
13.__________________________cityintheworldisParis(beau ful)

ENGLISHII
14.__________________________languageintheworldisEnglish(popular)
15.__________________________islandintheworldisGreenlander(large)
Completa las siguientes oraciones u lizando el adje vo en su grado superla vo:
1. Sal lloandTorreonare____________________________ci esinCoahuila.(large)
2.TheBravoRiveris______________riverinMexico.(important)
3.ThehighwayfromMexicoCitytoTolucais______intheworld.(expensive)
4.Chihuahuais__________________stateinMexico. (cold)
5.Climbingmountainsisoneof__________sportstoprac ce. (dangerous)
6.ElVa canis_________countryintheworld.(small)
7. TheCaribbeanbeachesare_________beachesintheworld.(beau ful)
8.HongKongis_______placeintheworld.(expensive)
Escribe el adje vo en paréntesis en su forma superla va:
1)Thechurchis________________________________(old)buildinginourtown.
2)Johnis________________________________(careful)driverIknow.
3)Ourcityis________________________________(polluted)inSpain.
4)Thatfilmwas________________________________(good)I'veseen.
5)Thischairis________________________________(comfortable)inthehouse.
6)Helenis________________________________(beau ful)girlinourclass.
7)Todaywas________________________________( ring)dayofmylife.
8)Lukeis________________________________(lucky)personIknow.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

9)Ecijais________________________________(hot)towninSpain.
10)Einsteinwas________________________________(clever)manofthetwen eth century.
3.1 Very and really
Estas dos palabras tienen mucho en común, ambas son adverbios, tiene definiciones similares, y las podemos usar para enfatizar, para intensificar lo que estamos diciendo.
Aunque tienen mucho en común no siemprepodemos usarlas indistintamente.
Very es un adverbio que se puede traducircomo “muy”
Really es un adverbio que también se puede traducircomo “muy”
Veamos algunos usos:
VERY REALLY
Adverbio
1. Extremadamente
a. Muy
Heisverycleverandveryhandsometoo.
Adverbio
1. Extremadamente
a. Muy
Ihadareallygood mewithyoulastweekend.
b. De verdad
TanaFrench’sbooksarereallygood.Youshould readthem.
2. Absolutamente
a. Muy
Wewillhaveitreadyattheveryearlieston Friday.
3. Como respuesta breve
a. Muy
2. Verdaderamente
a. De verdad
Youareright;hereallydoeslookalotlike HumphreyBogart.
b. Realmente
Itreallywasunexpected.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Issherich?Very.

c. En verdad
Ireallydon’tknowwhatyouaretalkingabout.
Adje vo Interjección
4. Exacto
a. Mismo
Thatverydayweboughtthehouse.
5. Extremo
a. Justo
Youwillfinditattheveryendofthecorridor.
b. Mero
Itisintheverymiddleofnowhere.
3. Expresa sorpresa
a. De verdad
Youaregoingtohaveanothersliceofpizza? Really?
b. En serio
YougotintoHarvard?Really?Congratula ons!
Really y very comoadverbiossonusadosparadescribiradje vos,verbosuotrosadverbios:
Really
ShethoughttheProjectwasreallyinteres ng.(adje vo) Hewasdrivingreallyslowly. (adverbio)
Ireallyenjoymyjob.(verbo)
Very
Esusadoparadescribiradje vosyadverbios,peronoverbos:
ShethoughttheProjectwasveryinteres ng.(adje vo) Hewasdrivingveryslowly. (adverbio)
Siestáshablandoacercadeunaacciónevitausar very. Despuésdeunpronombrenopodemos usar very, usamos really.
Ireallylikeit. Theyreallywanttofinishearly. Tonyreallyenjoyshisjob.
Completa las siguientes oraciones con really, very, o escribe both si pueden quedar las dos:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

1. I __________________ enjoy learning about different selling techniques.
2. How beneficial is it to have a _________________ strict manager?
3. She is __________________ good at coding.
4. He had to wait until the _ end to bring up the topic.
5. We _ want this company to thrive.
6. I _ enjoy networking events.
7. I don’t _ like meetings so much.
8. I find some tasks __________________ boring.
9. They sat at the __________________ back of the truck.
10. I am _ sorry. It won’t happen again.
11. I’m super involved in distance learning at the moment. ?
12. She _ makes her work seem easy.
13. They made me feel at home from the _ beginning.
14. I _ love my job!
15. They _ put a lot of effort into their projects.
16. They might actually be arriving at this __________________ moment.
17. The production cost was __________________ high.
18. The salaries in the ITindustryare currently __________________ high.
19. We still do not have enough women at the _ top.
20. Make sure employees understand their goals from the __________________ beginning.
Completa los siguientes enunciados con very o really:
The party on Sunday was __________________ fantastic. The weather was __________________ wonderful.Traffic in London was __________________ good, given it was the weekend. I went with James who is a chatterbox. __________________ unbearable.Butapartfromthis,getting tothe venue was very easy and I found a place to park just in front of the main entrance. When we went inside, the place was __________________ crowded (in fact, it was __________________ full !) and I was __________________ terrified at the

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

perspective of an evening surrounded by so many strangers but, in the end, I was __________________ lucky because one of my former high school classmates, Tonny, was there. It was __________________ interesting to catch up on all his news. When we left, I was __________________ upset...in fact, I was __________________ shattered, but don't tell anyone about it.
AUTOEVALUACIÓN
I. Selecciona la respuesta correcta de acuerdo con el orden correcto de los adjetivos:
1. Four ___________ ___________ ___________ tables.
a) wooden round small
b) small round wooden
c) small woo ___________ ___________ ___________
a) old little funny b) little old funny
c) little funny old d) funny little old
3.An ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ car.
a)expensivebrandnewbluestripedItalian
b)newblueexpensivebrandstripedItalian
c)blueexpensivebrandnewItalianstriped d)Italiannewbluestripedexpensivebrand
II. Completalas siguientes oraciones con los adjetivos de personalidad correctos:
4. I am ___________. I want to be rich.
a) talkative b) reserved
c) bad-tempered d) ambitious
5. My parents are ___________.They always thank people.
a) stingy b) humble
c) serious d) helpful
6. I used to be ___________, but now I am ___________.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
a) talkative / stingy
c) reserved / outgoing

b) outgoing / forgetful / humble
d) generous / charming
III. Completa las siguientes oraciones con los adjetivos de apariencia correctos:
7. How old is Cristy?
a) She’s medium height.
c) She has curly hair.
8. How tall is your father?
a) He has straight black hair.
c) He is pretty tall.
9. What does your friend look like?
a) I’m twenty years old.
c)They are tall.
b) She’s sixteen years old.
d) She has a mustache.
b) He is in his twenties.
c) He’s handsome.
b)They are pretty.
d) She’s fairly short, with black hair.
IV. Completa las siguientes oraciones con adjetivos descriptivos:
10. We drank some water from _______________________ bottles.
a) happy b) large c) dark d)
11. We saw a _______________________ painting in the museum.
a) young b) happy c) beautiful d) wealthy
12. She likes the _______________________ sweater.
a) green b) noisy c) busy d) experimental
V. Completa las siguientes oraciones con adjetivos comparativos.
13. The rabbit runs ___________ the cat
a) the fast c) more fastest b) the most faster d) faster than
14. Which city is _________________,Aguascalientes, Saltilloor Monterrey?

a) big
Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

ENGLISHII
c) more big
b) the biggest d) bigger
15. Living in the country is ________________________living in the city
a) cheaper than c) the cheap
b) cheapest d) more cheaper
VI. Completa las siguientes oraciones con adjetivos de igualdad.
16. Canada is _______________________Spain.
a) as beautiful as b) beautiful as c) more beautiful d) the most
17. The mountains are_______________________
a) high
b) as high as c) higher d) the highest
18. This book is _______________________ the film.
a) interesting as b) more interesting
c) the most interesting
d) as interesting as
VII. Completa las siguientes oraciones con adjetivos superlativos.
19. Cars that use fuel and electricity are ________________ cars in the world.
a) the modern
c) more modern
b) the most modern d) modern
20. The University of Mexico is one of _______________ universities inAmerica.
a) the oldest
c) more older
b) the most old d) old
21. Italy is ____________ country in Europe
a) more exciting
c) exciting
b) the most exciting d) more exciting than

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
VIII. Selecciona very o really según corresponda.

ENGLISHII
22. I'm ____________ excited about my new apartment because it's located in a very convenient area.
a) very b) really
23. The apartment is ____________ cheap. I don't have to spend a lot of money on rent.
a) very b) really
24. My bedroom is ____________ big.There is enough room for a pool table.
a) very b) really
UNIDAD II TALKINGABOUT THEPAST USING REGULAR VERBS
UNIDAD II
TALKING ABOUT THE PAST

Propósitodelaunidad:

UlizarelpasadosimpledelverboToBeasícomoelpasadosimple converbosregularesparahablaracercadediferentesaccionesque sucedieronenelpasadoatravésdesituacionesreales.



Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

APRENDIZAJES ESPERADOS
Elestudiante:
5.Muestrauncomportamientoquereflejalapráccadelosvalores instucionalesyenlainteracciónconsumaestroysusparesalrealizarlas diferentesacvidadesdelaunidad.
6.AplicaelpasadosimpledelverboToBeeneventospasados.
7.Ulizaelpasadosimpleconverbosregulares.
8.Praccaelvocabulariodelosverbosenpasado.


1. Simple Past To Be. PASADO DELVERBO SER / ESTAR (TO BE).
El pasado del verbo “To Be” equivale al verbo ser o estar del español, algunas expresiones pueden corresponder a tener o hacer, es un verbo irregular. El verbo tiene dos formas, que se utilizan de acuerdo con el sujeto de que estemos hablando y son: was / were:
Sujeto: I / you / we / they He / she / it
VerboTo Be en pasado: Was were
Recuerdaquelasformasdelverbo“ToBe”enpresentesonam,isyare;ycorresponden al pasado: am, is = was, are= were.
Las oraciones con pasado del verbo “To Be” se forman de la siguiente manera:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

afirmativas negativas interrogativas
I
He She was a singer last year. I He She was not a singer last year. Was I He She a singer? It was an amazing concert. It was not a good concert. Was It yesterday?
We
You They were late for the concert We You They were not at the concert last night. Were We You They at the concert?
Respuestas cortas:afirmativas Negativas I Yes, She was. He It I No, She wasn’t. He It We Yes, You were. They We No, You weren’t. They
CONTRACCIONES
was not wasn’t were not weren’t
Palabras interrogativas con el verbo “To Be” en pasado: Where¿Dónde?What time¿Aqué hora? Who ¿Quién? How ¿Cómo, cuanto o qué tan?
Ejemplos: How was the concert yesterday? It was great! Who was with you at the last week concert? All my friends. Where were you at 3 o’clock yesterday afternoon? I was at the concert. What time was theTV show yesterday? It was at 11:00 p.m.
Contesta las siguientes preguntas:

Universidad
Autónoma de Coahuila. Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.


1. Who is your favorite singer?
2. When was his/her last concert?
3. When were you in a concert?
4. Name 5 songs of your favorite singer: Completa las oraciones con la forma correcta del Verbo To Be en pasado:
1. When ______ you born?
2. Why ___ youruncle in BuenosAires last week?
3. What ___ your worst subject at school?
4. What ___ your favorites subjects at school?
5. John ___ a teacher, but now he is a pilot.
6. It ___ very cold last night.
7. Steve and Kylie ___ happy with theirtest results.
8. How much ___ the bill in the restaurant last night?
9. Our neighbors ___ very noisy this morning.
10. The waves at the beach ___ spectacular yesterday.
11. When ____ yourbest friend´s birthday?
12. It ____ very hot yesterday, was it?
13. After going to the gym,Krista ____ very tired.
14. The famous painting ____ on sale for $20 million.
15. There _____ no goals in the soccer match today.
16. Why _____ he late for work today?
17. The sunsets in Hawaii ___ beautiful.
18. That ____ a bad idea, Peter!
19. When ____ the last time you saw your family?
20. The children ___ in the park yesterday.
Marca con un was o were, según corresponda: Was (not)Were (not)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

Mary Diana Sara and Susan
Rosy and John
The weather I
The bus
You
Javier and Diego
Peter
Observa las siguientes imágenes, ¿dónde estaban ayer estas personas? Escribe una oración por cada imagen, recuerda usar el Verbo “To Be” en pasado:








1. Bill 2. Sara and Silvia 3. Jessica 4. Susan and Ray

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.








5. Ricky 6.Alejandra 7. Ben 8. The Smiths
9. Dennise 10. Lyz
11. Sandra 12. Cesar
13. Betty 14. Gloria 15. Enrique 1. Bill was at the hospital.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Completa con was (not)/ were (not).
1. John ____________ at the park yesterday.
2. Yesterday I ____________ at theTransportation Museum. There _________ any statues there, of course.
3. The ticket _________ expensive, it ________ only $5.
4. My family and I _________ downtown yesterday. The streets __________ crowded.
5. ___________ George and Mary at the souvenir store? No, they ____________.
6. _______ it cold yesterday? No, it __________. It _______ warm

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo. ENGLISHII

7. Chuck Berry _________ born in St.Louis, Missouri, in 1926. He __________ one of the stars of early rock and roll.
8. How __________ yourvacation inAfrica? It __________ a great trip.
9. I ________ in Nabia for about ten days.
10. How ______ the weather there? It _________ hot and sunny the whole time.
Completa las siguientes oraciones con lapalabra interrogativa correcta:
1. _____________ was your vacation in Peru, Sandra? It was great!
2. _____________ long were you there? Two weeks.
3.. _____________ were you last weekend?At the mountains.
4. _____________ was the concert yesterday? At six o’clock.
5. _____________ was with you? My friends went with me.
2. Time phrases.
Las expresiones de tiempo para el pasado se usan para decirnos cuando pasó algo en el pasado.Algunas de las expresiones de tiempo más usadas son:



Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Relaciona las frases de tiempo en ingles con su equivalente al español:
1.Ayer ( ) a. This morning
2. El fin de semana pasado ( ) b. Day before yesterday
3. Hoy ( ) c. Last night
4. Esta mañana ( ) d. Last month
5.Anoche ( ) e. Last spring
6.Anteayer ( ) f. Last year
7. El mes pasado ( ) g. Last winter
8. El año pasado ( ) h. yesterday
9. El invierno pasado ( ) i. today
10. La primavera pasada ( ) j. Last weekend
Contesta las siguientes preguntas utilizando las expresiones de tiempo:
When was the last time you went shopping? I went shopping three months ago.
When was the last time you…
1. Went on a date. _______________________________________________________
2. Cleaned your room. ____________________________________________________
3. Had a party. __________________________________________________________
4. Lost money. __________________________________________________________
5. Bought a CD. _________________________________________________________
6. Danced. _____________________________________________________________

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

7. Played a sport. _______________________________________________________
8. Got a present. ________________________________________________________
9. Saw an interesting movie. _______________________________________________
10. Studied until late at night. ______________________________________________
11. Talked to an old friend. ________________________________________________
12. Went to a good restaurant. _____________________________________________
13. Wrote a letter. _______________________________________________________
14. Watched a soccer match. ______________________________________________
15. Went swimming. _____________________________________________________
3. Simple past affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences: regular verbs.
Pasado Simple: verbos regulares.
En inglés existen verbos regulares e irregulares, los verbos regulares son aquellos que para formar su pasado se les agrega la terminación: “-ed”:
Ejemplos: work - worked clean – cleaned start – started Stay – stayed live – lived dance – danced
Si el verbo regular termina en consonante+ “y” se cambia la “y” por “i” y se le agrega la “-ed”:
Ejemplos: study – studied marry – married
Algunas veces si el verbo termina en vocal + una consonante, la consonante final se dobla:
Ejemplo: stop – stopped
En los verbosde dos omás sílabas no se doblala consonante sinose acentúa laúltima sílaba.
Ejemplo: happen – happened
Los verbos que terminan en “e” se agrega solamente la “d”.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Ejemplos: smile – smiled dance - danced

Para pronunciar la “-ed” de los verbos regulares en pasado se consideran las siguientes reglas:
1. Si la pronunciación de los verbos termina en “d” o “t” la “-ed” se pronuncia: como “id”.
Ejemplos: visited wanted added waited accepted
2. Si la pronunciación de los verbos termina en “r”, “n”, “i” o “l”, la “ed” se pronuncia como “d”.
Ejemplos: discovered specified studied answered called
3. Con el resto de las terminaciones la “ed” sepronuncia como “t”.
Ejemplos: talked worked helped arrived missed
Cambia los siguientes verbos a su forma en pasado:
Want End Fascinate
Start Invent Explore
Study Die Permit
Escribe el verbo en pasado de acuerdo con la imagen:



Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.









ELPASADO SIMPLE
El tiempo Pasado Simple se usa para describir eventos terminados en el pasado, es decir lo utilizamos para referirnos a situaciones y experiencias personales que ya terminaron.
Los enunciados en Pasado simple están ligados a expresiones adverbiales o de tiempo, éstas generalmente van al final del enunciado, aunque pueden encontrarse también al inicio del mismo:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

yesterday = ayer, last week / month / year = la semana/mes/año pasado, in 1989 = en 1989, three months ago = hace tres meses.
Las oraciones afirmativas se forman de la siguiente manera:
Sujeto Verbo en pasado complemento
I watched a great movieonTV yesterday
John played Soccer last week.
My grandparents moved to Florida last year.
Terry worked in a bank in 1985.
We played soccer yesterday.
Las oraciones negativas se forman como sigue:
Sujeto auxiliar negación verbo en infinitivo (base) complemento
Dany did not have breakfast this morning.
I did not watch TV last night.
They did not drink any coca cola last week.
We did not do much work yesterday.
Susan did not get up early yesterday.
CONTRACCIONES
did not didn’t

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Las oraciones interrogativas se forman como sigue:
Auxiliar sujeto verbo en infinitivo (base) complemento

Did you finish your homework?
Did Mary come yesterday?
Did your friends have a good vacation?
Did you see Joe yesterday?
Did it rain on Sunday?
Observa que en las oraciones afirmativas el verbo se usa igual con todas las personas, así como en las negativas e interrogativas se utiliza el auxiliar de la misma forma con todas las personas. En las oraciones interrogativas el signo solo se coloca al final.
Respuestas cortas: afirmativas negativas

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Simple past: Wh questions.

Paraformaroracionesconpalabrasinterrogativessecolocaprimerolapalabracon wh: (who, what, where, when) y la respuesta es generalmente un enunciado afirmativo.
Palabra interrogativa Auxiliary sujeto
Verbo en infinitivo (base) complemento
What Did Sue do last night?
Respuesta: She went to a party.
How Did the accident happen?
Respuesta: I don’t now, I think it was terrible.
Where Did your parents go on their vacation?
Respuesta: They went to Europe.
When Did Columbus discover America?
Respuesta: He discoveredAmerica in 1492.
Why Did you go to see the doctor
Respuesta: Because I was sick yesterday.
Who invented the first practical telephone?
Respuesta: Graham Bell.
Completa con los verbos del cuadro en pasado:
work travel develope board educate recive work enlist learn require sail
Cook's early life


Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

1. James Cook ____________ around to far reaches of the world reaching all seven continents during his lifetime.
2. He ___________ on three very lengthy journeys with two different sailing ships, encountering hardshipand triumph along the way.
3. Cook _________ basic schooling at the village school and was then sent to work for William Sanders inthe nearby fishing village of Staithes.
4. Cook ______________ a love and fascination for the sea, but he was not especially happy with his job amongst the hard working people of the land.
5. Cook's job as an apprentice ___________ him to become very familiar with the coal ships of the areaand he soon ____________ the ins and outs of the colliers type ships.
6. He __________ hard and soon had his first voyage aboardthe Whitby collier 'Freelove.'The coal ships or colliers were of sturdy construction, strong sailing abilities, and couldhandle a great deal of cargo and weight.
7. While Cook was at Whitby, he ____________ himself a great deal in navigation and mathematics.
8. By 1755, after nine years, and much service as ship's master, Cook left his ship and ___________ in the Royal Navy as an ordinary sailor.
9. He _________ the Eagle, a 60-gun ship, and was sent to the NorthAmerican Coast.
10. James Cook ____________ his way up through the ranks quickly in the navy, eventually rising high enough to command his own survey vessel.
Completa las siguientes oraciones afirmativas con el verbo en paréntesis en pasado:
1. They ________________ (play) football yesterday.
2. Mrs. Black ________________ (visit) her parents two days ago.
3. Tony ________________ (live) in London when he was a child.
4. Sarah ________________ (like) ice cream.
5. Mr. Brown ________________ (stop) work at half past five yesterday.
6. The children ________________ (start) school yesterday morning.
7. My friends ________________ (study)at Oxford University three years ago.
8. Sally ________________ (need) an operation last month.
9. I ________________ (watch) a very goodprogramme onTV lastnight.
10. We ________________ (dance) a lot at the disco last Saturday.
11. Ben and Letty ________________ (close) the shop last week.
12. My parents ________________ (travel) abroad last summer.
13.Alion ________________ (escape) from the zoo last night.
14. I ________________ (finish) my homework yesterday afternoon.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

15. My little sister ________________ (drop) the glass five minutes ago.
16. The thief ________________ (grab) the old woman’s bag.
17. You ________________ (borrow) my book two days ago.
18. My brother and I ________________ (help) our mother yesterday.
19. My grandparents ________________ (stay) at home last Sunday.
20. You ________________ (walk) to school yesterday morning.
Cambia las siguientes oraciones afirmativas a interrogativas:
1. They climbed the mountain yesterday.
2. He decided to leave his job last week.
3. She earned a lot of money in London lastyear.
4. I enjoyed the wedding on Sunday.
5. It happened late last night.
6. They rented a car on holiday last summer.
7. Philo Farnsworth invented the television in 1927.
8. We listened to the concert on the radio yesterday evening.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

9. John and Mary worked together when they were younger.
10. I received a nice letter fromAunt Jane this morning.
Completa las siguientes oraciones en forma negativa o afirmativa, utilizando los verbos del cuadro:
clean – die – enjoy – finish – cook – happen – live – open –play – rain – smoke – walk – start – stay – want – watch – play
1. Yesterday evening I _______________ television.
2. I _______________ my teeth three times yesterday.
3. Bernardo _______________ 20 cigarettes yesterday evening.
4. The concert last night _______________ at 7:30 and _______________ at 10:00 o´clock.
5. The accident _______________ last Sunday afternoon.
6. When I was a child, I _______________ to be a doctor.
7. Mozart _______________ from 1756 to 1791.
8. We _______________ our holiday last year. We _______________ at a very good hotel.
9. Today the weather is nice, but yesterday it _______________.
10. It was hot in the room, so I _______________ the window.
11. The weather was good yesterday afternoon, so we _______________ tennis.
12. William Shakespeare _______________ in 1616.
13. On Saturday I _______________ computer games with my cousins.
14. My mother _______________ dinner last night.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

15. I _______________ to school because there weren’t any buses.
Cambia las siguientes oraciones a la forma negativa:
1. I studied at Concordia University, in Montreal.
2. My family celebratedThanksgiving Day last year.
3.After work we went to Patty´s birthday party.
4. Did you like your last dancing class?
5. I liked Math andTechnical Drawing ten years ago.
6. Mary spent the best three months in her life in Ireland.
7. The boys took off the mudguards of their bicycles.
8. We saw some beautiful flowers.
9. They learned how to cook some traditional dishes.
10. I studied for the English test. Choose the correct Wh question: When What Why Where How Who

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

1. ____________didyou last see a film at the cinema? Last weekend.
2. ____________did she buy?An old car.
3. ____________did the building fall down? Because it was old.
4. ____________did they live? They lived in Japan.
5. ____________did they talk? About their homework.
6. ____________did he play hockey? Last weekend.
7. ____________did they travel across Canada? By bike.
8. ____________ did you do yesterday? I went to the movies.
9. ____________ time did you wash your hair this morning?At 8:00 o’clock.
10. ____________ did you go last night? To a restaurant.
11. ____________ When did Mahatma Ghandi die? In 1948.
12. ____________ did you come to school last Monday? By bus.
13. ____________ did you visit two days ago?To my grandparents.
Write the correct Wh question to complete the sentences: When How Who What Why
1. They wanted to see Fiona. _______________did they want to see?
2. I got up at 7 o'clock. _______________time did you get up?
3. She paid $10. _______________much did she pay?
4. He didn't like the movie. _______________didn't he like the movie?
5. We had dinner. _______________ did you have for dinner?
6. The meeting finished late. _______________ time did the meeting finish?
7. I ate an apple pie. _______________ kind of pie did you eat?
8. I played tennis lastweek. _______________did you play tennis?
9. They wrote to Ellen. _______________didthey write to?
10. I didn't eat the chicken. _______________didn't you eat the chicken?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ORDER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:

1. start / work/ time /what / did / you /yesterday? I started at two.
2. time /bed/ did/ to / last/ go / night/ what / he? He went at midnight.
3. in Italy /did/ where/ you/ stay? I stayed with some friends.
4. enjoy /show/ did/ they/the? No, they didn't.They did not like it.
5. when /your cousin /arrive/ did? He arrived at three I believe.
6. do /did/ you/ what/ night/ last? I watched the news on television.
7. who /you/ did/ stay/ yesterday/ with? I stayed with Sara.
8. happened / last/ what/ month? The president resigned.
9. did /to/ school/ how/ come/ you/ yesterday? I came on foot as usual.
10. what/ breakfast/ did/ have/ for/ you? I had a coffee with cookies.
I. Simple Past Be.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Complete the sentences with the appropriate form of the verb To Be in the past:
1. I ____________ late yesterday. a) were b) weren’t c) didn’t d) was
2. ______________ she drawing?
a) Was b) Did c) Were d)Weren’t
3. He _____________ at home yesterday, he went to school. a) was b) didn’t c) weren’t d) were
4. She ____________ wearing a beautiful dress lastThursday. a) did b) was c) were d) weren’t
5. _________________ the weather fine yesterday? a) Did b) Were c) Wasn’t d) Was
6. We _______________ interested in the movie, it was boring. a) wasn’t b) weren’t c) didn’t d) was
II. Time phrases.
Choose the appropriate time phrase:
1. I saw Maria _________________. a) next Sunday. b) soon c) this week d) yesterday.
2. The students took their spelling and vocabulary tests ______________. a) next month b) last Friday c) this week d) now
3. They got married _____________________. a) two years ago b) next year c) today d) soon
III. Pronunciation:
Choose the correct pronunciation of "ed" in the following words:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

1. We walked at the park yesterday. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
2. The students answered the questions quickly. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id
3. We waited a long time for the bus. a) "ed" sounds like d.
IV. Simple past: regular verbs.
b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
1. On Saturday, my friend and I _______________ to “Paseo Santa Lucia” because it was a beautiful day. a) walk b) walking c) walked d) walks
2. My sister _______________ me this weekend. a) didn’t b) calls c) calling d) didn’t call
3. Jaques-Yves Cousteau ___________ the French Oceanographic Campaigns. a) found b) founded c) founds d) founding
4. Steve Irwing ________ in 2009. a) die b) dies c) died d) did die
V. Simple past:Questions, short answers and negatives.
1. _______ you ________ the film last night?Yes, I _______.
a) Did / watched / did b) Watched / did / watch c) Watch / watch / watch d) Did / watch / did
2. ________ Jenny and Omar ___________ with their father? No, they ________.
a) Did / did / work
b) Did / work / didn’t c) Didn’t / worked / worked d) Didn’t / work / did
3. Javier ____________ soccer yesterday.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

a) play b) did play c) didn’t played d) did not play
4. Mary __________ her room yesterday morning. a) did not tidy b) did / tidy c) tidy not d) did not tidied
5. ______ Julia and Roberto ________ to the radio last Sunday?Yes, they _____. a) Did / listened / did b) Listened / did/ do c) Did / listen / did d) Do / listen / do
VI. Simple past:Wh questions.
1. ________ did Robert go to work yesterday? By bicycle. a) When b) How c) Who d) Where
2. ________ did you have lunch yesterday? In the post office. a) Where b) When c) Who d) How
3. ________ did you have lunch with your best friend? Yesterday. a) Where b) How c) How d) When
4. ________ did you have dinner with last night? WithAlice. a) How b) Where c) What d) Who
5. _________ time did you watch TV last night? At 8 o’clock. a) When b) What c) How d) Where
6. What time ______ he ________ yesterday?At 8am. a) did /got up b) got/up c) get/up d) did/get up
7. ________ did Peterhave lunch with yesterday? Nobody. He ate alone. a) Where b) How c) When d) Who
8. What time did Rosy finish work yesterday?At 6.30pm. a) When b) How c) What time d) Where
PROYECTO

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

ElsigloXXhasidoelmástrascendenteenlahistoriadelhombre,losacontecimientospolí cos, socialesyeconómicosseentrelazanentresíaligualque lascostumbres,lavidayelarte,ellos handeterminadoenelhombredehoyunaformadevida,depensarydesen rdiferente. Ha habido muchos eventos importantes en el siglo XX, tanto en ciencia, tecnología, deportes, cultura, etc. Muchos de ellos han mejorado la calidad de vida de las personas. Es importante conocernuestropasadoparacomprendernuestropresente,porloqueesimportanteconocer: “Whathappenedinthelastcentury?
PROYECTO
I. Realiza el proyecto: “What happened in the last century?”, cuyos pasos se mencionan a continuación:
1. Selecciona al menos tres de las siguientes categorías e investiga acerca de tres diferentes eventos, importantes a lo largo del siglo:
1. ¿Qué paso en los deportes?
2. ¿Qué pasó en la cultura?
3. ¿Qué pasó en la ciencia y tecnología?
4. ¿Qué pasó en la Historia?
5. ¿Qué pasó en la política?
En México, Estados Unidos, en el mundo.
2. Investiga en por lo menos 3 diferentes páginas. Se te sugieren las siguientes además de las que tu puedas encontrar:
http://www.portalplanetasedna.com.ar/sucesos001024.htm
http://www.portalplanetasedna.com.ar/linea_del_tiempo1.htm
http://mx.answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20080518135604AATEYec
http://www.portalplanetasedna.com.ar/siglo20.htm
http://www.infoplease.com/year/1900.html
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_important_events_happened_in_the_20th_century http://history1900s.about.com/od/famouscrimesscandals/u/events.htm
3. En cada evento tendrás que buscar, qué fue lo que pasó o en que consiste, quienesfueronlosprotagonistas,enquetiempopasó,quemejorasaportóalmundo en caso de que así sea, o en su caso, perjuicios.
4. En cada uno de los eventos agrega las razones por las que los seleccionaste.
5. Escribe un reporte, en el que vas a describir los resultados de tu investigación y las cosas que hiciste para llevarla a cabo así como incluir una conclusión.
6. Realiza una presentación en Power Point para compartir los resultados con tu maestro y otros compañeros.
7. Llena el formato de rúbrica de acuerdo con tu percepción.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Rúbrica para evaluar el proyecto:

Tarea: SINO
Incluye las tres categorías solicitadas
Incluye los tres eventos solicitados
Describe cada evento
Incluye los protagonistas de cada uno de los eventos
Incluye fotografías en cada evento
Presentación en Power Point
Incluye las referencias bibliográficas

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

UNIDAD III INSTRUCTIONS, RULESANDMORE
UNIDAD III
INSTRUCTIONS, RULES, AND MORE

Propósitodelaunidad:

Ulizarelpasadosimpleconverbosirregularesimperavosy modalesparaestablecerreglas,prohibicionesyobligacionesde formaoralyescrita.


APRENDIZAJES ESPERADOS
Elestudiante:
9.Muestrauncomportamientoquereflejalapráccadelosvalores instucionalesyenlainteracciónconsumaestroysusparesalrealizarlas diferentesacvidadesdelaunidad.
10.Ulizaelpasadosimpleconverbosirregularesparaexpresaracontecimientos pasados.
11.Emplealosimperavosparadarórdenes,instruccionesyadvertencias.


12.Aplicaelvocabularioylosmodalesparadarinstrucciones,establecerreglasy

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

1. Simple past: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences: irregular verbs.
Los verbos irregulares son aquellos que no siguen una regla para formar su pasado:
Ejemplos: begin – began get – got say – said
I ate chocolate yesterday. I went shopping yesterday.
Relaciona el verbo en presente con su forma en pasado:
Present tense verbs Past Tense Verbs
1. Hear ( )a) Caught
2. Tell ( )b) Saw
3. Grow ( )c) Fought
4. Come ( )d) Heard
5. Draw ( )e) Fell
6. Get ( )f) Grew
7. See ( )g)Told
8. Fight ( )h) Got
9. Fall ( )i) Drank
10. Catch ( )j) Came
11. drink ( )k) drew
Escribe el pasado simple de los siguientes verbos: get Buy Leave eat Know See pay Stand Go make Take Hear

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII give Do find put tell lose think speak cry

Selecciona la forma en pasado del verbo en cada oración y escríbela en la línea:
1. I _________________ all my homework in the study hall. (do, did)
2. She _________________ of a better way to do it. (thought, think)
3. We never _________________ his real name. (know,knew)
4. Anna _________________ her arm when she fell down the stairs. (broke, break)
5. The dog _________________ a hole inthe back yard. (dig, dug)
6. Mom _________________ cupcakes for my last birthday. (make, made)
7. When the phone _________________ it woke the baby. (rang, ring)
8. There was gum _________________ to the bottom of my shoe. (stick, stuck)
9. I _________________ a delicious salad yesterday. (ate, eat)
10. Peter _________________ a lot because he lost his favorite toy. (cry, cried)
¿Quién inventó la televisión a color? Investiga la historia de este aparato electrónico.


Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

(March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was an eminent scientist, inventor, engineer and innovator who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone.
Bell'sfather, grandfather, and brotherhad allbeen associated withwork on elocution and speech, and both his mother and wife were deaf, profoundly influencing Bell's life's work. His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices which eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the first U.S. patent for the telephone in 1876. In retrospect, Bell considered his most famous invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study.
Many other inventions marked Bell's later life, including groundbreaking work in optical telecommunications,hydrofoilsandaeronautics.In1888,AlexanderGrahamBellbecame one of the founding members of the National Geographic Society.
Alexander Bell was born in Edinburgh, Scotland on March 3, 1847.The family home was at 16 South Charlotte Street, and now has a commemorative marker at the doorstep, marking it as Alexander Graham Bell's birthplace. He had two brothers: Melville James Bell (1845–1870) and Edward Charles Bell (1848–1867). Both of his brothers died of tuberculosis. His father was ProfessorAlexander Melville Bell, and his mother was Eliza Grace (née Symonds). Although he was born "Alexander", at age 10, he made a plea to his father to have a middle name like his two brothers. For his 11th birthday, his father acquiesced and allowed him to adopt the middle name "Graham", chosen out of admiration for Alexander Graham, a Canadian being treated by his father and boarder whohadbecomeafamilyfriend.Tocloserelativesandfriendsheremained"Aleck"which his father continued to call him into later life.
Complete the following:
1. Graham Bell was born in 1847. True. False. We don't know.
2. He spent his childhood in Canada. True. False. We don't know.
3. He was deaf. True. False. We don't know.
4. Bell was awarded the first US patent for the invention of the telephone. True. False. We don't know.
Alexander Graham Bell

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

5. He was one of the founding members of the National Geographic Society. True. False. We don't know.
Change the following sentences into negative ones.
1. I left work ______________________________________________________
2. We visited the Learn English web site. ________________________________
3. She went to the shops. ____________________________________________
4. I watched television. ______________________________________________
5. The dog barked. _________________________________________________
6. They flew toToronto. _____________________________________________
7. I read the newspaper. _____________________________________________
8. Mr. Bean taught English yesterday. __________________________________
9. I had a bath. ____________________________________________________
10. I got up at 5 a.m. _________________________________________________
Change the following sentences into interrogative ones:
1. I went toAustralia in 1998.
2. I swam in the sea.
3. Peter took driver lessons.
4. I got up early.
5. I have an expensive car.
6. I didn´t know the answer.
Choose the correct pronunciation of "ed" in the following words:
1. We can't go swimming because the pool is covered. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

2. Tommy received a gift from his friend. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
3. Yesterday, they hiked to the top of the mountain. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
4. We played soccer last night. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
5. The car door is dented. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
6. Jennifer planted a tree in the garden. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
7. We hunted for her keys but could not find them. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
8. Olivia brushed her teeth before she went to bed. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
9. James rented the apartment for six months. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
10. The magician showed me a trick. a) "ed" sounds like d. b) "ed" sounds like t. c) "ed" sounds like id.
Rewritethesentencesinthecorrectorder,inaffirmative,negativeandinterrogative sentences.
1. my I days car two washed ago.
(+) ___________________________________________________________________ (-) (?)
2. They a went week. party last to (+)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII (-) (?)
3. They bought in house 2005. their (+) (-) (?)

4. I night. my did homework last (+) ___________________________________________________________________ (-) (?)
5. at and She nothing. stayed home did (+) (-) (?)
6. at and She nothing. stayed home did (+) (-) (?)

Universidad


Across Down
3. HIT 16. LAUGH 1. LEND 10. TELL 4. INVITE 18. EAT 2. GET 12. RUN 8. READ 19. ERASE 3. HEAR 15. STRIKE 10.TAKE 20.AIM 5. EMAIL 17. DRINK 11. DREAM 21. COME 6. DRIVE 22. MAKE 13. FALL 23. SPEAK 7. FIGHT 23. SEE 14. GIVE 24. GROW 9. DRAW
2. Imperatives
El imperativo es el tiempo verbal en inglés usado para expresar una orden, una petición, dar instrucciones, e incluso para aconsejar a alguien.
El imperativo se forma con el verbo en infinitivo sin el “to” y sin conjugación:
Close the door when you leave. Fill in the blanks.
El uso del imperativo suele ser bastante directo y, a veces, puede sonar un poco sin educación. Por lo tanto, tenemos que prestar atención al contexto cuando se use. Si es un pedido, por ejemplo, y que no parezca grosero, se utiliza “please”.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Turn the TV down, please.
Existen situaciones en que se encuentra el imperativo, por ejemplo: Placas de señalización: Stop Push Insert the coin
Los manuales de instrucción o recetas culinarias, y si se habla de procesos que deben seguir una orden, se utilizan las palabras como: “first” “then”, “next”.
Fist, break the eggs. Then, add the flour. After that, heat the pan for two minutes.
Forma negativa:
Para hacer una frase negativa en el imperativo utilizamos “do not” o “don’t” antes del verbo:
Do not smoke in the house. Don’t let the ball fall.
Selecciona los verbos del cuadro para completar el siguiente texto, recuerda que algunas oraciones pueden ser negativas:
Smoke bring eat ask throw touch take turn off enjoy Welcome to the City Museum. Before we start our tour, we’d like to inform you about the rules of the museum. For safety reasons, please respect the following rules:
1. ___________________ pictures withflash.
2. ___________________ as many questions as you can.
3. Please ___________________ or drink inside the museum.
4. ___________________ your visit as much as possible.
5. ___________________ your mobile phone during your visit.
6. ___________________ the items on display as they can break.
7. ___________________ inside the museum – Cigarettes are bad for your health.
8. ___________________ garbage on the floor.
9. ___________________ umbrellas or large packages tothe museum. We hope you enjoy your visit to the City Museum. Come back soon.
Completa el siguiente ejercicio con los verbos en el cuadro:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

Ask smoke wait forget give be come go close work
1. ___________________ a minute.
2. Do not ___________________ so hard.
3. ___________________ over here, please.
4. Do not ___________________ there.
5. ___________________ the door when you go outside.
6. Do not ___________________ so rude.
7. ___________________ your teacher
8. Do not ___________________ to tidy up your room.
9. ___________________ me your phone number so that I can call you.
10. Do not ___________________ inside the building.
Escribe las palabras en el orden correcto para formar imperativos:
1. hands / your / wash / !
2. lie / me / ! / don’t / to
3. go/ cinema / ! / the / let’s / to
4. TV / ! / don’t / watch
5. play / football / ! / let’s
6. clean / bedroom / ! / your
7. other / hit / don’t / each / !
8. not / argue / let’s /

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

9. toys / up / pick / your / all / !
10. down / sit / !
3. Health vocabulary
Enfermedades:













Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Stress
Bottle of:

An earache
Medicamentos y sus empaques.




Aspirin Cough syrup Sleeping pills

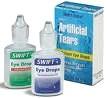

Throat spray Eye drops Vitamin
Abox of:




Antacid tablets Bandages Cold tablets Herbal tea
In Spray (Acan of):

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.




Foot spray Insect bit spray Sunburn spray
Apackage of:

Cough drops
Atube of:




Troath lozenges tissues

cream



Problemas de salud,medicamentos y remedios.

Universidad
Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENFERMEDAD:
Aheadache
Abackache
Sore muscles
Astomachache
Acold
Acough
The flu
Insomnia
Asore throat
Afever
Atoothache
Aburn

ENGLISHII
CONSEJO:
Take some aspirin.
Go to bed and rest.
See the doctor.
Get some medicine from the drugstore.
Use a heating pad on it.
Put some ointment on it.
See the doctor.
Use a heating pad on it.
Put some ointment on it.
It’s a good idea to see the doctor.
Try some antiacid.
Go to bed and rest.
Chop up some garlic and cook in chicken stock, then drink a cup every halfhour.
Take some aspirin.
Go to bed and rest.
Get some medicine from the drugstore.
It’s a good idea to see the doctor.
Drink lots of liquids.
Go to bed and rest.
Take some aspirin.
Don’t drink coffee at night.
Have a regular sleeping schedule.
Don’t eat beforebedtime.
Counting sheep may help.
See the doctor.
Get some medicine from the drugstore.
Don’t get out of bed.
See the doctor.
See the dentist.
Take some aspirin.
Put some ointment on it.
Put it under cold water.
Get some medicine from the drugstore.
See the doctor.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

Stress
Sore eyes
See the doctor. Rest.
Try some eye drops. See the doctor.
Escribe oraciones usando imperativos o el modal should, ya sea en su forma afirmativa o negativa según corresponda. Usa las palabras de los cuadros:
1.Foratoothache…
2.Forasoretroath…
3.Foraburn…
4.Forinsomnia…
5.Forafever…
6.Forabadcough…

1.Don’tgetoutofbed.
2.Usesomeskinlotion
3.Don’teatcolddrinks.
4.Don’tdrinkcoffeeat night.
5.Seethedentist.
6.Don’ttalktoomuch.

1. ______________________________________________________________.
2. ______________________________________________________________.
3. ______________________________________________________________.
4. ______________________________________________________________.
5. ______________________________________________________________.
6. ______________________________________________________________.
Contesta las siguientes preguntas usando imperativos o el modal should, ya sea en su forma afirmativa o negativa según corresponda:
1. What should you do for sore muscles? (+)
2. What should you do when you have a toothache? (-)
3. What should you do for an insect bite? (+)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

4. What should you do when you have a bad headache? (-)
5. What should you do for a sunburn? (+)
6. What should you do when you have a stomachache? (-)
7. What should you do for a burn? (+)
8. What should you do when you have a sore throat? (-)
9. What should you do for the hiccups? (+)
10. What should you do when you have the flu? (-)
Escribe el nombre de las enfermedades de acuerdo al dibujo:








Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

De acuerdo con los remedios de la izquierda escribe el nombre de la enfermedad que se puede curar:
Remedio:
Use a heating pad
Take some aspirin
See a dentist
Take a cough drop
Drink lots of hot water
Put it under cold water
Drink warm milk
Apply anti-itch cream
Use eye drops
Go to bed and rest
4. Should/ shouldn’t
Enfermedad:
El verbo modal “should” lo utilizamos en determinadas situaciones y una de las principales es para dar “consejos”:
Ejemplos:
If your headache doesn`t get better in a couple of days, you should go to the doctor. If you want to improve your language skills, you should try to read something in English.
También se utiliza para opinar sobre lo que creemos que sería la situación ideal: 1

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Education should be free for everyone. Women shouldn’t be paid less than men fordoing the same work.
Así mismo es útil para especular sobre lo que podría pasar, indicando lo que creemos que es probable:
Where is Joe? He finishes work at 6 p.m. today, so he should be here soon. The party on Saturday should be good – everyone is going.
Se puede usar should en el tiempo pasado para aludir a cosas que habrían sido una buena idea, pero no ocurrieron, sobre todo cuando lamentamos algo:
I should have told her I loved her. Clara shouldn’t have sent that e-mail.
Estructura: Afirmativa
Negativa
Sujeto + should + verbo infinitivo
Sujeto + should + not + verbo infinitivo
Interrogativa Should + sujeto + verbo infinitivo
Shouldesunverbomodal,porloquesiguelasmismasreglasqueotrosverbosmodales:
Regla:
1. Losverbosmodalesnuncavan seguidos por “to”, sino por un infinitivo sin “to”.
2. La forma negativa de “should” es “should not”, aunque normalmente utilizamos la contracción “shouldn’t”
Ejemplos:
You should study more if you want to pass that exam.
You shouldn’t listen to what James sayshe’s often wrong.
Thechildrendefinitelyshouldnotbeallowed in the study
3. En preguntas afirmativas, “should” suele servir para consultar si algo es buena idea, mientras que en las negativas suele confirmar lo que creemos que debería haber ocurrido o debería haberse hecho.
Should I turn off the lights?
Shouldn’t you have finished by now?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
4. Para utilizar los verbos modales en pasado seguimoslaestructura“verbomodal
+ have + participio pasado”:
“Should” puede emplearse asimismo en oraciones condicionales, cuando queremos ser más formales.

Jen should have listened to me. Paolo shouldn’t have eaten the last cake - it was for Jordi.
If you should want to cancel the holiday, please inform us within 7 days.
Completa las siguientes oraciones con el verbo que está entre paréntesis más el verbo modal should:
1. You _______ ____ to the gym, you will feel better. (go)
2. You touched all the animals in the farm.You _______ ______ your hands. (clean)
3. You _______ stop __________ junk food. It’s not good. (eat)
4. You are failing all the exams. Maybe, you _______ _______ harder. (study)
5. Your son looks dehydrated. He _______ _______ more water. (drink)
6. You don’t pay attention to me, you _______ ___ more attentive. (be)
7. Yourdog looks very thin. Maybe you _______ _______ its food (change)
8. Your mother needs a pause. She _______ ____ for a few days. (goaway)
Completa los espacios en blanco de las siguientes oraciones, usando la forma negativa del should para dar recomendaciones:
1. My father (drive)__________, he is very old and he gets easily distracted.
2. You (watch)__________ too much TV. It’s time you turn it off.
3. It’s very late. My daughter is in the park and she (be)__________ out.
4. Your children are missing you. You (work) __________ so much.
5. It’s a private meeting.You (record) _________ our conversation.
6. I am very worried. I ________ have (allow) ____ them to go out.
Completa las siguientes oraciones interrogativas, usando el verbo modal should más el verbo que hay entre paréntesis:
1. _______ I ________ him?, what do you think? (call)
2. I _______my job? I am not surewhether it will be a good option. (change)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

3. _______ we _______ Lucy to our wedding?We haven’t seen her for a long time. (invite)
4. _______ I ____ this dress? It’s so expensive, but I love it. (buy)
5. _______ my children _____ for this summer camp? I am not sure how safe it is. (sign up)
6. _______ we _____ to the city? In a short time, our sons will be teenagers and they willneed it. (move)
7. Why _______I _____ your exercises?! It’s unfair! (do)
8. When ______I _____ for university? (apply)
5. Necessity and prohibition Must / mustn’t
El verbo modal “must”se utiliza de la siguiente manera:
Afirmativo Para expresar un deber moral. You must respect older people. Para expresar obligación. We must wear uniform at school.
Para enfatizar la necesidad de algo. Humans must have drinking water at least every two days.
Deducir, seguro de que algo es verdadero.
Dinosaurs were very big; they must have eaten a lot.
Una fuerte recomendación. The ice cream here is delicious. You must try some.
Negativo Para expresar prohibición. Students mustn`t smoke at school. You must not step on the grass.
Escribe en la línea must or mustn’t para completar las siguientes oraciones:
1. You ______________ raise your hand to speak.
2. You ______________ study hard if you want to pass your exams.
3. You ______________ sleep in class.
4. You ______________ arrive late to school.
5. You ______________ listen to the teacher.
6. You ______________ bring your books toschool every day.
7. You ______________ play in class.
8. You ______________ finish your exercises on time.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
9. You ______________ bully your classmates.
10. You ______________ forget your homework.

11. You ______________ shout at the teacher or your classmates.
12. You ______________ use your mobile on class.
13. You ______________ ask the teacher if you don’t understand.
14. You ______________ eat in the classroom.
15. You ______________ cheat in your exams.
16. You ______________ pay attention to the teacher.
Escribeenlalínea must or mustn’t yelverbodelcuadroquecorresponda,además escribe el número de la oración en la imagen correcta:





Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.






ENGLISHII



Be brush eat fasten feed go keep listen Protect speak stop wear take tell watch
1. You ______________ junk food because it’s not healthy.
2. You ______________ your seat belt when you go by car.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
3. You ______________ the park clean to enjoy it.
4. You ______________ your dog twice a day to keep him fit.
5. You ______________ late for school.
6. You ______________ loudly in a library.
7. It`s our secret. Remember, you ______________ your brother.
8. I ______________ an umbrella because it’s raining.
9. We ______________ endangered species or they’ll dieout.
10. You ______________ too muchTV. It’s bad for your eyes.
11.Adriver ______________ when he sees this sign.
12. You ______________ your teeth after each meal.
13. You ______________ to the dentist if your tooth aches.
14. You ______________ to loud music late at night.

15. You ______________ a helmet to protect your head when you ride your bike.
6. Can / can’t
Can es un verbo modal, que se usa para expresar habilidad, posibilidad o pedirpermiso. Funciona como verbo auxiliar y antecede al verbo principal de la oración, ya que lo condicionan.
Estructura: Sujeto + can + verbo principal + complemento I can play the guitar
Habilidad: She can sing. He can run very fast.
Permiso: Can I ask you a favor? You can eat grapes if you want.
Oraciones negativas: Sujeto + can + not + verbo principal + complemento
I can not play the guitar
En las oraciones negativas podemos utilizar la negación con can’t o cannot.
Oraciones interrogativas: Can + sujeto + verbo principal + complemento + ?
Can you go to the party?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Respuestas cortas: yes, I can. No, I can’t.
Completa las siguientes oraciones de acuerdo con las imágenes:



Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Contesta las siguientes preguntas con respuestas cortas:
1. Can Simon play basketball?
2. Can Rosy and Dave ski?
3. Can Sarah play volleyball?
4. Can Sarah and Simpon play the guitar?
5. Can Rosy and Dave play chess?
6. Can Simon drive?
7. Can Sarasing?
8. Can Rosy and Dave ride a bike?

ENGLISHII
A.CompletaconCanocan’t:
1.Sarah__________playtheguitar.
2.Simon__________drive.
3.RosyandDave__________swim.
4.They__________playtennis.
5.Sarah__________paint.
6.She__________ski.
7.Simon__________rideahorse.
8.He__________skateboard.
B.Completaconlaspalabrascorrectasde acuerdoconlasimágenes:
1.RosyandDavecan__________,__________, _________and__________.
2.Theycan´t__________,__________or
3.Sarahcan__________,__________and
4.Shecan´t__________,__________or
5.Simoncan__________,__________and
6.Hecan´t__________,__________or

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Cambia las oraciones afirmativas a oraciones negativas e interrogativas:
1. Sara can windsurf.
______________________________________________________________
2. Rosy and Dave can play the trumpet.
______________________________________________________________
3. Simon can speak Spanish.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Escribe 8 oraciones sobre lo que puedes y no puedes hacer. 1. ______________________________________________________________
7. Obligation and absence of obligation:have to / don’t have to. Offers of help and possibility: may, can.
Have to / don`t have to
Se usa “have to” cuando piensas que es necesario hacer algo, o es obligatorio hacerlo. En las oraciones negativas significa que no es necesario hacerlo:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

I have to do my homework. You don’t have to work tomorrow.
Sandra has to go to the dentist. She doesn’t have to go now.
Estructura:
Oraciones afirmativas
Sujeto Have to Verbo
I / we / you / they have to work
He / she / ithas to work
Oraciones negativas
Sujeto negación Have to Verbo
I / we / you / they don’t have to work
He / she / it doesn’t have to work
Oraciones interrogativas Respuestas cortas
Auxiliar sujeto Have to Verbo Afirmativas Negativas
Do I/we/you / they have to work Yes, I do. No, I don´t
Does He / she / it have to work Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t
WH-questions
Palabra interrogativa auxiliar sujeto Have to verbo complemento
What do you have to do tomorrow. What does she have to do tonight? Respuestas
I have to work.
She has to do her homework.
Completalassiguientesoracionescon:haveto,don’thaveto,hasto,doesn’thave to
1.Marycan’tgotothecinema.She_____________________lookafterhersistertonight.
2. My parents can’t go to Italy.They _______________________ work this summer.
3. My friends _______________________ get up early tomorrow because it’s Sunday.
4. Caroline _______________________ work clean her car today because it’s raining.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

5. Children _______________________ work. First, they have to go to school.
6. Sorry, I can’t come tomorrow. I _______________________ go to the doctor.
7.Peter_______________________readalotofbooksbecausehe’sstudyingliterature.
8.Thatwoman_____________________carryallthosebags.Herhusbandcanhelpher.
9.You______________________getupearlytomorrowifyouwanttobethereatseven.
10. My father is an import-export manager. He _______________________ travel a lot.
11. You _______________________ do the ironing. I’ll do it for you. I love ironing.
12.Teresa can’t see very well so she _______________________ wear glasses.
Completa las oraciones con have to, don’t have to, has to, doesn’t have to y la información en el cuadro
Activities LisaTom
1. Make a cake Yes No
2.Do the homeworkYes Yes
3.Wash the car No Yes
4. Walk the dog Yes No
5. Study history No Yes
6. Set the table No No
7. Cut the Grass No Yes
8. Tidy the bedroomYes Yes
1. Tom _______________________ wash the car.
2. Lisa andTom _______________________ do the homework.
3. Tom _______________________ walk the dog.
4. Lisa _______________________ study history.
5. Tom _______________________ study history.
6. Lisa andTom _______________________ set the table.
7. Lisa _______________________ cut the grass.
8. Lisa _______________________ wash the car.
9. Tom _______________________ cut the grass.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
10. Tom _______________________ make a cake.
11. Tom _______________________ tidy the bedroom.
12. Lisa _______________________ make a cake.
May, can

May y can son dos verbos modales, como ya lo vimos, can se utiliza para expresar una habilidad o permiso en contextos coloquiales, may se usa para expresar posibilidad y pedir o dar permiso en contextos formales.
Sondifícilesdedistinguiryaquesetraducenigual.Suestructuraesigualalasanteriores:
Afirmativa: I may lose my job because of this mistake. Negativa: You may not play catch in the house. Interrogativa: May I go to the bathroom?
Can
May
Ejemplos
Pedir permiso Informal Formal May I have a glass of water? Can I have a glass ofwater?
Posibilidades Con seguridad Con duda It may get very cold at night. It can get very cold atnight. habilidades Solo can I can speak English very well. I can´t get up early.
Completa con “can” o “may” según sea más habitual o más formal:
1. My boss _____________speak English very fluently.
2. You _____________ take my dictionary for your exam. (formal)
3. Your sister come with us to the cinema. It depends on your mother. (formal)
4. You _____________ open the bottle with that corkscrew.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
5. You _____________ use my computer if you want. (formal)
6. _____________ you bring me a glass of water, please?
7. My father is very strong, he lift 100 kg.
8. You _____________ enter the party with this invitation.
9. You _____ ________find that book in the Central Library.

10. _____________ I switch on the light? I would like to read the newspaper. (informal)
11. Philip _____________ use his father's motorbike.
12. If you need it you _____________ use our lawnmower. (formal)
13. _____________ you help me to clean the swimming pool, please?
14. I use the company car forprivate trips. (informal)
15. There are rumours that the Spanish airline Iberia _____________ merge with British Airway.
16. We are going to the park; you come with us if you want. (formal)
17. With that telescope you see Mars.
18. You should buy lottery tickets; you _____________ become millionaire.
19. _____________ you help me to move this heavy box? I cannot do it on my own. (informal)
20. If you have any questions you ask me. (formal)
21. My brother works in theAir Force; he _____________ fly a fighter plane.
22. If you study hard you _____________ pass your exams.
23. During the flight you _____________ not use your mobile.
24. With my savings I _____________ buy a new car.
25. Mark doesn't answer the phone; he _____________have left his office because he didn't feel well.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

AUTOEVALUACIÓN
I. Simple past: irregular verbs.
1.We _______ a huge meal last night. a) eat b) eaten c) eating d) ate
2.My friend and her sister ____________ to visit me last year. a) came b) come c) coming d) comes
3. Silvia ________________ a wonderful cake for our friend's birthday party last weekend.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

ENGLISHII
a) made b) makes c) making d) make
4. I ________ all my homework in study hall. a) do b) doing c) done d) did
5. Mariana ________ of a better way to do it. a) think did b) didn’t think c) didn’t thought d) thought didn’t
6. ______ Sofy ________ her arm when she fell down the stairs? No, she _____ a) Does / break / does b) Did / broke / didn’t c) Didn’t / break / did d) Did / break / didn’t
7. __________ _______ the dog ________ a hole? In the back yard. a) When / did / dug b) Where / did / dig c) How / did / dig d) Why / did / dug
8. We never _________ her real name. a) knew b) Know c) Knowing d) Known
9. They __________________ the baby’s room. a) decorates b) did decorate c) didn’t decorate d) decorated did
10. ______ Sara ______ to you? Yes, she _____. a) Did / talked / did b) Did / did / talk c) Does / talk / does d) Did / talk / did
II. Imperativos. Selecciona la imagen o frase que corresponda:
11. Don’t walk the dog

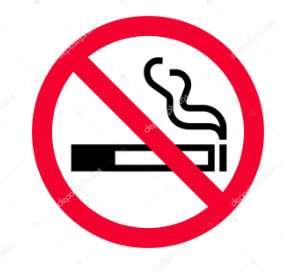

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.


a) Don’t take photos!
c) Don´t throw the garbage!
13. Don´t walk on the grass.


b) Don`t smoke!
d) Don’t eat!

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.





III. Contesta las siguientes preguntas de acuerdo al remedio correcto.
14. What should you do for itchy eyes? _________________
a) See a dentist.
c) Drink warm milk
b) Drink lots of hot water.
d) Useeye drops.
15. What should I do for an insect bite? _________________
a)Apply anti-itchcream.
c) Put it under cold water
b) Take a cough drop.
d) Go to bed and rest.
16. What should you do for a burn? ___________
c)
d)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
a) Usea heating pad.
c) Drink warm milk.
b) Put it under cold water.
d) Take some aspirin.

ENGLISHII
IV. Completa con Should / shouldn’t según corresponda:
17. You _________ miss to visit the museum, it’s very interesting.
a) shouldn’t b) can c)don’t can d) not should
18. When __________ we go to LosAngeles?Anytime, the weather is always nice.
a) not can b) should c) should are d) cans
19. Where ________ elderly people go in winters? To sunny places.
a) not can b) should c) should are d) cans
V. Completa con Must / mustn’t según corresponda:
20. You ______________ to the dentist with a tootache.
a) must go b) mustn’t go c) must goes d) mustn’t went
21. You ______________ late for school.
a) must be b) mustn’t are c) must is d) mustn’t be
22. You _______________ your pet twice aday.
a) mustn’t feeds b) must feed c) must feeds d) mustn’t feeds
VI. Completa con Can / can’t según corresponda:

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
23. My grandmother _________ go shopping every day.
a) not can

b) not should c) can d) cans
24. Nick ____________ travel toAmerica, he doesn’t have passport.
a) can’t
b) doesn’t can c) not should d) shoulds
25. I’m sorry. I __________ you up at the airport.
a) can’t pick
c) can picking
b) can to pick d) not can pick
VII. Completa con Have to / don`t have tosegún corresponda:
26. I ________________ clean the house.
a) have to b) has to c) doesn’t have to d) to have not
27. _________ Javier _________ work next weekend?
a) Do / have to b) Does / has to c) Do / has to d) Does / have to
28. My students __________________ their homework or they will not pass.
a) has to do b) have to do c) doesn’t have to d) don’t has to
VIII. Completa con May o Can según corresponda:
29. _________I _____ you, sir?
a) May b) May/help c) Help/may d) Help/help
30. I ____ play the guitar. My brother _____ play the accordion.
a) can/cans b) may /can c) can/can d) can / may

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
31. I ____________ to Paris on my next vacation.
a) go may b) may c) may go d) may goes

UNIDAD IV PLANSAND PREDICTIONS
UNIDAD
PLANS AND PREDICTIONS



Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Propósitodelaunidad:


Ulizarelempofuturoparahacerprediccionesyplanesenel trabajoyenlavidasocialatravésdelashabilidades comunicavas.
APRENDIZAJES ESPERADOS
Elestudiante:


7.Muestrauncomportamientoquereflejalapráccadelosvalores instucionalesyenlainteracciónconsumaestroysusparesalrealizarlas diferentesacvidadesdelaunidad.
8.Ulizaelempofuturoparaexpresarplanesyproyectosenformaoralyescrita.
9.ComparaelfuturoWillconelfuturoGoingtoenprediccionesy/osituaciones futuras.

PLANSAND PREDICTIONS




Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

h ps://bit.ly/3uBlAPe
1. Future:Going to
“Going to” no es un tiempo verbal, es una estructura especial que usamos para hablar acerca del futuro.
Se usael“begoingto” paratransmitiruna idea de futuro.Aunque hay muchas formasde expresar ideas en futuro en inglés, esta estructura tiene dos funciones principalmente:
1. Referirnos a planes futuros que ya hemos decidido. Refleja las intenciones del hablante para el futuro, aunque no necesariamente significa que ya hayamos empezado los preparativos, o que esas cosas vayan a suceder de verdad. Ejemplos:
When I’m older, I’m going to be an astronaut!
Next weekend I’m going to sleep until really late!
In two years’time, I’mgoing to move to Parisand study fashion design.
Are you going to eat anything? No, I'm not hungry.
A: I hear Sarah has won some money. What is she going to do with it?
B: She's going to buy a new car.
I'm just going to make a quick phone call. Can you wait for me?
This cheese smells horrible. I'm not going to eat it.
2. Para hacer predicciones en base a lo que vemos en el presente. Es decir estamos hablando de lo que pensamos que pasará. Ejemplos:
If she’s not careful she’s going to knock that glass over.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
It’s very cold outside –I think it’s going to snow.

Javier’s birthday party is going to be great – she was showing me the restaurant online.
También Podemos decir que algo va a pasar en el futuro:
The man isn´t looking where he is going. He is going to walk into the wall.
Lookatthoseblackclouds!lt'sgoingtorain.(Thecloudsaretherenow)
Ifeelterrible.IthinkI'mgoingtobesick.(Ifeelterriblenow)
Theeconomicsitua onisbadnowandthingsaregoingtogetworse
La estructura de “going to” es la siguiente:
Sujeto Verbo “To Be” “going to” Verbo en infinitivo Complemento Oraciones afirmativas I am going to go to the beach this weekend. She is going to have spaghetti for dinner tonight. They are going to release a new albumnext year.
Sujeto Verbo “To Be” Negación“going to” Verbo en infinitivo Complemento Oraciones negativas I am not going to study medicine anymore.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

He is not going to listen to what you say. We are not going to go to the wedding because we have to work.
Verbo “To Be” Sujeto “going to” Verbo en infinitivo Complemento
Oraciones interrogativas Am I going to finish the project on time?
Are you going to come to the party on Sunday? Is it going to rain tomorrow?
Respuestas cortas
Afirmativas Negativas
Yes, I he / she / it you / we / they am. is. are. No, I he / she / it you / we / they am not. is not. (isn’t) are not. (aren’t)
Palabras interrogativas:
Palabra interrogativa
Verbo “To Be” Sujeto Going to Verbo en infinitivo
What When Where Why How am is are I he / she / it you / we / they Going to travel?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Who travel with?
El “be going to” suele usarse en contextos informales, así casi siempre se usa con contracciones: “I’m”, “he’s”, “it’s”, “we’re”, “they’re”.
2. Time phrases
Usamos “going to” para hablar de planes futuros y usamos expresiones de empo para indicar cuando vamos a hacer las ac vidades, algunas de ellas son:




Consulta la traducción de las siguientes expresiones de empo para futuro:
Tonight Tomorrow Next week
At the weekend On Monday In five months
Next month In ten years On Thursday
Ejemplos:
TodayisAugust16th. Iamgoingtogo swimming tomorrow.

Todayisthe9th.dayofthemonth.Wearegoing togoonholydays next week.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

TodayisMonday.Theyearegoingtogosurfing on Thursday.


Theschoolfinishesat17:00.Heisgoingtoplay football a er school. Theyaregoingtogowater–skiing at the weekend.
Completa las siguientes oraciones usando “going to”.
1. He ______________________________his friend. (phone)
2. We ______________________________ a new computer game. (play)
3. My sister _________________________TV. (watch)
4. You ______________________________ a picnic nextTuesday. (have)
5. Jane ______________________________ to the office. (go)
6. They_______________________________ to the bus stop this afternoon. (walk)
7. His brother ____________________________a letter to his uncle today. (write)
8. She __________________________________ her aunt. (visit)
Escribe enunciados (+), (-) e (?) usando la información que se te proporciona.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Ejemplo: I / dry my clothes.
I am going to dry my clothes. I am not going to dry my clothes. Am I going to dry my clothes?
He / buy a car
They / paint the house.


Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
We / go to bed.
The students / go to the school for the last time next Monday.

ENGLISHII
Lee las siguientes situaciones y completa el dialogo. Usa going to.
1. You have decided to clean your room this morning.
FRIEND:Are you going out this morning?
YOU: No, I am going to clean my room this morning.
2. You bought a sweater, but it doesn't fit you very well. You have decided to take it back to the shop.
FRIEND:That sweater is too big for you.
You: I know, I

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

3. You have been offered a job, but you have decided not to accept it.
FRIEND: I hear you've been offered a job
You: That's right, but
4. You have to phone Sarah. It is morning now, and you have decided to phone her tonight.
FRIEND: Have you phoned Sarah yet?
You:
No______________________________________________________________
5. You are in a restaurant. The food is awful,and you've decided to complain FRIEND:This food is awful, isn't it?
You:Yes, it's disgusting. I
¿Qué va a pasar en estas situaciones? Usa “going to” y las palabras en paréntesis.
1. There are a lot of black clouds in the sky. (rain) It is going to rain__________________________________________________________
2. lt is 8.30. Tom is leaving his house He has to be at work at 8.45, but the journey takes 30 minutes (be late) He
3. There is a hole in the bottom of the boat.Alot of water is coming in through the hole. (sink)The boat
4. Lucy and Chris aredriving There is very little petrol left in the tank The nearest petrol station is a long way away. (run out)They
Corrige las siguientes oraciones con la forma correcta de “going to”. Hay un error en cada oración.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
I am going to doing my homework after school today.

2. She goes to play football on Sunday.
3. Look at the sky! It going to rain.
4. they are going to visit the museum this afternoon?
5. He doesn’t going to travel toArgentina this summer.
6. Look at the books!They are go to fall off the shelf.
Escribe las palabras en el orden correcto para hacer oraciones.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
1.goingto/Sandra/hermother/is/help
2.have/what/goingto/are/fordinner/you/?
3.attheuniversity/am/I/study/goingto/nextyear.

4.is/thedog/itsfood/eat/goingto/?
5.Lucia/return/is/toMexico/goingto/?/someday
Observa la imagen y escribe oraciones usando las palabras dadas. Usa “going to”

h ps://bit.ly/3B9YOQV

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
1.It/be/ahotandsunnyday.
2.JamesandDavid/swim/inthesea.
3.Thefamily/have/lunchonthebeach.
4.Paul/fall/overabag.
5.MrandMrsHill/ride/inaboat.
6.Phyllis/read/abook.
7.BarbaraandSusan/drink/somewater.


Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
8.I/finish/thisac vity.
3. Future Will / won’t

Usamos “will” cuando tomamos una decisión espontanea para hacer algo.
Will: se usa frecuentemente en las siguientes situaciones
Eventos futuros probables: It willsnow this weekend.
Decisiones o ideas espontáneas: I will pick you up tomorrow.
Voluntad para hacer una actividad: They willrepairmyTV tomorrow. That bag looks heavy. I will help you with it.
Dar órdenes: You will not go to the party!
Proponer o invitar algo: Will you marry me?
Estar de acuerdo en hacer algo:
Prometer hacer algo:
A: Can you give Tim this book?
B: Sure, I willl give it to him when I see him this afternoon.
Thanks for lending me the money. I will pay you back on Friday.
I won't tell anyone what happened. I promise.
Pedir a alguien que haga algo: Will you please turn the music down? I'm trying to concentrate.
Estructura: Sujeto
Auxiliair will Verbo en infinitivo Complemento

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Oraciones
Afirmativas I He / she / it

We / you / they will come to the countrynext year
Sujeto Auxiliar will negación Verbo en infinitivo Complemento
Oraciones negativas I He / she / it
We / you / they will not cook this week.
Auxiliar will Sujeto Verbo en infinitivo Complemento
Oraciones interrogativas will
He / she / it
We / you / they cook this week.
Respuestas cortas afirmativas
Yes, I He / she / it
Respuestas cortas negativas
We / you / they will. No, I He / she / it
We / you / they Will not (won’t)
Preguntas con palabras interrogativas
Palabra interrogativa Auxiliar will Sujeto Verbo en infinitivo Complemento
When Where
Why
How will I
He / she / it
We / you / they go tomorrow?
What will I
He / she / it
We / you / they do tomorrow
Who will I
He / she / it
We / you / they go with tomorrow?
Ejemplos:
-Oh, I've left the door open. I willgo and shut it.
-What would you like to drink?' I willhave an orange juice, please.'

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
-Did you phone Lucy?' 'Oh no, I forgot. I'llphone her now.'

ENGLISHII
NOTA: Usamos frecuentemente “will “con las siguientes expresiones: I think I ‘ll…. y I don’t think I’ll
-I feel a bit hungry. I think I'll have something to eat. -I don't think I'Ll go out tonight. I'm too tired.
Completa las siguientes oraciones con will /will not-won’t (pregunta/afirmativa/ negativa), en su forma apropiada.
1. ________________________ me £50? (you/ lend)
2.________________________ to the country. (they/not move)
3. _______________________ the exam in French. (Laura/ do)
4. When _________________________ us the file? (Kim/send)
5. ______________________________a mile in 5 minutes. (John/ run)
6.___________________________________ the garden bench? (your father/paint)
7. How many days ____________________ in Rome? (she/ stay)
8.____________________________________Grand Canyon National Park. (we/visit)
Completa con respuestas cortas usando “will” para las siguientes oraciones. Ejemplo: Will Maria come to the party? No, she won’t
Will you come early?
No, ______________
Will Jack play with us?
Yes, _______________
Will they be at home?
Will you and Sam go to the movies?
Yes, ______________
Will it snow?
Yes, _____________
Will you make dinner?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
No, _______________ No, _______________

Completa las oraciones con “I will” + el verbo apropiado del recuadro. try take teach have stay send do turn give
1. I’m too tired to walk home. I think ________________ a taxi.
2. lt's cold in this room. Is it? ________________ on the heating then.
3. Bye! Have a nice holiday!Thanks. _____________ you a postcard.
4. Willshe do the washing-up?' No, it's all right. ____________it later.
5. I don't know how to shut down this computer. OK, ___________________you.
6. Would you like tea or coffee? __________________. coffee, please.
7.Are you coming with us?' 'No, I think _________________ here.
8. Thanks for lending me the money. _______________________itback as soon as possible, OK?
9. A: I know you're busy, but can you finish this report this afternoon?
B: Well, _______________________ but I can't promise.
Completa el siguiente dialogo usando la forma correcta de “will” y el verbo entre paréntesis.
A– What do you think the future _____________ like? (be)
B – Ithink cars________________. (fly)
A– Really? What do you think the schools __________________ like? (be)
B – Ithink people _________________ in their houses via the Internet. (study)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
A– What ________ hospitals ________like? (be)

B - I think medicine_____________ totally different (be). We _________________ many of the diseases that wehave today.(not have)
Usa la forma correcta de “will” para completar las siguientes oraciones.
1.Therearemanydirtyshoes.I_________________(onlyclean).
2.Heshouldbehere.I_________________anotherminute. (not/wait).
3.Theseexercisesareverydifficult.Ifyouwant,I__________________themtoyou(explain)
4.It’sge nglate.IthinkI___________________homebeforeitgetsdark.(go)
5.Don’tworry,I_________________you.(never/leave)
6.We______________themgotothepartyun ltheyfinishtheirhomework.(not/let)
7.Iwillcomebackearlytomorrow.__________you_______awake?(be)
8.Michaelisverythirsty.I_________________himaglassofwater.(bring)
9.Ifyoudon’tleavemyhousenow,I__________________thepólice(call)
10.It’sstar ngtorain.I___________myumbrella! (get).
Escribe oraciones acerca de la vida de Tara en el futuro. Usa will y won’t

h ps://bit.ly/3mmH5zM
1. I/gotouniversity(+) I/study/tobeanarchitect(-) I will go to the university. I will study to be an architect.
2. I/live/inParis(+) I/liveinroo ops(-) _______________________________________________.
3. I/drive/abigcar.(-) I/ride/ayellowbicycle(+)

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

4. DexandBen/live/inParis(-) They/visitme/twiceayear(+)
Completa el siguiente ejercicio con “will” y las palabras del cuadro.
cook buy get not/tell visit
Lucia_____________anewhousenearthelake.Shetoldhermomaboutthehouse.Hermother __________ her every weekend. They ___________ anyone because they don’t want to be disturbedwhiletheyaretogether.
Lucia____________atelescopetoseethestars.Lucia’smother_____________ aspecialrecipe whiletheyareawayinthenewhouse.
4. Fortune - telling
Contestalassiguientespreguntas,escribeoracionescompletas: Hasanyoneevertoldyourfortune?
Doyoubelieveitispossibletotellsomeone’sfortunebyusingthelinesontheirhand?

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
ENGLISHII

Somepeoplethinkthelinesonyourpalmhavedifferentmeanings.Doyouknowwhatthese meaningsare?
Relaciona cada palabra con su definición:
1.Fate a.Theinsidepartofthehandwithinesonit.
2.Imagina onb.Big;important
3.Leadership c.Small;lessimportant
4.Major d.Apowerthatdecidesaperson’sfuture.
5.Minor e.Connec onbetweenideas,peopleorthings.
6.Palm f. Abilitytoleadpeople.
7.Rela onshipg.Crea vity,crea ngstoriesinthemind.
8.represent h.Show,mean,standfor.
Realiza el siguiente ejercicio sobre Palm Reading.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
https://bit.ly/2WpDpnU

Some people think you can learn a lot about the future by palm reading. Circle how are your lines:
1. LIFE LINE: long medium short
2. HEAD LINE: long medium short
3. HEART LINE: long medium short
4. SUN LINE: startsatthebo om startsfarfromthebo om
5. MARRIAGE LINES: farapart closetogether
Checaelsignificadodetuslíneas:
LIFE LINE: ifthisislong,youwillhavealonglife.
HEAD LINE: ifthisislong,itmeansyouareintelligent.
HEART LINE: ifyouhavealong-curvedline,youareverykind. Ifyouhavemanysmalllines,youwillhavemanyromances.
SUN LINE: if this line starts at the bo om of your hand you are going to be rich and successful.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Ifitstartsfarfromthebo om,youwillbesuccessfulwhenyouareold.
MARRIAGE LINES: ifyourmarriagelinesareclosetogether,youwillprobablygetmarried whenyouareveryyoung.
Escribe oraciones usando “going to” o “will” de acuerdo con la información de Palm Reading. What
your future?
5. Will vs Going to.
Will or going to se refieren a hechos futuros, pero se usan en contextos diferentes. Mientras que will seusaparaprometercosasyhablardedecisionesespontáneas, going toesmáscomún para hablar de hacer planes o intenciones.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
1. Futuro incierto:
I will travel the world in 10 years.
2. Predicciones:
She will get married to a rich man.
3. Reacciones espontáneas:
-There’s no milk in the fridge.
- I will buy some!
4. Promesas, ofertas, amenazas, etc.
I promiseI will study.

1. Planes: I am going to France this summer.
2. Situaciones obvias:
It is going to rain. (Hay nubes grises en el cielo).
3. Hechos planificados:
-There’s no milk in the fridge.
- I am going to buy some, it’s on the shopping list. (ya sabíamos que loíbamos a comprar).
4. Hechos que están a punto de ocurrir: Look, this car is going to crash!
Completa las siguientes oraciones usando Will o Going to, según corresponda:
1. Next summer I _______________ buy a new house.
2. I am quite tired; I _______________ go to bed now.
3. I believe Laura _______________ like her brand-new car.
4. Look at those guys!They _______________ rob the bank.
5. I promise, I _______________ do it again.
6. I think she _______________ crash my dad’s car.
7. I talked to John yesterday; we _______________ visit you tomorrow.
8. I am sorry dad; I _______________ drink and drive again.
9. Watch out!That man _______________ punch you.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
10. It is really hot in here; I _______________ open the window.

Completa usando “will”o “going to” apropiadamente, las siguientes oraciones.
1. Have you got any plans for tomorrow?
-Yes, I am _______________ visit my grandparents.
2. Why is she learning Spanish?
- She travel to Spain.
3. We arethirsty.
- Wait here. I_______________ get some water.
4. Meat or fish?
- I have some fish, please.
5. What do you want the keys for?
- I ______________close the door.
6. If you don't take a taxi, you _________________ arrive on time.
7. Why do you want so many oranges?
- I______________ make an orange juice.
8. Oh! I haven't got enough money to pay!
- Don't worry. I _________________ give you some.
9. We need one more player.
- __________________you play with us now?
10. Why are you switching on the TV?
- I __________________ watch a football match.

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Escoge “will “o “going to” para completar las siguientes oraciones de forma apropiada, usando los verbos en paréntesis.
1. What are you doing with those tools? I _________________________ (repair)the car.
2. Oh no!Thereisn’t any milk in the fridge? I ____________________(get) some from the store.
3. Did you phone Bob? Oh, no. I completely forgot. I _______________________ (phone) him now.
4. I’m really hungry! I _________________ (make) you something to eat, then.
5. I really must go now. If you wait a moment, I ____________________ (give) you a lift in my car.
6. Mary made a decision yesterday. She ___________________________ (change) her job
7. I _________________________(meet) some friends for coffee this afternoon.
8. Romeo is always late. I’m sure he______________________(not arrive ) on time.
9. The phone is ringing. I ________________________ (answer) it.
10. Sophia _______________________(start) her new job next week.
11.___________________________(they/win)thetennismatchtomorrow?Whatdoyou think?
12.Lookatthatdriver!He__________________________(have)anaccident.
13.Doyouwanttomeetmyfather?Comeon,I____________________________(introduce) you.
14.Doyouhaveplansforyourholiday? Yes,I_____________________________(go)toFrance.
15.LuciadecidedtolearnArabic.She_________________________(start)lessonsnextweek.
AUTOEVALUACIÓN

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

I. Complete using the structure of Going to for the next sentences.
1.Andy: What do you plan to do after you graduate from university?
Kim: I_______________ work in a hospital inAfrica to help the poor people.
a) is go to b) am going
c) going to
d) ’m going to
2. Pamela: Why are you carrying your laptop?
Susan: Because a friend of mine _____________ some homework while we travel on the train.
a) is go to doing
b) is going to do
c) going to do
d) are going to
3. Helena: If you take a look at these statistics, we can see that the economy __________________ worse very soon so we have to save as much money as we can.
a) is going be
b) is go to being
c) going to be
d) is going to be

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

II. Use the correct form of Will to complete the following sentences.
4.Alexa: Oh mygod!All the lights have gone off, there should have been a blackout.
Mike: Don’t panic. I __________ a look immediately.
a) will took
b) will taking
c) willtake
d) ’ll taken
5. Kyle: I can’t find the car keys; I don’t remember where I placed them.
Monica: My daughterand I _____________ you look for them!
a) will helping
b) will help
c) willhelped
d) won’t help
6. Paul: Hello!Alexa! did you remember to buy the tickets for the concert tonight at the football stadium?
Alexa: Oh no!. I forgot. I____________ them online now.
a) will buy
b) won’t buy

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
c) willbuying
d) will bought

III. Complete the following sentences using the most appropiate structure of Going to or Will
7.Andrea: We don’t have any bread to prepare the sandwiches for the picnic.
Blake: I know, I ______________ buy two loaves of bread. I took some money from your purse.
a) go to
b) will go
c) will
d) ’m going to
8. Susan: We don’t have any cokes for the party
Mike: Really? I ___________ some from the supermarket then.
a) am going to get
b) will get
c) won’t get
d) will going
9.Lucia: Why do you need to borrow my new suitcase?
Kyle: Because my daughter_______________ visit my sister in Spain next month.
a) will

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
b) is going to
c) won’t
d) isn’t going to
IV. Complete using the appropriate Time phrase.

10. Pauland Sheila are always going to walk their dog to the beach _________ going to bed.
a) on b) before c) after d) until
11. Maria: We need more tomatoes for the salad, why don’t you go to the store?
Lulu: No. I will never go ___ this time, because it is always crowded.
a) until b) in c) at d) on
12.SusanandRobertwillprobablygotoFranceandSpain_________________tospend some time with their family.
a) until b) last month

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
c) a week ago
d) next summer
Complete the following text with the words from the box.

prediction told fortune teller palm reader future palm
I went to a ______________________ yesterday. She ______________ me my ______________. How did she do it? She read my ______ ¡ Oh, she’s a ___________________. What did she say? I won’t tell you, or her ______________ won’t come true.
PROYECTO
PROYECTO
I.Realizaelproyecto“TriptoLondon”siguiendolospasosquesepresentanacon nuación:
1. Contestar las siguientes preguntas sobre Londres:
1. What is the nation´s current favorite food?
2. Where is the “home” of the sport golf?
3. What is the artist Chris Ofilifamous for?
4. What song is sung on NewYear’s Eve in the UK?
2. Transporte: Cómo se llega a Londres, cómo transportarse dentro de Londres: Contestar las preguntas:
1. What line(s) do you take to travel from Heathrow to London Bridge?
2. Where do you change trains?
3. Ingresar a la página http://www.thedungeons.com/ o cualquier otrapágina, donde encontraras información about Jack el destripador, y trata de poner en el orden correcto los siguientes eventos:
a)The killer was never found
b) Elizabeth Stride was killed
c) Mary Nicholl’s body was found

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
d) Louis Deimschutz disturbed the ripper
e) Catherine Edowes was attacked
f) Mary Nicholl’s throat was cut g)Angry mobs attacked suspects
ENGLISHII

4. Busca en varios sitios de Internet los nombres de los autores delos siguientes libros escritos entre 1850 y 1950 y contesta las siguientes preguntas:
a) Charles Dickens lived at _____________ when he wrote the __________ Papers. He moved there in ______ and lived there for ______ years.
b) Which writer from the Bloomsbury group wrote a book called WhereAngels Fear to Tread?
c)The writer P.G. Wodehouse was famous in particular fortwo characters. What were those characters’names?
d) What jobs did the characters do?
e) What kind of characters were they?
5. El viaje a Londres tendrá una duración de 48 horas, ¿a donde irias? ¿Que harías?, planea esas horas, asegurate de incluir como llegara esos lugares que visitarias.
6. Contesta las siguientes preguntas:
1. At what gate in which famous tower was the ghost of SirThomas Becket seen striking a wall with a crucifix?
2. What are the nicknames of the following London football teams: Crystal Palace and West Ham?
3. What two tube stations beginning with a ‘w’are best for going to the London Eye?
1. Name the dinosaur that lived in England in the Middle Jurassic period, which was carnivorous and could measure up to nine metres long.
1. What is the name of the pub in the London soap opera ‘Eastenders’?
1. What is ‘Kew Gardens’and where can you find it?
Algunas páginas que te pueden servir para buscar la información son las siguientes: BBC The Tower of London Crystal Palace
West Ham London Eye Kew
The Natural History Museum
7. Incluye las fuentes consultadas ya sea en páginas web o libros. Mínimo tres.
8. Realiza una presentación en Power Point para compartir los resultados con tu asesor y con otros compañeros.
9. Llena el formato de rúbrica de acuerdo con tu percepción.
Rúbrica para evaluar el proyecto:
Tarea: SiNo
Contestalaspreguntasdelpunto1. Contestalaspreguntasdelpunto2. OrdenaloseventossobreJackeldestripador Contestalaspreguntassobrelosautoresdelibros

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Presentaeli nerarioenLondres
Contestalaspreguntasdelpunto6.
Incluyelasfuentesconsultadas,porlomenostres PresentaciónenPowerPoint
VERBOS REGULARES.
Infinitivo Forma base Presente Pasado Pasado Participio Gerundio Significado
To accept accept accept(s) accepted accepted accepting aceptar
To answer answer answer(s) answered answered answering contestar
To arrive arrive arrive(s) arrived arrived arriveing llegar
To ask ask ask(s) asked asked asking preguntar
To clean clean clean(s) cleaned cleaned cleaning limpiar
To climb climb climb(s) climbed climbed climbing trepar
To close close close(s) closed closed closing cerrar
To cook cook cook(s) cooked cooked cooking cocinar
To change change change(s) changed changed changing cambiar
To dance dance dance(s) danced danced dancing bailar
To deliver deliver deliver (s) delivered delivered delivering entregar
To dress dress dress (s) dressed dressed dressing vestir
To enjoy enjoy enjoy (s) enjoyed enjoyed enjoying disfrutar
To erase erase erase (s) erased erased erasing borrar
To finish finish finish (s) finished finished finishing terminar
To fix fix fix (s) fixed fixed fixing Arreglar
To follow follow follow (s) followed followed following seguir
To help help help (s) helped helped helping ayudar
To hurry hurry hurry (s) hurried hurried hurrying apresurar
To invite invite invite (s) invited invited inviting invitar
To join join join (s) joined joined joining reunir
To jump jump jump (s) jumped jumped jumping brincar
To learn learn learn (s) learned learned learning aprender
To like like like (s) liked liked liking gustar
To listen listen listen (s) listened listened listening escuchar
To live live live (s) lived lived living vivir
To look look look (s) looked looked looking observar
To love love love (s) loved loved loving amar
To miss miss miss (s) missed missed missing extrañar
To need need need (s) needed needed needing necesitar
To open open open (s) opened opened opening abrir
To paint paint paint(s) painted painted painting pintar
To plan plan plan (s) planned planned planning planear
To play play play (s) played played playing jugar
To practice practice practice (s) practiced practiced practicing practicar
To push push push(s) pushed pushed pushing empujar
To repeat repeat repeat (s) repeated repeated repeating repetir
To show show show (s) showed showed showing mostrar
To start start start (s) started started starting empezar
To stay stay stay (s) stayed stayed staying permanecer
To stop stop stop (s) stopped stopped stopping parar
To study study study (s) studied studied studying estudiar
To talk talk talk (s) talked talked talking conversar

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

To travel travel travel (s) traveled traveled traveling viajar
To try try try (s) tried tried trying intentar
To turn turn turn (s) turned turned turning voltear
To use use use (s) used use using usar
To visit visit visit (s) visited visited visiting visitar
To wait wait wait (s) waited waited waiting esperar
To walk walk walk (s) walked walked walking Caminar
To want want want (s) wanted wanted wanting querer
To wash wash wash (s) washed washed washing lavar
To watch watch watch (s) watched watched watching ver
VERBOS IRREGULARES.
Infinitivo Forma base Presente Pasado Pasado Participio Gerundio Significado
To be be am, is, are was, were been being ser o estar
To become become become(s) became become becoming llegar a ser
To begin begin begin (s) began begun beginning empezar
To break break break (s) broke broken breaking romper
To bring bring bring(s) brought brought bringing traer
To build build build (s) built built building construir
To buy buy buy (s) bought bought buying comprar
To come come come (s) came come coming venir
To dream dream dream (s) dreamt dreamt dreaming soñar
To drink drink drink(s) drank drunk drinking beber
To drive drive drive (s) drove driven driving conducir
To do do do (s) did done doing hacer
To eat eat eat (s) ate eaten eating comer
To fall fall fall (s) fell fall - fallen falling caer
To feel feel feel (s) felt felt feeling sentir
To find find find s) found found finding encontrar
To fly fly fly (s) flew flown flying volar
To forget forget forget (s) forgot forgotten forgetting olvidar
To get get get (s) got gotten getting obtener
To give give give (s) gave given giving dar
To go go go (s) went gone going ir
To grow up grow up grow (s) up grew up grown up growing up crecer
To have have have, has had had having tener
To hear hear hear (s) heard heard hearing oir
To hit hit hit (s) hit hit hitting golpear
To keep keep keep (s) kept Kept keeping conservar
To know know know (s) knew known knowing saber
To leave leave leave (s) left left leaving salir
To lose lose lose (s) lost lost losing perder
To make make make (s) made made making hacer
To meet meet meet (s) met met meeting conocer
To read read read (s) read read reading leer
To ride ride ride (s) rode ridden riding montar
To run run run (s) ran run running correr
To see see see (s) saw seen seeing ver
To sell sell sell(s) sold sold selling vender
To send send send (s) sent sent sending enviar
To sing sing sing (s) sang sang singing cantar


Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

To sit sit sit (s) sat sat sitting sentarse
To sleep sleep sleep (s) slept slept sleeping dormir
To speak speak speak (s) spoke spoken speaking hablar
To spend spend spend (s) spent spent spending gastar
To swim swim swim (s) swam swum swimming nadar
To take take take (s) took taken taking tomar
To teach teach teach (s) taught taught teaching enseñar
To tell tell tell (s) told told telling decir
To think think think (s) thought thought thinking pensar
To throw throw throw (s) threw thrown throwing lanzar
To wake up wake up wake (s) up woke up waken up waking up despertar
To wear wear wear (s) wore worn wearing vestir
To win win win (s) won won winning ganar
To write write write (s) wrote written writing escribir
Bibliografía
Abaenglish.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.abaenglish.com/es/grama caingles/lower-intermediate/compara ve-adjec ves-regular-irregular/
Abaenglish.com.(9demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.abaenglish.com/es/verbosmodales-ingles/should/
Abaenglish.com.(9demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.abaenglish.com/es/verbosmodales-ingles/must/
Aprenderinglesrapidoyfacil.com.(6deenerode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.aprenderinglesrapidoyfacil.com/2013/05/09/adje vos-de-personalidad-eningles-pronunciacion-y-ejercicios-de-audio/
Aprenderinglesrapidoyfacil.com.(9demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.aprenderinglesrapidoyfacil.com/2016/12/03/ejercicios-de-impera vos/
Aulafacil.com.(6deenerode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.aulafacil.com/cursos/ingles/repaso-de-grama ca/ejercicios-orden-de-losadje vos-l22488
Aulafacil.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://www.aulafacil.com/cursos/ingles/repaso-de-grama ca/ejercicios-can-mayl22655

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Avi.cuaed.unam.mx.(5deabrilde2022).Obtenidode h ps://avi.cuaed.unam.mx/repositorio/moodle/pluginfile.php/1987/mod_resource/cont ent/17/contenido/index.html
Boabloodpashvissanom.hatenablog.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://boabloodpaghvissanom.hatenablog.com/entry/2019/10/15/010259
Bri shcouncil.es.(9demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.bri shcouncil.es/blog/shoulden-ingles
Bri shcouncil.es.(14demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.bri shcouncil.es/blog/begoing-to
Carranza,A.(3demayode2022). Crehana.com.Obtenidode h ps://www.crehana.com/co/blog/negocios/adje vos-de-personalidad/
Carranza,A.(3demayode2022). Ingenierogeek.com.Obtenidode h ps://www.ingenierogeek.com/2013/11/curso-ingles-medio-adje vos-compara vosuso-de-than-less-para-comparar.html
Curso-ingles-com.(9demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.cursoingles.com/prac car/ejercicios/impera ve-sentences
Cursosonlineyempleos.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://cursosonlineyempleos.com/ejercicios-de-compara vos-en-ingles-grama ca-yerrores-comunes-pdf/
Edworthy,T.(3demayode2022). Printerest.com.Obtenidode h ps://www.pinterest.com.mx/pin/174373816813022087/
English.lingolia.com.(9demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://english.lingolia.com/es/grama ca/verbos/impera vo/ejercicios Englishclub.com.(6deenerode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.englishclub.com/eslgames/grammar/adjec ve-order-1-1.htm
Englishlive.ef.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://englishlive.ef.com/eses/blog/grama ca-ingles/verbos-en-ingles-impera vo/
Englishspanishlink.com.(5deagostode2021).Obtenidode h ps://www.englishspanishlink.com/ejercicios-ingles/compara ves_4.htm

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.
Englishspanishlink.com.(5deagostode2021).Obtenidode

h ps://www.englishspanishlink.com/ejercicios-ingles/superla ve_1.htm
Englishspanishlink.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://www.englishspanishlink.com/ejercicios-ingles/past-simple-ques ons-regular.htm
Es.liveworksheets.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://es.liveworksheets.com/sp107006qz
Es.liveworksheets.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://es.liveworksheets.com/worksheets/en/English_as_a_Second_Language_(ESL)/M ust_or_mustn't/Must_or_mustn't_(classroom_rules)_lo2137pn
Es.liveworksheets.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://es.liveworksheets.com/worksheets/en/English_as_a_Second_Language_(ESL)/M ust_or_mustn't/Who_says_that$_-_must_or_mustn't_mv7319kb
Es.liveworksheets.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://es.liveworksheets.com/worksheets/en/English_as_a_Second_Language_(ESL)/M odal_verbs/Can_or_Can't_hk6230xe
Es.liveworksheets.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://es.liveworksheets.com/worksheets/en/English_as_a_Second_Language_(ESL)/Ha ve_to/Have_to_-_don't_have_to_yt33274sz
Eslprintables.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://www.eslprintables.com/vocabulary_worksheets/face_and_body/palm_reading_ predic ons/Palm_reading_3_pages__116347/ Estudiaringles.online.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://www.estudiaringles.online/ejercicios-adje vos-compara vos/ Gingerso ware.com.(6deenerode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://www.gingerso ware.com/content/grammar-rules/adjec ves/order-ofadjec ves/ Grammar.cl.(9demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.grammar.cl/english/must.htm
Idiomas.gcfglobal.org.(14demayode2022).Obtenidode
h ps://idiomas.gcfglobal.org/es/curso/ingles/b1/uso-de-may-y-might/

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Ingles.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.ingles.com/comparar/very/really#:~:text=%22Very%22%20es%20un%20ad verbio%20que,y%20%22really%22%20a%20con nuaci%C3%B3n.&text=He%20is%20very %20clever%20and,inteligente%20y%20muy%20guapo%20tambi%C3%A9n.
Ingles.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.ingles.com/guia/can-vs-may
Inglesclass4.blogspot.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h p://inglesclass4.blogspot.com/p/very-or-really.html
Inglesconcambridge.com.(5defebrerode2021).Obtenidode h ps://www.inglesconcambridge.com/adje vos-compara vos-superla vos-en-ingles
Inglesrapidoyfacil.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.aprenderinglesrapidoyfacil.com/2014/01/15/ejercicios-de-compara vosen-ingles-compara ves-exercises-in-english/
Mar nezCárdenas,J.M.,CanalesPérez,A.E.,Monjaraz,Z.,&Suarez,M.(2021). Inglés I. Sal llo: Ins tutodeEnseñanzaAbiertaUAdeC.
Murphy,R.(2012). English Grammar in Use (Fourthed.).(C.U.Press,Ed.)China:Cambridge UniversityPress.
Profesor-english.com.(14demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.profesoringles.com/cual-es-la-diferencia-entre-will-y-going-to/ Ringteacher.com.(4demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.ringteacher.com/materialesdidac cos/adje vos-ingles/adje vos-en-ingles/ Schneider,K.(3demayode2022). Printerest.com.Obtenidode h ps://www.pinterest.com.mx/pin/51369251989380359/ Shertonenglish.com.(3dejuliode2021).Obtenidode h p://www.shertonenglish.com/resources/es/pronuncia on/pronuncia on-ed.php
Superprof.es.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.superprof.es/apuntes/idiomas/ingles/grama cainglesa/adjec ves/exercises-compara ve-adjec ves.html

Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila.

Instituto de Enseñanza Abierta, Unidad Saltillo.

Superprof.es.(4demayode2022).Obtenidode h ps://www.superprof.es/apuntes/idiomas/ingles/grama ca-inglesa/verb-tense/simplepast-nega ve.html
Superteacherworksheets.com.(3dejuliode2021).Obtenidode h p://www.superteacherworksheets.com
Thats-cool-educa on.com.(5demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://www.thats-cooleduca on.com/orden-de-los-adje vos-en-ingles/
To Learn English.(3dejuliode2021).Obtenidodeh p://tolearnenglish.com
Whatsup.es.(6deenerode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://whatsup.es/blog/90-adje vospersonalidad-ingles-thats-great
Whatsup.es.(14demayode2022).Obtenidodeh ps://whatsup.es/blog/will-or-going-tocomo-saber-cualusar#:~:text=Will%20or%20going%20to%20se%20refieren%20a%20hechos%20futuros% 20pero,to%20do%20on%20your%20holidays%3F
