Improving Social Determinants of Health Screening: Examination of Patients with Limited English Proficiency Austin Fischer, 1Zucker
1 BS ,
Joseph Conigliaro, MD,
1, 2 MPH ,
Eun Ji Kim, MD, MS,
1, 2 Msc
School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, NY 2Northwell Health, Manhasset, NY
Background
Results
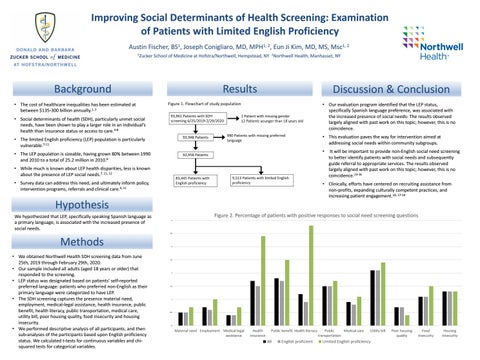
Discussion & Conclusion • Our evaluation program identified that the LEP status, specifically Spanish language preference, was associated with the increased presence of social needs- The results observed largely aligned with past work on this topic; however, this is no coincidence.
• The cost of healthcare inequalities has been estimated at between $135-300 billion annually.1, 2 • Social determinants of health (SDH), particularly unmet social needs, have been shown to play a larger role in an individual’s health than insurance status or access to care.3-8
• This evaluation paves the way for intervention aimed at addressing social needs within community subgroups.
• The limited English proficiency (LEP) population is particularly vulnerable.7-11
•
• The LEP population is sizeable, having grown 80% between 1990 and 2010 to a total of 25.2 million in 2010.6 • While much is known about LEP health disparities, less is known about the presence of LEP social needs.7, 11, 12 • Survey data can address this need, and ultimately inform policy, intervention programs, referrals and clinical care.4, 11
It will be important to provide non-English social need screening to better identify patients with social needs and subsequently guide referral to appropriate services. The results observed largely aligned with past work on this topic; however, this is no coincidence.13-16
• Clinically, efforts have centered on recruiting assistance from non-profits, expanding culturally competent practices, and increasing patient engagement.10, 17-19
Hypothesis We hypothesized that LEP, specifically speaking Spanish language as a primary language, is associated with the increased presence of social needs.
Figure 2. Percentage of patients with positive responses to social need screening questions 4
3.5
Methods • We obtained Northwell Health SDH screening data from June 25th, 2019 through February 29th, 2020. • Our sample included all adults (aged 18 years or older) that responded to the screening. • LEP status was designated based on patients’ self-reported preferred language: patients who preferred non-English as their primary language were categorized to have LEP. • The SDH screening captures the presence material need, employment, medical-legal assistance, health insurance, public benefit, health literacy, public transportation, medical care, utility bill, poor housing quality, food insecurity and housing insecurity. • We performed descriptive analysis of all participants, and then sub-analyses of the participants based upon English proficiency status. We calculated t-tests for continuous variables and chisquared tests for categorical variables.
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
Material need Employment Medical legal assistance
Health insurance
Public benefit Health literacy
All
English proficient
Public Medical care transportation
Utility bill
Limited English proficiency
Poor housing quality
Food insecurity
Housing insecurity