16 minute read
Lift mast – 7000
Main lift chain system
Damage
The chain should be replaced if damaged in any way.
Damaged discs
If a disc has broken on the chain, this can be due to overloading or corrosion.
The chain should be replaced.
Damaged bolts
It can be difficult to discover whether a bolt has broken. It can appear as bolt rotation and/or that the outer disc is loose.
The chain should be replaced.
Dirty chain
If a chain is very dirty it is first and foremost recommended that it is replaced. It can also be dismantled and cleaned as set out in the chapter “Cleaning”.
13.3.3 Cleaning
If a chain is very dirty it is recommended that it is replaced. Dirty chains should be cleaned before they are lubricated, e.g. by washing with solvent such as diesel or petrol. The chain should be blown dry using compressed air and lubricated directly after cleaning
NOTE!
Exercise care with degreasing agent as these can contain abrasives.
13.3.4 Lubrication
Mineral and synthetic oils can be used to relubricate Rexnord chains. NOTE!
Lubricant must not contain substances such as molybdenum disulphide, PTFE or the like.
A lift chain should be offloaded from the weight of the fork carriage (hanging free) when lubricated.
• Lubrication intervals:
-500 hours with normal operations
-100 hours when driving in rugged environments such as cold stores and corrosive environments.
The chains are sprayed with lubricant. Note the entire chain must be lubricated, even the fastening bolts. It is especially important that the part of the chain which runs over the chain sprocket is well lubricated. The lubricate must comply with the viscosity demands at respective temperatures as set out in the table below. The following lubricants are recommended:
Anticorit
* Equivalent products from another manufacturer may be used. NOTE!
Do not use a special rust protective agent to prevent rust on the lift chains. These agents impair the lubrication of the chains. Regular lubrication is the best method to prevent rust attack.
14- Peripherals – 8000
14.1 Battery charger (Inbuilt)
14.1.1 General
SMCI is a battery charger intended for valve-regulated or freely ventilated lead acid batteries. It is adapted for batteries from about 100 Ah up to 320 Ah.
The charger which uses advanced switch techniques is connected to a normal (grounded 230 V single phase) socket (B) and the built-in micro controller then controls charging following the pre-set charging curve. During charging the charging process is displayed with a status indicator on the standby housing (A).
The micro controller also controls charging with respect to charging time and temperature in the charger so that charging can be limited, e.g. if a fault occurs in some cell in the battery or when there is insufficient cooling of the charger.
SMCI 300 is delivered pre-set for 24 v and with software intended for charging valve-regulated or freely ventilated lead acid batteries.
The size and type of the battery are selected using the switch on the side of the fan(C) which is accessible via a slotted head screwdriver.
14.1.2 Charging
Connect the charger to the mains. When charging starts after a few seconds, the orange status indicator on the standby housing(A) lights up. Yhis indicator remains lit until the battery is fully charged and the indicator turns to green.
Charging time varies depending on the type of battery and the degree of discharge. Normally the charger is started after working hours and the battery is fully charged the next morning. A highly discharged freely ventilated battery of 320 Ah may need up to 14 hours re-charging time, a VR battery even longer.
Some time after charging (depending on, for example, type of battery) SMCI 300 switches to maitenance charging. The green indicator remains lit to show that the battery is fully cgarged.
When charging is completed, the mains plug is placed in the standby housing.
Peripherals – 8000
Battery charger (Inbuilt)
T-codeValid
14.1.3 Troubleshooting and service
First check whether the charger indicates an error. A red, blinking indicator means that the charger cannot detect that any battery is connected.Check the cables, pole terminals and other connections to the batteries. Measure battery voltage. If the charger still doesn´t work, send it to your supplier for repair.
14.1.4 Technical data
Size 250x115x67 mm
Weight 1,6 kg
Ambient temperature -25°C till +40°C
Mains voltage 90-255 V AC 45-400 Hz
(Reduced charging current for mains voltage below 200 V
Rated voltage 24 V DC
Rated current 30 A
Max output 750 W
Efficiency > 86%
Battery type Freely ventilated lead batteries (with water refilling). Valve regulated (VR) lead batteries.
Protection IP 20
General
Temperature regulated cooling fan, protected against faulty polarisation
14.1.5 Charging settings
15- TruckCom
User Manual for trucks using the “PowerDrive” platform. This Manual is valid for version 3.5 of TruckCom p/n 182147-008.
15.1 General
TruckCom is a communication program which communicates with trucks equipped with CAN (Controller Area Network) communication. It enables the following tasks to be performed:
•downloading truck control software.
•viewing and adjusting operator / truck parameters and hour meters. Additionally, the truck’s parameter set (including hour meter values) can be saved to file and reloaded later.
•viewing diagnostic data for various digital inputs / outputs and analogue data including voltages, currents and certain temperatures.
The program is a Windows program running under Microsoft® Windows® 95/98,Microsoft® Windows® XP/2000 and Microsoft® Windows® NT.
15.2 Connection
A CAN interface of the CPC-PP type is needed to connect it to the truck, with attendant cable. Connect the interface via the printer port on a PC. Connect the cable between the interface and the truck's CAN terminal.
The CAN interface is supplied with power from the truck electronics and is protected from any high voltages in the truck if a fault should occur.
15.3 Layout
15.3.1 Main program screen
The Main window opens when the program is started. This shows the menu bar, tool buttons, workspace, log window and status window.
15.3.2 Nodes
Devices which are connected to and communicate via the CAN interface are called nodes. The nodes detected on the bus are shown in the node window. The current node status and input component/information is shown with different icons.
15.3.3 Icons
Node OK is shown when contact is made with a node and no errors have been reported.
Node not connected is shown when there is no contact with a node in the network.
Node not OK is shown when an error has been reported by a node. Click on node to obtain more information.
Program version is shown when information is available on which software is installed. Click to obtain more information.
Information is shown when a node has information on, for example, error codes.
Truck report
GB“15.7Truck report function” on page 7
Parameters is shown when a node has information on a parameter.
Diagnostics Exit
15.3.4 Tool buttons and menu bar
The tool button bar allows direct access to the program’s most common functions. The menu bar allows access to all the program functions. Explanations of each menu bar item are given in the relevant section.
15.3.5 Information window
The right section of the main window contains a status window where different messages are shown.To see previous messages, use the scroll arrows in the right margin.
15.3.6 Status bar
There is a status bar at the bottom of the main window, which shows variable status when the program is run.
The following are shown from the left: Help text "pop-up" via the mouse cursor, connected/not connected to network, truck type connected, initiation result of CAN interface and the present time.
15.4 Connection function
To connect the PC the network, select the Scan units function. This can be done with the menu <Nodes | Scan units> or with the tool button [Scan nodes]
This should also be done when the truck is supplied with voltage and in normal drive mode.The program will now run a check and installation of the CAN interface. A diagnosis will also be carried out to check which units are connected in the system. The result of this diagnosis is shown in the Node window.
15.5 Disconnection function
Select the Disconnect function to disconnect from the network. This can be done with the menu <Nodes | Set PC off-Line> or with the tool button [Set PC off-Line].
The CAN interface is then reset and the CAN cable can be disconnected if so required. This enables connection to another truck without having to close the program.
15.6 Downloading program function
To download a new program to one of the nodes, select the Download software function. This can be done with the menu <Tools | Download software... > or with the tool button [Download]

15.6.1 Normal downloading (truck with key)
Select Open.. to open the file to be downloaded into a node. The file name, file type and version number are shown in the window for file information. If it is file for a controller, indicate which type of controller is to receive the file. Start downloading by selecting Start... and by restarting the truck by turning the key off and on twice. Restart must be made within 20 seconds from when the Start button has been activated.
Close the download window when the download is ready, and then disconnect the PC from the network. A new connection can now be made to verify the new program.
15.6.2 Normal downloading (truck with keypad)
Select Open to open the file to be downloaded into a node. The file name, file type and version number are shown in the file information dialogue box. If it is file for a controller, indicate which type of controller is to receive the file. Start downloading by depressing and then releasing the red key on the keypad.
The truck must be restarted within 20 seconds from when the Start key has been activated.
When downloading has been completed, close the download dialogue box and then disconnect the PC from the network. It is now possible to reconnect to verify the new application.
15.6.3 Emergency downloading (truck with keypad)
•Disconnect the battery connector.
•Select OK in the dialogue box.
•Keep the red key on the keypad depressed while reconnecting the battery connector.
•Release the red key to commence downloading.
15.6.4 Emergency downloading (truck with keypad)
E141 will be shown in the truck’s display when starting, if for any reason there is no program in the electronics card (interrupted downloading). Communication with the truck via the PC will then be minimised. Use “E141” to download the program in the card.
On some trucks, a counter, which continuously counts up, is displayed. NOTE!
Once programmed, the logic cards in some trucks can only be upgraded with the same basic firmware. In other words, it is not possible to replace the basic firmware (other machine type).
15.6.5 Downloading in old versions of logic card
To download to older versions of electronic cards which do not support restart with key, the button Old card... should be used instead of Start. Downloading is carried out in the same way, except that restart is done by using the battery lug instead of the key.
15.7 Truck report function
It is possible to generate a report to a file or disk with the truck’s configuration and status. Select menu <Tools | Generate truck report...> or with the tool button Truck report. Save the report in Report.file.

Example of information generated in the truck report:
[GENERAL]
REPORT DATE-TIME=2004-01-19 11:11:58
CPC-PP SERIAL No=8002041
MACHINE NUMBER=555555
CUSTOMER=CUSTOMER 1
TECHNICIAN=NONAME
[CAN NODES]
MAIN CARD=0
CURTIS DRIVE CONTROLLER=16
[MAIN CARD CONFIGURATION]
SOFTWARE=181179-001
HARDWARE=167833-004
SERIAL NO=53676
[DRIVE CONTROLLER CONFIGURATION]
SOFTWARE=5
DRIVE CURRENT LIMIT (A)=300
FIELD MAXIMUM (A)=34
SERIAL NO=52857
MFG Date:=26/05/03
HOUR METERS]
A IGNITION TIME=81
B TOTAL MOVEMENT=7
C DRIVE MOTOR TIME=7
D PUMP MOTOR TIME=0
S SERVICE TIME=7
The contents of certain rows can vary according to truck type.
15.8 Parameters function
To change the truck parameters, select the Parameter function. This can be done with the menu <Tools | Change parameters > or with the tool button Parameters.
NOTE!
The truck must in Normal mode (i.e. not Parameter mode) when connecting TruckCom. Otherwise TruckCom will report “Unable to determine truck brand”
The parameter numbers follow the description in the respective truck Service Manuals, section 5000.
The parameter window shows the information and the current settings for all parameters. The parameters are divided into 4 tabs.
•[Driver] - Driver; driver parameters and PIN code storing
•[Truck] - Truck; service parameters
•[Time] - Time; time-related service parameters
•[Option parameters] - Option parameters. (no. 15 to 19)
WARNING!
Do not attempt to make any adjustments to the option parameters unless you have sufficient knowledge of the truck’s options/ modified functions. Specially modified trucks may require that you have access to special service information.
Improper adjustment of the option service parameters may result in a malfunction.
15.9 Diagnostics function
To access diagnostics, select the Diagnostic function. This can be done with the menu <Tools | Diagnostic...> or with the tool button Diagnostic. NOTE!
If the value “---” is shown in a field, or a “read status LED” is red, the communication has been interrupted for some reason and error data cannot be shown.
NOTE!
The tab information displayed in the diagnostics mode depends on the type of truck connected.
15.9.1 Representation of signal colours
The screen dumps shown in the following section have been modified to improve legibility in black & white print.
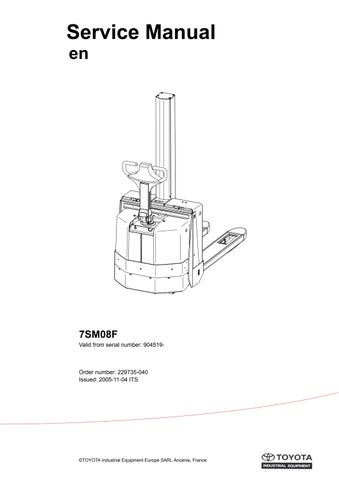
15.9.2 “Tiller arm” tab
Clicking on the tiller arm tab will display a dialogue showing the following:
• Speed lever -The status of the speed control and travel direction selector. The status of each individual hall element is displayed.
• Buttons -The status of the control buttons is displayed. “Sxx” refers to the switch designations as given in the circuit diagram.
• Option - Status of option buttons
• Battery - The measured battery voltage
•R14 - Shows the measured signal voltage from the lift/lower control
• R15 - Not used at present
15.9.3 “Drive Controller” tab (transistor regulator driving)
Clicking on the Drive Controller tab will display a dialogue showing the following:
•Status of digital inputs and outputs of the transistor regulator. pin refers to the motor controller pin designations as given in the circuit diagram.
• Field PWM - The effective power output supplied to the field circuit as a percentage.
• Armature PWM - The effective power output supplied to the armature circuit as a percentage
• Field current - The current flowing in the field circuit in Amperes.
• Armature current - The current flowing in the Armature circuit in Amperes
• Raw throttle data - The received speed control signal as a percentage.

• Temperature - The temperature of the output stage of the transistor controller in degrees Celsius
• Inp pin 10 - The input voltage from the mode/pressure sensor. “digital O” indicates the digital status of the input.
• Inp pin 11 -The input voltage from the man-on platform sensor. “digital O” indicates the digital status of the input.
15.9.4 “Pump controller” tab (transistor regulator pump)
If the truck is equipped with a lift/lower transistor regulator, the Pump controller tab displays the following:

•Status of digital inputs and outputs of the transistor regulator. pin refers to the motor controller pin designations as given in the circuit diagram.
•Field PWM, Armature PWM, Field current, Armature current, Temperature - See explanation in 15.9.3
• Raw throttle data - The received lift/lower signal as a percentage.
• Out pin9 - The output signal to the proportional lowering valve as a percentage.
• Inp pin 10 - The input voltage from the pressure sensor. “digital O” indicates the digital status of the input.
• Inp pin 11 - The input voltage from the pressure sensor. “digital O” indicates the digital status of the input.
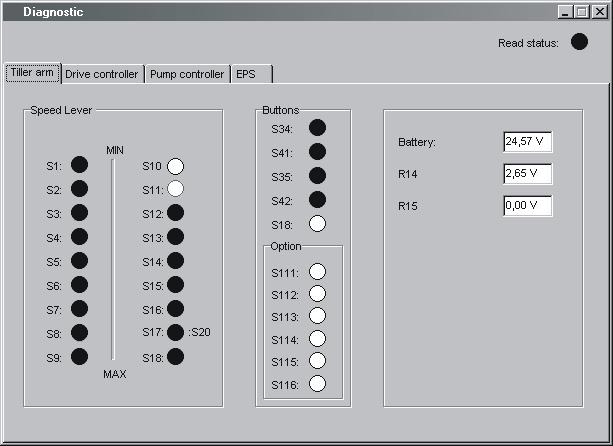
15.9.5 “EPS” (steering servo tab)
Clicking on the “EPS” tab will display a dialogue showing the following:
“Status”
•“Operational” - Indicates the status of the servo’s control system
•“EPS enabled” - Indicates the status of the servo’s power stage output.
•“Reference switch reached” - indicates status of drive wheel in centre reference switch.
•“Reference position found” - indicates whether a successful steering in centre has been performed.
•“EPS in power save mode” - Shows whether the steering servo is in the standby mode (following a certain amount of inactivity).
“Actual values” (Measured values)
•“Temperature EPS” - The temperature of the steering servo output stage in degrees Celsius.
•“DC bus voltage” - Supply voltage to steering servo
•“Wheel position” - Shows the estimated steering angle of the drive wheel.
•“Voltage analog input 1, pin5”- The measured DC input signal (0) from the steering potentiometer.
•“Voltage analog input 2, pin13”- The measured DC input signal (1) from the steering potentiometer.
•“Current” - The measured current supplied to the steer servo motor in Ampere
•“Actual velocity” -The measured rotational speed of the steer servo motor shaft in r.p.m.
15.9.6 SEU tab (Extra I/O module)
When the truck is equiped with a Spider Extension Unit (former Extra I/ O module) the SEU tab shows following:
•“INP X” - Shows the logical status for the digital inputs.
•“OUT X” - Shows the logical status for the digital outputs.
•“Analog input X” - Shows the voltage level on the analog inputs. See chapter 5000 for more information about the SEU and how the inputs and outputs are connected.
15.10 Other menu functions
15.10.1 Save to file
The truck parameters can be saved in the PC for downloading at a later date.Select <File | Save to file | Parameters>. All parameters in the nodes which are connected to the bus will be scanned in and saved in a file.If only the hour meters are needed, select <File | Save to file | Hour meters>.

15.10.2 Download from file
A set of parameters can be downloaded from the PC to the truck. Select <File | Load from file | Parameters >. The parameters in the file will be copied to the nodes connected to the bus. If only the hour meter settings are needed, select <File | Load from file | Hour meters >.
15.10.3 Reset CAN adapter
If problems should occur when resetting the CAN adapter connected to the PC, this can normally be done manually by making sure that the adapter is supplied with voltage and then selecting <Nodes | Reset CPC-PP>.
15.10.4 Delete error code log
To delete the truck’s error code log, start the truck in parameter mode and then select <Tools | Erase error log>.
15.10.5 Reset hour meter
To reset the truck’s hour meter, start the truck in drive mode and then select <Tools | Reset hour meters >.
15.10.6 Read error code log
To show the truck’s error code log, select <Tools | Read error log >.
15.10.7 Adjust date and time
To quickly adjust the truck’s data and time, select < Tools | Adjust date & time >. The time given in the PC will now be downloaded into the truck.
NOTE! This does not apply to trucks without a real-time clock.
15.10.8 Adjusting the hour meter on older cards
To adjust the hour meter on trucks with older cards, select <Tools | Adjust Hour meters>. The time given in the PC will now be downloaded into the truck.
15.10.9 Help About the TruckCom application
To see program information, select <Help | About TruckCom...> or use the tool button [Information].
15.10.10
Exit
To exit the program, select <File | Exit > or use the tool button [Exit].
15.11 Specifications
Table 35: CAN interface specification
15.12 Installation
NOTE!
The program must be installed from the hard disk.
NOTE!
The software application in the computer can be damaged, which is why the PC installation should be performed by someone with the required knowledge. TOYOTA does not accept any responsibility for any errors that occur during the installation.
NOTE!
All references to PC operating system actions, menus and commands are based on the English language version of Windows.
15.12.1 Installation on a PC with Windows 95/ 98
If a previous version of the TruckCom application has been installed on the PC, it will be necessary to edit the System.ini file.
Start the Msconfig.exe application by selecting the Start button, selecting Run and then typing msconfig.
•Click on System.ini and open the folder (386Enh).
•Unmark the option at Device=C:\Windows\Cpcppvd.vxd.
•Save the change and close the application.
Now continue with installationThe software application is supplied on a CD or via a network. Start installation by running X:\SETUP.EXE, where X:\ is the drive on which the installation application can be found.Then follow the on-screen instructions.
15.12.2 Installation on a PC with Windows XP/ 2000
To make the application work, it is necessary to enter a value in the Windows Registry and then make a few alterations in the Windows® Control panel.
Due to the built-in Windows security, this must be done manually.
The instructions below provide step-by-step guidance to enable these changes and make the interface operate under Windows XP and Windows 2000.The changes can be made either before or after TruckCom is installed.
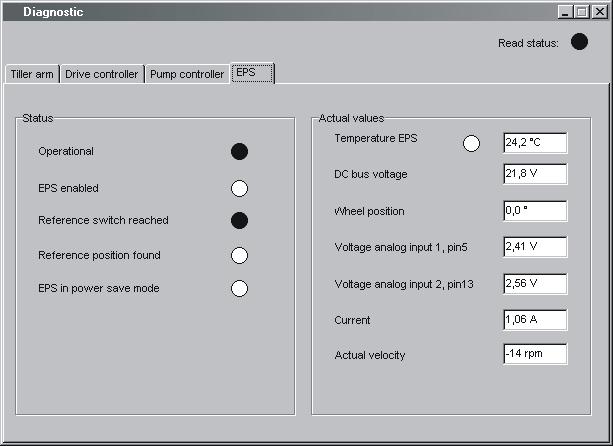
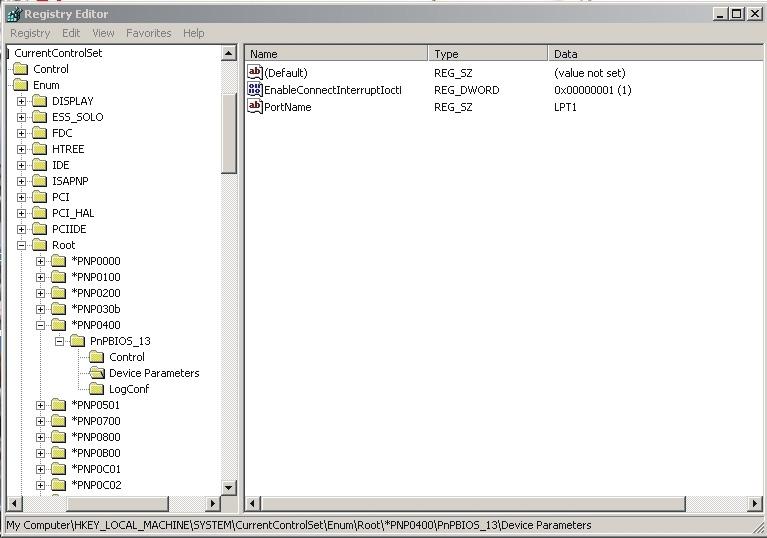
•Open the Registry Editor. To do this, select the Start button, then Run, type regedit and hit Enter.
•Mark the Enum folder which can be found under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet inside the Registry Editor.
•Select the Edit option, then Find and type PortName to search for the correct folder.

NOTE! The location of the folder differs between different computers (some may be \Enum\Root\.., while others could be \Enum\ACPI\ etc.). Thus be sure to search for the correct folder.
When the folder is found, check that LPTx (x=1, 2, 3, 4) is displayed in the PortName data field and that the folder name is Device Parameters.
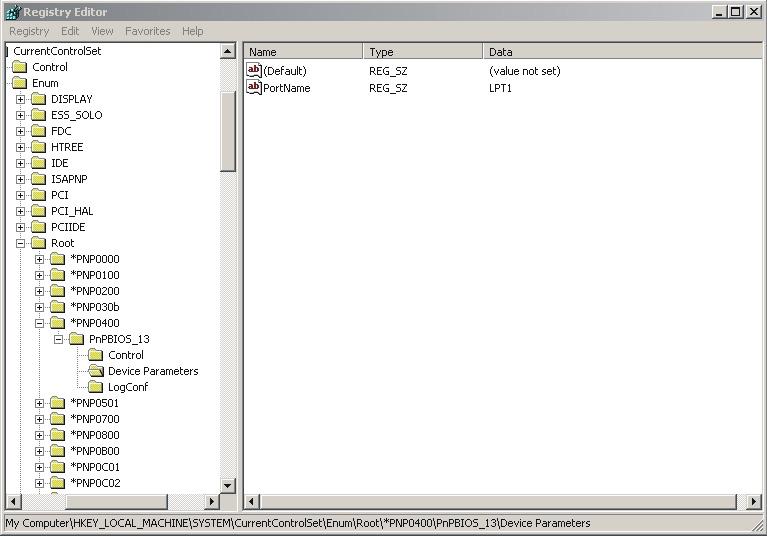
•Right-click with the mouse in the right box to enter a new value of the DWORD type and with the name EnableConnectInterruptIoctl.
•Change the value in data field 1 by right-clicking on the name and selecting Modify.
The Device Parameters folder should look like the one in the picture. The Registry change is now complete. Close the Registry Editor.

Changes in Windows Control Panel
•Select the Start button.
•Choose Settings, then Control Panel and double-click on System.
•Select Hardware.
•Click on Device Manager and open Ports (Com & LPT).

•Double-click on the LPT port to be changed, and select the Port Settings tab.
•Check the "Use any Interrupt assigned to the port" option and click on OK.

The software application is supplied on a CD or via a network. Start installation by running X:\SETUP.EXE, where X:\ is the drive on which the installation application can be found. Then follow the on-screen instructions.

15.12.3 Installation on a PC with Windows NT
The software application is supplied on a CD or via a network. Start installation by running X:\SETUP.EXE, where X:\ is the drive on which the installation application can be found. Then follow the on-screen instructions.
15.12.4 In case of communication problems with CAN
Make sure the computer settings for the printer port in the BIOS Setup are as follows:
Port address:0378
IRQ:7
Mode:Output only
For detailed information on how to change the Setup settings, refer to the User's Guide supplied with the computer.
15.12.5 To uninstall
To uninstall TruckCom under Windows:
•Select the Start button, Settings, Control Panel, Add/Remove Programs.
•Then select the TruckCom Program and click Change/Remove.
16- Destruction instructions
16.1 General
These instructions have been drawn up as part of the truck manufacturer’s environmental management program. An important motive is, by taking nature into consideration, to economise with resources. In other words, you should try to recycle all material as far as possible. This is to minimise the discharge of environmentally-hazardous substances.
The dismantling instructions are divided into different C-codes (parts and functions on the truck.) These C-codes are:
•0000 Chassis
•1000 Motors
•2000 Transmission/drive transmission
•3000 Brakes/belt/wheel system
•4000 Steering system
•5000 Electrical system
•6000 Hydraulics/pneumatics
•7000 Working function - lift mast
•8000 Auxiliary/installation equipment
•9000 Accessories/extra equipment
The instructions do not tell you the type of material the parts are made of, but refer you to different material containers where the parts should be collected. Some plastics are marked, which means some instructions refer to the marking to determine the collection container to use.
16.2 Procedure
When sorting a component part you must know what plastic parts, liquids, environmentally-hazardous substances and metals it incorporates.