
5 minute read
Maserati GranCabrio
Other electronic equipment
Electrical Systems and Devices
In addition to the equipment already mentioned, the on-board equipment may be supplemented with other electronic devices available on request, conceived to make driving safer and more comfortable.
• Interior (standard) and exterior (optional) electro-chromatic rear-view mirrors: these darken progressively as light intensity increases thereby preventing glare.
• Front parking sensors, available on request in addition to the standard rear parking sensors
• Garage remote control (home link): this allows up to three frequencies of three remote controls to be transferred directly to the car’s onboard system located on the driver’s sun visor.
• Tyre pressure monitoring sensors (TPMS): The Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) uses dedicated sensors to continually check tyre pressure while driving The system displays the pressure of each tyre on the instrument cluster, and warns the driver if the pressure falls below the ideal level or drops rapidly in case of a puncture This system is standard for USA and Japan specification vehicles
9. Body
Body structure
High-strength steel bearing monocoque with box-section panels and structure constructed in sheet galvanized, two-door cabriolet, four seats, longitudinal centre-front engine (between the two axles), rear wheel drive.
Subframes
Constructed in high-strength steel boxed sections; it integrates a tubular structure in the rear part to support suspensions and differential; front serves to support the suspensions and engine.
The front subframe is a modified unit from the Quattroporte Sport GT S to increase rigidity, while the rear one is a complete carry-over.
Safety
The passive safety performance of the monocoque is conforming to worldwide regulations, integration of various design technologies for weight /performance optimization: steel structural part, aluminum bonnet and bumper front reinforcement cross member, boot lid in thermosetting composite material

The GranCabrio equals entirely the passive safety performance of the coupé GranTurismo model, both for what concerns the protection of occupants as for pedestrian safety
Derived from the Quattroporte structure, with reduced wheelbase and rear overhang, designed to satisfy the most stringent American crash standards (FMVSS208, Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard), front structure compliant with ACEA1 “pedestrian impact” standards
Used materials
The new bearing frame design boasts a construction with a mix of materials and technologies for weight optimization: the structural part is made of steel, the bonnet and bumper front reinforcement member of aluminium, while the boot lid is constructed in thermosetting plastic material (SMC - Sheet Moulding Compound technology)
The boot lid consists of a single skin which incorporates the aerodynamic lip; SMC technology not only keeps the component’s weight down and is more resistant to minor damage and corrosion, it also allows for the application of an “under the skin” aerial which would not have been possible if a metal boot lid was used
Rigidity
The body of the GranCabrio has been designed to ensure, despite the lack of a hard roof, maximum performance in terms of structural rigidity This has greatly improved its handling, safety and comfort in all conditions – especially bearing in mind its powerful and effective mechanical systems
The new frame was developed at the expense of thousands of hours of computer time and at least as much time again spent on testing The rigidity of the new frame has set a new standard in the industry: the naked frame boasts a dynamic torsional frequency of 27 2 Hz
Given the wheelbase (2942 mm: the longest in its class) and the very slight increase in weight over the GranTurismo S (+100kg for the complete car), the frame and car rigidity values make the Maserati GranCabrio the new standard
Torsional rigidity: 75000 daN/mm
Flexural rigidity: 659 daN/mm
In order to obtain the best handling and performance, the base of the - already rigidframe has been extensively modified using light alloy components. The biggest innovations in structural design have concern the following components:
• Reinforced side sills
• Reinforced floor structure
• Reinforced door frame and A-pillars
• Reinforced transverse cross members
• Welded steel luggage compartment floor
• Reinforced transverse bar between front suspension struts
• Aluminium sub-floor structural reinforcement plate
• bolted structural reinforcement bars in the engine bay and underneath the vehicle





Soft top
The stylistic impact of the Maserati GranCabrio, both open and closed, would not have been possible if a foldaway hard top had been used, due to the many restrictions this choice would have imposed on the car’s engineers and designers.

The Maserati GranCabrio’s top employs state of the art technology in terms of materials, mechanism, cycle time and folding method.
The soft top solution offers the following advantages:
• Lightweight construction (only 65 Kg in total) which results in a lower centre of gravity
• Excellent thermal and acoustic isolation qualities of the multi-layer capote improves passenger comfort.
• Compact dimensions when folded away, having a minimal impact on the boot size.
• Stylistic advantages: both in open and in closed position the soft top allows to maintain the purity and elegance of the original design
• Various colours available for the top fabric: in combination with a wide range of body colours, offers this wide personalisation options to the costumers
The soft top can be opened and closed fully automatically in only 28 seconds as long as the driving speed does not exceed 30 km/h
The soft top is operated by a hydraulic-mechanical system and controlled by a central roof ECU (NCP).
In open condition, the soft top folds away completely under the tonneau cover.
Roof structure
The top’s frame is composed of 5 steel and aluminium spokes which support the 1,820mm x 1,480mm (approximate figures) of the fabric. The top has an integral tempered thermal glass rear window which makes the car just as drivable in all seasons.
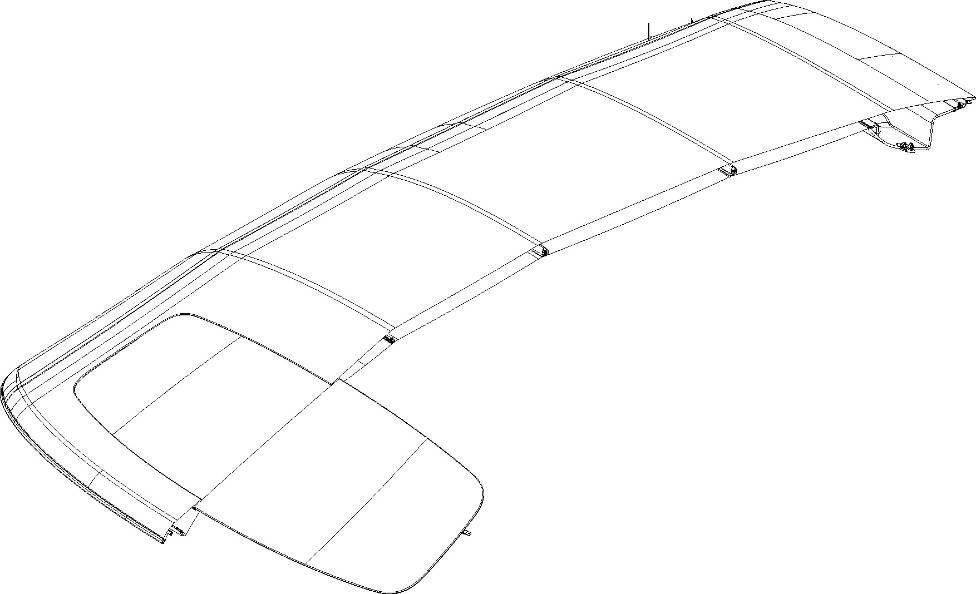
The style of the three-layer soft top has been optimised for aerodynamic and acoustic performance, just as the insulation materials and construction offer the best comfort when driving that current technologies can provide
The top has been subjected to extended rigorous testing in the most inhospitable and inaccessible corners of the world and in all weathers to ensure a long service life (e.g.: New Zealand for testing at -20°C, Sicily for 40°C, Sweden for -30 °C).
Its insulating central layer is designed to ensure unbeatable weather proofing, as well as acoustic insulation when the car is closed. This makes the GranCabrio suited for all year round use.

Roof colour options:
The canopy is composed of a triple-ply fabric, available in 6 colours:
• Black (std)
• Blue
• Java
• Burgundy
• Chocolate
• Titanium grey
The six colours available for the top, combined with the large range of exterior bodywork colours, give a total choice of 84 different colour combinations
Inner roof lining:
The inner roof lining highlights the enormous attention paid to the design of this part of the car: it has a clean profile without any of the disturbing components typical of softtops






The inner lining uses technical fabric as standard. On request can be opted for Eliade fabric which transmits warmth and exclusivity.
Inner lining choices:
• Black technical fabric (std )
• Beige Eliade fabric (opt )
• Beluga grey Eliade fabric (opt.)
Roof operation
Roof opening cycle:
Pull the switch A backwards and keep in position during the complete opening cycle
• Lowering of the four side windows
• Unlocking of the front roof latch on the windscreen frame
• Lifting of the rear part of the roof
• Opening of the tonneau cover
• Folding away of the roof in the rear storage area
• Closing of the tonneau cover
The opening cycle will interrupt in case the switch is released The different steps are illustrated on the info display of the instrument cluster:
Roof closing cycle:
Push the switch A forwards and keep in position during the complete closing cycle
• Lowering of the four side windows
• Opening of the tonneau cover
• Unfolding of the roof
• Lifting of the rear part of the roof
• Closing of the tonneau cover
• Lowering of the rear part of the roof
• Locking of the front roof latch to the windscreen frame
The closing cycle will interrupt in case the switch is released. The different steps are illustrated on the info display of the instrument cluster:








