2 minute read
THE MAIN CHANGES
Introduction of Rotary Pump:
•The earlier form of in-line pump used to generate 600 bar of injection pressure which was not sufficient enough to inject the fuel in enhance rate of atomization
•With the introduction of rotary fuel injection pump the pump pressure is increased upto 800 bar resulting into optimum atomization of fuel with enhanced pressure along with constant rate of fuel delivery
The Main Changes
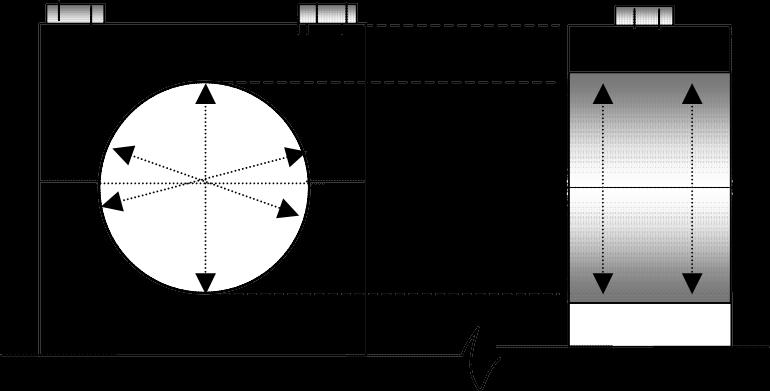
Changing in Bumping Clearance( In case of R1040/1080 Only):
Bumping clearance
•The bumping clearance is changed from 0.9 mm-1.1 mm range to 0.9 mm-1.05 mm range
•This is necessitated in order to optimum heat generation during compression resulting into better combustion
•Two numbers of gaskets are used as per the desired gasket.
•The part numbers of the gaskets are: (i) 4H.007.24.0 & (ii) 4H.007.11.0
•Note: Whenever replacing the gasket please ensure to replace as per the old thickness
The Main Changes
Injector is changed along with its’ spray orifice structure:
“P” Type Injector with “K” Factor
•The earlier form of Injector was “S”(Sack) type which used to cause fuel dribbling after injection
•This would have been major reason when engine will not satisfy the emission norms
•To avoid that, “P” type of injectors are used where the sack is eliminated
•This form of injector is used along with “K” factor
•“K” factor is the form of orifice which enhances the atomization of fuel into fine mist
THE MAIN CONCERN OF BS-III ENGINES
Towards The Cause Of Nitrogen Oxide Reduction
To reduce the Nox content of emitted exhaust gas the EGR(exhaust gas recirculation ) technology is used
THE MAIN CONCERN OF BS-III ENGINES
EGR(Exhaust Gas Re-Circulation) Feature:
•Lower oxides of Nitrogen (NOX ) emission caused by high combustion temperature
•EGR decreases the combustion temperatures
•Feeds small amount of exhaust back to combustion chambers
•There are two types of EGR i.e.- iEGR(Internal Exhaust Gas recirculation) & eEGR(External Exhaust gas re-circulation)
EGR REDUCES THE EMISSION
•The EGR system reduces the NOX production by circulating a small amounts of exhaust gases into the intake manifold
•The incoming exhaust gases into the combustion chamber mixes with the incoming air
•As the exhaust gas mixes with the air, The peak combustion temperature is reduced resulting into Overall reduction of NOX.
THE MAIN CONCERN OF BS-III ENGINES
iEGR-
•Internal circulation of hot exhaust gases
•Simple EGR technology
•Zero components
•Higher reliability
•The camshaft is modified to provide a secondary lift to Exhaust valve tappet for entering specific amount of exhaust gas inside combustion chamber
Benefits of EGR
•Lowers Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emissions caused by high combustion temps
•EGR decreases combustion temperatures
•Feeds small amounts of exhaust back to the combustion chamber
•This dilutes the air/fuel mixture, combustion temperatures are reduced
•Valve is open during engine cruise periods
The Main Changes
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Exhaust valve cam lobe is modified for effecting iEGR
•Once the CO, PM & HC are brought to the BSIII level, the combustion chamber temperature is increased unexpectedly
•The excessive combustion chamber temperature has caused the inert nitrogen gas to form more Nox with the presence of Oxygen (O2 )
•In order to restrict specific amount of oxygen(O2), the exhaust gas is re-circulated in the range of 10 % to 12% in case of R1040/1080 series & 17% to 20% in case of HA series of engines
•To achieve this re-circulation, in R1040/1080 1.7 mm secondary lift is given & in HA series 1.5 mm secondary lift is specified