1 minute read
Camshafts
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL LINKAGE
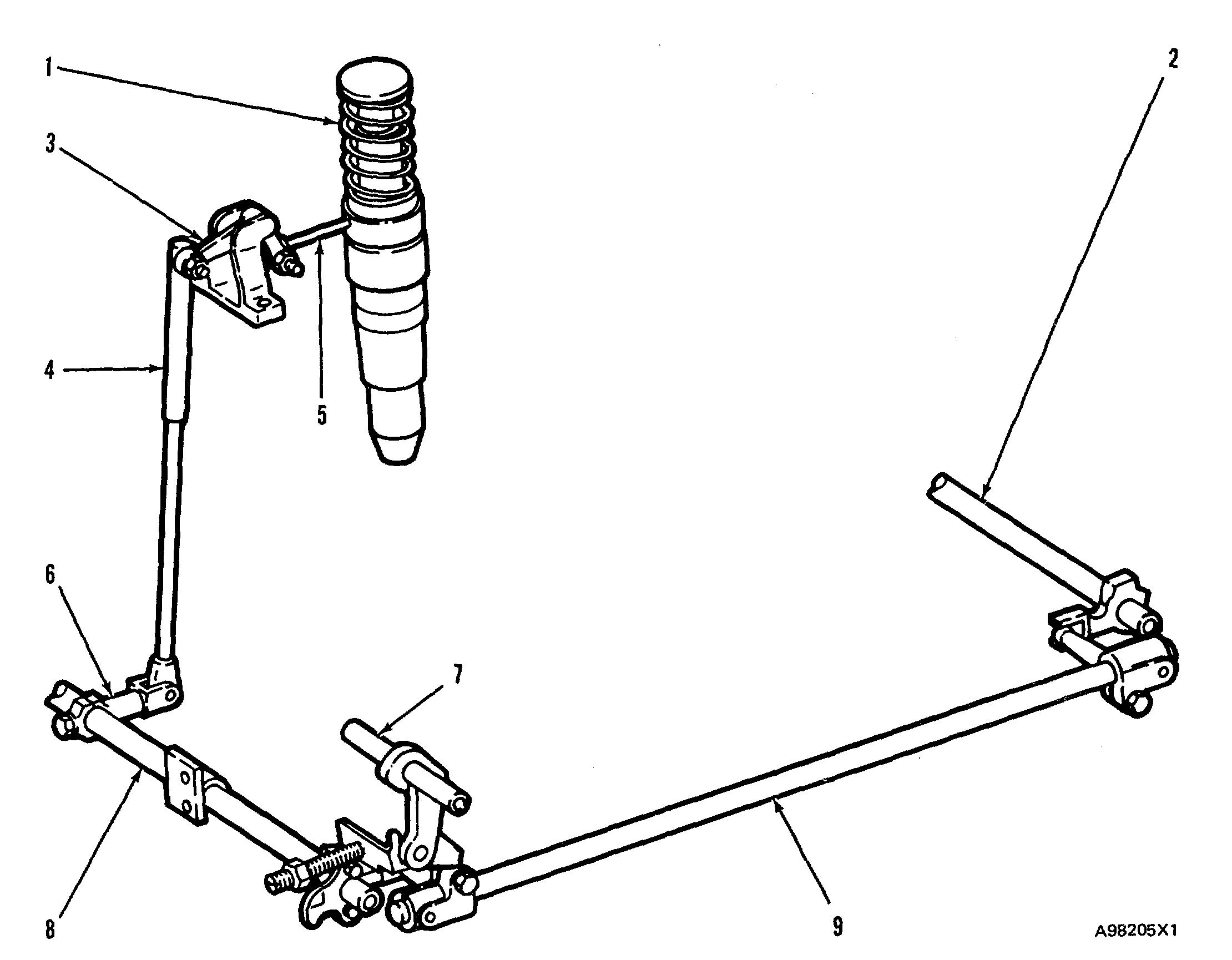
FUEL INJECTOR CONTROL LINKAGE 1. Injector. 2. Control shaft (left side). 3. Bellcrank. 4. Control rod. 5. Rack. 6. Lever. 7. Governor shaft. 8. Control shaft (right side}. 9. Cross shaft.
Advertisement
A fuel injector ( 1 ) is located in each cylinder head. The position of rack (5) controls the amount of fuel injected into-the cylinder. Pull the rack out of the injector for more fuel, push it in for less fuel.
Rack position is changed by bellcrank (3). The bellcrank is moved by control rod (4). The control rods have an adjustment screw on the top. The adjustment screw is used to synchronize the injectors. The control rods are spring loaded. If the rack of one injector sticks (will not move), it will still be possible for the governor to control the other racks so the engine can be shutdown. Each control rod on the right side of the engine is connected by a lever (6) to control shaft (8). When the rotation of governor shaft (7) is clockwise, as seen from in front of the engine, the action of the governor linkage moves control shaft (8) counterclockwise. That is, in the fuel "ON" direction.
Right control shaft (8) and left control shaft (2) are connected by cross shaft (9). The linkage between the injectors on the left side of the engine and control shaft (2) is similar to the linkage on the right side.
Should the linkage become disconnected from the governor, the weight of the control linkage will move the fuel injector racks to the fuel "SHUTOFF" position, and the engine will stop.





