NATURAL SCIENCE

License c 12 mont DiGitAL PRoject GLo BAL tHInKeRs 4 PRIMARY sample
1
SDG
LIVING ORGANISMS
• What is a living organism?
• Cells
• How we classify living organisms
• Plants
• The nutrition function in plants
• The reproduction function in plants
ANIMALS AND HUMAN BEINGS
• Animal characteristics and types
• The nutrition function in animals
• The interaction function in animals
• The reproduction function in animals
• Human beings and the vital functions
3
RockS AN d MINERA l S
• The layers of the Earth
• What is a rock?
• What do rocks look like?
• The properties of minerals
• Changes in landscapes 52
ECOSYSTEMS 4
PAGE 68
• Rocks in landscapes
Responsible production and consumption
• Adaptations
• Food chains and webs
• Balance in ecosystems
• Types of ecosystems
• How ecosystems help us
• Changing ecosystems
• Consequences of misusing ecosystems
• Using ecosystems sustainably




Sustainable cities and communities

TERM REVIEW
• Matter is all around us
PAGE 94 112
PAGE 90 132
MATTER AND ENERGY
6
• Matter changes
• Energy
• Heat and its effects 5
• The movement and deformation of objects
• Machines in our lives
Responsible consumption and production
• Design a machine
• Program a video game Industry, innovation and infrastructure PAGE
• Physical and emotional well-being 28 Life on land PAGE TERM REVIEW 48 PAGE

INDEX
TERM REVIEW
PAGE
• The interaction function in plants 8 Life on land PAGE
2 PAGE
• Habitats and ecosystems
Fo RCES AND MA c HINES
• Types of force
• How we classify matter
CONTENTS
THE WORLD AND... YOU! • LEARNING SITUATION SPECIFIC COMPETENCES - EVALUATION CRITERIA
In The World and... you! pupils research plants and trees in their area, creating a fact file to present to the class.
In The World and... you! pupils look at how some animal adaptations have inspired innovation in technology and science.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT
In The World and... you! pupils investigate how minerals are used in society and reflect on how we can use these natural resources responsibly.
In The World and... you! pupils create an educational piece of artwork to make people understand the importance of protecting marine environments.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT
In The World and... you! pupils conduct an experiment to see the water cycle in action and make an educational poster about using water responsibly.
In The World and... you! pupils are given an engineering challenge and asked to test different bridge designs to see which is the strongest.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT GLOBAL RESOURCES
2.3; 2.5; 5.1; 5.2
1.1; 2.1; 2.2; 5.1; 5.2
1.1; 5.1; 5.2; 5.3; 6.1; 6.2; 6.3
3.1; 3.2; 5.1; 5.2; 5.3; 6.1; 6.2
2.1; 2.3; 2.4; 2.5; 3.1; 3.2; 6.3
2.1; 2.3; 2.4; 2.5; 5.1; 5.2; 5.3; 6.1; 6.2
LIVING ORGANISMS

Wow! There are lots of plants here!
Yes, and they are all very different.
How can we classify them to understand them better?

eight 15 8 1
Hi! My name is Laura and this is my dog, Sally. She is so cute! She jumps on my bed every morning to wake me up. I don’t need an alarm clock!

Then, we have breakfast together. She is very greedy and tries to steal my toast! But I don’t give her any of my breakfast. She eats special dog food because not all human food is healthy for dogs.
After breakfast I go to school and Sally sleeps and plays with her toys. When I get home, we go to the park for a walk and Sally plays with the other dogs. I love watching her running and jumping. While she plays, I talk to my friends.
Then we go home and after doing my homework and having dinner it’s time for bed. Sally sleeps in my bedroom. She has got a comfortable bed on the floor. Sometimes she makes noises in her sleep. I think she is dreaming about chasing birds or rabbits! Maybe in the future she will have puppies. I hope so!
Answer the questions.
Who is Sally?
How does Laura wake up in the morning?
Why doesn’t Laura give Sally her toast?
What do Laura and Sally do when they are in the park?
What does Sally sometimes do when she is asleep?

What vital functions appear in the text? Name them and give an example of each one.



1 Look at the picture.
2
Can you answer Jane’s question?
1 Listen and read.
9 nine Let’s explore Cells Vital functions LIVInG OrGAnISMS Animals Plants Other living organisms Present simple with when When she is asleep, Sally... Language Bank
WHAT IS A LIVING ORGANISM?

Refresh What have all living organisms got in common?



2 Living organisms
There are different types of living organisms.

Plants

Animals

Algae, fungi, bacteria and other microbes



Aquatic organisms live in water, like oceans, seas, rivers and ponds. Land organisms live on land.

1 Look at the pictures and answer the questions.


a) What are the names of the living organisms?
b) Which ones are aquatic organisms?
c) Which animal can live in water and on land?
10
ten
3 How can we recognise a living organism?
All living organisms perform the three vital functions: nutrition, interaction and reproduction.

Nutrition
Living organisms need food, water and air to live, grow and obtain energy. They excrete waste products. There are different types of nutrition.
Heterotrophic nutrition is when living organisms feed on other living organisms.






• Herbivores feed on plants.
• Carnivores feed on other animals.

• Omnivores feed on plants and other animals.
Autotrophic nutrition is when living organisms make their own food.
Interaction
Living organisms feel and react to the world around them.
Reproduction
Living organisms produce offspring. Reproduction can be:
• Sexual, between a male and a female of the same species.
• Asexual, when a single parent produces a new offspring.
2 Look at the pictures. Which vital function does each one show?
• Think Choose a living organism you like. Look for information about its vital functions and present it to the class.

11 eleven
c a
Nutrition Interaction Reproduction
Refresh How many body systems can you name?
4 What are cells?
All living organisms have got cells. They are microscopic units that perform the three vital functions. Cells can be different shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Unicellular organisms have got one cell. Bacteria are unicellular organisms.




Multicellular organisms have got more than one cell. Humans are multicellular organisms.


Parts of a cell
• The cell membrane protects the cytoplasm and other elements inside the cell.


• The cytoplasm contains organelles (small organs) that perform a specific function together.

• The nucleus controls the cell.

Cells join together to form tissues.
Organs are made of tissue and are part of a body system.

In a body system, the organs perform a specific function together.
Think 1 How are bacteria and humans different?
• Find similarities and differences between these cells.
Language Bank


Relative clauses



Nucleus
These cells are microscopic units which/that perform the three vital functions.
12
twelve
CeLlS
cell
cell
Unicellular organisms Animal
Plant
Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane
HOW We ClASSIFY LIVING ORGANISMS
Refresh How can we organise living organisms into groups?
5 How are living organisms classified?


Living organisms are classified into five groups called Kingdoms. The organisms in each kingdom share the same characteristics.
KINGDOM FUNGI
Unicellular
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Can’t move on their own
KINGDOM
ANIMALIA
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Can move on their own
KINGDOM PROTISTA
Unicellular
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Autotrophic
KINGDOM PLANTAE

Multicellular
Autotrophic
Can’t move on their own
KINGDOM MONERA

Unicellular
Autotrophic
Heterotrophic
Some are beneficial
Some are harmful
1 Match the words to the definitions.
a) With one cell heterotrophic
b) With more than one cell autotrophic

c) Make their own food unicellular
d) Feed on other living organisms multicellular
2
Which Kingdom do the living organisms belong to?
a) bear b) bacteria
c) protozoa

d) mushrooms
e) pine tree

13 thirteen
PlANTS
Refresh What are the main parts of a plant?
6 The parts of a plant
The parts of a flower
The pistil is the female part that contains ovules.


The parts of a plant
The stamen is the male part that produces pollen.

Petals form the corolla (a group of petals).
The ovule is inside the pistil.
Sepals of the calyx that protect the flower.
How plants reproduce
The petiole attaches the leaf to the stem.
The stem holds the plant up. The food circulates inside.

Pollen reaches the pistil.
The pistil forms a fruit and the ovules become seeds.
1 Name the female and male parts of a plant.
2
7 Listen and answer the questions.
Roots fix plants in the soil and absorb water and minerals.
Language Bank


Zero conditional
a) What happens if plants have got liquid water, air and soil?
b) What happens if plants have only got air and soil?


If plants have got light, liquid water, air and soil, they grow.

14 fourteen
leaf
8
Types of plants
Trees (pine, oak…)
Bushes (rosemary, rose…)



• A hard, thick stem called a trunk.
• Branches grow from the trunk high above the ground.

• Produce seeds and flowers.
Grasses (poppies, wheat…)

Types of plants
• One or many hard, thin stems that grow from the roots.
• Produce seeds and flowers.
Plants without seeds and flowers
• Thin, green, flexible stems.
• Produce seeds and flowers.
Some have got spores. For example, ferns and mosses.

Think 3 Which types of plants are the biggest? Which are the smallest?
Think 4 Look back at page 11. What type of reproduction have plants without seeds or flowers got?
• Imagine you are a bee. How do you help plants reproduction? Act it out.
15
fifteen
THe NuTRITION fuNCTION IN pLANTS
Refresh Do plants eat and breathe like human beings?
9 What is photosynthesis?
Plants haven’t got sense organs and so they don’t eat and breathe like human beings. They use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. This process is called photosynthesis.


Phloem sap transports nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Chlorophyll in the leaves helps to absorb energy from sunlight.
Xylem sap carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves.
The plant uses stored sugars for growth and basic functions.
16 sixteen
Oxygen O2 NIGHT Cellular respiration DAY Photosynthesis Sunlight Oxygen O2 Water Minerals Carbon dioxide CO2 Carbon dioxide CO2
1
10 Do plants breathe?
Human beings inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Plants do the opposite! They collect carbon dioxide and release oxygen.


What waste products do plants produce?


Oxygen through photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide through respiration

Excess water (vapour) through transpiration

11 Listen to a biologist explaining the process of photosynthesis. Choose the correct options.


a) Green / Yellow plants use light from the Sun.
b) The process of respiration / photosynthesis helps plants to produce their own food.
c) Chlorophyll / Roots absorb sunlight.
d) During the day, plants produce oxygen / carbon dioxide.
2 Are plants active at night? Explain your answer.
3 These living organisms also use photosynthesis to produce their own food. What are they? What Kingdom do they belong to?
plastic bag
• Look at the picture of the plant. What process is the experiment looking for evidence of?
17 seventeen
a b
Refresh Why do you think flowers are so colourful and smell so nice?
12 How do plants reproduce?

Most plants reproduce through the following processes:

pollination
Pollination
fertilisation
seed and fruit formation
germination
Pollen from the stamens of one flower reaches the pistil of another flower of the same type. Pollen can be transported in different ways.
By the wind. Some plants have adapted to help pollination occur without insects or birds. They produce a lot of very light pollen that is easily transported by the wind.

By water. The pollen floats on the surface of the water until it reaches the flower of another plant.
By animals. Pollen sticks to the bodies of birds and insects like bees and butterflies. As they move between flowers the pollen travels with them. These animals, called pollinators, also eat fruits and expel the seeds as waste.
The plants produce colourful flowers and a sweet, sugary liquid called nectar to attract animals.


1 Look at the pictures. What do they show?
Think 2 Why don’t plants that are pollinated by the wind have colourful flowers or a sweet scent? How have they adapted to help pollination?

Language Bank
Present Perfect
Some plants have adapted by…

18 eighteen
THe RepROduCTION fuNCTION IN pLANTS
Wheat is pollinated by the wind.
Pondweed is pollinated by water.
b a
Coneflowers are pollinated by birds and insects.
Fertilisation
13 Fertilisation

The ovule (egg) joins with the pollen inside the pistil.

Seed and fruit formation
Within the pistil, the embryo develops inside a layer of nutrients and the protective outer seed shell. At the same time, the pistil changes shape and size and becomes the fruit that nourishes and protects the developing seeds inside.
Germination
When the fruit and its seeds leave the parent plant, they need to reach a place with the right conditions of temperature and water. The embryo in the seed develops into a new plant.


fertilised ovule

The pollen grain goes down into the ovule and fertilises it.
pistil becomes a fruit


... and becomes a new plant.
Germination
The seed opens. The embryo develops a root and a stem...

14 Complete the summary with the words in the box.
pollinators embryo flower pollination
pistil colour nectar fruit
Insects and birds are called a) … because they help in the process of b) … . They feed on the c) … of flowers, attracted by their d) … and smell. The pollen sticks to their bodies and the animal transports it to other e) … . It travels down the f) … and fertilises the ovule inside, forming an g) … . It later becomes a seed and then a h)
• Find out about asexual reproduction in plants. Name four methods and give an example plant for each one.
Seed and fruit formation
19 nineteen
3
The
The fertilised ovule becomes a seed.
skin pulp seed
THe INTeRACTION FuNCTION IN PlANTS

Refresh Plants can’t move. So, how do they interact with the environment?
15 How do plants react to the environment?
Reactions to light. Green stems grow towards their main source of light and can twist or bend to reach it.
The leaves and flowers of many plants change the direction they face to follow the Sun.

Many plants produce or open their flowers or lose their leaves depending on the amount of daily sunlight they receive.


1
Reactions to water. Plants use their roots to find water. The main root grows down, and other, smaller roots explore other parts of the soil.


Reactions to contact. Stems of climbing plants can grow over and around any object they touch. Some plants produce toxic substances to stop insects or even trap them.


What is phototrophism?
Think 2 What does the prefix photo- mean?

20 twenty
Sunflowers follow the Sun. Green stems grow towards the light. California poppies open their flowers in the sun.
Plants roots detect water below and around the plant.
The venus flytrap traps flies. Climbing plants wrap around objects.
16 Plants and the seasons
Plants react to the changes in the seasons.
In spring, there are more hours of daylight and it is warmer. Plants respond by producing leaves, buds, and flowers.
Insects and birds are very active in spring. In autumn, there are less hours of daylight and it gets colder. Plants lose their flowers to prevent damage from the cold.
Deciduous trees lose their leaves. Evergreen trees keep their leaves.


3 Answer the questions in your notebook.
a) Why do many plants change the direction they face?
b) What do plants use their roots for?
c) Why do some plants produce toxic substances?


d) Why do plants lose their flowers in autumn?
• Think Choose a deciduous tree you can find in your area. Find pictures of it during spring, summer, autumn and winter. Make a poster and share it with the class.

Infinitive of purpose

Plants lose their flowers to prevent damage from the cold.

21 twenty-one
Spring Summer Autumn Winter
Maple trees are deciduous. Pine trees are evergreen.
Language Bank
THe wORLd ANd... YOu!
There are lots of things to investigate! We can use the Internet to do research and share the information on a safe space.
1 Look at the pictures and answer the questions.




a) What are the parts of the tree in pictures a-c?
b) What type of tree is it?

c) Is it deciduous or evergreen?
THINk!
2 Answer the questions.
a) What substance in the leaves makes them green?
b) How does pollination occur in this tree? Explain your answer.


c) Were photos b and c taken at the same time? Explain your answer.

LOOK! 22 twenty-two
a
b
c
It’s time to research some plants and trees in your neighbourhood!

3 Follow the instructions.
Step one.
Decide where you will do your research. A local park or green area, the school garden…




Step two.
• Visit the place you have chosen.
• Choose two plants to study and make notes on their appearance.
• Make sketches and take photos of the leaves, flowers, seeds and fruits.

• Remember! Your research will be affected by the season!



Step three. Do research and find out more about the plants you have chosen.
Step four. Create a plants fact file. Include pictures and information about your plants.
Step five. Present your fact file to the class.
We went to the local park. This is what we found…
Materials
• A notebook or sketchpad
• A pencil
• A pen
• Coloured pencils
• Internet

23 twenty-three
ACT!
Choose a location. Make notes and sketches. Do research.
Oh no! Dad’s vegetable garden! That cat dug up the seeds!
And look! There are lots of flies on the plants too!
We need to protect the seeds and plants from animals.
Yes, but we don’t want to hurt the animals.
Animals don’t like aromatic plants! We can plant them around the vegetables!

The next day…
Animals have a much stronger sense of smell than humans. They don’t like plants with strong smells.

Look! Fluffy doesn’t like lavender!
Thank you for saving my vegetables! We can use the herbs for cooking too.
Mmmmmmm!
I love pasta with fresh herbs!
You must be a good cook, Dad!
Perfect! Let’s buy basil, lavender, rosemary and mint.
Yes, but not too many!
1 What problem have the friends got?

2 What solution does Alex suggest?



3 What else do we use plants for, apart from eating?
Me too! But I thought animals didn’t like herbs!
24 twenty-four STORY TIMe!
17
ROSEMARY ROSEMARY MINT MINT BASIL BASIL BASIL LAVENDER LAVENDER
1 Think and fill in the gaps.
Nutrition Interaction
Vital functions
? React to light, water and contact

25
MAP YOuR IdeAS!
Cells Reproduction Nutrition ?
?
Fungi
Sexual ?
Animalia
? ? ?
twenty-five
PlAntS LIVInG ORGanISMS tHe FIVE KInGDOMS
LeT'S ReVIeW!
1 Look at the pictures. Which Kingdom do the living organisms belong to?

2 What vital function are they talking about?
I’m hungry!
I’m a dad! I’m hot!
3 Organise the words to create a diagram showing the relationship between them.
Organ System Tissue Cell
4 Copy and label the diagram of the parts of a plant.


5 Match the definitions to the stages of plant sexual reproduction.




Pollination Fertilisation
Seed and fruit formation Germination
a) The union of the pollen grain and the ovule.
b) A new plant starts to grow.
c) Pollen travels from the stamens of one flower to the pistil of another.


d) The embryo becomes the seed and the pistil becomes the fruit.



26 twenty-six
a b c
a b d c e a b c d
1 Find the words.
a) Organisms that live in oceans, seas, rivers and ponds.

b) Organisms that live on dry land.
c) The name given to something that performs the three vital functions.

d) This vital function gives our body energy.
e) These animals feed on plants.
f) This vital function allows living organisms to produce offspring.
g) Microscopic units that perform the three vital functions.
h) It protects the cytoplasm and other contents of the cell inside.
i) It is formed when different tissues group together.
j) When pollen travels from the stamens of one flower to the pistil of another.
k) The process plants perform to make their own food.
l) A type of reproduction where living organisms reproduce themselves.
m) They fix a plant to the soil and absorb water and minerals.
n) The name given to a group of petals.
MY pROGReSS
• I know the different types of living organisms.
• I understand the vital functions in animals and plants.


• I know what a cell is.
• I can name the parts of a plant.
• I can classify plants by how they reproduce.
Copy the sentences in your notebook.
Draw a smiley
27 GlOSSARY! twenty-seven
ANIMALS AND HUMAN BEINGS
My objectives are:


• To learn about the characteristics of animals.
• To know how to classify animals.
• To learn about the vital functions of nutrition, interaction and reproduction.
• To understand the importance of physical and emotional well-being.

Watch and learn!
• What is the difference between a vertebrate and an invertebrate?




It looks like a helicopter!
Animals have inspired lots of inventions!
twenty-eight 15
28 2
What is this animal?
1 Look at the picture and answer the questions.
a) What kind of animal is Jane looking at?
b) Is it a carnivore, a herbivore or an omnivore?
c) What type of ecosystem does it live in? 2 18
Strange animals!
Last week, my teacher asked the class to investigate some strange animals. We found a lot, and some look really scary! Lots of animals have got an unusual appearance because they have adapted to their environment to survive.
In tropical forests, in Africa, North and South America, Asia and Australia, there is an insect called a Brazilian Membracidae. It has got tiny balls on its head which make it look like a helicopter! It looks scary but it doesn’t hurt humans. It only measures about half a centimetre and it feeds on the sap of some plants.
We also discovered the Star-Nosed Mole from North America. Its nose has got 22 pink tentacles and it measures between 17 cm and 20 cm! It uses the tentacles to identify food, because it is almost completely blind. It lives in areas with moist soil, like woods, marshes and fields.

It eats worms, aquatic insects, snails, fish and some small amphibians. Do you know any strange animals?
 by Laura, Class 4
by Laura, Class 4
3 Match the words in bold in the text to the definitions.


a) Slightly wet.
c) Something that makes you feel fear.
e) Low land that contains a lot of water.
b) A fluid inside plants.
d) When you can’t see anything.
f) Unusual, surprising or difficult to explain.
29 twenty-nine
Listen and read.
AnIMAlS Vital functions Types Nutrition Interaction Vertebrates Reproduction Invertebrates
Let's explore
ANIMAL CHARACTERISTICS AND TYPES
Refresh Where does the oxygen we breathe come from?
19 What characteristics do animals share?

All animals share some characteristics.
They don’t make their own food. They feed on other living organisms.

They breathe oxygen and expel carbon dioxide from air or water.




They have got sense organs to see, hear, smell, taste and touch.
They feel sensations and can detect movement.
They move between places using their locomotor system.

1 Animals move! Think of two animals for each of the movements below.

climb run swim fly walk
Think 2 What are the five sense organs in animals?

3 Look at the picture on the right. What differences are there between the dog and the trees? Make a list.

30
thirty
20 What are vertebrates?

Vertebrates
Have got an internal skeleton and a backbone
Cold-blooded
Their body temperature varies with the environment
Warm-blooded
They have a constant body temperature
• Aquatic animals
• Most are oviparous
• Have got scales, fins and a tail


• Breathe underwater through gills
Fish Reptiles
• Land and aquatic animals that breathe air
• Most are oviparous and lay eggs on dry land
• Have got four legs and sharp claws (except snakes)

• Have got scales and some have got a hard shell
Amphibians

• Land animals that live close to water


• Oviparous and lay eggs in water
• Have got thin, moist skin that absorbs oxygen
• Land or aquatic animals
• Viviparous
• Usually have got fur
• Can have got arms, hands, legs, fins or wings

Mammals Birds
• Land animals
• Oviparous
• Have got feathers, wings and a beak
• Most can fly

31 thirty-one
The life cycle of a frog
21 What are invertebrates?
Cnidaria
Invertebrates
Haven’t got an internal skeleton or a backbone Are oviparous

• Some swim, like jellyfish
• Some lived fixed in one place, like coral and anemones
• Jellyfish use poisonous tentacles to hunt
• Have got very long bodies divided into segments or rings

Worms
Echinoderms

• Can be aquatic, like a leech, or live on dry land, like an earthworm

• Are usually shaped like a star or a ball
• They are covered in a shell with spines
• Land and aquatic animals

Molluscs
Arthropods
• Some have got a hard shell to protect their bodies, like a snail

• Have got armour plates and various numbers of legs
• Some have got wings and can fly
• Some live in water, like crabs

• Some live on land, like spiders or insects like flies
Think 4 What is the difference between a viviparous and an oviparous animal?
5 Find another animal that belongs to each group. Has it got any special characteristics?
32 thirty-two
ThE NutRItIoN fuNCtIoN
Refresh What do living organisms need to survive?

22 What is nutrition?
Nutrition is when living organisms use food, water and oxygen to survive. One of the main differences between plants and animals is the way they obtain nutrients.
Plants are autotrophs. They make their own food through photosynthesis.

Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through their leaves.

Animals are heterotrophs. They feed on other living organisms.


• Carnivores feed on other animals that they catch. Some carnivores are scavengers. They eat the bodies of dead animals they haven’t caught.



• Herbivores feed on plants.
Plants absorb water and minerals from the soil through their roots.
• Omnivores feed on meat and plants.

Nutrition is also the way living organisms breathe and expel waste substances and carbon dioxide. Some of them expel carbon dioxide through gills or lungs and all of them use their excretory system and excretory glands to expel other substances.
23 Listen. What four body systems are involved in nutrition?
33 thirty-three 1
THE INTERACTION FuNCTION IN ANIMALS
Refresh How do animals react when they sense danger?
24 How do animals interact with the world around them?
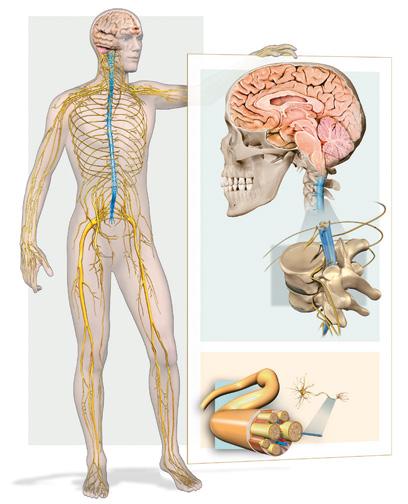
Animals, including human beings, receive information and also interact with their environment using their sense organs, their nervous system and their locomotor system. The sense organs receive information from the environment and the body.


The nervous system receives and processes this information. In response, it transmits signals to and from different parts of the body.
The locomotor system receives the signals from the nervous system and a physical reaction occurs.
Effectors are parts of our bodies that respond to these signals. In the locomotor system these effectors are our muscles


The interaction function in vertebrates
The nervous system receives the information and transmits signals.

34
thirty-four
Sense organs collect information.
The locomotor system allows the animal to move.
nerves brain spinal cord skin nose tongue eyes ears
Which sense organs are associated with the senses?

taste hearing smell touch sight
2 Match the parts of the body to their functions.
nervous system locomotor system sense organs

a) To allow movement
b) To collect information from the environment and the body


c) To receive and process information and to transmit signals


3 Look at the pictures. What stage of interaction can you see in each one?

• Choose an invertebrate and find out about:



• its sense organs
• its nervous system
• its locomotor system
35 1
thirty-five a b
THE REPRODuCTION FuNCTION IN ANIMALS
Refresh Do all animals reproduce in the same way?
25 How do animals reproduce?
There are two main types of reproduction in animals: sexual and asexual. In sexual reproduction, a male and a female sex cell combine to create new offspring.
Oviparous animals lay eggs. The baby animal is born when it breaks out of the eggshell.
The offspring of viviparous animals develop and grow inside their mother’s womb. The mother gives birth.


Birds lay eggs in a nest.

Female lions give birth to cubs.

Snakes lay eggs underground.

Female horses give birth to foals.

Fish lay eggs in water.
Female sheep give birth to lambs.

In asexual reproduction, the animal reproduces by itself. Most invertebrates reproduce in this way, but some vertebrates do too.
Sponges and honey bees are invertebrates that reproduce asexually.


Sharks and Komodo dragons are vertebrates that reproduce asexually.


36 thirty-six
1 Rewrite the sentences to make them true.
a) In sexual reproduction, you don’t need a male and a female sex cell.

b) Horses can be oviparous or viviparous.
c) Viviparous animals break out of eggshells.

d) Only invertebrates reproduce asexually.
2 The offspring of different animals have got different names. Which animals do these young come from?


calf puppy chick kitten
Think 3 Look at the different types of reproduction. Answer the questions for each one.

a) Is it sexual or asexual reproduction?


b) What exactly is happening?
c) Which label below matches the drawing?

Fragmentation
Lay eggs
Give birth Budding
• How do jellyfish reproduce? Draw a diagram to explain the process.


How...?
How do jellyfish reproduce?
They reproduce by...
37 thirty-seven
Language
a c b d
Bank
THE VITAL FuNCTIONS IN HuMAN BEINGS
Refresh What are the vital functions?
What systems are used in the nutrition function?
The digestive system obtains nutrients from food.
The respiratory system obtains oxygen from the air.


The circulatory system takes the nutrients and oxygen to all of the different parts of the body and the waste to the excretory organs.


1 Which system does the information describe?

a) It obtains nutrients from food.
b) It obtains oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.
c) It removes waste from the body.
d) It transports different substances around the body.
The respiratory system expels carbon dioxide.
The kidneys expel salt and other types of waste in urine. The sweat glands expel salts and other types of waste as sweat.


38 26
thirty-eight Obtaining nutrients Obtaining Distributing substances Expelling waste
The digestion process
27 How do human beings interact?

The human interaction function obtains information from the world around us and from our body and reacts to it. Our sense organs receive the information.

Our nervous system receives signals from the sense organs. It interprets the information and generates more nerve signals around our body to prepare for a reaction.
Effectors respond to the nerve signals. They are the muscles and the glands.

• Muscles allow us to react by changing positions and moving from one place to another.
• Glands produce different substances when they receive a nerve signal, like saliva glands.

How do human beings reproduce?
Male and female sex cells are needed to produce offspring.
The female reproductive system produces ova (eggs), female sex cells.


The male reproductive system produces spermatozoa, male sex cells.
2 Choose the correct options to complete the sentence.
Human beings are viviparous / oviparous and reproduce asexually / sexually.
• Think of a situation that each effector reacts to and say how it reacts.
39
thirty-nine
ears nose mouth and tongue eyes skin The sense organs brain encephalon spinal cord nerves cerebellum brainstem
nervous
The
system
uterus vagina vulva ovaries urethra penis testicles scrotum
PHYSICAL AND EMOTIONAL WELL-BEING
Refresh Why is our mental health so important?

What can we do to keep our bodies healthy?
A Healthy body!
Digestive system
• Eat a healthy, balanced diet. Your body needs:
Vitamins and minerals
Proteins to help you grow
Carbohydrates for energy
Healthy fats for your cells
Calcium for your bones
• Eat regular meals.
• Eat slowly.
• Don’t eat spoiled food.
• Wash your hands before and after eating.
• Brush your teeth after meals.
Excretory system
• Drink lots of water

• Wash every day
• Wear clean clothes every day
Respiratory system
• Breathe through your nose. The hairs inside your nose clean the air!

• Do regular exercise to keep your lungs healthy.

Circulatory system
• Do regular exercise to keep your heart healthy.
• Don’t eat much food that contains a lot of fats and salt.

1 Look at the food wheel and answer the questions.

a) How many foods can you name?
b) What type of food is in each section?
body-regulating food
40 forty 28
i n g f o o d
energy-producing food body-build
29 What can we do to keep our mind healthy?
Our mental health is just as important as our physical health: you can’t have one without the other. Here are some tips to keep you healthy and happy!
Top tips to feel good!
• Express your feelings
• Look after your body
• Do things you enjoy
• Get lots of sleep
• Spend time outside away from a screen
• Don’t be afraid to ask for help
• Report bullies immediately

• Eat healthy food
1 Match the information to the tips above.
a) Sharing our problems is the first important step in solving them.
b) Our bodies needs lots of rest to function correctly.
c) Too much time online can negatively affect our sleep and our mood.


d) Hobbies help us to relax and reduce stress.
e) No one can make us feel unhappy or scared.
f) Taking care of our bodies increases our self-esteem.
g) A balanced diet keeps our bodies strong.
h) Talking about our emotions can help us to understand them better.
• Breathing techniques can help to control stress and anxiety. Try one! Repeat the steps several times.

Step one: Breathe in to a count of four.
Step two: Hold your breath to a count of four.
Step three: Breathe out to a count of four.
Step four: Pause for a count of four.
41 forty-one
4 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1
1 Look at the pictures and answer the questions.

a) What inventions can you see in pictures a-c?


b) What living organisms can you see in pictures d-f?




ThINk!
2 What is the connection between pictures a-c and d-f?

3 Which living organism do you think inspired each invention?
Biomimicry is when scientists and engineers develop new things, inspired by nature. The natural world is amazing, and we can learn a lot from it!



42 ThE wOrLd ANd... yOU! LoOK!
forty-two a d b e c f
You are going to imagine a new material, process or product inspired by a animal for a class innovation fair.






4 Follow the instructions.
Step one: Choose an animal that you think can teach us something.
Step two: Create a physical model of the animal and a summary of its characteristics.
Step three: Discuss the appearance of the animal and its behaviour. What can we learn from it?
Spiders have eight legs and eight eyes! Spider webs are incredibly strong!


Step four: Create an ideas board, showing all of the ways we could learn from the animal. Include drawings and notes.
Step five: Present your model and your ideas board to the class.
Step six: Do research and find out if any of your ideas already exist!


43
AcT! forty-three
What a mess! Look at my clean clothes! I have to remove the nests.
What’s that sound?
Can you see anything inside?
It takes a lot of effort to build the nests. The birds return to them every year.
No! The birds are protected! It’s illegal to remove the nests!
Cheep, cheep, cheep!
There are baby birds in the nest!
We can put your clothesline in the patio. There are no nests there!
Aunty! Have you got any worms for the birds?
We can use my binoculars to see the nest!
1 Why does Jane’s aunty want to move the nests?

2 What does Pip see through his binoculars?

3 Find out what laws protect birds where you live. What can you do to help protect them?




They sound hungry
Ugh!
44 StOrY TIME! 30
forty-four
1 Think and fill in the gaps.
AnIMAlS
Vital functions
Types
Invertebrates ? Interaction ?
Asexual

Reproduction
?
Oviparous
? ?
Heterotrophs Herbivores
45
IdEAS!
MAP Your
forty-five
LET'S REVIEW!
1 Which characteristics do all animals share?
a) They feed on other living organisms.
c) They breathe oxygen and expel carbon dioxide.
e) They move from one place to another.
b) They have got fur.
d) They have got sense organs.
f) They have got two or four legs.
2 Copy and complete the table with ticks ( ) to show the characteristics of the animals.
Group Vertebrate Invertebrate Oviparous Viviparous
Mammals
Worms
Birds
Cnidaria
Molluscs
Reptiles
Amphibians
Echinoderms



Fish
Arthropods
Work in your notebook!
3 Think of an example of an animal from each group in activity 1.
4 Match the word groups to a vital function.



Group 1
autotroph
heterotroph
carnivore
herbivore
omnivore
Group 2
sexual
asexual
viviparous womb
oviparous
Group 3
sense organs

nervous system
locomotor system
muscles
glands
5 Write a simple definition for the words in activity 4.
46
forty-six
1 Find the words.
a) Animals with an internal skeleton and a backbone.
b) Animals without an internal skeleton and a backbone.
c) Aquatic animals that breathe underwater through gills.

d) Animals with long bodies, sometimes divided into segments or rings.
e) Living organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis.
f) Animals that only feed on meat.
g) Animals that eat meat and plants.
h) The vital function of living organisms needing food, water and oxygen to survive.

i) The vital function which allows us to obtain information from the world and to react to it.

j) The type of reproduction in which a living organism reproduces itself.
k) The type of reproduction that needs a male and a female sex cell.
l) The parts of our bodies that respond to nerve signals.
m) The name given to living organisms that lay eggs.
n) A type of invertebrate usually shaped like a star or a ball.
My pRoGrESS
• I know the characteristics of animals.
• I know how to classify animals.
• I understand the vital functions of nutrition, interaction and reproduction.

• I understand the importance of physical and emotional well-being.
Copy the sentences in your notebook.
Draw a smiley
47 GLOSSARy!
forty-seven a b c
1 31 Listen and choose the correct words to complete the text.
All living organisms need a) food / light , air and water to live. Humans and animals look for food. Plants make their own food through the process of b) transpiration / photosynthesis. They absorb carbon dioxide through their c) flowers / leaves and stems and absorb d) air / water through their roots. The e) light / heat from the Sun gives them the energy they need. Photosynthesis produces the f) oxygen / carbon dioxide that humans and animals need to breathe.
2 Copy and label the picture of a cell.

3 Match the information.
Grasses, bushes and trees Heterotrophs and autotrophs
Unicellular and multicellular Algae, fungi and bacteria



a) Some living organisms are not animals or plants.
b) There are living organisms with one or more than one cell.
c) The nutrition function is not the same in all living organisms.
d) There are three basic types of plants.
forty-eight 48
Units 1 2 a b c
TERM REV IEW
4 Choose the correct definition of photosynthesis.
a) Plants use water and oxygen from the air to produce energy in the form of sugars.
b) Plants use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of sugars.
c) The roots of plants absorb nutrients from the ground that plants convert into sugars.
5 What characteristics do all animals share?



6 Look at the picture and answer the questions.

a) Which animals can you see?
b) Are the animals vertebrates or invertebrates?




c) Is each animal a carnivore, a herbivore or an omnivore?
d) Which animal is oviparous?
7 Describe and guess animals with a partner. It’s a honeybee!
It’s an invertebrate. It reproduces asexually. It flies between flowers.
8 Which is the one odd out? Give reasons for your answers.


a) nutrition digestive system respiratory system muscles
b) interaction carbon dioxide sense organs offspring
c) reproduction spermatozoa effectors ova
49 forty-nine
PROJECTS THATLEAVE ANIMPRINT

Eco-ActIon MagazInE
What is composting and how can it help the planet? Find out and try it yourself!
Can you write an article about composting for the magazine?

Waste is when we don’t know what to do with something or when we throw something away.
What happens to food waste?

What is organic waste? What bin does it belong in? What can we do with organic waste?
What is composting?
Brainstorm all the questions that come to mind.
The answers might surprise you!
DESIGN
Composting uses waste organic matter. Find out about composting and become an expert!
What questions do you want to answer in your article?
Form groups and assign a question to each group. Do research and find useful, simple information.
DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT fifty 50 2 1
I
THINK
PIENSA D I SEÑA
Is your article ready?
Read it together in detail. This is very important. Invite other classes to the presentation. Make your presentation dynamic and fun so that other students feel motivated to write articles for the magazine. Share your knowledge to help protect the planet!
3 MAKE
Organise the information. Use simple language to help readers understand what composting is. Include photos and illustrations to give visual support. Run a spellcheck and reference your sources. You must respect intellectual property rights!



5 CHECK COMPRUEBA
I was very surprised to learn that...
51 fifty-one
CONSTRUY E 4 PRESENT PRESENTA
rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior permission of the publishers.
© GRUPO ANAYA, S.A., 2023 - C/ Valentín Beato, 21 - 28037 Madrid. All







































































































































































































