
PRIMARY
12MONTH LICENCE DIGITAL PROJECT INCLUDED
2
Globalaction Natural Science

2
LEARNING EXPERIENCE TARGET IN ACTION SDG
• Learning experience: A short text and pictures of children in everyday situations (looking through a magnifying glass, doing sport, etc.) introduce the study of the human body.
• Target in action: List some sports that boys and girls can do together.

• Learning experience: An adaptation of the fourth right of childhood, and pictures of children smiling, doing sport, etc. encourage reflection on the idea of wellbeing, especially for people who struggle to maintain healthy habits because of their circumstances.
• Target in action: Design a poster with ideas for helping people who live in poverty.

4
• Learning experience: A short text and a picture of a girl swimming among animals introduce the study of living beings and the need to respect them.
• Target in action: Create a wall display about respecting animals on land and in the sea.

• Learning experience: A text about spring and a photo of a girl looking through binoculars and surrounded by illustrations of living beings, introduce the importance of understanding and protecting living beings.
• Target in action: Create a wall display about the importance of animals and how you can protect them.
5
• Learning experience: A text on the importance of the Earth, and a picture of a girl, plants, animals and wind turbines introduce the topic of matter and energy, as well as energy saving.
• Target in action: Create a poster to help combat climate change.
6
• Learning experience: An image of a robot hand introduces two projects, one involving the construction of a simple machine and the other requiring the use of ICT.
• Target in action: Create a sustainable project.



Gender equality
What are we going to learn?
Your body 8 44
I love animals!
1
3
Looking after nature
A clean planet! 80
Looking after your body 24 60
All about
98 PAGE.
technology
No poverty Life below water Climate action Life on land Sustainable cities and communities INTERDISCIPLINAR
TERM 1 REVIEW STEAM: Marie Curie
TERM 2 REVIEW STEAM: Jane Goodall
TERM 3 REVIEW STEAM: Hedy Lamarr
KNOWLEDGE TO LEARN, APPLY AND INVESTIGATE
• Your body.
• Breathing and eating.
• Transporting substances and excreting waste.
• Noticing things and reacting.
• Moving.
• Changing throughout life.
• Health and illness.
• Food.
• How to eat well.
• Good hygiene.
• Moving and resting.
• Feeling emotions.
• There are many living beings.
• Classifying Animals.
• Discovering mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates.
• Observing and respecting animals.
Competence-based activities
• Let’s get some fresh air!
• Let’s think: How does your body get the substances you need?
• Taking your pulse.
• Let’s pretend.
Competence-based activities
• Emergency situations.
• How long can we keep food for?
• Let’s think: What steps do you take for good hygiene?
• Move your body.
• Can you identify your emotions?
• Put yourself in their place.
Competence-based activities
• Classifying helps us understand.
• Investigate.
• Let’s think: Putting things in order.
• Are some animals ‘bad’?
Competence-based activities
• Plants are everywhere!
• Plants are really important!
• Plants are fascinating!
• Observing nature.
• We are part of nature.
• We want nature to be healthy.
• Using outlines.
• Plant food.
• Plants are really important.
• Do plants react to light?
• Seed hunters.
• Natural balance.
• Let’s think: The What if…
• What is matter?
• How do we use matter?
• How does matter change state?
• How does matter change?
• Where is energy?
• How can we look after the planet?
Competence-based activities
• How can we measure mass and volume?
• Experimenting with matter.
• Let’s think: What is water like in nature?
• Look! No hands!
• Take action for the planet.
Competence-based activities
• Everyday technology.
• ICT.
• What is a project?
• My first project: build.
• My second project: programing.
• Internet research.
• Why do we need projects?
• Let’s think: Building a machine.
• Let’s think: Creating a computer program.
• Let’s think: Creating a computer program (continued).
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · A picture is worth…: Changes around us
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Commit to birds: Food and drink for birds
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Tic-Tac-Smile!: Investigating the past
Get to know your book
What is the use of what I learn?


Each unit gives a learning experience and an objective.
Follow the thread!

We discover basic knowledge through a learning situation.


Skills activities
Learning by doing motivating tasks...

Take note!

Dis c o v e r ing m a m m a ls, bir ds, r ep tile s, a mp hibia n s, fish a n d in v e r te br a te s Obs e r v ing a n d r e sp e c ting a n im a ls 3 14
SDG
W hat do I know?










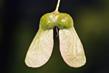
1 Write the names of the parts of the plants. Look





























Choose a living being in your local area, complete this logic wheel. Create a wall display classroom about living beings and add your




Threats What it interacts




13 thirteen You breathe with your respiratory system. You eat with your digestive system. Take note! 78 79 Are feeding stations for birds important? What food can you put on them? Ask an adult to help you search the internet for some examples of feeding stations made from recycled materials. Draw the feeding station you want to make on a piece of paper. Label your design with the recycled materials you want to use: cans, bottles, lolly sticks, cartons, etc. Decide what food you want to put on it and where to put the water. Ask an adult to help you build your feeding station. Make all the parts and put them together. Put food and water on your station. Ask an adult to help you hang your feeding station where you want it. Take photos of the birds that come to eat and drink. Show them to your classmates. What do you know about birds now? Are you helping these animals? Is the feeding station an improvement to the local environment? Birds in towns have problems finding food and drink. Can you help them? FOOD AND DRINK FOR BIRDS TERM 2 seventy - nine seventy - eight Let’s make a feeding station for birds! Commit to birds: DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT 4 PRESENTA PRESENT e nt a 1 P nsa THINK D seña 2 DESIGN 3 C ONSTRUYE MAKE ru e TEST 5 C ompru a PROJECTS THATANIMPRINT LEAVE U4 PORTFOLIO TARGET IN ACTION What do I know? seventy - four Choose a living being in your local area, then copy and complete this logic wheel. Create a wall display in your classroom about living beings and add your logic wheel. 1 Write the names of the parts of the plants. 2 Look at the picture of a maple. Complete the sentences. – It is a because of the stem (trunk). – It is because of how it reacts in autumn. – It produces fruit with to reproduce. – It is really important because 4 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es fruit with seeds 3 Match the problems and solutions. Air pollution. Extinction of living beings. Too much waste. Separate and recycle waste. Use transport that doesn’t pollute. Protect the natural environment. Colour like this: 40 41 REVIEW TERM sTEAM 4 Unscramble the letters to find the answer to the question. forty - one forty 1 Match these cards to make pairs. 2 Play ‘taboo’ with this part of the body! 3 Some of these sentences are lies. Put a cross in the boxes next to the lies. Listen to the poem and share it with your family. Marie Curie Do you know about a scientist Whose first name was Marie? Her last name was Sklodowska, Then she changed it for Curie. She discovered that some minerals Had the wonderful ability, To produce strange rays and particles, And she called it radiactivity These beams are very interesting And they have amazing powers. They can travel through a brick wall Through a hand or through a flower. Marie discovered two elements That were naturally radioactive: They are Pollonium and Radium. She was really creative! Mary had amazing talent, So it is not a surprise That she got a nobel prize And not once; she got it twice! s p a r d i c e u q Give clues to help work out the part of the body. Write two words. You can’t use the words ‘circulatory’ or ‘beat’. The thorax is in the trunk. The intestines are in the abdomen. The lungs are part of the digestive system. Waste leaves the body in the urine. The biceps is a very long bone. Adulthood starts at 8 years old. and What is the large muscle in your leg? PORTFOLIO
L et’s reflect
TARGET IN ACTION
1
at the picture of a maple.
the
of the stem (trunk). because of how it reacts in – It produces fruit with to reproduce. – It is really important because fruit with seeds
Complete
sentences. because
My living being is Actions to protect it
with Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it U3 53 fifty - three amphibians, … Look at the animals. Complete. 1 A m45p67h45 67 45n<=s, ~òu de™ <= r ÄÅs, a r:; HIr45 :; JK >?r89a45 :; TU w>? 67™ Δ BCa r:;Þ, z{kVW 45>. Atu67 *+ 45m45p67h45 67 89 45n<= *+ 45r:; Mñó ~ò h 45 `a u45® a n89∂ 89 45y 45> w a :; ®. Frog Toad Newt 1 Let’s Putting things in order. a45® g 67™ 3 2 4 U3 … amphibians, … Look at the animals. Complete. 1 AVWm45p67h45 67b>? 89a45n<=s, Ãs~òu89de™ *+a<=s Δjkr89 BCgÄÅs, *+a45r:;Þ »vDE HIr45 :; JKb>?r89a45 :; TUs »w>? 45 67™ ΔbBCa45r:;Þ, sz{kVW 45>. Atu67¬ *+a45m45p67h45 67b>? 89a45n<=s *+a45r:;Þ Mñó 23s~ò† Δh89a45vDEÞ Δ`a >?u45® *+a45n89∂ Δ89a45y » 45> »wBCa45 :; HI®. Frog Toad 1 2 Why do amphibians live next to fresh water or in very damp places? Make a sentence: Let’s think Putting things in order. babies and their Because need their water eggs 3 2 4 1 7 5 8 6 *+^_a45® NOg »t67™ Δ :;Þ 3 1 2 4 eggs tadpole tadpole with legs frog U1 13 thirteen The digestive system uses food to get substances that your body needs. It removes the waste that you don’t need. Write the names of the body parts. 2 You breathe with your system.respiratory You eat with your digestive system. Take note! Put the stages in order. Let’s think How does your body get the substances you need? This is the digestive system. Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Intestines Travelling to the stomach Chewing Excreting waste Getting substances Digesting STEAM space Discover a female scientist solving a mystery.
Term review With fun activities. Interdisciplinary Project To integrate the different areas of knowledge with a common goal. Icons Cooperative learning Emotional education Gamification ICT
Learning to think Audio Assessment Tar ge t i n a c t i o n Portfolio We check what we have learned and reflect on it.
And for each term...
SDG
Your digital project























A project that offers you all the content of the course through the digital book, along with a wide variety of resources. Discover another way of learning that is simple, intuitive and compatible with any platform and device.


How do you access it?

U3 54 55 fifty - five fifty - four Look at the animal. Complete. 1 Order the letters. Circle the fish that doesn’t live in the sea. 2 Invertebrates are the most abundant animals. There are lots of different types. Match. 1 Look at the pictures again. Which are marine animals? Choose two. Write their names. 2 Shared interpretation Say how these invertebrates are similar and different. 3 … and invertebrates fish, … FVW <= z{™, ~òu89de™ *+ <= 45r67b JK¬, *+ 45r:; v HIr45 :;JK r89 45 :;TUs. Ttuh HIy 45 45 DE *+a45n89∂ Δ r:;NO 4567h:; 45> Mñó ~ò Δ <= z{™ 45r:;Þ *+^_ HIr:;NO∂ > 45n89∂ Δh89a v Δ ® ~òw>? 45m45m45 45n89g. Mñóa n y a r:; fins scales S T A ¹ H R T HKSRA NATU HYAVCNO AYR EAKH CDO TOTRU There are lots of different marine and land animals. They are all important. Take note! Long body. No shell. No legs. Shaped like a bag. Poisonous tentacles. No shell. Muscular body. Shell or no shell. Tentacles or none. Shell. Several pairs of legs. Some have wings. Shaped like a ball or a star. Spiny shell. ∑ Δ ø ÑÖ 98 ninety-eight pollution. They use lots of energy. Eve yday techno ogy What a pro ect? My f rst project bu d ng F o o w t h e t h r e a d ! n orma ion and Commun cation Techno ogy CT 1 2 3 4 6 All about technology Target in action Create machines and computer programs that promote sustainable technology. In this unit… What do you think? Can you imagine the world without machines and technology? What is it like? Technology is about imagining new things. Close your eyes and free your imagination!
You have all the necessary instructions to access it next to the first page of your book. Go to Liria
11
What does it offer?
It contains diversity of resources; it is much more than a reproduction of the paper book.

With them you can: Do exercises interactive activities Study interactive summaries, outlines... Learn audios, videos, gameroom... Assess self-assessment, portfolio...


What’s it like?
A global response for a diverse educational environment.

Intuitive
Easy to use. Multi device
You can use it with any type of device (computer, tablet, smartphone…) to any screen size and resolution.


Downloadable
It allows you to work without an Internet connection and download it on more than one device.
Synchronically
Any changes you make are automatically synced when you connect to any of the devices you’re using it on.

Universal Compatible with all operating systems, virtual learning environments (EVA) and educational platforms (LMS) most used in schools.


99 ninety-nine My se o d programming 5
DOC to the cabin! needs you!
1 Your body
Redhead, blond, dark-haired, tall, short... The world is really diverse!

What do you think?
Can everyone do the same sports?
Today, everybody can do the sport they want. Men and women do some sports separately, like gymnastics, and some sports together.

In this unit...
Target in action
List some sports that boys and girls can do together.


Your body the thread!

2
Breathing and eating
8 eight









9 nine Transporting substances and excreting waste Moving Noticing things and reacting Changing throughout life 3 6 5
1
Your body
Your body can help you do sports and other activities.
Your body lets you live!
What is your body like on the outside? Trace the missing arrows.
Upper limbs
Arm Hand
Lower limbs



Leg
Foot

Head Face Trunk Back Thorax Abdomen
Write the words in the correct place. 2
Forehead Ears Cheeks

Lips
Chin
Eyebrows
Eyes
Nose
Mouth
mouth hand foot forehead back leg thorax arm

Head Trunk Limbs
Circle three words that mean abdomen. 3
face stomach back belly tummy thorax
10 1 ten
You have muscles and bones under your skin. You have a brain, lungs, heart and other organs inside your body.



Ideas pool

What do you need to stay alive?

Write down an idea. Then tell your group.
Take note!
Your body has outside parts that you can see, and inside parts that you can’t see. You use all these parts to play sports!

U1 11 eleven Match. 4
5
Inside the head Brain Stomach Intestines Lungs Heart lnside the thorax Inside the abdomen Muscles Bones Brain Heart Stomach Intestines Lungs Under the skin Inside the body
Breathing and eating
You need to breathe and eat well to play sports.
You breathe in to get oxygen. You breathe out the air you don’t need.
You do this with your respiratory system.
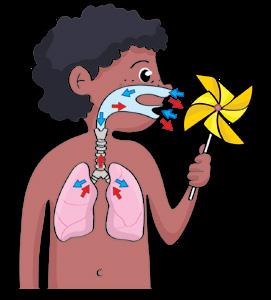
How does air go in and out when you breathe? Write the missing words.
– Where does air come in and out?
– Where does the air go?
This is the respiratory system. in out

Let’s get some fresh air!
1 Breathe in and out. Watch your chest. Tick the correct box.
• My chest expands when I breathe in.
• My chest expands when I breathe out.
2 What do you do when you get some fresh air? Tick the box.
• I go outside, I ride my bike, or I do other outdoor activities.

• I brush my teeth and stay indoors.

12 twelve 2
1 Ttuh45r89 >?u89gfg™ » 67h:;Þ *+o>?® Txyø » 67h:;Þ , »w@Ah45i89de™ » 89a67kvwÞ »t67h:;Þ *+o>?xVWy`ag|} HI>.
Nose Mouth Lungs
The digestive system uses food to get substances that your body needs. It removes the waste that you don’t need.
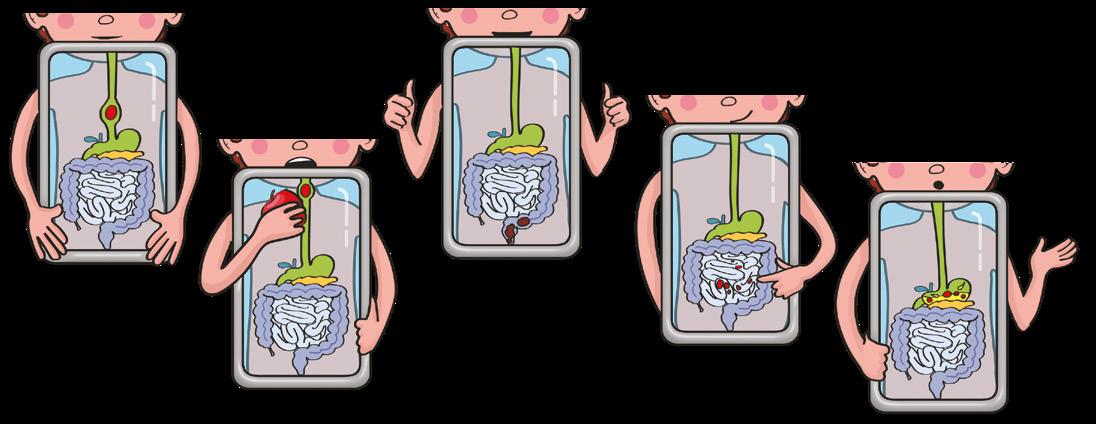

Let’s think
How does your body get the substances you need?
Put the stages in order.
Travelling to the stomach
Excreting waste
This is the digestive system.
Oesophagus
Chewing
Getting substances
Digesting
Write the names of the body parts. 2

Take note!
You breathe with your respiratory system. You eat with your digestive system.

U1 13 thirteen
Mouth
Stomach
Intestines
Transporting substances and excreting waste
Being active helps you stay healthy. It makes your heart strong.
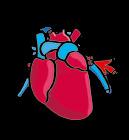
This is the circulatory system.
The circulatory system uses blood to take substances around your body. For example, oxygen. It collects substances that you don’t need.
Blood moves around the body inside the blood vessels. The heart pumps the blood.
See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es




Draw the body part that moves the blood. Write its name. Put your hand on this part of your body. Can you feel it?

Taking your pulse
Take your pulse to feel your heart working! Put two fingers on the blood vessels in your wrist. Can you feel the beats? These are from your heart.
Count how many beats you feel in one minute (get a partner to help you). First, count when you are resting. Then, count after some exercise. Write down your results and tell the class.
Resting After exercise
14 3
fourteen
1
Heart
Blood vessels
This is the excretory system.
The excretory system removes waste that you don’t need. The blood collects the waste. The waste leaves your body in the urine.

Kidneys Bladder
Timeline Put in order from 1 to 3.

The blood takes waste to the kidneys.
Write the missing words. Then colour like this: for the kidneys for the bladder
Waste turns into urine in the kidneys.


The urine stays in the bladder before it leaves the body. Take nota!
The circulatory system takes substances around the body. The excretory system removessubstances from the body.

U1 15 fifteen
2
Wxya<=s~ò :;Þ »t45u45r45n<=s » 45n45 89ø »u45r45 45n:;Þ » 45> »t67h:;Þ Upqr45i45n:;Þ *+g`aoDE TUs » 89ø » 67h:;Þ ΔbDE JK `ao>?r:;Þ Δ :; NOa45v>?i45n89g »t67h:;Þ ΔbBC BCd45y.
3
1


Noticing things and reacting
When you do sports, you notice things. You react with your body.
You use your senses, your brain and your nerves to make your body move.


Write the missing words. Then match..
tasting seeing touching hearing smelling


Put the words in the sentences. 2

How do you hear music?


16 sixteen 4
Yxyo>?u45® ÃsÇÉ HIn<=sÇÉÞ *+o@A *+d:; HIt:; NOhi <=s » 67h:;Þ ÃsÑÖo>?u45n89∂. Ttuh:;Þ » 89a67kvwÞ »t67h:;Þ »i45n67 `a >?r45m89a45 45i89o>?> » 89ø »t67h:;Þ »t89ø »t:; JK 67¬ »y`ao>?u45® ΔbBC BCd45y »w@Ah89a45† »t89ø *+d89ø.
Ãs~ò 89gfgh45† Ãs~òm:; JK 67¬
1 2 hearing nerves brain
How do you look after your senses? Tick the correct boxes.

– Read in places with good light.
– Rub your eyes with dirty hands.
– Listen to music softly.
– Avoid noisy places.

– Don’t eat very hot food or very cold food.
– Stick out your tongue.

– Touch very hot surfaces.

– Keep your skin clean.
– Blow your nose when you need to.
– Close your eyes.
What happens if you touch a cactus? Number the sentences in order from 1 to 3.
The brain tells your hand to move.

You notice the prick with your touch sense.
The nerves send information to the brain.


Take note!
You use your senses, your brain and your nerves to notice things. You react with your body.

U1 17 seventeen
3
4
Moving
You move your body when you do sports.
Movement is a way to react. You move with your locomotor system:
Skeleton
It is made up of bones and joints
Muscles
They are connected to your skeleton. They contract and relax to move your body.

Look at the pictures of the locomotor system. Add the missing arrows.
Wrist Skull
Elbow
Humerus
Shoulder
Ribs
Femur
Knee
Tibia

Ankle
Frontalis

Biceps
Pectoralis
Abdominals
Quadriceps
Calf
18 5
eighteen
1
Match and colour.
Bones
Wrist Biceps
3
Joints
Femur Abdominals
4

Muscles
Ankle Calf
– What emotion is the boy showing?

– What muscle makes lines on your forehead?

What parts of the skeleton protect your brain, your lungs and your heart? Write the names. Point to them on your body.
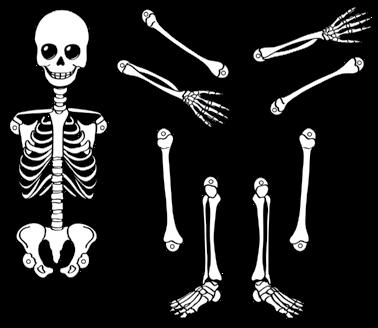
Dancing skeleton. 5
– Copy these bones on a piece of card. Cut out the pieces and make holes to join them.





– Join the pieces with a butterfly pin.
– Move the pieces to make your skeleton dance!
Go to anayaeducacion.es to find a big version of the bones.
Take note!
You use your locomotor system to dance, walk, do sports, etc.

U1 19 nineteen
2
Changing throughout life
You can do sports at any age.
These are the life stages:

until 12 years old Adolescence Childhood



until 20 years old until 70 years old from 70 years old Adulthood





Old age

Write


20 twenty 6
1
Match.
the life stages for these ages. 2 61 42 79 56 15 9 Childhood Old age Adulthood
0 years
Are you changing? Ask your family or look at baby photographs. 3
– Are you bigger? Complete the sentences.
– Colour the things that you can do.
How do adults help you? Write your favourite idea. 4


Let’s pretend
Pretend to be people in different life stages.
• Use a mirror to help you.
• Ask someone to guess the life stage.


Take note!
The life stages are childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age.
U1 21 twenty - one
Walk Complete tables Draw Add Read Plant seeds Swim Lie Talk Cook Write Ride a bike
I »wBCa<=s »†*+a67 67¬. Nñó >?∑ I’»µ . I »wDE HIi89gfgh:; NO∂ . Nñóo>?∑ I »wDE HIi89gfg™ .
W hat do I know?
1 Draw these body parts.

2 Write the names of these body parts. Then match.

3 Look at the picture and answer the questions.
– What life stages are the people in?
– Tick the box to show who is growing.


– Who knows how to do more things? Choose. The person on the right / left knows more because they are older / younger
4 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es.

22 PORTFOLIO
twenty - two Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it
Circulatory Respiratory Digestive Excretory *+a45n89∂ . brain mouth stomach eyes lungs bladder nose humerus tibia calf
TARGET IN ACTION
Sports are fun. They keep your body healthy. Think of ways for girls and boys to do sports together. For example:




Write down your ideas. Then share your ideas with your class.
L et’s reflect

1 How do you feel? Choose a face.
On my own

With others

U1 23
twenty - three
Ixyd:; NOa<=s Δ `a >?® Ãs~òp89o>?r45t<=s
2 Looking after your body
Children have the right to live well. You also have a duty to look after others.


What do you think?
Do you sometimes feel very hungry?

Do you get ill?
Who helps you?

Context
Lots of people don’t have clean water, food, a school or a health centre.


In this unit...
Target in action
Design a poster with ideas for helping people who live in poverty.
Follow the thread!
Health and illness
24 twenty - four
Food 2










25 twenty - five
hygiene 4 1
to eat well 3 Moving and resting Feeling emotions 6
Good
How
Health and illness

It is hard for people who live in poverty to look after their health.
You are healthy when your body works properly. You feel good and you interact well with others. When this does not happen, you are ill. The common cold and the flu are types of illness. When you are ill you get symptoms, like a cough or a fever.
Healthy habits can stop you from getting ill. For example:




– What symptom is this? Write it down.
– What illness can cause this symptom? Give an example.



– Do you ever have this illness? Tick the box.
Yes No
How does it make you feel?
26 1 twenty - six
Eating well Washing Doing exercise Going to the doctor Sleeping and resting Preventing accidents
1
To prevent back pain…
To cure an illness and check your health…



3
To prevent accidents…
Think of a rule that can help people in your school prevent accidents. Design a mini poster to explain it.
4

… go to the doctor.
… use protective equipment, like a helmet.
… sit properly and don’t carry a heavy bag.
Look at the picture. What do these children do to look after their health? What pain does it prevent?

Emergency situations

What do you need to do if there is a serious accident? Tick the box(es).
– Tell an adult.
– Ask for help.
– Call 112.
– Abandon the victim.
Take note!
Health and illness are opposites.
U2 27 twenty - seven Match. 2
Some people don’t have enough food. Sometimes, food makes people ill.
Types of food:
Natural
We can eat natural foods as we find them. For example, milk, eggs, and some fruit and vegetables.





Processed
We transform natural foods to make processed foods. For example, we transform milk to make cheese and cereals to bread.






Match. 1

It is made from cereals.
It is made from milk. They come from plants. We can eat them as we find them.
Natural food
Processed food


28 twenty - eight 2
Food
We can preserve foods to make them last longer.
How do people preserve these foods? Write your answers.




How long can we keep food for?
Foods can change and go bad.
Bad food can make you ill.
Check the label for the ‘use by date’. You can eat the food safely before this date, and the quality will be good.





See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es





Which of these foods can you eat? Tick the box(es).

Take note!
Foods can be natural or processed. We can preserve them to make them last longer.




U2 29 twenty - nine
2
In salt In vinegar Vacuum pack Cold storage
How to eat well
It is hard for people who live in poverty to follow a healthy diet.
You get the energy and substances that you need from food and water. Eating well means eating lots of different foods.

These foods give you energy.
These foods give your body substances that it needs to work properly.
See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es

These foods give you substances to help you grow and get strong.

30 3
thirty
Write one example for each type of food. 1




They give more energy than other types of food.
They give you substances to help you grow and get strong.
They give your body what it needs to work properly.
2

How many meals do children your age need? Colour the correct number.
Two 5 1 000 000 A thousand 10 + 1
3
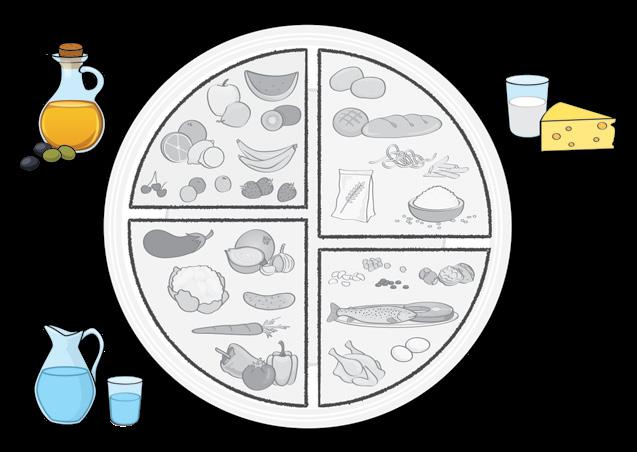
Find out what you need to eat and drink for your main meals. Then use the code to colour the food groups.
Fruits Cereals and potatoes
Vegetables Meat, fish and eggs
I’m a plate of healthy food.
Take note!
Think and share with a partner
What happens if you don’t eat well?
What happens if you eat too much/too little? What happens if you don’t drink enough water? Think and share your answer.
To be healthy, grow and get strong, you need to drink water and follow a varied diet.

U2 31 thirty - one
4
Good hygiene
Lots of people don’t have clean water for drinking or cleaning.

You can prevent illness by cleaning yourself, the things you use and where you live. This type of cleaning is called hygiene.

How to follow good hygiene:


Have a shower or a bath.
Wash your hands often with:
– soap, before and after eating.
– hand sanitiser, when you enter and leave indoor spaces.
Brush your teeth after you eat.

Keep your home clean.
Drink from your own bottle or cup.
What natural substance do you need to keep yourself clean? Say its name to your partner. Can you imagine a world without this substance? Why or why not?


Wash raw fruit and vegetables before you eat them.

32 thirty - two 4
1
What steps do you take for good hygiene?


What do you need to clean before and after you eat? Write.
What foods do you need to wash to prevent illness? Circle the correct ones. 3 Ideas













pool How can you keep your house clean? Share your ideas with the class. Write your favourite idea.
Take note! Let’s think
If someone has the flu and you drink from their bottle, can you get ill? Tick the box. Yes No

U2 33 thirty - three
2
4
5 Bno JK`ao>?r:;Þ: Atu jkt:; HI®:
You need water for good hygiene and to prevent illness. Order.
Moving and resting
Some people can’t do physical activity or get enough rest.
How to stay healthy:
Do physical exercise
Doing sports or another physical activity makes you strong and helps you to feel good. You can protect your body to stop you getting hurt. For example, you can wear a helmet and knee pads.

Rest and sleep
Children your age need to sleep at least ten hours.

What physical activity do you enjoy? Write.
What is this kind of protection called? Write.
How does exercise make you feel? What does it give you? Colour your answers.
Fun
Tired
Angry Bored
Good health Friends




Team spirit
How do you feel when you run, dance or do sports? Colour.


34 5
thirty - four
1
2
3
4
Elbow pads

Goggles Helmet


Shin pads

– Do you sleep enough? Tick the box. Yes No


– How do you feel when you sleep well and rest? Mark your answer.
I’m happy and I can concentrate.
Move your body.
Do these actions:
– swim – run

– sleep – dance
I feel bad, angry or sad, and I can’t concentrate.
I don’t feel anything special.

Take note!
Ask a partner to guess what you are doing. You need to do exercise safely and sleep for ten hours every day.
U2 35 thirty - five Complete the crossword. 5
6
Feeling emotions
Helping people in need makes you feel good.
There are different ways to express your emotions and feelings:
– Talking and doing things with your friends.
– Telling someone you trust about your problems.
– Solving problems without getting angry or fighting.
– Helping people in need, and asking for help when you need it.


Can you identify your emotions?
People get excited when they are happy. They get agitated when they are angry or scared. When you feel these emotions, your body responds.
1 What makes you excited or agitated?
2 What happens when you feel excited or anxious? Tick the box(es).
I tremble I sweat
I don’t sleep well
My heart beats fast My body hurts
I can’t breathe properly
When you feel angry with someone, what do you need to do? Tick the box(es). 1
Try to understand why you feel that way.
Say sorry and find solutions.
Talk about what happened and say how you feel.
Say nothing, shout, argue and fight.
36 thirty - six 6
Nothing
Put yourself in their place.
Read and answer the questions.
• How does Luis feel? Write and draw.


Hi, I’m Luis. I don’t have clean water for washing.

• Imagine you are Luis. How do you feel? Tick your answer.
Happy Sad I don’t know Scared Nothing
• Imagine that Luis is different from the rest of the class. Do you all treat him the same? Tick the box.
Yes No I don’t know
• Ideas pool How can you help Luis? Think and share your ideas.

• Write your favourite idea for helping Luis.
Take note!
Identify and express your emotions, and respect how other people feel, to be healthy.
U2 37 thirty - seven
W hat do I know?
1 Draw an object. Then invent a rule to prevent accidents.
2 Write.
A food that you preserve in vacuum packs. Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it


A food that you preserve in salt.
3 Circle the foods that give your body what it needs to grow and get strong.


4 What do you need to do to be healthy? Tick the box(es).
– Eat two meals a day and sleep for three hours.
– Drink water and follow a varied diet.


– Identify and express your emotions.
– Do exercise: sport, dance, etc.
5 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es

38 PORTFOLIO
thirty - eight
A food that you preserve in cold storage.
Think of ideas for helping people in poverty and for improving their health and well being. Write your ideas here. Then make a poster.
1 Write your answers. When did you feel...?

Happy Sad

Surprised Scared
2 How did you do? Colour like this: Great Average I can improve
– Asking for help.

– Learning new things.
– Trying hard.
– Working well on my own.
U2 39
thirty - nine
TARGET IN ACTION L et’s reflect
1 Match these cards to make pairs.
2 Play ‘taboo’ with this part of the body!
Give clues to help work out the part of the body. Write two words. You can’t use the words ‘circulatory’ or ‘beat’.

and

3 Some of these sentences are lies. Put a cross in the boxes next to the lies.
The thorax is in the trunk.


The intestines are in the abdomen.
The lungs are part of the digestive system.
Waste leaves the body in the urine.

The biceps is a very long bone.
Adulthood starts at 8 years old.
40 TERM forty
4 Unscramble the letters to find the answer to the question.
What is the large muscle in your leg?
sTEAM

Marie Curie

Do you know about a scientist
Whose first name was Marie?
Her last name was Sklodowska, Then she changed it for Curie.
She discovered that some minerals Had the wonderful ability, To produce strange rays and particles, And she called it radiactivity
These beams are very interesting And they have amazing powers. They can travel through a brick wall Through a hand or through a flower.
Marie discovered two elements
That were naturally radioactive: They are Pollonium and Radium. She was really creative!

Mary had amazing talent, So it is not a surprise That she got a nobel prize And not once; she got it twice!
Listen to the poem and share it with your family.

41 REVIEW
forty - one
s p a r d i c e u q
PROJECTS THATANIMPRINT LEAVE
DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT

A picture is worth...
CHANGES AROUND US
People change a lot over the years. Think about it, your body changes, the way you think changes, the things you buy change… Everything changes!
Let’s take a ‘snapshot’ of the changes in shops and the products we consume.
Do you know where the products you consume come from?
Think about products like fruit, fish, bread and milk. Where do people grow, catch or make them? Where do you buy them? Answer the questions and discuss them in class.
Choose a food shop and prepare the information you need to get your ‘snapshot’ of it: What does it sell? Where is it?… Then, write questions to interview someone who works there. For example, “ Which products are very popular? ”


42
forty - two
1 P i ensa THINK
2
D iseña
DESIGN
Perform your interview and take photographs of the shop, the person you interview and the products.


4 PRESENTA PRESENT
Select your favourite photos and create a photo gallery. Write short descriptions under the photos. Give your gallery a title.
TEST 5
What can you learn from your ‘snapshot’?
Think about the products you buy, the shops that sell them, etc.

43
TERM 1 forty - three
P resent a 3 CONSTRUYE MAKE C o n stru y e
C o mpru e b a

2
LEARNING EXPERIENCE TARGET IN ACTION SDG
• Learning experience: A short text and pictures of children in everyday situations (looking through a magnifying glass, doing sport, etc.) introduce the study of the human body.
• Target in action: List some sports that boys and girls can do together.

• Learning experience: An adaptation of the fourth right of childhood, and pictures of children smiling, doing sport, etc. encourage reflection on the idea of wellbeing, especially for people who struggle to maintain healthy habits because of their circumstances.
• Target in action: Design a poster with ideas for helping people who live in poverty.

4
• Learning experience: A short text and a picture of a girl swimming among animals introduce the study of living beings and the need to respect them.
• Target in action: Create a wall display about respecting animals on land and in the sea.

• Learning experience: A text about spring and a photo of a girl looking through binoculars and surrounded by illustrations of living beings, introduce the importance of understanding and protecting living beings.
• Target in action: Create a wall display about the importance of animals and how you can protect them.
5
• Learning experience: A text on the importance of the Earth, and a picture of a girl, plants, animals and wind turbines introduce the topic of matter and energy, as well as energy saving.
• Target in action: Create a poster to help combat climate change.
6
• Learning experience: An image of a robot hand introduces two projects, one involving the construction of a simple machine and the other requiring the use of ICT.
• Target in action: Create a sustainable project.



Gender equality
What are we going to learn?
Your body 8 44
I love animals!
1
3
Looking after nature
A clean planet! 80
Looking after your body 24 60
All about
98 PAGE.
technology
No poverty Life below water Climate action Life on land Sustainable cities and communities INTERDISCIPLINAR
TERM 1 REVIEW STEAM: Marie Curie
TERM 2 REVIEW STEAM: Jane Goodall
TERM 3 REVIEW STEAM: Hedy Lamarr
KNOWLEDGE TO LEARN, APPLY AND INVESTIGATE
• Your body.
• Breathing and eating.
• Transporting substances and excreting waste.
• Noticing things and reacting.
• Moving.
• Changing throughout life.
• Health and illness.
• Food.
• How to eat well.
• Good hygiene.
• Moving and resting.
• Feeling emotions.
• There are many living beings.
• Classifying Animals.
• Discovering mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates.
• Observing and respecting animals.
Competence-based activities
• Let’s get some fresh air!
• Let’s think: How does your body get the substances you need?
• Taking your pulse.
• Let’s pretend.
Competence-based activities
• Emergency situations.
• How long can we keep food for?
• Let’s think: What steps do you take for good hygiene?
• Move your body.
• Can you identify your emotions?
• Put yourself in their place.
Competence-based activities
• Classifying helps us understand.
• Investigate.
• Let’s think: Putting things in order.
• Are some animals ‘bad’?
Competence-based activities
• Plants are everywhere!
• Plants are really important!
• Plants are fascinating!
• Observing nature.
• We are part of nature.
• We want nature to be healthy.
• Using outlines.
• Plant food.
• Plants are really important.
• Do plants react to light?
• Seed hunters.
• Natural balance.
• Let’s think: The What if…
• What is matter?
• How do we use matter?
• How does matter change state?
• How does matter change?
• Where is energy?
• How can we look after the planet?
Competence-based activities
• How can we measure mass and volume?
• Experimenting with matter.
• Let’s think: What is water like in nature?
• Look! No hands!
• Take action for the planet.
Competence-based activities
• Everyday technology.
• ICT.
• What is a project?
• My first project: build.
• My second project: programing.
• Internet research.
• Why do we need projects?
• Let’s think: Building a machine.
• Let’s think: Creating a computer program.
• Let’s think: Creating a computer program (continued).
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · A picture is worth…: Changes around us
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Commit to birds: Food and drink for birds
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Tic-Tac-Smile!: Investigating the past
Get to know your book
What is the use of what I learn?


Each unit gives a learning experience and an objective.
Follow the thread!

We discover basic knowledge through a learning situation.


Skills activities
Learning by doing motivating tasks...


Take note!

Dis c o v e r ing m a m m a ls, bir ds, r ep tile s, a mp hibia n s, fish a n d in v e r te br a te s Obs e r v ing a n d r e sp e c ting a n im a ls 3 14
SDG
W hat do I know?










1 Write the names of the parts of the plants. Look

































Choose a living being in your local area, complete this logic wheel. Create a wall display classroom about living beings and add your





Threats What it interacts




13 thirteen You breathe with your respiratory system. You eat with your digestive system. Take note! 78 79 Are feeding stations for birds important? What food can you put on them? Ask an adult to help you search the internet for some examples of feeding stations made from recycled materials. Draw the feeding station you want to make on a piece of paper. Label your design with the recycled materials you want to use: cans, bottles, lolly sticks, cartons, etc. Decide what food you want to put on it and where to put the water. Ask an adult to help you build your feeding station. Make all the parts and put them together. Put food and water on your station. Ask an adult to help you hang your feeding station where you want it. Take photos of the birds that come to eat and drink. Show them to your classmates. What do you know about birds now? Are you helping these animals? Is the feeding station an improvement to the local environment? Birds in towns have problems finding food and drink. Can you help them? FOOD AND DRINK FOR BIRDS TERM 2 seventy - nine seventy - eight Let’s make a feeding station for birds! Commit to birds: DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT 4 PRESENTA PRESENT e nt a 1 P nsa THINK D seña 2 DESIGN 3 C ONSTRUYE MAKE ru e TEST 5 C ompru a PROJECTS THATANIMPRINT LEAVE U4 PORTFOLIO TARGET IN ACTION What do I know? seventy - four Choose a living being in your local area, then copy and complete this logic wheel. Create a wall display in your classroom about living beings and add your logic wheel. 1 Write the names of the parts of the plants. 2 Look at the picture of a maple. Complete the sentences. – It is a because of the stem (trunk). – It is because of how it reacts in autumn. – It produces fruit with to reproduce. – It is really important because 4 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es fruit with seeds 3 Match the problems and solutions. Air pollution. Extinction of living beings. Too much waste. Separate and recycle waste. Use transport that doesn’t pollute. Protect the natural environment. Colour like this: 40 41 REVIEW TERM sTEAM 4 Unscramble the letters to find the answer to the question. forty - one forty 1 Match these cards to make pairs. 2 Play ‘taboo’ with this part of the body! 3 Some of these sentences are lies. Put a cross in the boxes next to the lies. Listen to the poem and share it with your family. Marie Curie Do you know about a scientist Whose first name was Marie? Her last name was Sklodowska, Then she changed it for Curie. She discovered that some minerals Had the wonderful ability, To produce strange rays and particles, And she called it radiactivity These beams are very interesting And they have amazing powers. They can travel through a brick wall Through a hand or through a flower. Marie discovered two elements That were naturally radioactive: They are Pollonium and Radium. She was really creative! Mary had amazing talent, So it is not a surprise That she got a nobel prize And not once; she got it twice! s p a r d i c e u q Give clues to help work out the part of the body. Write two words. You can’t use the words ‘circulatory’ or ‘beat’. The thorax is in the trunk. The intestines are in the abdomen. The lungs are part of the digestive system. Waste leaves the body in the urine. The biceps is a very long bone. Adulthood starts at 8 years old. and What is the large muscle in your leg? PORTFOLIO
L et’s reflect
TARGET IN ACTION
1
at the picture of a maple.
the
of the stem (trunk). because of how it reacts in – It produces fruit with to reproduce. – It is really important because fruit with seeds
Complete
sentences. because
My living being is Actions to protect it
with Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it U3 53 fifty - three amphibians, … Look at the animals. Complete. 1 A m45p67h45 67 45n<=s, ~òu de™ <= r ÄÅs, a r:; HIr45 :; JK >?r89a45 :; TU w>? 67™ Δ BCa r:;Þ, z{kVW 45>. Atu67 *+ 45m45p67h45 67 89 45n<= *+ 45r:; Mñó ~ò h 45 `a u45® a n89∂ 89 45y 45> w a :; ®. Frog Toad Newt 1 Let’s Putting things in order. a45® g 67™ 3 2 4 U3 … amphibians, … Look at the animals. Complete. 1 AVWm45p67h45 67b>? 89a45n<=s, Ãs~òu89de™ *+a<=s Δjkr89 BCgÄÅs, *+a45r:;Þ »vDE HIr45 :; JKb>?r89a45 :; TUs »w>? 45 67™ ΔbBCa45r:;Þ, sz{kVW 45>. Atu67¬ *+a45m45p67h45 67b>? 89a45n<=s *+a45r:;Þ Mñó 23s~ò† Δh89a45vDEÞ Δ`a >?u45® *+a45n89∂ Δ89a45y » 45> »wBCa45 :; HI®. Frog Toad 1 2 Why do amphibians live next to fresh water or in very damp places? Make a sentence: Let’s think Putting things in order. babies and their Because need their water eggs 3 2 4 1 7 5 8 6 *+^_a45® NOg »t67™ Δ :;Þ 3 1 2 4 eggs tadpole tadpole with legs frog U1 13 thirteen The digestive system uses food to get substances that your body needs. It removes the waste that you don’t need. Write the names of the body parts. 2 You breathe with your system.respiratory You eat with your digestive system. Take note! Put the stages in order. Let’s think How does your body get the substances you need? This is the digestive system. Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Intestines Travelling to the stomach Chewing Excreting waste Getting substances Digesting STEAM space Discover a female scientist solving a mystery.
Term review With fun activities. Interdisciplinary Project To integrate the different areas of knowledge with a common goal. Icons Cooperative learning Emotional education Gamification ICT
Learning to think Audio Assessment Tar ge t i n a c t i o n Portfolio We check what we have learned and reflect on it.
And for each term...
SDG
Your digital project























A project that offers you all the content of the course through the digital book, along with a wide variety of resources. Discover another way of learning that is simple, intuitive and compatible with any platform and device.


How do you access it?

U3 54 55 fifty - five fifty - four Look at the animal. Complete. 1 Order the letters. Circle the fish that doesn’t live in the sea. 2 Invertebrates are the most abundant animals. There are lots of different types. Match. 1 Look at the pictures again. Which are marine animals? Choose two. Write their names. 2 Shared interpretation Say how these invertebrates are similar and different. 3 … and invertebrates fish, … FVW <= z{™, ~òu89de™ *+ <= 45r67b JK¬, *+ 45r:; v HIr45 :;JK r89 45 :;TUs. Ttuh HIy 45 45 DE *+a45n89∂ Δ r:;NO 4567h:; 45> Mñó ~ò Δ <= z{™ 45r:;Þ *+^_ HIr:;NO∂ > 45n89∂ Δh89a v Δ ® ~òw>? 45m45m45 45n89g. Mñóa n y a r:; fins scales S T A ¹ H R T HKSRA NATU HYAVCNO AYR EAKH CDO TOTRU There are lots of different marine and land animals. They are all important. Take note! Long body. No shell. No legs. Shaped like a bag. Poisonous tentacles. No shell. Muscular body. Shell or no shell. Tentacles or none. Shell. Several pairs of legs. Some have wings. Shaped like a ball or a star. Spiny shell. ∑ Δ ø ÑÖ 98 ninety-eight pollution. They use lots of energy. Eve yday techno ogy What a pro ect? My f rst project bu d ng F o o w t h e t h r e a d ! n orma ion and Commun cation Techno ogy CT 1 2 3 4 6 All about technology Target in action Create machines and computer programs that promote sustainable technology. In this unit… What do you think? Can you imagine the world without machines and technology? What is it like? Technology is about imagining new things. Close your eyes and free your imagination!
You have all the necessary instructions to access it next to the first page of your book. Go to Liria
11
What does it offer?
It contains diversity of resources; it is much more than a reproduction of the paper book.

With them you can: Do exercises interactive activities Study interactive summaries, outlines... Learn audios, videos, gameroom... Assess self-assessment, portfolio...


What’s it like?
A global response for a diverse educational environment.

Intuitive
Easy to use. Multi device
You can use it with any type of device (computer, tablet, smartphone…) to any screen size and resolution.


Downloadable
It allows you to work without an Internet connection and download it on more than one device.
Synchronically
Any changes you make are automatically synced when you connect to any of the devices you’re using it on.

Universal Compatible with all operating systems, virtual learning environments (EVA) and educational platforms (LMS) most used in schools.


99 ninety-nine My se o d programming 5
DOC to the cabin! needs you!
1 Your body
Redhead, blond, dark-haired, tall, short... The world is really diverse!

What do you think?
Can everyone do the same sports?
Today, everybody can do the sport they want. Men and women do some sports separately, like gymnastics, and some sports together.

In this unit...
Target in action
List some sports that boys and girls can do together.


Your body the thread!

2
Breathing and eating
8 eight










9 nine Transporting substances and excreting waste Moving Noticing things and reacting Changing throughout life 3 6 5
1
Your body
Your body can help you do sports and other activities.
Your body lets you live!
What is your body like on the outside? Trace the missing arrows.
Upper limbs
Arm Hand
Lower limbs



Leg
Foot

Head Face Trunk Back Thorax Abdomen
Write the words in the correct place. 2
Forehead Ears Cheeks

Lips
Chin
Eyebrows
Eyes
Nose
Mouth
mouth hand foot forehead back leg thorax arm

Head Trunk Limbs
Circle three words that mean abdomen. 3
face stomach back belly tummy thorax
10 1 ten
You have muscles and bones under your skin. You have a brain, lungs, heart and other organs inside your body.



Ideas pool

What do you need to stay alive?

Write down an idea. Then tell your group.
Take note!
Your body has outside parts that you can see, and inside parts that you can’t see. You use all these parts to play sports!

U1 11 eleven Match. 4
5
Inside the head Brain Stomach Intestines Lungs Heart lnside the thorax Inside the abdomen Muscles Bones Brain Heart Stomach Intestines Lungs Under the skin Inside the body
Breathing and eating
You need to breathe and eat well to play sports.
You breathe in to get oxygen. You breathe out the air you don’t need.
You do this with your respiratory system.


How does air go in and out when you breathe? Write the missing words.
– Where does air come in and out?
– Where does the air go?
This is the respiratory system. in out

Let’s get some fresh air!
1 Breathe in and out. Watch your chest. Tick the correct box.
• My chest expands when I breathe in.
• My chest expands when I breathe out.
2 What do you do when you get some fresh air? Tick the box.
• I go outside, I ride my bike, or I do other outdoor activities.

• I brush my teeth and stay indoors.

12 twelve 2
1 Ttuh45r89 >?u89gfg™ » 67h:;Þ *+o>?® Txyø » 67h:;Þ , »w@Ah45i89de™ » 89a67kvwÞ »t67h:;Þ *+o>?xVWy`ag|} HI>.
Nose Mouth Lungs
This is the digestive system.
The digestive system uses food to get substances that your body needs. It removes the waste that you don’t need.




Let’s think
How does your body get the substances you need?
Put the stages in order.
Travelling to the stomach
Excreting waste
Chewing
Getting substances
Oesophagus
Digesting
Write the names of the body parts. 2

Take note!
You breathe with your respiratory system. You eat with your digestive system.

U1 13 thirteen
Mouth
Stomach
Intestines
Transporting substances and excreting waste
Being active helps you stay healthy. It makes your heart strong.
This is the circulatory system.
The circulatory system uses blood to take substances around your body. For example, oxygen. It collects substances that you don’t need.

Blood moves around the body inside the blood vessels. The heart pumps the blood.
See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es




Draw the body part that moves the blood. Write its name. Put your hand on this part of your body. Can you feel it?

Taking your pulse
Take your pulse to feel your heart working! Put two fingers on the blood vessels in your wrist. Can you feel the beats? These are from your heart.
Count how many beats you feel in one minute (get a partner to help you). First, count when you are resting. Then, count after some exercise. Write down your results and tell the class.
Resting After exercise
14 3
fourteen
1
Heart
Blood vessels
This is the excretory system.
The excretory system removes waste that you don’t need. The blood collects the waste. The waste leaves your body in the urine.

Kidneys Bladder
Timeline Put in order from 1 to 3.

The blood takes waste to the kidneys.
Write the missing words. Then colour like this: for the kidneys for the bladder
Waste turns into urine in the kidneys.


The urine stays in the bladder before it leaves the body. Take nota!
The circulatory system takes substances around the body. The excretory system removessubstances from the body.

U1 15 fifteen
2
Wxya<=s~ò :;Þ »t45u45r45n<=s » 45n45 89ø »u45r45 45n:;Þ » 45> »t67h:;Þ Upqr45i45n:;Þ *+g`aoDE TUs » 89ø » 67h:;Þ ΔbDE JK `ao>?r:;Þ Δ :; NOa45v>?i45n89g »t67h:;Þ ΔbBC BCd45y.
3
1


Noticing things and reacting
When you do sports, you notice things. You react with your body.
You use your senses, your brain and your nerves to make your body move.


Write the missing words. Then match..
tasting seeing touching hearing smelling


Put the words in the sentences. 2

How do you hear music?


16 sixteen 4
Yxyo>?u45® ÃsÇÉ HIn<=sÇÉÞ *+o@A *+d:; HIt:; NOhi <=s » 67h:;Þ ÃsÑÖo>?u45n89∂. Ttuh:;Þ » 89a67kvwÞ »t67h:;Þ »i45n67 `a >?r45m89a45 45i89o>?> » 89ø »t67h:;Þ »t89ø »t:; JK 67¬ »y`ao>?u45® ΔbBC BCd45y »w@Ah89a45† »t89ø *+d89ø.
Ãs~ò 89gfgh45† Ãs~òm:; JK 67¬
1 2 hearing nerves brain
How do you look after your senses? Tick the correct boxes.

– Read in places with good light.
– Rub your eyes with dirty hands.
– Listen to music softly.
– Avoid noisy places.

– Don’t eat very hot food or very cold food.
– Stick out your tongue.

– Touch very hot surfaces.

– Keep your skin clean.
– Blow your nose when you need to.
– Close your eyes.
What happens if you touch a cactus? Number the sentences in order from 1 to 3.
The brain tells your hand to move.

You notice the prick with your touch sense.
The nerves send information to the brain.


Take note!
You use your senses, your brain and your nerves to notice things. You react with your body.

U1 17 seventeen
3
4
Moving
You move your body when you do sports.
Movement is a way to react. You move with your locomotor system:
Skeleton
It is made up of bones and joints
Muscles
They are connected to your skeleton. They contract and relax to move your body.

Look at the pictures of the locomotor system. Add the missing arrows.
Wrist Skull
Elbow
Humerus
Shoulder
Ribs
Femur
Knee
Tibia

Ankle
Frontalis

Biceps
Pectoralis
Abdominals
Quadriceps
Calf
18 5
eighteen
1
Match and colour.
Bones
Wrist Biceps
3
Joints
Femur Abdominals
4

Muscles
Ankle Calf
– What emotion is the boy showing?

– What muscle makes lines on your forehead?

What parts of the skeleton protect your brain, your lungs and your heart? Write the names. Point to them on your body.

Dancing skeleton. 5
– Copy these bones on a piece of card. Cut out the pieces and make holes to join them.





– Join the pieces with a butterfly pin.
– Move the pieces to make your skeleton dance!
Go to anayaeducacion.es to find a big version of the bones.
Take note!
You use your locomotor system to dance, walk, do sports, etc.

U1 19 nineteen
2
Changing throughout life
You can do sports at any age.
These are the life stages:

until 12 years old Adolescence Childhood



until 20 years old until 70 years old from 70 years old Adulthood





Old age

Write


20 twenty 6
1
Match.
the life stages for these ages. 2 61 42 79 56 15 9 Childhood Old age Adulthood
0 years
Are you changing? Ask your family or look at baby photographs. 3
– Are you bigger? Complete the sentences.
– Colour the things that you can do.
How do adults help you? Write your favourite idea. 4


Let’s pretend
Pretend to be people in different life stages.
• Use a mirror to help you.
• Ask someone to guess the life stage.


Take note!
The life stages are childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age.
U1 21 twenty - one
Walk Complete tables Draw Add Read Plant seeds Swim Lie Talk Cook Write Ride a bike
I »wBCa<=s »†*+a67 67¬. Nñó >?∑ I’»µ . I »wDE HIi89gfgh:; NO∂ . Nñóo>?∑ I »wDE HIi89gfg™ .
W hat do I know?
1 Draw these body parts.



2 Write the names of these body parts. Then match.

3 Look at the picture and answer the questions.

– What life stages are the people in?
– Tick the box to show who is growing.


– Who knows how to do more things? Choose. The person on the right / left knows more because they are older / younger
4 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es.

22 PORTFOLIO
twenty - two Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it
Circulatory Respiratory Digestive Excretory *+a45n89∂ . brain mouth stomach eyes lungs bladder nose humerus tibia calf
TARGET IN ACTION
Sports are fun. They keep your body healthy. Think of ways for girls and boys to do sports together. For example:




Write down your ideas. Then share your ideas with your class.
L et’s reflect

1 How do you feel? Choose a face.
On my own

With others

U1 23
twenty - three
Ixyd:; NOa<=s Δ `a >?® Ãs~òp89o>?r45t<=s
2 Looking after your body
Children have the right to live well. You also have a duty to look after others.


What do you think?
Do you sometimes feel very hungry?

Do you get ill?
Who helps you?

Context
Lots of people don’t have clean water, food, a school or a health centre.


In this unit...
Target in action
Design a poster with ideas for helping people who live in poverty.
Follow the thread!
Health and illness
24 twenty - four
Food 2










25 twenty - five
hygiene 4 1
to eat well 3 Moving and resting Feeling emotions 6
Good
How
Health and illness

It is hard for people who live in poverty to look after their health.
You are healthy when your body works properly. You feel good and you interact well with others. When this does not happen, you are ill. The common cold and the flu are types of illness. When you are ill you get symptoms, like a cough or a fever.
Healthy habits can stop you from getting ill. For example:





– What symptom is this? Write it down.
– What illness can cause this symptom? Give an example.



– Do you ever have this illness? Tick the box.
Yes No
How does it make you feel?
26 1 twenty - six
Eating well Washing Doing exercise Going to the doctor Sleeping and resting Preventing accidents
1
To prevent back pain…
To cure an illness and check your health…



3
To prevent accidents…
Think of a rule that can help people in your school prevent accidents. Design a mini poster to explain it.
4

… go to the doctor.
… use protective equipment, like a helmet.
… sit properly and don’t carry a heavy bag.
Look at the picture. What do these children do to look after their health? What pain does it prevent?

Emergency situations

What do you need to do if there is a serious accident? Tick the box(es).
– Tell an adult.
– Ask for help.
– Call 112.
– Abandon the victim.
Take note!
Health and illness are opposites.
U2 27 twenty - seven Match. 2
Some people don’t have enough food. Sometimes, food makes people ill.
Types of food:
Natural
We can eat natural foods as we find them. For example, milk, eggs, and some fruit and vegetables.





Processed
We transform natural foods to make processed foods. For example, we transform milk to make cheese and cereals to bread.






Match. 1

It is made from cereals.
It is made from milk. They come from plants. We can eat them as we find them.
Natural food
Processed food


28 twenty - eight 2
Food
We can preserve foods to make them last longer.
How do people preserve these foods? Write your answers.




How long can we keep food for?
Foods can change and go bad.
Bad food can make you ill.
Check the label for the ‘use by date’. You can eat the food safely before this date, and the quality will be good.





See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es





Which of these foods can you eat? Tick the box(es).

Take note!
Foods can be natural or processed. We can preserve them to make them last longer.




U2 29 twenty - nine
2
In salt In vinegar Vacuum pack Cold storage
How to eat well
It is hard for people who live in poverty to follow a healthy diet.
You get the energy and substances that you need from food and water. Eating well means eating lots of different foods.

These foods give you energy.
These foods give your body substances that it needs to work properly.
See ‘Let me tell you’ on anayaeducacion.es

These foods give you substances to help you grow and get strong.

30 3
thirty
Write one example for each type of food. 1




They give more energy than other types of food.
They give you substances to help you grow and get strong.
They give your body what it needs to work properly.
2

How many meals do children your age need? Colour the correct number.
Two 5 1 000 000 A thousand 10 + 1
3
Find out what you need to eat and drink for your main meals. Then use the code to colour the food groups.
Fruits Cereals and potatoes
Vegetables Meat, fish and eggs
I’m a plate of healthy food.
Take note!
Think and share with a partner
What happens if you don’t eat well?
What happens if you eat too much/too little? What happens if you don’t drink enough water? Think and share your answer.

To be healthy, grow and get strong, you need to drink water and follow a varied diet.

U2 31 thirty - one
4
Good hygiene
Lots of people don’t have clean water for drinking or cleaning.

You can prevent illness by cleaning yourself, the things you use and where you live. This type of cleaning is called hygiene.

How to follow good hygiene:


Have a shower or a bath.
Wash your hands often with:
– soap, before and after eating.
– hand sanitiser, when you enter and leave indoor spaces.
Brush your teeth after you eat.

Keep your home clean.
Drink from your own bottle or cup.
What natural substance do you need to keep yourself clean? Say its name to your partner. Can you imagine a world without this substance? Why or why not?


Wash raw fruit and vegetables before you eat them.

32 thirty - two 4
1
What steps do you take for good hygiene?


What do you need to clean before and after you eat? Write.
What foods do you need to wash to prevent illness? Circle the correct ones. 3 Ideas













pool How can you keep your house clean? Share your ideas with the class. Write your favourite idea.
Take note! Let’s think
If someone has the flu and you drink from their bottle, can you get ill? Tick the box. Yes No

U2 33 thirty - three
2
4
5 Bno JK`ao>?r:;Þ: Atu jkt:; HI®:
You need water for good hygiene and to prevent illness. Order.
Moving and resting
Some people can’t do physical activity or get enough rest.
How to stay healthy:
Do physical exercise
Doing sports or another physical activity makes you strong and helps you to feel good. You can protect your body to stop you getting hurt. For example, you can wear a helmet and knee pads.

Rest and sleep
Children your age need to sleep at least ten hours.

What physical activity do you enjoy? Write.
What is this kind of protection called? Write.
How does exercise make you feel? What does it give you? Colour your answers.
Fun
Tired
Angry Bored
Good health Friends




Team spirit
How do you feel when you run, dance or do sports? Colour.


34 5
thirty - four
1
2
3
4
Elbow pads

Goggles Helmet


Shin pads

– Do you sleep enough? Tick the box. Yes No


– How do you feel when you sleep well and rest? Mark your answer.
I’m happy and I can concentrate.
Move your body.
Do these actions:
– swim – run

– sleep – dance
I feel bad, angry or sad, and I can’t concentrate.
I don’t feel anything special.

Take note!
Ask a partner to guess what you are doing. You need to do exercise safely and sleep for ten hours every day.
U2 35 thirty - five Complete the crossword. 5
6
Feeling emotions
Helping people in need makes you feel good.
There are different ways to express your emotions and feelings:
– Talking and doing things with your friends.
– Telling someone you trust about your problems.
– Solving problems without getting angry or fighting.
– Helping people in need, and asking for help when you need it.


Can you identify your emotions?
People get excited when they are happy. They get agitated when they are angry or scared. When you feel these emotions, your body responds.
1 What makes you excited or agitated?
2 What happens when you feel excited or anxious? Tick the box(es).
I tremble I sweat
I don’t sleep well
My heart beats fast My body hurts
I can’t breathe properly
When you feel angry with someone, what do you need to do? Tick the box(es). 1
Try to understand why you feel that way.
Say sorry and find solutions.
Talk about what happened and say how you feel.
Say nothing, shout, argue and fight.
36 thirty - six 6
Nothing
Put yourself in their place.
Read and answer the questions.
• How does Luis feel? Write and draw.


Hi, I’m Luis. I don’t have clean water for washing.

• Imagine you are Luis. How do you feel? Tick your answer.
Happy Sad I don’t know Scared Nothing
• Imagine that Luis is different from the rest of the class. Do you all treat him the same? Tick the box.
Yes No I don’t know
• Ideas pool How can you help Luis? Think and share your ideas.

• Write your favourite idea for helping Luis.
Take note!
Identify and express your emotions, and respect how other people feel, to be healthy.
U2 37 thirty - seven
W hat do I know?
1 Draw an object. Then invent a rule to prevent accidents.
2 Write.
A food that you preserve in salt.
A food that you preserve in vacuum packs. Colour like this: I need help I don’t know how to do it I know how to do it


3 Circle the foods that give your body what it needs to grow and get strong.


4 What do you need to do to be healthy? Tick the box(es).
– Eat two meals a day and sleep for three hours.
– Drink water and follow a varied diet.


– Identify and express your emotions.
– Do exercise: sport, dance, etc.
5 Remember to complete your photo album for this unit on anayaeducacion.es

38 PORTFOLIO
thirty - eight
A food that you preserve in cold storage.
Think of ideas for helping people in poverty and for improving their health and well being. Write your ideas here. Then make a poster.
1 Write your answers. When did you feel...?

Happy Sad

Surprised Scared
2 How did you do? Colour like this: Great Average I can improve
– Asking for help.

– Learning new things.
– Trying hard.
– Working well on my own.
U2 39
thirty - nine
TARGET IN ACTION L et’s reflect
1 Match these cards to make pairs.
2 Play ‘taboo’ with this part of the body!
Give clues to help work out the part of the body. Write two words. You can’t use the words ‘circulatory’ or ‘beat’.

and

3 Some of these sentences are lies. Put a cross in the boxes next to the lies.
The thorax is in the trunk.


The intestines are in the abdomen.
The lungs are part of the digestive system.

Waste leaves the body in the urine.



The biceps is a very long bone.
Adulthood starts at 8 years old.

40 TERM forty
4 Unscramble the letters to find the answer to the question.
What is the large muscle in your leg?
sTEAM

Marie Curie

Do you know about a scientist
Whose first name was Marie?
Her last name was Sklodowska, Then she changed it for Curie.
She discovered that some minerals Had the wonderful ability, To produce strange rays and particles, And she called it radiactivity
These beams are very interesting And they have amazing powers. They can travel through a brick wall Through a hand or through a flower.
Marie discovered two elements
That were naturally radioactive: They are Pollonium and Radium. She was really creative!

Mary had amazing talent, So it is not a surprise That she got a nobel prize And not once; she got it twice!
Listen to the poem and share it with your family.

41 REVIEW
forty - one
s p a r d i c e u q
PROJECTS THATANIMPRINT LEAVE
DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT

A picture is worth...
CHANGES AROUND US
People change a lot over the years. Think about it, your body changes, the way you think changes, the things you buy change… Everything changes!
Let’s take a ‘snapshot’ of the changes in shops and the products we consume.
Do you know where the products you consume come from?
Think about products like fruit, fish, bread and milk. Where do people grow, catch or make them? Where do you buy them? Answer the questions and discuss them in class.
Choose a food shop and prepare the information you need to get your ‘snapshot’ of it: What does it sell? Where is it?… Then, write questions to interview someone who works there. For example, “ Which products are very popular? ”


42
forty - two
1 P i ensa THINK
2
D iseña
DESIGN
Perform your interview and take photographs of the shop, the person you interview and the products.


4 PRESENTA PRESENT
Select your favourite photos and create a photo gallery. Write short descriptions under the photos. Give your gallery a title.
TEST 5
What can you learn from your ‘snapshot’?
Think about the products you buy, the shops that sell them, etc.

43
TERM 1 forty - three
P resent a 3 CONSTRUYE MAKE C o n stru y e
C o mpru e b a






























































































































































































































