1
ä 1.1 Basic concepts
CHEMICAL CHANGES
In a chemical reaction, we begin with substances called reactants, which are there before the chemical change. Then, new substances appear called products, which are a result of the chemical change. The reactants must be in contact for a chemical change to occur. Physical changes occur during the process too, which make the change visible. You can see some examples below.
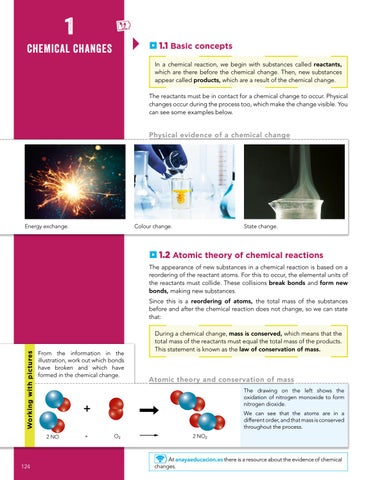
Physical evidence of a chemical change
Energy exchange.
Colour change.
State change.
ä 1.2 Atomic theory of chemical reactions The appearance of new substances in a chemical reaction is based on a reordering of the reactant atoms. For this to occur, the elemental units of the reactants must collide. These collisions break bonds and form new bonds, making new substances.
Working with pictures
Since this is a reordering of atoms, the total mass of the substances before and after the chemical reaction does not change, so we can state that:
From the information in the illustration, work out which bonds have broken and which have formed in the chemical change.
Atomic theory and conservation of mass The drawing on the left shows the oxidation of nitrogen monoxide to form nitrogen dioxide.
+ 2 NO
124
During a chemical change, mass is conserved, which means that the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. This statement is known as the law of conservation of mass.
+
We can see that the atoms are in a different order, and that mass is conserved throughout the process. O2
2 NO2
At anayaeducacion.es there is a resource about the evidence of chemical changes.