

Knowledge Series: Expansion Joint Performance Characteristics

DISCLAIMER
While the FSA makes every reasonable attempt to ensure that the information contained in this document is accurate and curren t, the FSA, its officers, directors, volunteers, and authorized agents are not responsible for any errors or omissions contained therein nor are they responsible for any results obtained from the use of or reliance upon its content. All information is provided “AS IS,” with no guarantee of completeness, accuracy, timeliness or of the results obtained, and without warranty of any kind, express or impl ied. In no event shall FSA or its officers, directors, volunteers, or authorized agents be liable to you or anyone else for any decision made or action taken in reliance on the information contained herein or for any for any consequential, indirect, special, or similar damages, even if advised of the possibility of such damages. The information contained in this document is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. It also includes references to certain standards that may change over time and should be interpreted only in light of particular circumstances. It is your sole responsibility to confirm the current state of any referred to standards. FSA reserves the right to modify or update the document content and to modify this Disclaimer at any time, effective upon posting of an up dated version of this Disclaimer.
© (April, 2023), Fluid Sealing Association. All Rights Reserved.
Expansion Joint Motions
• Axial Compression: The dimensional reduction or shortening in the face-to-face parallel length of the joint measured along the longitudinal axis.

• Axial Elongation: The dimensional increase or lengthening in the face-to-face parallel length of the joint measured along the longitudinal axis.

• Lateral Movement: The movement or relating displacement of the two ends of the joint perpendicular to its longitudinal axis.


Expansion Joint Motions
• Vibration: The ability of a flexible connector to absorb mechanical oscillations in the system, usually high frequency.

• Angular Movement: The angular displacement of the longitudinal axis of the expansion joint from its initial straight-line position, measured in degrees. This is a combination of axial compression and axial elongation.

• Torsional Movement: The twisting of one end of an expansion joint with respect to the other end about its longitudinal axis, measured in degrees.


Sound Limiting Characteristics
• The ability of a rubber expansion joint to limit or interrupt the transmission of a sound from operating equipment to the piping system.
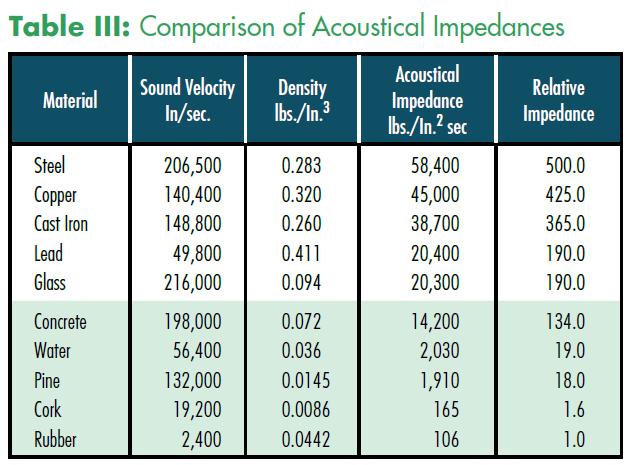
• Acoustical impedance is defined as the product of material density times velocity of sound in the material. In acoustical systems, low impedance corresponds to low sound transmission. Relative impedance is based on Rubber = 1.0

• The pressure ratings decrease with size and/or temperature increases from 200 PSIG to 30 PSIG operating pressure, dependent upon construction design.
• If requirements exceed these ratings, special constructions can be designed to meet the required conditions. Contact manufacturer for more information.


Resistance To Fluids and Hydrostatic Testing
• Resistance To Fluids: The superior corrosion resistance characteristic of natural rubber and synthetic elastomers permits the safe handling of a wide variety of materials within the pressure limits and temperature characteristics noted above. Contact the manufacturer for a special elastomer recommendation.
• Hydrostatic Testing: If required, joints can be hydrostatically tested up to 1.5 times the Maximum Allowable Working Pressure of the product, for a minimum of 10 minutes without leaks.

Force Pounds and Spring Rates
• Force Pounds: The total load required to deflect an expansion joint a distance equal to the maximum rated movement of the product. This force figure is expressed in pounds for compression, elongation and lateral movements. The force figure is expressed in foot-pounds for angular deflection.
• Spring Rates: The force in pounds required to deflect an expansion joint one inch in compression and elongation or in a lateral direction. For angular movement the spring rate is the force needed in foot-pounds to deflect the expansion joint one degree.

Spring Rates Filled Arch & Multi-Arch
• Spring Rates, Filled Arch: The spring rate of a Filled Arch Type expansion joint is approximately 4 times that of a standard open arch type. This rate will vary with manufacturers and is dependent upon the material used in the filled arch section of the expansion joint.
• Spring Rates, Multi-Arch: The spring rate for a Multi-Arch Type expansion joint is equal to the rate for a Single Arch Type product divided by the number of arches.

Seismic Testing
• It is the position of the Expansion Joint Division that although seismic testing may apply to rigid components of a piping system, it does not apply to an individual non-metallic expansion joint due to its inherent flexibility.
• The problem is further complicated by the absence of any definitive specification.
• The industry is unable to quote on seismic testing unless specific information on test procedures and results required become available.

Cycle Life
• One full movement cycle is defined as the sum of the total movements incurred when an expansion joint fully compresses from the neutral position then moves to the position of maximum allowed elongation and finally returns to neutral.
• Cycle life depends not only on the amount of movement, but also on the frequency of cycles or cycle rate.
• Cycle life can also be affected by installation practices, temperature and type of media being handled.
• Cycle testing can involve full movement cycling of an expansion joint at the rate of 10 cycles per minute at rated maximum temperatures and pressures to various duration, without failure.
• Much longer cycle life occurs with reduced movements.

For additional technical information regarding Expansion Joint Performance Characteristics consult the Fluid Sealing Associations Technical Handbook for Expansion Joints Piping (https://www.fluidsealing.com/)


