booksbooks
Getting Started With Java Using Eclipse

Mastering the Language and the Development Platform
 Bernhard Steppan
[Bernhard Steppan]
Bernhard Steppan
[Bernhard Steppan]
[Getting Started With Java Using Eclipse]
[Mastering the Language and the Development Platform]
All information, procedures and illustrations contained in this book have been prepared to the best of our knowledge and tested with care. Nevertheless, errors cannot be completely ruled out. For this reason, the information contained in this book is not associated with any obligation or guarantee of any kind. Consequently, the authors and publishers assume no responsibility and will not accept any liability, consequential or otherwise, arising in any way from the use of this program material - or any part thereof. Likewise, authors and publishers do not guarantee that described procedures etc. are free of third party intellectual property rights. The reproduction of common names, trade names, product designations, etc. in this work does not justify the assumption that such names are to be considered free in the sense of trademark and brand protection legislation and may therefore be used by anyone, even without special identification.
978-3-89576-561-2
978-3-89576-562-9
This work is protected by copyright.
All rights reserved, including those of translation, reprint and reproduction of the book or parts thereof. No part of this work may be reproduced in any form (photocopy, microfilm or any other process), not even for the purpose of teaching - with the exception of the special cases mentioned in §§ 53, 54 URG -, or processed, copied or distributed using electronic systems without the written permission of the publisher.
Contents Preface .......................................................................................... XXI PartIBasics ................................................................................. 1 1ProgrammingBasics ................................................................. 3 1.1Introduction............................................................................... 3 1.2TheLanguageoftheMachineWorld................................................... 4 1.3High-LevelProgrammingLanguages.................................................. 5 1.4DevelopmentEnvironment............................................................. 7 1.4.1Compiler......................................................................... 7 1.4.2Editor............................................................................. 7 1.4.3ProjectManagement........................................................... 7 1.5RuntimeEnvironment................................................................... 8 1.6Summary................................................................................... 8 1.7Literature................................................................................... 9 1.8Exercises................................................................................... 9 2TechnologyOverview 11 2.1Introduction............................................................................... 11 2.2Overview................................................................................... 12 2.2.1TheEarlyDaysofJava......................................................... 12 2.2.2TheGrowthPeriodofJava..................................................... 13 2.2.3ThePresenceAndFutureofJava............................................. 14 2.3WhyJava?.................................................................................. 15 2.3.1EasytoRead..................................................................... 15 2.3.2Object-Oriented................................................................ 15 2.3.3SafeAndRobust................................................................ 15
2.3.4VeryPowerful................................................................... 16 2.3.5UniversallyUseable............................................................ 16 2.3.6FreeofCharge.................................................................. 16 2.3.7OpenSource.................................................................... 16 2.3.8EasilyPortable.................................................................. 16 2.3.9EasilyExpandable.............................................................. 17 2.3.10EasytoDevelopAndTest...................................................... 17 2.4WhatBelongstoJava?.................................................................... 18 2.4.1JavaProgrammingLanguage................................................. 18 2.4.2JavaVirtualMachine........................................................... 18 2.4.3JavaClassLibraries............................................................. 20 2.4.4JavaDevelopmentTools....................................................... 20 2.5JavaVersions............................................................................... 21 2.6JavaEditions............................................................................... 21 2.6.1JavaStandardEdition.......................................................... 21 2.6.2JavaEnterpriseEdition........................................................ 21 2.6.3JavaMicroEdition.............................................................. 21 2.7Summary................................................................................... 22 2.8Literature................................................................................... 22 2.9Exercises................................................................................... 22 3Object-OrientedProgramming 23 3.1Introduction............................................................................... 23 3.2Overview................................................................................... 24 3.3Object...................................................................................... 25 3.4Class........................................................................................ 26 3.4.1Properties........................................................................ 26 3.4.2Methods......................................................................... 28 3.5Abstraction................................................................................ 30 3.6Inheritance................................................................................ 31 3.6.1BaseClasses..................................................................... 32 3.6.2DerivedClasses................................................................. 33 3.6.3MultipleInheritance........................................................... 33 3.7AccessProtection......................................................................... 34 3.8Relationships.............................................................................. 36 3.8.1RelationshipsWithoutInheritance.......................................... 36 3.8.2InheritanceRelationships..................................................... 38 3.9DesignFlaws.............................................................................. 40 VI Contents
Contents VII 3.10Refactoring................................................................................ 41 3.11Modeling................................................................................... 41 3.12Persistence................................................................................. 41 3.13Polymorphism............................................................................. 41 3.13.1StaticPolymorphism........................................................... 42 3.13.2DynamicPolymorphism...................................................... 42 3.14DesignRules............................................................................... 43 3.15Summary................................................................................... 43 3.16Literature................................................................................... 44 3.17Exercises................................................................................... 44 4DevelopmentEnvironment ......................................................... 45 4.1Introduction............................................................................... 45 4.2Installation................................................................................. 46 4.2.1OperatingSystem.............................................................. 46 4.2.2InstallJava....................................................................... 47 4.2.3InstallEclipse................................................................... 50 4.2.4InstallSamplePrograms....................................................... 55 4.2.5InstallationCheck.............................................................. 58 4.3EclipseIntroduction...................................................................... 60 4.3.1Overview......................................................................... 60 4.3.2Workbench...................................................................... 60 4.3.3Perspectives,ViewsandEditors.............................................. 61 4.3.4PackageExplorer............................................................... 62 4.3.5JavaEditor....................................................................... 63 4.3.6CodeFormatter................................................................. 66 4.3.7BuildSystem.................................................................... 68 4.3.8Debugger........................................................................ 68 4.3.9ModularStructure.............................................................. 69 4.3.10EclipseWorkspace............................................................. 70 4.3.11SoftwareUpdate................................................................ 72 4.3.12HelpSystem..................................................................... 73 4.4Summary................................................................................... 74 4.5Literature................................................................................... 74 4.6Exercises................................................................................... 75
VIII Contents PartIIJavaLanguage 79 5ProgramStructure 81 5.1Introduction............................................................................... 81 5.2Overview................................................................................... 82 5.3LanguageElements....................................................................... 83 5.3.1Comments....................................................................... 84 5.3.2Packages......................................................................... 84 5.3.3Classes........................................................................... 84 5.3.4Methods......................................................................... 85 5.3.5Statements...................................................................... 86 5.4StructureoftheProgram................................................................. 88 5.5ProgramFlow.............................................................................. 89 5.6ReservedKeywords....................................................................... 90 5.7Summary................................................................................... 91 5.8Tutorial..................................................................................... 92 5.9Exercises................................................................................... 92 6Variables .................................................................................. 93 6.1Introduction............................................................................... 93 6.2Overview................................................................................... 94 6.2.1VariablePurpose............................................................... 94 6.2.2VariableTypes.................................................................. 94 6.2.3VariableUsage.................................................................. 95 6.3LocalVariables............................................................................ 97 6.4Parameters................................................................................. 98 6.5InstanceVariables........................................................................ 99 6.5.1IndividualInstanceVariables................................................. 99 6.5.2InstanceVariable»this«........................................................ 100 6.6ClassVariables............................................................................ 102 6.7Constants.................................................................................. 104 6.8Summary................................................................................... 105 6.9Literature................................................................................... 106 6.10Tutorial..................................................................................... 106 6.11Exercises................................................................................... 107
Contents IX 7Statements 109 7.1Introduction............................................................................... 109 7.2Overview................................................................................... 110 7.2.1StatementPurpose............................................................. 110 7.2.2StatementTypes................................................................ 111 7.3Declaration................................................................................ 111 7.4Assignment................................................................................ 113 7.4.1JavaAssignmentStructure.................................................... 113 7.4.2JavaAssignmentsAreNotEqualtoMathematicalEquations............ 113 7.4.3Isx=yEqualtoy=x?.......................................................... 114 7.4.4CombinationofDeclarationandValueAssignment...................... 115 7.5Block........................................................................................ 116 7.6VariableCall............................................................................... 119 7.7MethodCall................................................................................ 120 7.8Summary................................................................................... 121 7.9Literature................................................................................... 122 7.10Tutorial..................................................................................... 122 7.11Exercises................................................................................... 122 8PrimitiveDataTypes ................................................................. 123 8.1Introduction............................................................................... 123 8.2Overview................................................................................... 124 8.2.1PurposeofPrimitiveDataTypes............................................. 124 8.2.2TypesofPrimitiveDataTypes................................................ 124 8.2.3UseofPrimitiveDataTypes................................................... 124 8.3IntegerDataTypes........................................................................ 128 8.3.1DataType»byte«................................................................ 128 8.3.2DataType»short«.............................................................. 129 8.3.3DataType»int«................................................................. 130 8.3.4DataType»long«............................................................... 131 8.4FloatingPointDataTypes............................................................... 131 8.4.1DataType»float«............................................................... 132 8.4.2DataType»double«............................................................ 133 8.5CharacterDataType...................................................................... 134 8.6BooleanDataType........................................................................ 134 8.7Summary................................................................................... 135 8.8Literature................................................................................... 136 8.9Tutorial..................................................................................... 136 8.10Exercises................................................................................... 137
X Contents 9ClassesandObjects 139 9.1Introduction............................................................................... 139 9.2Overview................................................................................... 140 9.2.1PurposeofaClass.............................................................. 140 9.2.2TypesofClasses................................................................. 141 9.2.3DefinitionofClasses........................................................... 141 9.2.4UseofClasses................................................................... 142 9.3AnonymousClasses...................................................................... 144 9.3.1DefinitionofConcreteClasses............................................... 144 9.3.2CreationofObjectsofaConcreteClass..................................... 146 9.3.3InnerClasses.................................................................... 147 9.3.4LocalClasses.................................................................... 149 9.3.5AnonymousClasses............................................................ 150 9.3.6Inheritance...................................................................... 152 9.4AbstractClasses........................................................................... 157 9.5Interfaces.................................................................................. 158 9.6Generics.................................................................................... 162 9.6.1DefinitionofGenericClasses................................................. 162 9.6.2CreationofGenericObjects.................................................. 163 9.7Summary................................................................................... 167 9.8Literature................................................................................... 167 9.9Tutorial..................................................................................... 167 9.10Exercises................................................................................... 168 10Enumerations 169 10.1Introduction............................................................................... 169 10.2Overview................................................................................... 170 10.2.1PurposeofEnums.............................................................. 170 10.2.2DefinitionAndDeclarationofEnums....................................... 171 10.2.3UsageofEnums................................................................ 172 10.3EnumClasses.............................................................................. 173 10.3.1Constructor..................................................................... 174 10.3.2Method»value()«............................................................... 174 10.3.3SeparateSimpleEnumClass................................................. 174 10.3.4SeparateExtendedEnumClass.............................................. 176 10.3.5InnerExtendedEnumClass.................................................. 177 10.4Summary................................................................................... 178 10.5Literature................................................................................... 178 10.6Tutorial..................................................................................... 179 10.7Exercises................................................................................... 179
Contents XI 11Arrays 181 11.1Introduction............................................................................... 181 11.2Overview................................................................................... 182 11.2.1PurposeofArrays............................................................... 182 11.2.2TypesofArrays.................................................................. 182 11.2.3UsageofArrays................................................................. 183 11.3Summary................................................................................... 187 11.4Tutorial..................................................................................... 188 11.5Exercises................................................................................... 188 12Methods ................................................................................... 189 12.1Introduction............................................................................... 189 12.2Overview................................................................................... 190 12.2.1MethodPurpose................................................................ 190 12.2.2MethodTypes................................................................... 191 12.2.3MethodDefinition............................................................. 192 12.2.4MethodUsage.................................................................. 195 12.3Constructors............................................................................... 197 12.3.1DefaultConstructors........................................................... 198 12.3.2ConstructorsWithoutParameters........................................... 199 12.3.3ConstructorsWithParameters............................................... 200 12.4Destructors................................................................................ 202 12.5Operations................................................................................. 204 12.6GetterMethods............................................................................ 205 12.6.1Definition........................................................................ 205 12.6.2Usage............................................................................. 207 12.7SetterMethods............................................................................ 208 12.7.1Definition........................................................................ 208 12.7.2Usage............................................................................. 209 12.8Summary................................................................................... 210 12.9Literature................................................................................... 211 12.10Tutorial..................................................................................... 211 12.11Exercises................................................................................... 211 13Operators 213 13.1Introduction............................................................................... 213 13.2Overview................................................................................... 214 13.2.1OperatorTypes................................................................. 214 13.2.2OperatorPrecedence.......................................................... 214
XII Contents 13.3ArithmeticOperators..................................................................... 215 13.3.1UnaryPlusOperator........................................................... 215 13.3.2UnaryMinusOperator......................................................... 216 13.3.3AdditionOperator.............................................................. 217 13.3.4SubtractionOperator.......................................................... 218 13.3.5MultiplicationOperator....................................................... 219 13.3.6DivisionOperator.............................................................. 219 13.3.7RemainderOperator........................................................... 220 13.3.8Pre-incrementOperator....................................................... 220 13.4RelationalOperators..................................................................... 223 13.4.1»Equalto«Operator............................................................ 224 13.4.2»NotEqualto«Operator....................................................... 224 13.4.3»LessThan«Operator.......................................................... 225 13.4.4»LessThanorEqualto«Operator............................................ 225 13.4.5»GreaterThan«Operator...................................................... 226 13.4.6»GreaterThanOrEqualTo«Operator....................................... 226 13.4.7TypeComparisonOperator................................................... 227 13.5LogicalOperators......................................................................... 230 13.5.1LogicalComplementOperator............................................... 230 13.5.2ANDOperator................................................................... 230 13.5.3OROperator..................................................................... 232 13.5.4TernaryOperator............................................................... 232 13.6BitwiseOperators......................................................................... 233 13.7AssignmentOperators................................................................... 233 13.8NewOperator............................................................................. 234 13.9CastOperator.............................................................................. 235 13.10AccessOperators.......................................................................... 237 13.10.1DotOperator.................................................................... 237 13.10.2LambdaOperator.............................................................. 239 13.11Summary................................................................................... 240 13.12Literature................................................................................... 240 13.13Tutorial..................................................................................... 240 13.14Exercises................................................................................... 240 14ConditionalStatements ............................................................. 241 14.1Introduction............................................................................... 241 14.2Overview................................................................................... 242 14.3»IfThenElse«Statement................................................................. 242
Contents XIII 14.4TernaryOperator.......................................................................... 243 14.5SwitchStatement......................................................................... 245 14.5.1SwitchStatementattheLevelofJava6...................................... 245 14.5.2SwitchStatementattheLevelofJava7...................................... 246 14.5.3YieldStatement................................................................. 247 14.5.4LambdaExpression............................................................ 248 14.6Summary................................................................................... 249 14.7Literature................................................................................... 249 14.8Tutorial..................................................................................... 249 14.9Exercises................................................................................... 249 15Loops ...................................................................................... 251 15.1Introduction............................................................................... 251 15.2Overview................................................................................... 252 15.2.1PurposeofLoops............................................................... 252 15.2.2TypesofLoops.................................................................. 252 15.3WhileLoop................................................................................. 253 15.4DoLoop.................................................................................... 254 15.5SimpleForLoop........................................................................... 255 15.6ExtendedForLoop....................................................................... 256 15.7Summary................................................................................... 257 15.8Literature................................................................................... 257 15.9Tutorial..................................................................................... 258 15.10Exercises................................................................................... 258 16PackagesandModules 259 16.1Introduction............................................................................... 259 16.2Overview................................................................................... 260 16.3Packages................................................................................... 260 16.3.1ClassImport..................................................................... 260 16.4Modules.................................................................................... 264 16.5Summary................................................................................... 267 16.6Tutorial..................................................................................... 267 16.7Exercises................................................................................... 267 17ExceptionHandling ................................................................... 269 17.1Introduction............................................................................... 269 17.2Overview................................................................................... 270 17.2.1Motivation....................................................................... 270
XIV Contents 17.2.2TypesofErrors.................................................................. 270 17.2.3UseofExceptionHandling.................................................... 270 17.3BaseClass»Throwable«.................................................................. 273 17.4Class»Error«............................................................................... 274 17.4.1Subclass»OutOfMemoryError«.............................................. 275 17.4.2Subclass»StackOverflowError«............................................... 277 17.5Class»Exception«......................................................................... 278 17.5.1Subclass»RuntimeException«................................................ 278 17.5.2Subclass»IOException«....................................................... 278 17.5.3Self-ProgrammedExceptions................................................. 279 17.6Summary................................................................................... 282 17.7Literature................................................................................... 282 17.8Tutorial..................................................................................... 283 17.9Exercises................................................................................... 283 18Documentation 285 18.1Introduction............................................................................... 285 18.2Overview................................................................................... 286 18.3LineComments........................................................................... 286 18.4BlockComments.......................................................................... 287 18.5DocumentationComments............................................................. 287 18.6Summary................................................................................... 288 18.7Literature................................................................................... 289 18.8Tutorial..................................................................................... 289 18.9Exercises................................................................................... 290 19Annotations ............................................................................. 291 19.1Introduction............................................................................... 291 19.2Overview................................................................................... 292 19.2.1AnnotationPurposes.......................................................... 292 19.2.2AnnotationTypes............................................................... 292 19.2.3PredefinedAnnotations....................................................... 293 19.2.4UseofAnnotations............................................................. 294 19.3CompilerControlAnnotations.......................................................... 296 19.3.1Annotations»Deprecated«.................................................... 296 19.3.2Annotations»SuppressWarnings«........................................... 298 19.3.3Annotation»Override«......................................................... 304 19.4Summary................................................................................... 307 19.5Literature................................................................................... 307 19.6Tutorial..................................................................................... 307 19.7Exercises................................................................................... 307
Contents XV PartIIIJavaTechnology 309 20DevelopmentProcesses ............................................................ 311 20.1Introduction............................................................................... 311 20.2Overview................................................................................... 312 20.2.1CorrelationBetweenPhasesAndActivities................................. 313 20.2.2Activities......................................................................... 314 20.2.3Tools.............................................................................. 315 20.3PlanningPhase............................................................................ 315 20.3.1OrderClarification............................................................. 315 20.3.2RequirementsCapture......................................................... 315 20.4ConstructionPhase....................................................................... 316 20.4.1Analysis.......................................................................... 316 20.4.2Design............................................................................ 317 20.4.3Implementation................................................................ 318 20.4.4Test............................................................................... 330 20.5OperatingPhase.......................................................................... 335 20.5.1Deployment..................................................................... 335 20.5.2Maintenance.................................................................... 337 20.6Summary................................................................................... 337 20.7Literature................................................................................... 338 20.8Exercises................................................................................... 338 21RuntimeEnvironment 339 21.1Introduction............................................................................... 339 21.2Overview................................................................................... 340 21.3Bytecode................................................................................... 341 21.4JavaVirtualMachine..................................................................... 344 21.4.1ArtificialComputer............................................................. 344 21.4.2Interpretermode............................................................... 345 21.4.3JITcompilermode............................................................. 346 21.4.4HotspotMode................................................................... 346 21.4.5GarbageCollector.............................................................. 347 21.5Libraries.................................................................................... 347 21.5.1NativeLibraries................................................................. 347 21.5.2ClassLibraries.................................................................. 348 21.5.3ResourcesAndPropertyFiles................................................. 348 21.6Portability.................................................................................. 349 21.6.1BinaryCompatibleBytecode................................................. 349
XVI Contents 21.6.2PortingPrerequisites........................................................... 349 21.7ProgramStart.............................................................................. 350 21.7.1StartScript....................................................................... 350 21.7.2NativeWrapper................................................................. 351 21.8JVMConfiguration........................................................................ 353 21.9Summary................................................................................... 353 21.10Literature................................................................................... 354 21.11Exercises................................................................................... 355 22ClassLibraries ......................................................................... 357 22.1Introduction............................................................................... 357 22.2Overview................................................................................... 358 22.2.1AreasofApplication............................................................ 359 22.2.2Reuse............................................................................. 359 22.2.3Documentation................................................................. 359 22.2.4LanguageExtension............................................................ 359 22.2.5TypesofClassLibraries........................................................ 359 22.3JavaStandardEdition.................................................................... 359 22.3.1BaseClasses..................................................................... 360 22.3.2Class»System«.................................................................. 368 22.3.3Threads.......................................................................... 371 22.3.4Streams.......................................................................... 372 22.3.5Properties........................................................................ 374 22.3.6ContainerClasses.............................................................. 376 22.3.7AbstractWindowingToolkit.................................................. 377 22.3.8Swing............................................................................. 386 22.3.9JavaBeans........................................................................ 389 22.3.10Applets........................................................................... 390 22.3.11JavaDatabaseConnectivity(JDBC).......................................... 390 22.3.12JavaNativeInterface........................................................... 391 22.3.13RemoteMethodInvocation................................................... 392 22.4JavaEnterpriseEdition................................................................... 393 22.4.1EntityBeans..................................................................... 394 22.4.2SessionBeans................................................................... 394 22.4.3MessageDrivenBeans......................................................... 394 22.4.4Interfaces........................................................................ 394 22.5JavaMicroEdition........................................................................ 395 22.6ExternalClassLibraries.................................................................. 396
Contents XVII 22.6.1ApacheSoftwareFoundation................................................. 396 22.6.2EclipseCommunity............................................................ 396 22.6.3SourceForge..................................................................... 396 22.6.4OtherOpen-SourceSoftware................................................. 396 22.6.5CommercialSoftware.......................................................... 397 22.7Summary................................................................................... 397 22.8Literature................................................................................... 398 22.9Exercises................................................................................... 398 23Rules ....................................................................................... 399 23.1Introduction............................................................................... 399 23.2Overview................................................................................... 400 23.3WritingConventions..................................................................... 401 23.4AccessProtection......................................................................... 402 23.4.1FourLevelsofAccessProtection............................................. 402 23.4.2AccessLevel»private«......................................................... 403 23.4.3AccessLevel»default«......................................................... 403 23.4.4AccessLevel»protected«...................................................... 403 23.4.5AccessLevel»public«.......................................................... 403 23.4.6CaseStudy....................................................................... 403 23.4.7ScopeofVariables.............................................................. 409 23.5EvaluationOrder.......................................................................... 413 23.5.1DotBeforeDash................................................................ 414 23.5.2DotBeforeDot.................................................................. 415 23.6TypeConversion.......................................................................... 417 23.6.1ImplicitConversion............................................................ 417 23.6.2ExplicitConversion............................................................ 419 23.7Polymorphism............................................................................. 422 23.7.1MethodOverloading........................................................... 422 23.7.2MethodOverriding............................................................. 424 23.8Summary................................................................................... 428 23.9Literature................................................................................... 428 23.10Exercises................................................................................... 429 24Algorithms 431 24.1Introduction............................................................................... 431 24.2Overview................................................................................... 432 24.2.1DevelopingAlgorithms........................................................ 432 24.2.2TypesofAlgorithms............................................................ 433
XVIII Contents 24.2.3UseofAlgorithms.............................................................. 433 24.3DevelopAlgorithms...................................................................... 433 24.3.1SortingAlgorithms............................................................. 433 24.3.2GraphicsAlgorithms........................................................... 434 24.4AlgorithmUsage.......................................................................... 442 24.4.1SortingAlgorithms............................................................. 442 24.4.2SearchAlgorithms.............................................................. 444 24.5Summary................................................................................... 445 24.6Literature................................................................................... 445 24.7Exercises................................................................................... 446 PartIVJavaProjects 447 25SwingPrograms 449 25.1Introduction............................................................................... 449 25.2Requirements............................................................................. 450 25.3AnalysisandDesign...................................................................... 450 25.3.1UserInterface................................................................... 451 25.3.2ProgramLogic.................................................................. 451 25.4Implementation........................................................................... 454 25.4.1StartEclipseWiththeWorkspace»Exercises«.............................. 454 25.4.2CreateNewJavaproject»SwingPrograms«................................. 455 25.4.3CreateNewclass»CourseStatisticsApp«.................................... 455 25.4.4ImplementClass»CourseStatisticsApp«.................................... 455 25.4.5CreateNewClass»MainWindow«............................................ 456 25.4.6ImplementingClass»MainWindow«........................................ 457 25.4.7ImplementingClass»CsvParser«............................................. 468 25.4.8ImplementingtheClass»TableFilter«....................................... 469 25.5Test.......................................................................................... 472 25.6Deployment............................................................................... 472 25.7Summary................................................................................... 474 PartVAppendix 475 26FrequentErrors 477 26.1Introduction............................................................................... 477 26.2JavaErrors................................................................................. 477 26.2.1CannotMakeaStaticReferenceToTheNon-StaticField................ 477
Contents XIX 26.2.2Outputofa»null«Value....................................................... 478 26.2.3NullPointerException.......................................................... 479 26.2.4MissingBreakinCaseStatement............................................. 481 26.2.5IncorrectComparison......................................................... 482 26.2.6UnhandledExceptions........................................................ 485 26.2.7NoClassDefFoundError........................................................ 486 26.2.8ClassNotFoundException..................................................... 486 26.3EclipseErrors.............................................................................. 486 26.3.1EclipseCouldNotBeStarted................................................. 486 26.3.2ChaoticEclipsePerspective................................................... 486 26.3.3MissingWindow................................................................ 487 26.4Summary................................................................................... 487 26.5Literature................................................................................... 487 27Glossary .................................................................................. 489 Index .............................................................................................. 491
Preface
Javaiscurrentlyundisputedlythemostimportantprogramminglanguage.Therefore, manywouldliketolearnJava.Unfortunately,gettingstartedisnoteasy,becauseprogrammingwithJavarequiresatleasttwothings:masteringtheprogramminglanguage and masteringadevelopmentenvironment.Thisisthereasonwhythisbookwaswritten.With thehelpofmanyexamples,itshowshowthelanguageisstructured.Inaddition,thebook usestheexampleoftheEclipsedevelopmentenvironmenttoteachyouhowtodevelop Javaprogramswiththistool.
Oh dear, five parts with 28 chapters and over 500 pages –at the end readers still think they can program me!
Thefirstpart»Basics«givesyoutheJavaandEclipsebasicknowledge.Thispartlaysthe programmingfoundations,givesyouanoverviewofJavatechnology,andshowsyouwhat isspecialaboutobject-orientedprogramming.AchapterabouttheEclipsedevelopment environmentcompletesthispart.
Inthesecondpart»JavaLanguage«everythingrevolvesaroundthesubtletiesoftheJava language.ThisiswherethefirstsmallJavaapplicationsarecreated.Thispartoffersa mixtureofknowledgepartandpracticalexercises.Attheendofeachchapter,youwillfind tasksthatyoucandoonyourown.Withthesolutionstothetasksattheendofthisbook youcheckthelearningsuccess.
Robertfromthemachineworldaccompaniesyouthroughthebook.
Javatechnologyisthefocusofthethirdpart»JavaTechnology«.Additionally,thispartintroducesyoutotherulesyoumustobservewhenprogramming,whatclasslibrariesare andwhatadvantagestheyhave.Inaddition,youwilllearnhowtotestprograms,what algorithmsareandhowtoprogramthem.
AlargerJavaprojectisthefocusofthefourthpart.Hereyouwillapplyalltheelementsfrom thepreviouspartsonanapplicationwithagraphicaluserinterface.Theprojectshowshow todevelopalargerapplicationpiecebypiecewiththeEclipsedevelopmentenvironment.







Thefifthpart,»Appendix«,concludesthisbookwithsolutionstothetasks,withbasicsof informationprocessingandachapteronthemostcommonmistakesthatcanoccurwhen workingwithEclipse.

ThePlot
Asaplot,Ibasedthebookonthe(fictional)programmingcourse»JavawithEclipse«taught byProfessorRothtofourstudents.Theprogrammingcourseisaccompaniedbytherobot named»Robert«and–amongmanyothers–mainlybythesefivecharactersthroughout thebook:
We accompany you with many programming examples around this programming course through this book and wish you already a lot of fun!
XXII Preface
TheprogrammingcoursewithLukas,Anna,ProfessorRoth,JuliaandFlorian
Who is the book for?
This book is aimed at active readers. You don’t want ready-made solutions, you want to program yourself. Without actively programming yourself and staying on the ball until your self-written program runs, you will not learn Java. The book contains a tempting number of ready programmed examples that you can run at the click of a button. Only reach for the sample solutions if you get stuck. First, try to enter the programs yourself and learn from the mistakes. Only by actively programming will you master Java and the Eclipse development environment.
Bonus Material
The book contains plenty of examples that can be easily imported into the Eclipse environment as solutions. You can easily download them from the Elektor publishing company homepage www.elektor.com/books/programming. Among these downloads, you will also find a bonus chapter, which is not printed due to space limitations. It explains the programming of so-called terminal programs.
Font Conventions
Various parts of the text are highlighted as follows for better readability:
Keywordsinbodytext
Keywordsinheadlines
Variablesinbodytext
Variablesinheadlines
Window(graphicaluserinterface) EclipseIDELauncher
GUIelement(graphicaluserinterface) Finish
Menu(graphicaluserinterface) File
Menucommand(graphicaluserinterface) Menu File New JavaProject Files
Directorypaths
Listing(sourcecodefromsampleprograms)
Programoutput
Preface XXIII
Meaning
Person
»Person«
TextPart
Datatypesinbodytext
Datatypesinheadlines
implements
»implements«
roland
»roland«
Samples.zip
C:/Programs/Eclipse
1 package
2 publicclass Robot{ 3(...) 4}
programmingcourse;
Result=true
http://eclipse.org (...) Duetospacelimitationspartofthesource codeismissing
URL
Acknowledgements
Iwouldliketothankeveryonewhosupportedmeinwritingthisbook:theElektorpublishingcompanyandmyeditorFerdinandteWalvaartforhistrustinmyworkandhisgreat patience.IwouldliketothanktheHanserpublishingcompanywhohasgivenpermission totranslatetheoriginalGermanmanuscript.
Asalways,mywifeChristianehasbeenverysupportiveofthisproject.Manythanksfor yourhelp!IwouldalsoliketothankAlinaNeacsu,whocleanedmybookmanuscriptof spellingmistakes.ManythanksalsotoValeriyKachaev(Studiostoks),fromwhomthetemplatesoftherobotcartoonscome.
HowtoContactUs
Despitethegreatestcare,itisnotalwayspossibletoavoidoverlookingoneoranothererror inabook.Ifyoufinderrors,havesuggestionsforimprovement,orquestions,justsendme ane-mailat java-eclipse@steppan.net .Iwillansweryourquestionsassoonaspossible andtrytoincludeyoursuggestionsforimprovementinupcomingeditions.Youcanfind themostrecentadditionsandfurtherinformationat http://www.programmingcourse.net NowIhopeyouenjoyreadinganddevelopingyourJavaprogramswithEclipse!
BernhardSteppan
Wiesbaden,March2023
XXIV Preface
PARTI Basics
Tobeabletodevelopcomputerprograms,youneedtomasterthebasics.Chapter»ProgrammingBasics«laysthegroundworkforprogrammingJavaapplications.Inchapter 2, »TechnologyOverview«,youwilllearnwhatJavahasincommonwithotherprogramming languagesandhowJavadiffersfromotherlanguages. Did you know that Java is slang for co ee? And that Java is not just a programming language?





Sure!







Afterwards, it continues with the chapter »Object-Oriented Programming«. It shows what is special about object-oriented programming and how object-oriented programs are structured. The chapter »Development Environment« concludes this part of the book with the installation of the development environment and introduction to »Eclipse«.

2
Figure 1: To develop computer programs, you need to master the basics.
1 ProgrammingBasics
1.1Introduction
Programmingmeanswritingcomputerprograms.Computerprogramsconsistofoneor morecommandsinaprogramminglanguage.TherobotnamedRobertpresentsasimple JavaprogramtothestudentsinProfessorRoth’sprogrammingcourse(Figure 1.1).
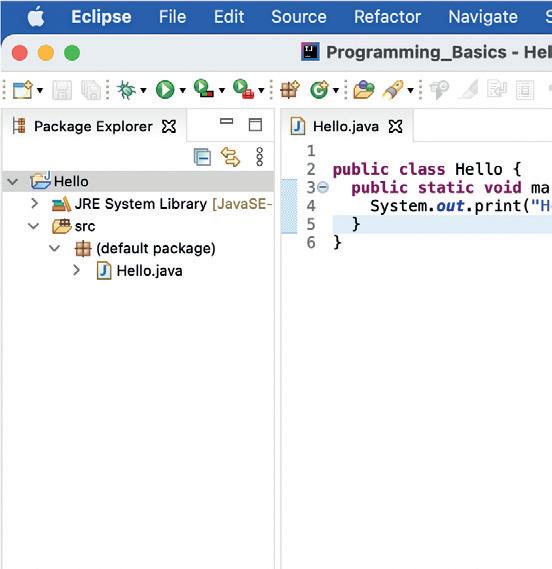
class Hello { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("Hello!"); } }
This simple Java program outputs the greeting »Hello!« on the screen. The text of the program »class Hello …« is called source code.
Figure 1.1: Robert from the machine world is the expert for machine programs.
Thestudentsoftheprogrammingcoursethinkthattherearealotofinstructionsforsucha simpleprogram.AnnawouldliketoknowfromProfessorRothwhetheritcouldbesimpler:
Why do computers have to be programmed in such a complicated way? Why can't you just tell them what you want, like Alexa and Siri?
»EvenAlexa,CortanaandSiri«,saysProfessorRoth,»arejustcomputerprograms.«These programsweredevelopedsothathumanscancontrolcomputersviaspeech.ButAlexa &Co.canonlydothefewtasksforwhichtheywerespeciallyprogrammed.Ifyouwant thecomputertoperformothertasks,suchaswordprocessing,youhavetowriteaspecial programforit.TheseprogramscanbedevelopedinJava,forexample.
1.2TheLanguageoftheMachineWorld
Whenwespeakofcomputerstoday,wealwaysmean digital computers.Thesemachines understandonlytheirdigitalmachinelanguage.Digitalmeansthatthecomputeruses binarycodeforallinformation.Therefore,thecomputer’smachinelanguageconsistsonly ofasequenceofzerosandones.
However,thecomputer’smachinelanguage,withitssequencesofzerosandones,isextremelydifficultforhumanstounderstand.Toprogramcomputersdirectlyinmachine codewouldthereforebecompletelyabsurd.Itwouldtakeaverylongtimeandtheprobabilityoferrorswouldbehigh.
Ifyouwanttoprogramthecomputerclosetothemachine,youuseanauxiliarylanguage. Thisauxiliarylanguageiscalledassemblerlanguageorassemblerforshort.ProfessorRoth presentsasimpleexampletohisprogrammingclass.LiketheJavaprogrambefore,itsimplyoutputsthecharacterstring»Hello!«onthescreen(Figure 1.3).
ProfessorRoth’sprogrammingcoursefindstheassemblylanguageprogramquitedifficult tounderstand.Howcouldonlyprogrammerslearnsuchaterriblelanguage?Theanswer issimple,because,intheearlydaysofcomputerstherewerenohigh-levellanguageslike
4 1ProgrammingBasics
Figure 1.2: Is it really still appropriate today to type in programs?
Java.Programmershadtopaycloseattentiontothecomputer’sprocessorswhentheyprogrammedthemachineinassemblylanguage.
An assembler program is specific to the hardware of a computer. It is therefore difficult to transfer from one type of computer to another.
org 100h start: mov dx,hallo
mov ah,09h int 21h
mov al, 0 mov ah,4Ch int 21h section .data hallo: db 'Hello!', 13, 10, '$'
Assembler programs are much longer compared to functionally equivalent Java programs. They consist of many small-part commands which, taken alone, do little. Therefore, one needs many of these commands to write a larger program. This program is written specifically for one type of computer. It is difficult to transfer to another type of computer. Besides the high cost of developing such programs, a major disadvantage of the assembly language is that it is difficult to transfer from one type of computer to another. However, the small-part instructions do not have only disadvantages. They have the advantage that a good programmer can use them to create very lean and fast machine programs. They also often require far less main memory than comparable programs written in a high-level language.
1.3High-LevelProgrammingLanguages
Itseemstobesomehowbewitched:Computersonlyunderstandtheirspecificmachine language.We,ontheotherhand,withoutspecialprogrammingtraining,understandonly
1.3High-LevelProgrammingLanguages 5
Figure 1.3: This assembler program also outputs »Hello!«.
ournativelanguageandmaybeoneortwoforeignlanguages.Howcanwebridgethishuge gapbetweenthemachineworldandthehumanworld?
WecaneitherdevelopevenmorepowerfulprogramslikeAlexa,CortanaandSiri,sothat thecomputersexecuteeverythingwewant.Orwecanlearnthecomputer’slanguageifwe wanttodevelopspecialprogramsfortasksthatAlexa&Co.can’tdo–no,thosearen’tthe onlyoptions,becausethereis,fortunately,athirdway.
Programmingacomplexprograminassemblerisnolongerup-to-date.That’swhypeople startedveryearlytodevelopprogramminglanguageslikeJava.Theselanguagesforma bridgebetweenthe(formosthumans)difficulttounderstandmachinelanguageandthe (formostmachines)difficulttounderstandhumanlanguage.Theselanguagesarecalled high-levelprogramminglanguagesorhigh-levellanguagesforshort.



010101001101110
000111110101101110111
1111001110100001110


0011101010111011
I am so glad that there are high-level programming languages ...


High-level programming languages are much easier for a human to learn and understand than the language of the machine world. But how does it work? How do you translate a high-level language into the language of the machine world? For this purpose, a trick has been thought of. This trick is a special program that translates the source code of a highlevel language like Java into the language of the machine world. This program is called a compiler and is part of a development environment.

6 1ProgrammingBasics
Figure 1.4: High-level programming languages are mediators between humans and machines.
1.4DevelopmentEnvironment
1.4.1Compiler
ThecompilerisoneofthecorecomponentsofadevelopmentenvironmentlikeEclipse.It transfersthesourcecodeofaJavaprogramintothelanguageofthemachineworld.The sourcecodeisthetextthatwasseeninfigures 1.1 and 1.3.
1.4.2Editor
Intheeditoryouenterthesourcecodeofaprogramasinawordprocessor.Aneditoralso providesprogramdevelopmentsupport,suchasadviceonhowtofixtheerrorsthatare displayed.

1.4.3 Project Management
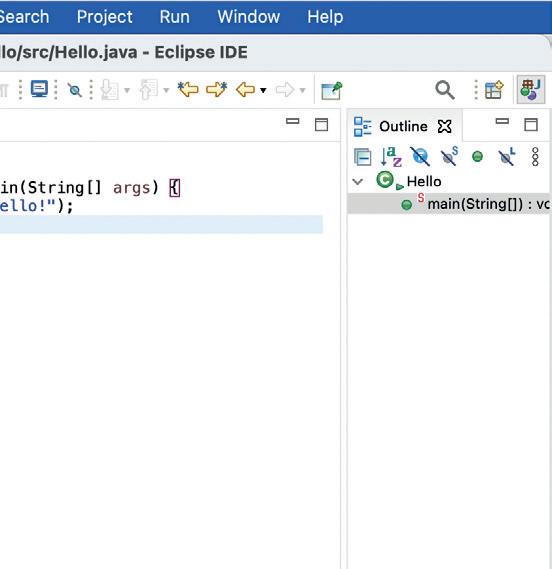
Java programs usually consist of a large number of files. So that you do not lose the overview, the Java development environment has a project management. It shows which files belong to a project.
1.4DevelopmentEnvironment 7
Menus
Editor with source code
Project Management Console
Toolbar
Figure 1.5: Editor, compiler and project management of the Eclipse development environment
1.5RuntimeEnvironment
Javaprogramsrequireaspecialruntimeenvironment.Inotherwords:Javaprogramsonly runwithanadditionalprogramonyourcomputer.Youdon’tnoticethisatfirst,becausethe Eclipsedevelopmentenvironmentcallsthisruntimeenvironmentinthebackgroundwhen yourunaJavaprogram.Tounderstandwhatthisruntimeenvironmentisallabout,turnto thenextchapter.ItshowsyouhowJavahasevolvedandwhyaJavaruntimeenvironment isnecessaryatall.
1.6Summary
Programmingmeanswritingcomputerprograms.Computerprogramsconsistofoneor morecommandsinaprogramminglanguage.Thesecommandsarewrittenintheformof atext.Inprogramming,thistextiscalledsourcecode.Computersexpectthecommands inmachinelanguage.We,ontheotherhand,speakinourhumanlanguage.Tobridgethis gap,computerscientistshavedevelopedhigh-levellanguages.Javaisoneofthesehighlevellanguages.
Computer programs consist of one or more commands. You can program these commands conveniently in Java – instead of in the difficult to understand machine language.
class JavaProgram { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("My name is Robert!"); }
To translate a high-level language program into machine language so that the computer can execute it, you need an additional program. This translation program is called a compiler. The compiler is part of the development environment. This consists (among other things) still of an editor and project management. With the help of the editor, you write the source code of a program. The project administration administers the different files, which belong to a project.
8 1ProgrammingBasics
}
Figure 1.6: Computer programs consist of commands of a programming language
1.7Literature
BernhardSteppan:»ABriefHistoryofProgrammingLanguages«; https://www.programmingcourse.net/articles/a_brief_history_of_programming_languages
1.8Exercises
Todeepenyourknowledge,pleasegoto https://www.programmingcourse.net/books/java_ with_eclipse/programming_basics andworkontheexerciseslistedthere.Thereyouwill alsofindthesolutionstotheexercises.
1.7Literature 9
A
abstract 90
Abstractclass 157, 485
AbstractMethod 485
AbstractWindowingToolkit 373
Abstraction 30
Accesslevels 398
AccessProtection 34, 194, 398
Accuracy 126
Activities 310
Additionoperator 216
Aggregation 37
Algorithms 427
–use 438
Analysis 310
And-operator 226
annotation 150
Anonymousclass 150
Applets 12, 386
Arithmeticoperators 214
Arrays 181
Assemblerlanguage 4
assert 90
Assignment 113
Assignmentoperator 228
Association 37
Attribute 26
Attributes 26
AWT 373
B
BaseClass 32
Bitwiseoperators 228
Block 116
BlockComments 282
boolean 90, 134
BorderLayout 376
break 90
BuildSystem 68 byte 90, 128
C
Cannotmakeastaticreference... 473 case 90
Castoperator 231, 413 catch 90 char 90, 134
CharacterDataType 134
Characters 134
Class 23, 26, 163, 256, 485
class 90
Classattribute 485
ClassImport 256
ClassLibraries 353
Classmethod 485
Classmethods 191
Classoperation 485
Classvariable 485
ClassVariables 102
ClassNotFoundException 482
Comparativeoperators 222
Compile 321
Compiler 7, 68, 321
Composition 38
ConcreteClass 145
concreteclass 485
Conditionalstatements 237
ConfigurationFiles 370
const 90
Constant 27
Constants 104
ConstructionPhase 308
Constructor 28
Constructors 198
Constructorswithoutparameters 199
Container 372
Index
continue 90
Coprocessor 126
Createobjects 146
D
Debugger 68
Declaration 111, 146 default 90, 399
Defaultconstructors 198 derive 152
Derivedclasses 33
Design 310
DesignFlaws 40
DesignRules 43
Destructor 28
Destructors 203
DevelopingAlgorithms 428
DevelopmentEnvironment 7, 45
DevelopmentProcesses 307
Differenceoperator 217
DivisionOperator 218 do 90
DoLoop 250
DocumentationComments 283
double 90, 133
Dynamicimport 256
DynamicPolymorphism 42
E
EclipseDevelopmentEnvironment 50
EclipseIDE 50, 50
EclipsePlug-ins 69
EclipseProjectManagement 62
Editor 7, 63
else 90
Encapsulation 34, 194, 398
EnterpriseJavaBeans 389, 390
EntityBeans 390
enum 90
EnumerationType 170
EqualityOperator 223
EventControl 386
EventHandling 373
exports 90 extends 90, 152
F false 90
FileReader 368
FileWriter 369
final 90, 152, 156
finalize 203
finally 90
FixedPointNumber 128
float 90, 132 for 90
ForLoop,extended 252
ForLoop,simple 251
Function 204
Garbagecollector 343
Generalization 38, 486
Genericclass 163
Generics 163
GetterMethods 29, 205
Glossary 485
goto 90
Greateroperator 225
Greaterthanorequaltooperator 225
GridBagLayout 379
H
HelpSystem 73
High-levelprogramminglanguage 5
HomeInterface 390
HotJava 12
HotSwap 68
Identifier 27
if 90
IfStatement 238
implements 90
Import 256
import 90
Importstatement 256
InequalityOperato 223
Inheritance 31, 486
inheritance 152
Innerclass 147
InstallationEclipseIDE 50
Instance 25, 146, 486
instanceof 90
Instances 146
Instantiation 486
int 90, 130
Integer 128
IntegerLiterals 128
Interface 159
interface 90
Interfaces 159
Java2MicroEdition 390
492 Index
G
I
J
JavaClassLibraries 353
JavaDatabaseConnectivity 386
JavaEditor 63
JavaEnterpriseEdition 389
JavaKeywords 90
JavaME 390
JavaMicroEdition 390
JavaNativeInterface 387
JavaRuntimeEnvironment 335
JavaStandardEdition 355
java.base 356
JavaBean 386
JDBC 386
Jigsaw 13
JNI 387
JRE 335
JSE 355
JVM 340
JVMConfiguration 349
K
Keyword 90
Keywords 90
L
Lambdaoperator 234
LayoutManagers 376
Lessoperator 224
Lessorequaloperator 224
Linecomments 282
LocalClass 149
LogicalOperators 226
long 90, 131
Loops 247
M
Machinelanguage 4, 5
MessageDrivenBeans 390
Method 485
method 486
Methodbody 195
MethodCall 120
Methodimplementation 195
MethodOverloading 418
MethodOverriding 420
Methods 28, 189
Model 41
Modeling 41
ModularStructure 69
Module 260
module 90
Modules 260
Modulooperator 219
MultipleInheritance 33
N
Namespace 258
Namespaces 258
native 90
New 146
new 90
NewOperator 230
NoClassDefFoundError 482
Non-operator 226
NPE 475
null 90
NullPointerException 475
O
Oak 12
Object 23, 25, 357, 486
Objectvariable 99, 486
ObjectVariables 99
OOA/OOD 41
OpenJDK 13
Operation 29, 204
OperationPhase 308
Operator 213
Or-operator 227
Overloading 418
Overriding 420
P
Package 256
package 90
PackageExplorer 62
Packages 256
Parameter 98
Persistence 41
Perspective 61
Perspektive 61
PlanningPhase 308
Polymorphism 41, 418
Postdecrementoperator 221
Postincrementoperator 220
Predecrementoperator 221
Preincrementoperator 219
PreventOverriding 423
private 90, 399
Productoperator 218
Programming 3
Projectmanagement 7
Properties 26, 370
Property 26
Index 493
protected 90, 399
public 90, 399
Q
Questionmarkoperator 229
Quotientoperator 218
R
Refactoring 41
Relationship 36
Relationshipswithoutinheritance 36
Releasememory 343
RemoteInterface 390
RemoteMethodInvocation 388
Requirements 310 requires 90
Restructuring 41
return 90
RMI 388
Runtime 366
RuntimeEnvironment 335
Runtimeenvironment 8
S
SessionBeans 390
SetterMethods 28, 208
short 90, 129
Sign 126
SoftwareUpdate 72
Sorting 429, 438
State 27
StatefulSessionBeans 390
StatelessSessionBeans 390
Statements 109
States 27
static 90, 191, 486
StaticPolymorphism 42
strictfp 90
String 359
StringBuffer 363
SunMicrosystems 12
super 90, 155, 486
SuperclassObject 357
Swing 373, 382
SwingPrograms 445
switch 90
Switchstatement 241
synchronized 90
System 364
T
Test 310
this 90, 100, 154, 486
threads 367
throw 90
throws 90
Tools 311
transient 90
Translate 321
true 90
try 90
TypeCasting 413
Typeviolation 163
TypesofAlgorithms 429
Typesofloops 248
V
ValueAssignment 115
Valuerange 126
var 90
Variable 27
VariableCall 119
Virtualmachine 340
void 90
volatile 90
W
while 90
Whileloop 249
Workbench 60
Workspace 70
WrapperClass 363
WrapperClasses 361
WriteFiles 368
494 Index
Getting Started With Java Using Eclipse
Mastering the Language and the Development Platform

Many people would like to learn Java but getting started is not easy since programming with Java requires at least two things: mastering the programming language and the development environment. With the help of many examples, this book shows how the language is structured. In addition, it employs the Eclipse development environment as an example of a powerful tool to teach developing Java programs.
In Basics, the first part of the book, you acquire your Java and Eclipse basic knowledge. This part lays the programming foundations, gives you an overview of Java technology, and shows you what is special about object-oriented programming.
In the second part called Java Language, everything revolves around the subtleties of the Java language and this is where the first small Java applications are created, aided by a fine blend of the knowledge part and practical exercises.
Java Technology is both the name and the focus of the third part which also introduces you to the rules to observe when programming, what class libraries are and what advantages they have. In addition, you will learn how to test programs, what algorithms are, and how to program them.
The fourth part, Java Projects, enables you to apply all the previous elements in an application with a graphical user interface. The project shows how to develop a larger application piece by piece with the Eclipse development environment. The Appendix concludes with a section on frequent errors that can occur when working with Eclipse, and a Glossary.
All sample programs discussed in the book, and bonus material, are contained in an archive file which is available free of charge from the Publishers’ website www.elektor.com/books. On this site, search for: Java Eclipse. The tasks and solutions mentioned in the book are at: www.programmingcourse.net/courses/java_with_eclipse/.
Bernhard Steppan is a Java developer from the very beginning. He has written several C++ and Java books as well as numerous articles on programming languages, IT architecture, development tools, and other IT topics. Bernhard Steppan lives in Wiesbaden (Germany) and works as Chief IT Architect for DB Systel, the systems house of Deutsche Bahn.
Elektor International Media BV www.elektor.com booksbooks

 Bernhard Steppan
[Bernhard Steppan]
Bernhard Steppan
[Bernhard Steppan]





