Neurointerventional Services: Visiting Consultant Program
Heart and Vascular Center, Victoria Hospital, Yangon
Bringing world-class cerebrovascular interventions to Myanmar through specialized expertise and advanced techniques.




Heart and Vascular Center, Victoria Hospital, Yangon
Bringing world-class cerebrovascular interventions to Myanmar through specialized expertise and advanced techniques.




Interventional Neuroradiologist
Bengaluru, India
Visit Dates: August 15-17, 2025
Dr. Reddy specializes in minimally invasive treatments for complex cerebrovascular disorders, having performed over 5000 successful interventions.
His expertise encompasses aneurysm management, stroke treatment, and vascular malformation procedures.


Cerebrovascular Interventions
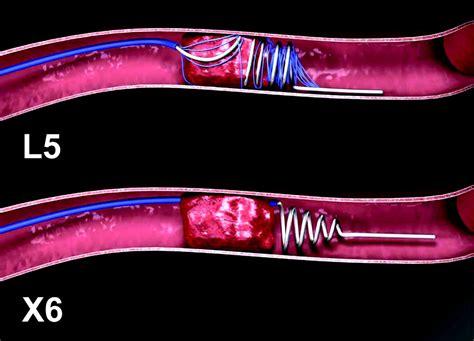
Aneurysm Management
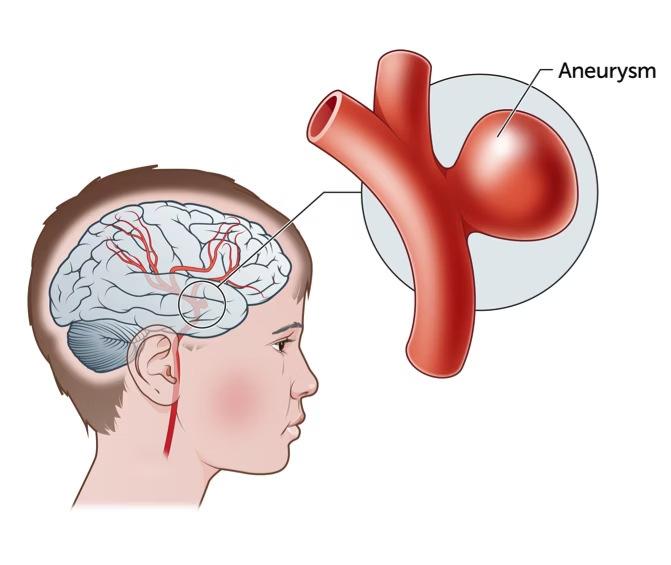
Coil embolization: Platinum coils placed within aneurysm to induce thrombosis
Stent-assisted coiling: Stent provides structural support for complex aneurysms
Balloon-assisted coiling: Temporary balloon inflation stabilizes coil placement
Flow diverter placement: Redirects blood flow away from aneurysm neck
These minimally invasive techniques provide alternatives to conventional neurosurgery, reducing recovery time and procedural risks for appropriate candidates.


Our visiting consultant program brings advanced stroke intervention capabilities to Yangon, providing crucial time-sensitive treatments for eligible patients.
Available Procedures:
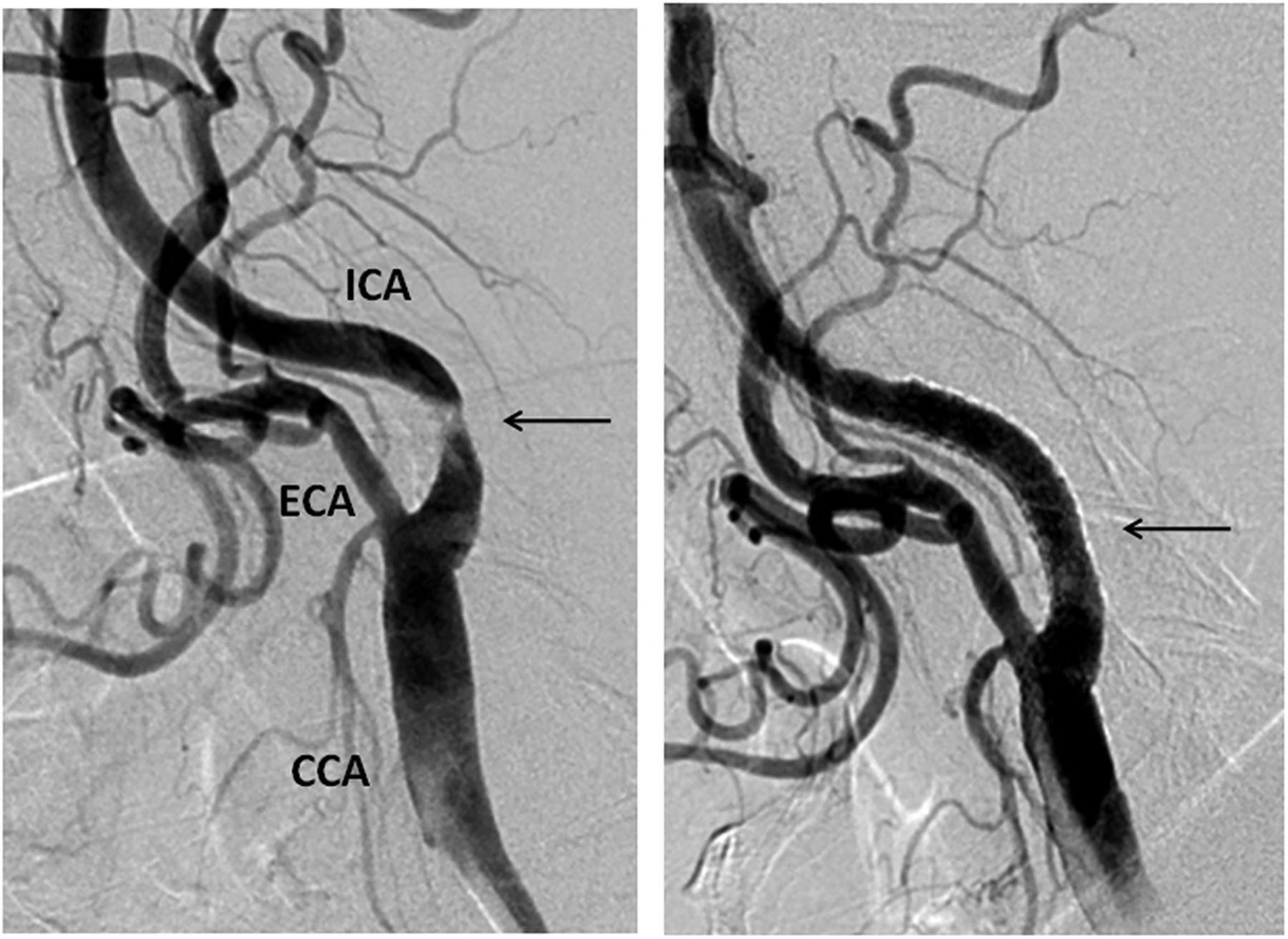
Carotid artery stenting: Endovascular treatment for significant stenosis causing TIAs or strokes
Intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD) stenting: Targeted treatment for narrowed cerebral vessels resistant to medical management
These interventions significantly reduce stroke recurrence risk in properly selected patients with specific anatomical features and clinical presentations.


Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) Embolization
Staged endovascular occlusion of feeding arteries using liquid embolic agents (Onyx, nBCA) to reduce bleeding risk and facilitate subsequent surgical resection when appropriate.
Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) Embolization
Direct occlusion of abnormal arteriovenous connections using coils, liquid embolics, or vascular plugs to eliminate shunting and prevent neurological deterioration.
Precise endovascular navigation to treat spinal vascular malformations causing myelopathy, radiculopathy, or hemorrhage risk with specialized microcatheters and embolic materials.



Cerebral venous thrombosis can cause severe neurological deficits if left untreated.
Interventions
Endovascular thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy for patients with deteriorating neurological status despite anticoagulation.
Precision stent placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) with venous sinus stenosis, providing immediate pressure gradient reduction and symptom relief.
These specialized interventions address rare but potentially devastating cerebrovascular conditions that may not respond to conventional medical management.


Pre-surgical Meningioma
Embolization
Devascularization of hypervascular meningiomas 24-48 hours before surgical resection, reducing intraoperative blood loss by up to 70% and facilitating complete tumor removal.

Angiofibroma Embolization
Preoperative embolization of feeding vessels from external carotid artery branches, minimizing surgical hemorrhage risk in these highly vascular tumors affecting adolescent males.
Vertebral Body Hemangioma
Embolization
Direct puncture or transarterial embolization of symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas causing pain or neurological symptoms from spinal cord compression.


Innovative treatment for chronic subdural hematomas, particularly in elderly or anticoagulated patients. This procedure targets the pathological vascular membranes responsible for hematoma expansion, providing an alternative to surgical drainage.
Clinical outcomes show 70-80% resolution rates without craniotomy, significantly reducing recurrence compared to conventional surgery.

High-resolution vascular imaging providing definitive assessment of:
Aneurysm morphology and dimensions
AVM angioarchitecture and flow dynamics
Collateral circulation in occlusive disease
Vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage




Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
Hunt & Hess grade 1-3 subarachnoid hemorrhage patients with aneurysms amenable to endovascular treatment.
Early intervention (within 72 hours) significantly reduces rebleeding risk and improves neurological outcomes.
Patients with extensive dural sinus thrombosis, worsening despite therapeutic anticoagulation, particularly those with altered mental status, focal deficits, or intracranial hemorrhage.
Arteriovenous malformations with flowrelated aneurysms, venous stenosis, or deep venous drainage patterns indicating elevated rupture risk. Targeted embolization can stabilize high-risk features.
Success Rate
For unruptured aneurysm occlusion with modern endovascular techniques
Stroke Reduction
In symptomatic carotid stenosis patients receiving appropriate intervention
Recurrence Prevention
For chronic subdural hematomas treated with MMA embolization vs. surgery alone
Unruptured aneurysms suitable for endovascular treatment based on location, morphology, and neck-to-dome ratio
Symptomatic carotid stenosis >70% or asymptomatic >80% with favorable anatomy for stenting
Intracranial stenosis >70% with recurrent strokes despite optimal medical therapy
Chronic subdural hematoma candidates for MMA embolization with recurrent collections or high surgical risk


Ideal candidates for pre-surgical embolization include:
Meningiomas >3cm with significant external carotid artery supply
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA) in adolescent males with extensive vascularity
Paragangliomas of the head and neck region
Embolization is typically performed 24-48 hours before planned surgical resection to maximize benefit while avoiding revascularization.

Considered for embolization when presenting with:
Progressive painful symptoms
Pathological fracture risk
Epidural extension causing cord compression
Planned surgical stabilization


Aneurysm dimensions, neck width, dometo-neck ratio, and presence of daughter sacs impact treatment approach.
High-resolution CTA/MRA/DSA studies are essential for appropriate treatment planning.
Location
Anatomical position affects device selection and technical approach (e.g., sidewall vs. bifurcation).
Age, comorbidities, antiplatelet tolerance, and prior treatments influence risk-benefit assessment.


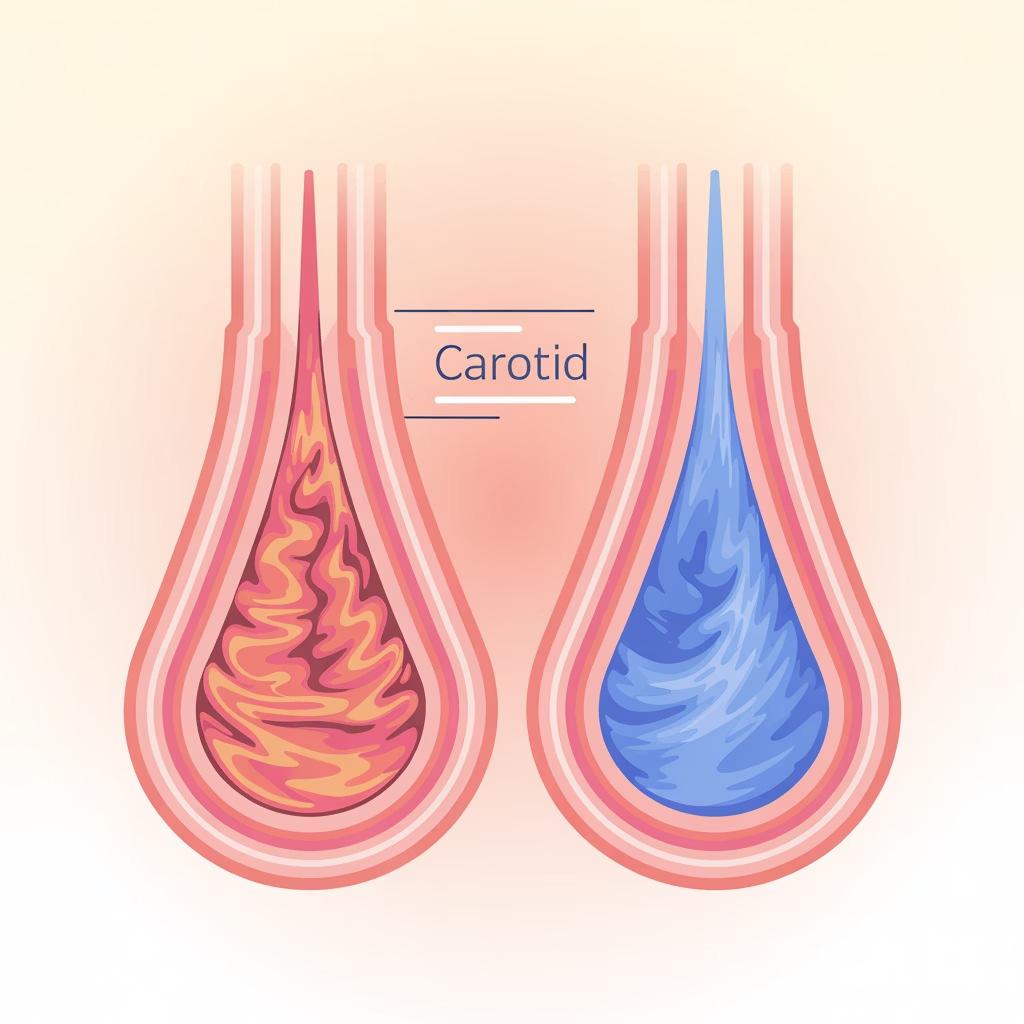
Carotid ultrasound showing >70% stenosis (left)
compared to normal flow (right)
Symptomatic stenosis >70% with recent TIA or minor stroke
Asymptomatic stenosis >80% with high-risk plaque features
Contralateral occlusion increasing hemodynamic significance
Favorable arch anatomy for endovascular access
Stenosis >70% with recurrent events despite aggressive medical therapy
Absence of perforator-rich segments reducing procedural risk
Complete imaging workup including vessel wall MRI to characterize plaque
Good distal vascular bed with limited chronic ischemic change


Spetzler-Martin Grading
Comprehensive AVM evaluation using established grading system that incorporates:
Size (<3cm, 3-6cm, >6cm)
Venous drainage pattern (superficial vs. deep)
Eloquence of adjacent brain regions
Grades 1-3 typically considered for intervention, while grades 4-5 require individualized multidisciplinary approach.
Eloquent Location Assessment
Functional MRI and tractography to determine proximity to:
Primary motor/sensory cortex
Language areas
Visual cortex
Hypothalamus, thalamus, brainstem
Hemorrhage History
Prior hemorrhage significantly impacts management decisions:
Increases annual rebleed risk (4-8% vs. 1-3%)
May identify specific angioarchitectural risk factors
Often lowers threshold for intervention





Medical History & Examination
Complete neurological assessment
Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) documentation
Cardiovascular risk evaluation Prior cerebrovascular events Medication history, especially antiplatelets/anticoa gulants
Laboratory Investigations
Complete blood count with platelet function
Coagulation profile (PT, aPTT, INR)
Renal function tests (Creatinine, eGFR)
Electrolytes and blood glucose
Type and crossmatch for potential transfusion
Assessment
ASA physical status classification
Airway evaluation
Cardiopulmonary reserve assessment
Anesthetic risk stratification NPO status verification

High-resolution Vascular Imaging
Comprehensive imaging is critical for procedural planning and risk assessment. All cases require recent (within 30 days) advanced neurovascular studies:
CT Angiography
Multi-phase acquisition with arterial and venous phases
Submillimeter slice thickness
Volumetric dataset for multiplanar reconstructions
Previous Intervention Documentation
MR Angiography
Time-of-flight and contrastenhanced sequences
High-resolution vessel wall imaging when indicated
Perfusion studies for ICAD evaluation
Prior procedure reports with device specifications
Follow-up imaging results
Complications or technical challenges encountered
3D reconstruction provides critical anatomical insights for procedural planning and device selection. When available, please include DICOM datasets for advanced 3D workstation analysis prior to the procedure.
Neurosurgery consultation: Alternative or adjunctive surgical options assessment
Neurology assessment: Baseline neurological status and clinical risk evaluation
Anesthesia evaluation: Procedural sedation/anesthesia planning and periprocedural management
Critical care coordination: Post-procedure monitoring protocols and complication contingency planning

Joint review of complex cases: Consensus-based decision making for high-risk pathologies
Treatment planning sessions: Detailed procedural strategy development with contingency options
Post-procedure care protocols: Standardized monitoring and management guidelines
Our multidisciplinary approach ensures comprehensive patient evaluation and optimal treatment selection, combining the expertise of multiple specialists to achieve the best possible outcomes.


Case Referrals and Consultations
Facility
Heart and Vascular Center
Victoria Hospital, Yangon
52 Strand Road
Kyauktada Township
Yangon, Myanmar
Required Documentation
Patient demographics
Clinical summary
Relevant imaging studies
Urgency level indication
Preferred procedure dates
Department Contact
Daw Theint Nwel Saw
Manager, HVC team
Phone: +95 9765127712
Available Monday-Friday
8:00 AM - 5:00 PM MMT



August 15-17, 2025
Day 1 (August 15)
1 8:00 AM - 10:00 AM
Case reviews and selection with local team 2 10:30 AM - 12:30 PM
Emergency consultations and triage
3 1:30 PM - 4:00 PM
Procedure planning and equipment preparation 4 4:00 PM - 5:30 PM
Lecture: "Advanced Aneurysm Treatment Techniques" Day 2-3 (August 16-17)
1 7:30 AM - 8:30 AM
Pre-procedure assessment and planning
2 8:30 AM - 4:30 PM
Interventional procedures (3-4 cases per day)
3 4:30 PM - 5:30 PM
Post-procedure rounds and patient assessment 4 5:30 PM - 7:00 PM
Case discussions and teaching sessions



Interactive review of complex cases with detailed analysis of decision-making processes, technical approaches, and outcome assessment. Participants can present challenging cases for collaborative input.
Structured discussion of potential complications in neurointerventional procedures and evidence-based management strategies, including vasospasm, thromboembolism, and vessel perforation protocols.

Detailed explanation of specialized techniques including coiling strategies, stent deployment methods, and navigation of challenging vascular anatomy with tips for access in difficult arch configurations.
Overview of latest advancements in neurointerventional devices, materials, and imaging techniques with practical applications for resource-appropriate implementation in the local setting.
Special hands-on training sessions will be available for trainees, including catheter handling workshops, case-based learning sessions, and career guidance in neurointerventional specialization.
International Guidelines Adherence
All procedures follow current recommendations from major societies including the World Federation of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology (WFITN) and the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery (SNIS).
Comprehensive Informed Consent
Detailed discussion of procedural risks, benefits, and alternatives with standardized documentation in native language when possible, including procedure-specific complication rates.
Detailed Procedure Documentation
Structured reporting templates capturing essential technical details, devices used, complications encountered, and immediate angiographic outcomes with standardized terminology.

Immediate assessment: Detailed neurological examination within 24 hours of procedure
30-day follow-up: Clinical evaluation and non-invasive imaging as appropriate
Long-term surveillance: Standardized protocols based on pathology and intervention type
Registry participation: Data contribution to international neurointerventional outcomes databases when feasible


We Welcome Cases For:
Wide-necked, fusiform, or dissecting aneurysms requiring advanced techniques beyond standard coiling
Stroke Prevention
Carotid and intracranial stenosis interventions for patients with recurrent symptoms despite medical therapy
AVMs and dural AVFs requiring targeted embolization as definitive treatment or pre-surgical preparation
Novel applications of neurointerventional techniques for challenging cerebrovascular pathologies
Pre-surgical devascularization of hypervascular tumors to reduce operative blood loss and improve resection


3 Days of Availability
Limited appointments during Dr. Reddy's visit (August 15-17, 2025)
4 Procedure Slots
Maximum capacity for complex neurointerventional cases
14 Consultation Slots
Available for case evaluations and treatment planning
Early submission ensures optimal scheduling and preparation
Together, we can provide world-class neurointerventional care to our patients in Myanmar. Our collaborative approach combines international expertise with local knowledge for optimal outcomes. Contact Information
Reach out to the Heart and Vascular Center team to discuss potential cases and schedule consultations during Dr. Reddy's visit.
Daw Theint Nwel Saw: +95 9765127712
Email: neuro.coordinator@victoriahospital.mm

