


Building Brighter Futures Together Combined and Co-ordinated Sciences Better teaching and learning for Cambridge IGCSETM 17 April 2023




Building Brighter Futures Together
•
•
David Martindill
Head of Science
•
Author for Cambridge University Press
Online professional learning tutor and experienced examiner
Objectives
1. How can we make our teaching and learning more ________ ?

2. What is ________ assessment and how can we use it?
3. How can we ________ better lessons?

Building Brighter Futures Together
Objectives
1. How can we make our teaching and learning more ____A____?

2. What is ____B____ assessment and how can we use it?
3. How can we ____C____ better lessons?

Building Brighter Futures Together
Objectives
1. How can we make our teaching and learning more active?

2. What is formative assessment and how can we use it?
3. How can we plan better lessons?

Building Brighter Futures Together
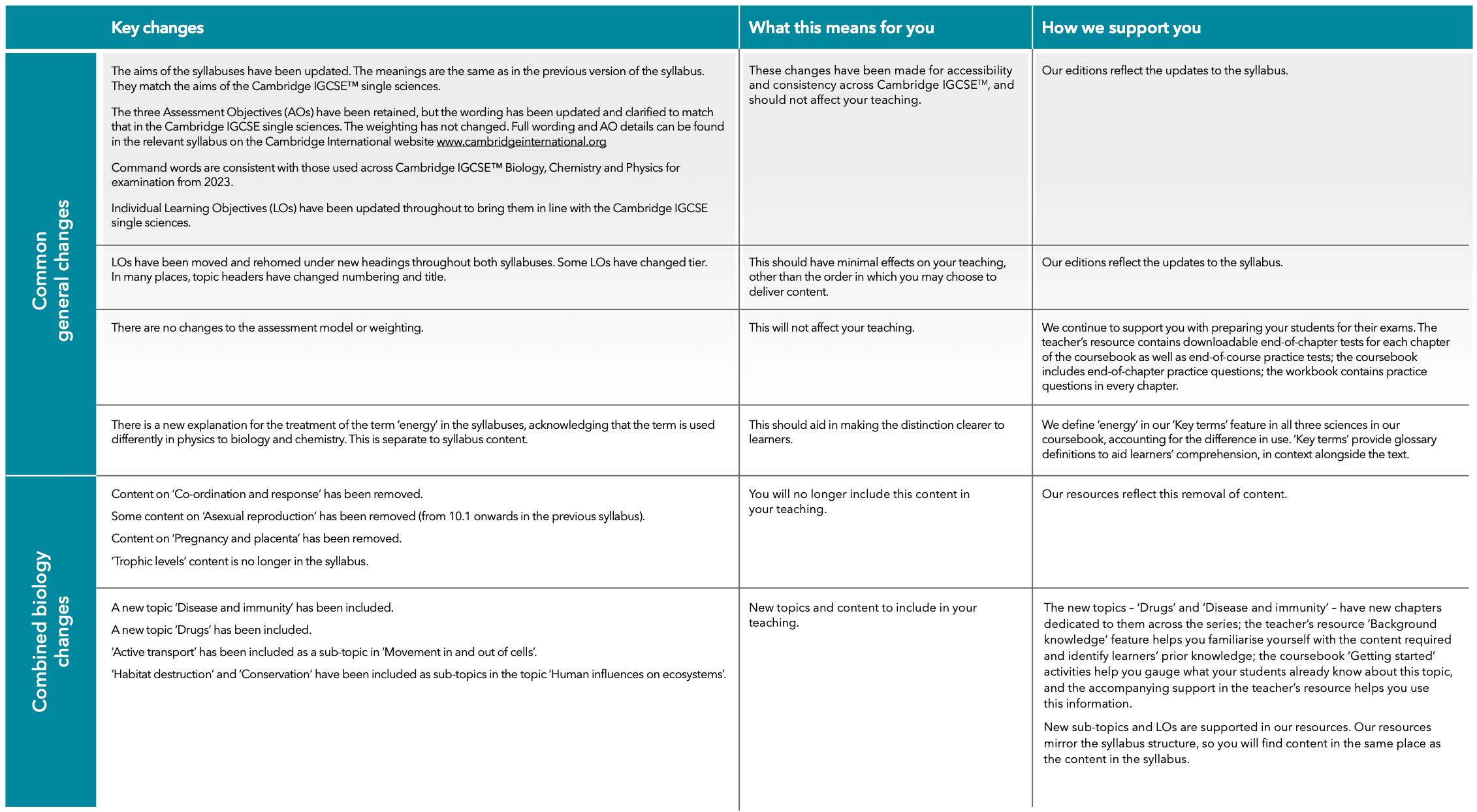
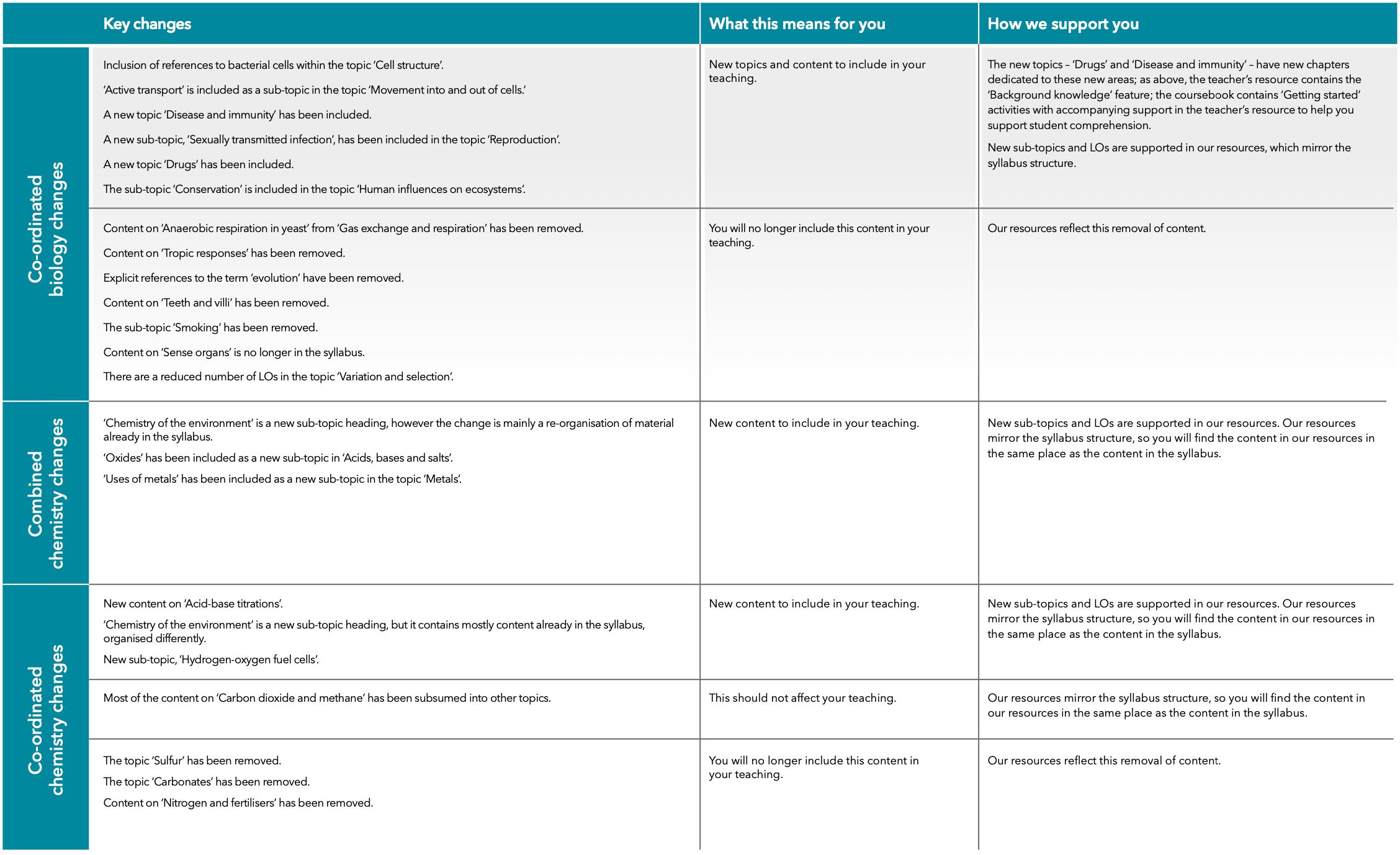
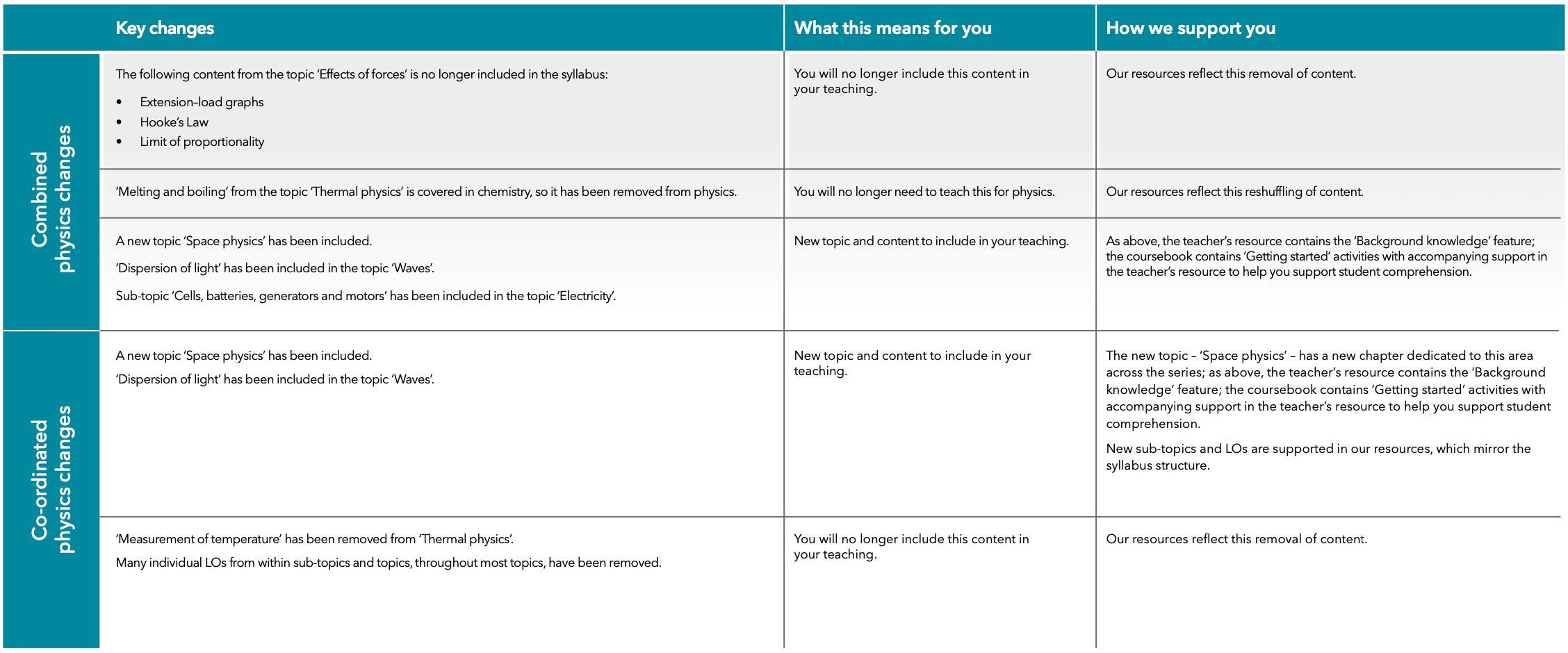
Combined and Co-ordinated Sciences – new Syllabus


Building Brighter Futures Together
New Syllabus

For examinations in 2025, 2026 and 2027

New resources from Cambridge


Building Brighter Futures Together
Building Brighter Futures Together





 Building Brighter Futures
Building Brighter Futures


Building Brighter Futures Together
Active Learning Part 1


Building Brighter Futures Together
Which classroom is better?




Building Brighter Futures Together
What is our job as teachers? or




Building Brighter Futures Together




Building Brighter Futures Together
=
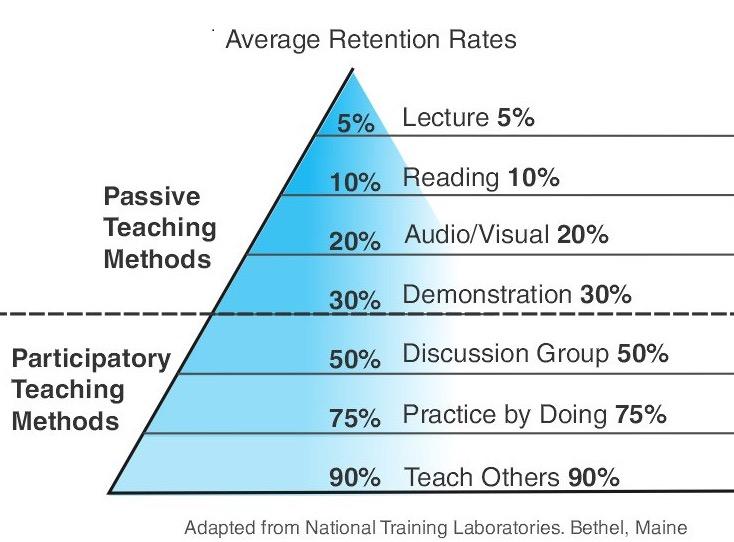
The traditional model of instruction is when knowledge is transmitted from a teacher to learners
= Learners should do something in lessons


Building Brighter Futures Together
“Active Learning describes a classroom approach which says that learners are active in the learning process by building their own knowledge and understanding”
Science teaching moves away from: Science teaching moves towards:

Teacher talks more than learners. Learners engage in on-task discussion in pairs and small groups.
Classrooms are mainly quiet.
Questions and debate are evident.
Learners learn by memorisation. Learners learn from a range of sources.
Mistakes are seen as negative. Mistakes are an opportunity to learn.
Lessons focus on the completion of written tasks. Lessons focus on working towards clearly understood learning outcomes.
Teacher talk is usually information and instructions. Teacher talk is with learners to confirm understanding and support learner-to-learner discussions.

Building Brighter Futures Together


Building Brighter Futures Together
What is our job as teachers? or and




Building Brighter Futures Together
If Active Learning is new to you…

Start with a small amount and build on this slowly
• Think, Pair, Share
• What’s the question?
• Converting information from text into a picture

• Summarising the content of a lesson in a ‘Tweet’
• Taboo
Building Brighter Futures Together
Example active learning activity: Taboo

Learners are to describe a concept to their peer without mentioning 3-4 key terms. This forces them to reconsider their vocabulary and consider deeply their knowledge of the topic.
Differentiation is easy – increase the number of taboo words

Examples include:
• photosynthesis (without ‘light,’ ‘glucose’ or ‘oxygen.’)
• electrolysis (without ‘electrode,’ ‘electrolyte,’ or ‘current.’)
Building Brighter Futures Together
Let’s get active!
Please rank order the following 5 tasks:
1. Answer an extended-response question.

2. Design a laboratory investigation.
3. Listen to a lecture.

4. Make a poster.
5. Phone a friend to discuss homework.
Please type your rank order into the Chat Box. E.g. 2-4-5-1-3
Building Brighter Futures Together
Any task can be active
1. Answer an extended-response question… … in small groups, with each member responsible for a different part.
2. Design a laboratory investigation… … using a list of equipment they they have selected from around the house.
3. Listen to a lecture... … while completing a missing-word worksheet to reinforce what is covered.


Building Brighter Futures Together
Any task can be active
4. Make a poster… … with a number of others and in competition with other groups.

5. Phone a friend to discuss homework… … halfway through completing it.

Building Brighter Futures Together


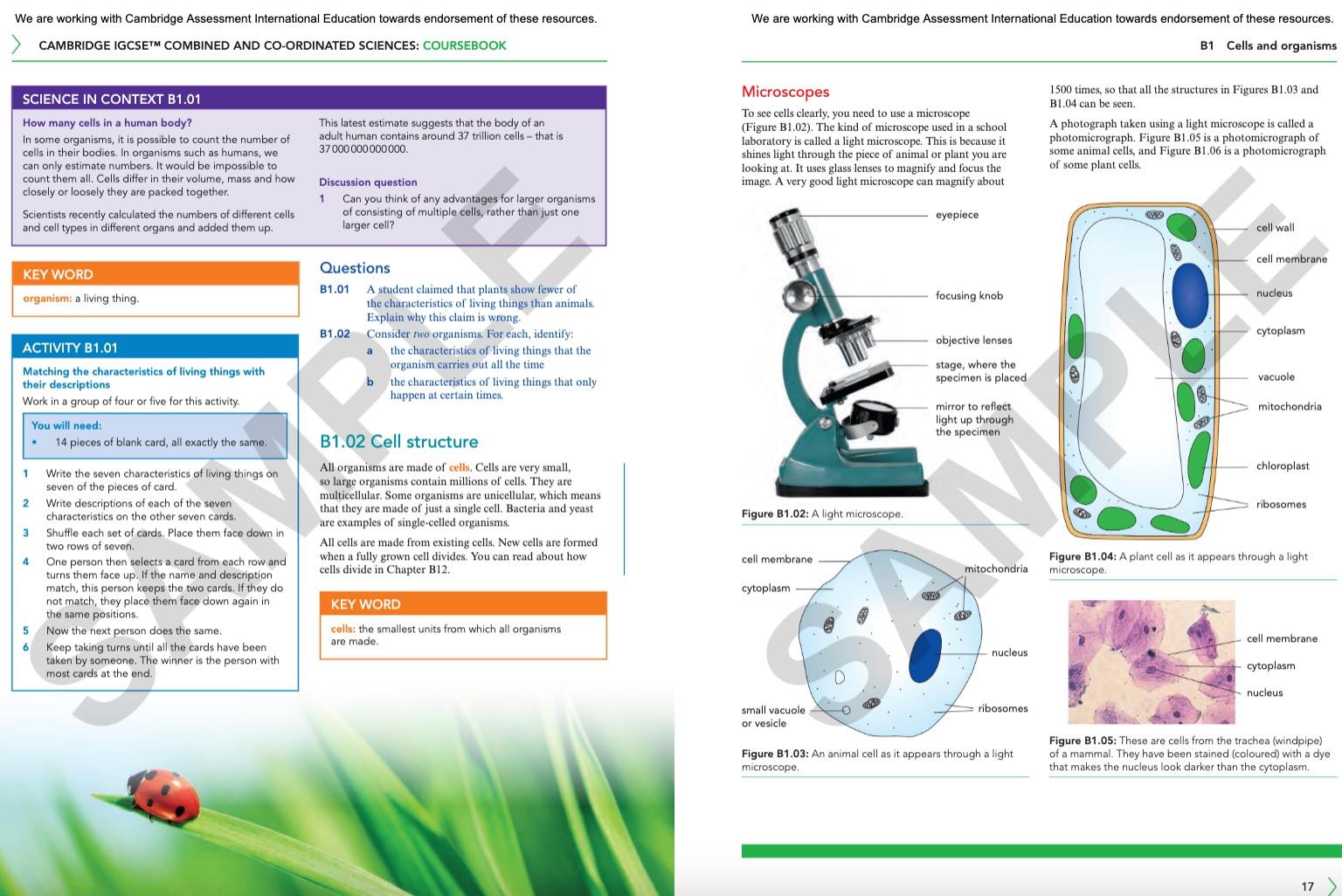
Building Brighter Futures



Building Brighter Futures Together

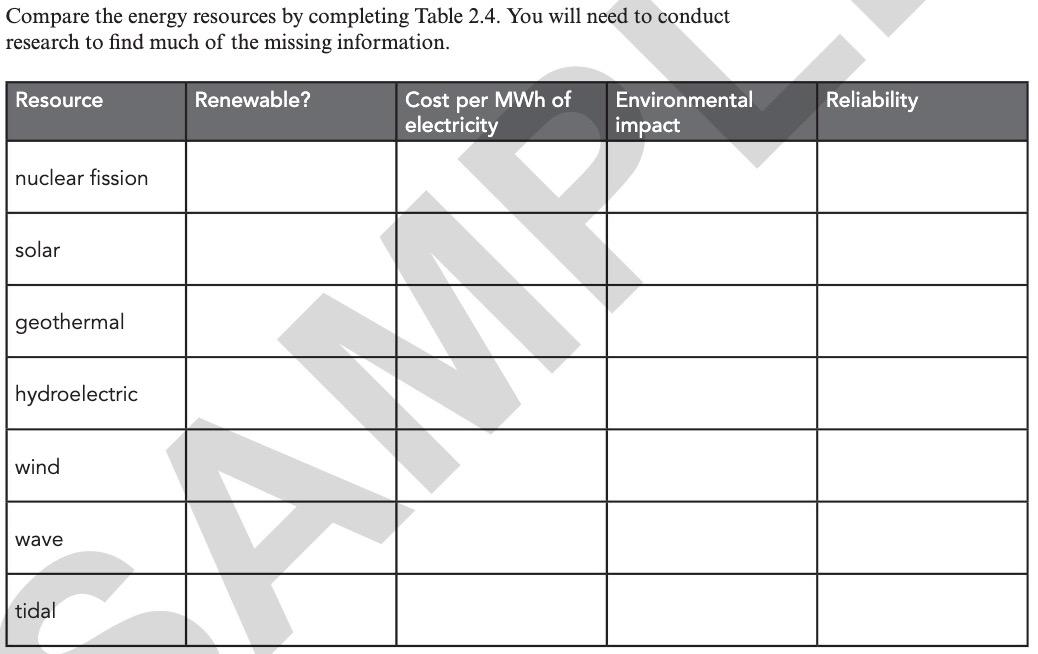

Building Brighter Futures Together
Formative assessment Part 2


Building Brighter Futures Together
Types of assessment
Formative assessment
Provides information to help
learners improve

Summative assessment
Questioning
Traffic lights
Thumbs up and down
Feedback ONGOING

Provides information that shows how much learners have understood
Tests
Exams
Coursework
FINAL
Building Brighter Futures Together
What is wrong with this feedback?


Building Brighter Futures Together
Types of feedback
Type of feedback
Impact
Grade
Grade + Comment
Little impact or negative
Little impact
Just comment
Positive impact
Comment + Action
Strong positive impact


Building Brighter Futures Together
Feedback should: Be positive

Tell learners where they are in their learning
Help them to improve

Building Brighter Futures Together
What


Building Brighter Futures Together WWW and EBI
Went Well What feedback
give? • WWW = • EBI = Even Better If
would you
AfL activity: Odd one out
Give learners three words, and ask them to find as many ways as possible to identify the ‘odd one out.’

This is a very clever way of encouraging holistic thinking.

Examples include:
• friction, pressure, air resistance
• solid, liquid, gas
Building Brighter Futures Together
Building Brighter Futures
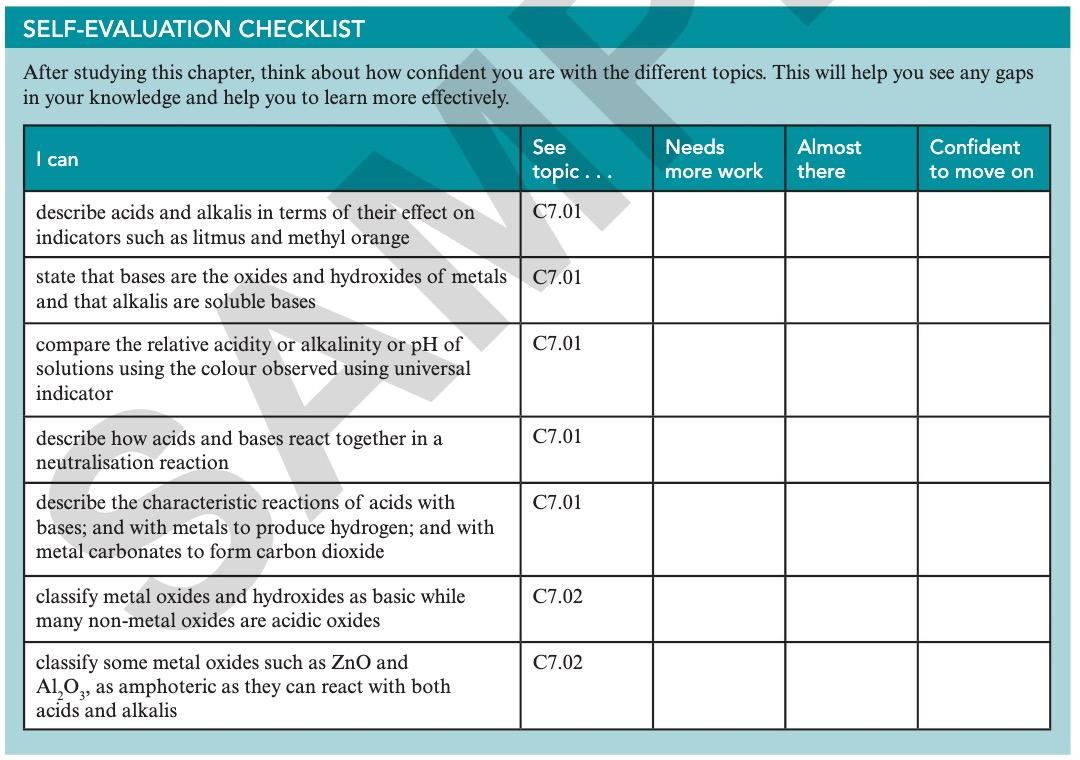





Building Brighter Futures Together
Part 3
Case study: Planning a lesson


Building Brighter Futures Together


Building Brighter Futures Together Transpiration B8.3 – Core and Supplement © Cambridge University Press 2021



Building Brighter Futures Together
Planning a lesson
Identify the learning objectives


Building Brighter Futures Together
The objectives must be measurable. Know about the process of transpiration matter State what is meant by transpiration





Describe the effect of various factors on the rate of transpiration
Explain the effect of various factors on the rate of transpiration
The problem with the first one: How do you know that they know?

Building Brighter Futures Together
Use command words



State Describe Explain

Building Brighter Futures Together
Planning a lesson
What do we want them to learn?

How are we going to teach them this?

Building Brighter Futures Together
Introduction: Assess prior knowledge

Share learning intentions and outcomes
Create an enthusiasm for learning and the reason for the lesson

Building Brighter Futures Together
Lesson Activities and Resources
Break the lesson into several ‘chunks’
Each ‘chunk’ is an activity Can be teacher centred or learner centred or both

Introduction
Main activities (several)
Plenary/ review of learning

Building Brighter Futures Together
Example plenary activity: What’s the story?
Given a number of key terms, learners are asked to produce a short paragraph using all/ most/ some of them in the correct context. This removes the ‘cognitive load’ of AO1 (recalling key words) and facilitates their demonstration of higher-level skills (AO2).


Examples include:
acid, alkali, pH, high, low
refraction, total internal reflection, critical angle, normal
Building Brighter Futures Together
•
•
Three example activities

All three activities allow the teacher to circulate during the activity, to monitor and address misconceptions and misunderstandings as learners engage in their dialogue.

Building Brighter Futures Together



 Building Brighter Futures
Building Brighter Futures

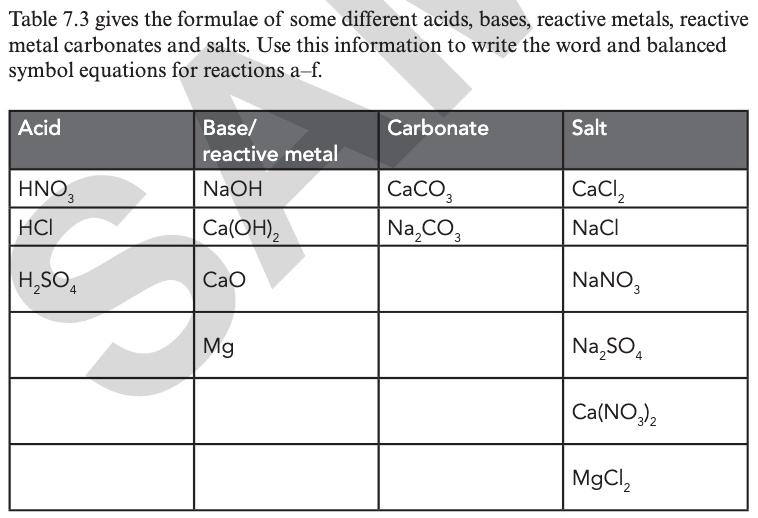

Building Brighter Futures Together
Building Brighter Futures Together





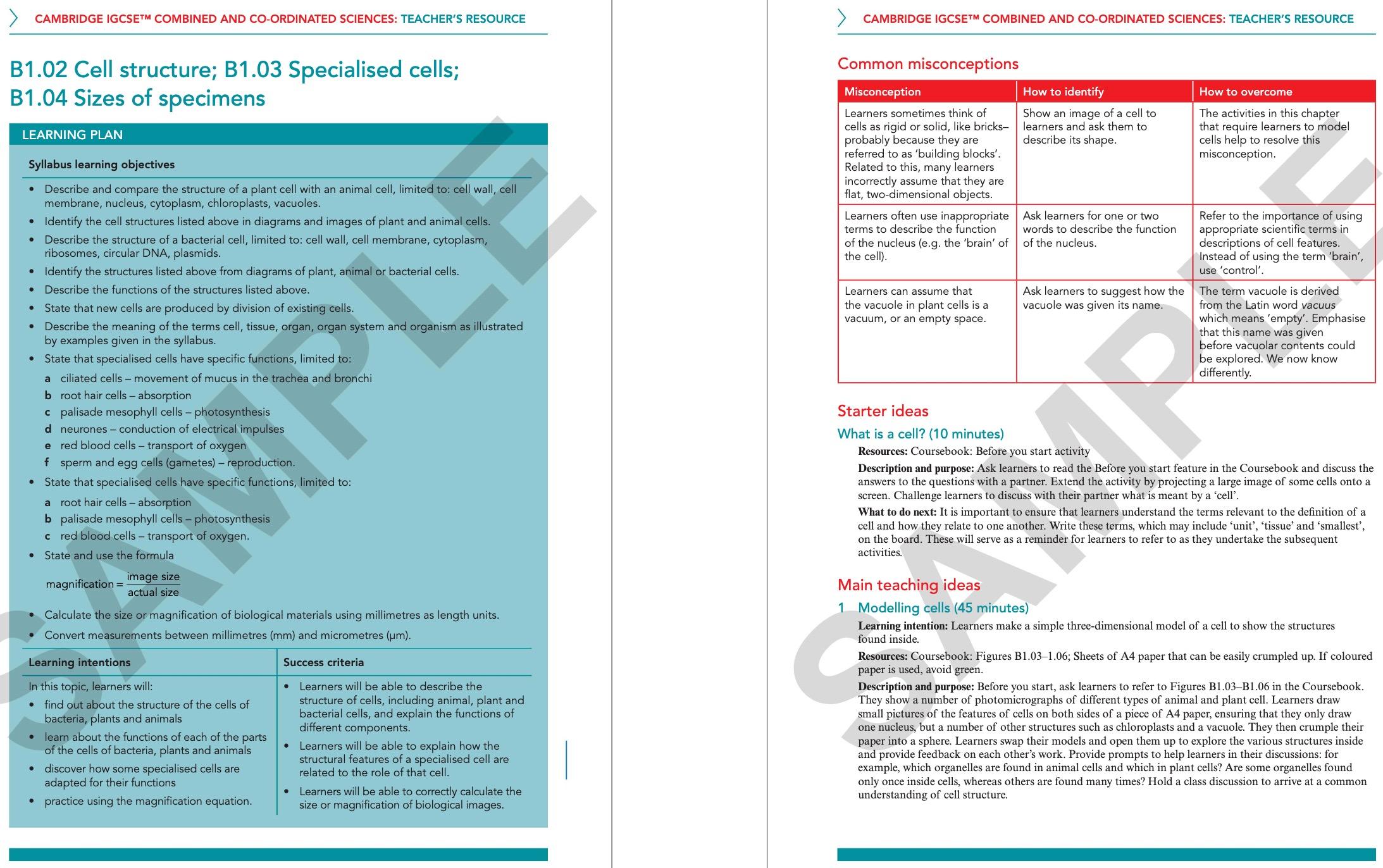
Building Brighter Futures
Building Brighter Futures



Any questions?


Building Brighter Futures Together
Any questions?
What opportunities are there for truly co-ordinated teaching and learning?

Why are some of the topics the same as those in Cambridge Lower Secondary?

Why do we not just teach learners the information and knowledge that they need?
Why is it important for children to ask questions and feel safe to make mistakes?
Building Brighter Futures Together


 Building Brighter Futures Together
Building Brighter Futures Together

















 Building Brighter Futures
Building Brighter Futures




















 Building Brighter Futures
Building Brighter Futures






