The project is being implemented with the support of UNICEF Ukraine and with financial support from the Government of Norway.

Implemented by: Partner:






The project is being implemented with the support of UNICEF Ukraine and with financial support from the Government of Norway.

Implemented by: Partner:





C.C. is a 13-year-old patient for spinal cord compression (SCI)

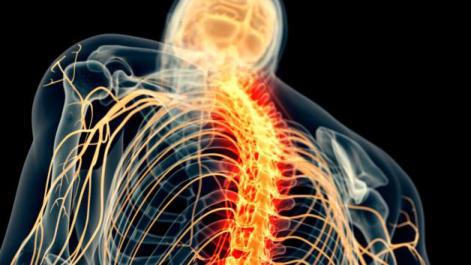
The compression is from a burst fracture at the C6 level caused by an accidental fall into the swimming pool
Subjected on the same day at another center to C6 somatectomy and C5-C7 arthrodesis with titanium body, plate and anterior screws


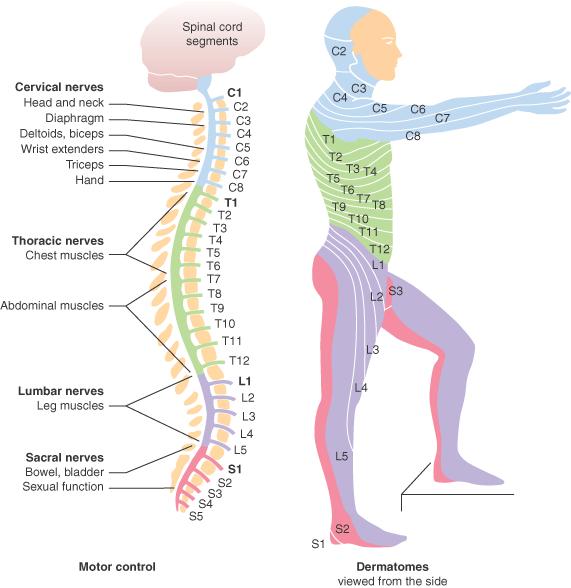

Functional framework of tetraparesis with greater involvement of the Lower Limb Articular Areas


UPPER LIMBS: - possible activation for the direct proximal joints
SENSITIVITY: - alterata. altered. The patient reports persistent pain, especially at the dorsal level.

Initially, the treatment is carried out in the room. In this initial phase, parents are instructed in correct postural hygiene, aimed at preventing damage resulting from immobility.
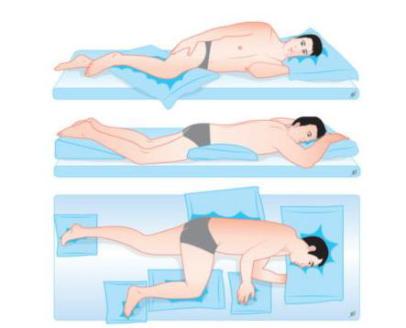
Examples of correct bed postures
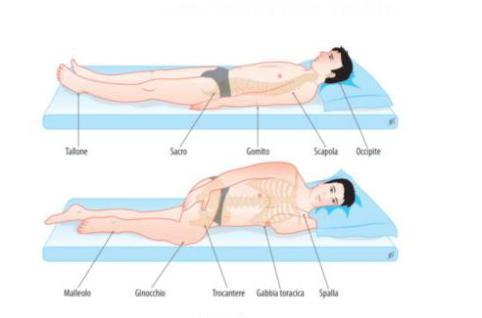
Body areas where pressure sores most commonly develop


Chiara also wears positioning braces throughout the day.
Stretching exercises and assisted passive/active mobilization are performed on all four limbs.









Proprioceptive Neuromuscular
Facilitation (PNF)

Therapeutic Awareness
Exercise

Electro-stimulation

Stretching & Muscle
Strengthening
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) is a therapeutic approach defined as promoting the response of the nerve impulses to recruit muscles through stimulation of the proprioceptors in addition to other sensory stimuli (tactile, visual or verbal) in the beginning that decrease overtime as learning progresses.
Principles are stimuli used in practice that can be exteroceptive (e.g. tactile, verbal/auditory or visual) or proprioceptive stimuli (e.g. resistance, traction, approximation and stretching), all of which are incorporated in all PNF practice with small variations according to patients' condition and treatment goals.

D1 diagonal. Please note that wrist and fingers flexion with supination and radial deviation are done for flexion pattern while the opposite is done for extension pattern.

D2 diagonal. Please note that wrist and fingers extension with supination and radial deviation are done for flexion pattern while the opposite is done for extension pattern.
Cognitive exercise therapy is a therapeutic intervention that aims to reorganize the central nervous system through learning motor function recovery.
This therapy emphasizes the close relationship of motor function to the activation of cognitive processes in the brain, such as perception, attention, memory, judgment, and language. Cognitive exercise therapy allows various movements or actions to be performed through cognitive training processes, rather than movement training through interaction between the body and environment, to build a brain schema with four principles.
Attention
Somatosensory information.
Specific treatment instruments or tools
To develop and maximize the ability to organize the spatial, temporal, and intensity factors of the exercise sequence in the interaction between the body and environment.

FES implemented in individuals after SCI has been associated with bone and muscle health and strength, improved blood circulation and tissue healing, and pain management.
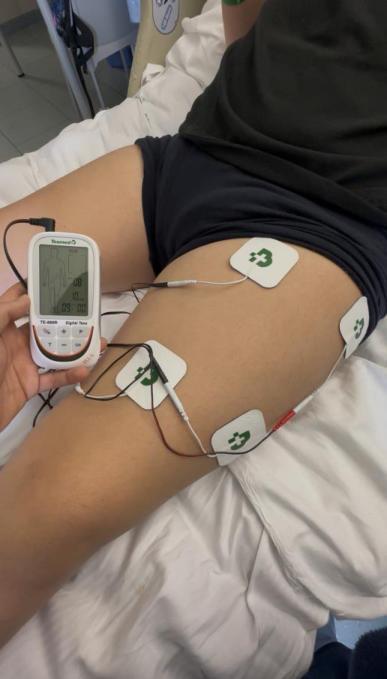


Mobilizations and stretching of the four limbs to prevent complications of hypomobility, ROM limitations and muscle-tendon retractions

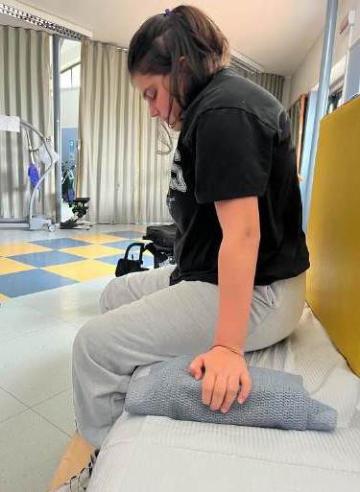


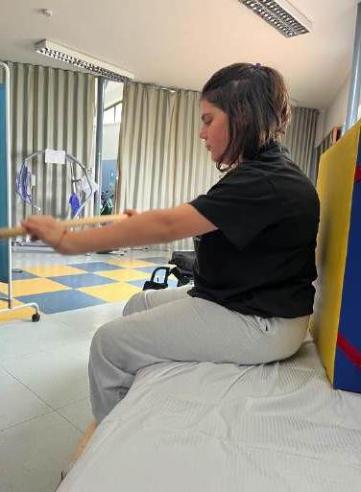
• Trunk control exercises in a sitting position with the lower limbs supported
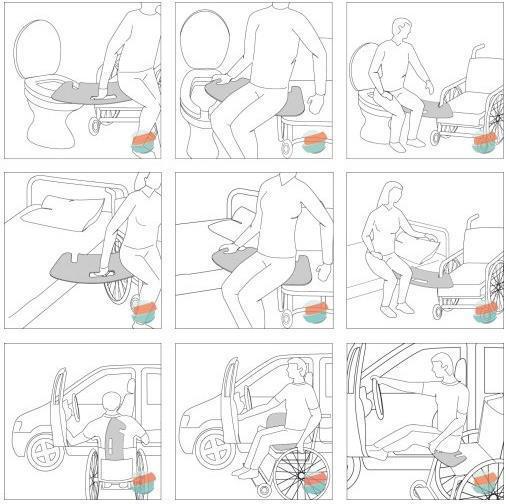
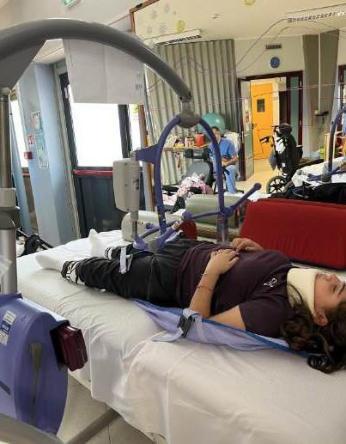
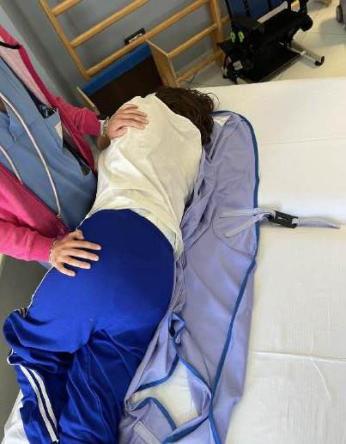

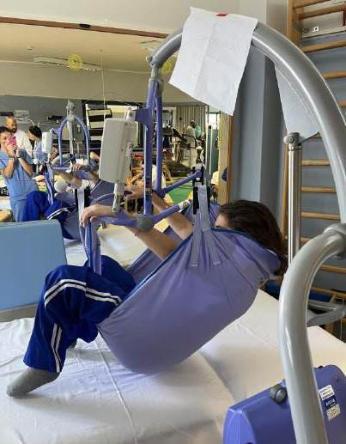
bed-to-weelchair and weelchair-to-bed transfer with/without the high-sliding board





Our patient is currently continuing her rehabilitation program with the goals mentioned above at a community center.
This also demonstrates the importance of rehabilitation continuity from the hospital to community-based treatment, which is essential to achieving all of the patient's goals.
Indeed, the patient plays a central role in her treatment journey and must be treated comprehensively.
Il presente documento Ë stato elaborato da Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Ges˘
I contenuti sono strettamente riservati; Ë vietata la riproduzione e la divulgazione, anche solo parziale, senza il benestare scritto di Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Ges˘.