Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



 Dr. Paolo Tomà
Head of Imaging Department
Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospitals
Dr. Paolo Tomà
Head of Imaging Department
Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospitals
Background


Classic CXR and CT appearences of COVID-19 described in adults
Literature on chest imaging of children with COVID-19 is limited

CT widely used in adults, & in children in some centres
Children with COVID-19 experience milder illness than adults
• New studies: higher than previously recognized rate of severe illness and MIS-C in pediatric COVID-19
• Infants (< 1yr) more vulnerable to severe infection
of Covid 19 infection
Imaging
in children
Royal College of Physicians. Every breath we take: the lifelong impact of air pollution. Report of a working party. London: RCP, 2016.
3 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
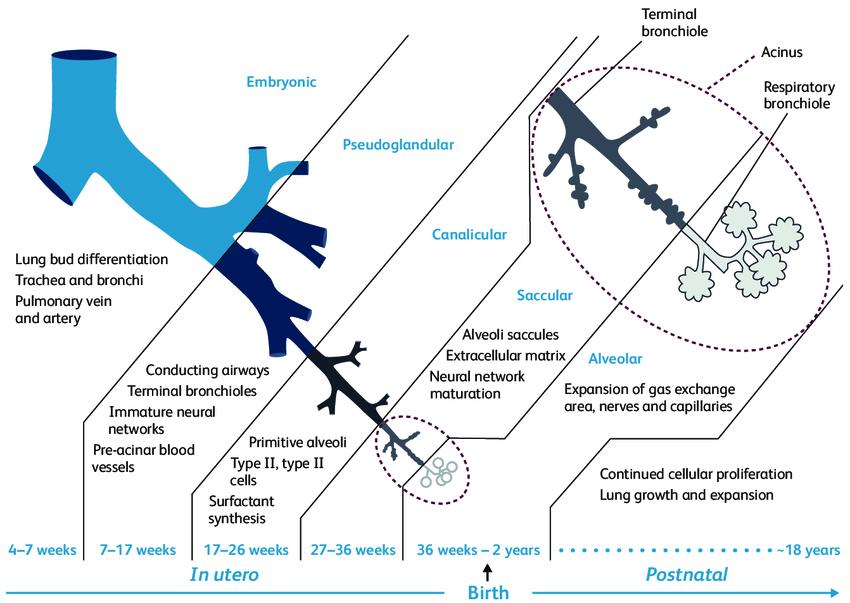
Due to immature lung anatomy & developing immune system, pediatric patients are often particularly susceptible
COVID-19 Chest Pediatric Imaging Pubblications

Small sample size

4 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children Early pandemic
Not radiology journals
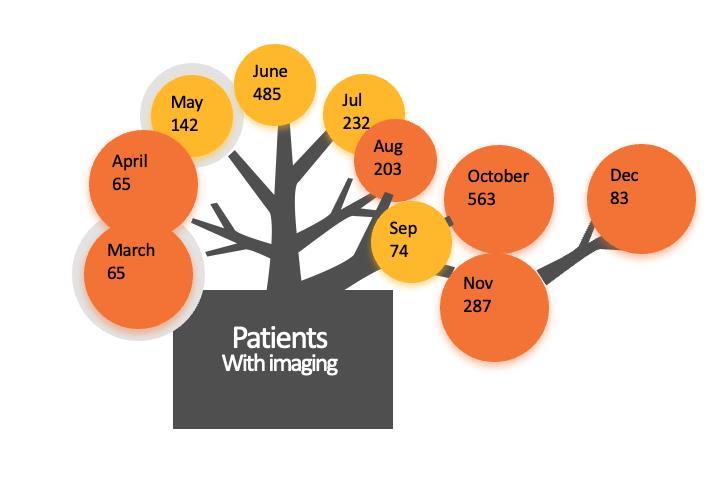


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children 91 ESPR


Journal • Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children • 39%
CT CXR



7 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Parameters


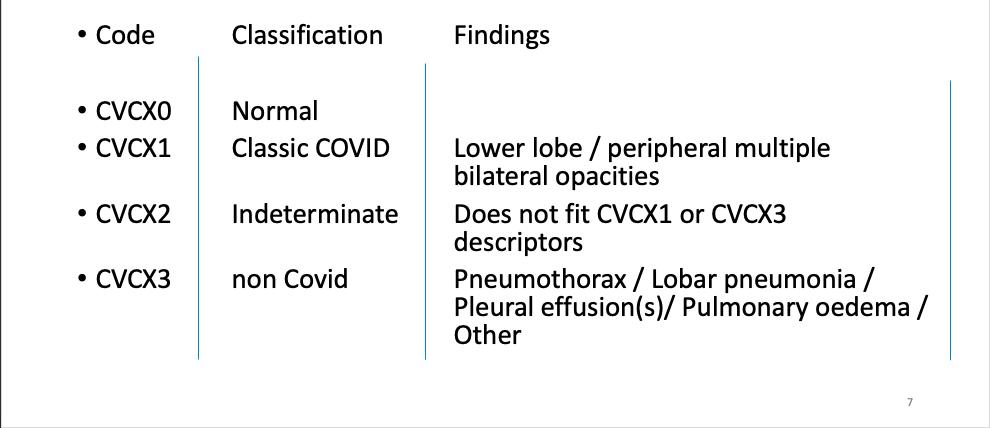
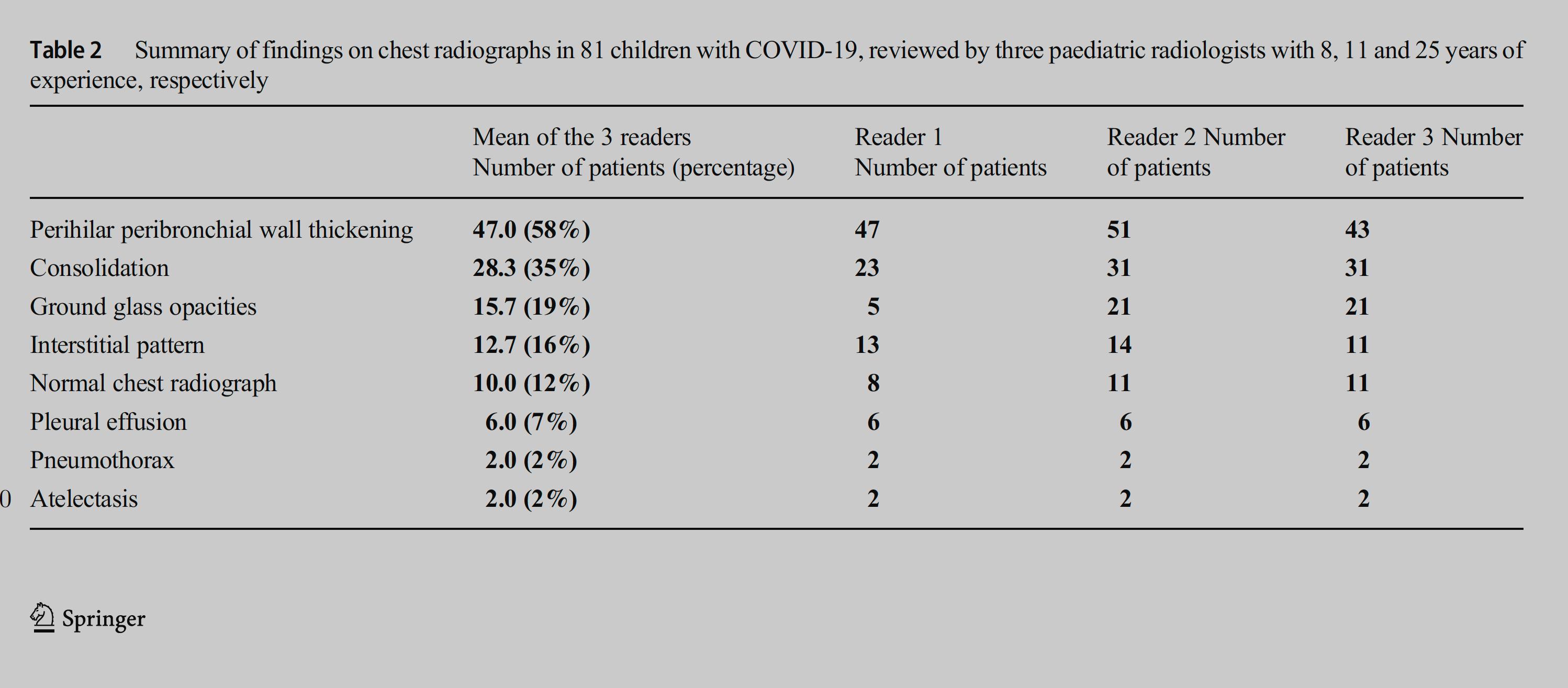
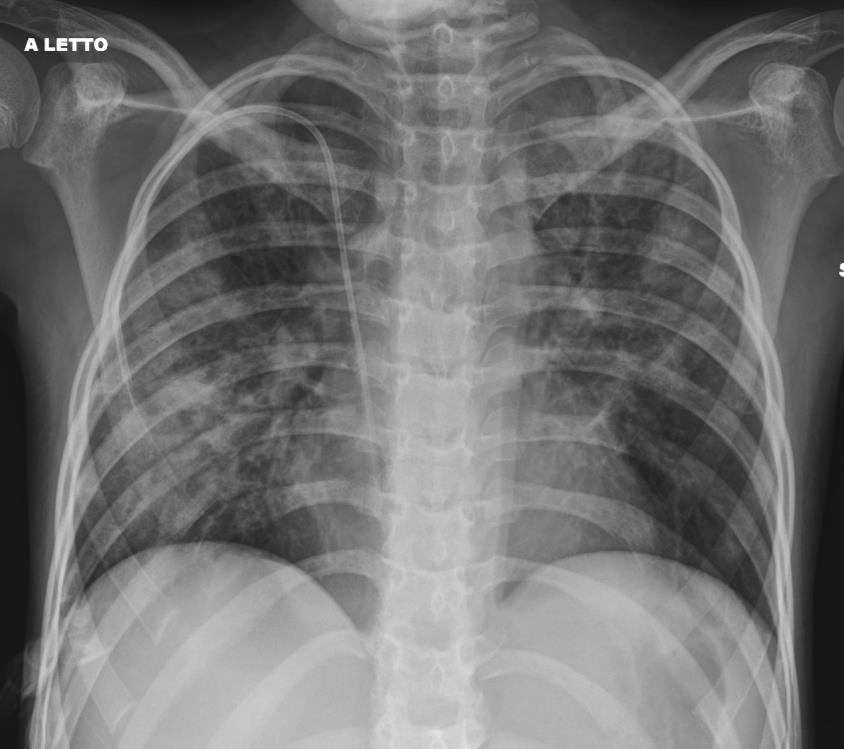
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children CXR 8 38% 3% 51% 8%
Consolidation 35%
Collapse 3%
PeriBronchial thickening
51%


Hyperexpansion 7%
Effusion 4%

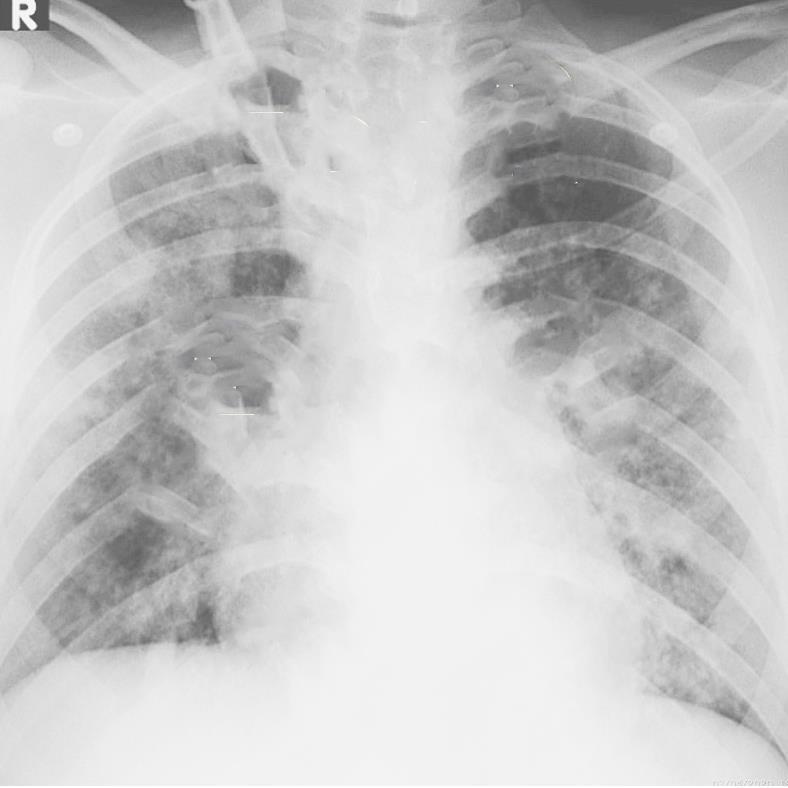
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children CXR 9 C O V I D
Birmingham
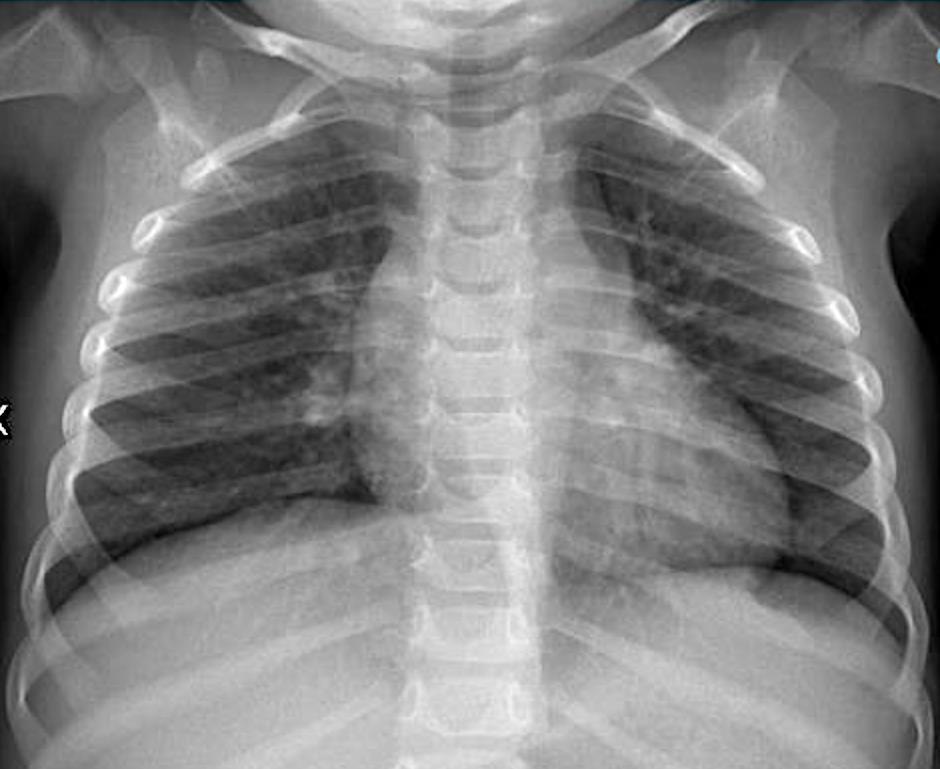


Covid 19 CXR Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
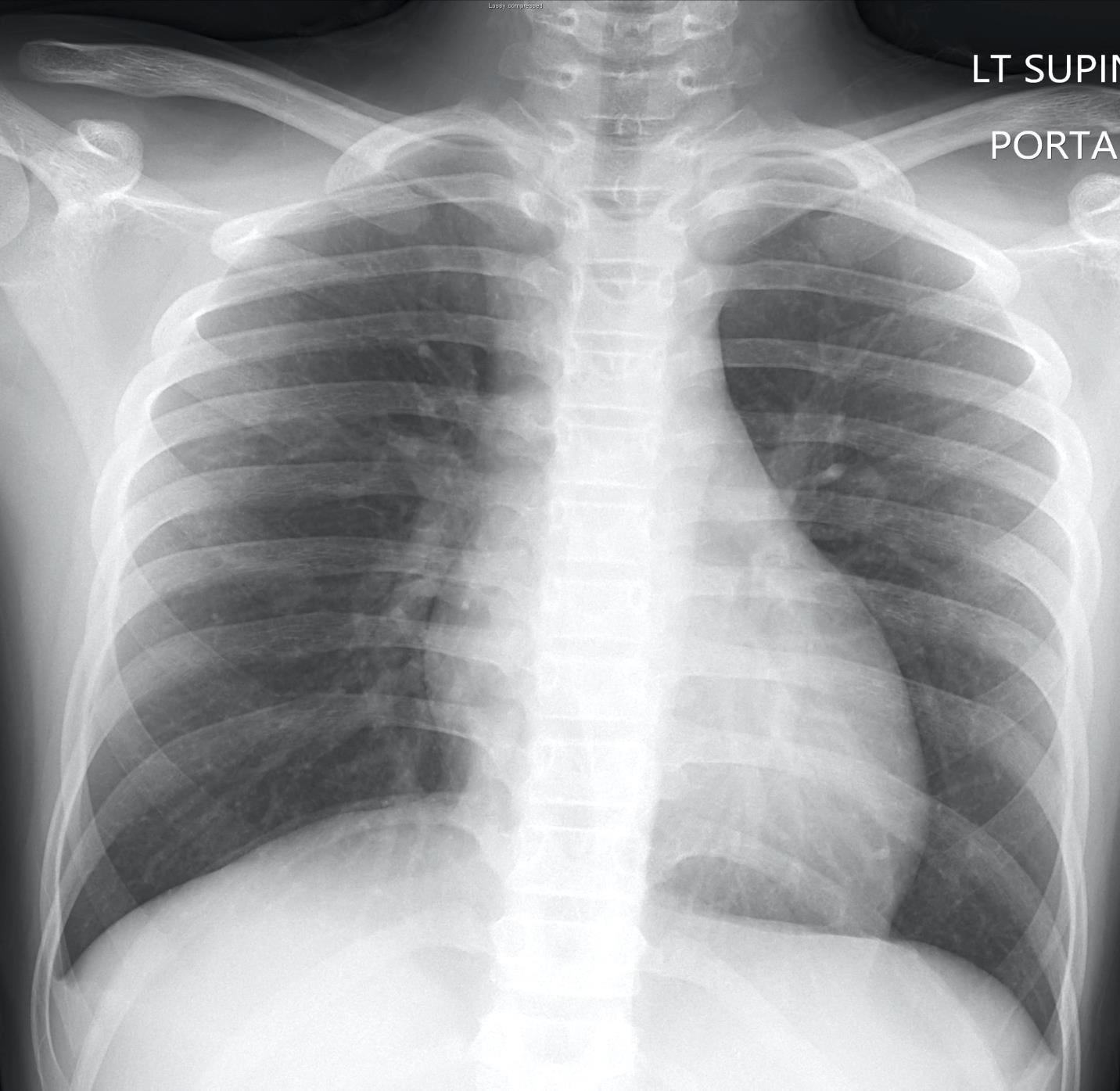


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
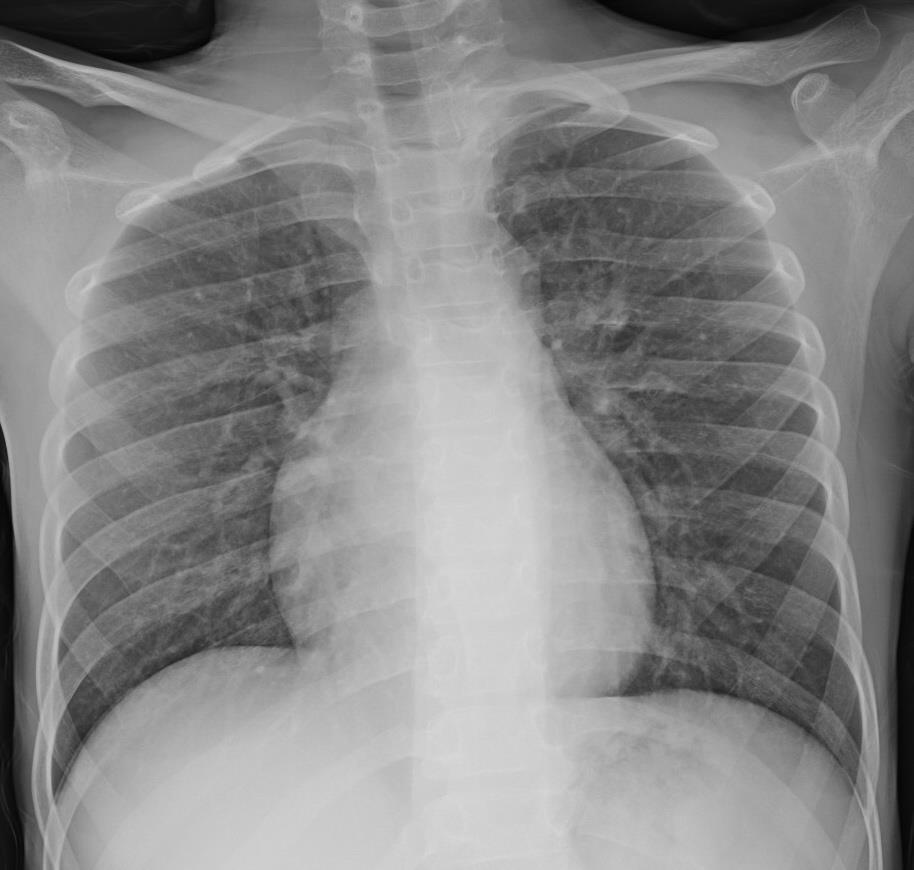


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
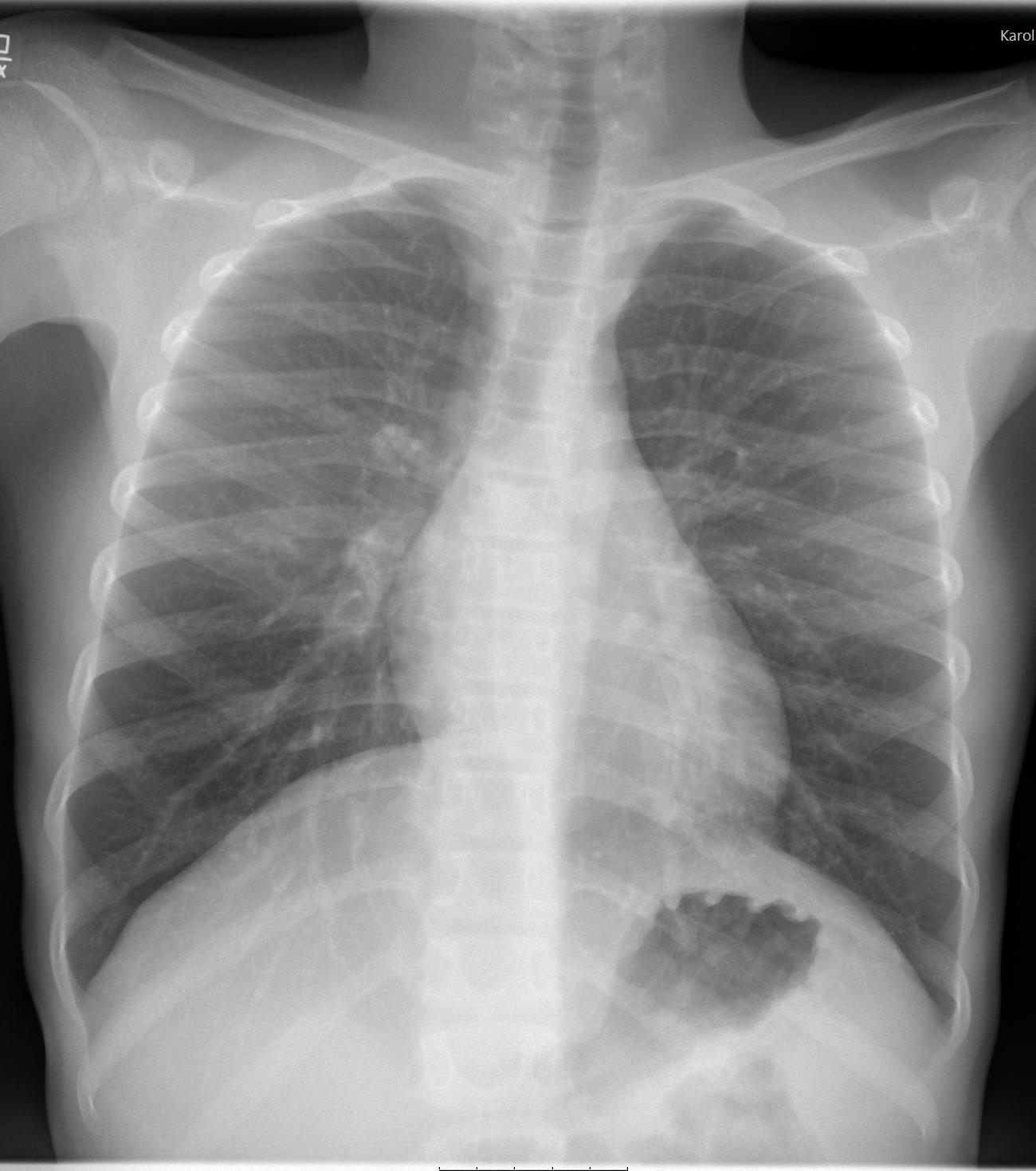


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



Imaging of Covid 19 infection in Children
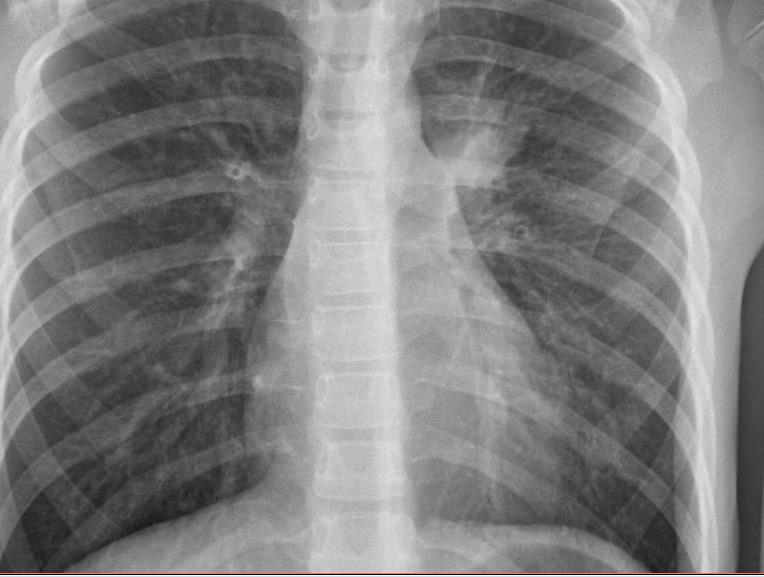


Mycoplasma Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Mycoplasma
Chlamydia


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
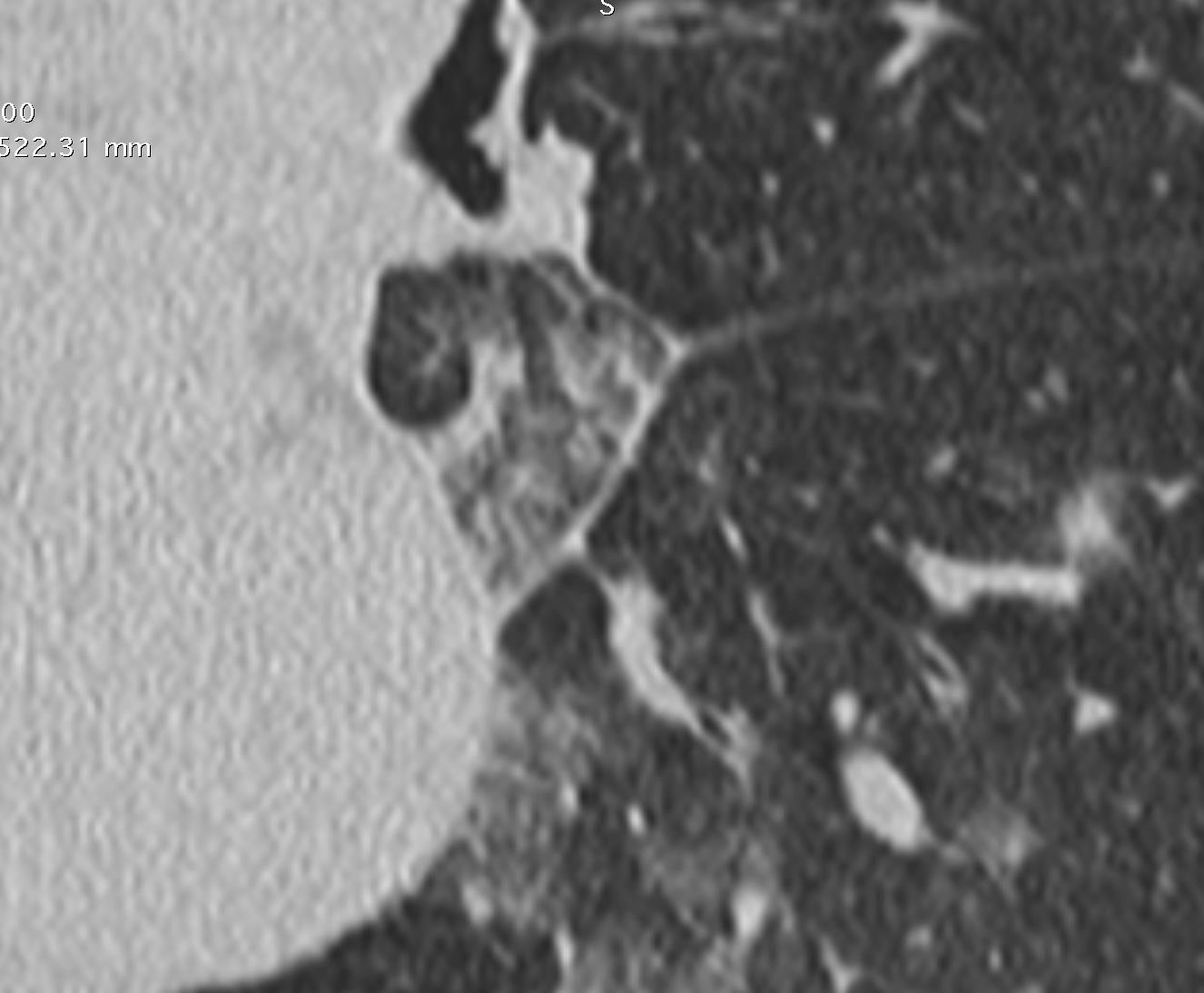
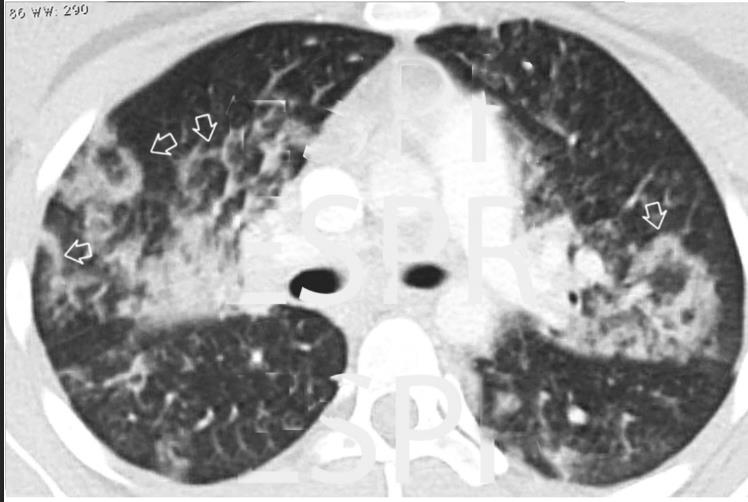
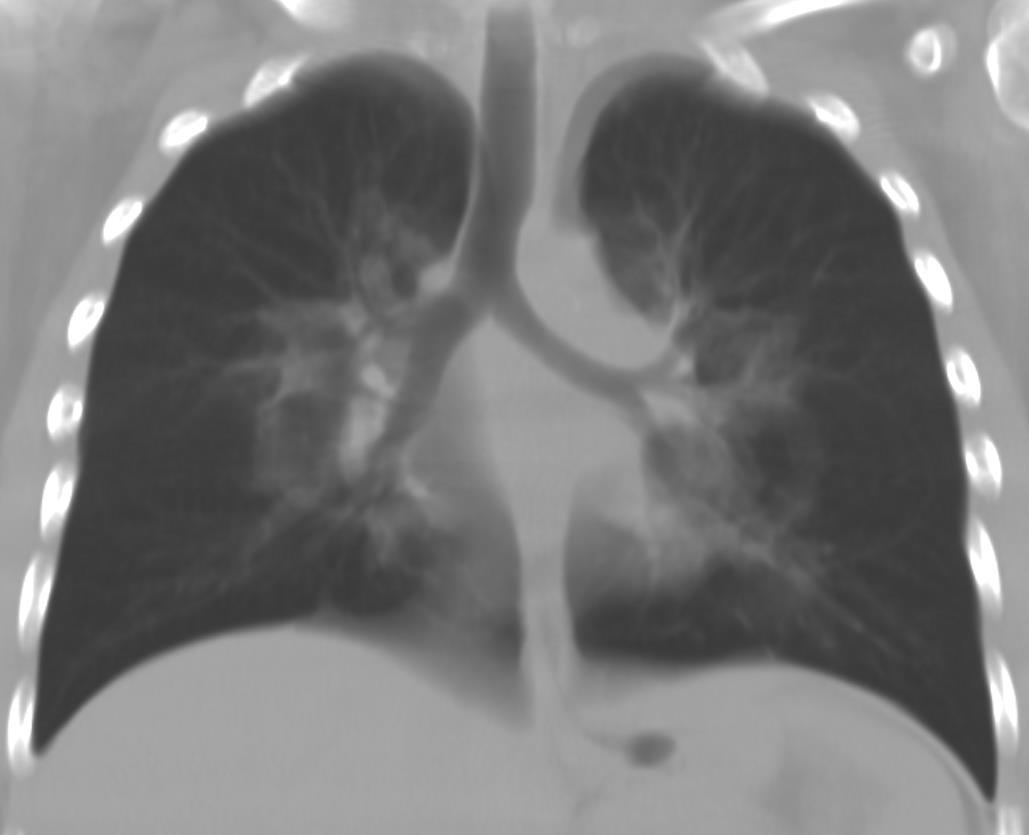
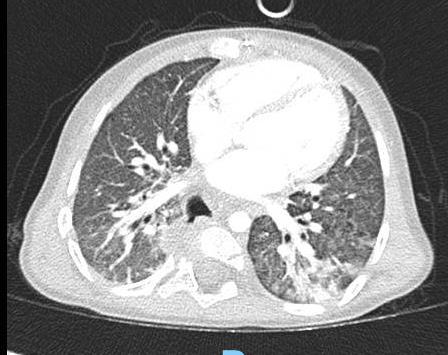
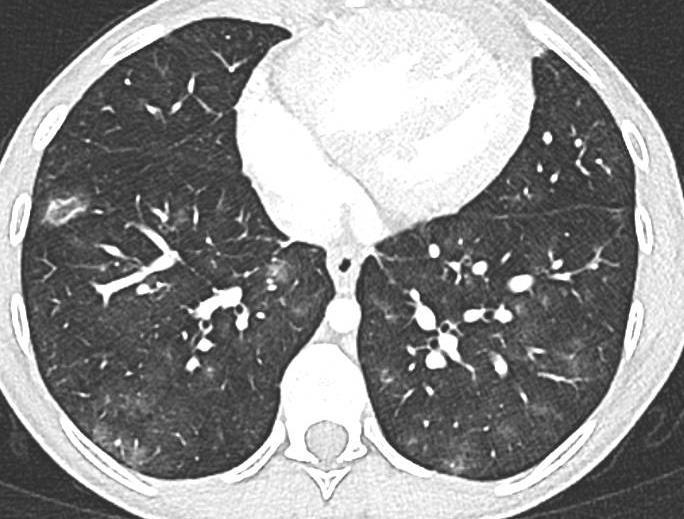
Acute Pediatric COVID-19: CT



21 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
3 Phases
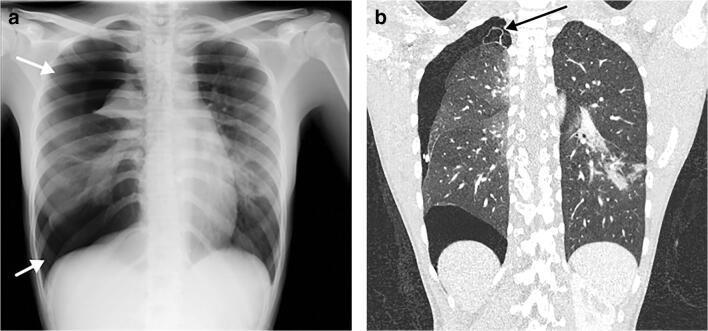
Early: "Halo" sign

Local infection
Progressive: Diffuse GGO


Developed: Consolidation
Surr vasc congestion
Inflammation - adj alveoli
Alveoli fill with fluid/cells
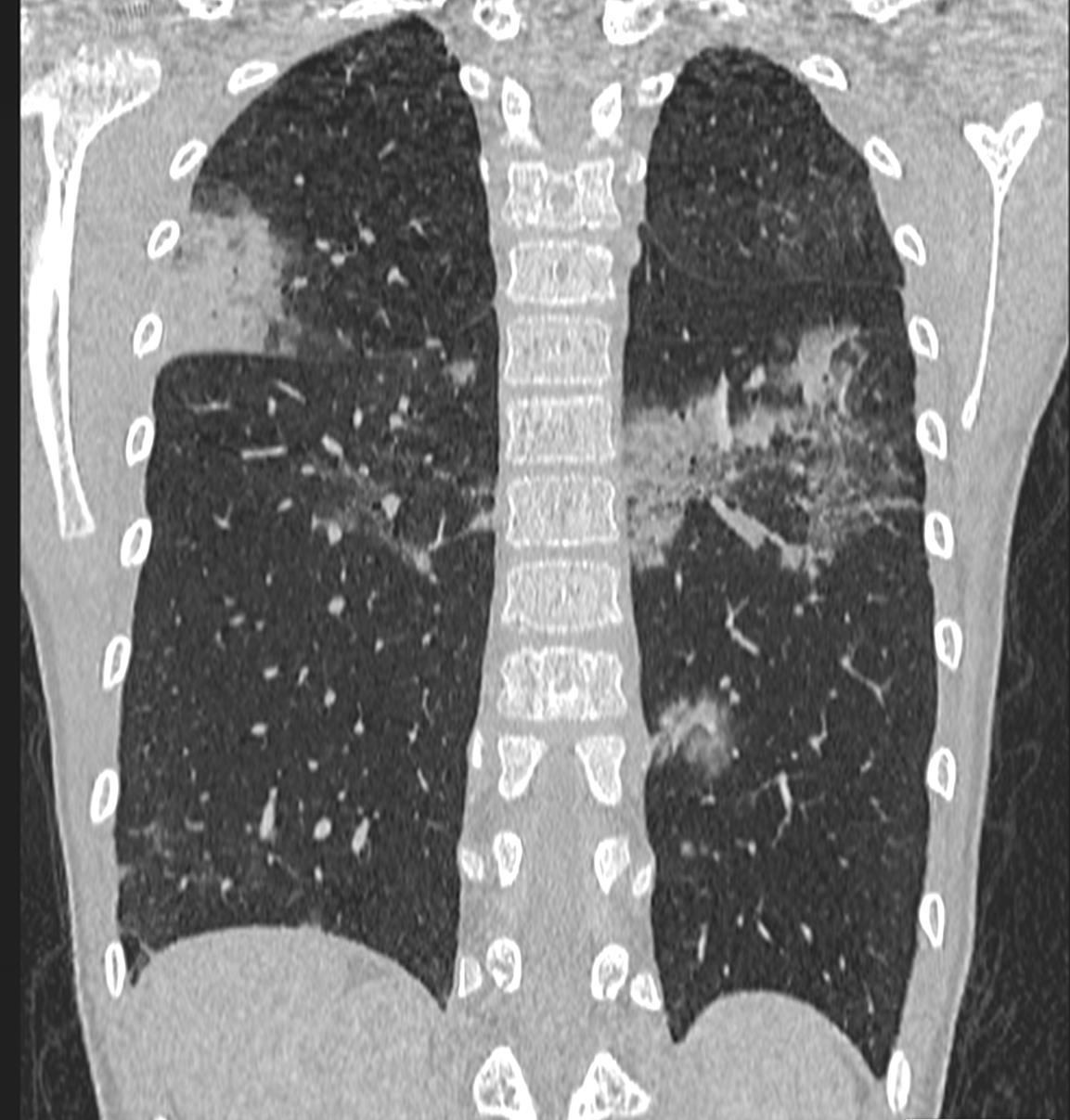
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Early: "Halo" sign


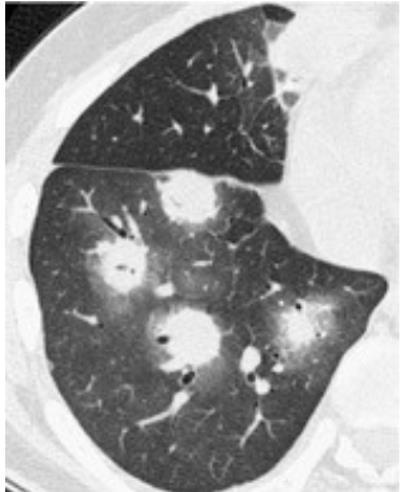
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Local infection Surr vasc congestion
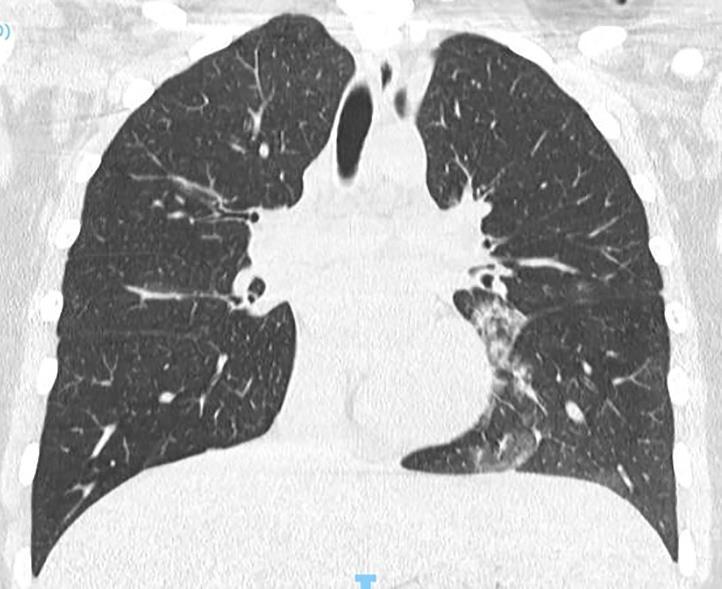
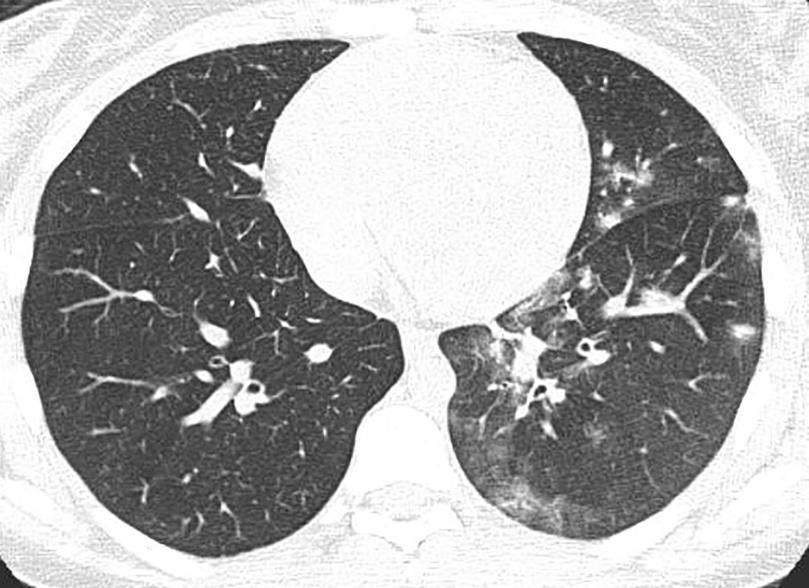
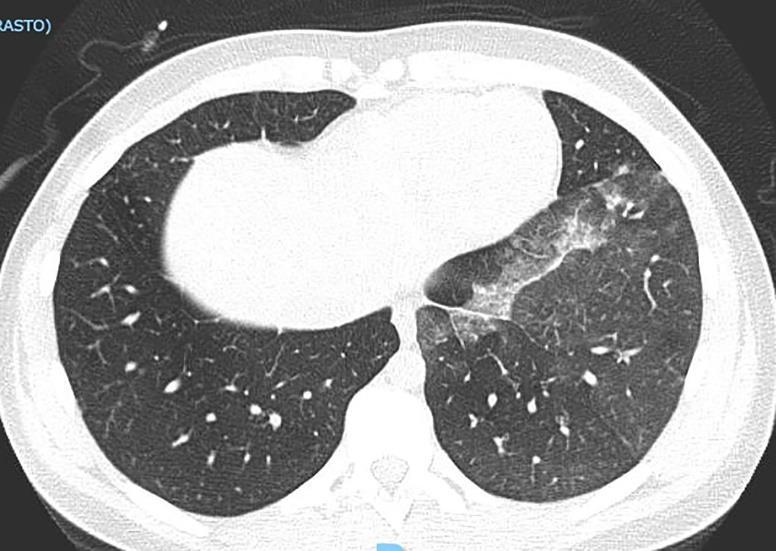
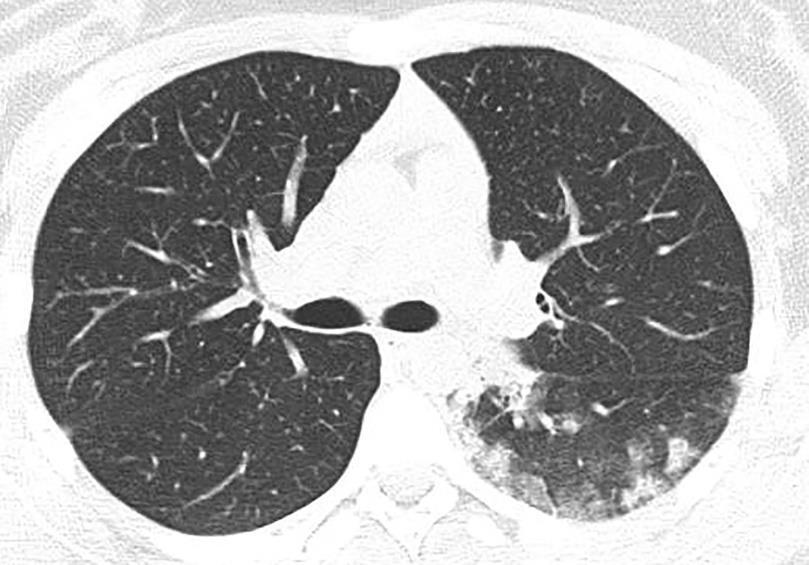
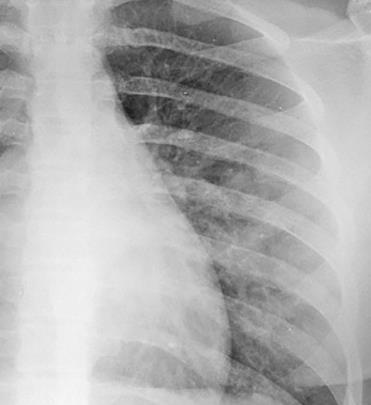
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Apicale sinistraa Medio -Basale sinistra
Basale sinistra Basale sinistra
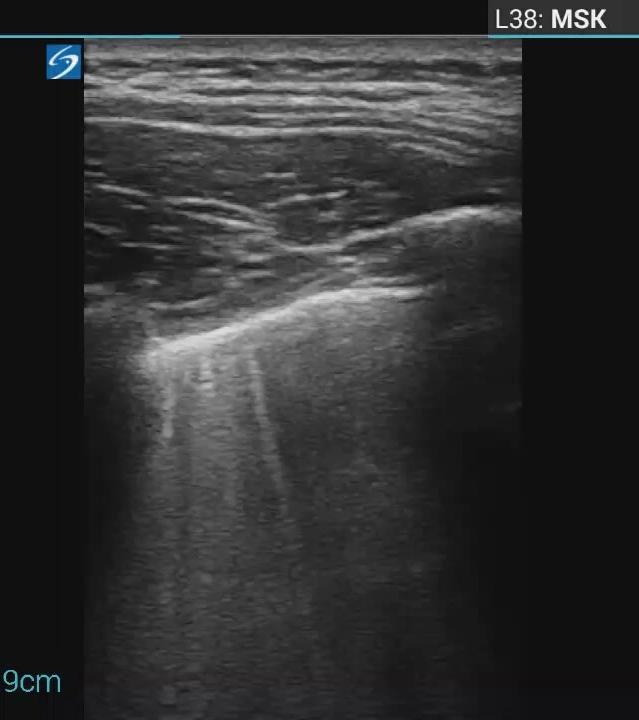

Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
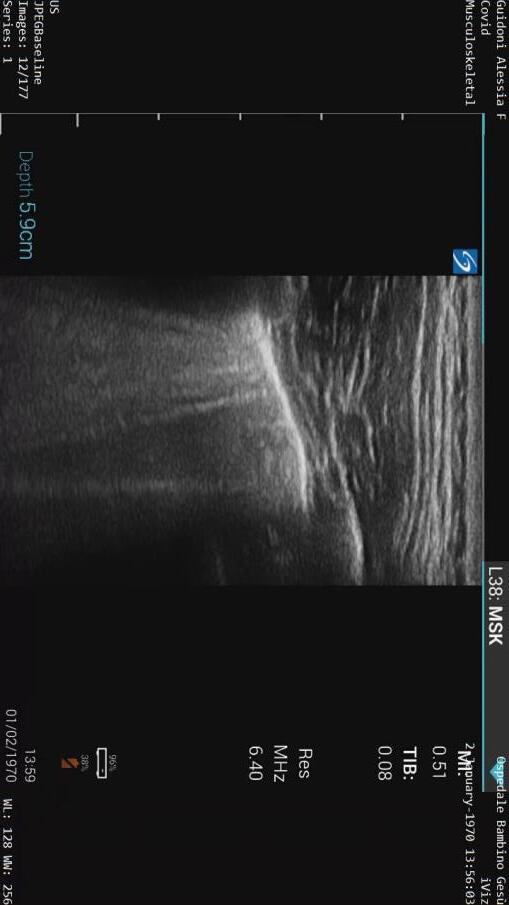
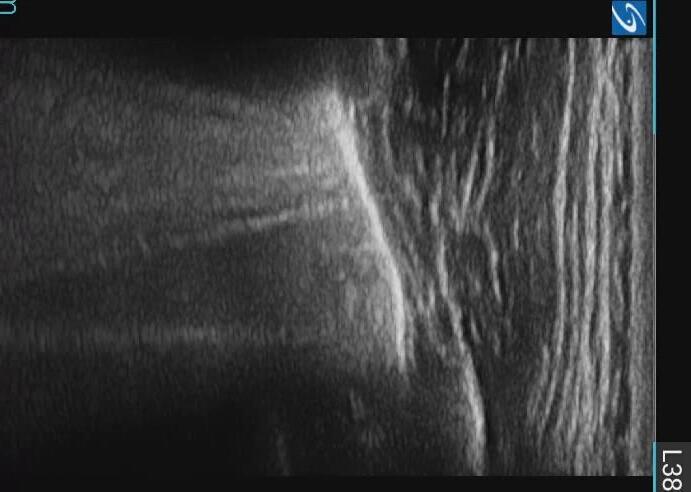
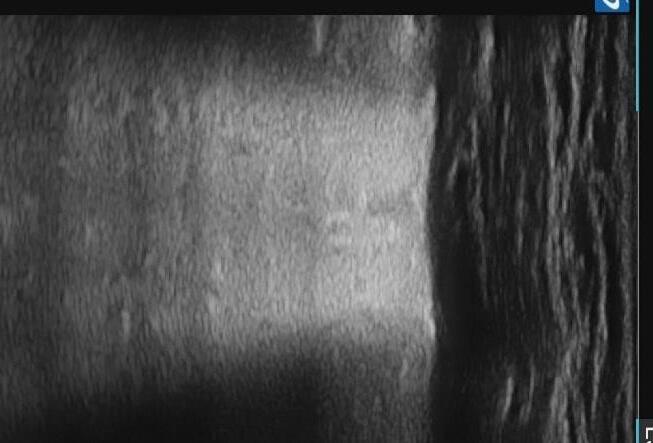
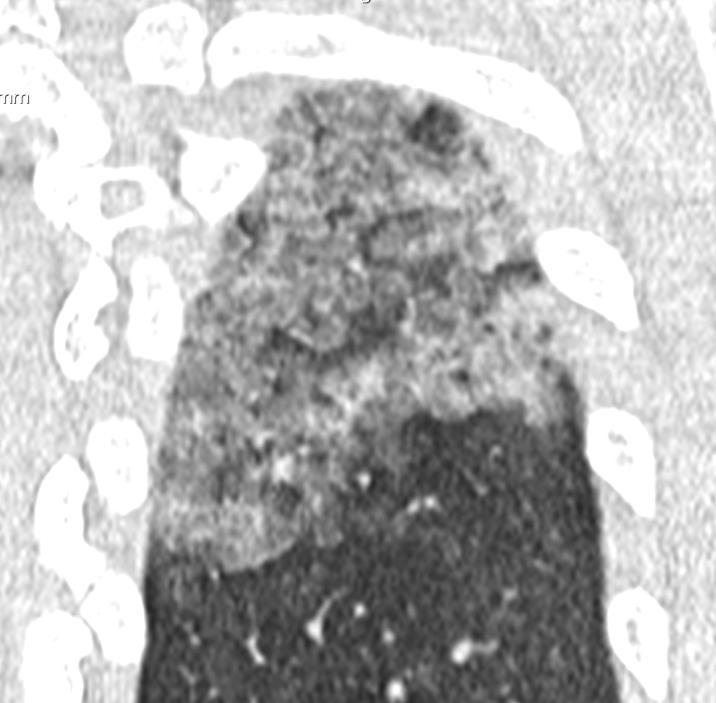

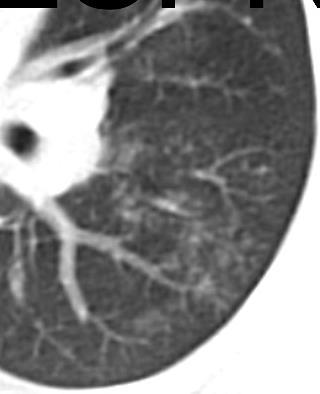
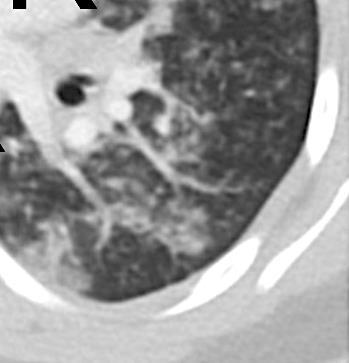

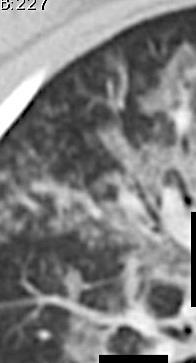

Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Lung Disorders CXR
COVID 19
• Patchy bilateral GGO, Consolidations or both

• Peripheral and lower lung zone predominance
H1N1
• Bilateral & hyperinflation (early)
• GGO +/- consolidation
• Bilateral, central, & symmetric distribution
EVALI
• Bilateral multifocal GGO consolidation or both
• Lower lung zone predominance
CT
• Bilateral & multifocal GGO, +/Consolidations or both
• Halo sign
• Peripheral and subpleural
• Bronchovascular thickening
• GGO +/- consolidation
• Central lung predominance
Helpful Imaging Features

• Halo sign (Early)
CMV
Adenovirus
• Bilateral & symmetric GGO +/consolidation
• Subpleural sparing
• Atoll sign
• Diffuse
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Nodules
• Multifocal
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Centrilobular Nodules
Varicella zoster virus
• Multifocal
• Surrounding halo GGO
• 1–10 mm (in late phase, calcification)
Influenza
• Hyperinflation
• Bronchovascular thickening (early)
• GGO +/- consolidation (later)
• Central
• Subpleural spacing
• Atoll sign

RSV
• Airway, multifocal
• Consolidations
• GGO
• Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
• Airway, multifocal
• Centrilobular Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
31 Titolo Presentazione
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Lung Disorders CXR CT Helpful Imaging Features
COVID 19
• Patchy bilateral GGO, Consolidations or both
• Bilateral & multifocal GGO, +/Consolidations or both
• Halo sign (Early)
COVID 19
H1N1
EVALI
CMV
Adenovirus
Varicella zoster virus
Influenza
RSV
• Peripheral and lower lung zone predominance
• Bilateral & hyperinflation (early)
• GGO +/- consolidation
• Patchy bilateral GGO, Consolidations or both
• Bilateral, central, & symmetric distribution
• Bilateral multifocal GGO consolidation or both
• Lower lung zone predominance
• Peripheral and lower lung zone predominance
• Halo sign
• Peripheral and subpleural
• Bronchovascular thickening
• GGO +/- consolidation
• Central lung predominance
• Bilateral & multifocal GGO, +/Consolidations or both
• Halo sign
• Bilateral & symmetric GGO +/consolidation
• Halo sign (Early)
• Hyperinflation
• Bronchovascular thickening (early)
• GGO +/- consolidation (later)
• Central
• Subpleural spacing
• Atoll sign
• Subpleural sparing
• Atoll sign

• Peripheral and subpleural
• Diffuse
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Nodules
• Multifocal
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Centrilobular Nodules
• Multifocal
• Surrounding halo GGO
• 1–10 mm (in late phase, calcification)
• Airway, multifocal
• Consolidations
• GGO
• Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
• Airway, multifocal
• Centrilobular Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
32 Titolo Presentazione Lung
CXR CT Helpful Imaging Features
Disorders


33 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



34
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



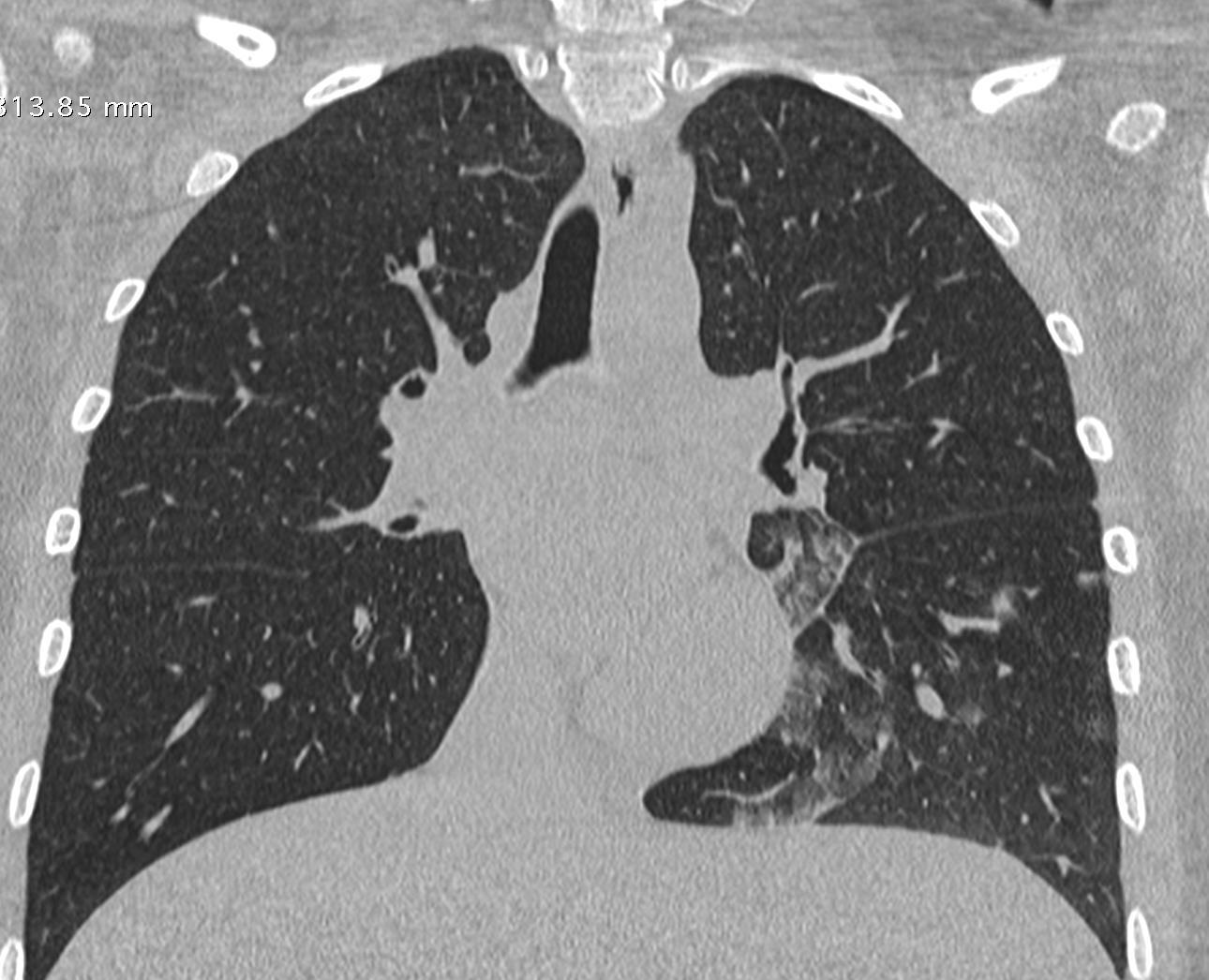
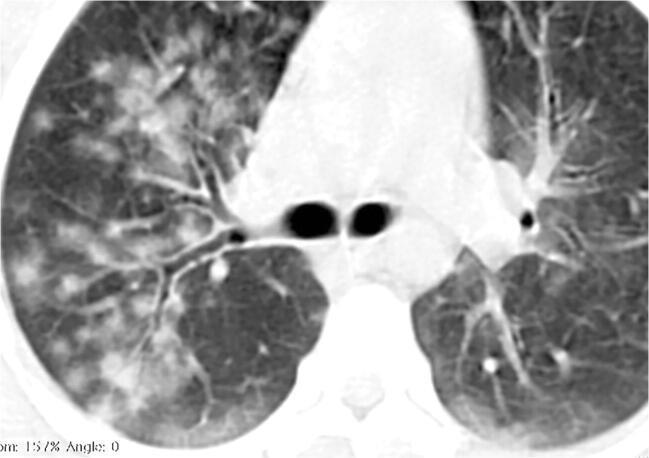
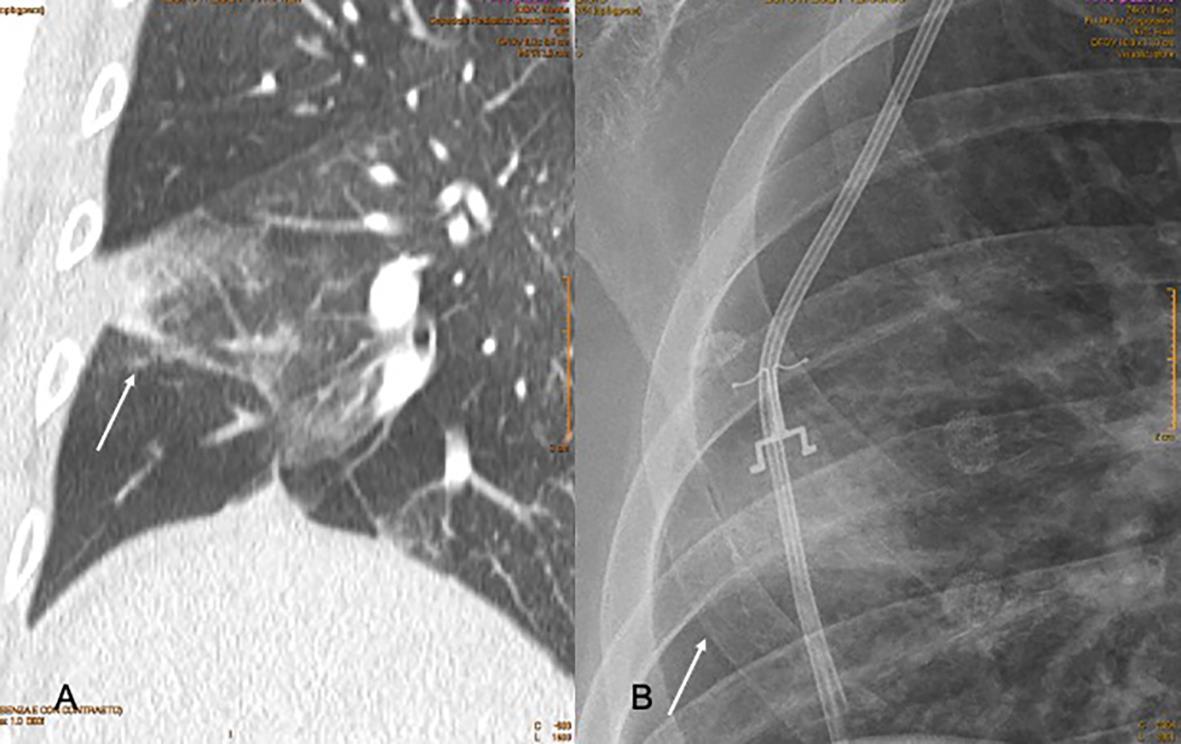
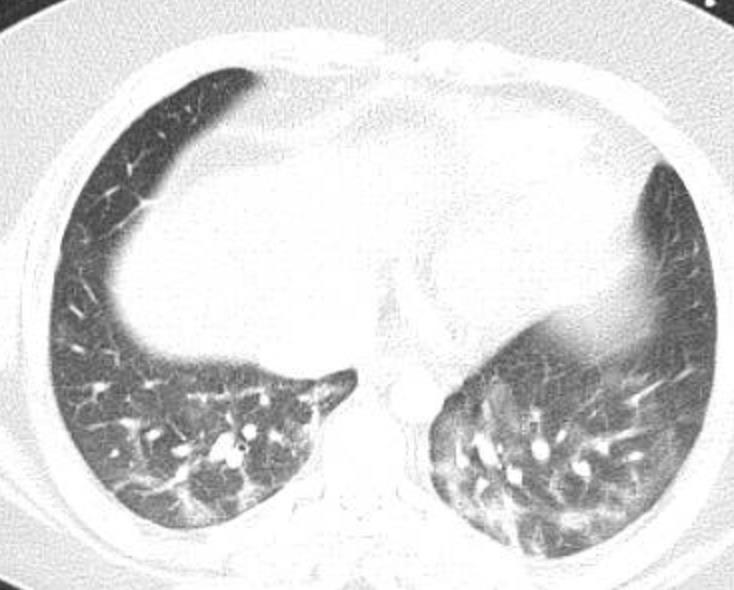
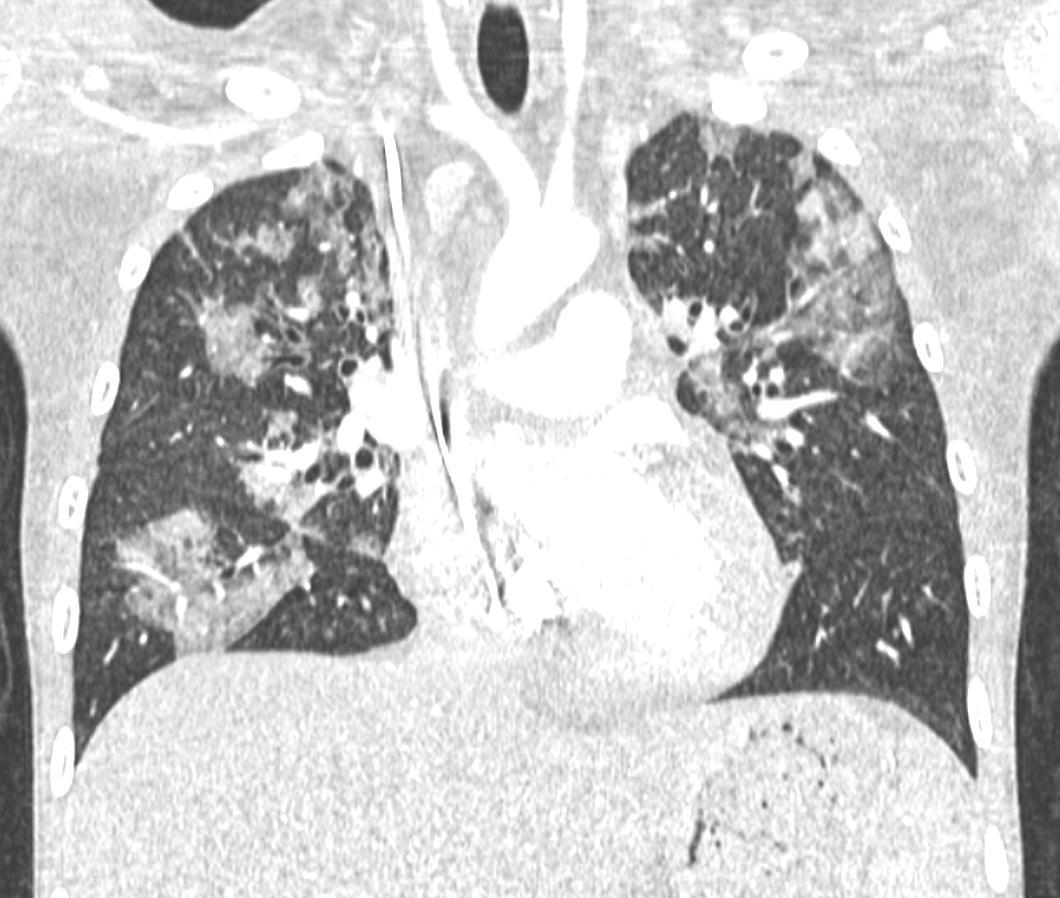
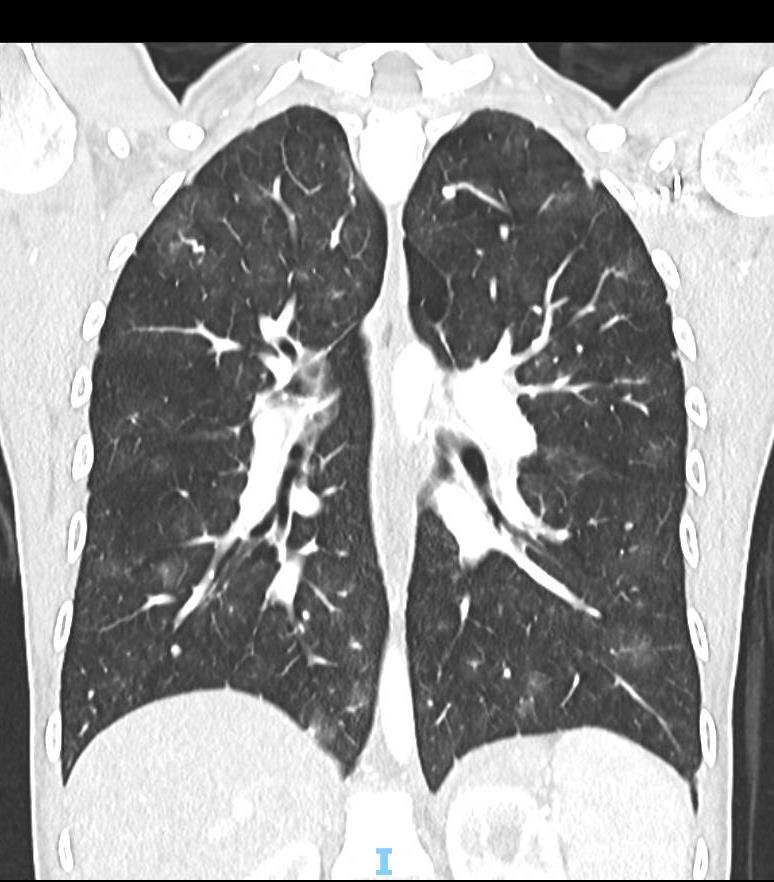
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children COVID 19 Late
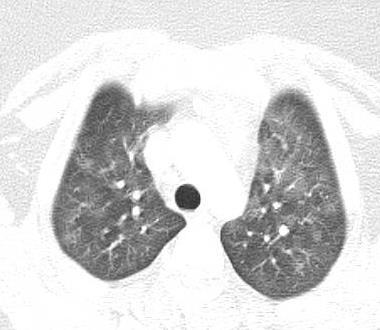
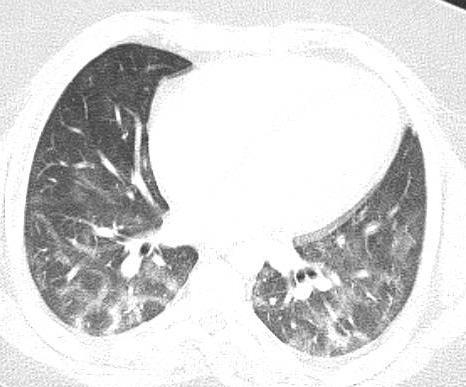
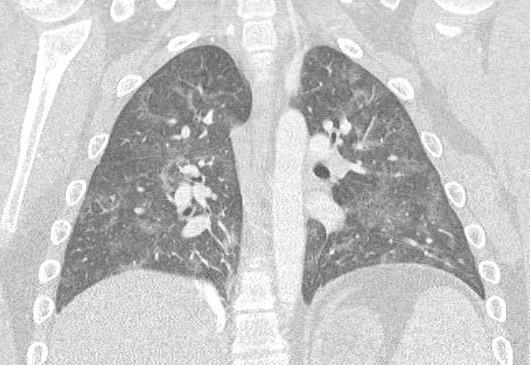


Late


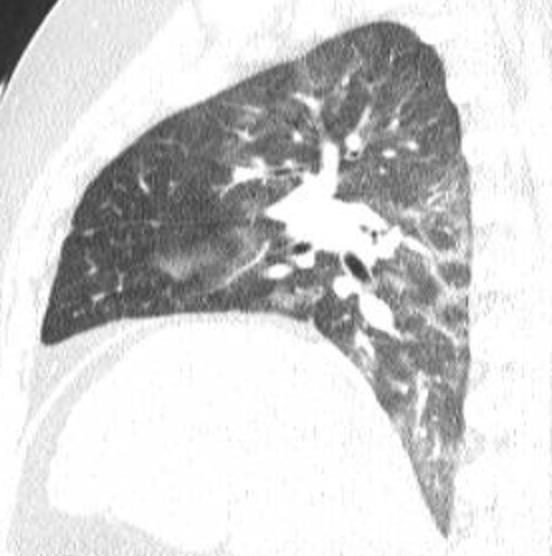
37
Late
Lung Disorders CXR
COVID 19
• Patchy bilateral GGO, Consolidations or both

• Peripheral and lower lung zone predominance
EVALI
CT
• Bilateral & multifocal GGO, +/Consolidations or both
• Halo sign
• Peripheral and subpleural
• Bilateral multifocal GGO consolidation or both
• Lower lung zone predominance
H1N1
• Bilateral & symmetric GGO +/- consolidation
• Subpleural sparing
• Atoll sign
Helpful Imaging Features

• Halo sign (Early)
CMV
• Bilateral & hyperinflation (early)
• GGO +/consolidation
• Bilateral, central, & symmetric distribution
• Bronchovascular thickening
• GGO +/- consolidation
• Central lung predominance
• Subpleural spacing
• Atoll sign

• Diffuse
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Nodules
• Hyperinflation
• Bronchovascular thickening (early)
• GGO +/consolidation (later)
• Central
Titolo Presentazione
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
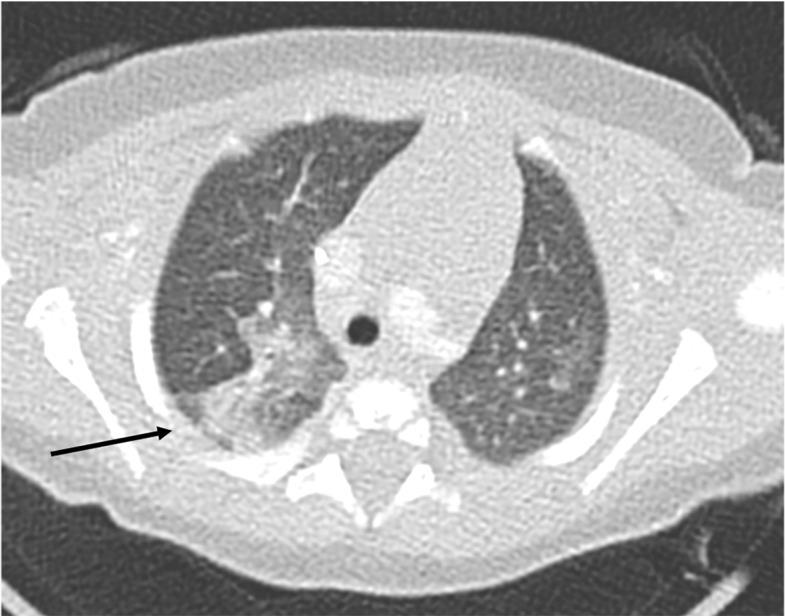
EVALI

E-cigarette, or Vaping, product use–Associated Lung Injury


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children




BOOP
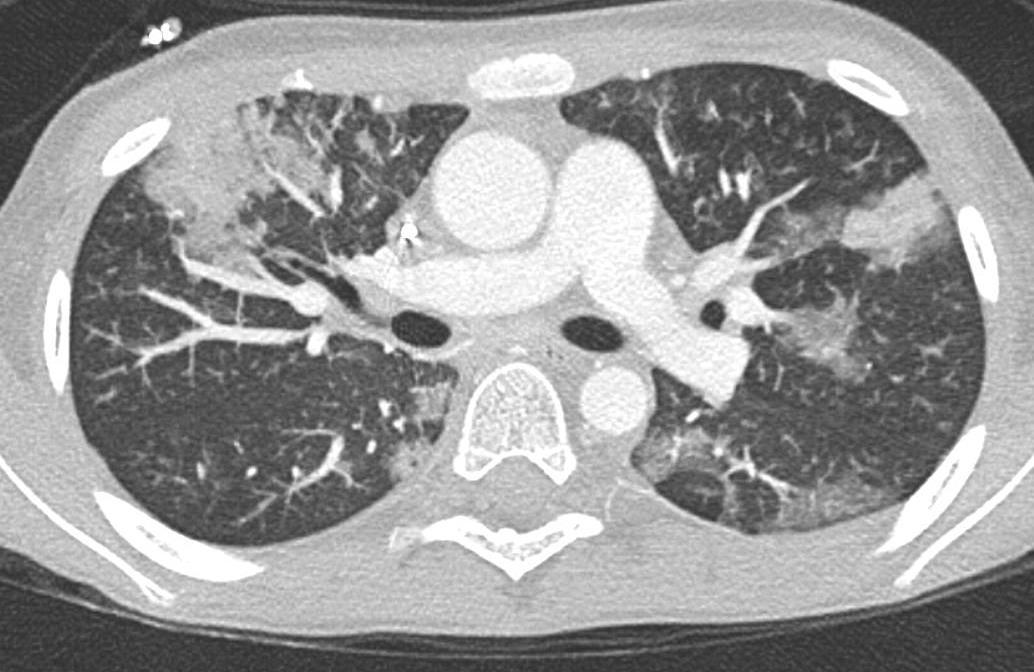


H1N1
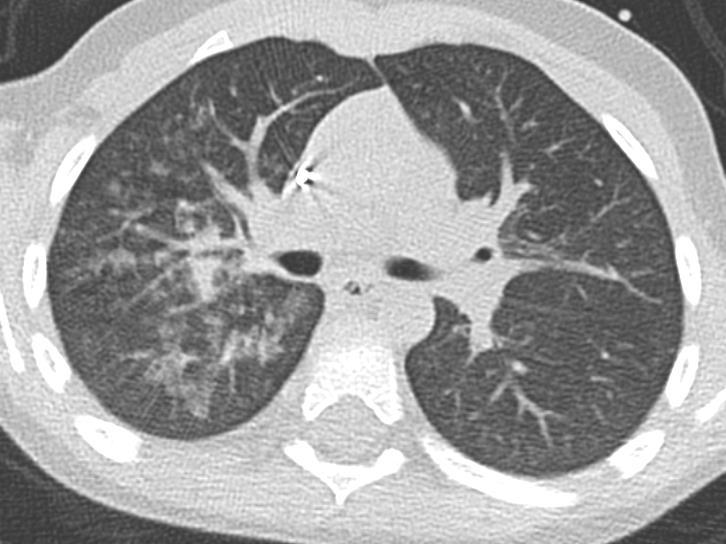
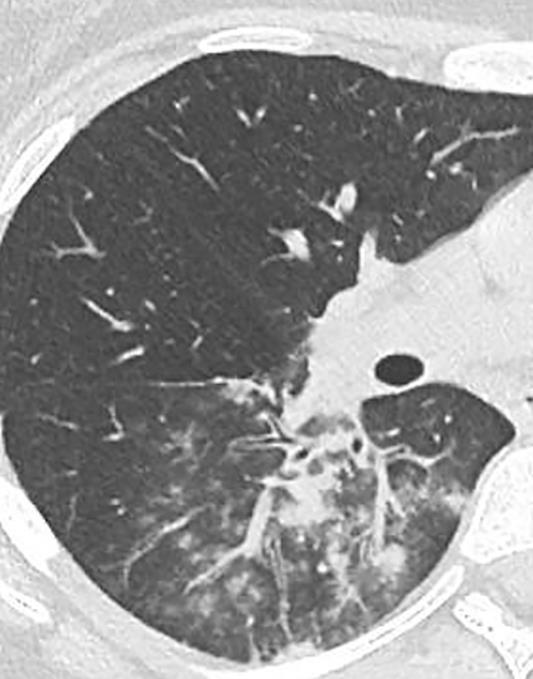
CMV Covid 19 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
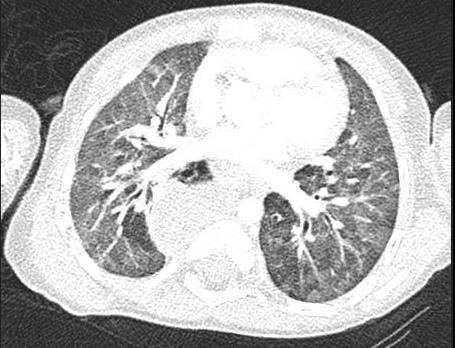


PCP
Rhinovirus
Lung
COVID 19
• Patchy bilateral GGO, Consolidations or both

• Peripheral and lower lung zone predominance
Adenovirus
Helpful Imaging Features

• Bilateral & multifocal GGO, +/Consolidations or both
• Halo sign
• Peripheral and subpleural
• Multifocal
• Consolidation
• GGO
• Centrilobular Nodules
Varicella
zoster virus
• Multifocal
• Surrounding halo GGO
• 1–10 mm (in late phase, calcification)

Influenza
• Halo sign (Early)
RSV
• Airway, multifocal
• Consolidations
• GGO
• Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
• Airway, multifocal
• Centrilobular Nodules
• Bronchial Wall Thickening
Titolo Presentazione
Disorders CXR CT
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
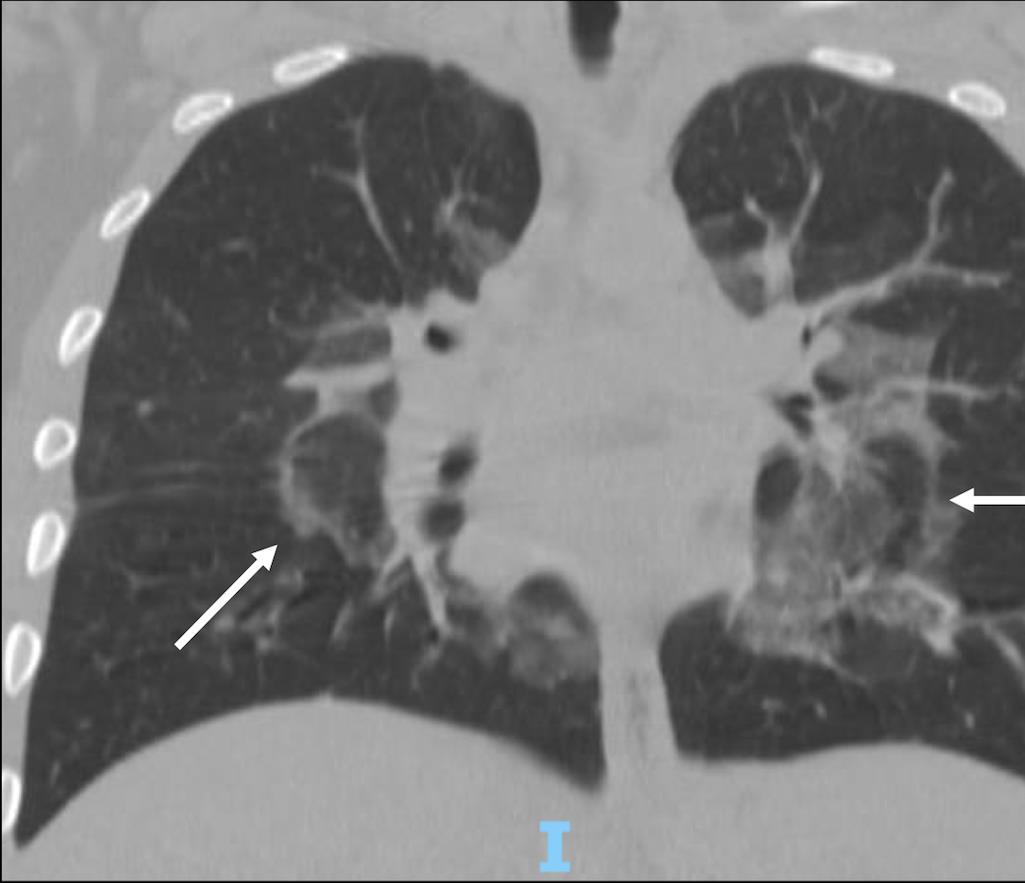
ADENOVIRUS
Bronchiolar and alveolar damage
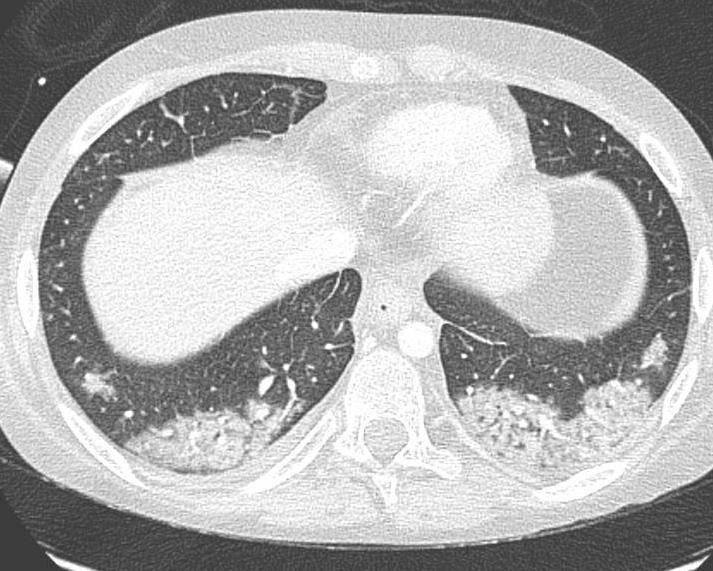

Chickenpox
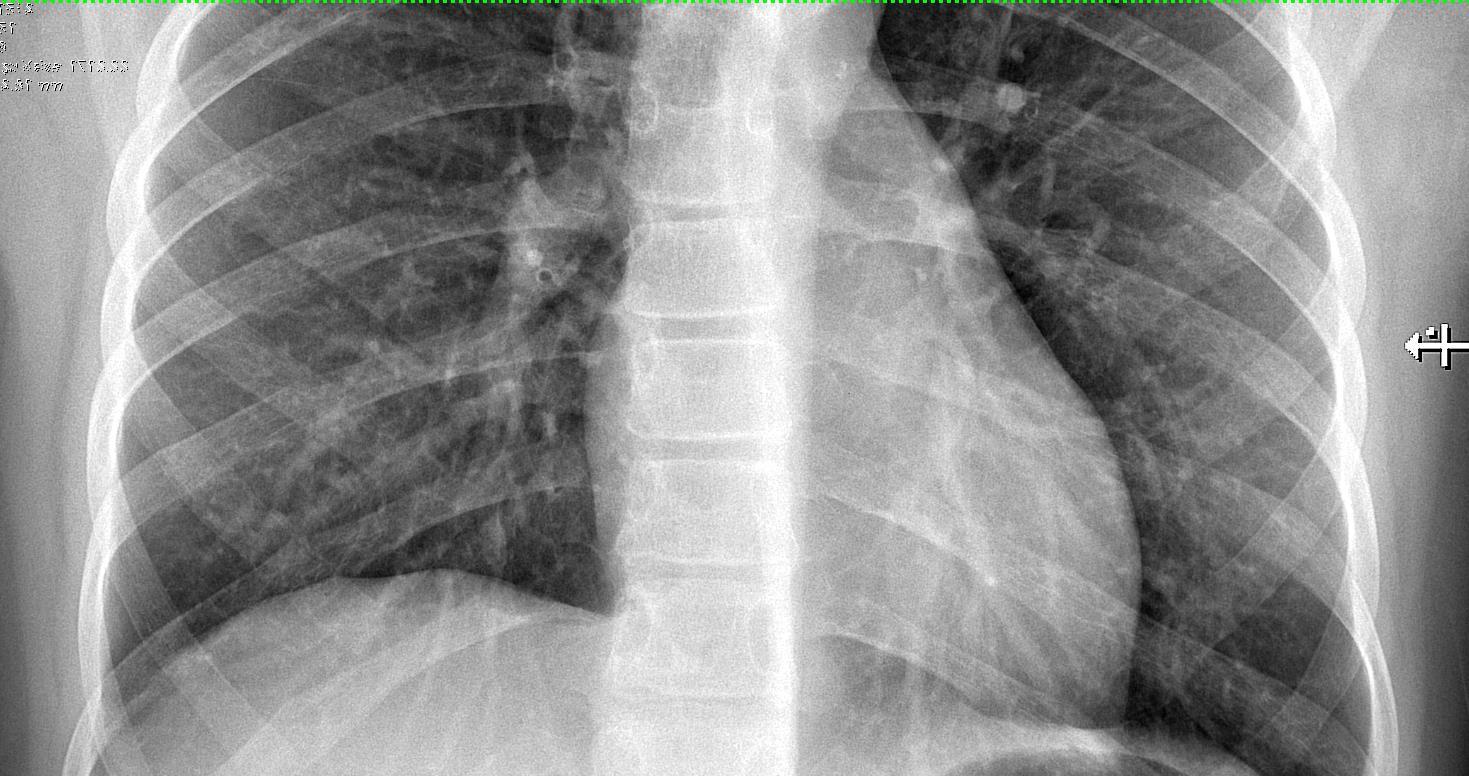
47
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
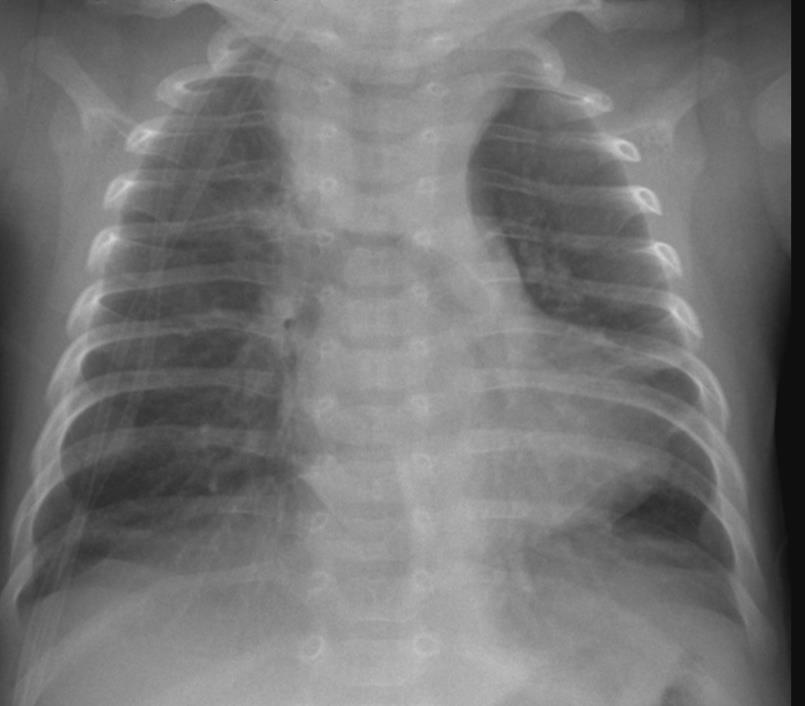


6 RSV Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
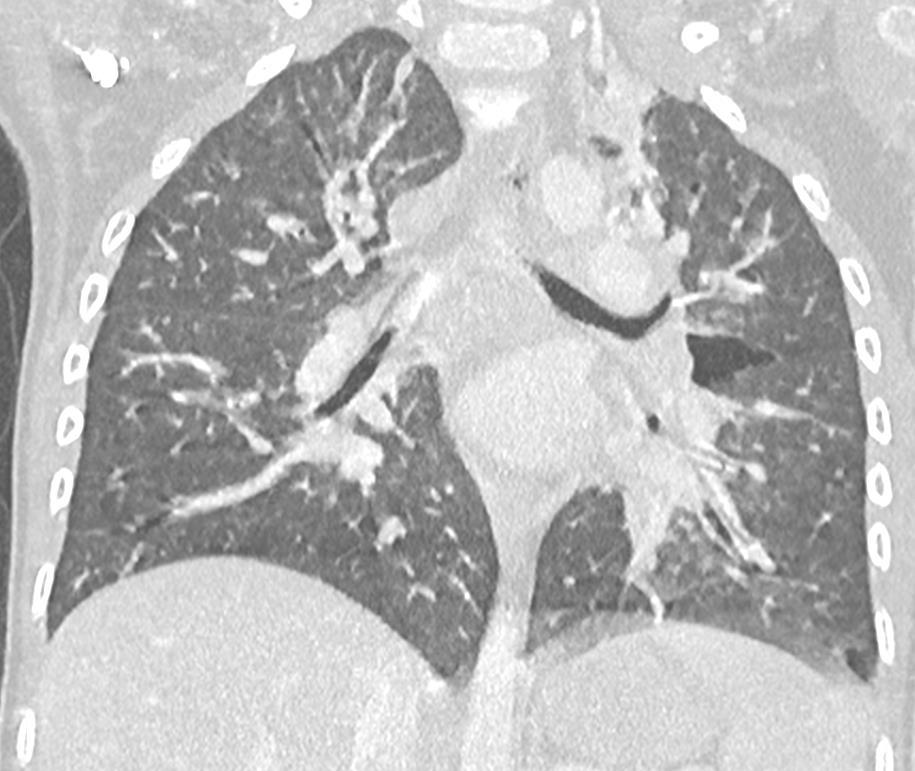



49 Bocavirus
Pediatric COVID-19: MIS-C (Multisystem inflammatory syndrome –Covid)

• Serious condition where different body parts can be inflamed

• Characterized by severe, febrile inflammatory illness
• Elevated inflammatory markers
• "Cytokine storm

• 2 - 4 weeks after infection or exposure
• 80 - 100% + SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
• School-age children
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in the Context of Global SARS
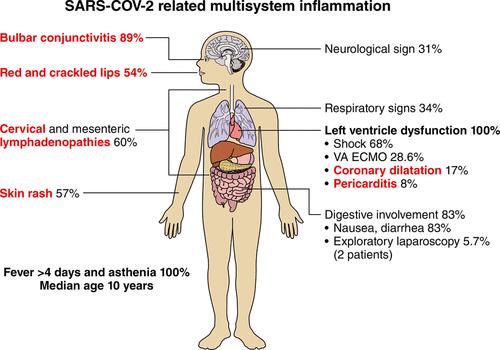
CoV-2 Pandemic, Volume: 142, Issue: 5, Pages: 429-436, DOI: (10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048360)


© 2020 American Heart Association, Inc.


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
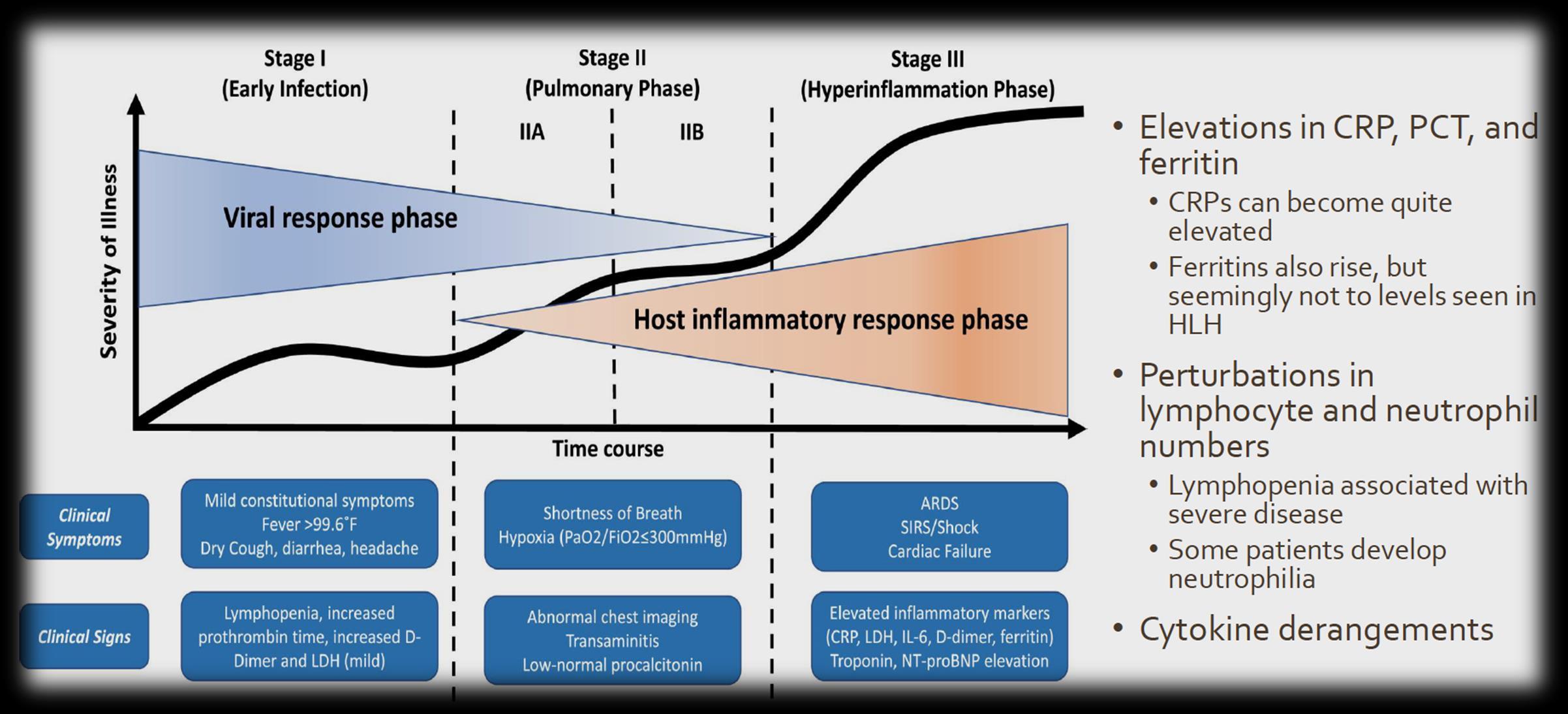
COVID-19: phases of illness Siddiqi HK et al Journal of Heart and Lung Trasplantation DOI:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
CF ARDS Emboli


MIS-C Main signs
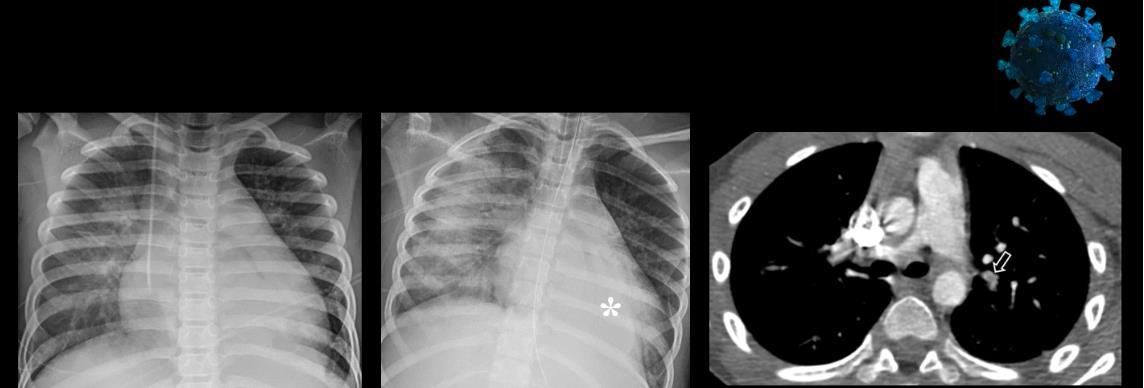
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Pediatric COVID-19: MIS-C

Thoracic abnormalities
Cardiovascular abnormalities
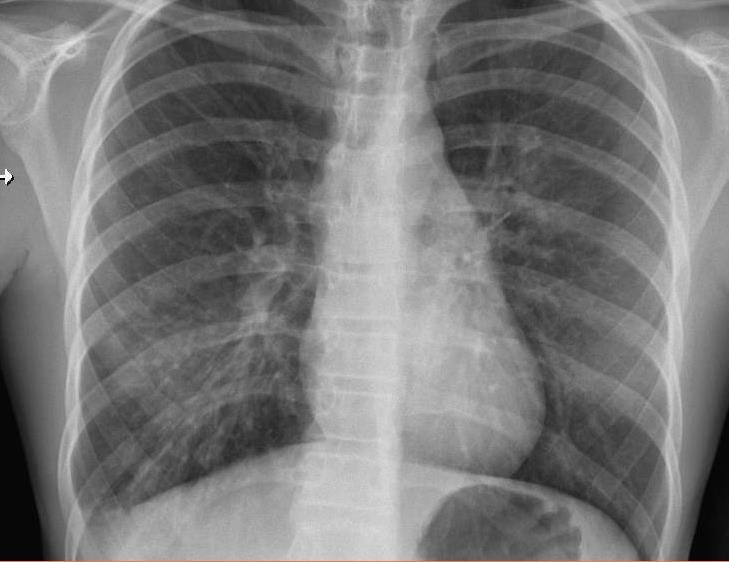
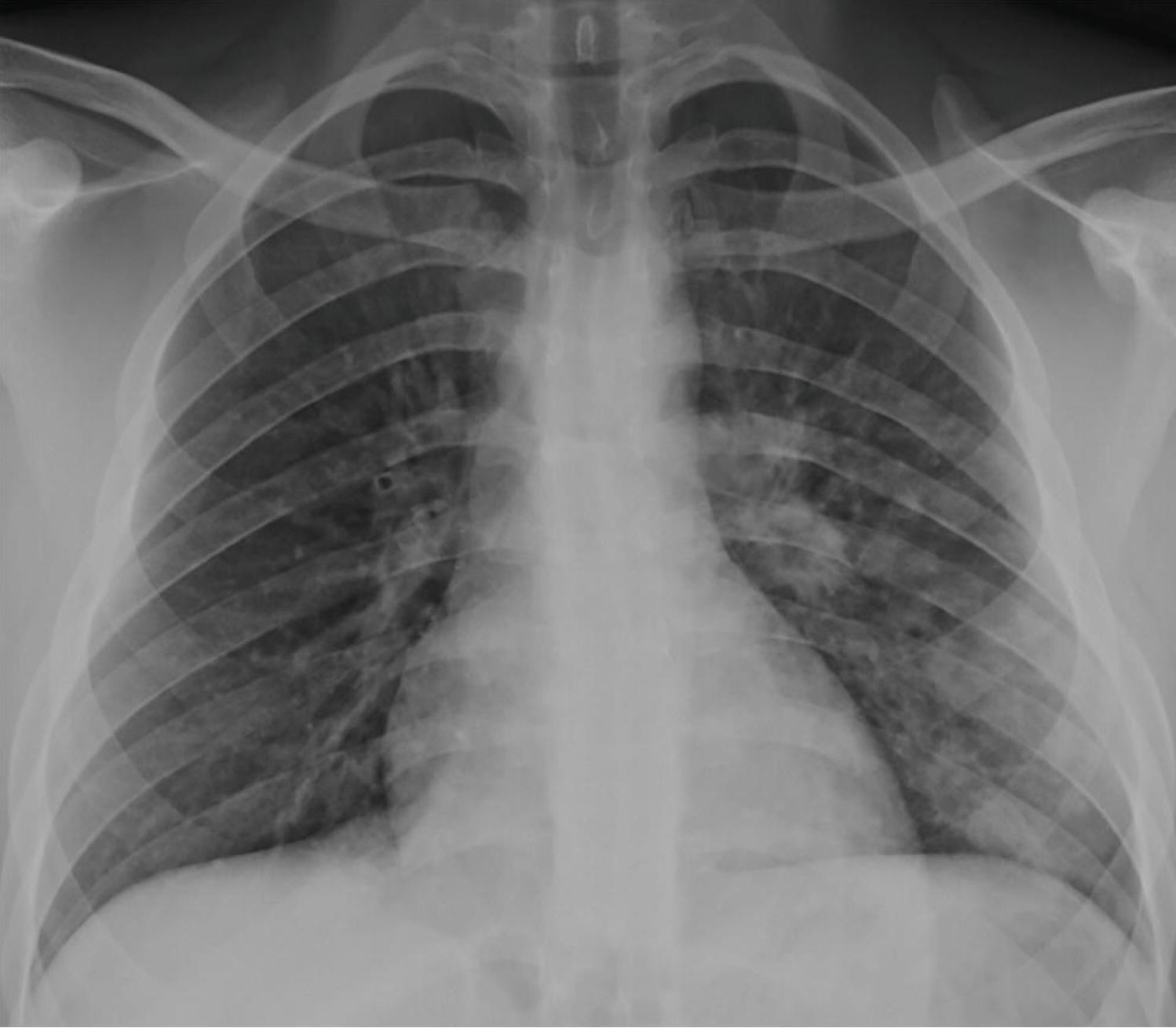
Cardiomegaly
CHF or cardiogenic edema
Pulmonary parenchymal abnormalities
Lower lobe atelectasis
Bilateral opacities( ARDS)
Consolidation
Pleural abnormalities
Small pleural effusion
Mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy
Abdominal abnormalities
Solid viscera abnormalities
Hepatomegaly


Echogenic kidneys
Splenomegaly
Hollow viscera abnormalities
Gallbladder wall thickening
Bowel wall thickening
Bowel dilation
Gastric distention
Urinary bladder thickening
Peritoneal abnormalities
Small ascites
Mesenteric abnormalities
Mesenteric lymphadenopathy
54 Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Intramural lymphocytic infiltrate
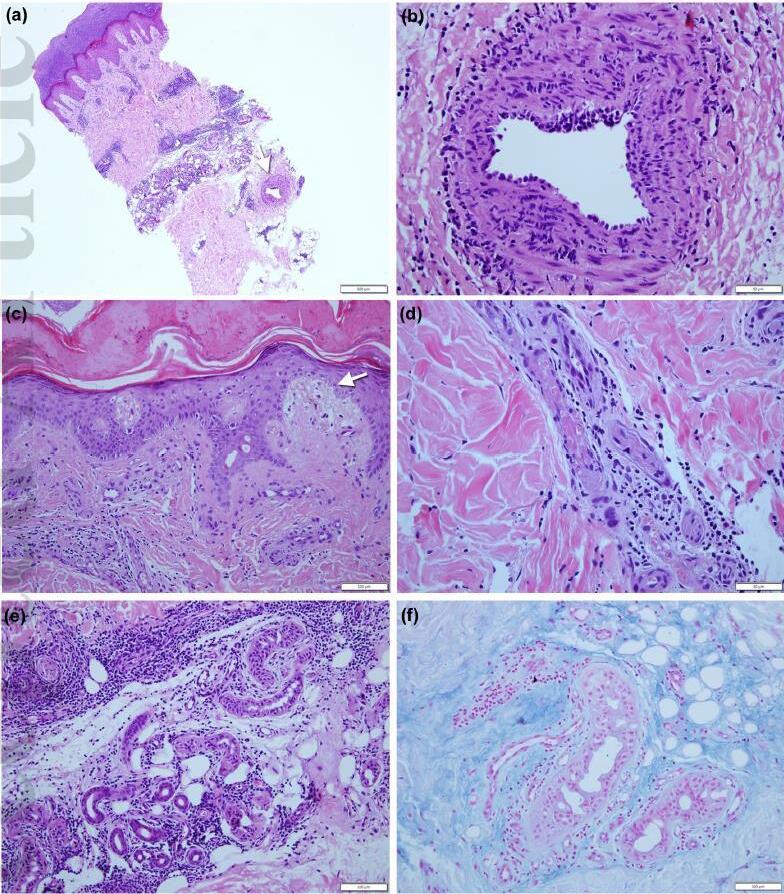
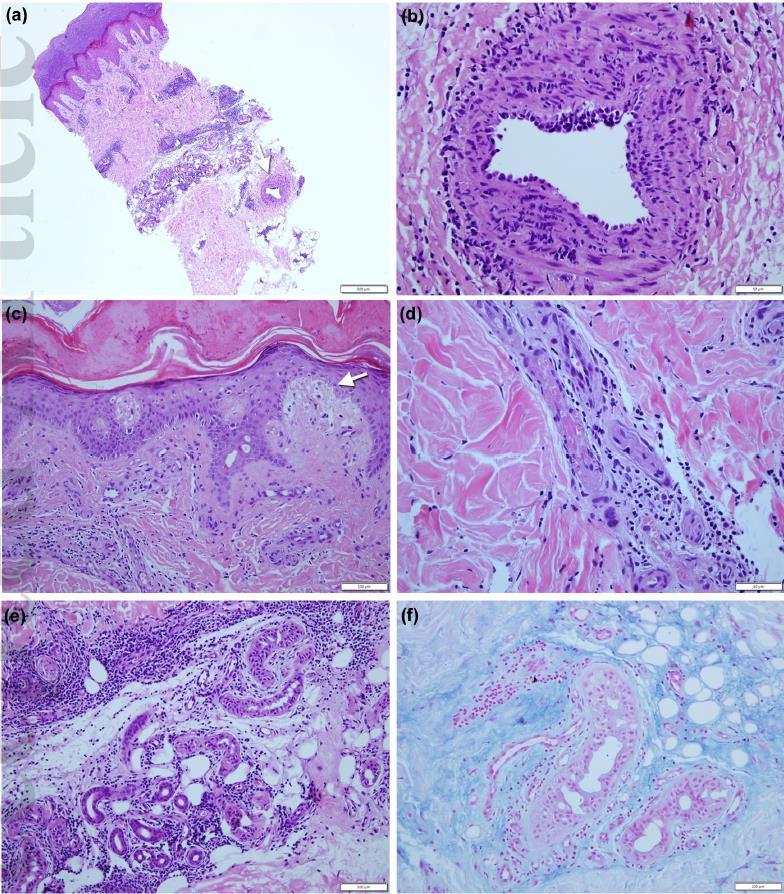
Chilblain-like lesions
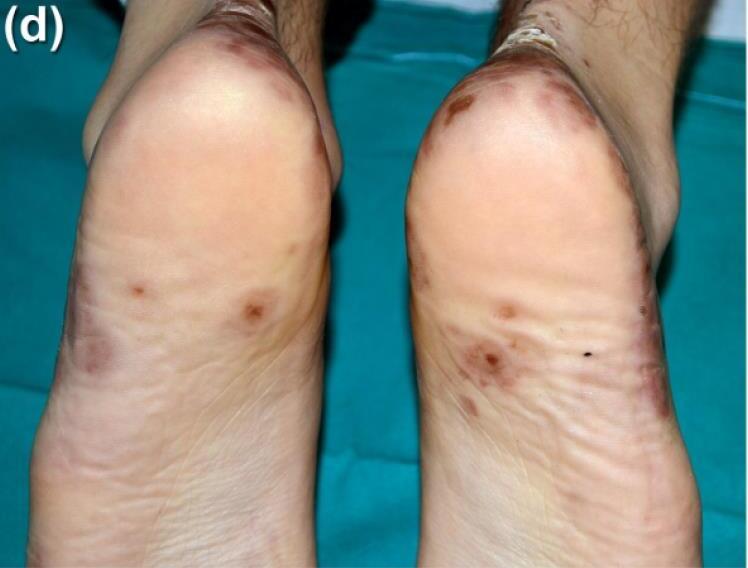
19 cases


El Hachem JDV 2020
Perineural dermal inflammatory infiltrate
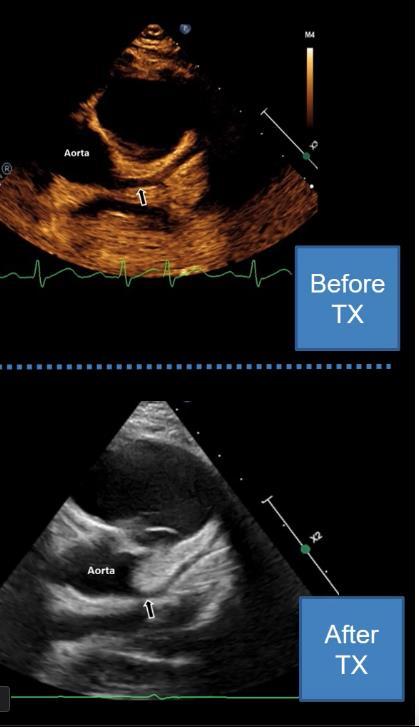
Thrombus


57
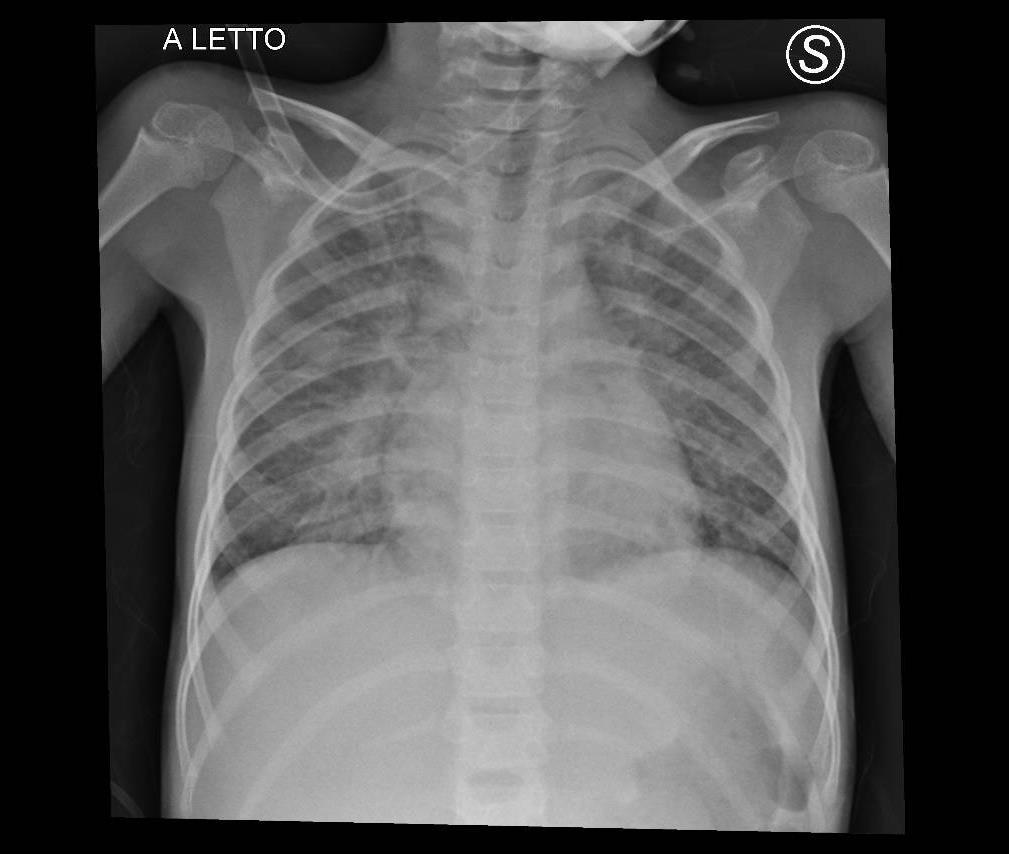
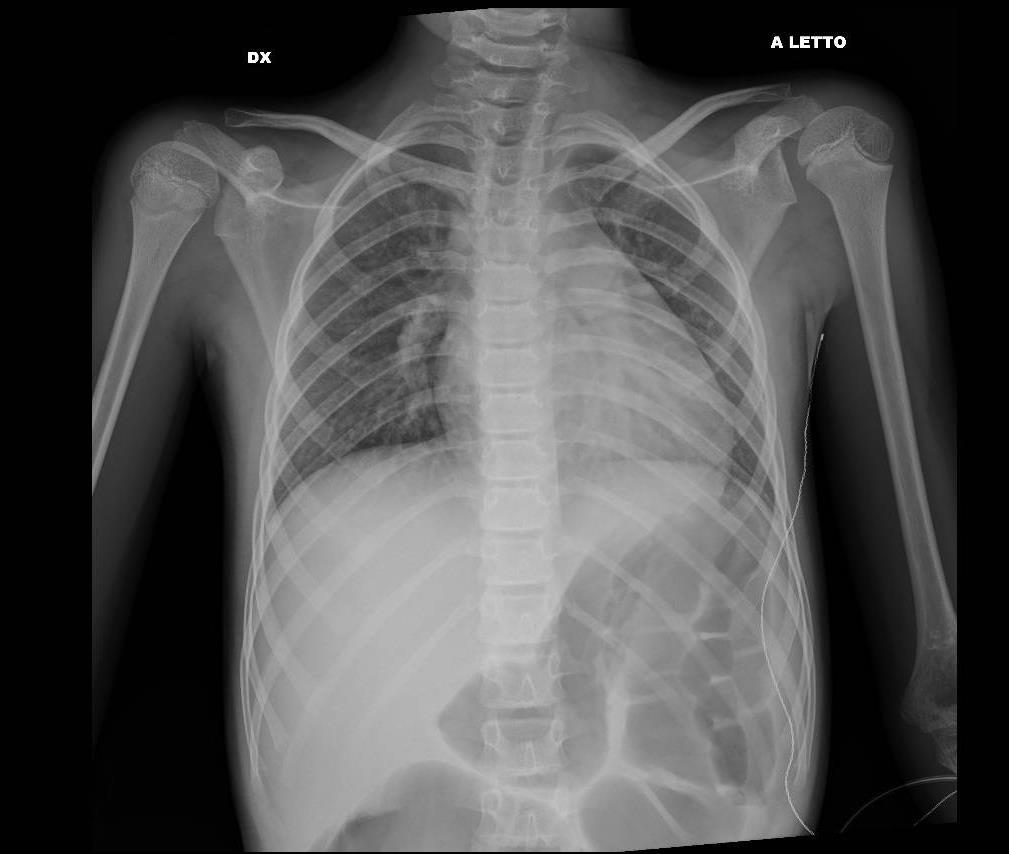
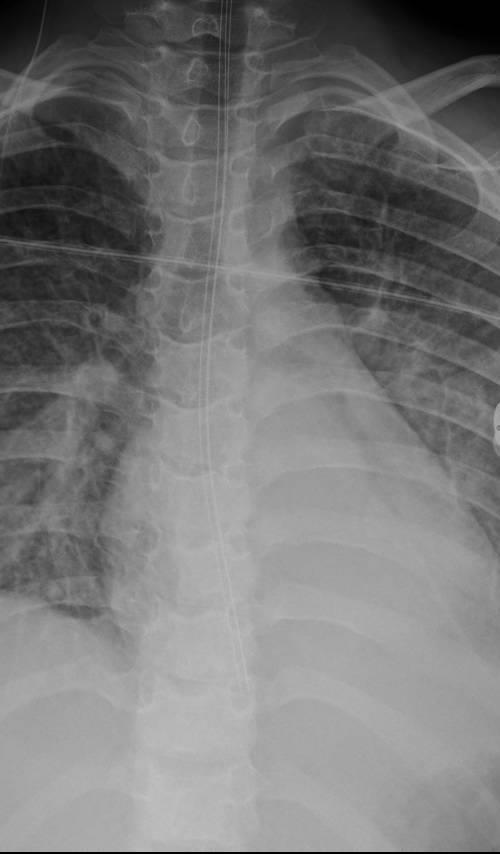
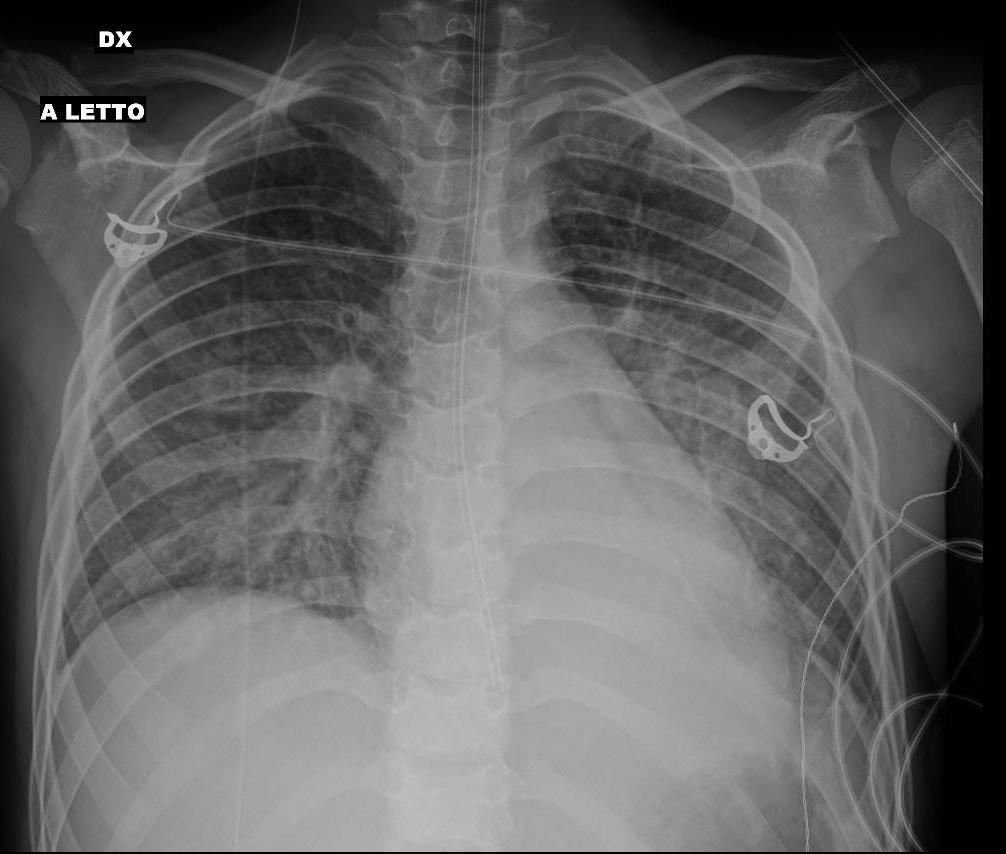
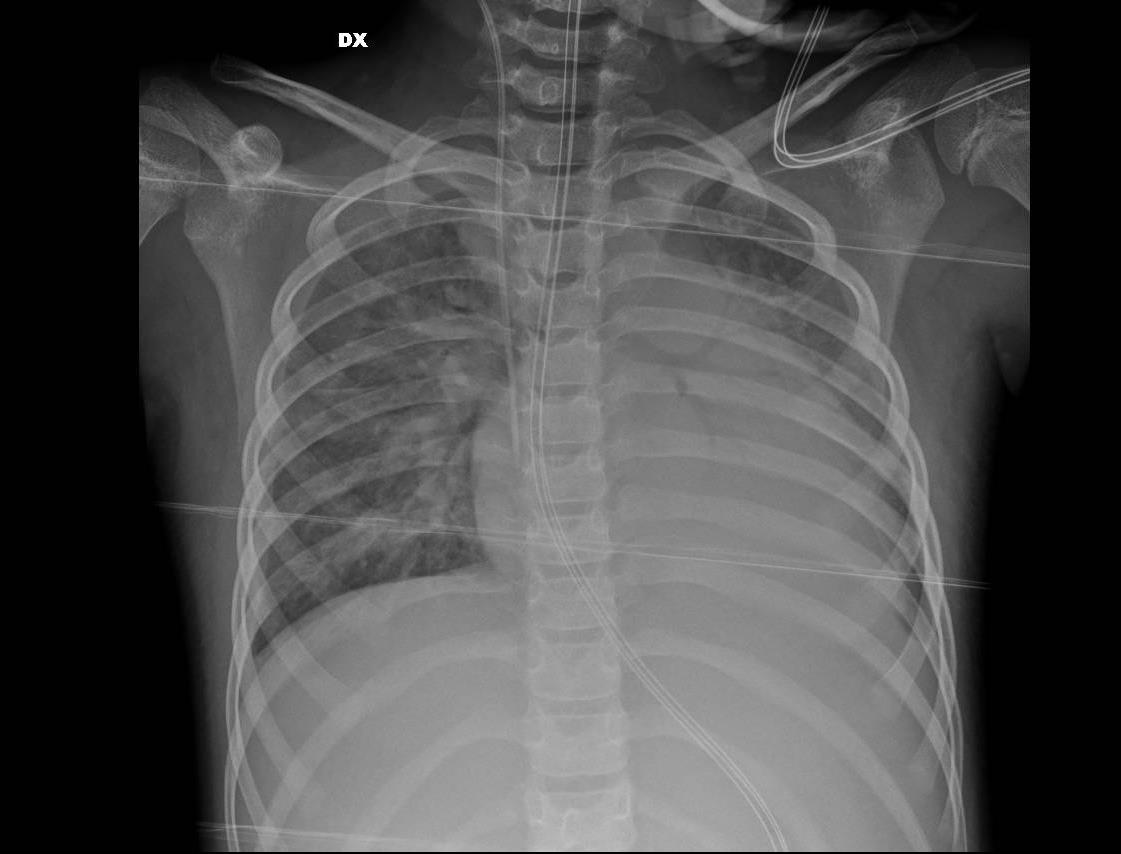
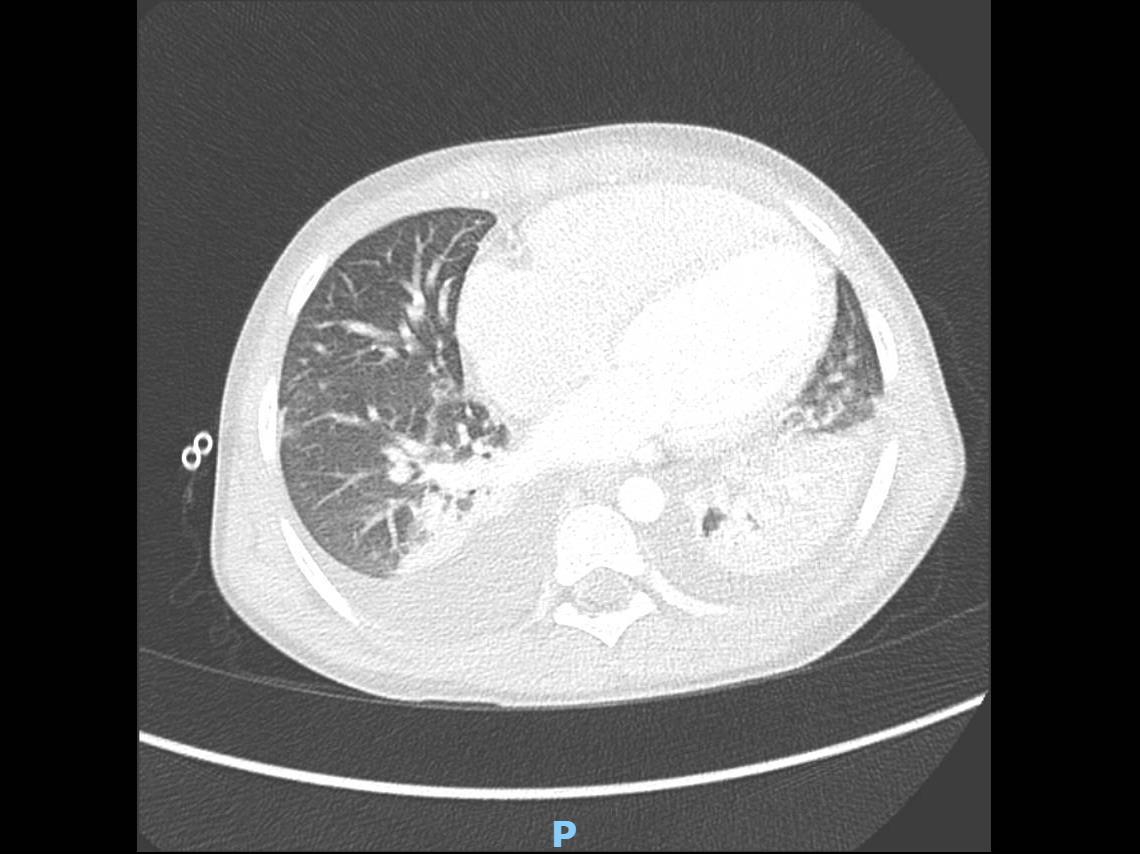
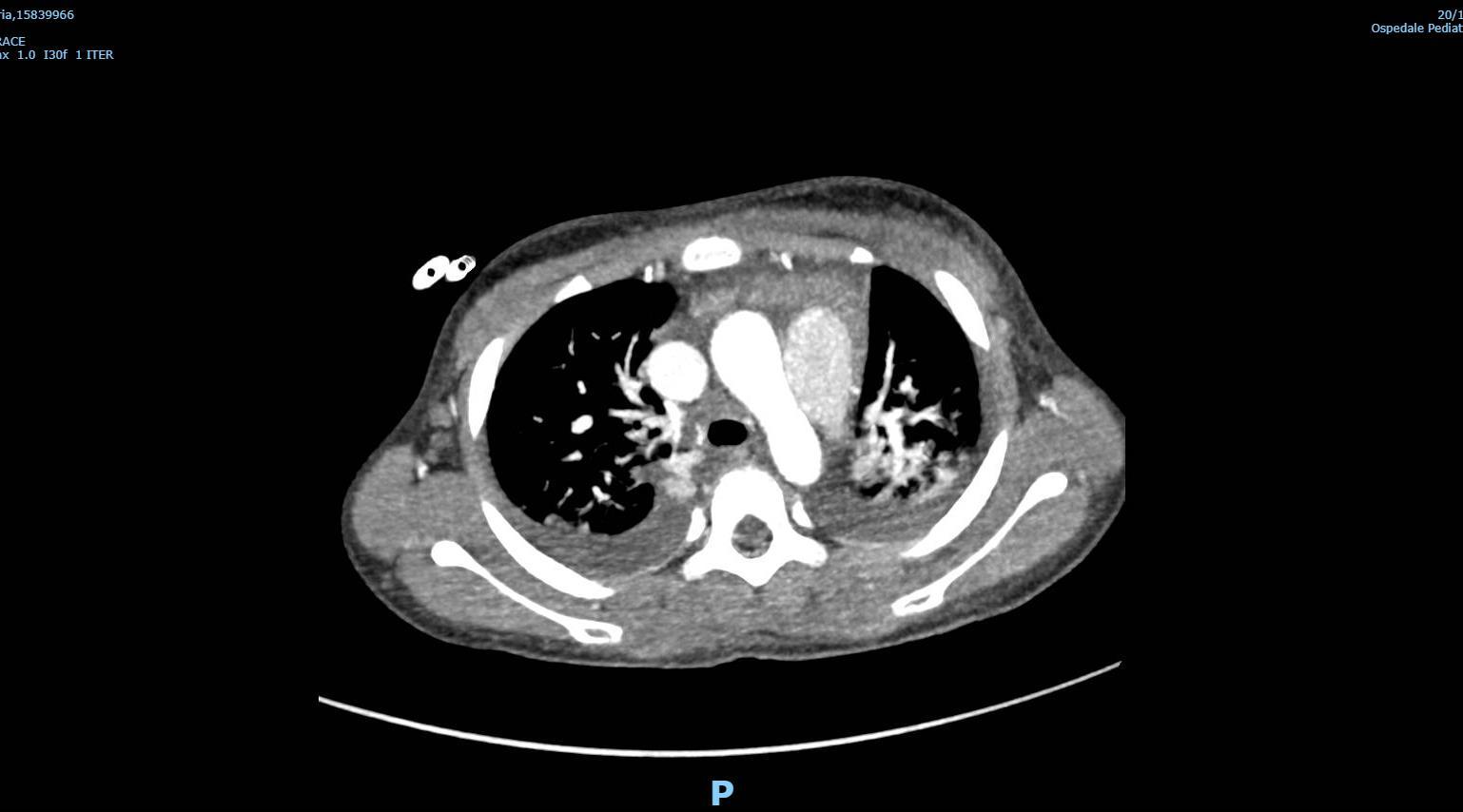
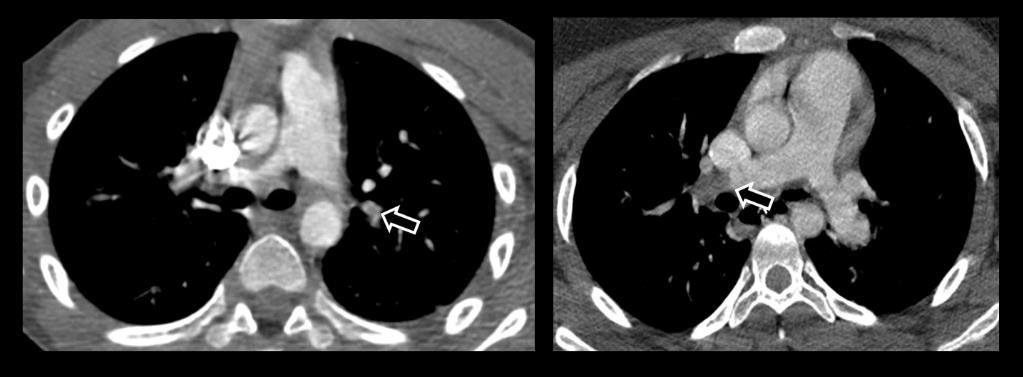
MIS-C Embolism


Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children

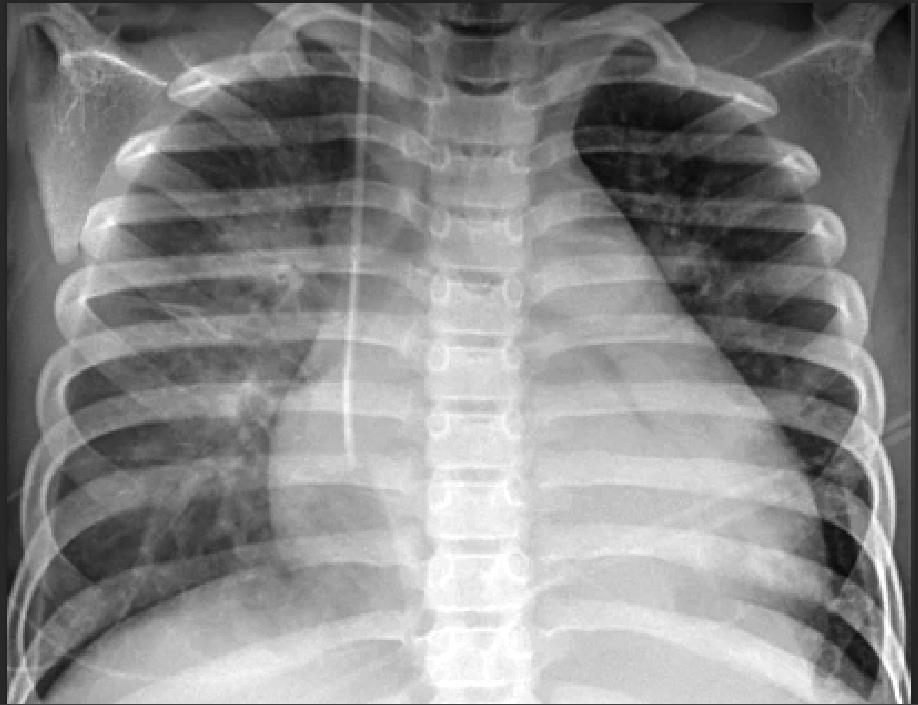
MIS-C: Heart failure






60 Embolus Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
MIS-C
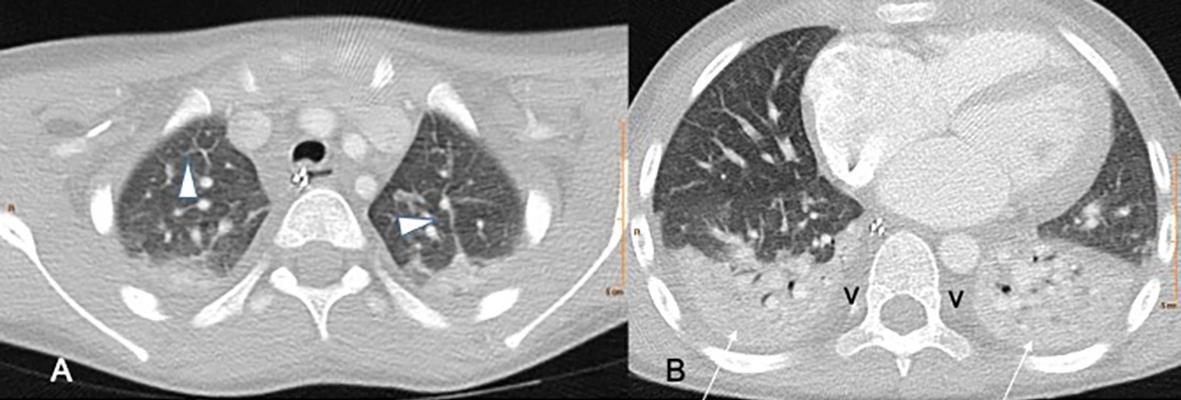


61
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
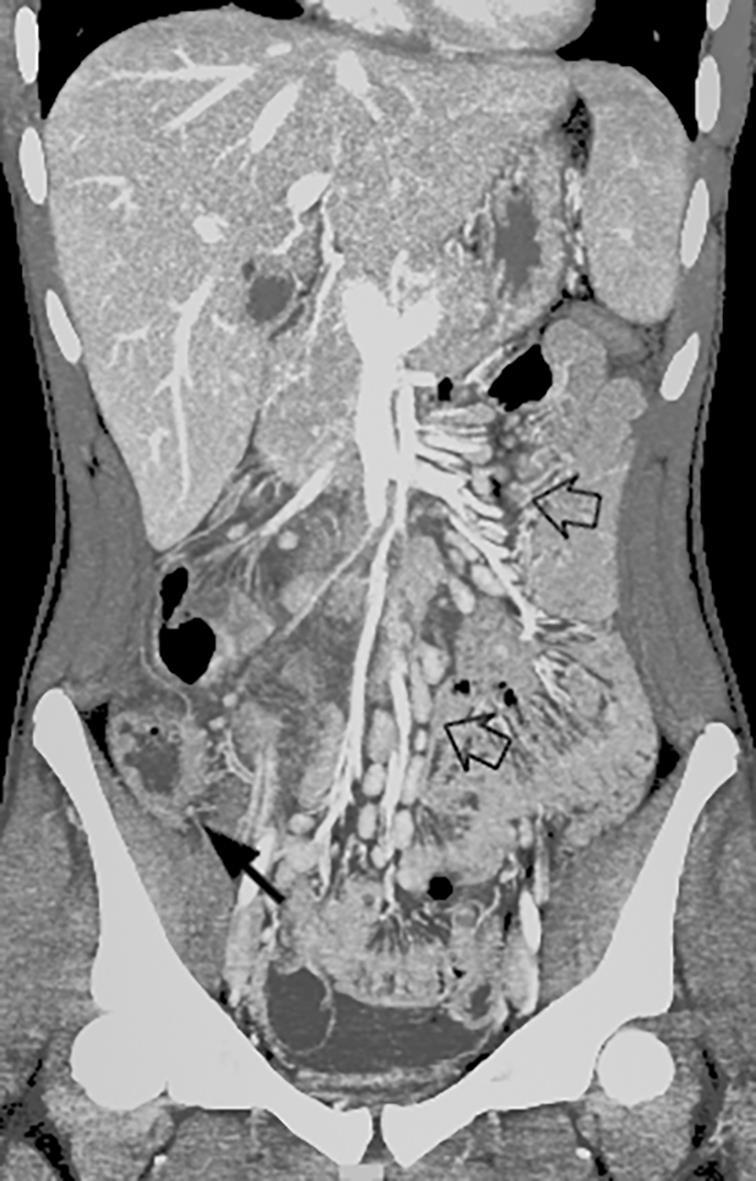
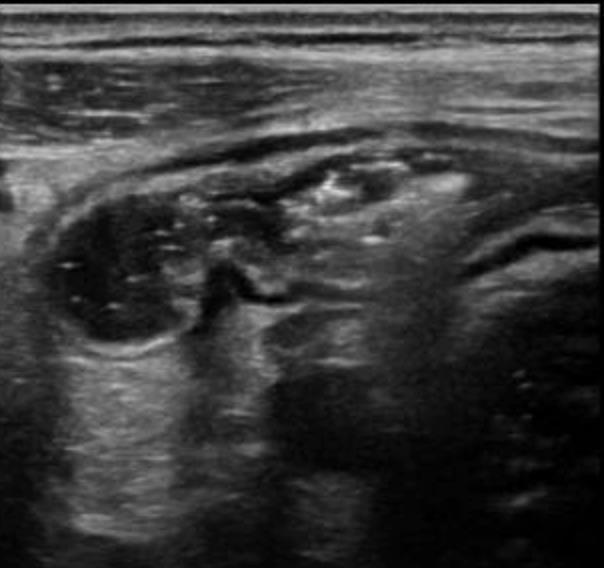
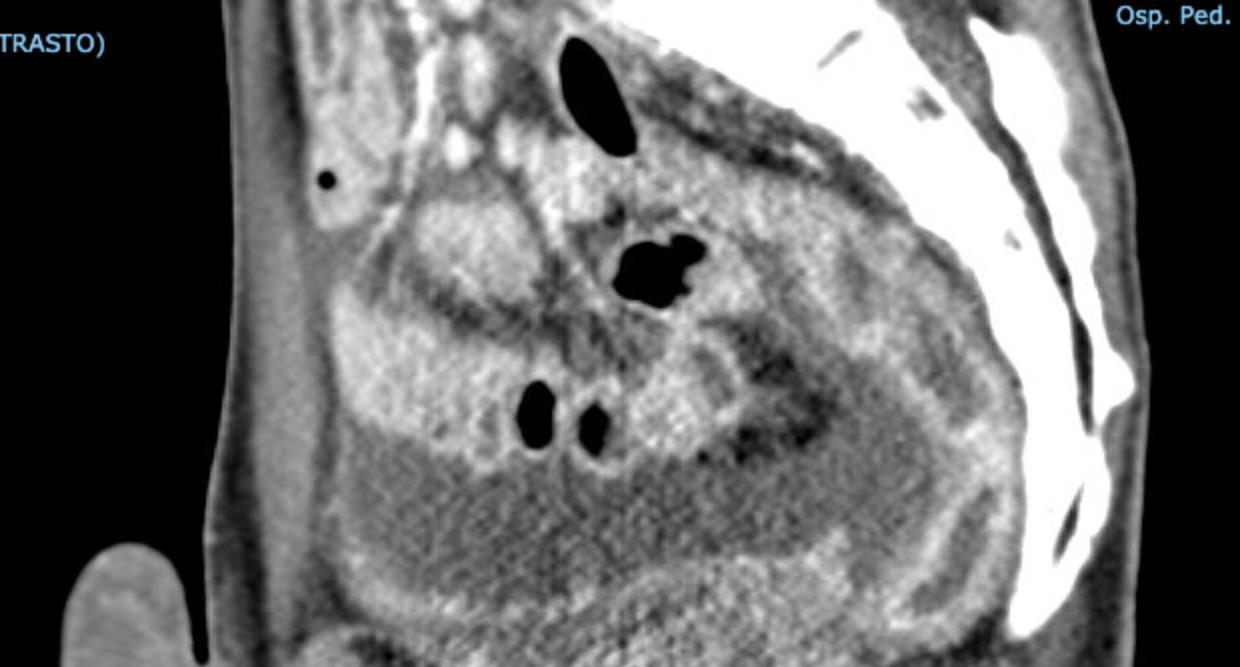
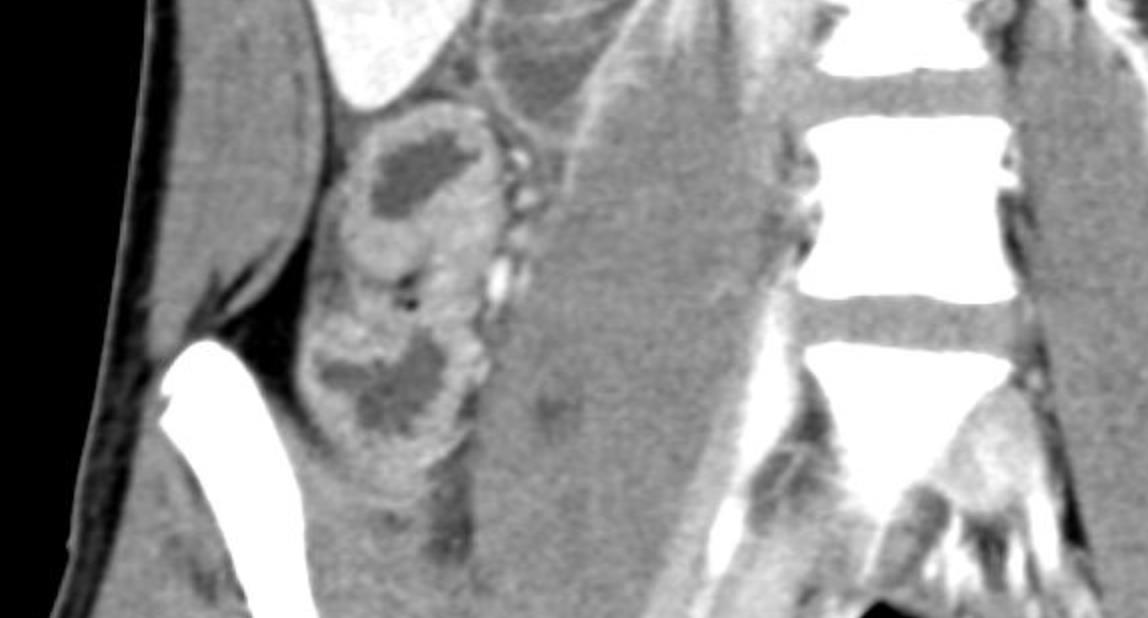
• Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms (abdominal pain, diarrhoea and vomiting) are prevalent in MIS-C
• Abdominal pain in 62%
• Up to 90% any GI symptom


• Anumber of studies have described abdominal imaging findings including ascites, bowel wall thickening and mesenteric lymphadenopathy

62
MIS-C
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children

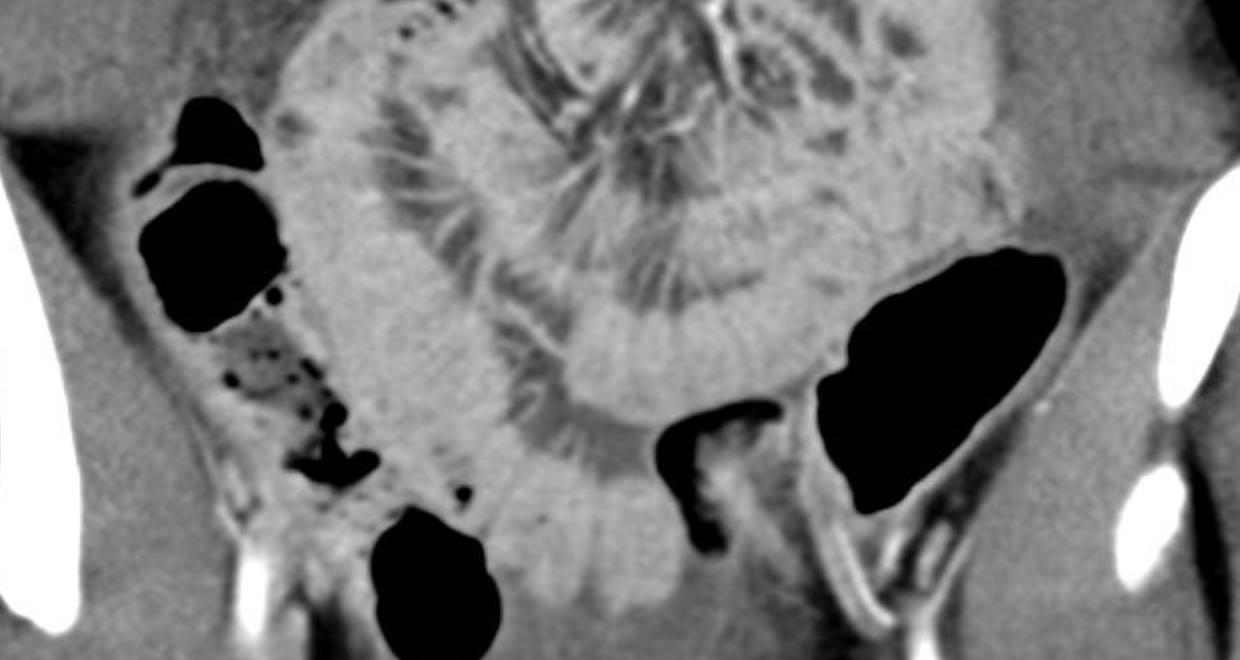
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Pediatric COVID-19


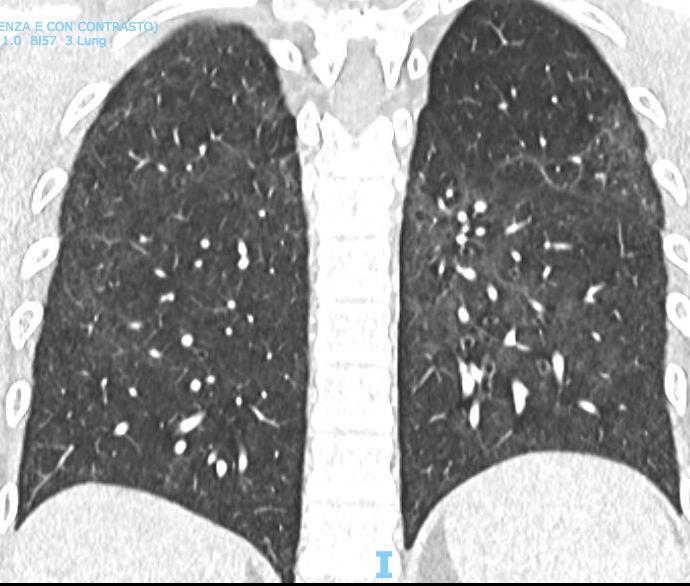
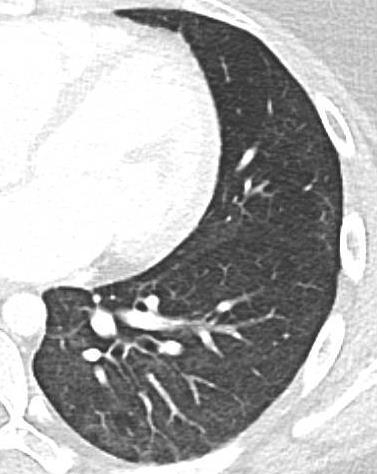
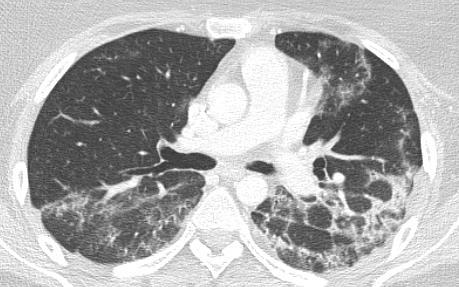
OUTCOME
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children
Relapsing Polychondritis


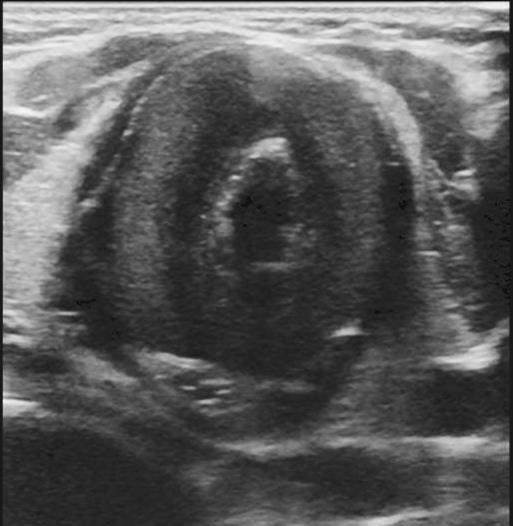
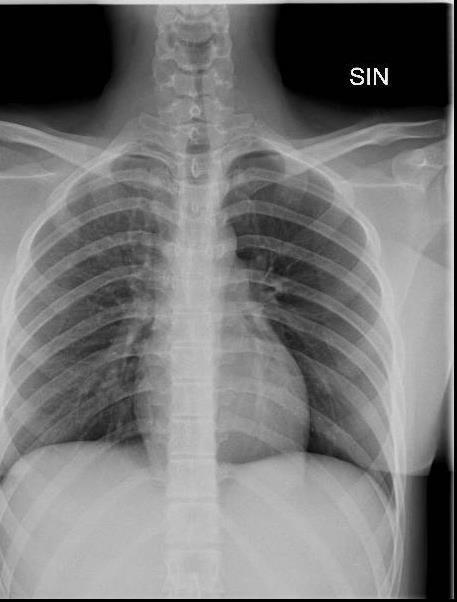
Imaging of Covid 19 infection in children



 Dr. Paolo Tomà
Head of Imaging Department
Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospitals
Dr. Paolo Tomà
Head of Imaging Department
Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospitals



























































































































