


Carbon steel plate is fabricated from an alloy composed of carbon and iron. It has high tensile strength, which makes it protected against damages and capable to handle high range of pressure without breaking or fracturing. It has three categories of carbon steel, which falls into three groups such as low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel and ultrahigh carbon steel.
This below given weight chart of carbon steel plate will provide the buyer a crucial information which will be helpful for taking decision for purchasing it. It will provide you the estimated weight for your application








Black carbon steel plate refers to the steel plate which has not gone through the method of galvanization for protection against corrosive. It rather goes through a chemical process called blackening which results into the evolution of tough iron oxide or magnetic surface. This surface gives protection against corrosion and abrasion, although it gives less structural strength and this makes it less known compared to carbon steel in most of the application
Carbon Steel Plate Sizes
















Carbon steel plate grades are described according to its carbon element, which remarkably affect its features as a result its applications.
In accordance to its different carbon element, it is divided into four groups, where low carbon steel is applicable to make thin wall thickness element, medium carbon steel is applicable for making mechanical parts and springs and high carbon and ultra-high carbon is used for making heavy-duty tools




ASTM Standards
ASTM A283 Gr A, B, C Carbon structural common material
ASTM A537 heat treated cs plate in structural steel and fusion welded pressure vessels
ASTM A36 CS Plate common standard
ASTM A516 vessel steel, boilar plate
ASTM A573 structural steel plate
ASTM A737 pressure vessels steel plate, boiler plate
ASTM A572 highr mechanical strength than than A36
Killed carbon steel plate is totally deoxidized carbon steel, which is been completely deoxidized by including a factor before casting process. Thus, there is minimum gas area which presents while hardening. It has various grades to fit into appropriate engineering purpose
7.8 grams per cubic centimetre (g/cm³)
0.284 0.284 pounds per cubic inch (lb/in³)





Weight = Area X Density X Thickness
Area = Length X Width
Width * Length * Thickness * Density = Weight
EG:
48″ * 96″ * .1875″ * 0.284 lb/in3 = 245 lb




It is used for grilling purpose, as it has exceptional heat conductivity as well as heat holding quality. It is very similar to cast iron plate which are made from iron. Where, 99% of iron helps to give matte look and 1% carbon gives smoother finish and reduces its breakable look












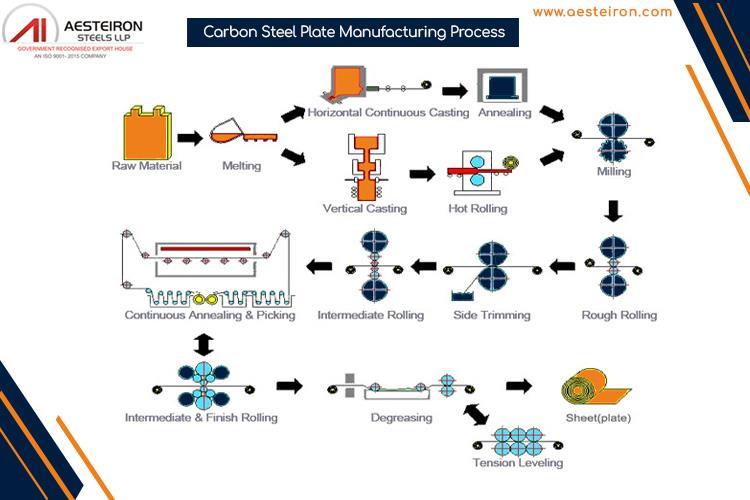
1]
2] Blast Furnace Operation:
heated with a blast of hot air, causing a chemical reaction that reduces iron ore to molten iron
3] Steelmaking:
Basic Oxygen Furnace
Electric Arc Furnace
Refining



4] Casting: molten steel is poured into a continuous casting machine
5] Hot Rolling: Reheating, Rolling
6] Plate Cutting and Finishing rolled plates are cut to the required dimensions surface treatment
7] Quality Control: inspected for defects and dimensional accuracy
8] Packaging and Shipping
➔ Construction
➔ Manufacturing
➔ Storage Tanks




