
Phytocompounds/ Phytochemistry/ Natural
Compound-Based Projects


























This project focused on utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) and cheminformatics to design, screen, and prioritize novel anticancer compounds targeting oncogenic proteins (e.g., EGFR, BCL2). The pipeline combined deep learning-based molecular generation, molecular docking, ADMETprediction,andQSARmodelingtoidentifyhigh-potentialdrugcandidates.






• EmployedGenerativeAdversarialNetworks(GANs)trainedon ChEMBLanticancermolecules.
• Generated>1000virtualmoleculesandfilteredby:
⚬ Structuraldiversity
⚬ Drug-likenessfilters(Lipinski'srules)


• UsedSwissADME,pkCSM,andADMETlabtoevaluate:
⚬ Absorption
⚬ Distribution
⚬ Metabolism
⚬ Excretion
⚬ Toxicity




• TopcompoundsdockedwithAutoDockVinaagainsttarget protein(e.g.,EGFR).
• InteractionresiduesvisualizedwithPyMOLandLigPlot+.



• ExtractedmoleculardescriptorsviaPaDEL.
• ModeledbiologicalactivityusingRandomForestand SupportVectorRegression(SVR).
• InterpretedfeaturecontributionusingSHAPvalues



Threeleadcompounds(Lead_1,Lead_2, Lead_3)outperformedcontroldrugindocking scores.


ADMETprofilingconfirmedgood pharmacokineticbehavior
QSARanalysispredictedhighinhibitorypotential basedonmoleculardescriptors.
Alltopleadsshowed:
⚬ Highbindingaffinity(<-9kcal/mol)
⚬ Favorablebioavailabilityandsafetyprofile



AllAI-designedcompoundsshowed strongerbindingthanthecontrol drug.

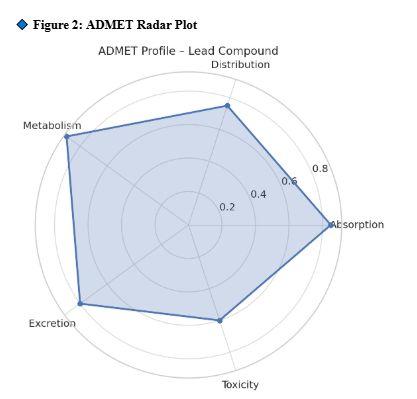

ADMETprofileofLead_1indicating astrongbalanceofbioavailability,low toxicity,andgoodmetabolicstability.


Descriptivechemicalproperties
(MolWeight,LogP,TPSA)oflead compounds.


ThisprojectdemonstratedthesuccessfuluseofAI-assisted compounddesignintegratedwithbioinformaticsand cheminformaticstoolsforanticancerdrugdiscovery.














AI-poweredlead discoverypipelinefully established. Producedviable candidateswith therapeuticpotential. Generatedacomprehensive insilicoprofileforlead optimizationandpreclinical testing.


