What Are the Barriers to Career Development?
l
65
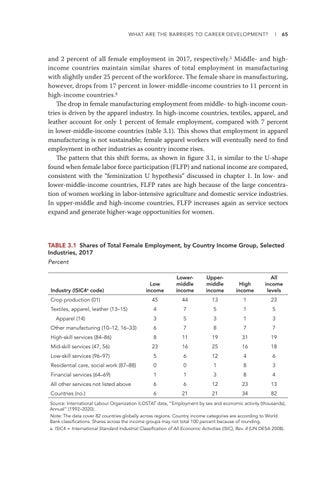
and 2 percent of all female employment in 2017, respectively.5 Middle- and highincome countries maintain similar shares of total employment in manufacturing with slightly under 25 percent of the workforce. The female share in manufacturing, however, drops from 17 percent in lower-middle-income countries to 11 percent in high-income countries.6 The drop in female manufacturing employment from middle- to high-income countries is driven by the apparel industry. In high-income countries, textiles, apparel, and leather account for only 1 percent of female employment, compared with 7 percent in lower-middle-income countries (table 3.1). This shows that employment in apparel manufacturing is not sustainable; female apparel workers will eventually need to find employment in other industries as country income rises. The pattern that this shift forms, as shown in figure 3.1, is similar to the U-shape found when female labor force participation (FLFP) and national income are compared, consistent with the “feminization U hypothesis” discussed in chapter 1. In low- and lower-middle-income countries, FLFP rates are high because of the large concentration of women working in labor-intensive agriculture and domestic service industries. In upper-middle and high-income countries, FLFP increases again as service sectors expand and generate higher-wage opportunities for women.
TABLE 3.1 Shares of Total Female Employment, by Country Income Group, Selected Industries, 2017 Percent
Low income
Lowermiddle income
Uppermiddle income
High income
All income levels
Crop production (01)
45
44
13
1
23
Textiles, apparel, leather (13–15)
4
7
5
1
5
3
5
3
1
3
6
7
8
7
7
Industry (ISIC4a code)
Apparel (14) Other manufacturing (10–12, 16–33) High-skill services (84–86)
8
11
19
31
19
Mid-skill services (47, 56)
23
16
25
16
18
Low-skill services (96–97)
5
6
12
4
6
Residential care, social work (87–88)
0
0
1
8
3
Financial services (64–69)
1
1
3
8
4
All other services not listed above
6
6
12
23
13
Countries (no.)
6
21
21
34
82
Source: International Labour Organization ILOSTAT data, “Employment by sex and economic activity (thousands), Annual” (1992–2020). Note: The data cover 82 countries globally across regions. Country income categories are according to World Bank classifications. Shares across the income groups may not total 100 percent because of rounding. a. ISIC4 = International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC), Rev. 4 (UN DESA 2008).