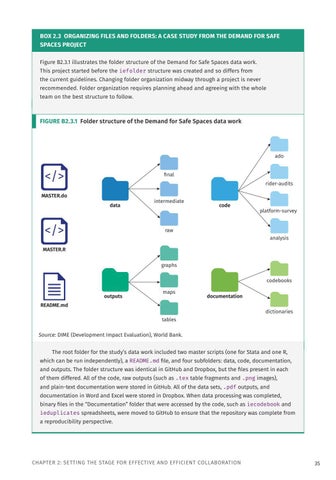
BOX 2.3 ORGANIZING FILES AND FOLDERS: A CASE STUDY FROM THE DEMAND FOR SAFE SPACES PROJECT Figure B2.3.1 illustrates the folder structure of the Demand for Safe Spaces data work. This project started before the iefolder structure was created and so differs from
the current guidelines. Changing folder organization midway through a project is never recommended. Folder organization requires planning ahead and agreeing with the whole team on the best structure to follow.
FIGURE B2.3.1 Folder structure of the Demand for Safe Spaces data work
ado
</>
final rider-audits
MASTER.do data
</>
intermediate
code
platform-survey
raw analysis
MASTER.R graphs codebooks outputs
maps
documentation
README.md
dictionaries tables
Source: DIME (Development Impact Evaluation), World Bank.
The root folder for the study’s data work included two master scripts (one for Stata and one R, which can be run independently), a README.md file, and four subfolders: data, code, documentation, and outputs. The folder structure was identical in GitHub and Dropbox, but the files present in each of them differed. All of the code, raw outputs (such as .tex table fragments and .png images), and plain-text documentation were stored in GitHub. All of the data sets, .pdf outputs, and
documentation in Word and Excel were stored in Dropbox. When data processing was completed, binary files in the “Documentation” folder that were accessed by the code, such as iecodebook and
ieduplicates spreadsheets, were moved to GitHub to ensure that the repository was complete from a reproducibility perspective.
CHAPTER 2: SETTING THE STAGE FOR EFFECTIVE AND EFFICIENT COLLABORATION
35