

Waterford Public Schools




Vision of the graduate

Our Vision of the Graduate aims to empower each student to be resilient, innovative, and develop a global perspective. Our Vision of the Graduate nurtures a community of lifelong learners equipped with critical thinking skills, compassion, and a drive for excellence, positioning them to flourish in a constantly evolving world.
Effective Communicators


Information Analysts

Critical Thinkers

Self-Directed Learners

Responsible Citizens
1A: Listen actively to understand information.
1B: Use an appropriate method of communication.
1C: Create a logical and evidence-based argument.
1D: Deliver a clear and effective presentation or performance.
2A: Use appropriate research tools to acquire information from a variety of sources.
2B: Evaluate different perspectives, biases, and levels of credibility.
2C: Analyze information gathered from research tools to demonstrate understanding.
3A: Make reasonable predictions of a real-world issue.
3B: Analyze data in order to justify a claim.
4A: Persevere through challenging situations with flexibility and resourcefulness.
4B: Recognize how thoughts, feelings, and actions affect achievement.
4C: Work independently towards achieving a meaningful goal.
5A: Demonstrate respect for all cultures, identities, and perspectives.
5B: Practice responsible digital citizenship.

K-5 Math Vision Statement
Our goal is for students to experience the joy of math and to understand its real-world applications. Our schools embrace perseverance and celebrate mistakes as opportunities to develop a growth mindset. Therefore, we are committed to creating both challenging and supportive math experiences for all students.
Students will:
• use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words.
• make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer
• engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning
• participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ideas, strategies, and approaches.
• recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another.
• apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation
• understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem
We believe all students are capable math learners. By encouraging a positive and inclusive learning environment, students develop a deeper understanding of mathematics that cultivates joy and encourages lifelong learning. We empower them to work toward grade-level goals by becoming increasingly fluent and able to break down complex problems.
Instructional staff will:
• Build from students’personal knowledge, experiences, and attitudes
• Work to ensure a deep understanding of foundational skills to aid in more complex thinking
• Strengthen computational fluency through models, strategies, and practice
• Use of student-led tasks and hands-on learning opportunities that promote curiosity and engagement
• Facilitate regular mathematical discourse to engage in purposeful questioning to develop a deeper understanding
• Provide multiple entry points to solve problems, promoting student agency
• Grow student self-efficacy because of students' experience with challenging problems that they persevered through


Kindergarten Math
Kindergarten Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Kindergarten Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 0
Title: Setting the Classroom Culture
How do we find things in our classroom? Together, we will explore where we can find our math tools and how to take care of them. Take a peek into our year of math.
● Where can we find our math centers?
● What are the math routines?
● What is a mathematician?
Established Goals
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Note: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards; it supports the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards (Common Core)
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Mistakes are part of learning and can help me grow.
● Working together and listening to each other, strengthens mathematical understanding.
● There are multiple strategies to solve a problem, and it's okay to try more than one.
● Being stuck is normal, and there are strategies for moving forward.
● What patterns do I see in numbers and shapes, and how do they help me?
● How can I use tools and pictures to help me solve problems?
● What can I learn by collecting, sorting, and talking about things I see around me?
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom norms and routines for math time
● How to use the tools and resources available in the classroom.
● What a productive struggle looks and feels like.
● Strategies to show perseverance (e.g., selftalk, trying a different strategy, asking a partner).
● Sentence starters will be used to guide respectful language for agreeing and disagreeing in math discussions
● Using rubrics and group norms helps identify positive and poor collaboration
● Self-monitoring and reflection help improve both problem-solving and behavior
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can use math tools like number paths, tenframes, and cubes to solve problems.
● I can talk about my math thinking and listen to my classmates’ ideas.
● I can collect and sort objects and talk about what I notice.
● I can add and subtract small numbers to solve problems.
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like selftalk, trial and error, and regrouping.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries or Reflections that respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes & Checklists during group tasks and partner work (e.g., who participates, uses self-talk, problem-solving strategies, or supports peers).
● Problem-Solving Checklist used by students (introduced in Building Shapes) to self-monitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think..
● Throughout the school year, a Collaboration Rubric will be used as an ongoing tool to monitor and support students' development of positive behaviors while working in partnerships.
Kindergarten Math: Unit 0
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Yearlong Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines
Learning Targets:
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can use math tools like number paths, ten-frames, and cubes to solve problems.
● I can talk about my math thinking and listen to my classmates’ ideas.
● I can collect and sort objects and talk about what I notice.
● I can add and subtract small numbers to solve problems.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a year-long focus to strengthen number sense through problemsolving context.
Essential Questions:
● What patterns do I see in numbers and shapes, and how do they help me?
● How can I use tools and pictures to help me solve problems?
● How can I show my math thinking and learn from others?
● What can I learn by collecting, sorting, and talking about things I see around me?
● Daily 15-minute routines feature five components: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Days in School, Pattern Shapes, and Number Line/Number Path.
● Students lead classroom routines by adding to displays, sorting collections, and sharing their thinking to develop number sense and pattern awareness.
● Hands-on tools, movement, and conversation support problem solving, math talk, and developing confidence as young mathematicians.
Second Topic: Setting the Culture through Think! Mathematics!
Estimated # of Lessons: 10 Days
Learning Targets:
Kindergarten Math: Unit 0
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like self-talk, trial and error, and regrouping.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
● Lesson 1 Focus: The Most Magnificent Thing to foster a growth mindset and self-awareness
○ Activities:
■ Roll Reveal Reflect
● Lesson 2 Focus: Place It to cultivate perseverance and problem-solving
○ Activities:
■ Place it
● Lesson 3 Focus: Finding Five to foster communication and embrace differences
○ Activities:
■ Finding Five
● Lesson 4 Focus: Disagreeing is Okay! We Can Still Be Friends to master respectful communication in challenging situations
○ Activities:
■ Disagreeing is okay!
■ Partner Cards
■ My Favorite Cards
■ What's Better Cards
● Lesson 5 Focus: Balloon Ride to cultivate independence and collaboration through problemsolving
○ Activities:
■ Balloon Ride
● Lesson 6 Focus: Building Shapes to teach that collective effort can lead to greater accomplishments than individual work alone
○ Activities:
■ Building Shapes
■ Problem-Solving Checklist
■ Shape Cards
Kindergarten Math: Unit 0
● Lesson 7 Focus: Hula Number to emphasize the importance of planning and reflection in successful collaboration
■ Hula Numbers
● Lesson 8 Focus: Balloon Walk to foster a collaborative classroom culture
○ Activities:
■ Balloon Walk
● Lesson 9 Focus: Folding Paper to shift the focus from speedy calculation to appreciating the beauty of mathematical patterns and the larger problem-solving context
○ Activities:
■ Problem-Solving Checklist
■ Folding Paper
● Lesson 10 Focus: Hexagon Havoc to empower students to leverage resources independently
○ Activities:
■ Hexagon Havoc
■ Hexagon Template
Additional Resources:
● The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
Course Name: Kindergarten Math
Est. # of Lessons: 54
Unit 1 Title: Number: Let’s Play
Unit Overview:
Did you see that? Numbers are all around us. Explore with numbers by finding them in our world, writing using multisensory ways, and finding patterns.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● K.CC.A.1 – Count to 100 by ones and tens
● K.CC.A.2 – Count forward from any given number
● K.CC.A.3 – Write numbers from 0 to 20
● K.CC.B.4 – Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities (cardinality)
● K.CC.B.5 – Count objects (line, array, circle, or scattered up to 20)
● K.CC.C.6 – Compare sets using greater than, less than, or equal
● K.CC.C.7 – Compare written numerals
● K.MD.B.3 – Classify objects and count the number in each category
● K.NBT.A.1 – Compose and decompose teen numbers using 10 as a unit (introduced in Topic 5)
● K.G.A.1 - Describe objects in the environment
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP4, MP5 – Model with mathematics and use tools; VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP6 – Attend to Precision; VOG: Effective Communicator)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP1, MP2 – Reasoning and perseverance; VOG: Critical Thinker, SelfDirected Learner)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers can be expressed differently using objects, pictures, spoken words, and written numerals but still mean the same thing (or have the same value).
● The number of objects in a group doesn’t change unless added to or taken away from.
● Numbers are used to describe groups of objects to help count, compare, and organize.
● Numbers have an order to assist in counting forwards and backwards.
● Numbers can describe real-world
● What patterns do I see in numbers and shapes, and how do they help me?
● How can I organize and sort a group of items?
● How can I use patterns to help me count and solve problems?
● How can I show a number in different ways?
● How can I use math words and symbols to explain my thinking?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
quantities (e.g., age, number of items, the date) that assist us in our daily lives.
Knowledge
● The correct counting sequence from 0 to 100
● Numerals are symbols that represent quantities that represent amounts
● Numbers have a specific order and come before or after other numbers
● Represent numbers using objects, drawings, and symbols
● The last number said when counting tells how many are in the group (cardinality)
● Teen numbers are made up of a ten and some more
Key Vocabulary: number, count, more, less/fewer, greater than, group, same/equal, compare, set, match, how many, number words, numeral, ten ones, sort/classify
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can count objects in a set with one-to-one correspondence up to 20.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
● I can show a number using objects, drawings, and numerals.
● I can count a group of objects and tell how many there are.
● I can show a number in different ways.
● I can compare two groups and tell which has more, fewer, or the same.
● I can build and take apart teen numbers using tens and ones.
● I can use math words and symbols to explain my thinking clearly.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● Counting Evidence of Learning Rubric
Level Indicators 1-3
● Primarily achieved through Observations: How students count verbally, sort objects, recognize quantities (cardinal numbers), and name object positions in a sequence using ordinal numbers. Recording Template
● Think! Pad: Open-ended prompts that are provided for screening, consolidation, and assessment activities.
● Student Activity Book: Supports students in learning math through playful problemsolving and collaborative exploration.
● Shelf Days: Hands-on activities that extend and reinforce concepts from group lessons, providing opportunities for students to independently explore and practice key math ideas.
● Throughout the school year, a Collaboration Rubric will be used as an ongoing tool to monitor and support students' development of positive behaviors while working in partnerships.
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Exploration( Anchor Task): Begin all lessons with an exploration (Anchor Task) to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to structure the classroom dialogue to meet the intended outcome.
Practice (Activity Time): Each lesson includes student practice through play. Materials, prepared work, and games to support the anchor task are placed in work areas, centers, or shelves for independent or partner work.
Reflection: Requires students to think more deeply about their learning and can take a variety of forms. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and student Think! Pad pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Counting Sequence
Learning Targets:
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
Estimated # of Lessons: 11
Essential Questions:
● What patterns do I see in numbers and shapes, and how do they help me?
Key: Lesson (1.1.1) Chapter. Topic. Lesson Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson purpose. Green: Think! Pad (TP) and Student Activity Book (SAB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1.1.1 Focus (2 days): Counting Screening to recognize how numbers are used in the environment
○ Activities:
■ Number Walk
■ Find a Given Number
■ Handle and Care for Manipulatives
○ Reflect
■ I Spy with my eye numbers everywhere TP pg. 6
● Lesson 1.1.2 Focus( 2 days): Writing Numerals (0-9) to prepare students for writing numerals to represent quantity.
○ Activities:
■ Pin Pushing SAB pg. 6
■ Tracing Sandpaper Numerals
■ Shaving Cream
■ Air Writing
■ Playdough Writing
■ Race to the Top SAB pg. 7-8
○ Reflect
■ My favorite number TP pg. 7
■ Numeral Writing TP pg. 8-10
● Lesson 1.1.3 Focus (1 day): Verbal Counting to count forward from any given number by 1s and 10s to 100.
○ Activities:
■ Counting in Sequence
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
■ Task Cards- Beat the Clock
■ Task Cards- Broken Paths
■ Differentiated Hundred Board Cards
○ Reflect
■ Who will say 10? TP pg. 11
● Lesson 1.1.4 Focus (4 days): Number Line Counting to use a number line as a visual model for practicing the counting sequence
○ Activities:
■ Creating Number Lines
■ Task Cards- Mystery Number
○ Reflect
■ I can count on and back TP pg. 12
■ I can estimate TP pg. 13
● Topic 1 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations on the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Counting. Also found in Teacher Guide
Second Topic: Sorting
Learning Targets:
● I can compare two groups and tell which has more, fewer, or the same.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 9
Essential Questions:
● How can I organize and sort a group of items?
● Lesson 1.2.1 Focus (1 day): Counting Screening to recognize how items are organized in the environment
○ Activities:
■ Nature Walk
○ Reflect
■ A Look Around TP pg. 14
■ These are the same TP pg. 15
● Lesson 1.2.2 Focus (2 days): Same and Different to describe the attributes of an item in terms of same, exactly the same, and different
○ Activities:
■ Same and Different
○ Reflect
■ I can sort like this TP pg. 16,17
● Lesson 1.2.3 Focus (2 days): Sort and Compare to create a set based on a single attribute
○ Activities:
■ Sorting Circles SAB pg. 14
■ Organizing the Classroom
○ Reflect
■ Things I sort TP pg. 19
■ Read my mind TP pg. 20
● Lesson 1.2.4 Focus (1 day): Sort Using Multiple Attributes to create sets based on more than one attribute
○ Activities:
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
■ Read My Friend’s Mind (Pictorial) SAB pg. 15
■ Sort Using Multiple Attributes SAB pg. 16
● Lesson 1.2.5 Focus (1 day): Which Does Not Belong? to identify which item does not belong based on an attribute
○ Activities:
■ Which Object is Not Like the Others?
○ Reflect
■ Does Not Belong TP pg. 21
● Topic 2 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations on the topic
Third Topic: Numbers to 10
Learning Targets:
● I can count objects in a set with one-toone correspondence up to 20.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
● I can count a group of objects and tell how many there are.
● I can show a number in different ways.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 17
Essential Questions:
● How can I show a number in different ways?
● Lesson 1.3.1 Focus (2 days): Number Screening to count numbers in the environment
○ Activities:
■ Counting Walk
■ Handling and Care for Manipulatives
■ Winner Winner Score Sheet
■ Student Dot Cards
○ Reflect
■ Look what I can count TP pg. 22
■ My favorite number TP pg. 23
● Lesson 1.3.2 Focus (5 days): Quantities 1-10 to name quantities 1-10, associate the numeral with the quantity, build and compare quantities greater than and less than.
○ Activities:
■ Naming Numbers
■ Association of Numeral with Quantity
■ Comparing Numbers
■ Student Question Cards
○ Reflect
■ I can compare numbers TP pg. 24
● Lesson 1.3.3 Focus (5 days): Rational Counting to match different representations of numbers to a quantity.
○ Activities:
■ Estimating and Counting with Objects
■ Counting with Pictorial Representations
■ Matho SAB pg. 21
○ Reflect
■ I can represent a number in many ways TP pg. 25
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
● Lesson 1.3.4 Focus (1 day): Building the Number Stair to represent units as a set that indicates a quantity
○ Activities:
■ Building the Number Stair
■ Associating Numeral with Quantity
■ Place Value Cards SAB pg. 22-23
○ Reflect
■ My number stair TP pg. 26- 27
● Lesson 1.3.5 Focus (1 day): Zero as a Set to associate zero with the empty set
○ Activities:
■ Mystery Numbers- Who is Holding the Zero?
○ Reflect
■ I can represent numbers TP pg. 28-29
● Extension E.1.3.1 (1 day): Odd and Even Numbers to recognize patterns and communicate with understanding the patterns of even and odd numbers
○ Activities:
■ Looking for Patterns
■ Task Cards- House Number
■ Task Cards- Snail Watching
● Topic 3 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations on the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Counting. Also found in Teacher Guide
Fourth Topic: Ordinal Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can build and take apart teen numbers using tens and ones.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How can I use patterns to help me count and solve problems?
● Lesson 1.4.1 Focus (1 day): Position in a Line to identify and name the position in a line
○ Activities:
■ Describe Positions in a Line SAB pg. 24-25
○ Reflect
■ Animal Parade TP pg. 30
● Lesson 1.4.2 Focus Events Over Time (2 days) to order events over time
○ Activities:
■ Getting Ready for School
■ Going on a Picnic SAB pg. 26-28
○ Reflect
■ Going on a picnic TP pg. 31
● Topic 4 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Counting Also found in Teacher Guide
Kindergarten Math: Unit 1
Fifth Topic: Numbers to 20
Learning Targets:
● I can look for patterns in numbers, shapes, and things I see every day.
● I can count objects in a set with one-toone correspondence up to 20.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 12
Essential Questions:
● How can I show a number in different ways?
● How can I use math words and symbols to explain my thinking?
● Lesson 1.5.1 Focus(5 days): Counting to 20 to count teen numbers using ten as a benchmark
○ Activities:
■ Counting to 20- Grouping by Making Sets of 10 SAB pg. 29-33
■ Counting by Making Sets of 10 Using a Ten Frame
● Lesson 1.5.2 Focus (3 days): Building Teen Numbers to build teen numbers using 10 as a benchmark
○ Activities:
■ Build Teen Numbers
■ Making Teen Quantities
■ Association of Quantity and Symbol
○ Reflect
■ Numbers 11-20 TP pg. 32
■ How many? TP pg. 33
● Extensions E.1.5.1 Focus (2 days): Numbers Beyond 20 to use patterns in numbers to build numbers to 100.
○ Activities:
■ Counting 10-90: Grouping by making sets of 10
■ Association of Quantity and Symbol
■ Patterns with the Hundred Board
■ Constructing the Quantity and Symbolizing Quantities from 10-90 with Tens and Units
○ Reflect:
■ I can represent numbers in many ways TP pg. 34
■ Numeral Writing TP pg. 3
● Topic 5 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Counting. Also found in Teacher Guide
Kindergarten Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Kindergarten Math
Est. # of Lessons: 33
Unit 2 Title: Measurements: Who’s Taller?
Unit Overview:
What is taller? What is heavier? What is almost full? Next, we move from recognizing numbers to using them. We explore how numbers can help us measure, describe, and compare attributes like length, weight, and capacity.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● K.MD.A.1: Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight. Describe several measurable attributes of a single object.
● K.MD.A.2: Directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in common to see which has “more of”/“less of” the attribute, and describe the difference.
● K.MD.B.3: Classify objects into categories; count the number of objects in each category and sort the categories by count
● K.CC.B.4 – Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities (cardinality)
● K.CC.B.5 – Count objects (line, array, circle, or scattered up to 20)
● K.CC.C.6 – Compare sets using greater than, less than, or equal
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 4: Model with mathematics, MP 5: Use appropriate tools strategically) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7: Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6: Attend to Precision) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Length, height, weight, and capacity are attributes of objects that can be measured.
● Compare measurable attributes to decide which is longer, taller, heavier, or holds more.
Knowledge
● Measurement means finding the length, height, weight, or capacity of an object
● Objects can be compared directly (e.g., taller/shorter, heavier/lighter)
● Everyday items and simple tools help to
● What attributes of an object can I measure?
● How do I compare the measurements of two objects?
● What tools can help me measure this object? How do I use them to describe the object?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can describe how objects are different or the same by size or weight.
● I can tell which object is longer, taller, heavier, or holds more.
● I can compare two objects and explain which
Kindergarten Math: Unit 2
measure objects (e.g., cubes, hands, scoops, containers)
● Measurement words help to describe and explain observations
Key Vocabulary: measure, length, height, weight, capacity, compare, longer/shorter, taller/shorter, heavier/lighter, holds more, holds less, size
is more or less.
● I can use cubes, hands, or other tools to measure how big or full something is.
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● Measurement Evidence of Learning Rubric
○ Level indicators 1-3
Formative Assessment
● Primarily achieved through Observations: Students' strategies for measuring length, weight, capacity, and for collecting and representing data. Recording Template
● Think! Pad: Open-ended prompts that are provided for screening, consolidation, and assessment activities.
● Student Activity Book: Supports students in learning math through playful problemsolving and collaborative exploration.
● Shelf Days: Hands-on activities that extend and reinforce concepts from group lessons, providing opportunities for students to independently explore and practice key math ideas.
● Throughout the school year, a Collaboration Rubric will be used as an ongoing tool to monitor and support students' development of positive behaviors while working in partnerships.
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Exploration( Anchor Task): Begin all lessons with an exploration (Anchor Task) to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to structure the classroom dialogue to meet the intended outcome.
Practice (Activity Time): Each lesson includes student practice through play. Materials, prepared work, and games to support the anchor task are placed in work areas, centers, or shelves for independent or partner work.
Reflection: Requires students to think more deeply about their learning and can take a variety of forms. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and student Think! Pad pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Length
Learning Targets:
● I can tell which object is longer, taller,
Estimated # of Lessons: 20
Essential Questions:
● What attributes of an object can I measure?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 2
heavier, or holds more.
● I can tell which object is longer, taller, heavier, or holds more.
● How do I compare the measurements of two objects?
● What tools can help me measure this object? How do I use them to describe the object?
Key: Lesson (2.6.1) Chapter. Topic. Lesson: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson purpose, Green: Think! Pad (TP) and Student Activity Book (SAB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 2.6.1 Focus (2 days): Measurement Screening to look for objects in the environment that can be described based on measurable attributes such as length, weight, and volume
○ Activities:
■ Measurement Walk
○ Reflect
■ This is what I can measure TP pg. 38
■ I spy with my eye objects that are big TP pg. 39
● Lesson 2.6.2 Focus (1 day): Longer or Shorter? to directly compare two objects to determine which is longer or shorter
○ Activities:
■ Sort by Measurable Attribute (Long/Short)
○ Reflect
■ I can draw objects TP pg. 40
■ I can draw a line TP pg. 41
● Lesson 2.6.3 Focus (2 days): Height to describe length in terms of height and order based on height
○ Activities:
■ A Class Photo
■ Ordering Boxes by Height
○ Reflect
■ I can order Heights TP pg. 42
■ Height TP pg. 43
■ I am a ladybug. What is tall to me? TP pg. 44
■ I am a giraffe. What is tall to me? TP pg. 45
● Lesson 2.6.4 Focus (2 days): Length and Width to compare the length and width of paper to a benchmark, such as straws
○ Activities:
■ Length and Height
○ Reflect
■ This is my string TP pg. 46-47
● Lesson 2.6.5 Focus (3 days): Tricky Lengths to estimate which object is longer when presented in different shapes or orientations
○ Activities:
■ Tricky Lengths
○ Reflect
■ My tricky ribbon TP pg. 48-49
● Lesson 2.6.6 Focus (3 days): Measure Length to estimate and confirm which object is the longest, given objects of different size, shape, and orientation
○ Activities:
■ Measuring the Table Top SAB pg. 34
Kindergarten Math: Unit 2
■ Measuring Lengths SAB pg. 35
○ Reflect
■ I can measure a friend’s height with paper clips TP pg. 50
■ I can draw a friend 4 paper clips tall TP pg. 51
● Lesson 2.6.7 Focus (3 days): Tools! Tools! to choose the best unit to measure and compare the lengths of objects
○ Activities:
■ Choosing a Tool SAB pg. 36-37
■ Task Cards- Draw It
○ Reflect
■ I can use two tools to measure the same object TP pg. 52-53
● Lesson 2.6.8 Focus (2 days): Stay on the Path! to choose the best unit to measure and compare lengths of objects
○ Activities:
■ Longest Path SAB pg. 38
○ Reflect(think!Pad)
■ How long is each pencil? TP pg. 54-55
■ Measure Me TP pg. 56
■ I can make something long look short TP pg. 57
● Topic 6 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Measurement Also found in the Teacher Guide
Second Topic: Weight Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Learning Targets:
● I can describe how objects are different or the same by size or weight.
● I can tell which object is longer, taller, heavier, or holds more.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● What attributes of an object can I measure?
● How do I compare the measurements of two objects?
● What tools can help me measure this object? How do I use them to describe the object?
● Lesson 2.7.1 Focus (1 day): Weight to pre-assess what vocabulary students use to describe heavy and light
○ Activities:
■ Feeling Weight
○ Reflect
■ Objects that weigh about the same as a box of pasta TP pg. 5758
■ Pre-assessment Weight TP pg. 59
● Lesson 2.7.2 Focus (1 day): Mystery Bags- Heavy and Light to directly compare two objects to determine which is heavier/lighter
○ Activities:
■ Heavy and Light
○ Reflect
■ I can feel light TP pg. 60
■ I can feel heavy TP pg. 61
Kindergarten Math: Unit 2
● Lesson 2.7.3 Focus (2 days): Heavier and Lighter to use a tool to compare the weight of two objects
○ Activities:
■ Using a Tool to Compare Weight Materials SAB pg. 39-40
○ Reflect
■ I can compare TP pg. 62-63
■ I can compare by holding TP pg. 64
● Lesson 2.7.4 Focus (1 day): Tricky Weights to estimate and compare the weights of objects
○ Activities:
■ Measurement Walk
■ Task Cards- Balancing Fruit SAB pg. 41
○ Reflect
■ Heavier/lighter TP pg. 65
■ Is this possible? TP pg. 66
■ Tricky Weights TP pg. 67
● Topic 7 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Third Topic: Capacity Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Learning Targets:
● I can use cubes, hands, or other tools to measure how big or full something is.
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● What attributes of an object can I measure?
● How do I compare the measurements of two objects?
● What tools can help me measure this object? How do I use them to describe the object?
● Lesson 2.8.1 Focus (1 day): Full and Empty to estimate and compare the capacity of containers
○ Activities:
■ Full and Empty
○ Reflect
■ This fits in my shoe box TP pg. 68
■ This does not fit in my shoe box TP pg. 69
■ I can show TP pg. 70
● Lesson 2.8.2 Focus (1 day): Which Holds More? Which Holds Less? to estimate and compare the capacity of different-sized containers
○ Activities:
■ Experimenting with Capacity SAB pg. 42
● Lesson 2.8.3 Focus (2 days): Compare and Measure Capacity to estimate and compare the number of units used to fill a container
○ Activities:
■ Comparing Capacity of Containers
■ Task Cards- Fill It! SAB pg. 43
○ Reflect
■ How can this be? TP pg. 71
■ This is what I can measure TP pg. 72-73
● Topic 8 Focus (2 days): Practice/Shelf Work/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Kindergarten Math
Est. # of Lessons: 54
Unit 3 Title: Operations: How Many?
Unit Overview:
What do you see in the picture? We now dive into using numbers to solve story problems. We learn how putting together and joining are addition, and taking apart is subtraction. We finish by creating our own story problems.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● K.OA.A.1: Represent addition and subtraction with objects, fingers, mental images, drawings, sounds, acting out situations, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations.
● K.OA.A.2: Solve addition and subtraction word problems and add and subtract within 10, using concrete objects or drawings to represent the problem.
● K.OA.A.3: Decompose numbers less than or equal to 10 into pairs in more than one way.
● K.OA.A.4: For any number from 1 to 9, find the number that makes 10 when added to the given number.
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 4: Model with mathematics, MP 5: Use appropriate tools strategically) (VOG: Information Analysts, Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6: Attend to Precision, MP 1: Make sense of problems) (VOG: Effective Communicators, Self-Directed Learners)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7: Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 1: Persevere in solving problems, MP 2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Problem Solvers)
Understandings
● Addition shows the combination of quantities that make up a total.
● Subtraction helps to take away and find what is missing.
● Numbers can be broken apart and put together in different ways.
● Strategies help to become fluent with
Essential Questions
● What does it mean to add?
● What does it mean to subtract?
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving word problems? (acting it out, objects, drawings, expressions)
● What tools or strategies can I use to help solve math problems?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
adding and subtracting small numbers.
Knowledge
● Math stories can be about combining, putting together, taking apart, or taking away.
● How to represent word problems using objects, pictures, fingers, or number sentences to show their thinking.
● Numbers can be taken apart (decomposed) into two or more parts and put together (composed) in different ways.
● Number combinations (addition facts) that make up sums up to 10.
Key Vocabulary: add, plus (+), subtract/take away, minus (–), Same as, number sentence/expression, part, whole, total, more, less/fewer, count on, put together, take apart, missing part, story problem, number bond, joining/leaving stories
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can show how I solved an addition word problem using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
● I can show how I solved subtraction word problems using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
● I can explain the strategy I used when solving addition word problems within 10.
● I can explain the strategy I used when solving subtraction story problems within 10.
● I can group numbers in different ways (compose and decompose) to make it easier to solve problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● Operations Evidence of Learning Rubric
○ Level indicators 1-3
Formative Assessment
● Primarily achieved through Observations: The focus will be on how students use addition and subtraction as efficient counting strategies. During partner or small group work, attention will be given to how students build and use models such as drawings, number lines, or manipulatives and how they create multiple representations to demonstrate their thinking. Recording Template
● Think! Pad: Open-ended prompts that are provided for screening, consolidation, and assessment activities.
● Student Activity Book: Supports students in learning math through playful problemsolving and collaborative exploration.
● Shelf Days: Hands-on activities that extend and reinforce concepts from group lessons, providing opportunities for students to independently explore and practice key math
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
ideas.
● Throughout the school year, a Collaboration Rubric will be used as an ongoing tool to monitor and support students' development of positive behaviors while working in partnerships.
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Exploration( Anchor Task): Begin all lessons with an exploration (Anchor Task) to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to structure the classroom dialogue to meet the intended outcome. Practice (Activity Time): Each lesson includes student practice through play. Materials, prepared work, and games to support the anchor task are placed in work areas, centers, or shelves for independent or partner work.
Reflection: Requires students to think more deeply about their learning and can take a variety of forms. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and student Think! Pad pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Visualizing Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can group numbers in different ways (compose and decompose) to make it easier to solve problems.
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● What tools or strategies can I use to help solve math problems?
Key: Lesson (4.12.1) Chapter. Topic. Lesson Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson purpose, Green: Think! Pad (TP) and Student Activity Book (SAB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4.12.1 Focus (1 day): Subitizing to count by “seeing” groups of numbers quickly
○ Activities:
■ Matho
○ Reflect
■ Draw dots to it is easy to tell how many TP pg. 20
■ Draw dots so it is hard to tell how many TP pg. 21
● Lesson 4.12.2 Focus (1 day): Representing and Reading Data to represent and see data in different forms
○ Activities:
■ Race to 20 SAB pg. 64
■ Data Collection - Graph
■ Data Collection
● Lesson 4.12.3 Focus (1 day): Reading and Comparing Data to collect, graph, and interpret data
○ Activities:
■ Collect data about topics and events
■ Race to 20 (from 4.12.2)
● Topic 12 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Additional Resources:
● From Fives and Tens to Automaticity (Fosnot), Introducing the 5-bead rack, pg. 9-15 Strings A1-A12
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught prior to explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
Second Topic: Addition and Subtraction Structures
Rhoda Red and Loretta Leghorn (CFLM Unit)
Learning Targets:
● I can show how I solved an addition word problem using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
● I can show how I solved subtraction word problems using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 25
Essential Questions:
● What does it mean to add?
● What does it mean to subtract?
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving word problems? (acting it out, objects, drawings, expressions)
● Lesson 4.13.1 Focus (3 days): Action Stories (Give/Take)- Part 1 to sort pictures based on action taking place and represent verbally, by acting out, with words and numbers
○ Activities:
■ Card sort SAB pg. 65-67
○ Reflect
■ My story TP pg. 22-23
● CFLM Focus: Rhoda Red (5 days) to decompose and compose numbers within 5 using a number rack
○ Activities:
■ Days 1-5
● CFLM Focus: Loretta Leghorn (5 days) to decompose and compose numbers within 10 using a number rack
○ Activities:
■ Days 6-10
● Lesson 4.13.2 Focus (3 days): Action Stories (Give/Take)- Part 2 to model the action in a story with manipulatives
○ Activities:
■ Read The Doorbell Rang by Pat Hutchins
■ Model it
■ Task Story - Story Die
○ Reflect
■ My story: Method 1, Method 2 TP pg. 24-25
● Lesson 4.13.3 Focus (3 day): Action Stories (Give/Take)- Part 3 to create a picture that represents the action of joining or separating
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
○ Activities:
■ Blank Farm Scene SAB pg. 68-71
■ Problem Structure-Outcome Unknown
■ Problem Structure- Action Unknown
■ Problem Structure- Opening Unknown
○ Reflect
■ At the farm TP pg. 26-27
● Lesson 4.13.4 Focus (3 day): Action Stories (Give/Take)- Part 4 to model word problems using manipulatives, numbers, words, and symbols
○ Activities:
■ Solve it
○ Reflect
■ Create it TP pg. 28-29
● Lesson 4.13.5 Focus (1 day): Race to 10 to model and record the number sentence for the action taking place
○ Activities:
■ Race to 10
■ Race to 10 Die
○ Reflect
■ Race to 10 TP pg. 30-31
■ What is the question? TP pg. 32
● Topic 13 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Operations Also found in Teacher Guide
Additional Resources:
● Are You All Here (Alessi, Fosnot)
● The Gangs All Here (Alessi, Fosnot)
● From Fives and Tens to Automaticity (Fosnot)
○ Introducing symbols, pg. 16-20 Strings B1-B9
○ Partial Envisioning pg. 21-22 Strings C1-C5
● Number Poem:
○ Five Little Bees
○ Five Tall Snowmen
○ 4 Small Fish
Third Topic: Addition and Subtraction StructuresPart-Whole
Learning Targets:
● I can show how I solved an addition word problem using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
● I can show how I solved subtraction word problems using actions, objects, drawings, or expressions.
Estimated # of Lessons: 18
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving word problems? (acting it out, objects, drawings, expressions)
● What tools or strategies can I use to help solve math problems?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4.14.1 Focus (3 days) Naming Sets to use the number bond to represent the part-whole relationship
○ Activities:
■ “What do you see in the picture?” SAB pg. 72-76
■ Model it
○ Reflect
■ Part-Whole TP pg. 33
■ I see TP pg. 34-35
● Lesson 4.14.2 Focus (3 days): Parts of 3, 4, 5 to break apart a number in different ways
○ Activities:
■ Domino collect
■ Create Dominoes
○ Reflect
■ My domino TP pg. 36-37
● Lesson 4.14.3 Focus (2 days): Parts of 6 to use number bonds to describe the parts that make up shapes
○ Activities:
■ 6 Square tiles
■ Create Shapes
○ Reflect
■ I can show 6 TP pg. 38-39
● Lesson 4.14.4 Focus (2 days): Parts of 7 to use a story to make bonds of 7
○ Activities:
■ Count and Quack by Keith Baker
■ Show 7
■ Human Number Bonds
○ Reflect
■ How many ways? TP pg. 40-41
● Lesson 4.14.5 Focus (2 days): Parts of 8 to toss bean bags to make bonds of 8
○ Activities:
■ Parts of 8 Game SAB pg. 77
■ Chains of 8
○ Reflect
■ Break-Apart 8 TP pg. 42-43
● Lesson 4.14.6 Focus (2 days): Parts of 9 to use number bonds to make 9
○ Activities:
■ How Many Ways? SAB pg. 78
○ Reflect
■ My favorite way to make 9 TP pg. 44
■ Challenging way to make 9 TP pg. 45
● Lesson 4.14.7 Focus (2 days): Parts of 10 to play classic card games in making bonds of 10
○ Activities:
■ Fish for Ten
○ Reflect
■ Fish for Ten TP pg. 46-47
■ At the farm TP pg. 48-49
■ Number Bonds TP pg. 50-51
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
■ Many ways to add TP pg. 52-54
■ Many ways to subtract TP pg. 55-57
● Topic 14 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Operations Also found in Teacher Guide
Additional Resources:
● From Fives and Tens to Automaticity (Fosnot)
○ Full Envisioning pg. 23-25 Strings D1-D8
○ Introducing the 10-bead rack pg. 26-31 Strings E1-E11
○ Making 10 pg. 32- 35 Strings F1-F7
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
Fourth Topic: Developing Fluency within Addition and Subtraction
Learning Targets:
● I can explain the strategy I used when solving addition word problems within 10.
● I can explain the strategy I used when solving subtraction story problems within 10.
● I can group numbers in different ways (compose and decompose) to make it easier to solve problems.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving word problems? (acting it out, objects, drawings, expressions)
● What tools or strategies can I use to help solve math problems?
● Lesson 4.15.1 Focus (1 day): Counting to practice the count-on strategy in developing fluency
○ Activities:
■ First to 10
■ Shoot-Practice Counting On
■ Differentiated Hundred Boards Cards
○ Reflect
■ First to 10 TP pg. 58-61
● Lesson 4.15.2 Focus (1 day): Doubles to practice doubles in developing fluency
○ Activities:
■ Doubles with fingers
■ Shoot
■ Dominoes-Sort Doubles
■ Dominoes- Sort Strategies
■ Doubles This Game Board
○ Reflect
■ I see doubles TP pg. 62-63
● Lesson 4.15.3 Focus (1 day): Combinations of 10 to develop fluency strategies
○ Activities:
■ Sort (by strategy)
■ Matho-Fact Strategies
■ Hop
○ Reflect
■ I see 5 and… TP pg. 64
■ I see 10 and… TP pg. 65
● Extension E.4.15.1 Focus (1 day): Relational Sense Equality to use balance scales to understand equality
○ Activities:
■ Balance it
■ Task Cards- Balance It
■ Task Cards- Fruit Frenzy
● Topic 15 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
Kindergarten Math: Unit 3
● Teacher Reproducibles Operations Also found in Teacher Guide
Additional Resources:
● From Fives and Tens to Automaticity (Fosnot)
○ Partial Envisioning pg.36-41 Strings G1-G17
○ Full Envisioning pg.42-45 Strings H1-H11
● Number Poem:
○ Doubles
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Kindergarten Math
Est. # of Lessons: 30
Unit 4 Title: Geometry: Shapes Everywhere!
Unit Overview:
What shapes do you see around you? We know that numbers are all around us. Let’s take a walk and see shapes all around us, too! We identify and describe the attributes of shapes. Then, we create shapes with our new shape knowledge.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● K.G.A.1: Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes and describe their relative positions (e.g., above, below, beside, in front of, behind, next to).
● K.G.A.2: Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientation or overall size.
● K.G.A.3: Identify shapes as twodimensional (“flat”) or three-dimensional (“solid”)
● K.G.B.4: Analyze and compare 2D and 3D shapes using informal language (e.g., sides, corners, edges, faces).
● K.G.B.5: Model shapes in the world by building and drawing them.
● K.G.B.6: Compose simple shapes to form larger shapes.
Understandings
● Describe, compare, and classify 2-D and 3D shapes by their attributes.
● Shapes can stay the same even if turned, flipped, or moved. (Orientation and size do not change identity)
● Build and draw shapes to model things that can be seen in the world.
● Shapes can be used to build new shapes
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 4 –Model with mathematics, MP 5 – Use appropriate tools strategically) (VOG: Information Analysts, Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 – Attend to Precision, MP 1 –Make sense of problems) (VOG: Effective Communicators, Self-Directed Learners)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 – Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 – Persevere in problemsolving) (VOG: Creative Innovators, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How are shapes alike and different?
● How can I build or draw a shape?
● How can I use shapes to make new shapes?
● How do I use my words to describe the location of objects?
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
and represent objects.
● Positional words help to describe where something is located in relation to other objects.
Knowledge
● Shapes have names like circle, square, triangle, rectangle, hexagon, cube, cone, cylinder, and sphere
● Shapes can be flat (2D) or solid (3D)
● Describe 2D shapes using sides and corners, and 3D shapes using faces, edges, and vertices
● Objects have positions in space that can be described using words like above, below, beside, behind, in front of, and next to
Key Vocabulary: shape, flat shape / solid shape, 2D / 3D, circle, square, triangle, rectangle, hexagon, cube, sphere, cylinder, cone, side, corner, face, edge, vertex, turn, flip, slide, move, above, below, beside, behind, next to, in front of, model, same/different, combine/take apart
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can name flat and solid shapes.
● I can describe attributes of two-dimensional (flat) shapes based on the number of sides and corners.
● I can describe attributes of three-dimensional shapes based on their faces, edges, and vertices.
● I can build and draw 2-D (flat) and 3-D (solid) shapes
● I can use shapes to create a new shape.
● I can figure out and explain where things are by using positional words (next to, between, behind, etc.).
● I can follow and give directions using math words that describe where something is.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● Geometry Evidence of Learning Rubric
○ Level indicators 1-3
● Primarily achieved through Observations: Spatial Relationships: Look for students using positional language (e.g., above, below, next to) as they follow and give directions during play or guided tasks. Notice how they describe where objects are located and how they navigate space. Attributes and Classification: Pay attention to how students describe and compare the attributes of objects (such as shape, size, and number of sides or corners) and use this understanding to classify, identify, and name both 2D and 3D shapes.
Composing and Decomposing Shapes: Watch for students building shapes from smaller parts (e.g., using pattern blocks or tangrams) and taking apart shapes to explore how they are made. This demonstrates their understanding of how shapes relate to one
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
another. Recording Template
● Think! Pad: A collection of Open-ended prompts used for screening, consolidation, and assessment, allowing students to show their thinking and deepen understanding.
● Student Activity Book: Supports students in learning math through playful problemsolving and collaborative exploration.
● Shelf Days: Hands-on activities that extend and reinforce concepts from group lessons, providing opportunities for students to independently explore and practice key math ideas.
● Throughout the school year, a Collaboration Rubric will be used as an ongoing tool to monitor and support students' development of positive behaviors while working in partnerships.
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Exploration( Anchor Task): Begin all lessons with an exploration (Anchor Task) to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to structure the classroom dialogue to meet the intended outcome.
Practice (Activity Time): Each lesson includes student practice through play. Materials, prepared work, and games to support the anchor task are placed in work areas, centers, or shelves for independent or partner work.
Reflection: Requires students to think more deeply about their learning and can take a variety of forms. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and student Think! Pad pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Spatial Relationships
Learning Targets:
● I can name flat and solid shapes.
● I can describe attributes of twodimensional (flat) shapes based on the number of sides and corners.
● I can describe attributes of threedimensional shapes based on their faces, edges, and vertices.
● I can figure out and explain where things are by using positional words (next to, between, behind, etc.).
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How are shapes alike and different?
Key: Lesson (3.9.1) Chapter. Topic. Lesson Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Think! Pad (TP) and Student Activity Book (SAB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3.9.1 Focus (2 days): Shape Screening to recognize shapes in the environment and how they are used
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
○ Activities:
■ Shape Walk
■ Find a Given Shape
○ Reflect:
■ I can see shapes TP pg. 6-7
● Lesson 3.9.2 Focus (2 days): Describing Location and Position to use positional words to place an object relative to another
○ Activities:
■ Describing Position of an Object SAB pg. 44-45
■ Reversing the Point of Reference
○ Reflect:
■ I can show a position TP pg. 8
■ I can show next to TP pg. 9
■ Describe the position TP pg. 10
● Lesson 3.9.3 Focus (1 day): Describing Position Using Right and Left to describe, name, and interpret relative positions of objects using the language of right and left
○ Activities:
■ Hokey Pokey
■ Sort- right and left
■ Left, Center, Right Game
● Lesson 3.9.4 Focus (3 days): Creating Mental Maps to use visualization of a familiar area and spatial reasoning to create a map based on a mental picture.
○ Activities:
■ Record it SAB pg. 46-47
■ Follow the Directions
● Topic 9 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Second Topic: Shapes & Attributes
Learning Targets:
● I can name flat and solid shapes.
● I can describe attributes of twodimensional (flat) shapes based on the number of sides and corners.
● I can describe attributes of threedimensional shapes based on their faces, edges, and vertices.
● I can build and draw 2-D (flat) and 3-D (solid) shapes
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 11
Essential Questions:
● How are shapes alike and different?
● How can I build or draw a shape?
● How do I use my words to describe the location of objects?
● Lesson 3.10.1 Focus (1 day): Naming 3D Shapes to name familiar 3D shapes and find them in the environment
○ Activities:
■ Mystery Bag SAB pg. 48-51
■ Find It!
■ Which One Does Not Belong
■ Capture Game Board- create a die with pictures of shapes. Students move the
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
number of spaces based on the number of sides.
○ Reflect:
■ Shapes I find at home TP pg. 11
● Lesson 3.10.2 Focus (2 days): Sorting 3D Shapes by Attributes to collect and sort objects that have similar geometric attributes
○ Activities:
■ Geometry Sort
■ Mystery Solids
■ Object or Picture Sort
■ Matho
■ Task Cards- Place it
○ Reflect
■ Sorting Shapes TP pg. 12
● Lesson 3.10.3 Focus (3 days): Identifying 2D Faces on 3D Shapes to examine 3D shapes to find 2D shapes
○ Activities:
■ Find 2D Figures in 3D Objects
■ Sort: SAB pg. 52
■ Matching Faces
■ Building 2D and 3D
○ Reflect
■ I can see 2D shapes in 3D objects TP pg. 13
● Lesson 3.10.4 Focus (2 days): Building and Patterning with Shapes to create and analyze patterns using shapes
○ Activities:
■ Build and Create New Patterns with 2D and 3D Shapes
■ Copy It
○ Reflect
■ I can make patterns TP pg. 14
● Lesson 3.10.5F Focus (1 day): No Peeking! to create and use geometric terms to describe a design to a partner in order to make an exact copy
○ Presentation:
■ Shape Matho
● Topic 10 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Geometry. Also found in Teacher Guide
Third Topic: Composing and Decomposing Shapes Estimated # of Lessons: 9
Learning Targets:
● I can use shapes to create a new shape.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I build or draw a shape?
● How can I use shapes to make new shapes?
● Lesson 3.11.1 Focus (1 day): Shapes from Shapes to combine a single shape to construct new shapes
Kindergarten Math: Unit 4
○ Activities:
■ Make Shapes SAB pg. 53-54
■ Find Shapes
■ Task Card- How Many?
○ Reflect
■ I can use ▲ to make __ TP pg. 15
■ Tricky triangles TP pg. 16
● Lesson 3.11.2 Focus (1 day): Building to Make Something That “Looks Like” to build images and new shapes using other shapes
○ Activities:
■ “Look like” SAB pg. 55
○ Reflect
■ Look how I copy using shapes TP pg. 17
● Lesson 3.11.3 Focus (1 day): Creating a Copy Based on an Image to build a copy of an image using shapes
○ Activities:
■ Image Build
■ Build Patterns
■ Create it! SAB pg. 56-62
■ Designer
■ Quick Flash
○ Reflect
■ I can see shapes in shapes TP pg. 18
● Extensions E.3.11.1 Focus (1 day): Reflection and Rotation to explore positional changes described by a change in position created by flipping or reflecting
○ Activities:
■ Flip it! SAB pg. 63
● Extensions E.3.11.2 Focus (1 day): Symmetry to create images that introduce the idea of symmetry
○ Activities:
■ Symmetry
● Extensions E.3.11.3 Focus (1 day): Creating Images to apply transformations to shapes to make new shapes and images
○ Activities:
■ Tangrams SAB pg. 63
■ Task Cards- Shape Machine
○ Reflect
■ I can see shapes TP pg. 19
● Extensions E.3.11.4 Focus (1 day): Creating Nets to examine 3D shapes a bit closer by finding the 2D shapes that make them
○ Activities:
■ Decomposing 3D shapes
● Topic 11 Focus (2 days): Shelf Work/ Practice/Assessment to practice presentations from the topic
Developing Roots Resources:
● Teacher Reproducibles Geometry. Also found in Teacher Guide
Grade 1 Math
Grade 1 Math

Grade 1 Math

Grade 1 Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 0 Title: Setting the Classroom Culture
Unit Overview:
Creating a collaborative environment where students appreciate productive noise and productive struggle. Learning that communication, perseverance, collaboration, and reflection are key to being successful mathematicians.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
Note: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards; it supports the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards (Common Core)
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Mistakes are part of learning and can help me grow.
● Working together and listening to each other, strengthens mathematical understanding.
● There are multiple strategies to solve a problem, and it's okay to try more than one.
● Being stuck is normal, and there are strategies for moving forward.
● How can patterns help me solve problems and figure out what comes next?
● What tools and strategies can I use to solve math problems and explain my thinking?
● How do pictures and models help me understand and show my math ideas?
● How can I use data to learn more about things around me?
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom norms and routines for math time
● How to use the tools and resources available in the classroom
● What a productive struggle looks and feels like
● Strategies to show perseverance (e.g., selftalk, trying a different strategy, asking a partner)
● Sentence starters will be used to guide respectful language for agreeing and disagreeing in math discussions
● Using rubrics and group norms helps identify positive and poor collaboration
● Self-monitoring and reflection help improve both problem-solving and behavior
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can notice and describe patterns in numbers, shapes, and problem situations.
● I can use math tools like number paths, clocks, and ten-frames to help me solve problems.
● I can use what I know about addition and subtraction to solve problems quickly and accurately.
● I can collect, organize, and talk about data to help me figure things out.
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like selftalk, trial and error, and regrouping.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries or Reflections that respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes & Checklists during group tasks and partner work (e.g., who participates, uses self-talk, problem-solving strategies, or supports peers).
● Problem Solving Checklist used by students (introduced in Ice Cream Scoops) to selfmonitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think.
● Perseverance Rubric or T-Chart (from 9 Lives) developed with the class and used for self and peer feedback.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 0
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
First Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines
Learning Targets:
● I can notice and describe patterns in numbers, shapes, and problem situations.
● I can use math tools like number paths, clocks, and ten-frames to help me solve problems.
● I can show and tell how I solved a problem and listen carefully to my classmates' ideas.
● I can use what I know about addition and subtraction to solve problems quickly and accurately.
● I can collect, organize, and talk about data to help me figure things out.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a year-long focus to strengthen number sense through problemsolving context.
Essential Questions:
● How can patterns help me solve problems and figure out what comes next?
● What tools and strategies can I use to solve math problems and explain my thinking?
● How do pictures and models help me understand and show my math ideas?
● How can I use data to learn more about things around me?
● Daily 15-minute sessions featuring five key workouts: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Days in School, Computational Fluency, and Number Path
● Student-led updates to visual displays and data charts provide hands-on practice with counting, place value, data, and number patterns.
● Games, visual models, and math talks support reasoning, problem solving, and the development of each student’s mathematical identity.
Second Topic: Setting the Classroom Culture Through Think Mathematics
Learning Targets:
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like self-talk, trial and error, and regrouping.
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose
Grade 1 Math: Unit 0
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read aloud The Most Magnificent Thing and reflect on times frustration was felt, and introduce the concept of self-talk, and the creation of a problem-solving strategies anchor chart.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Partners play Crazy Colors in order to emphasize the importance of verbalizing thought process and clearly communicating with a partner.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using a Venn Diagram to identify similarities and differences with their peers to reinforce understanding and empathy, while offering choices empowers students and fosters a positive classroom culture.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Establish norms for finding their randomized partners while playing Which One is Better/ My Favorite Card, to implement sentence starters to build a foundation that it is okay to agree and disagree in partnerships.
● Lesson 5: Play the game, Winner Winner! to build their ability to work and solve problems independently, while introducing the independent checklist.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Building Shapes activity and the Collaboration T-chart to introduce the use of the Problem Solving Checklist and to create a Collaboration Rubric.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Next Door Number Neighbors to reflect and practice how to work positively in a group, reinforcing the collaboration rubric and introducing the “one marker” rule.
Lesson 8 Focus: Use the Ice Cream Scoops Word Problem to reinforce the Problem Solving Checklist, which continues to build problem-solving habits and routines, as well as introducing Mild, Medium, and Spicy tasks.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Use the Folding Paper Task to continue to reinforce the Problem Solving Checklist, which continues to build problem-solving habits and routines, and Mild, Medium, and Spicy tasks.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Play 9 Lives to practice persevering through challenging problems, and introduce hanging problems while using the Perseverance T-chart to create a Perseverance Rubric
Think! Math Resources (online):
● Think Mathematics Online Toolbox: Setting the Classroom Culture- Grade 1
Additional Resources:
● The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Grade 1 Math: Unit 1
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 1 Title: Numbers to 20: Number Adventures!
Unit Overview:
Let's go on a number adventure! We practice counting and writing numbers, just like number explorers. We can play with numbers and see how they “fit together” and “break apart.” We also discover the magic of teen numbers by identifying the value of the tens and ones place.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.NBT.A.1- Count to 20, forward and backward, beginning from any number less than 20.
● 1. NBT. B.2- Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones
● 1. NBT. B.3- Compare two numbers between 1 and 20 using comparison symbols (<, >,=).
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers) -
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers follow a sequence that allows counting both forwards and backwards.
● The value of a number is represented in different ways to help work with quantities more efficiently and effectively.
● Numbers can be used to describe groups of objects to count, compare, and organize them.
● Numbers can describe real-world quantities (e.g., age, number of items, time) that assist in our daily lives.
● How can I show a number in different ways?
● How can I use patterns to help me count and solve problems?
● How can I use math words and symbols to explain my thinking?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 1
Knowledge
● The correct counting sequence from 0 to 20 (forward and backward)
● Number names and written numerals from 0 to 20
● Numbers have a specific order and come before or after other numbers
● How to represent numbers using objects, drawings, and symbols
● Digits in a two-digit number represent tens and ones (place value)
● How to compare numbers using terms and symbols such as more, less, equal, >, <, =
Key Vocabulary: order, place value, and comparison (e.g., digit, ten, one, greater, less, equal)
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can count forward and backward from any number less than 20.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
● I can show a number using objects, drawings, and numerals.
● I can explain what each digit in a two-digit number means (tens and ones).
● I can compare two numbers using symbols like >, <, and =.
● I can describe real-world situations using numbers and math vocabulary.
● I can use math words and symbols to explain my thinking clearly.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 1 Assessment
● Observations: Students counting forward and backward within 20 during count arounds.
● Math journal: Compare the number of cherries that the children have.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of number comparisons using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Representing numbers in different ways. (pg.11)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Counting and Writing Numbers to 20
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Grade 1 Math: Unit 1
Learning Targets
● I can count forward and backward from any number less than 20.
● I can recognize and write numbers from 0 to 20.
● I can show a number using objects, drawings, and numerals.
● I can describe real-world situations using numbers and math vocabulary.
Essential Questions:
● How can I show a number in different ways?
● How can I use patterns to help me count and solve problems?
● How can I use math words and symbols to explain my thinking?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Choral counting 1-20 forward and backwards, and representing their thinking with a numeral to sequence numbers and use number patterns.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Represent numbers from 11-20 to write numerals, words, number path, cube, and ten frame(s).
● Grade 1
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Textbook 1A pg. 1-12
● Workbook 1A pg. 1-8
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Number and Operations in Base Ten
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot)
Second Topic: Comparing and Ordering Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can explain what each digit in a two-digit number means (tens and ones).
● I can use math words and symbols to explain my thinking clearly.
● I can describe real-world situations using numbers and math vocabulary.
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How can I use patterns to help me count and solve problems?
● How can I use math words and symbols to explain my thinking?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 1
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3 Focus: Comparing numbers within 20 to use math vocabulary: more than, fewer than, greater than, less than.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Comparing and ordering numbers to use the digits in the tens place and the ones place to identify greater/less/equal to.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Making number patterns to develop an understanding of sequencing numbers and using key vocabulary.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 1
● Textbook 1A pg. 13-28
● Workbook 1A pg. 9-22
● Mind Workout
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Apples in the Basket
○ Make the Sentence True
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Rocks Word Problem
○ Apples and Bananas Word Problem
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Number and Operations in Base Tenenen
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 12- 18
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 25
Unit 2 Title: Addition within 20: Exploring the Magic of Addition
Unit Overview:
Let's set off on an exciting new quest to add! We continue to explore how numbers "fit together" by playing with addition. We use math tools, games, and hands-on activities to add up to 20. We discover number secrets and become addition experts as we solve fun and challenging addition problems.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.OA.A.1- Use addition within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, putting together, and comparing
● 1.OA.A.2- Solve word problems that call for the addition of 3 whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20
● 1.OA.B.3- Apply properties of operations to add
● 1.OA.C.5- Relate counting to addition (e.g., counting on)
● 1.OA.C.6- Add within 20, demonstrating fluency for sums up to 10 and using strategies for sums more significant than 10.
● 1.OA.D.7- Understand the meaning of the equal sign and determine if addition and subtraction equations are true or false.
● 1.OA.D.8- Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. (e.g., 8 +?=11, 5 = ?-3, 3 + 3 =?)
Understandings
● Addition shows the combination of quantities that make up a total.
● Solving addition problems involves progressing from less efficient methods (like three times counting) to more effective strategies (like using a derived fact).
● In addition, the order in which numbers are added doesn’t change the total (commutative property).
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another.(MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving addition problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to solve addition problems?
● How can patterns help me solve addition facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
● The equal sign means both sides of the equation are the same or balanced.
Knowledge
● Represent addition problems using drawings, tools, or equations
● Addition is a way to combine or put together quantities
● Comprehend word problems involving adding to, putting together, and comparing with unknowns in various positions
● Number combinations (addition facts) that make up sums up to 20
● Mental math strategies for adding
● The equal sign means “the same as.”
● Read and write addition equations
● Math symbols: +, =,? have meaning
Key Vocabulary: add, sum, total, plus, equal, counting on, make ten, doubles, near doubles, commutative property, associative property,
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can use efficient strategies to solve addition problems and explain how I solved it using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world addition problems within 20.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can group numbers in different ways to make it easier.
2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 2 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are solving problems using various strategies independently and with partners on vertical surfaces.
● Math journal: Students will solve 1 word problem from Practice 9 and 10.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of addition within 20 using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Find the unknown that makes an addition equation true. (pg.71)
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught prior to explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
STAGE
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
First Topic: Double Decker Bus (CFLM Unit)
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve addition problems and explain how I solved them using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world addition problems within 20.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can group numbers in different ways to make it easier.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving addition problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● How can patterns help me solve addition facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read The Double Decker Bus- The story of a double-decker bus will be used to support future lessons and the introduction of the math rack model to support using the fivestructure.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Investigate how many people are on the bus and play Passenger Pairs game to further support the five-structure and the development of more efficient addition strategies.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use math racks to role play Moving Between the Decks, which further develops the use of the five- and ten-structures to support students using compensation and equivalence.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Combinations of Ten provides an exploration of the combinations of whole numbers that sum to ten to highlight the strategies of counting on and counting back.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Addition on the Arithmetic Rack supports using the combinations of whole numbers that sum to ten for the development of subtraction strategies.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtraction on the Arithmetic Rack to support the development of subtraction strategies.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Writing/Sharing Bus Stories will support the use of computation strategies learned and further develop the use of the five- and ten-structures.
Additional Resources:-
● Double Decker Bus Lesson Plan
● Double Decker Bus ( Fosnot)
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
Second Topic: Part - Part - Whole
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
addition problems and explain how I solved it using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world addition problems within 20.
solving addition problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Fluency Days should be built into developing fluency for subtraction within 10 (See the link below- Toolkit unit 2)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Making Number Bonds to decompose a number from 1 to 10 into two parts.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 2, Textbook 1A, pg. 23-24
● Textbook 1A pg. 23-26
● Workbook 1A pg. 23-26
● Mind Workout
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Number Bond
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey Number Bond
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade1 OA OA
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 18- 29
Third Topic: Strategies to solve addition problems Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve addition problems and explain how I solved it using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world addition problems within 20.
● I can group numbers in different ways to make it easier.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving addition problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to solve addition problems?
● How can patterns help me solve addition facts faster?
Note: The Lessons in this topic are to develop efficient addition strategies.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Adding by counting, Counting all, or counting and using the Fluency game from Unit 2 Toolkit- Counting On.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Adding doubles within 20 and fluency from Unit 2 Toolkit- Doubles.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Adding by Making 10 and fluency game from Unit 2 Toolkit- Make 10.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Adding ones to add a two-digit number and a one-digit number by adding ones.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Adding three numbers to deepen their understanding of number relationships, rather than relying solely on sequential addition.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency Practice: Unit 2 Toolkit
● Textbook 1A pg. 39-60
● Workbook 1A pg. 27-38
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Spikey's Math Work
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's Marbles
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 33-48
Fourth Topic: Solving Addition Word Problems Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve addition problems and explain how I solved it using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world addition problems within 20.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can group numbers in different ways to make it easier.
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 7 Focus: Choosing addition strategies to approach problems using the most efficient strategies.
● Lesson 8 Focus: Completing addition equations to build a solid understanding of the structure of equations and the relationship of numbers.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Solving word problems to interpret, analyze, and apply mathematical operations in a meaningful context.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Solving word problems involving the addition of 3 numbers to deepen their understanding of number relationships, rather than relying solely on sequential addition.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency Practice: Unit 2 Toolkit
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving addition problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to solve addition problems?
● How can patterns help me solve addition facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 2
● Textbook 1A pg. 61- 82
● Workbook 1A pg. 39-46
● Mind Workout Textbook 1A pg.83, Workbook 1A pg.47
● Math Journal Textbook 1A pg. 83, Workbook 1A pg. 48
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Who said it?
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's Score
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade1 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 33-48
Grade 1 Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 20
Unit 3 Title: Subtraction within 20: The Great Take Away
Unit Overview:
How about we drift off on an adventure of taking away? Now that we have learned how numbers fit together, let's explore how they "break apart." We explore different strategies to help us subtract and find the difference between numbers. As we practice subtracting within 20, we discover helpful tricks to solve subtraction problems along the way!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.OA.A.1- Use subtraction within 20 to solve problems involving situations of taking from, taking apart, and comparing
● 1. OA.B.4- Understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem.
● 1.OA.C.5- Relate counting to subtraction (e.g., counting back).
● 1.OA.C.6- Subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for differences within 10 and using strategies for differences greater than 10.
● 1.OA.D.7- Understand the meaning of the equal sign and determine if subtraction equations are true or false.
● 1.OA.D.8- Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. (e.g., 8 +?=11, 5 = ?-3, 3 + 3 =?)
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another.(MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Subtraction helps to compare, take away, and find what is missing.
● Solving subtraction problems involves moving beyond counting back to more efficient strategies.
● The equal sign means both sides of the equation are the same or balanced.
● The relationships between addition and subtraction assist in finding missing numbers in an equation.
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving subtraction problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to subtract problems?
● How can patterns help me solve subtraction facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
● How can I use the relationship between addition and subtraction to solve problems?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 3
Knowledge
● Represent subtraction problems using drawings, tools, or equations
● Comprehend word problems involving taking from, taking apart, and comparing
● Mental math strategies for subtraction
● The equal sign means “the same as.”
● Read and write subtraction equations
● Math symbols: -, =,? have meaning
Key Vocabulary: subtract, difference, minus, make ten, related facts, fact family
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can use efficient strategies to solve subtraction problems and explain how I solved them using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world subtraction problems within 20.
● I can apply what I know about addition to help solve subtraction problems.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can decompose numbers in different ways to make it easier to subtract.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 3 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are solving problems using various strategies independently and with partners on vertical surfaces.
● Math journals: Students will solve 1 word problem from Practice 8.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of subtraction within 20 using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Choose strategies to subtract within 20. (pg. 108)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Subtraction Strategies within 20 Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve subtraction problems and explain how I solved them using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world subtraction problems within 20.
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving subtraction problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to subtract problems?
● How can patterns help me solve subtraction
Grade 1 Math: Unit 3
● I can decompose numbers in different ways to make it easier to subtract. facts faster?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Fluency Days should be built into developing fluency for subtraction within 20 (See the link belowToolkit Unit 3). The Lessons in this topic are to develop efficient subtraction strategies.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Subtracting by crossing out to show that the amount is smaller.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Subtracting by counting by counting back and counting on.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Subtracting by subtracting ones within 20 to encourage them to group the greater number into a ten and ones.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Subtracting from 10 within 20 to encourage them to decompose the greater number and subtract using 10. Complete the Fluency Game by subtracting from 10.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Choosing subtraction strategies to allow them to choose and apply the most efficient strategy.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 3, Workbook 1A pg. 53-54
● Textbook 1A pg. 85-100
● Workbook 1A pg. 53-60
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Butterflies
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's Crayons
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Operations and Algebraic Thinking
Second Topic: Using Related Facts
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve subtraction problems and explain how I solved them using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world subtraction problems within 20.
● I can apply what I know about addition to help solve subtraction problems.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can decompose numbers in different ways to make it easier to subtract.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving subtraction problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to subtract problems?
● How can patterns help me solve subtraction facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
● How can I use the relationship between addition and subtraction to solve problems?
● Lesson 6 Focus: Making Fact Families to make a family of addition and subtraction facts within 20.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Completing equations to find the unknown number that makes an addition
Grade 1 Math: Unit 3
equation or a subtraction equation true.
● Fluency Fun Day: Introduce “Salute” subtraction to work on the relationship between addition and subtraction.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency “Fun Day” Practice: Toolkit-Unit 3
● Textbook 1A pg. 111-120
● Workbook 1A pg. 67-70
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Move a number
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1-
Third Topic: Solving Subtraction Word Problems
Learning Targets:
● I can use efficient strategies to solve subtraction problems and explain how I solved them using drawings, tools, or equations.
● I can solve real-world subtraction problems within 20.
● I can apply what I know about addition to help solve subtraction problems.
● I can decide if an equation is true by thinking about both sides of the equal sign.
● I can decompose numbers in different ways to make it easier to subtract.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● In what ways can I show my thinking when solving subtraction problems? (objects, drawings, number sentences, equations)
● What mental math strategies can I use to subtract problems?
● How can patterns help me solve subtraction facts faster?
● Is this equation true? How do I know?
● How can I use the relationship between addition and subtraction to solve problems?
● Lesson 8 Focus: Solving Word Problems provides opportunities for students to solve word problems involving subtraction of two numbers within 20 and apply subtraction strategies.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 3
● Textbook 1A pg. 121-124
● Workbook 1A pg. 71-72
● Mind Workout: Textbook 1A pg. 125, Workbook 1A pg. 73
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Curly Reads
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Operations and Algebraic Thinking
● Unit Review- Workbook 1A pg. 75-78
Grade 1 Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 5
Unit 4 Title: Ordinal Numbers and Positions: Who’s First!
Unit Overview:
Get ready to sprint into learning as we race to understand ordinal numbers. While the learning focus so far has been describing how many (cardinal numbers), we now focus on position and order (ordinal numbers). We discover the correct words to describe positions, as we speed toward the finish line of learning.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
NOTE: This is not a first-grade standard but rather a continuation of Kindergarten. It is also connected to Think! Mathematics resource for this unit.
● Understand and use ordinal numbers (first through tenth) and positional words to describe order and location in a variety of contexts.
Understandings
● Ordinal numbers tell the position or order of objects in a sequence.
● Positional words help to describe where something is located in relation to other objects.
● Explaining order and location for clarity involves the use of ordinal numbers and positional words.
Knowledge
● The difference between cardinal and ordinal numbers
Key Vocabulary: first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, ordinal numbers, cardinal numbers
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How do I describe the order and sequence of numbers?
● How can I use my words to describe the order and location of objects?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can figure out and explain where things are by using order words (first through tenth) and position words (next to, between, behind, etc.).
● I can follow and give directions using math words that describe order and where something is.
● I can explain my reasoning to others using clear math words about location and order.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 4
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 4 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are using ordinal and positional language correctly.
● Math journal: Students will describe where they are in a photo using positional concepts (pg. 90).
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of ordinal numbers and positions using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Describe the relative position of people in a picture using ordinal numbers. (pg.140)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students’ ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Describing Positions
Learning Targets:
● I can figure out and explain where things are by using order words (first through tenth) and position words (next to, between, behind, etc.).
● I can follow and give directions using math words that describe order and where something is.
● I can explain my reasoning to others using clear math words about location and order.
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the order and sequence of numbers?
● How can I use my words to describe the order and location of objects?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Describing positions in a race to develop an understanding of ordinal numbers and key vocabulary (first, second, etc.)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Describing positions helps students understand where people or objects are in a row by using key vocabulary (before, after, next to, etc.).
Grade 1 Math: Unit 4
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 4
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 4
● Textbook 1A pg. 129- 142
● Workbook 1A pg. 83-88
● Mind Workout: Textbook 1A pg. 143, Workbook 1A pg. 89
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Fill in the Blank
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's House
● Unit Review- Think! Mathematics Workbook 1A pg.91-92
Grade 1 Math: Unit 5
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 11
Unit 5 Title: Shapes: Celebrating Shape Explorers!
Unit Overview:
Let’s set off on a shape adventure! We build on our shape knowledge we gained in Kindergarten to deepen our understanding of 2D and 3D shapes and explore their attributes in new ways. We uncover how shapes fit together and break apart through sorting, building, and hands-on fun.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.G.A.1- Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles are closed and have three sides) versus non-defining (e.g., color, size, orientation).
● 1.G.A.2- Compose two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes to create new shapes.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. ( (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another.(MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings Essential Questions
● 2-D and 3-D shapes can be described, compared, and classified by their attributes.
● Shapes can be used to build new shapes and represent objects.
● Objects in the world can be characterized by their shape.
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How are shapes alike and different?
● How can I use shapes to make new shapes?
● Where do I see shapes in the world around me?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Defining attributes describe what makes a shape (e.g., number of sides, vertices, closed shape)
● Non-defining attributes (e.g., size, color, orientation) do not affect the name/type of
● I can tell the difference between defining and non-defining attributes of a shape.
● I can identify and describe two-dimensional shapes based on the number of sides and vertices.
the shape
Grade 1 Math: Unit 5
Key Vocabulary: side, corner, edge, face, vertex, 2D shape, 3-D shape
● I can identify and describe attributes of threedimensional shapes based on the number of faces and sides.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
● I can compose new two-dimensional shapes by combining smaller 2D shapes
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 5 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are sorting and classifying shapes.
● Math journal: Students will pick one 2D shape and write at least 3 defining attributes of that shape.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of 2D and 3D shapes using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Identify the attributes of 3D shapes. (pg. 172)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students’ ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: 2-D Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can tell the difference between defining and non-defining attributes of a shape.
● I can identify and describe twodimensional shapes based on the number of sides and vertices.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
● I can compose new two-dimensional shapes by combining smaller 2D shapes
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How are shapes alike and different?
● How can I use shapes to make new shapes?
● Where do I see shapes in the world around me?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Grade 1 Math: Unit 5
● Lesson 1 Identify 2D shapes (squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, hexagons, and trapezoids) based on their attributes (sides and vertices).
● Lesson 2 Sorting shapes with a focus on two-dimensional shapes to focus on math vocabulary: defining and non-defining attributes.
● Lesson 3 Composing 2D Shapes to create a composite shape, which helps students see how smaller shapes can fit together to form larger ones
● Lesson 4 Composing 2D figures helps students understand how shapes can be combined in different ways.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit-Unit 5
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 4
● Textbook 1A pg.147-166
● Workbook 1A pg. 93-104
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Spikey Sorts Shapes
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Gumballs
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Geometry
● Geometry Flash Cards
● Math In Practice- Module 14
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 80-91
Second Topic: 3-D Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can tell the difference between defining and non-defining attributes of a shape.
● I can identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional shapes based on the number of faces and sides.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How are shapes alike and different?
● How can I use shapes to make new shapes?
● Where do I see shapes in the world around me?
● Lesson 5 Focus: Identifying 3-D shapes (cubes, rectangular prisms, cones, cylinders, and spheres) using their attributes, which helps them recognize shapes around them and build key vocabulary.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Sorting 3-D solids helps students compare shapes by their attributes, building understanding of key vocabulary.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Building Structures to allow for the composition of new 3-D shapes to strengthen understanding of how shapes fit together.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit-Unit 5
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 4
● Textbook 1A pg. 167- 182
Grade 1 Math: Unit 5
● Workbook 1A pg. 105-110
● Mind Workout: Textbook 1A pg. 183, Workbook 1A pg. 111
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Which Shape Belongs?
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Driving with Spikey
● Unit Review- Workbook 1A pg. 113-116
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Geometry
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 92-97
Grade 1 Math: Unit 6
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 9
Unit 6 Title: Equal Parts: Aabra Ka Daabra…now it’s Fair!
Unit Overview:
Let the fair share magic begin. In this adventure, we learn how to take shapes and split them into equal parts, and make sure everyone gets a fair share.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.G.A.3- Partitioning circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares using words such as halves, fourths, and quarters, and understand that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attend to Precision) (VOG: Effective Communicator)
Understandings
● Dividing a shape into pieces doesn't always mean all the pieces are the same size.
● The more equal parts a whole is divided into, the smaller each part becomes.
● Equal parts of a whole may look different, but still represent the same amount.
● Understanding equal parts helps to solve real-world problems about sharing, fairness, and parts of a whole.
Essential Questions
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● A whole can be divided into equal parts
● Equal parts must be the same size, even if they look different or are arranged
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction words (halves, half of, fourths, quarters,
Grade 1 Math: Unit 6
differently
● We use specific words to describe and explain parts of a whole (halves, fourths, quarters)
Key Vocabulary: whole, equal parts, half/halves, fourths/quarters, partition, share, divide, fourths of).
● I can explain why equal parts do not always look the same.
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 6 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are partitioning shapes into equal/fair shares.
● Math journal: Students will explain partitioning and equal parts by completing Practice 3, questions 3 and 5.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of equal parts and partitioning using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Show halves and fourths (quarters) (pg. 196)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Equal Parts
Learning Targets:
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction words (halves, half of, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can explain why equal parts do not always look the same.
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
Estimated # of Lessons: 9
Essential Questions:
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 6
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: For these lessons, students will use the process of paper folding, which is an effective approach for students to understand partitioning. Students are expected to demonstrate that parts are identical, which is vital in establishing the foundations of naming fractions.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Making Halves to partition rectangles and circles into two equal shares, which helps students understand equal parts and build key vocabulary like half, and half of.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Making Fourths to partition rectangles and circles into four equal shares, which helps students understand equal parts and use key vocabulary: fourths and quarters, and use the phrases fourth of and quarter of.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Comparing parts of equal shares helps students understand that decomposing into more equal shares creates smaller shares.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 6
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 6
● Textbook 1A pg. 187-202
● Workbook 1A pg. 117-122
● Mind Workout Textbook 1A pg. 203, Workbook 1A pg. 123
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Magnatiles
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Curly's Marbles
● Unit Review Workbook 1A pg. 125-126
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Geometry
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 98-101
Grade 1 Math: Unit 7
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 20
Unit 7 Title: Numbers to 120: Unlocking the secret to how numbers change
Unit Overview:
Let’s ride the wave of numbers all the way to 120! We now move from shapes back to numbers. This time we play with larger numbers and explore how they fit together. We decompose numbers into tens and ones and use place value and number patterns to discover how numbers grow and change.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.NBT.A.1- Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. Read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral.
● 1.NBT.B.2- Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones.
● 1.NBT.B.3- Compare two-digit numbers based on the meaning of the tens and ones digits, using <, >, and = symbols.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Objects and sets of objects can be given numerical descriptions.
● Numbers follow a predictable pattern that helps to count, read, and write them, starting at any point.
● Numbers can be represented differently (with objects, drawings, numerals, or words) to show their value and make sense of quantities.
Knowledge
● Number structure patterns can be used to count forwards and backwards from any number up to 120
● How do I use tens and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
● How do I compare two-digit numbers using tens and ones?
● How do I show the value of a number in different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can count to 120 starting from any given number less than 120.
● I can extend the counting sequence to read
Grade 1 Math: Unit 7
● Each digit in a two-digit number represents a specific place value
● <,>, and = symbols are used to compare two-digit numbers based on place value
● Two-digit numbers are made of tens and ones
● Understanding groups of tens and ones in two-digit numbers helps to compare and explain their values
Key Vocabulary: one hundred one, one hundred two, one hundred three...one hundred twenty, tens, ones, greater than(>), less than(<), equal to(=), number line, place value, numeral, digit, quantity and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
● I can explain the value of digits in a two-digit number.
● I can compare two-digit numbers using symbols. (<,>,+) based on place value.
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 7 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students' strategies for counting when organizing their collections.
● Math journals: Students will use greater than and less than clues in order to identify the mystery number (Practice 6, question 8)
● Exit tickets: Assessing place value understanding using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: With partners, represent numbers in more than one way. (pg. 26)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught prior to explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
First Topic: Organizing and Collecting (CFLM) Estimated # of Lessons: 11
Learning Targets:
● I can extend the counting sequence to read and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
● I can explain the value of digits in a twodigit number.
Essential Questions:
● How do I use tens and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 7
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
Learning Activities:
● How do I show the value of a number in different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
● Lesson 1 Focus: Taking inventory: Read The Masloppy Family to set the context of organizing and taking inventory, which will highlight children’s early strategies for counting and keeping track.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Continuing the Inventory allows for continued inventory investigations, and the subsequent math congress gives children a chance to discuss and share their work.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Making Packs of Ten is a mini-lesson of quick images that supports children in developing more efficient counting strategies. The investigation encourages children to consider grouping as a way to count more efficiently.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Making the Class Inventory Chart- a math congress that focuses on the place value patterns that occur when making groups of ten. The subsequent investigation gives children an opportunity to explore those patterns further.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Adding to the Class Inventory Chart- A math congress gives children a chance to discuss and share their work from Day Four. The investigation involves children figuring out how to get to the next multiple of ten.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Recording the orders for full packs and playing Rolling for Tens- A math congress highlights some new place value patterns. The Rolling for Tens game helps children to learn and develop fluency with combinations of ten, using two or more addends.
● Lesson 8 Focus: Collecting Stamps- The Collecting Stamps game and subsequent math congress focus on efficient strategies for addition.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Completing the Inventory with the new orders- A mini lesson of quick images builds on the place value patterns children explored during their inventory work. The investigation and math congress explore using place value patterns when adding multiples of ten.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Games- A mini lesson of quick images focuses on adding ten to a number. The Collecting Stamps game provides further opportunities to employ strategies developed throughout the unit.
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1
● Organizing and Collecting-Day by Day
● The Masloppy Family (Fosnot)
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
Second Topic: Counting to 120
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Learning Targets: Essential Questions:
Grade 1 Math: Unit 7
● I can count to 120 starting from any given number less than 120.
● I can extend the counting sequence to read and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
● I can explain the value of digits in a twodigit number.
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
● How do I use tens and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
● How do I compare two-digit numbers using tens and ones?
● How do I show the value of a number in different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Count to 40 or count back to 0, starting at any number less than 40, to develop fluency in counting up to 120.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Count to 120 or count back to 0, starting at any number less than 120, to develop counting patterns from 0-120.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Counting by 10’s to relate multiples of 10 to the number of tens that they are composed of, to develop an understanding of place value, and aid in efficient counting.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 7
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 7
● Textbook 1B pg. 3-16
● Workbook 1B pg. 1-6
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Make the Equation True
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ -Buzz's Stickers
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Numbers and Operations in Base Ten
Third Topic: Understanding Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can extend the counting sequence to read and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
● I can explain the value of digits in a twodigit number.
● I can compare two-digit numbers using symbols. (<,>,+) based on place value.
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I use tens and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
● How do I compare two-digit numbers using tens and ones?
● How do I show the value of a number in
Grade 1 Math: Unit 7
to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
Learning Activities:
different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Representing two-digit numbers with tens and ones expands their understanding of place value and number patterns.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Representing numbers to decompose a two- or three-digit number into different tens and ones further supports their understanding of place value and number patterns.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Comparing and Ordering Numbers- using place value to compare and order three numbers to develop their understanding of relationships between numbers.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Making Number Patterns to apply learned strategies and understand counting patterns.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 7
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 7
● Textbook 1B pg. 17-42
● Workbook 1B pg. 7-24
● Mind Workout Textbook 1B pg. 43, Workbook 1B pg. 26
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Tens and Ones
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Buzz's Toy
● Unit Review Workbook 1B pg. 27-30
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Numbers and Operations in Base Ten
Grade 1 Math: Unit 8
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 20
Unit 8 Title: Addition and Subtraction within 100: A Journey up to 100
Unit Overview:
Get ready to explore new territory in the land of numbers! Next, we tackle sums and differences within 100 and use regrouping to solve challenging problems. We show how far we have come by using what we know about "fitting together and breaking apart" to work with larger numbers in new ways.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.OA.C.6- Add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency in addition and subtraction within 10.
● 1. NBT. C.4- Add within 100 using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
● 1.NBT.C.6- Mentally find 10 more or less than a given two-digit number without counting.
● 1.NBT.C.5- Subtract multiples of 10 from numbers within 100 using place value and properties of operations.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers can be broken apart and put together in different ways to help add and subtract.
● The numeric value changes based on its location (in the tens and ones).
● The most effective strategy for adding and subtracting is often determined by the problem.
● Understanding how numbers are structured helps to mentally solve problems.
Knowledge
● Two-digit numbers are made up of tens and ones, and this place value structure
● How can I use tens and ones to help me add and subtract from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition or subtraction problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)? Which one is best given the problem?
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can add within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 8
helps to solve problems
● Addition and subtraction are related operations
● Different models can be used to represent the same problem
● Use place value to mentally find 10 more or 10 less than a number
● Subtracting multiples of 10 can be done efficiently using reasoning and structure
Key Vocabulary: regroup, make a ten
● I can subtract multiples of 10 from numbers within 100 using what I know about place value.
● I can find 10 more or 10 less than a given number without counting.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
● I can use the relationship between addition and subtraction to help me solve problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 8 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students' use of strategies during problem-solving.
● Math journal: Students will solve 45 + 7 and explain their addition strategy.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of place value and mental math using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Add a two-digit number to a one-digit number with regrouping. (pg. 71)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Addition Strategies
Learning Targets:
● I can add within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can find 10 more or 10 less than a given number without counting.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
Estimated # of Lessons: 8
Essential Questions:
● How can I use tens and ones to help me add and subtract from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition or subtraction problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)? Which one is best given the problem?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Grade 1 Math: Unit 8
Learning Activities:
Note: Students should be applying efficient strategies such as making ten, using place value, decomposing, etc. The algorithm should not be highlighted if used by students, as it is a fourth-grade standard. Fluency Days should be built into develop fluency for addition within 20 (See the link below- Toolkit-Unit 8)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Finding 10 more than a two-digit number mentally to provide a strategy to use for addition and subtraction.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Adding ones will provide a strategy of adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number without regrouping.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Adding tens will provide opportunities for adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Adding tens and ones to add two two-digit numbers within 100 without regrouping.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Adding with regrouping to add a two-digit number and a one-digit number as a strategy to solve problems.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Adding with regrouping. To add two two-digit numbers within 100 with regrouping (Optional: Second Grade Standard). This could be modified by using two-digit numbers by adding a one-digit number.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 8
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 8
● Create opportunities to include “I have, who has 10 more, 10 less” activities
● Textbook 1B pg. 49-78
● Workbook 1B pg. 31-56
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Make an Addition Equation
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Buzz's Cars
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Numbers and Operations in Base Ten and 1.OA.6
● CFLM Unit: Measuring for the Art Show
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 64-71
Second Topic: Subtraction Strategies Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract multiples of 10 from numbers within 100 using what I know about place value.
● I can find 10 more or 10 less than a given number without counting.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use tens and ones to help me add and subtract from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition or subtraction problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)? Which one is best given the problem?
Note: Fluency Days should be built into developing fluency for subtraction within 20 (See the link below-Toolkit
Grade 1 Math: Unit 8
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 8
● Textbook 1B pg. 93-96
● Workbook 1B pg. 67-68
● Mind Workout Text Book 1B pg. 87, Workbook 1B pg. 69
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Make a Sum
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Buzz's Candy
● Think! Math Unit Review Workbook 1B pg. 71-74
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 56-77
Grade 1 Math: Unit 9
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 8
Unit 9 Title:
Length and Height: A Hands-On Measurement Adventure
Unit Overview:
Get ready to discover the world of measurement! Our next adventure takes us into measuring length, where we explore how small units like our hands or feet can be powerful measuring tools. We measure and record attributes of objects, then use numbers to describe, compare, and create objects in our world.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.MD.A. 1- Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using the third object.
● 1.MD.A. 2- Express the length of an object as a whole number of length units by laying multiple copies of a shorter object (the length unit) end to end. Understand that the measurement length is the number of same-size units without gaps or overlaps.
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings
● Length and height are attributes of objects that can be measured and compared.
● The choice of a mathematical tool depends on the known information and the desired outcome.
Knowledge
● Objects can be compared directly (side by side) or indirectly using a third object
● Measurement means finding how long or tall something is using repeated, samesized units
● Units must be placed end to end without
Essential Questions
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can compare and order objects by length.
● I can compare the lengths of two or three objects using longer, shorter, and taller words.
● I can compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 9
gaps or overlaps for accurate measurement
● The length or height of an object is the number of same-size units it takes to match its size
Key Vocabulary: non-standard unit, standard unit, ruler, end to end, overlaps
● I can measure how long something is by lining up same-size units with no gaps or overlaps.
● I can use manipulatives to measure the length of objects.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 9 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students measuring and comparing objects.
● Math journal: Students will explain whether the character is correct regarding her measurement of the blue and red ribbon.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of measurement concepts using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Express the length of an object as a whole number using length units. (pg. 113)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Comparing Lengths and Heights Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Learning Targets:
● I can compare and order objects by length.
● I can compare the lengths of two or three objects using longer, shorter, and taller words.
● I can compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object.
● I can measure how long something is by lining up same-size units with no gaps or overlaps.
● I can use manipulatives to measure the length of objects.
● I can describe and explain my
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 9
measurement process.
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths.
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Foundations for students to understand reading a ruler are begun through the process of using nonstandard tools to measure length and height.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Comparing Lengths and/or heights of three objects helps students build measurement skills and understand how to order objects by size.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Comparing Lengths and/or heights of two objects using a third object helps students understand indirect comparison to support the development of measurement and reasoning skills.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 9
● Textbook 1B pg. 101-108
● Workbook 1B pg. 81-88
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Spikey's Bracelets
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's Ribbon
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 102-104
Second Topic: Measuring Length, Height, and Distance Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Learning Targets:
● I can compare and order objects by length.
● I can compare the lengths of two or three objects using longer, shorter, and taller words.
● I can compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object.
● I can measure how long something is by lining up same-size units with no gaps or overlaps.
● I can use manipulatives to measure the length of objects.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths.
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 9
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3: Measuring lengths and heights of an object in terms of a smaller object that represents 1 unit.
● Lesson 4: Measuring distance in terms of a hand or a foot that represents 1 unit.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 9
● Textbook 1B pg. 101-118
● Workbook 1B pg. 81-94
● Mind Workout Textbook pg. 119, Workbook pg. 95
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Spikey's Dice
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Spikey's String
● Unit Review Workbook 1B pg. 97-100
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Measurement and Data
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 105-107
Grade 1 Math: Unit 10
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 8
Unit 10 Title: Time: Climb Aboard Our Magical Time Machine
Unit Overview:
Climb aboard our magical time machine-it’s time to explore the world of clocks and calendars! We move from measuring objects to measuring time, learning to tell and write time on both analog and digital clocks. As we travel through the day, we discover how days become months and twelve months make a year.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.MD.B.3- Tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem(MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Analog and digital clocks show time differently but represent the same information.
● Understanding time helps to make sense of daily routines and solve real-world problems.
Knowledge
● Time can be measured using clocks and calendars
● A clock shows time in hours and half hours
● An analog clock has a short hour hand and a long minute hand that point to numbers to show time
● A digital clock shows time using numerals
● How do the hands on a clock show time?
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on an analog clock.
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on a digital clock.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
● I can explain the difference between an
Grade 1 Math: Unit 10
and a colon (2:00)
● The minute hand at six means “half past” the hour
● The hour hand points to the current hour (or just past it when it’s half-past)
● Time is used to organize daily events and routines
Key Vocabulary: time, clock, hour, half-hour, analog, digital, o’clock, minute hand, hour hand, morning, afternoon, evening, a.m., p.m., colon
analog and a digital clock.
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe daily routines.
2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 10 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students' ability to read clocks to the hour and half hour.
● Math journal: Students will explain what they know about an analog clock using words and pictures.
● Exit Slips: Assessing understanding of time concepts using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Students will work in pairs to make an analog clock and tell time to the hour and half-hour. (pg. 137)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Telling Time
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on an analog clock.
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on a digital clock.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
● I can explain the difference between an analog and a digital clock.
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How do the hands on a clock show time?
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
STAGE
Grade 1 Math: Unit 10
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe daily routines.
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Time to the hour to tell and write time in hours using analog and digital clocks to include vocabulary, afternoon, analog clock, day, digital clock, evening, hour, hour hand, minute, minute hand, morning, night, and o’clock.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Time to the half hour to tell and write time in half-hours using analog and digital clocks to include vocabulary such as half past.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 10
● Textbook 1B pg. 125-140
● Workbook 1B pg. 101-108
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ At the Table
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Guppies at the Aquarium
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 107-111
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 11- Telling Time to the Hour and Half Hour pg. 257-275
Second Topic: Sequencing Activities Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on an analog clock.
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on a digital clock.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
● I can explain the difference between an analog and a digital clock.
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe daily routines.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How do the hands on a clock show time?
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Sequence activities throughout a day by time to gain an understanding of the concept of time.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 10
● Textbook 1B pg. 141-144
● Workbook 1B pg. 101-102
● Problem(s) of the Week
Grade 1 Math: Unit 10
○ What's Missing
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Angelfish at the Aquarium
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Measurement and Data
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 107-111
Third Topic: Calendar
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on an analog clock.
● I can read and write the time to the hour and half hour on a digital clock.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
● I can explain the difference between an analog and a digital clock.
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe daily routines.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do the hands on a clock show time?
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Using a Calendar to recognize days, weeks, and months, which helps students understand how days, weeks, and months work together to measure time and organize the year.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 10
● Textbook 1B pg. 145-150
● Workbook 1B pg. 111-114
● Mindworkout Textbook 1B pg. 151, Workbook 1B pg. 115
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Buzz's Race
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Fish at the aquarium
● Unit Review Workbook 1B, pg. 117-120
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond (Day, Fosnot) pg. 107-111
Grade 1 Math: Unit 11
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 8
Unit 11 Title: Data: Charting Our Way Through the
Jungle of Data
Unit Overview:
Grab your binoculars, we're heading out on a Data Safari! In this adventure, we learn how information and objects can be collected, sorted, and displayed. By grouping and organizing everyday items, we discover how everything around us can become data. We turn our findings into charts and graphs as we uncover the hidden patterns in our world.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.MD.C.4- Organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories; ask and answer questions about the total number of data points, how many are in each category, and how many more or less are in one category than another.
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation(MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Organizing information into categories helps to identify patterns, make comparisons, and answer questions.
● Math vocabulary and numbers are used to describe and explain what the data shows.
Knowledge
● Data is information that can be organized into categories
● A category is a group of related items
● Graphs show how many are in each category
● What is this data telling me?
● How can I use data to explain what I see?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can collect and organize data into up to three categories.
● I can create graphs or charts to represent my data.
● I can label my data clearly using words and
Grade 1 Math: Unit 11
● Data is used to answer questions
○ How many in each category?
○ How many in all?
○ How many more or fewer?
Key Vocabulary: data, graph, chart, category, bar graph, picture graph numbers.
● I can interpret data and answer questions based on graphs or charts.
● I can compare data by finding how many more or fewer are in one category than another.
● I can use data to help solve problems and make decisions.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 11 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observation: Students sorting and organizing data.
● Math journal: Students will independently complete the Activity Time (pg. 168), representing and interpreting data they collect.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of graphs using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Students will develop a question to ask another class, collect data based on the responses, create a graph to represent the data, and analyze their findings.
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students’ ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Data Collections Estimated # of Lessons: 8
Learning Targets:
● I can collect and organize data into up to three categories.
● I can create graphs or charts to represent my data.
● I can label my data clearly using words and numbers.
● I can interpret data and answer questions based on graphs or charts.
● I can compare data by finding how many
Essential Questions:
● What is this data telling me?
● How can I use data to explain what I see?
Grade 1 Math: Unit 11
more or fewer are in one category than another.
● I can use data to help solve problems and make decisions.
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Collecting data helps students organize and represent information in categories, building an understanding that data is all around us and can be used to answer questions.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Making Tally charts- helps students collect, organize, and represent data in a simple, visual way.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Describing tally charts helps students interpret data and understand what the information shows
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 11
● Textbook 1B pg. 157-170
● Workbook 1B pg. 121-128
● Mindworkout Textbook 1B pg. 171, Workbook 1B pg. 129
● Problem(s) of the Week
○ Curly Reads
○ Tally the Vehicles
● Word Problem(s)of the Week
○ Curly's Tulips
● Unit Review Workbook 1B pg 131-132
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Measurement and Data
Grade 1 Math: Unit 12
Course Name: Grade 1 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 8
Unit 12 Title: Money Quest: The Adventure of Coins, Bills, and Big Deals!
Unit Overview:
Step into the marketplace-it's time for a Money Quest! We use our number skills and grouping strategies to understand how money helps us buy and trade. We get to know pennies, nickels, dimes, quarters, and dollars-and learn the value of each. Then, we use our skills to work by counting up coins and bills to see how much money we have.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 1.NBT.A.1- Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120.
● 1.NBT.B.3- Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparison with the symbols >, <, =.
NOTE: This is not a first-grade standard but rather a precursor for second grade. It is also connected to Think! Mathematics resource for this unit.
● Recognize and identify the value of pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters
Understandings
● Each coin has a name, a value, and a symbol that shows how much it’s worth.
● Drawings, models, and coins can be used to show and solve money problems.
Knowledge
● Each coin has a name, value, and appearance
● The symbol for cents is ¢
● Coins can be grouped and modeled to show total amounts
Key Vocabulary: penny, nickel, dime, quarter, cent(¢), value, dollar, buy, sell, more, less, equal, worth, save, spend
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem(MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Essential Questions
● How can I use coins and models to show amounts of money?
● What strategies help me count coins quickly and accurately?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can identify and name pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters.
● I can tell how much each coin is worth.
● I can skip count by 5s and 10s to help me count money.
● I can count money by combining the values of coins to find the total.
● I can compare amounts of money using more than, less than, or equal to.
Grade 1 Math: Unit 12
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 1 Unit 12 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students identifying and sorting coins.
● Math journal: Students will write or draw the coins they would use to buy a pack of gum for 53¢and explain how they counted the coins.
● Exit tickets: Assessing knowledge of coin values using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with a partner, use a sorting mat to recognize and sort coins. (pg. 178)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students’ ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Coins
Learning Targets:
● I can identify and name pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters.
● I can tell how much each coin is worth.
● I can skip count by 5s and 10s to help me count money.
● I can count money by combining the values of coins to find the total.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How can I use coins and models to show amounts of money?
● What strategies help me count coins quickly and accurately?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Although money is not a targeted topic in the Grade 1 standards, this unit serves as an introduction to help students strengthen their grasp on recognizing coins and dollar bills, as well as their values, in order for them to solve problems related to money in Grade 2.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Recognizing Coins- Students recognize pennies, dimes, nickels, and quarters, and
Grade 1 Math: Unit 12
the value of each coin to build on the concept of money.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Counting money in cents to tell the amount of money in cents.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 12
● Textbook 1B pg. 175-186
● Workbook 1B pg. 133-136
● Problem(s) of the Week:
○ Curly's Coins
● Word Problem(s)of the Week:
○ Curly's Candy
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1 Number and Operations in Base Ten and 2. MD.8
Second Topic: Dollar Bills
Learning Targets:
● I can tell how much each coin is worth.
● I can skip count by 5s and 10s to help me count money.
● I can count money by combining the values of coins to find the total.
● I can compare amounts of money using more than, less than, or equal to.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How can I use coins and models to show amounts of money?
● What strategies help me count coins quickly and accurately?
Note: Although money is not a targeted topic in the Grade 1 standards, this unit serves as an introduction to help students strengthen their grasp on recognizing coins and dollar bills, as well as their values, in order for them to solve problems related to money in Grade 2.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Recognizing dollar bills and their value helps students build a foundation for understanding and using money in real-life situations.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Counting money in dollars to apply knowledge of addition to find ways to make up a sum of money.
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Toolkit-Unit 12
● Fluency Practice: Toolkit-Unit 12
● Textbook 1B pg. 187-196
● Workbook 1B pg.137-140
● Mindworkout Textbook 1B pg, 197, Workbook 1B pg. 141
● Problem(s) of the Week:
○ Which is True?
● Word Problem(s)of the Week:
○ Buzz has Coins
● Unit Review Workbook 1B pg. 143-144
Grade 1 Math: Unit 12
Additional Resources:
Note: The use of additional resources supports deeper exploration of content and helps reinforce key concepts.
● Coherence Map Grade 1
Grade 2 Math

Grade 2 Math
Grade 2 Math

Grade 2 Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 0 Title: Setting the Classroom Culture
Unit Overview:
Creating a collaborative environment where students appreciate productive noise and productive struggle. Learning that communication, perseverance, collaboration, and reflection are key to being successful mathematicians.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
Note: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards; it supports the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards (Common Core)
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Mistakes are part of learning and can help me grow.
● Working together and listening to each other strengthens mathematical understanding.
● There are multiple strategies to solve a problem, and it's okay to try more than one.
● Being stuck is normal, and there are strategies for moving forward.
● How can patterns help me solve problems and figure out what comes next?
● What tools and strategies can I use to solve math problems and explain my thinking?
● How do pictures and models help me understand and show my math ideas?
● How can I use data to learn more about things around me?
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom norms and routines for math time
● How to use the tools and resources available in the classroom
● What a productive struggle looks and feels like
● Strategies to show perseverance (e.g., selftalk, trying a different strategy, asking a partner)
● Sentence starters will be used to guide respectful language for agreeing and disagreeing in math discussions
● Using rubrics and group norms helps identify positive and poor collaboration
● Self-monitoring and reflection help improve both problem-solving and behavior
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can notice and describe patterns in numbers, shapes, and problem situations.
● I can use math tools like number paths, clocks, and ten-frames to help me solve problems.
● I can use what I know about addition and subtraction to solve problems quickly and accurately.
● I can collect, organize, and talk about data to help me figure things out.
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like selftalk, trial and error, and regrouping.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries or Reflections that respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes & Checklists during group tasks and partner work (e.g., who participates, uses self-talk, problem-solving strategies, or supports peers).
● Problem Solving Checklist used by students (introduced in Ice Cream Scoops) to selfmonitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think.
● Perseverance Rubric or T-Chart (from 9 Lives) developed with the class and used for self and peer feedback.
Grade 2 Math: Unit 0
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
First Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a year-long focus to strengthen number sense through problemsolving context.
Learning Targets:
● I can notice and describe patterns in numbers, shapes, and problem situations.
● I can use math tools like number paths, clocks, and ten-frames to help me solve problems.
● I can show and tell how I solved a problem and listen carefully to my classmates' ideas.
● I can use what I know about addition and subtraction to solve problems quickly and accurately.
● I can collect, organize, and talk about data to help me figure things out.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can patterns help me solve problems and figure out what comes next?
● What tools and strategies can I use to solve math problems and explain my thinking?
● How do pictures and models help me understand and show my math ideas?
● How can I use data to learn more about things around me?
● Daily 15-minute sessions featuring five key workouts: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Days in School, Computational Fluency, and Number Path
● Student-led updates to visual displays and data charts provide hands-on practice with counting, place value, data, and number patterns.
● Games, visual models, and math talks support reasoning, problem solving, and the development of each student’s mathematical identity.
Second Topic: Setting the Classroom Culture Through Think Mathematics Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Learning Targets
● I can work flexibly with different partners.
● I can use self-talk and reflect on frustration.
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can communicate clearly using mathematical language and justify my thinking.
● I can use a problem-solving checklist or rubric to monitor my thinking and effort.
● I can practice perseverance when a problem feels challenging by using strategies like self-talk, trial and error, and
Essential Questions:
● What do I do when I feel stuck in math?
● What makes a good math partner or teammate?
● How can I explain my math thinking so others understand me?
● What can I do if someone disagrees with my math idea?
● What can I learn from my classmates during math?
regrouping.
Grade 2 Math: Unit 0
Learning Activities:
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read aloud The Most Magnificent Thing and reflect on times frustration was felt, and introduce the concept of self-talk, and the creation of a problem-solving strategies anchor chart.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Partners play Crazy Colors in order to emphasize the importance of verbalizing thought process and clearly communicating with a partner.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using a Venn Diagram to identify similarities and differences with their peers to reinforce understanding and empathy, while offering choices empowers students and fosters a positive classroom culture.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Establish norms for finding their randomized partners while playing Which One is Better/ My Favorite Card, to implement sentence starters to build a foundation that it is okay to agree and disagree in partnerships.
● Lesson 5: Play the game, Winner Winner! to build their ability to work and solve problems independently, while introducing the independent checklist.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Building Shapes activity and the Collaboration T-chart to introduce the use of the Problem Solving Checklist and to create a Collaboration Rubric.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Next Door Number Neighbors to reflect and practice how to work positively in a group, reinforcing the collaboration rubric and introducing the “one marker” rule.
● Lesson 8 Focus: Use the Ice Cream Scoops Word Problem to reinforce the Problem Solving Checklist, which continues to build problem-solving habits and routines, as well as introducing Mild, Medium, and Spicy tasks.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Use the Folding Paper Task to continue to reinforce the Problem Solving Checklist, which continues to build problem-solving habits and routines, and Mild, Medium, and Spicy tasks.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Play 9 Lives to practice persevering through challenging problems, and introduce hanging problems while using the Perseverance T-chart to create a Perseverance Rubric
Think! Math Resources (online):
● Think Mathematics Online Toolbox: Setting the Classroom Culture- Grade 2
Additional Resources:
● The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Grade 2 Math: Unit 1
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 11
Unit 1 Title: Numbers to 1,000: Tidying Up
With Our Teacher
Unit Overview:
The classroom is a mess! Pencils are scattered, erasers are everywhere, and markers are in a jumble! The Math Squad is on the case! It’s time to group items to make counting easier. With quick thinking and smart strategies, the squad helps get everything sorted and organized in no time.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.NBT.A.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones.
● 2.NBT.A.2 Count within 1,000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, 100s
● 2.NBT.A.3 Read and write numbers up to 1,000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form
● 2.NBT.A.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on the meaning of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits, using >, =, and < symbols
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners Critical Thinkers)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure ) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Objects and sets of objects can be given numerical descriptions.
● Numbers follow a predictable pattern that helps me count, read, and write them, starting at any point.
● Numbers can be represented differently (with objects, drawings, numerals, or words) to show their value and make sense of quantities.
● Understanding how numbers are built helps me solve problems and make reasonable decisions in everyday situations.
Knowledge
● Number structure patterns can be used to
● How do I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
● How do I compare three-digit numbers using hundreds, tens, and ones?
● How do I show the value of a number in different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can count within 1000, skip-count by 5s,
Grade 2 Math: Unit 1
count forwards and backwards from any number up to 1000
● Each digit in a three-digit number represents a specific place value
● <,>, and = symbols are used to compare three-digit numbers based on place value
● Three-digit numbers are made of hundreds, tens, and ones
Key Vocabulary: standard form, word form, expanded form, thousand, 3-digit number, column, row
10s, 100s
● I can extend the counting sequence to read and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
● I can explain the value of digits in a threedigit number.
● I can compare three-digit numbers using symbols. (<,>,+) based on place value.
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 1 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students' strategies for counting by 1s, 10s, 100s, to 1,000.
● Math journal: Showing different ways to decompose a given 3-digit number; 721
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of place value using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Compare numbers within 1,000 (pg. 24)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students’ ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Counting 1s, 10s, and 100s
Learning Targets:
● I can count within 1000, skip-count by 5s, 10s, 100s
● I can extend the counting sequence to read and write numbers to represent objects and drawings.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How do I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me count, read, and understand the value of a number?
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Grade 2 Math: Unit 1
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Solidify an understanding of place value by using base-ten blocks to count by 100s.
TB 2A pg. 3-8 WB pg.1-4
● Lesson 2 Focus: Using manipulatives and an understanding of place value to count by 100s, 10s, and 1s to 1,000. TB 2A pg. 9-12 WB pg. 5-8
Second Topic: Representing, Comparing, and Ordering Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can explain the value of digits in a threedigit number.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
● I can compare three-digit numbers using symbols. (<,>,+) based on place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How do I show the value of a number in different ways? What does it help me see and solve?
● How do I compare three-digit numbers using hundreds, tens, and ones?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use base ten numerals, word form, and expanded form to read and write numbers to 1,000. TB 2A pg. 13-18 WB pg. 9-12
● Lesson 4 Focus: Play a game using place value manipulatives to compare numbers to 1,000. TB 2A pg. 19-26 WB pg. 13-16
Third Topic: Making number patterns
Learning Targets:
● I can find and describe patterns in numbers to help me count and understand place value.
● I can use what I know about numbers to solve problems and explain my thinking.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● What are some patterns I notice as I count or write numbers? How does that help me become a more powerful mathematician?
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use key vocabulary terms (columns and rows) to recognize and create number patterns. TB 2A pg. 27-32 WB pg. 17-18
● Lesson 6 Focus: Use knowledge of place value to create and complete number patterns. TB 2A pg. 33-38 WB pg. 19-20
Think Math Additional Resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2A pg. 39 WB pg. 21
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 40 WB pg. 22
● Unit Review WB pg. 23-30
● Unit 1 Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
Grade 2 Math: Unit 1
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 (Aument, Fosnot) pg. 78-87 (Choose between count arounds-great exercises to use as time fillers, year-round)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○
○
○
○
2.NBT.A.1 Three digits of a three-digit number represent hundreds, tens, and ones.
2.NBT.A.2 Count within 1,000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, 100s
2.NBT.A.3 Read and write numbers up to 1,000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form
2.NBT.A.4 Compare two three-digit numbers using >, =, and < symbols
● Coherence Map Grade 2 NBT (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 20
Unit 2
Title: Addition and Subtraction within 100: Farmer’s Market Fiasco
Unit Overview:
Next mission: the farmer’s market! The vendors need help keeping track of their produce. The Math Squad jumps into action, using addition and subtraction to figure out how many fruits and veggies each vendor has. With teamwork and number power, the squad saves the day.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems
● 2.OA.B.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies
● 2.NBT.B.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction
● 2. NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
● 2.NBT.B.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers can be broken apart and put together in different ways to help add and subtract.
● Understanding how numbers are structured helps mentally solve problems.
● The most effective strategy for adding and subtracting is often determined by the problem.
● Word problems can be interpreted and represented using equations or models.
Knowledge
● Two-digit numbers are made up of tens and ones, and this place value structure
● What are some of the different strategies I can use to solve addition and subtraction problems? Which one is best given the problem?
● How can I use tens and ones to help me add and subtract from any number?
● How do I write an equation that matches the problem?
● How do I use what we know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies.
Grade 2 Math: Unit 2
helps me solve problems
● Addition and subtraction are related operations
● Different models can be used to represent the same problem
Key Vocabulary: addend, partial sum, bar model
● I can add within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can subtract within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
● I can use the relationship between addition and subtraction to help me solve problems.
● I can solve one- and two-step word problems, involving putting together, taking apart, and comparing with unknown numbers in all positions.
● I can add up to four two-digit numbers.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 2 Assessment
● Observations: Students’ strategies and ability to use place value and properties of operations to add and subtract.
● Math journal: Students will solve at least 1 word problem from Practice 8 and 9.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of addition and subtraction within 100 using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with partners, students will add two 2-digit numbers. (pg. 55)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Addition within 100
Learning Targets:
● I can add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies.
● I can add within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
● I can add up to four two-digit numbers.
Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Essential Questions:
● What are some of the different strategies I can use to solve addition problems?
● Which one is best given the problem?
● How can I use tens and ones to help me add numbers?
● How do I write an equation that matches the problem?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 2
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for addition within 20
● Lesson 1 focus: Using different strategies to add fluently within 20 to strengthen number sense and promote flexibility in problem solving to prepare for more complex problems. TB 2A pg. 45-50 WB pg. 31-32
● Lesson 2 focus: Apply known strategies and place value understanding to fluently add two-digit numbers using methods such as decomposing numbers, making tens, and using open number lines. TB 2A pg. 51-56 WB pg. 33-36
● Lesson 3 focus: Apply place value understanding to accurately and efficiently add three two-digit numbers. TB 2A pg.57-60 WB pg. 37-40
Second Topic: Subtraction within 100
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract within 100 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● What are some of the different strategies I can use to solve subtraction problems?
● Which one is best given the problem?
● How can I use tens and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do I write an equation that matches the problem?
Note: Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for subtraction within 20
● Lesson 4 focus: Using different strategies to subtract fluently within 20 to strengthen number sense and promote flexibility in problem solving to prepare for more complex problems. TB 2A pg 61-66 WB pg. 43-44
● Lesson 5 focus: Apply known strategies and place value understanding to fluently subtract twodigit numbers using methods such as decomposing numbers, making tens, and using open number lines. TB 2A pg 67- 72 WB pg. 45-48
● Lesson 6 focus: Continue applying various subtraction strategies and engage in math games to enhance and strengthen mental math strategies. TB 2A pg. 73-78 WB pg. 49-52
Third Topic: Relating Addition to Subtraction Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Learning Targets:
● I can use the relationship between addition and subtraction to help me solve problems.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How do I use what we know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
● Lesson 7 focus: Apply addition strategies such as decomposition, open number lines, hundreds charts, and interactive games to investigate how we can use addition to find the difference between two numbers. TB 2A pg. 79-82 WB pg. 53-54
Grade 2 Math: Unit 2
Fourth Topic: Solving word problems
Learning Targets:
● I can solve one- and two-step word problems, involving putting together, taking apart, and comparing with unknown numbers in all positions.
● I can show and explain my work using models, equations, or tools.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How do I write an equation that matches the problem?
● How do I use what we know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
● Lesson 8 focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) along with bar models to solve word problems involving addition and subtraction within 100. TB 2A pg. 83- 88 WB pg. 55-64
● Lesson 9 focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) along with bar models to solve two-step word problems involving addition and subtraction within 100. TB 2A pg. 89-96 WB pg. 65-72
Think Math Additional Resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2A pg. 97 WB pg. 73
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 97 WB pg. 74
● Unit Review WB pg. 75-78
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 (Aument, Fosnot) pg. 40-49 (B1-B20), 54-60 (B27B38)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.OA.A.1 Addition and subtraction within 100 word problems
○ 2.OA.B.2 Add and subtract within 20
○ 2.NBT.B.5 Add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value/relationship between addition and subtraction
○ 2. NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
○ 2.NBT.B.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations.
● Coherence Map Grade 2 NBT and OA (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 15
Unit 3 Title: Equal Groups : Thinking Through the Theme Park
Unit Overview:
After saving the day at the farmer’s market, the Math Squad heads to their next mission-the theme park! It’s busier than ever, but something’s not right ride lines are uneven, bumper cars are unbalanced, and the roller coaster seats aren’t filled just right. The Squad jumps into action again, using the power of equal groups to make everything fair and fun for everyone!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.OA.C.3 Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even number of members.
● 2.OA.C.4 Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays.
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers can be even or odd depending on whether they can be paired evenly.
● Repeated addition is a useful strategy for solving problems with equal groups.
● The same value can be represented in multiple ways.
● How can I prove whether a number is odd or even?
● What patterns do I notice when I add or group even and odd numbers?
● How do arrays help me find totals, and how can I describe the patterns they create?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Arrays help me see and describe groups in a structured way
Key Vocabulary: equal groups, even number, odd number, pairs, rectangular array
● I can identify and explain whether a number is odd or even.
● I can arrange objects into equal groups and describe them numerically.
● I can use repeated addition to find the total number of objects.
● I can make and describe rectangular arrays
Grade 2 Math: Unit 3
using rows and columns.
● I can write equations to represent arrays and equal groups.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 3 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ strategies for determining if a number is odd or even.
● Math journal: Determining if 7 + 6 is an even or odd sum.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of equal groups and the connection to odd/even using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working in pairs, make rectangular arrays with a specific number of rows and columns to find the total. (pg. 115)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught prior to explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
First Topic: Beads and Shoes, Making Twos (CFLM Unit)
Learning Targets:
● I can arrange objects into equal groups and describe them numerically.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How can I arrange objects into equal groups and describe them?
● Lesson 1 Focus: Investigate different doubling scenarios to determine if a number is odd or even.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Begin to use more efficient strategies (counting by 2s) to determine if a number is odd or even.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Notice patterns to predict other numbers that are odd or even.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Make connections to support automatizing double facts.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use double facts to support solving near-doubles problems.
Additional Resources:
● CFLM Shoes Outline
● Madeline by Ludwig Bemelmans
Grade 2 Math: Unit 3
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Making equal groups
Learning Targets:
● I can arrange objects into equal groups and describe them numerically.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How can I prove whether a number is odd or even?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Use manipulatives (Unifix cubes) and skip counting strategies to create and identify equal groups. TB 2A pg. 101-104 WB pg. 79-80
Second Topic: Recognizing odd and even numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can identify and explain whether a number is odd or even.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How can I prove whether a number is odd or even?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use prior knowledge of doubles, emphasizing the idea of pairs, to determine if a number is even or odd. TB 2A pg. 105-108 WB pg. 81-84
Third Topic: Making rectangular arrays
Learning Targets:
● I can make and describe rectangular arrays using rows and columns.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● What patterns do I notice when I add or group even and odd numbers?
● How do arrays help me find totals, and how can I describe the patterns they create?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use rows, columns, skip counting, and rectangular arrays to organize objects and count efficiently. TB 2A pg. 109-112 WB pg. 85-86
Fourth Topic: Adding equal groups
Learning Targets:
● I can write equations to represent arrays and equal groups.
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● What patterns do I notice when I add or group even and odd numbers?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 3
● I can use repeated addition to find the total number of objects.
● How do arrays help me find totals, and how can I describe the patterns they create?
●
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use knowledge of rectangular array strategies (skip counting and repeated addition) along with hands-on materials in a game format to add equal groups. TB 2A pg. 113-116 WB pg. 87-88
Think Math Additional Resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2A pg. 117 WB pg. 89
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 117 WB pg. 90
● Unit Review WB pg. 91-98
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.OA.C.3 Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even number of members.
○ 2.OA.C.4 Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays.
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)
○ Even Steven & Odd Todd pg. 75, 76
○ Making Arrays pg. 80, 81
● Coherence Map Grade 2 OA (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 13
Unit 4 Title: Shapes: Shape Secrets
Unit Overview:
After making the theme park fair and fun, the Math Squad gets a special call from the art museum! The museum is getting ready for a big kids’ event- but there’s a problem. No one knows how to spot the shapes in the artwork! The Squad races over to help students explore the museum and find 2D and 3D shapes hiding in the art. Another mystery solved with math!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.G.A.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or equal faces.
● 2.G.A.2 Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of the same-size squares and count to find the total number.
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Understandings Essential Questions
● 2-D and 3-D shapes can be described, compared, and classified by their attributes.
● Objects in the world can be characterized by their shape.
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How do patterns help me understand how shapes are organized?
● What shapes can I create? How do I show its attributes?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Defining attributes describe what makes a shape (e.g., number of sides, vertices, faces, edges, and closed shape)
● I can identify and describe two-dimensional polygons based on the number of sides and vertices.
● I can identify and describe attributes of three-
Grade 2 Math: Unit 4
Key Vocabulary: polygon, angle, pentagon, quadrilateral, partition
dimensional shapes based on the number of faces and edges.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
● I can partition rectangles into rows and columns and count squares.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 4 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ hands-on investigations manipulating 2D and 3D shapes.
● Math journal: What is the missing shape in each pattern? (Practice 5 Question 2) Explain how you figured it out.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of polygons and 3D shapes using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with partners, drawing and explaining their polygon. (pg. 134)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Recognizing Polygons
Learning Targets:
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce key math vocabulary to identify, describe, and distinguish between polygons and non-polygons. TB 2A pg. 121-124 WB pg. 99, 100
Second Topic: Identifying and Drawing 2Dimensional Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can identify and describe two-
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 4
dimensional polygons based on the number of sides and vertices.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
Learning Activities:
● What shapes can I create? How do I show its attributes?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Using manipulatives and new key vocabulary (angle, pentagon, quadrilateral) to recognize, identify, and classify shapes based on their attributes. TB 2A pg. 125, 124 WB pg. 101106
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use manipulatives (dot grid paper) and knowledge of shape attributes to draw two-dimensional shapes. TB 2A pg. 131-136 WB pg. 107-110
Third Topic: Partitioning Rectangles
Learning Targets:
● I can partition rectangles into rows and columns and count squares.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● What shapes can I create? How do I show its attributes?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use knowledge of shape attributes, along with rows and columns, to partition two-dimensional shapes into equal parts. TB 2A pg. 137-140 WB pg. 111-112
Fourth Topic: Making Patterns with 2Dimensional Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can identify and describe twodimensional polygons based on the number of sides and vertices.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How do patterns help me understand how shapes are organized?
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use knowledge of shapes and their attributes (through a game) to identify rules, and predict outcomes for building patterns. TB 2A pg. 141-144 WB pg. 113-116
Fifth Topic: Identifying and Making Patterns with 3-Dimensional Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional shapes based on the number of faces and edges.
● I can compare and classify shapes based on their attributes.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I describe the attributes of a shape?
● How do patterns help me understand how shapes are organized?
● Lesson 6 Focus: Using manipulatives and new key vocabulary (face, edge, vertex), to recognize,
Grade 2 Math: Unit 4
identify, and classify three-dimensional shapes based on their attributes. TB 2A pg. 145-150 WB pg. 117, 118
● Lesson 7 Focus: Use knowledge of three-dimensional shapes and their attributes (through a game) to identify rules, and predict outcomes for building patterns. TB 2A pg. 151-154 WB pg. 119-122
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2A pg. 155 WB pg. 123
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 156 WB pg. 124
● Unit Review WB pg. 125-130
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○
○
2.G.A.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or equal faces.
2.G.A.2 Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of the same-size squares and count to find the total number.
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) Module 14, pg. 311-326
● Coherence Map Grade 2 Geometry(Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 5
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 9
Unit 5 Title: Partitioning Shapes: Sharing is Caring
Unit Overview:
Just as the Math Squad finishes helping students find shapes, a new problem pops up-the art museum’s shipment didn’t arrive! Now there aren’t enough craft supplies for everyone. The Squad must step in to help students figure out how to fairly share the materials. It’s time to use equal parts and smart thinking to save craft hour!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.G.A.3 Partitioning circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, fourths, half of, a third of, a fourth of, and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, or four fourths
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings
● Just because a whole is divided into parts does not mean that the parts are equal.
● The more equal parts a whole is divided into, the smaller each part becomes.
● Equal parts of a whole may look different, but still represent the same amount.
● Understanding equal parts helps me solve real-world problems about sharing, fairness, and parts of a whole.
Knowledge
● A whole can be divided into equal parts
● Equal parts must be the same size, even if
Essential Questions
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction
Grade 2 Math: Unit 5
they look different or are arranged differently
● Dividing a whole into more parts makes each part smaller
● Specific words are used to describe and explain parts of a whole (halves, thirds, fourths, quarters)
Key Vocabulary: third, fraction
words (halves, half of, thirds, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can explain why equal parts do not always look the same.
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 5 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ language use and understanding of making equal parts when working with partners.
● Math journal: Show students a rectangle not partitioned equally and ask, “ Is this divided equally?” Explain your reasoning.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of partitioning shapes into equal parts using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Partition rectangles into three equal shares. (pg. 175)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Making equal parts
Learning Targets:
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction words (halves, half of, thirds, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can explain why equal parts do not always look the same.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 5
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Use hands-on discovery to identify shapes that show equal parts. TB 2A pg. 161164 WB pg. 131-132
Second Topic: Making halves
Learning Targets:
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction words (halves, half of, thirds, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use hands-on discovery and key vocabulary (fraction) to partition rectangles and circles into two equal shares TB 2A pg. 165-168 WB pg. 133, 134
Third Topic: Making fourths
Learning Targets:
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction words (halves, half of, thirds, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use hands-on discovery and key vocabulary (fraction) to partition rectangles and circles into four equal shares. TB 2A pg. 169-172 WB pg. 135, 136
Fourth Topic: Making thirds
Learning Targets:
● I can partition a shape into equal parts.
● I can describe equal parts using fraction
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How do I divide a shape into equal parts? How do I know the parts are equal?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 5
words (halves, half of, thirds, fourths, quarters, fourths of).
● I can show and label equal parts using drawings and models.
● I can compare the size of parts when a whole is divided into more or fewer equal shares.
Learning Activities:
● How do I describe what happens to the size of each part when I make more equal shares?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use hands-on discovery and key vocabulary (fraction) to partition rectangles and circles into three equal shares. TB 2A pg. 173-176 WB pg. 137-138
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workouts TB 2A pg. 177 WB pg. 139
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 177 WB pg. 140
● Unit Review WB pg. 141-144
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.G.A.3 Partitioning circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, fourths.
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) Module 15 pg. 327-342
● Coherence Map Grade 2 Geometry (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 6
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 11
Unit 6 Title: Time: Clock Explorers
Unit Overview:
After saving the art museum, the Math Squad gets a call from a friend who is never on time! They keep missing important events and activities. The Squad steps in to teach their friend how to read clocks and use a calendar to keep track of the days. With practice and teamwork, their friend learns to be on time for every adventure!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.MD.C.7 Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes using a.m. and p.m.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Analog and digital clocks show time differently, but represent the same information.
● Understanding time helps me make sense of daily routines and solve real-world problems.
Knowledge
● Time can be measured in hours and minutes
● A clock shows time in hours and half hours, and minutes
● An analog clock has a short hour hand and a long minute hand that point to numbers to show time
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using an analog clock.
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using digital clocks.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe
Grade 2 Math: Unit 6
● A digital clock shows time using numerals and a colon (2:00)
Key Vocabulary: a.m., p.m., noon, midnight daily routines.
● Each number on the clock is worth 5 minutes
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 6 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ ability to accurately tell time to the nearest 5 minutes.
● Math journal: Students will label an analog clock with the time 7:40 and explain how they know they are correct.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of telling time using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: In groups of 3 or 4, tell and write time in different ways. (pg. 194)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Telling time using a.m. and p.m.
Learning Targets:
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Note: Using the Recall, dedicate one day to reviewing and assessing students' proficiency in telling time to the hour and half-hour, extending this foundational review for an additional day or two if needed. TB 2A pg. 180 Math in Practice (focus on hour and half hour) - characteristics of an analog clock
● Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (a.m., p.m., midnight, noon) to recognize different times of the day. TB 2A pg. 181-184 WB pg. 145-148
Second Topic: Telling time to five minutes
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
Grade 2 Math: Unit 6
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using an analog clock.
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using digital clocks.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Using analog and digital clocks to tell time to the nearest 5 minutes. TB 2A pg. 185-190 WB pg. 149-152
Third Topic: Telling and writing time
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using an analog clock.
● I can read and write time to the nearest five minutes using digital clocks.
● I can describe the position of the hour and minute hands on a clock.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How can I show and write time in different ways?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use knowledge of time to tell and write time in different ways. TB 2A pg. 191196 WB pg. 153-154
Fourth Topic: Using a calendar
Learning Targets:
● I can use time-related vocabulary to describe daily routines.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How do we use time-related vocabulary to describe the year, month, and day?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Introduce the use of a calendar to know the number of days in a month and year, and write the date in more than one way. TB 2A pg. 197-200 WB pg. 155-158
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2A pg. 201 WB pg. 159
● Math Journal TB 2A pg. 202-203 WB pg. 160
● Unit Review WB pg. 161-162
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
Grade 2 Math: Unit 6
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 (Day, Fosnot) pg. 134 (E24, E25)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.MD.C.7 Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes using a.m. and p.m.
● Coherence Map Grade 2 MD (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 7
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 7 Title: Addition within 1,000: Carnival Calculations
Unit Overview:
With their friend now arriving on time, the Math Squad heads to their next mission-the school carnival! From figuring out how many balloons and streamers they need to adding up the total amount of prizes won, the squad uses their big number skills to bring it all together. Thanks to their addition power, the carnival is a success!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.NBT.B.5 Fluently add within 100 using strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
● 2.NBT.B.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
● 2.NBT.B.8 Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100-900
● 2.NBT.B.7 Add within 1,000 using concrete models, drawings, and strategies based on place value, properties of operations; relate the strategy to a written method
● 2.NBT.B.9 Explain why addition strategies work, using place value and properties of operations
Understandings
● Numbers can be broken apart and put together in different ways to help add.
● The numeric value changes based on its location (in the hundreds, tens, and ones).
● The most effective strategy for adding is often determined by the problem.
● Understanding how numbers are structured helps facilitate mentally solving problems.
Knowledge
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me add from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition or subtraction problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)? Which one is best given the problem?
● How do I combine numbers efficiently when a place value column reaches or exceeds ten?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 7
● Three-digit numbers are made up of hundreds, tens, and ones, and this place value structure helps us solve problems
● Different models can be used to represent the same problem
● Using place value, I can mentally find 10 or 100 more than a number
● Regrouping is necessary when the sum of a place value column is greater than 9
Key Vocabulary: addend, hundreds, partial sum, properties of operations (commutative, associative)
● I can add within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can use regrouping when a place value column exceeds ten in an addition problem.
● I can show my strategy and explain my solution using models, equations, or tools.
● I can write the number within 1,000 that is 10 more and 100 more than the given number without counting.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 7 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are solving addition problems using various strategies independently and with partners on vertical surfaces.
● Math journal: Students will be given the equation: 345 + 47 = 385. They will prove whether this is correct or not, showing their work.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of addition within 1,000 using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with a partner, add two 3-digit numbers. (pg. 40)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Adding four numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can add within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me add from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition problem (ie, drawings,
Grade 2 Math: Unit 7
models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)?
● Which one is best given the problem?
● How do I combine numbers efficiently when a place value column reaches or exceeds ten?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities: Fluency Practice: Develop fluency for adding 3 one or two-digit numbers.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Apply place value understanding to accurately and efficiently add four two-digit numbers. TB 2B pg. 3-10 WB pg. 3-6
Second Topic: Finding 10 or 100 more
Learning Targets:
● I can write the number within 1,000 that is 10 more and 100 more than the given number without counting.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me add from any number?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use place value knowledge to find 10 more or 100 more of a two-digit or threedigit number. TB 2B pg. 11-16 WB pg. 7-8
Third Topic: Adding without regrouping
Learning Targets:
● I can add within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can show my strategy and explain my solution using models, equations, or tools.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me add from any number?
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)?
● Which one is best given the problem?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use a variety of strategies to add within 1,000 without regrouping. TB 2B pg. 1724 WB pg. 9-14
Fourth Topic: Adding with regrouping
Learning Targets:
● I can add within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can use regrouping when a place value column exceeds ten in an addition problem.
● I can show my strategy and explain my solution using models, equations, or tools.
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● What are some different strategies I can use to solve an addition problem (ie, drawings, models, equations, decomposing and composing numbers)?
● Which one is best given the problem?
● How do I combine numbers efficiently when
Learning Activities:
Grade 2 Math: Unit 7
a place value column reaches or exceeds ten?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use a variety of strategies to add within 1,000 with regrouping. TB 2B pg. 25-32 WB pg. 15-16
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use a variety of strategies to add a three-digit number and a two-digit number, or two three-digit numbers with regrouping. TB 2B pg. 33-42 WB pg. 17-22
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2B pg. 43 WB pg. 23
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 43 WB pg. 24
● Unit Review WB pg. 25-26
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 (Day, Fosnot) pg. 88-93 (C24-C32)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○
○
○
○
○
2.NBT.B.5 Fluently add within 100 using strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction
2.NBT.B.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
2.NBT.B.8 Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100-900
2.NBT.B.7 Add within 1,000 using concrete models, drawings, and strategies based on place value, properties of operations; relate the strategy to a written method
2.NBT.B.9 Explain why addition strategies work, using place value and properties of operations
● Coherence Map Grade 2 NBT (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 8
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 8 Title: Subtraction within 1000: Carnival Calculations
Unit Overview:
Just when everything seems perfect, a new challenge pops up- supplies are missing, and tickets aren’t adding up! The Math Squad jumps into action, using their subtraction skills to figure out what’s left, what’s been used, and what’s still needed. From missing prizes to ticket mix-ups, they keep the carnival fun going!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.NBT.B.5 Fluently subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
● 2.NBT. B.7 Subtract within 1,000 using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
● 2.NBT.B.9 Explain why subtraction strategies work using place value and the properties of operations.
● 2.NBT.B.8 Mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100-900
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Numbers can be broken apart and put together in different ways to help me subtract.
● The numeric value changes based on its location (in the hundreds, tens, and ones).
● The most effective strategy for subtracting is often determined by the problem.
● Understanding how numbers are structured helps to mentally solve problems.
Knowledge
● Three-digit numbers are made up of hundreds, tens, and ones, and this place
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How do I find the difference between numbers when I need to unbundle from a greater place value?
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can subtract two- and three-digit numbers with and without regrouping.
Grade 2 Math: Unit 8
value structure helps to solve problems
● Different models can be used to represent the same problem
● Mentally find 10 and 100 less than a number within 1,000 utilizing place value understanding
● Addition and subtraction are related operations
● Unbundling and regrouping is sometimes needed when subtracting
Key Vocabulary: unbundling
● I can subtract within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can write the number within 1,000 that is 10 less and 100 less than the given number without counting.
● I can use the relationship between addition and subtraction to help me solve problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 8 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students are solving subtraction problems using various strategies independently and with partners on vertical surfaces.
● Math journal: Students will solve 1 word problem from Practice 5.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of subtraction within 1,000 using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with a partner, subtract two 3-digit numbers. (pg. 74)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Finding 10 or 100 less
Learning Targets:
● I can write the number within 1,000 that is 10 less and 100 less than the given number without counting.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How do I find the difference between numbers when I need to unbundle from a greater place value?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 8
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for subtracting 5, 10, and 100 from a given number.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Using knowledge of place value to find 10 or 100 less than a three-digit number. TB 2B pg. 47-52 WB pg. 29-30
Second Topic: Subtracting without regrouping Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract two- and three-digit numbers with and without regrouping.
● I can subtract within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How do I find the difference between numbers when I need to unbundle from a greater place value?
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Using knowledge of place value to subtract within 1,000 using a variety of strategies without regrouping. TB 2B pg. 53-58 WB pg. 31-36
Third Topic: Subtracting with Regrouping Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract two- and three-digit numbers with and without regrouping.
● I can subtract within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How do I find the difference between numbers when I need to unbundle from a greater place value?
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using knowledge of place value to subtract within 1,000 using a variety of strategies with regrouping. TB 2B pg. 59-66 WB pg. 37-38
● Lesson 4 Focus: Using knowledge of place value to subtract within 1,000 using a variety of strategies with regrouping. TB 2B pg. 67-76 WB pg. 39-46
Grade 2 Math: Unit 8
Fourth Topic: Solving word problems
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract two- and three-digit numbers with and without regrouping.
● I can subtract within 1000 using models, drawings, and place value strategies.
● I can use the relationship between addition and subtraction to help me solve problems.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How can I use hundreds, tens, and ones to help me subtract from any number?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How do I find the difference between numbers when I need to unbundle from a greater place value?
● How do I use what I know about the relationship between addition and subtraction to efficiently solve problems?
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) along with bar models to solve word problems involving addition and subtraction within 1,000. TB 2B pg. 77-80 WB pg. 47-52
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2B pg. 81 WB pg. 53
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 81 WB pg. 54
● Unit Review WB pg. 55-60
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 (Day, Fosnot) pg. 96,97 (C37-C40)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.NBT.B.5 Fluently subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
○ 2.NBT. B.7 Subtract within 1,000 using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
○ 2.NBT.B.9 Explain why subtraction strategies work using place value and the properties of operations.
○ 2.NBT.B.8 Mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100-900
● Coherence Map Grade 2 NBT (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 9
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 9
Title: Length and Height in Customary Units: Mighty Measures
Unit Overview:
After the carnival excitement, the Math Squad hears about something strange happening around townthings are the wrong size! Shoes are too big, pants are too short, and furniture doesn’t fit where it should. The squad sets off to investigate, using measurement tools to check lengths, heights, and weights. With rulers, yardsticks, and measuring tapes in hand, they work to fix the mix-ups and make sure everything is just the right size again!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.MD.A.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools.
● 2.MD.A.2 Measure the length of an object twice using different units of different lengths.
● 2.MD.A.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another.
● 2.MD.A.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches and feet.
● 2.MD.B.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths.
● 2.MD.B.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram.
Understandings
● Length and height are attributes of objects that can be measured and compared.
● Measurements with the same unit can be compared and combined.
Knowledge
● Measurement means finding how long or tall something is using repeated, samesized units
● The length or height of an object is the number of same-size units it takes to
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. inches, feet, and yards, ruler, yardstick).
● I can solve problems that involve measuring
Grade 2 Math: Unit 9
match its size
● Different units and tools are used to measure accurately, depending on the situation
● Number lines help represent and compare lengths
Key Vocabulary: customary units, inches, feet, yards, rulers, yardsticks, measuring tapes, length, height, estimate, number line and comparing lengths and heights.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
● I can represent a measurement using a number line.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 9 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ ability to accurately measure using customary units.
● Math journal: How long is a foot? How long is a yard? … (pg. 120)
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of measuring using customary units using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with a partner, Measure and compare the length of an object in inches, feet, and yards. (pg. 102)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Measuring and comparing inches Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. inches, feet, and yards, ruler, yardstick).
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities: Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (inch, width) to measure and compare the
Grade 2 Math: Unit 9
lengths of objects in inches. TB 2B pg. 85- 92 WB pg. 65-70
Second Topic: Measuring and comparing in feet
Learning Targets:
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. inches, feet, and yards, ruler, yardstick).
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (foot) to measure and compare the lengths of objects in feet.TB 2B pg. 93-98 WB pg. 71-76
Third Topic: Measuring and comparing in yards
Learning Targets:
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. inches, feet, and yards, ruler, yardstick).
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (yard, yardstick) to measure and compare the lengths of objects in yards. TB 2B pg. 99-104 WB pg. 77-80
Fourth Topic: Estimating lengths and heights
Learning Targets:
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths and heights.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Select and use an appropriate tool to estimate and measure the lengths and heights of objects. TB 2B pg. 105-110 WB pg.81-82
Fifth Topic: Solving word problems
Learning Targets:
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths and heights.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 9
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) to solve for length and height in customary units. TB 2B pg. 111-118 WB pg. 83-86
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2B pg. 119 WB pg. 87
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 120 WB pg. 88
● Unit Review WB pg. 89-94
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○
○
○
2.MD.A.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools
2.MD.A.2 Measure the length of an object twice using different units of different lengths.
2.MD.A.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another.
○ 2.MD.A.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches and feet.
○ 2.MD.B.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths.
○
2.MD.B.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram.
● Coherence Map Grade 2 MD (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 10
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 9
Unit 10 Title: Length and Height in
Unit Overview:
Metric Units: Mighty Measures
Strange things are happening at school, too-nothing seems to measure up! Just in time, a new student arrives from a country that uses metric units, and she’s ready to teach the Math Squad some new measuring tricks. Using centimeters and meters, the squad learns a new way to measure. Together, they solve the mystery and bring order back to school-just in time.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.MD.A.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools
● 2.MD.A.2 Measure the length of an object twice using different units of different lengths.
● 2.MD.A.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another.
● 2.MD.A.3 Estimate lengths using units of centimeters and meters
● 2.MD.B.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths.
● 2.MD.B.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram.
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Length and height are attributes of objects that can be measured and compared.
● Measurements with the same unit can be compared and combined.
Knowledge
● Measurement means finding how long or tall something is using repeated, samesized units
● The length or height of an object is the number of same-size units it takes to match its size
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. centimeters, meters, rulers, meter sticks).
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths and heights using
Grade 2 Math: Unit 10
● Different units and tools are used to measure accurately, depending on the situation
● Number lines help represent and compare lengths
● Metric units help describe and compare the length and height of objects, using tools that are familiar ( like rulers) and unfamiliar (like meter sticks)
Key Vocabulary: centimeter, meter, metric units, meter stick metric units.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
● I can use number lines to show metric lengths.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 10 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ ability to accurately measure using metric units.
● Math journal: Show the picture below (pg. 100), measured in cm, that isn’t aligned at zero, and state that the length is 14cm. Students will respond to, “Is this measurement accurate?” Prove how you know.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of measuring using metric units using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: Working with a partner, estimate and measure the lengths or heights of objects using centimeters or meters. (pg. 141)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Measuring and comparing in centimeters Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
Grade 2 Math: Unit 10
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. centimeters, meters, rulers, meter sticks).
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (centimeters) to measure and compare the lengths of objects in centimeters. 2B pg. 125-130 WB pg. 95-100
Second Topic: Measuring and comparing in centimeters and meters
Learning Targets:
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. centimeters, meters, rulers, meter sticks).
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (meter) to measure and compare the lengths of objects in centimeters and meters. 2B pg. 131-136 WB pg. 101-108
Third Topic: Estimating lengths and heights
Learning Targets:
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths and heights using metric units.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Select and use an appropriate tool to estimate and measure the lengths and heights of objects using metric units. 2B pg. 137-144 WB pg. 109-112
Fourth Topic: Solving word problems
Learning Targets:
● I can measure how long or tall something is by utilizing the correct tool and unit of measurement. (ie. centimeters, meters,
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How do I compare and measure two or more objects? What tools can I use to improve accuracy?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 10
rulers, meter sticks).
● I can solve problems that involve measuring and comparing lengths and heights using metric units.
● I can describe and explain my measurement process.
● I can use number lines to show metric lengths.
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) to solve for length and height in metric units. TB 2B pg.145-150 WB pg. 113-18
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2B pg. 151 WB pg. 119
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 152 WB pg. 120
● Unit Review WB pg. 121- 128
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○
○
○
○
○
○
2.MD.A.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools
2.MD.A.2 Measure the length of an object twice using different units of different lengths.
2.MD.A.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another.
2.MD.A.3 Estimate lengths using units of centimeters and meters
2.MD.B.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths.
2.MD.B.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram.
● Coherence Map Grade 2 MD(Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 11
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 11 Title: Money:
Money Matters
Unit Overview:
The Math Squad’s next mission takes them around town, where people need help with using their money for their needs and wants! It’s time for the squad to step in and show everyone how to count and understand the value of coins and bills. The Squad teaches the town how to make smart choices and use their money wisely. Math to the rescue-again!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.MD.C.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies using $ and ¢symbols appropriately.
● 2.NBT.A.2 Count within 1,000; skipcounting by 5s, 10s, and 100s
Understandings
● Different coins and bills have specific values that can be combined in many ways to represent the same amount of money.
● Counting by ones, fives, tens, and hundreds helps to figure out the total value of a group of coins and bills.
● Counting and combining money helps to solve everyday problems like figuring out how much things cost.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: SelfDirected Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Essential Questions
● How much money is this? How do I express this?
● How can understanding the value of coins and bills help me make decisions when using money?
● What strategies am I using to accurately count money? What are some other strategies that may be more efficient?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Money can be represented using combinations of coins and bills
● Place value and skip-counting strategies
● I can identify currency ( bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, pennies) and their values.
● I can write amounts of money using $ and ¢
Grade 2 Math: Unit 11
can be used to count money
● Money problems can be solved using addition and subtraction
● Symbols ($, ¢) are used to represent dollars and cents in written form
● Skip counting by 5, 10, and 25’s.
Key Vocabulary: penny (1¢), nickel (5¢), dime (10¢), quarter (25¢), bill values, $1, $5, $10, $20, money, cent, value, change, combination
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
● I can solve addition and subtraction word problems involving money.
● I can compare amounts to determine if it is equal, more than, or less than.
● I can use the least amount of coins (and bills) to represent a given amount of money.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 11 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students’ strategies when counting and problem-solving the Misloppy Family Trip.
● Math journal: How much is in Lauren’s savings box? (Practice 5 Question 3) Explain how you figured it out.
● Exit tickets: Assessing understanding of finding money totals using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: With a partner, find the total value of coins and dollar bills. (pg.164)
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught prior to explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
First Topic: Trades, Jumps and Stops (CFLM unit) Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Learning Targets:
● I can group coins into equivalent amounts.
Essential Questions:
● How can I group coins into equivalent amounts using substitution rather than arithmetic?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 11
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Use knowledge of coin values to make equivalent coin amounts, demonstrating this through the substitution of different coin combinations. pg. 13-18
● Lesson 2 Focus: Play a game to reinforce substitution of equivalent amounts. pg. 19-23
● Lesson 3 Focus: Play a game to reinforce substitution of equivalent amounts and challenge students to exchange coins to compare expressions. pg. 24-29
● Lesson 4 Focus: Play a game to make expressions and look for equivalence. pg. 30-35
● Lesson 5 Focus: Conduct an investigation to determine the effectiveness of the "Subtracting 5 by Compensation" strategy, which involves using the steps of adding 5 and then subtracting 10. pg. 36-39
Additional Resources:
● CFLM Trades, Jumps, and Stops outline
● The Masloppy Family Goes to New York (Fosnot)
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
Second Topic: Counting money
Learning Targets:
● I can identify currency ( bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, pennies) and their values.
● I can write amounts of money using $ and
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How much money is this? How do I express this?
● How can understanding the value of coins and bills help me make decisions when using money?
● What strategies am I using to accurately count money? What are some other strategies that may be more efficient?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Use knowledge of monetary values to calculate totals of different combinations of coins and bills. TB 2B pg. 157-160 WB pg. 129-132
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use knowledge of monetary values to calculate totals of different combinations of coins and bills. TB 2B pg. 161-166 WB pg. 133-134
Third Topic: Changing units of money
Learning Targets:
● I can identify currency ( bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, pennies) and their values.
● I can write amounts of money using $ and
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How much money is this? How do I express this?
● How can understanding the value of coins and bills help me make decisions when using
Grade 2 Math: Unit 11
¢.
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
● I can use the least amount of coins (and bills) to represent a given amount of money. money?
Learning Activities:
● What strategies am I using to accurately count money? What are some other strategies that may be more efficient?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Use knowledge of monetary values to convert between dollars and cents. TB 2B pg. 167-170 WB pg. 135-136
Fourth Topic: Calculating change
Learning Targets:
● I can identify currency ( bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, pennies) and their values.
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
● I can write amounts of money using $ and
● I can use the least amount of coins (and bills) to represent a given amount of money.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How much money is this? How do I express this?
● How can understanding the value of coins and bills help me make decisions when using money?
● What strategies am I using to accurately count money? What are some other strategies that may be more efficient?
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use knowledge of monetary values to calculate change received. TB 2B pg. 171174 WB pg. 137-138
Fifth Topic: Solving word problems
Learning Targets:
● I can identify currency ( bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, pennies) and their values.
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
● I can write amounts of money using $ and
● I can count combinations of money using skip-counting strategies.
● I can solve addition and subtraction word problems involving money.
● I can compare amounts to determine if it is equal, more than, or less than.
● I can use the least amount of coins (and bills) to represent a given amount of
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● What strategies am I using to accurately count money? What are some other strategies that may be more efficient?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 11
money.
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) along with knowledge of monetary values to solve word problems involving money. TB 2B pg. 175-178 WB pg. 139-142
● Lesson 6 Focus: Use a 4-step problem-solving strategy (Understand, Plan, Carry out, Look back) along with knowledge of monetary values to solve word problems involving money. TB 2B pg. 179-184 WB pg. 143-144
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB 2B pg. 185 WB pg. 145
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 185 WB pg. 146
● Unit Review WB pg. 147-150
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.MD.C.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies using $ and ¢symbols appropriately.
○ 2.NBT.A.2 Count within 1,000; skip-counting by 5s, 10s, and 100s
● Coherence Map Grade 2 MD and NBT. 2 (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 2 Math: Unit 12
Course Name: Grade 2 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 15
Unit 12 Title: Picture Graphs and Bar Graphs: Data Discovery Dash
Unit Overview:
For their final mission, the Math Squad heads out to explore animal observatories around town! With their super skills, they observe, collect, and sort information about all kinds of creatures. They organize what they find into graphs and tables, turning data into discoveries! By the end of the mission, the squad has become a team of young data experts-ready for whatever math adventure comes next!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 2.MD.D.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph to represent data in four categories
● 2.MD.D.9 Generate measurement data by measuring the lengths of several objects and show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole-number units
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings
● Data can be represented visually and used to help solve problems.
Essential Questions
● How can I choose the best type of graph to clearly show and compare data?
● How does organizing data into categories help me solve problems or make decisions?
● What does a line plot tell me about the measurements, and how can I use it to explain my thinking?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● A bar graph and a picture graph are tools used to organize and compare data
● Data can be grouped into categories to make it easier to see patterns or answer questions
● I can collect, organize, and represent data using picture graphs, bar graphs, and line plots.
● I can measure and record lengths using whole-number units and show the data on a
Grade 2 Math: Unit 12
● A line plot displays data along a number line and helps compare measurements.
● Each "X" or mark on a line plot represents one measured object
● A line plot can show how often each measurement occurs (frequency)
● Different types of graphs are useful for different kinds of data
Key Vocabulary: line plot, key, bar graph, title, analyze line plot.
● I can compare data on a graph or line plot to answer questions and explain my thinking.
● I can choose the best graph or display to represent my data clearly and accurately.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I chose.
● I can use consistent units when collecting and displaying measurement data.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 2 Unit 12 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Observations: Students peer discussions and collaborations while creating graphs and interpreting the data.
● Math journal: Using the line plot from the summary (pg. 220) Answer the questions posed by the friends.
● Exit tickets:Assessing understanding of using data to create and interpret graphs using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Activity Time: With a partner, collect, and interpret data with up to four categories (pg. 207)
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin all lessons with an Anchor Task to activate, engage, and guide students' ideas to create the board plan.
Activity Time in each lesson provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to student needs.
First Topic: Making and Describing Picture Graphs Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Learning Targets:
● I can collect, organize, and represent data using picture graphs, bar graphs, and line plots.
● I can compare data on a graph or line plot to answer questions and explain my thinking.
● I can choose the best graph or display to
Essential Questions:
● How can I choose the best type of graph to clearly show and compare data?
● How does organizing data into categories help me solve problems or make decisions?
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Grade 2 Math: Unit 12
represent my data clearly and accurately.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I chose.
● I can use consistent units when collecting and displaying measurement data.
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (key, picture graph, title) and draw a picture graph to represent a data set with up to four categories. TB 2B pg. 189- 192 WB pg. 151-152
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use knowledge of data representation to interpret a picture graph with up to four categories.TB 2B pg. 193-198 WB pg. 153-154
Second Topic: Make and describe bar graphs
Learning Targets:
● I can collect, organize, and represent data using picture graphs, bar graphs, and line plots.
● I can compare data on a graph or line plot to answer questions and explain my thinking.
● I can choose the best graph or display to represent my data clearly and accurately.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I chose.
● I can use consistent units when collecting and displaying measurement data.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How can I choose the best type of graph to clearly show and compare data?
● How does organizing data into categories help me solve problems or make decisions?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (bar graph) and draw a bar graph to represent a data set with up to four categories. TB 2B pg. 199-204 WB pg. 155-156
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use knowledge of data representation to interpret a bar graph with up to four categories. TB 2B pg. 205-208 WB pg. 157-158
Third Topic: Make and describe line plots
Learning Targets:
● I can collect, organize, and represent data using picture graphs, bar graphs, and line plots.
● I can measure and record lengths using whole-number units and show the data on a line plot.
● I can compare data on a graph or line plot to answer questions and explain my thinking.
● I can choose the best graph or display to
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
● How can I choose the best type of graph to clearly show and compare data?
● How does organizing data into categories help me solve problems or make decisions?
● What does a line plot tell me about the measurements, and how can I use it to explain my thinking?
Grade 2 Math: Unit 12
represent my data clearly and accurately.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I chose.
● I can use consistent units when collecting and displaying measurement data.
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 5 Focus: Introduce key vocabulary (line plot) and draw a line plot to represent a data set. TB 2B pg. 209-212 WB pg. 159, 160
● Lesson 6 Focus: Use knowledge of data representation to interpret a line plot. TB 2B pg. 213-216 WB pg. 161-162
Think Math additional resources:
● Mind Workout TB pg. 2B 217 WB pg. 163
● Math Journal TB 2B pg. 218 WB pg. 164
● Unit Review TB 2B pg. 165-168
● Unit Resources
● Problem of the week - can be used as spiral review, math talks, and warmups.
○ Problem of the week Folder
● Word problem of the week: for you to share and discuss with your students, incorporating and applying the ideas of modeling, equations, and computation strategies to solve word problems (mild, medium, and spicy options)
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 2 ( Aument, Fosnot) pg. 140-142 (E36, E37, E38)
● K-5 Resources (links lead you to activities that match the standard)
○ 2.MD.D.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph to represent data in four categories
○
2.MD.D.9 Generate measurement data by measuring the lengths of several objects and show the measurements by making a line plot.
● Coherence Map (Use the provided link to directly access the relevant standards for small group instruction.)
Grade 3 Math

Grade 3 Math
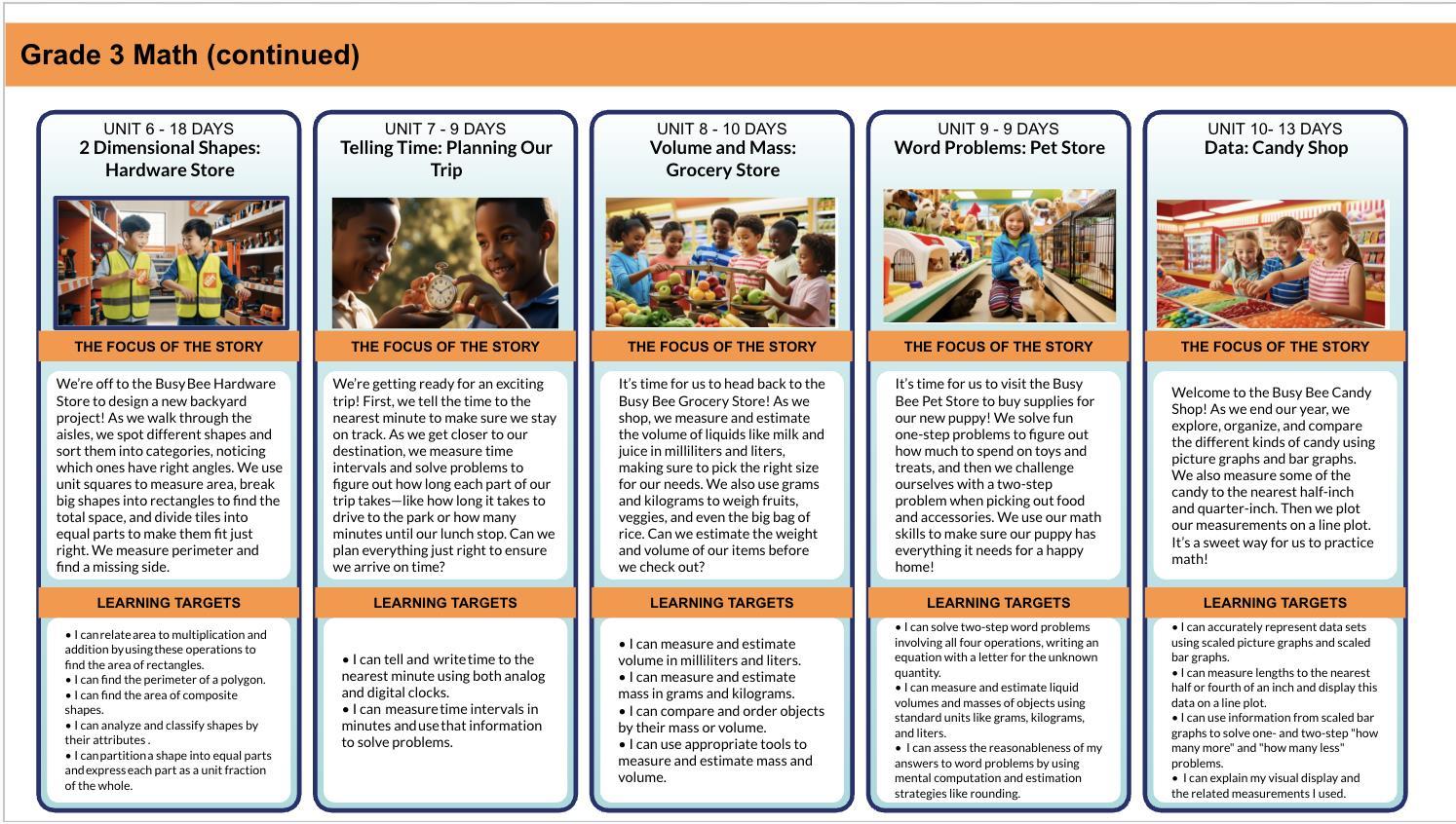
Grade 3 Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 0 Title: Setting the Culture
Unit Overview:
Creating a collaborative environment where students appreciate productive noise and productive struggle. Learning that communication, perseverance, collaboration, and reflection are key to being successful mathematicians.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
NOTE: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards. The lessons in this unit support the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards:
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Understandings
● Mistakes and challenges help me grow as a math thinker.
● Talking and working with others can lead to stronger ideas, new strategies, and deepen learning.
● Using patterns, tools, and efficient strategies helps us solve problems and understand the world.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom expectations and routines that support collaborative math learning
● How to select and use mathematical tools and models strategically to support problem solving
● What productive struggle looks like and how to recognize when and how to revise thinking or try a new approach
● How to contribute respectfully and thoughtfully in math discussions by sharing ideas, asking questions, and giving feedback
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers and fractions with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
Summative Assessment
Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
First Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines
Learning Targets:
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries or Reflections that respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes & Checklists during group tasks and partner work (e.g., who participates, uses self-talk, problem-solving strategies, or supports peers).
● Problem Solving Checklist used by students to self-monitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think.
Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a yearlong focus to strengthen number sense through problem-solving context.
Essential Questions:
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Grade 3 Math: Unit 0
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions, decimals, and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
Learning Activities:
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● Daily 15-minute sessions featuring five key workouts: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Solving Problems, Computational Fluency, and Number Strings
● Student-led updates to key displays for hands-on engagement and routine development. Use of manipulatives, math talks, visual models, and discussion to foster deep conceptual understanding.
● Emphasis on mathematical discourse, reasoning, problem solving, and identity as a mathematician.
Second Topic: Setting the Culture through Think! Mathematics!
Learning Targets
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
Estimated # of Lessons: 10 Days
Essential Questions:
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Objective, Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read The Most Magnificent Thing to foster a growth mindset and self-awareness.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use Crazy Colors activity to cultivate metacognition and perseverance.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using Venn Diagrams to foster communication and embracing differences.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use activity Disagreeing is Okay! We Can Still Be Friends to support respectful communication in challenging situations.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Initiate Fluency Routines to cultivate independence and collaboration through problem solving.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Try Saving Sam to teach students the power of cooperation and perseverance.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 0
● Lesson 7 Focus: Using the Next Door Numbers task to assist students in planning and reflecting so they can understand the foundations of effective group work.
● Lesson 8 Focus: Solve Ice Cream Scoops to foster a collaborative classroom culture.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Use the Folding Paper task to shift from speedy calculations to appreciating mathematical insight.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Play the Nine Lives game to empower students to leverage resources independently.
Think! Math Resources (online):
● Think Mathematics Online Toolbox
● Meet the Character Videos and Posters Slideshow
Additional Resources:
● The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Grade 3 Math: Unit 1
Course Name Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 13
Unit 1 Title: Numbers to 10,000: Shop Smart
Unit Overview:
We continue our math adventure as a squad by coming along on a trip to the Busy Bee Craft Store- it’s time to stock up on supplies! As you explore the aisles, we read and write numbers up to 10,000, break big numbers into thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones, and use place value to compare and sort items by cost. Don’t forget to check if the numbers are odd or even. Try rounding prices to the nearest 10 or 100 to help you shop smart!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
● 3.NBT.A.1- Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings
● Numbers can be represented in various forms to help solve problems.
● Knowledge of place value is essential for comparing, ordering, and rounding numbers efficiently and accurately.
● Rounding provides an estimate of a number that makes operations easier.
Knowledge
● Place value- ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands
● Number forms such as standard, word, and expanded form
● Rounding numbers
Key Vocabulary: ten thousand, rounding
Essential Questions
● How can I represent numbers in different ways?
● How can I use place value to round and solve problems?
● How can I use rounding in real-life situations?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can count within 10,000 starting at any given number.
● I can read and write numbers in standard, word, and expanded form.
● I can decompose four-digit numbers.
● I can compare and order numbers.
● I can round numbers to the nearest ten and
Grade 3 Math: Unit 1
hundreds.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 1 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of representing numbers in standard, word, and expanded form, comparing and ordering 4digit numbers, rounding to the nearest ten and hundred
● Error Analysis: James says 4,206 is greater than 4,620 because 206 is bigger than 620. Do you agree? Explain his mistake and how to correctly compare the number
● Math Journal: Write about two different ways to show the number 3,204 using place value. Why are both correct?
● Activity Time: Represent 4-digit numbers in more than one way
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Understanding Place Value to 10,000 Estimated # of Lessons: 3 days
Learning Targets:
● I can count within 10,000 starting at any given number.
● I can read and write numbers in standard, word, and expanded form.
● I can decompose four-digit numbers.
Essential Questions:
● How can I represent numbers in different ways?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: LessonPurpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials List: base-ten blocks, number disks, number bond template, place value chart
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Accurately count by 1,000s to 10,000 to recognize patterns in our base ten system. (TB 3A pg. 1-8 and WB 3A pg. 1-2)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 1
● Lesson 2 Focus: Count by 1,000s, 10s, and 1s to 10,000 to expand understanding of the place value system.
(TB 3A pg. 9-12 and WB 3A pg. 3-6)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Represent numbers to read and write numbers to 10,000 using base-ten numerals, word form, and expanded form.
(TB 3A pg. 13-18 and WB 3A pg. 7-12)
Second Topic: Comparing, Ordering and Rounding Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can compare and order numbers.
● I can round numbers to the nearest ten and hundreds.
Estimated # of Lessons: 10 days
Essential Questions:
● How can I use place value to round and solve problems?
Materials: number cards 1-100, number line template, place value cards, base-ten blocks, number disks, place value chart, number bond template
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4 Focus: (2 days) Compare and order numbers within 10,000 to understand place value and prepare for rounding and estimating. (TB 3A pg. 19-24 and WB 3A pg, 13-18)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Recognize odd and even numbers to recognize patterns and express an even number as a sum of doubles. (TB 3A pg. 25-28 and WB 3A pg. 19-20)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Round numbers to the nearest 10 to understand place value in order to develop strong estimation abilities. (TB 3A pg. 29-34 and WB 3A pg. 21-22)
● Lesson 7: (2 days) Round numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 to understand place value in order to develop strong estimation abilities. (TB 3A pg. 35-38 and WB 3A pg. 23-24)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 3A pg. 39-40 and WB 3A pg. 25)
● Math Journal (WB 3A pg. 26)
● Unit Review (WB 3A pg. 27-30)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 1- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - August and September
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Addition/Subtraction Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson- Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources grade 3 math centers pg. 245-255
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) pg. 135-152
● Coherence Map Website (3.NBT.1)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 2 Title:
Addition and Subtraction within 1,000: Toy Store
Unit Overview:
Welcome to the Busy Bee Toy Store. Imagine we have $1,000 to spend at the store. But here’s the trick: We need to round prices to ensure we don’t spend too much, add up our purchases to know our total, and subtract when we pay to see how much money we have left. Along the way, we discover patterns in numbers, like how adding two even numbers makes an even number and solve word problems!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
● 3.NBT.1- Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
● 3.NBT.2- Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
● 3.OA.8- Solve two-step word problems using four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answering using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
● 3.OA.9- Identify arithmetic patterns and explain them using properties of operations.
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Estimation helps determine the reasonableness of an answer.
● There are various strategies for addition and subtraction, and choosing an efficient one is important.
● Understanding benchmark numbers and place value is foundational to developing strong number sense, estimation skills, and efficient mental math strategies.
Knowledge
● How can I use place value to guide my problem-solving when adding and subtracting?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve addition and subtraction problems?
● How can we check for reasonableness when solving problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 2
● Rules for rounding numbers
● Addition and subtraction strategies
● Properties of addition- associative and commutative
Key Vocabulary: benchmark numbers
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 10.
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 100.
● I can solve problems by rounding numbers to make estimates.
● I can add and subtract numbers within 1,000 using place value strategies
● I can explain how addition and subtraction are related and use the relationship to solve problems.
● I can choose an efficient strategy to add and subtract within 1,000.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving addition and subtraction.
● I can demonstrate my understanding of benchmark numbers when rounding and explain my reasoning with an example.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 2 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of estimating sums and differences and explaining if an answer is reasonable and solving two-step word problems.
● Error Analysis: Ava solved 543 + 218 and got 751. Do you think she’s correct? Show how to solve it and explain what mistake she might have made.
● Math Journal: How is estimating an answer before solving helpful?
● Activity Time: Adding two 3-digit numbers, Subtract two 3-digit numbers
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the
student's needs.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 2
First Topic: Using Place Value Strategies for Addition
Learning Targets:
● I can add numbers within 1,000 using place value strategies.
● I can choose an efficient strategy to add within 1,000.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving addition.
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 10.
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 100.
● I can solve problems by rounding numbers to make estimates.
● I can demonstrate my understanding of benchmark numbers when rounding and explain my reasoning with an example.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3 days
Essential Questions:
● How can I use place value to guide my problem-solving when adding?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve addition?
● How can we check for reasonableness when solving problems?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1 Focus: Develop fluency for addition within 1,000 to efficiently and accurately compute problems. (WB 3A pg. 31-32)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Estimate sums to 1,000 to assess the reasonableness of their answers and to develop strong mental math and problem-solving skills. (TB 3A pg. 43-46 and WB 3A pg. 33-34)
● Lesson 2 Focus: (2 days) Choose addition strategies: to fluently add within 1,000 using a variety of strategies. (TB 3A pg. 47-54 and WB 3A pg. 35-42)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Add odd and even numbers to recognize patterns. (TB 3A pg. 55-58 and WB 3A pg. 43-44)
Second Topic: Using Place Value Strategies for Subtraction
Learning Targets:
● I can subtract numbers within 1,000 using place value strategies.
● can choose an efficient strategy to subtract within 1,000.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving subtraction.
● I can explain how addition and subtraction
Estimated # of Lessons: 9 days
Essential Questions:
● How can I use place value to guide my problem-solving when subtracting?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve subtraction problems?
● How can we check for reasonableness when solving problems?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 2
are related and use the relationship to solve problems.
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 10.
● I can use place value to round numbers to the nearest 100.
● I can solve problems by rounding numbers to make estimates.
● I can demonstrate my understanding of benchmark numbers when rounding and explain my reasoning with an example.
Materials: N/A
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 2 Focus: Develop fluency for subtraction within 1,000 to efficiently and accurately compute problems. (WB 3A pg. 31-32)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Estimate differences within 1,000 to assess the reasonableness of their answers and to develop strong mental math and problem-solving skills. (TB 3A pg. 59-62 and WB 3A pg. 47-48)
● Lesson 5 Focus:(2 days) Choose subtraction strategies to fluently subtract within 1,000 (TB 3A pg. 63-70 and WB 3A pg. 49-56)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Solve word problems to support mathematical practices, make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (TB 3A pg. 71-74 and WB 3A pg. 57-58)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 3A pg. 75 and WB 3A pg. 59)
● Math Journal (TB 3A pg. 75 and WB 3A pg. 60)
● Unit Review (WB 3A pg. 61-64)
● Cumulative Review 1(WB 3A pg. 65-68)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 2- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - October
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Addition/Subtraction Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson- Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources grade 3 math centers pages 256-273
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 152- 171
● Coherence Map Website (3.NBT.1 and 2 and 3.OA.8 and 9)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons:15
Unit 3 Title: Multiplication and Division: Grocery Store
Unit Overview:
Grab a cart! We're headed to the Busy Bee Grocery Store! As we shop, we multiply to find the total number of items in equal groups, like boxes of granola bars or packs of juice. We also divide things into equal groups to help organize our cart and make fact families to show how multiplication and division are connected. It’s math in action while we shop!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3. OA.1- Interpret products of whole numbers.
● 3 .OA.2- Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers.
● 3. OA.4- Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers.
● 3. OA.5- Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.
● 3 .OA.6- Understand division as an unknown factor problem.
● 3 .OA.7- Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division or the properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
● 3 .OA.8- Solve two-step word problems using four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answering using mental computation and estimation strategies, including rounding.
Understandings
● Mathematical properties and strategies can be applied to solve multiplication and division problems efficiently and accurately.
Transfer Goals
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Essential Questions
● How can I represent a multiplication problem with a drawing or array? What does it help me see?
● How can I use my understanding of how multiplication and division are related to find a missing number in an equation?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 3
Knowledge
● Multiplication is a way to find the total number of items in equal groups
● Division is a way to share or group a total number of items equally
● Division can be understood as finding a missing factor in a multiplication problem
● All products of two one-digit numbers and use that knowledge to divide fluently within 100
Key Vocabulary: factor, divide, multiplication equation, multiply, times, divisor, quotient, dividend, product
● Which strategy am I using to help me check if my answer is reasonable? Are there other strategies that may be more efficient?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can model multiplication as equal groups given a scenario.
● I can explain what a multiplication equation means using objects, drawings, or words.
● I can model division as sharing or making equal groups given a scenario.
● I can explain what a division equation means using objects, drawings, or words.
● I can write equations that match a multiplication or division word problem.
● I can find the missing number in a multiplication or division equation.
● I can use the commutative and associative properties to multiply.
● I can use what I know about the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving multiplication and division.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 3 Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of arrays and equal groups, division as sharing and grouping, relationship between multiplication and division
● Error Analysis: Liam says 3 × 5 = 15, so 15 ÷ 5 = 5. Do you agree? Explain what he misunderstood about division.
● Math Journal: How are multiplication and division connected? Write about how you used both in the same problem.
● Activity Time: Show equal groups of objects, find the product of whole numbers, and write each multiplication equation
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Grade 3 Math: Unit 3
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Understanding Equal Groups and Arrays
Learning Targets:
● I can model multiplication as equal groups given a scenario.
● I can explain what a multiplication equation means using objects, drawings, or words.
● I can write equations that match a multiplication word problem.
● I can find the missing number in a multiplication equation.
● I can use the commutative and associative properties to multiply.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving multiplication.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● What does it mean to multiply, and how is it different from other operations?
● How can I represent a multiplication problem with a drawing or array? What does it help me see?
● Which strategy am I using to help me check if my answer is reasonable? Are there other strategies that may be more efficient?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials List: counters, number cards (1-9), square tiles
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus (2 days): Multiply to interpret products of whole numbers as the total number of objects in identical groups. (TB 3A pg. 79-84 and WB 3A pg. 69-70)
● Lesson 2 Focus (2 days): Use Arrays to Interpret products of whole numbers as the total number of objects in identical groups arranged in arrays. (TB 3A pg. 85-90 and WB 3A pg. 71-72)
Second Topic: Division
Learning Targets:
● I can model division as sharing or making equal groups given a scenario.
● I can explain what a division equation means using objects, drawings, or words.
● I can write equations that match a division word problem.
● I can find the missing number in a division equation.
● I can solve two-step word problems involving division.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● What does it mean to divide, and how is it different from other operations?
● How can I represent a division problem with a drawing or array? What does it help me see?
● Which strategy am I using to help me check if my answer is reasonable? Are there other strategies that may be more efficient?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 3
Materials List: unit cubes
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3 Focus (2 days): Divide and Group to interpret quotients of whole numbers as the number of shares when objects are partitioned into equal shares. (TB 3A pg. 91-94 and WB 3A pg. 73-74)
● Lesson 4 Focus (2 days): Divide and Share to interpret quotients of whole numbers as the number of objects in each share when the objects are partitioned equally. (TB 3A pg. 95-98 and WB 3A pg. 75-76)
Third Topic: Relating Division to Multiplication Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Learning Targets:
● I can use what I know about the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems.
● I can write equations that match a multiplication or division word problem.
Materials List: unit cubes
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use my understanding of how multiplication and division are related to find a missing number in an equation?
● Lesson 5 Focus: Making fact families to understand the inverse relationship between the two operations and to build fluency with multiplication and division facts. (TB pages 99-102 and WB pages 77-78)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Multiply by 1 and 0 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pg. 103-106 and WB 3A pg. 79-80)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Understand division involving 1 and 0 to establish patterns and build fluency in division facts. (TB 3A pg. 107-110 and WB 3A pg. 81-82)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 3A pg. 111 and WB 3A pg. 83)
● Math Journal (TB 3A pg. 112 and WB 3A pg. 84)
● Unit Review (WB 3A pg. 85-86)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 3- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - November
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 10-82
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 9-41
● Coherence Map Website- (OA Standards)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 30
Unit 4 Title: Multiplication and Division Patterns: Grocery Store
Unit Overview:
As we continue to shop at the Busy Bee Grocery Store, we will organize items into groups and use arrays to arrange them neatly. As we get to the checkout, we realize we need to share our haul fairly among our friends, and this leads us to think about how we can divide items equally so we know how many each person will receive.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3.OA.4- Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers.
● 3.OA.5- Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.
● 3.OA.6- Understand division as an unknown factor problem.
● 3.OA.7- Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division or the properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
● 3.OA.9- Identify arithmetic patterns and explain them using properties of operations.
● 3.NBT.3- Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Multiplication and division are related operations that assist in solving problems involving equal groups, arrays, and unknown values.
● Mathematical properties and place value strategies can be used to solve problems more efficiently and to explain patterns in numbers.
● Fluency with multiplication and division
● How can I use multiplication and division facts, patterns, and properties to find unknown numbers and solve problems?
● What strategies help me multiply and divide efficiently, and explain my thinking?
● How can I recognize and explain number patterns using what I know about math properties and place value?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 4
facts builds a strong foundation for solving more complex problems and understanding higher-level math.
Knowledge
● Multiplication and division are inverse operations
● Division can be used to find a missing factor in a multiplication equation
● Multiply one-digit numbers by multiples of 10 using place value and properties of operations
Key Vocabulary: multiple, multiplication fact table
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can solve and explain multiplication and division problems, including when a number is missing.
● I can apply math properties like commutative and associative to make multiplication and division easier.
● I can use multiplication to help me understand and solve division problems.
● I can recall multiplication facts and use them to fluently multiply and divide numbers within 100.
● I can identify and explain arithmetic patterns using properties of operations.
● I can multiply a 1-digit number by a multiple of ten.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 4 Assessment
● IAB- Operations and Algebraic Thinking
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of multiplication and division patterns, multiplying by multiples of 10, the associative property
● Error Analysis:Sophia says 6 × 3 = 24 because she skip-counted by 6 three times. Do you agree with her strategy and answer? Explain.
● Math Journal: Describe a pattern you noticed when multiplying numbers. How could that pattern help you solve other problems?
● Activity Time: Multiply whole numbers by 2, 5, or 10, Multiply whole numbers by 4 and 8, Multiply and divide whole numbers by 1-digit number
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 4
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Multiplication and Division Patterns Estimated # of Lessons: 20
Learning Targets:
● I can solve and explain multiplication and division problems, including when a number is missing.
● I can apply math properties like commutative and associative to make multiplication and division easier.
● I can use multiplication to help me understand and solve division problems.
● I can recall multiplication facts and use them to fluently multiply and divide numbers within 100.
● I can identify and explain arithmetic patterns using properties of operations.
● I can multiply a 1-digit number by a multiple of ten.
Essential Questions:
● How can I use multiplication and division facts, patterns, and properties to find unknown numbers and solve problems?
● What strategies help me multiply and divide efficiently and explain my thinking?
● How can I recognize and explain number patterns using what I know about math properties and place value?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: number cards (1-9), counters, number line template, square tiles, unit cubes, dot cards (2-9)
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1 Focus: Count by 2s, 5s, and 10s to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (WB 3A pages 87-88)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Multiply by 2 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 117-122 WB 3A pages 89-92)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Multiply by 5 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 123-128 and WB 3A pages 93-96)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Multiply by 10 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 129-134 and WB 3A pages 97-100)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Divide by 2, 5, 10 to establish patterns and build fluency with division facts. (TB 3A pages 135-138 and WB 3A pages 101-108)
● Lesson 5 Focus:Multiply by 3 and 6 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 139-142 and WB 3A pages 109-114)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Divide by 3 and 6 to establish patterns and build fluency with division facts. ( TB 3A pg. 143-146 and WB 3A pages 115-118)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Multiply by 4 and 8 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 147-152 and WB 3A pages 119-124)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Divide by 4 and 8 to establish patterns and build fluency with division facts.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 4
(TB 3A pages 153-156 and WB 3A pages 125-128)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Multiply and divide by 7 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication and division facts. (TB 3A pages 157-162 and WB 3A pages 129-132)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Multiply and divide by 9 to establish patterns and build fluency with multiplication facts. (TB 3A pages 163-168 and WB 3A pages 133-136)
● Lesson 11 Focus: Multiply three 1-digit numbers to apply and understand the associative property of multiplication. (TB 3A pages 169 -172 and WB 3A pages 137-138)
● Lesson 12 Focus: Multiply whole numbers 1-10 by multiples of 10 to connect multiplication with place value understanding, develop efficient mental computation strategies.( TB 3A pages 173176 and WB 3A pages 139-140)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB page 177 and WB page 141)
● Math journal (TB page 178 and WB page 142)
● Unit Review (WB pages 143-146)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 4- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - December
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 94-279
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 61- 115
● Coherence Map Website- (OA Standards)
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- Students will apply their understanding of multiplication using a ratio table to new learning of division through engaging with real-world problems, or “contexts,” that challenge them to apply and extend their learning. Concepts and skills are explicitly taught and then deepened through scaffolded experiences that build on prior lessons within the unit. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and Math Congress discussions, students revisit and refine earlier strategies, strengthen their understanding, and connect new ideas to those already explored. This intentional progression supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical concepts, articulate their reasoning, and develop a strong, connected foundation for future learning.
First Topic: The Big Dinner
Learning Targets:
● I can solve and explain multiplication and division problems, including when a number is missing.
Estimated Number of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How can I use multiplication and division facts, patterns, and properties to find unknown numbers and solve problems?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 4
● I can apply math properties like commutative and associative to make multiplication and division easier.
● I can use multiplication to help me understand and solve division problems.
● I can identify and explain arithmetic patterns using properties of operations.
Learning Activities:
● What strategies help me multiply and divide efficiently and explain my thinking?
● How can I recognize and explain number patterns using what I know about math properties and place value?
● Day 1 Focus: Pricing the Ingredients to make use of arithmetic patterns to build ratio tables.
● Day 2 Focus: Buying the turkey to attend to precision and make connections between strategies.
● Day 3 Focus: Charts for the grocer-turkey- to look for patterns to solve other problems.
● Days 4 and 5 Focus: Charts for the grocer- apples and carrots to examine patterns and relationships between problems and use partial products and proportional reasoning to justify their answers.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 5
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 20
Unit 5 Title: Fractions: Pizza Store
Unit Overview:
We are off to the Busy Bee pizza shop! We slice pizzas into equal parts and learn how to name each slice as a fraction. We use number lines to show where those fractions belong, figure out when differentlooking slices are actually the same size, and compare different slices to decide which customer is getting the biggest piece. We serve up fair shares and smart fraction deals for every pizza order!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
● 3.NF.1- Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b.
● 3.NF.2- Understand a fraction as a number on the number line; represent a fraction on a number line diagram.
● 3.NF.3- Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size.
Understandings
● Fractions represent parts of a whole that have been divided into equal pieces, helping to describe quantities in between whole numbers.
● Different fractions can represent the same amount, meaning some fractions are equivalent even if they look different.
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How does my understanding of partitioning shapes help me describe and make sense of fractions?
● How do I find equivalent fractions?
● How does a fraction show a part of a whole, and how can it help me describe equal parts?
● How can I represent and compare fractions with models or drawings?
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 5
Knowledge
● Fractions have a specific notation that includes a numerator and denominator
● A fraction represents parts of a whole that is divided into equal parts
● Some fractions are equivalent because they represent the same portion of a whole, even if they look different
● Fractions can be shown and understood on a number line, to visualize their size and order
Key Vocabulary: equivalent fractions, numerator, denominator, sixth, eighth, like denominators, like numerators, whole number, line plots
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can use models to represent fractions.
● I can accurately plot fractions on a number line and justify their positions by understanding their component parts.
● I can identify, generate, and explain why some fractions are equivalent by using models and number lines.
● I can compare fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 5 Assessment
● IAB-Number and Operations- Fractions
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of naming and writing unit and non-unit fractions, placing fractions on number lines, identifying equivalent fractions, comparing fractions with like denominators or numerators
● Error Analysis: Noah says that 1/4 is greater than 1/2 because 4 is a bigger number than 2. Do you agree? Explain his mistake and how to compare fractions.
● Math Journal: Explain how a number line can help you understand fractions. Give an example.
● Activity Time: Compare two fractions
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 5
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Fraction Concepts and Models
Learning Targets:
● I can use models to represent fractions.
● I can accurately plot fractions on a number line and justify their positions by understanding their component parts.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How does my understanding of partitioning shapes help me describe and make sense of fractions?
● How does a fraction show a part of a whole, and how can it help me describe equal parts?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: paper cut-outs, number line template and strips of paper
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1: Identify the numerator and denominator to understand it as the quantity formed by one part when a whole is partitioned into equal parts. (TB 3A pages 183-188 and WB 3A pages 147148)
● Lesson 2: Represent fractions on a number line to develop a deeper understanding of fraction size, order, and their relationship to whole numbers. ( TB 3A pages 189-192 and WB 3A pages 147148)
Second Topic: Equivalent Fractions Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Learning Targets:
● I can identify, generate, and explain why some fractions are equivalent by using models and number lines.
Essential Questions:
● How do I find equivalent fractions?
Materials: number line template, scissors, paper cut outs
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3: Find equivalent fractions to understand that different fractions can represent the same value, supporting their ability to compare and simplify fractions. (TB 3A pages 193-198 and WB 3A pages 151-152)
● Lesson 4: Represent whole numbers as fractions to recognize fractions that are equivalent to whole fractions. (TB 3A pages 199-204 and WB 3A pages 153-154)
Third Topic: Comparing Fractions Estimate # of Lessons: 4
Learning Targets:
● I can compare fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size.
Essential Questions
● How can I represent and compare fractions with models or drawings
Grade 3 Math: Unit 5
Materials: scissors and paper cut-outs
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 5 Focus: Compare fractions with the same numerator or denominator to recognize that comparisons of fractions are valid only when the fractions refer to the same whole. (TB 3A pages 205-212 and WB 3A pages 155-158)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3A page 213 and WB 3B page 159)
● Math journal (TB 3A page 213 and WB 3A page 160)
● Unit Review (WB 3A pages 161-164)
● Cumulative Review 2 (WB 3A pages 165-170)
● Mid-Year Review (WB 3A pages 171-176)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 5- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - January
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson- Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 287-329
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 192-228
● Coherence Map Website (3.NF.1-3)
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- Students will apply their understanding of ordering fractions to new learning of line plots through engaging with real-world problems, or “contexts,” that challenge them to apply and extend their learning. Concepts and skills are explicitly taught and then deepened through scaffolded experiences that build on prior lessons within the unit. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and Math Congress discussions, students revisit and refine earlier strategies, strengthen their understanding, and connect new ideas to those already explored. This intentional progression supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical concepts, articulate their reasoning, and develop a strong, connected foundation for future learning.
First Topic: All About Sharks/ Number Detectives (CFLM)
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Learning Targets:
Grade 3 Math: Unit 5
● I can accurately plot fractions on a number line and justify their positions by understanding their component parts.
● I can measure lengths to the nearest half or fourth of an inch and display this data on a line plot.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I used.
Essential Questions:
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
● How can I represent and compare fractions with models or drawings?
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
Materials: CFLM book and supplemental materials
Learning Activities:
● Day 1 Focus: A shark sighting to develop the context and investigate, and create ways to organize data.
● Day 2 Focus: Working with line plots to look for relationships between the various lengths of sharks.
● Day 3 Focus: Estimating heights to estimate and compare lengths and build line plots of the data.
● Day 4 Focus: Measuring shark lengths to analyze the shape of the data and build graphs.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 6
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 18
Unit 6
Title:Two-Dimensional
Shapes: Hardware Store
Unit Overview:
We’re off to the Busy Bee Hardware Store to design a new backyard project! As we walk through the aisles, we spot different shapes and sort them into categories, noticing which ones have right angles. We use unit squares to measure area, break big shapes into rectangles to find the total space, and divide tiles into equal parts to make them fit just right. We will measure the perimeter and find a missing side.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3.G.1-Understand that shapes in different categories may share attributes, and that the shared attributes can define a larger category. recognize rhombus, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, and draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories.
● 3.G.2-Partition shapes into parts with equal areas. Express the area of each part as a unit fraction of the whole.
● 3. MD.7- Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition.
● 3. MD.8- Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths, finding an unknown side length, and exhibiting rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas with the same length area and different perimeters.
Understandings
● Shapes can share attributes, and those shared attributes help to group and classify them into broader categories like quadrilaterals.
● Partitioning shapes into equal parts assists in understanding fractions and how each part relates to the whole.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (MP3 Constructing viable arguments and critiquing the reasoning of others) (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Essential Questions
● How can shared attributes help me group and describe different shapes?
● How does partitioning shapes into equal parts help me to deepen my understanding of unit fractions?
● How can I measure the space inside a twodimensional shape? What patterns am I seeing based on my measurements?
● How can I use what I know to find the
Grade 3 Math: Unit 6
Knowledge
● Area is the measure of the space inside a two-dimensional figure
● Perimeter is the measure of the distance around a two-dimensional figure
● Area and perimeter are calculated using different methods
● Figures can have the same area but different perimeters
● Attributes of two-dimensional shapes
● Composite shapes are made up of two or more polygons (a closed shape with more than 2 sides and corners)
Key Vocabulary: area, perimeter, length, width, composite shape
perimeter of a polygon?
Skills
(Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can relate area to multiplication and addition by using these operations to find the area of rectangles.
● I can find the perimeter of a polygon.
● I can find the area of composite shapes.
● I can analyze and classify shapes by their attributes and recognize that shapes like squares, rectangles, and rhombuses are all types of quadrilaterals.
● I can partition a shape into equal parts and express each part as a unit fraction of the whole.
● I can listen to and ask clarifying questions about another strategy my classmate used.
● I can explain and show my thinking to others about a strategy I used.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 6 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of identifying and classifying quadrilaterals, recognizing and labeling right angles, calculating area using unit squares, finding perimeter by adding side lengths, comparing area and perimeter of different rectangles
● Error Analysis: Olivia says all shapes with four equal sides are squares. Do you agree? Explain her mistake using shape attributes.
● Math Journal: Choose a quadrilateral and describe how you know it is not a square. Use words like sides, angles, and right angles in your explanation.
● Activity Time: Find the area of a rectangle by decomposing it into smaller rectangles. Distinguish between linear and area measures
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 6
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Attributes of Polygons
Learning Targets:
● I can analyze and classify shapes by their attributes and recognize that shapes like squares, rectangles, and rhombuses are all types of quadrilaterals.
Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Essential Questions:
● How can shared attributes help me group and describe different shapes?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: paper cutouts (circle, hexagon, square, trapezoid, triangle), 2D shape manipulatives, set square
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Describe polygons to assist in understanding that shapes in different categories may share attributes and can be defined by a larger category. (TB 3B pages 3-8 and WB 3B pages 1-4)
Second Topic: Area
Learning Targets:
● I can relate area to multiplication and addition by using these operations to find the area of rectangles.
● I can find the area of composite shapes.
● I can partition a shape into equal parts and express each part as a unit fraction of the whole.
Materials: square tiles
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How can I measure the space inside a twodimensional shape? What patterns am I seeing based on my measurements?
● How does partitioning shapes into equal parts help me to deepen my understanding of unit fractions?
● Lesson 2 Focus: Find an area to develop a foundational understanding of area as a measurable attribute and to connect area to multiplication. (TB 3B pages 9-14 and WB 3B pages 5-8)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Find the area of rectangles to develop the area formula conceptually and reinforce multiplication as repeated addition/arrays. (TB 3B pages 15-20 and WB 3B pages 9-14)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Decompose the area of a rectangle to recognize that area is additive. (TB 3B pages 21-26 and WB 3B pages 15-16)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Find the area of composite figures to recognize that area is additive. (TB 3B pages 27-32 and WB 3B pages 17-22)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Partition figures to make equal areas and express areas as a fraction of the whole figure. (TB 3B pages 33-36 and WB 3B pages 23-34)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 6
Third Topic: Problem Solving with Area and Perimeter
Learning Targets:
● I can find the perimeter of a polygon.
Materials: paper cut-outs (rectangles), square tiles
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How can I use what I know to find the perimeter of a polygon?
● Lesson 7 Focus: Find perimeter to understand the fundamental concept of perimeter as a linear measure and provide practical application for their addition skills. (TB 3B pages 37-42 and WB 3B pages 25-30)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Find the unknown side length of a polygon to deepen an understanding of perimeter and introduce fundamental algebraic reasoning. (TB 3B pages 43-46 and WB 3B pages 31-32)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Compare area and perimeter to distinguish between linear and area measures. (TB 3B pages 47-54 and WB 3B pages 33-34)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Solve word problems to find the area and perimeter of polygons. (TB 3B pages 55-58 and WB 3B pages 35-38)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3B page 59 and WB 3B page 39)
● Math journal (TB 3B page 59 and WB 3B page 40)
● Unit Review (WB 3B pages 41-46)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 6- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - February
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 385-460
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 291-322
● Coherence Map Website (3.G.1-2; 3.MD.7-8)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 7
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 9
Unit 7 Title: Time: Planning a Trip
Unit Overview:
We’re getting ready for an exciting trip! First, we tell the time to the nearest minute to make sure we stay on track. As we get closer to our destination, we measure time intervals and solve problems to figure out how long each part of our trip takes like how long it takes to drive to the park or how many minutes until our lunch stop. Can we plan everything just right to ensure we arrive on time?
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
● 3. MD.1- Tell and write time to the nearest minute and measure time intervals in minutes. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of time intervals in minutes.
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Understanding time helps make sense of daily routines and solve real world problems.
Knowledge
● Clocks can be read to the nearest minute using both analog and digital formats
● Time can be measured to different degrees (half hour, quarter hour, 5 minute, minute)
Key Vocabulary: duration, time interval, elapsed time
● How do I use what I know about time to solve problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can tell and write time to the nearest minute using both analog and digital clocks.
● I can measure time intervals in minutes and use that information to solve problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 7 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of telling time to the nearest minute, finding elapsed time using a number line, or counting
Grade 3 Math: Unit 7
strategy
● Error Analysis: Daniel says the time from 3:20 to 3:50 is 40 minutes because 50 – 20 = 30, and then he added 10 more. What mistake did Daniel make, and what is the correct time interval?
● Math Journal: Explain how you would figure out how long your recess is if it starts at 10:15 and ends at 10:40. What strategies help you find elapsed time?
● Activity Time: Measure time intervals in minutes
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Tell and write time to the nearest minute and measure time intervals in minutes.
Learning Targets:
● I can tell and write time to the nearest minute using both analog and digital clocks.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I use what I know about time to solve problems?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: analog clock, blank cards
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Telling time to the nearest minute to develop mathematical reasoning to prepare for more complex problems. (TB pages 63-68 and WB pages 47-52)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Measuring and Comparing Time to find the start time or end time, and help make sense of the real world. (TB 3B pages 69-74 and WB 3B pages 53-58)
Second Topic: Solve word problems involving time.
Learning Targets:
● I can measure time intervals in minutes and use that information to solve problems.
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How do I use what I know about time to solve problems?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 7
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3 Focus: Solve word problems to include addition and subtraction of time intervals to make sense of real-world problems. (TB 3B pages 75-78 and WB 3B pages 59-60)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Using a Calendar to determine the number of days and/or weeks during before or after an event. (TB 3B pages 79-82 and WB 3B pages 61-62)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3B page 83 and WB 3B page 63)
● Math journal (TB 3B page 83 and WB 3B page 64)
● Unit Review (WB 3B pages 65-68)
● Cumulative Review 3 (WB 3B pages 69-74)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 7- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - March
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson -Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 330-340
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 241- 257
● Coherence Map Website (3, MD.1)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 8
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 8 Title: Volume and Mass: Grocery Store
Unit Overview:
It’s time for us to head back to the Busy Bee Grocery Store! As we shop, we measure and estimate the volume of liquids like milk and juice in milliliters and liters, making sure to pick the right size for our needs. We also use grams and kilograms to weigh fruits, veggies, and even the big bag of rice. Can we estimate the weight and volume of our items before we check out?
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3.MD.2- Measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units of grams (g), kilograms (kg), and liters (l).1 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide to solve one-step word problems involving masses or volumes that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as a beaker with a measurement scale) to represent the problem.
Understandings
● Volume is how much a container can hold.
● Mass is how heavy or light an object is based on what it is made up of
● Standard units provide a consistent way to measure and compare objects
● Measurement helps to describe and compare physical properties in real-life situations.
Knowledge
● Mass and volume can be estimated or measured using tools such as scales and measuring containers.
● One-step word problems involving the same units can be solved using basic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
Key Vocabulary: liter, milliliter, capacity, balance scale, mass, gram, kilogram, weighing scale
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How do I measure how much "stuff" an object has?
● What makes some objects feel heavier or lighter than others?
● How do I measure how much space something takes up?
● What determines how much a container can hold?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure and estimate volume in milliliters and liters.
● I can measure and estimate mass in grams and kilograms.
● I can compare and order objects by their mass or volume.
● I can use appropriate tools to measure and estimate mass and volume.
Grade 3 Math: Unit 8
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 8 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of measuring and estimating in milliliters and liters, measuring and estimating in grams and kilograms, choosing appropriate units for volume and mass, comparing and reasoning about the mass and volume of real-world objects
● Error Analysis:Mason says a watermelon has a mass of 5 grams. Does this seem reasonable? Give a better estimate.
● Math Journal: Write about a time you had to measure a liquid. What did you use to measure and how could you have used estimation to help you?
● Activity Time: Estimate the volume of a liquid in liters
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Volume
Learning Targets:
● I can measure and estimate volume in milliliters and liters.
● I can use appropriate tools to measure and estimate mass and volume.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I measure how much "stuff" an object has?
● What determines how much a container can hold?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: measuring scale, 1L container
Learning Activities:
Grade 3 Math: Unit 8
● Lesson 1 Focus: Measure the volume of liquid to develop measurement benchmarks and understand unit size within the metric system. (TB 3B pages 87-92 and WB 3B pages 75-78)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Estimate and measure volume of liquid to develop measurement benchmarks and understand unit size within the metric system. (TB 3B pages 93-98 and WB 3B pages 79-84)
Second Topic: Mass
Learning Targets:
● I can measure and estimate mass in grams and kilograms.
● I can compare and order objects by their mass or volume.
● I can use appropriate tools to measure and estimate mass and volume.
Estimated # of Lessons: 3
Essential Questions:
● How do I measure how much "stuff" an object has?
● What makes some objects feel heavier or lighter than others?
● How do I measure how much space something takes up?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: balance scale, weights, weighing scale
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3 Focus: Compare masses to build a foundation for standard unit measurement (grams and kilograms) and to develop estimation skills. (TB 3B pages 99-104 and WB 3B pages 85-86)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Measure mass of an object in grams and kilograms to develop measurement benchmarks and understand unit size within the metric system. (TB 3B pages 105-110 and WB 3B pages 87-88)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Estimate the mass of an object to build a foundation for standard unit measurement (grams and kilograms) and to develop estimation skills. (TB 3B pages 111-118 and WB 3B pages 89-94)
End Of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3B page 119 and WB page 95)
● Math journal (TB 3B page 120 and WB 3B page 96)
● Unit Review (WB 3B pages 97-102)
Think! Math Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 8- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - April
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson -Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources grade 3 math centers pages 344-355
Grade 3 Math: Unit 9
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 9
Unit 9 Title: Word Problems: Pet Store
Unit Overview:
It’s time for us to visit the Busy Bee Pet Store to buy supplies for our new puppy! We solve fun one step problems to figure out how much to spend on toys and treats, and then we challenge ourselves with a two step problem when picking out food and accessories. We use our math skills to make sure our puppy has everything it needs for a happy home!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3.OA.8- Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
● 3.MD.2- Measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units of grams (g), kilograms (kg), and liters (l).1 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide to solve one-step word problems involving masses or volumes that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as a beaker with a measurement scale) to represent the problem.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Understanding the structure of a problem helps to choose appropriate operations and strategies to find a solution.
● Solutions to mathematical problems must be reasonable and can be checked using estimation.
● How do I decide if a word problem is asking about how much "stuff" or how much "space"?
● What tools or strategies can help me solve real-life problems about how heavy or how much liquid something is? How can I use estimation to check if my answer makes sense?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Letters can be used to represent an unknown quantity in an equation
● Mass or volume problems must be solved using quantities given in the same units
● I can solve two-step word problems involving all four operations, writing an equation with a letter for the unknown quantity.
● I can measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units
Grade 3 Math: Unit 9
Key Vocabulary: No New Vocabulary like grams, kilograms, and liters.
● I can assess the reasonableness of my answers to word problems by using mental computation and estimation strategies like rounding.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 9 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of solving one- and two-step word problems, representing unknowns with a letter, applying knowledge of volume, mass, or time to solve problems and explaining and justifying solutions
● Error Analysis: Sam pours 500 mL of juice into each of 4 cups. How much juice does he use?” Nina solved it by doing 500 + 4 = 504 mL. What mistake did Nina make?
● Math Journal: Describe how you solve a twostep word problem. How do you check your answer?
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Solving Word Problems involving volume and mass
Learning Targets:
● I can measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units like grams, kilograms, and liters.
● I can assess the reasonableness of my answers to word problems by using mental computation and estimation strategies like rounding.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I decide if a word problem is asking about how much "stuff" or how much "space"?
● What tools or strategies can help me solve real-life problems about how heavy or how much liquid something is? How can I use estimation to check if my answer makes sense?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 9
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) page
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Solve word problems to involve volume and mass in metric units. (TB 3B pages 125-130 and WB 3B 103-106)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Solve word problems to involve volume and mass in metric units. (TB 3B pages 131-136 and WB 3B pages 107-108)
Second Topic: Solving word problems involving the four operations
Learning Targets:
● I can solve two-step word problems involving all four operations, writing an equation with a letter for the unknown quantity.
● I can assess the reasonableness of my answers to word problems by using mental computation and estimation strategies like rounding.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I decide if a word problem is asking about how much "stuff" or how much "space"?
● What tools or strategies can help me solve real-life problems about how heavy or how much liquid something is? How can I use estimation to check if my answer makes sense?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities
● Lesson 3 Focus: Solving word problems to solve word problems involving the four operations. (TB 3B pages 137-140 and WB 3B pages 109-110)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Solve word problems to solve word problems involving the four operations. (TB 3B pages 141-144 and WB 3B pages 111-114)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3B page 145 and WB 3B page 115)
● Math journal (TB 3B page 145 and WB 3B page 116)
● Unit Review (WB 3B pages 117-120)
Think! Math Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 9- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - May
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources Grade 3 math centers pages 226- 230
● Math In Practice (O’Connell) p. 116-135
● Coherence Map Website (3,OA.8 and 3.MD.2)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 10
Course Name: Grade 3 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 13
Unit 10 Title: Data: Candy Shop
Unit Overview:
Welcome to the Busy Bee Candy Shop! As we end our year, we explore, organize, and compare the different kinds of candy using picture graphs and bar graphs. We also measure some of the candy to the nearest half inch and quarter inch. Then we plot our measurements on a line plot. It’s a sweet way for us to practice math!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 3.MD.3- Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step "how many more" and "how many less" problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs.
● 3.MD.4- Generate measurement data by measuring lengths using rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch. Show the data by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in appropriate units— whole numbers, halves, or quarters.
Understandings
● Data can be organized and represented in various ways to reveal important information and answer questions.
● Effective measurement involves understanding appropriate tools and units, and knowing how to record and display the results.
● Visual displays of data allow for comparison of quantities and solving problems involving "how many more" or "how many less."
Knowledge
● Picture graphs use symbols or pictures to represent data
● Bar graphs use bars of different lengths or
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
● How precise do I need to be to represent my findings?
● What stories can data tell me, and how can I use those stories to solve problems?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can accurately represent data sets using scaled picture graphs and scaled bar graphs.
● I can measure lengths to the nearest half or
Grade 3 Math: Unit 10
heights to represent data
● Scales on a graph tells how many units each symbol or bar represents
● Line plot displays measurement data on a number line
● Lengths can be measured using rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch
Key Vocabulary: scaled picture graph, scaled bar graph
fourth of an inch and display this data on a line plot.
● I can use information from scaled bar graphs to solve one- and two-step "how many more" and "how many less" problems.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I used.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 3 Unit 10 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of drawing scaled picture and bar graphs, interpreting scaled graphs to solve problems, measuring and plotting data to the nearest ½ or ¼ inch on a line plot, using graphs to compare categories and answer "how many more/fewer" questions.
● Math Journal: What are some things you notice when you look at a line plot or bar graph? How can these graphs help you make decisions?
● Activity Time: Interpret data on a scaled graph with up to four categories
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Making Graphs
Learning Targets:
● I can accurately represent data sets using scaled picture graphs and scaled bar graphs
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
Grade 3 Math: Unit 10
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Make Picture Graphs to represent a data set with up to four categories. (TB B3 pages 149-153 and WB B3 pages 121-122)
● Lesson 2: Make Bar Graphs to represent a data set with several categories. (TB B3 pages 155-160 and WB B3 pages 123-124)
Second Topic: Solving Problems with Graphs Estimated # of Lessons: 1
Learning Targets:
● I can use information from scaled bar graphs to solve one- and two-step "how many more" and "how many less" problems.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● What stories can data tell me, and how can I use those stories to solve problems?
● Lesson 3 Focus: Solve problems with graphs to answer "how many more" and "how many less" problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs. (TB B3 pages 161-166 and WB B3 pages 125-130)
Third Topic: Making and Interpreting Line Plots Estimated # of lessons: 2
Learning Targets:
● I can measure lengths to the nearest half or fourth of an inch and display this data on a line plot.
● I can explain my visual display and the related measurements I used.
Essential Questions:
● How do I organize and display data to make it understandable and useful?
● How precise do I need to be to represent my findings?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: measuring tape, ruler, yardstick
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 4 Focus: Collect measurement data to generate measurement by measuring lengths using rules marked with halves and fourths of an inch. (TB B3 pages 167-170 and WB B3 pages 131132)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Making Line Plots to Show the data by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in appropriate units— whole numbers, halves, or quarters. (TB B3 pages 171176 and WB B3 pages 133-134)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind workout (TB 3B page 177 and WB page 135)
● Math journal (TB 3B page 178 and WB 3B page 136)
● Unit Review (WB 3B pages 137-140)
● Cumulative Review 4 (WB 3B pages 141-144)
Grade 3 Math: Unit 10
● End-of Year Review (WB 3B pages 145-155)
Think! Math Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 10- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - June
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Problem Strings for Fluency and Beyond Grade 3 (Mosesson- Teig, Fosnot)
● K-5 Resources grade 3 math centers pages 259-384
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) p. 272-291
● Coherence Map Website (3.MD.3-4)
Grade 4 Math

Grade 4 Math
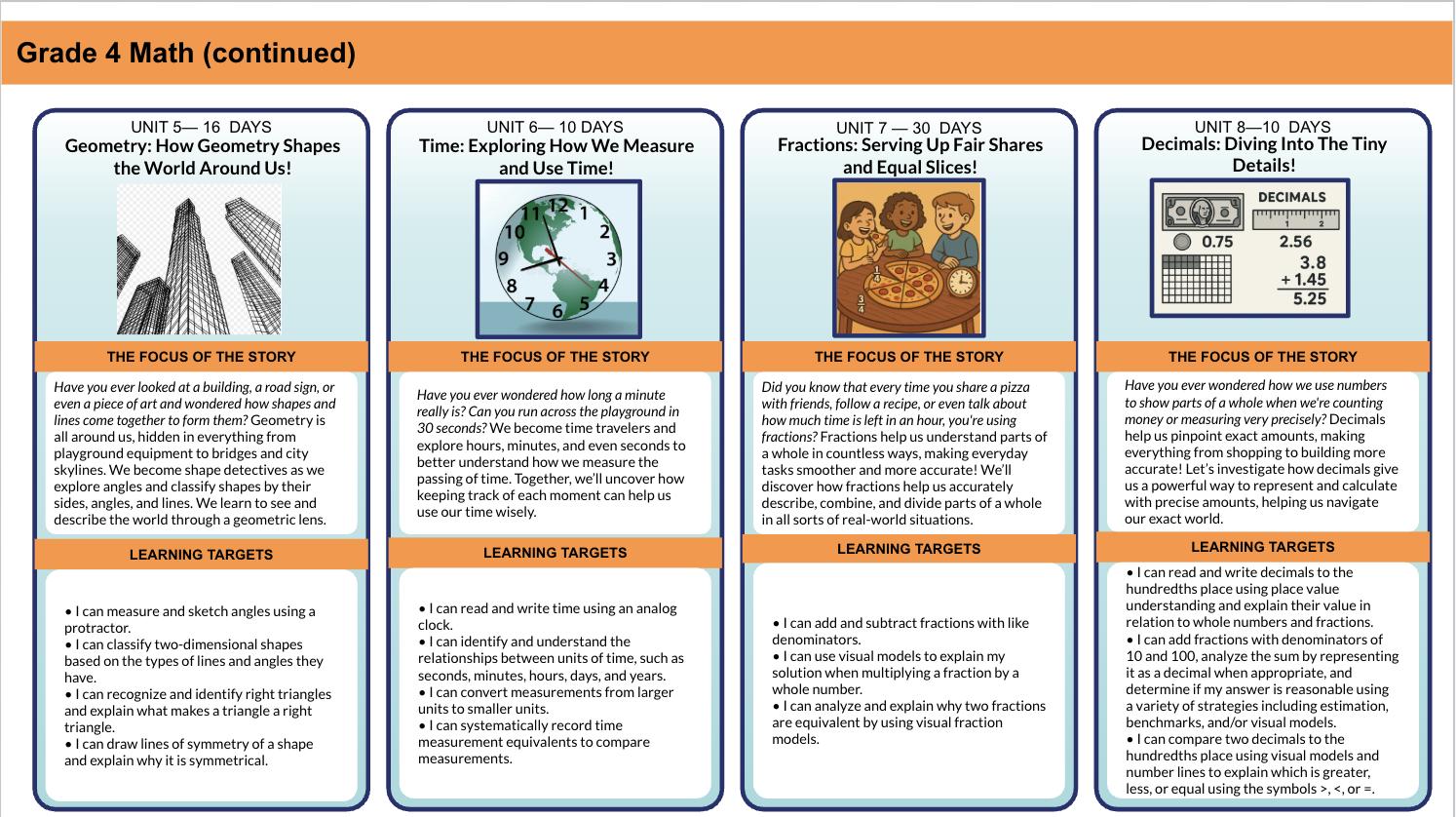
Grade 4 Math
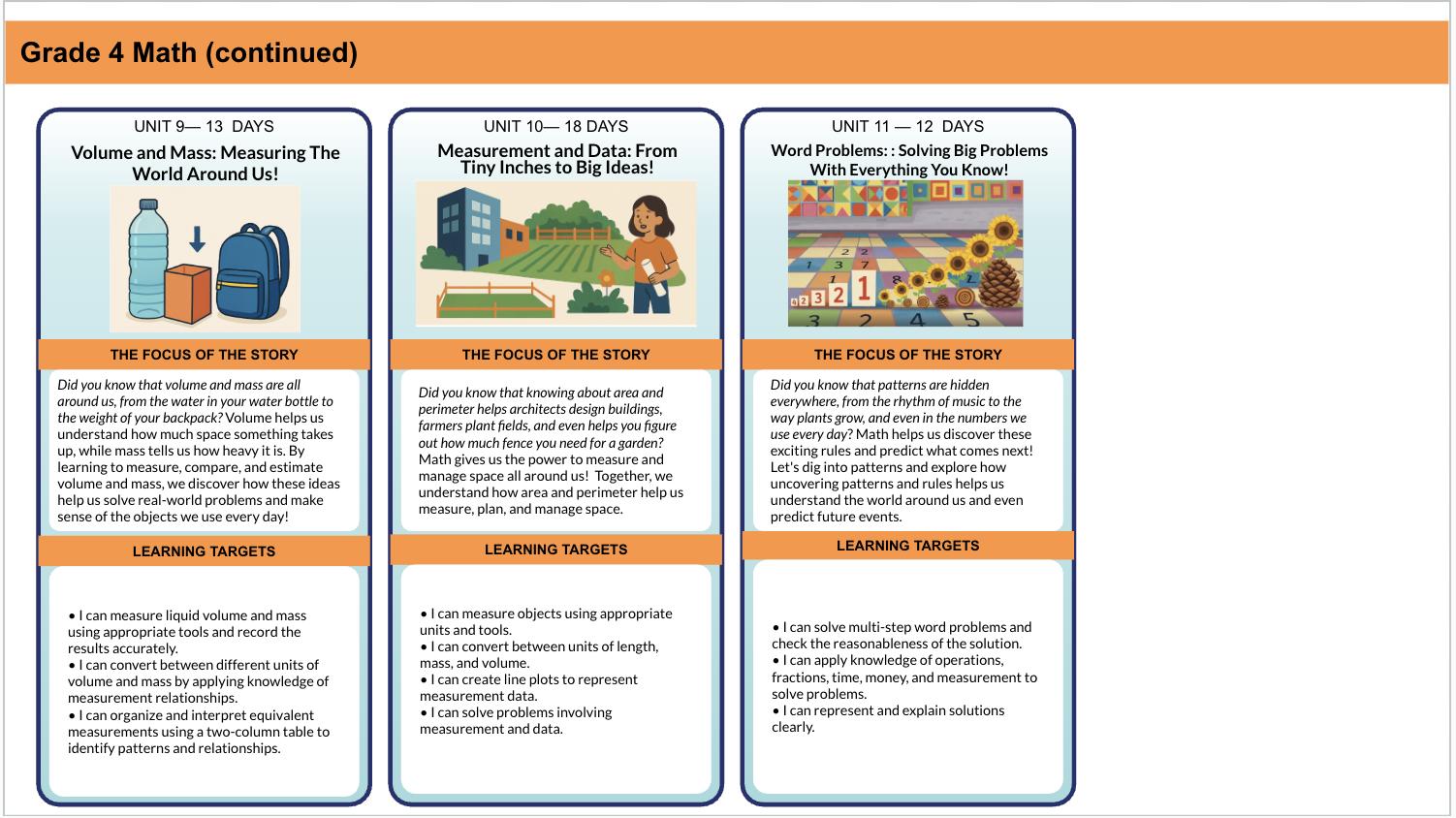
Grade 4 Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Grade 4
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 0 Title: Setting the Culture
Unit Overview:
Creating a collaborative environment where students appreciate productive noise and productive struggle. Learning that communication, perseverance, collaboration, and reflection are key to being successful mathematicians.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals Transfer Goals
NOTE: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards. The lessons in this unit support the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards:
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Understandings
● Mistakes and challenges help me grow as a math thinker.
● Talking and working with others can lead to stronger ideas, new strategies, and deepen learning.
● Using patterns, tools, and efficient strategies helps us solve problems and understand the world.
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
Grade 4 Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom expectations and routines that support collaborative math learning
● How to select and use mathematical tools and models strategically to support problem solving
● What productive struggle looks like and how to recognize when and how to revise thinking or try a new approach
● How to contribute respectfully and thoughtfully in math discussions by sharing ideas, asking questions, and giving feedback
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers and fractions with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
Summative Assessment
Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
First Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries- Have students respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes and ChecklistsMonitor during group tasks and partner work (suggested topics could be: who participates and frequency, who uses self-talk, problemsolving strategies)
● Problem Solving Checklist - used by students to self-monitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think.
Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a yearlong focus to strengthen number sense through problem-solving context.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Learning Targets:
Grade 4 Math: Unit 0
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers and fractions with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● Daily 15-minute sessions featuring five key workouts: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Solving Problems, Computational Fluency, and Number Lines.
● Student-led updates to key displays for hands-on engagement and routine development. Use of manipulatives, math talks, visual models, and discussion to foster deep conceptual understanding.
● Emphasis on mathematical discourse, reasoning, problem solving, and identity as a mathematician.
Second Topic: Setting the Culture through Think! Mathematics!
Learning Targets
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
Learning Activities:
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read The Most Magnificent Thing to foster a growth mindset and self-awareness.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use Crazy Colors activity to cultivate metacognition and perseverance.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using Venn Diagrams to foster communication and embrace differences.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use activity Disagreeing is Okay! We Can Still Be Friends to support respectful communication in challenging situations.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Initiate Fluency Routines to cultivate independence and collaboration through problem solving.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 0
● Lesson 6 Focus: Try Saving Sam to teach students the power of cooperation and perseverance.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Using the Tax Collector activity to assist students in planning and reflecting so they can understand the foundations of effective group work
● Lesson 8 Focus: Solve How Many Legs to foster a collaborative classroom culture.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Use the Folding Paper task to shift from speedy calculations to appreciating mathematical insight.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Play the Nine Lives game to empower students to leverage resources independently.
Think! Math Resources (online):
● Think Mathematics Online Toolbox
Additional Resources:
● The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Grade 4 Math: Unit 1
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 1 Title: Numbers to 1,000,000: What Does a Million Look Like
Unit Overview:
Have you ever wondered how the number of people in your house compares to the number of people on your street? Or how many people live in your town compared to your whole state? Together, we explore big numbers up to 1,000,000 as we solve real-world problems.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.NBT.A.1: Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right.
● 4.NBT.A.2: Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on the meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
● 4.NBT.A.3: Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place.
Understandings
● Numbers can be represented in different ways without changing their value.
● The position of a digit in a number determines its value and the relationship it has to other digits.
● Understanding place value is fundamental for reading, writing, comparing, and rounding decimals.
Knowledge
● Place value is based on groups of ten
● The position of a digit determines its value
● Rounding provides an estimate of a number
Transfer Goals
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (MP3 Constructing viable arguments and critiquing the reasoning of others) (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
● What strategies can I use to decide which digit to round and how?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is multiplied by powers of 10.
● I can use what I know about place value to compare numbers using >, <, and =.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 1
Key Vocabulary: hundred thousand, period, million
● I can read and write numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form.
● I can round to any place using place value.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 1 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of representing, rounding, and comparing numbers.
● Error Analysis: A student says 409,876, rounded to the nearest ten thousand, is 500,000. Is the student correct? Explain
● Math Journal: What does the digit 3 represent in the number 534,218?
● Activity Time: Compare multi-digit numbers
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Understanding and Working with Numbers to 1,000,000
Learning Targets:
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is multiplied by powers of 10.
● I can use what I know about place value to compare numbers using >, <, and =.
● I can read and write numbers in standard form, word form, and expanded form.
● I can round to any place using place value.
Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Essential Questions:
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
● What strategies can I use to decide which digit to round and how?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: number discs, place-value cards, and place-value chart
Grade 4 Math: Unit 1
Learning Activities:
● Lessons 1 & 2 Focus: Representing numbers to 1,000,000 to represent and read numbers up to one million in standard, word, and expanded form. (TB 4A pg. 3-12 WB 4A pg. 1-12)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Recognize the relationship between a digit in one place in a multi-digit number and a digit to its right to build understanding of how the same digit can have different values depending on its place. (TB 4A pg. 13-16 WB 4A pg. 13-14)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Comparing and ordering multi-digit numbers to understand how each digit’s position affects its value. (TB 4A pg. 17-22 WB 4A pg. 15-18)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Round whole numbers to any place to estimate and reason about quantities in real-world contexts. (TB 4A pg. 23-26 WB 4A pg. 19-22)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 4A pg. 27 WB 4A pg. 23)
● Math Journal (TB 4A pg. 27 WB 4A pg. 24)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 25-28)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 1- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Place Value (Answer sheets are available for each month): August, Weeks 14; October, Week 1, Week 2, Week 3, and Week 5; March, Week 2; May, Week 2
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from August and/or September
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) - Module 3
● Puzzle Packing Companies CFLM (Context For Learning Mathematics) Lessons 1-4
● K-5 Resources
○ Place Value (pg. 57-71)
○ Generate and Analyze Patterns (pg.73-88)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target D
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Website (4.NBT.A.1)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 2 Title: Addition and Subtraction: Step it Up
Unit Overview:
Have you ever wondered how many steps you take in a day? What about your whole family? Or even your entire class? We investigate these ideas as we accurately and efficiently add and subtract large numbers. We also continue to strengthen our use of rounding and estimation to be powerful problem solvers.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies, including rounding.
● 4.NBT.4- Fluently add and subtract multidigit whole numbers using the standard algorithm
Understandings
● Multi-digit addition and subtraction rely on understanding place value and the properties of operations.
● Estimating sums and differences helps determine whether results are reasonable.
● Real-world problems often require choosing an operation and an efficient strategy based on context.
Knowledge
● Addition and subtraction are inverse operations
● Understanding place value is critical for aligning digits and grouping and ungrouping correctly
● Estimation is effective for determining reasonableness
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Essential Questions
● How does place value guide my problemsolving when adding and subtracting?
● How can I use what I know about numbers and operations to solve problems accurately and efficiently?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can estimate sums and differences of numbers to 1,000,000.
● I can add multi-digit whole numbers fluently using the standard algorithm.
● I can subtract multi-digit whole numbers fluently using the standard algorithm.
● I can choose efficient strategies to solve
Grade 4 Math: Unit 2
Key Vocabulary: estimate, regrouping, algorithm addition and subtraction problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 2 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of finding sums and differences between multidigit numbers with and without regrouping.
● Error Analysis: A student subtracted 632,058 – 478,239 and got 164,281. Do you agree or disagree? If you disagree, show the correct steps.
● Math Journal: Solve 364,109 + 487,625. How can you use estimation to check to make sure your answer is reasonable?
● Activity Time: Add two 4-digit numbers and subtract two multi-digit numbers
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Adding and Subtracting Up to One Million
Learning Targets:
● I can estimate sums and differences of numbers to 1,000,000.
● I can add multi-digit whole numbers fluently using the standard algorithm.
● I can subtract multi-digit whole numbers fluently using the standard algorithm.
● I can choose efficient strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems.
Estimated # of Lessons: 12
Essential Questions:
● How does place value guide my problemsolving when adding and subtracting?
● How can I use what I know about numbers and operations to solve problems accurately and efficiently?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters, number discs
Grade 4 Math: Unit 2
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for addition within 1,000 to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4A 29-30)
● Lessons 1 Focus: Add thousands or hundreds to multi-digit whole numbers; Subtract thousands or hundreds from multi-digit whole numbers to deepen students’ understanding of place value. (TB 4A pg. 31-34, WB 4A pg. 31-32)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Estimating sums to 1,000,000 to assess the reasonableness of answers (TB 4A pg. 35-38, WB 4A pg. 33-36)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Add multi-digit whole numbers without regrouping fluently to deepen students’ understanding of place value. (TB 4A pg. 39-42, WB 4A pg. 37-38)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Add multi-digit whole numbers with regrouping fluently to reinforce place value and build the foundation for future skills (TB 4A pg. 43-48, WB 4A pg. 39-42)
● Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for subtraction within 1,000 to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4A 43-44)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Estimate differences within 1,000,000 to assess the reasonableness of answers (WB 4A 49-52, WB 4A 45-48)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtract multi-digit whole numbers fluently without regrouping to deepen students’ understanding of place value. (WB 4A 53-56, WB 4A 49-50)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Subtract multi-digit whole numbers fluently with regrouping to reinforce place value and build the foundation for future skills (WB 4A 57-62, WB 4A 51-54)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4A 63 WB 4A pg. 55)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4A 63 WB 4A pg. 56)
● Unit Review (WB 4A pg. 57-60)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 2- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Addition(Answer sheets are available for each month): Week May 1; Subtraction (Answer sheets are available for each month): September Week 3
● Word Problem of the Week- Choose a problem from October
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessment
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice- (O’Connell) Module 4
● K-5 Resources- Operations to Perform Multi-digit addition and subtraction (pg. 91-95)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target E
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Website (4.NBT.B.4)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 18
Unit 3 Title: Multiplication and Division: Math Masterpieces
Unit Overview:
Have you ever wondered how many steps you take in a day? What about your whole family? Or even your entire class? We investigate these ideas as we accurately and efficiently add and subtract large numbers. We also continue to strengthen our use of rounding and estimation to be powerful problem solvers.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.OA.4- Find all factor pairs for a whole number in the range 1-100. Recognize that a whole number is a multiple of each of its factors. Determine whether a given whole number in the range 1-100 is a multiple of a given one-digit number. Determine whether a given whole number in the range 1-100 is prime or composite.
● 4.OA.1- Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 × 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations.
● 4.NBT.5- Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
● 4.NBT.6- Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
● Multiplication and division are connected operations that can be used to solve problems, model comparisons, and represent thinking in different ways.
● Using place value strategies and models helps to multiply and divide larger numbers accurately and to explain their reasoning clearly.
Knowledge
● Determine whether a number between 1 and 100 is prime or composite based on its factors
● There are various strategies for multi-digit multiplication and division
● Remainders must be interpreted within the context of a problem
● A factor pair consists of two numbers that, when multiplied together, equal a given number
● Multiplication equations can represent a comparison, such as understanding 35 = 5 × 7 as “35 is 5 times as many as 7.”
Key Vocabulary: factor pair, prime number, composite number, remainder, divisible, partial quotient
● How can I use the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems?
● What strategies am I using to estimate and check if my answers are reasonable?
● What does a remainder tell me, and how do I decide what to do with it in a problem?
● How can understanding factors and multiples help me determine if a number is prime, composite, or divisible by another number?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can find all factor pairs for whole numbers within 100.
● I can identify prime and composite numbers.
● I can multiply multi-digit numbers by 1-digit and 2-digit numbers and explain using visual models.
● I can divide multi-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers and explain using visual models.
● I can interpret remainders in division problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 3 Assessment
● IAB- Number and Operations in Base Ten
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of factor pairs, multiples of whole numbers, determining if a number is prime or composite, multiplying multi-digit numbers, dividing multi-digit numbers by 1 digit, and dividing 2-digit by 2-digit numbers
● Error Analysis: A student divided 154 ÷ 6 and got 24 with a remainder of 2. Do you agree? Justify your answer with a model and words.
● Math Journal: List all factor pairs of 36. Is this number a prime or composite number? Explain your thinking.
● Activity Time: Determine whether a given
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
whole number is prime or composite, Multiply a multi-digit number and a 1 digit number, Write division equations involving whole-number quotients
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- CFLM is designed to be taught before explicitly teaching concepts and skills in a unit. Students engage with real-world problems, or "contexts," that spark curiosity and exploration. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and class discussions (called Math Congresses), students build on their existing knowledge, develop strategies, and create mathematical models. This approach supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical ideas, explain their reasoning, make meaningful connections, and develop a strong foundation for future learning.
First Topic: Number Detectives (CFLM)
Learning Targets:
● I can find all factor pairs for whole numbers within 100.
● I can identify prime and composite numbers.
Estimated # of Lessons: 4
Essential Questions:
● How can understanding factors and multiples help me determine if a number is prime, composite, or divisible by another number?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: math journals, anchor chart paper
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Investigate numbers 2, 3, and 4 to determine if each is divisible by 322.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Gallery walk and Congress on the previous lesson for students to read and write mathematical arguments to convince peers of insights.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Multiply numbers by 9 and 10 to investigate divisibility rules of 9 and other numbers.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Gallery walk and Congress on the previous lesson for students to read and write mathematical arguments to convince peers of insights.
● Lessons 5 and 6 are skipped.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Investigate the number of factors a number has to determine prime and composite numbers.
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students. NOTE: Some students may be using methods to solve the problem that are not grade-level appropriate. For example, if a student is using the multiplication algorithm to multiply numbers, the strategy should be included but not explicitly taught.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the
student's needs.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
Second Topic: Factors, Multiples, and Prime & Composite Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can find all factor pairs for whole numbers within 100.
● I can identify prime and composite numbers.
Estimated # of Lessons: 2
Essential Questions:
● How can understanding factors and multiples help me determine if a number is prime, composite, or divisible by another number?
Materials: two sets of number cards (1-9), square tiles, number discs, unit cubes
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 0: Develop fluency for multiplication within 100 to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4A pg. 65-66)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Find factor pairs of a whole number; Recognize that a whole number is a multiple of each of its factors; Determine whether a whole number is a multiple of a given one-digit number to reinforce multiplication and division, build pattern recognition, and prepare students for fractions. (TB 4A pg. 67-70, WB 4A pg. 63-66)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Determine whether a whole number is prime or composite to build number sense and support multiplication and division. (TB 4A 71-76, WB 4A pg. 67-68)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Problem of the Week - Factors, Prime and Composite (Answer sheets are available for each month): September Week 4; October Week 4; November Week 3; February Week 2 and Week 3
● Word Problem of the Week- Choose a problem from November
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessment
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) - Module 2
● The Teacher’s Lounge CFLM (Context For Learning Mathematics) Lessons 1-4
● Math K-5 Resources-GAIN FAMILIARITY WITH FACTORS AND MULTIPLES (pg.44-49)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map: Familiarity with Factors and Multiples: 4.OA.B.4
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
Third Topic: Multiplication
Learning Targets:
● I can multiply multi-digit numbers by 1digit and 2-digit numbers and explain using visual models.
Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Essential Questions:
● How can I use the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems?
● What strategies am I using to estimate and check if my answers are reasonable?
● What does a remainder tell me, and how do I decide what to do with it in a problem?
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
Materials: two sets of number cards (1-9), square tiles, number discs, unit cubes
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 3 Focus: Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison; Represent multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations to reason abstractly and quantitatively. (TB 4A pg. 77-80 WB 4A pg. 69-70)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Multiply 1-digit or 2-digit numbers by multiples of 10, 100, or 1,000 to reinforce place value understanding and to promote mental math strategies. (TB 4A pg. 81-84, WB 4A pg. 71-74)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Multiply a 2-digit number and a 1-digit number to develop their understanding of multiplication and prepare them for more advanced math. (TB 4A pg. 85-90, WB 4A pg. 75-78)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Multiply a multi-digit number and a 1-digit number to develop their understanding of multiplication and prepare them for more advanced math. (TB 4A pg. 91-96, WB 4A pg. 79-86)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Multiply two multiples of 10 to develop their understanding of multiplication and prepare them for more advanced math. (TB 4A pg. 97-100, WB 4A pg. 87-88)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Multiply two 2-digit numbers to develop their understanding of multiplication and prepare them for more advanced math. (TB 4A pg. 101-104, WB 4A pg. 89-92)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Problem of the Week - Multiplication(Answer sheets are available for each month): September Week 1, November Week 3, January Week 1, February Week 1, April Week 3, May Week 3
● Word Problem of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice- Module 1 and Module 5
● Math K-5 Resources-USE PLACE VALUE UNDERSTANDING AND PROPERTIES OF OPERATIONS TO PERFORM MULTI-DIGIT ARITHMETIC pages 97-148
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Multiplicative Comparison: (4.OA.A.1) and Multiplication: (4.NBT.B.5)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Fosnot)
Third Topic: Division
Learning Targets:
● I can divide multi-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers and explain using visual models.
● I can interpret remainders in division problems.
Estimated # of Lessons: 5
Essential Questions:
● How can I use the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems?
● What does a remainder tell me, and how do I decide what to do with it in a problem?
Materials: two sets of number cards (1-9), square tiles, number discs, unit cubes
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for division within 100 to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4A pg. 93-94)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Divide tens, hundreds, and thousands by 1-digit numbers to reinforce division and students’ understanding of place value, build pattern recognition, and prepare students for
Grade 4 Math: Unit 3
fractions. (TB 4A pg. 105-108, WB 4A pg. 95-96)
● Lessons 10 -12 focus: Find whole number quotients and remainders with divisors up to 10 to solve real-world problems involving comparison, grouping, and equal sharing to deepen understanding of operations. (TB 4A pg. 109-122, WB 4A pg. 97-110)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 4A pg. 123 WB 4A pg. 111)
● Math Journal (TB 4A pg. 123 WB 4A pg. 112)
● Unit Review (WB 4A pg. 113-118)
● Cumulative Review 1 (WB 4A pg. 119-122)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 3- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
Problem of the Week - Division (Answer sheets are available for each month): September Week 2, November Week 1, December Week 3, January Week 3, April Week 1, May Week 4
● Word Problem of the Week- Choose a problem that correlates with the month
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Math in Practice- Module 6
● Math K-5 Resources- Use Place Value Understanding and Properties of Operations to Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic (pages 150-176)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target E
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: The Baker
● Coherence Map Division: (4.NBT.B.6)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 7
Unit 4 Title: Number Patterns and Shape Patterns: Bringing Everything Together
Unit Overview:
Have you ever noticed that patterns are everywhere around us? When you think about patterns, do you picture numbers and shapes? We become skilled at figuring out tricky patterns and seeing things that aren't obvious right away.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.OA.5- Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings
● Patterns have rules that can be used to predict or identify missing values.
● Patterns can appear in many forms and are foundational to algebraic thinking.
● Exploring and describing patterns helps build reasoning skills that support generalization.
Essential Questions
● How do patterns help me make predictions or find relationships in math?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Patterns have rules that can be used to describe how they change or grow
● Patterns can be used to make predictions
● Represent and extend patterns both visually and numerically
Key Vocabulary: sequences
● I can identify patterns and explain what's happening using mathematical language.
● I can create a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule and explain the rule I used to create the pattern.
● I can extend patterns and predict future terms.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 4
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 4 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of identifying patterns and extending them.
● Error Analysis: Liam was given this rule: "Start at 2 and multiply by 2." He wrote this number pattern: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 What mistake did Liam make?
Explain what he did wrong and show the correct pattern.
● Math Journal: Draw a growing pattern using triangles and circles. Explain how you could find the tenth figure.
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Recognizing and Describing Patterns in Numbers and Shapes
Learning Targets:
● I can identify patterns and explain what's happening using mathematical language.
● I can create a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule and explain the rule I used to create the pattern.
● I can extend patterns and predict future terms.
Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Essential Questions:
● How do patterns help me make predictions or find relationships in math?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: 2D shape manipulatives, 3D shape manipulatives, counters, hundred chart, paper cut-outs
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Identify the rule of a number pattern; Complete number patterns to develop
Grade 4 Math: Unit 4
critical thinking, recognize relationships, and prepare for higher-level math concepts. (TB 4A pg. 127-130, WB 4A pg. 123-124)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Generate a number pattern that follows a given rule to develop critical thinking, recognize relationships, and prepare for higher-level math concepts. (TB 4A pg. 131-134, WB 4A pg. 125-126)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Make patterns using two-dimensional shapes to build foundational skills in geometry, spatial reasoning, and mathematical thinking. (TB 4A pg. 135-138, WB 4A pg. 127-128)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Make patterns using two-dimensional shapes; Identify arithmetic patterns. to build essential skills in mathematical reasoning, problem-solving, and future algebraic thinking (TB 4A pg. 139-142, WB 4A pg. 129-130)
End Of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4A 143, WB 4A pg. 131)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4A 143, WB 4A pg. 132)
● Unit Review (WB 4A pg. 133-134)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 4- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - Patterns(Answer sheets are available for each month): November Week 1, January Week 4, June Week 1
● Word Problem of the Week- Choose a problem from December
Additional Resources:
● Math K-5 Resources-Generate and Analyze Patterns (pg. 44-55)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target C
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Generalize and Analyze Patterns: (4.OA.C.5)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 5
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 16
Unit 5 Title: Geometry:
Unit Overview:
How Geometry Shapes the World Around Us
Have you ever looked at a building, a road sign, or even a piece of art and wondered how shapes and lines come together to form them? Geometry is all around us, hidden in everything from playground equipment to bridges and city skylines. We become shape detectives as we explore angles and classify shapes by their sides, angles, and lines. We learn to see and describe the world through a geometric lens.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.G.1- Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures.
● 4.G.2-Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, or the presence or absence of angles of a specified size. Recognize right triangles as a category, and identify right triangles.
● 4.G.3-Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts. Identify line-symmetric figures and draw lines of symmetry.
● 4.MD.5- Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and understand concepts of angle measurement
● 4.MD.6-Measure angles in whole-number degrees using a protractor. Sketch angles of specified measure.
● 4.MD.7- Recognize angle measure as additive. When an angle is decomposed into non-overlapping parts, the angle measure of the whole is the sum of the angle measures of the parts. Solve addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems, e.g., by using an equation with a symbol for the unknown angle measure.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 5
Understandings Essential Questions
● Shapes can be described and classified based on their attributes, such as angles, lines, and symmetry, to describe and analyze them more precisely.
Knowledge
● Shapes are defined by their basic geometric building blocks
● Angles are classified by their size
● Geometric figures can be categorized based on their properties
● Angles are measurable and additive
Key Vocabulary: point, line, line segment, ray, acute angle, obtuse angle, right angle, degree, protractor, intersect, perpendicular, parallel, acute triangle, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, right triangle, scalene triangle, parallelogram, line of symmetry, symmetrical
● How can I describe and classify shapes using geometric terms?
● How can I use tools and/or strategies to measure, draw, and find unknown angles?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure and sketch angles using a protractor.
● I can identify and draw parallel and perpendicular lines.
● I can identify and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles (right, acute, and obtuse).
● I can classify two-dimensional shapes based on the types of lines and angles they have.
● I can recognize and identify right triangles and explain what makes a triangle a right triangle.
● I can find unknown angles by using addition or subtraction and what I know about angle relationships.
● I can draw lines of symmetry of a shape and explain why it is symmetrical.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 5 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of acute and obtuse angles, measure angles using a protractor, identify parallel and perpendicular lines, find symmetry, and additive angle measures using angle parts
● Error Analysis: Two angles add up to 90°. One angle is 35°. Talia says the other angle is 75°. Do you agree with Talia? Explain her mistake and show the correct answer.
● Math Journal: Draw and label: a point, a line, a ray, and a line segment. Then draw an acute, right, and obtuse angle
● Activity Time: Drawing, measuring, and recognizing angle measures as additive, and drawing lines of symmetry on two-dimensional figures
Grade 4 Math: Unit 5
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Understanding Geometry
Learning Targets:
● I can measure and sketch angles using a protractor.
● I can identify and draw parallel and perpendicular lines.
● I can identify and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles (right, acute, and obtuse).
● I can classify two-dimensional shapes based on the types of lines and angles they have.
● I can recognize and identify right triangles and explain what makes a triangle a right triangle.
● I can find unknown angles by using addition or subtraction and what I know about angle relationships.
● I can draw lines of symmetry of a shape and explain why it is symmetrical.
Estimated # of Lessons: 14
Essential Questions:
● How can I describe and classify shapes using geometric terms?
● How can I use tools and/or strategies to measure, draw, and find unknown angles?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: blank cards, set square, protractor, square grid
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Identify and draw points, lines, line segments, and rays to understand the basic building blocks of geometry. (TB 4A pg. 147-150, WB 4A pg. 135-136)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Identify acute angles, obtuse angles, and right angles to recognize and understand angles as a key part of geometry and everyday problem-solving. (TB 4A pg. 151-154, WB 4A pg. 137-140)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Measure angles using a protractor; Recognize angle measure as additive to deepen their understanding of geometry and support critical thinking and problem-solving. (TB 4A pg. 155-162, WB 4A pg. 141-144)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 5
● Lesson 4 Focus: Draw angles of a specified measure to develop precision, deepen their understanding of geometry, and build important problem-solving skills. (TB 4A pg. 163-166, WB 4A pg. 145-148)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Solve for an unknown angle measure to support critical thinking and problemsolving. (TB 4A pg. 167-172, WB 4A pg. 149-150)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Identify and draw perpendicular lines to build geometric knowledge and recognize important relationships in both math and the real world. (TB 4A pg. 173-176, WB 4A pg. 151-152)
● Lesson 7 & 8 Focus: Identify and draw parallel lines to build geometric knowledge and recognize important relationships in both math and the real world. (TB 4A pg. 177-186, WB 4A pg. 153-156)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Identify acute triangles, equilateral triangles, isosceles triangles, right triangles, and scalene triangles to build a strong foundation in geometry and help them develop essential mathematical thinking skills. (TB 4A pg. 187-190, WB 4A pg. 157-158)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Identify polygons and classify them based on the presence of parallel and/or perpendicular lines and the type of angles they have to build a deeper understanding of geometric concepts and develop critical thinking skills. (TB 4A pg. 191-196, WB 4A pg. 159-160)
● Lesson 11 & 12 Focus: Identify and draw lines of symmetry using two-dimensional figures to strengthen students’ understanding of geometry, pattern recognition, and spatial reasoning. (TB 4A pg. 197-204, WB 4A pg. 161-164)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4A 205, WB 4A pg. 165)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4A 206, WB 4A pg. 132)
● Unit Review (WB 4A pg. 167-172)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 5- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - Angles(Answer sheets are available for each month): November Week 2, December Week 2, March Week 3
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from January
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) - Module 14
● The Skateboard Lane CFLM (Context For Learning Mathematics) Lessons 1-4
● K-5 Resources-
○ Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts of Angle and Measure Angles (pg. 281301)
○ Draw And Identify Lines And Angles, And Classify Shapes By Properties Of Their Lines And Angles (pg. 305-321)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target K and L
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: Squares and Circles
● Coherence Map Geometry: (4.G.A.1-3)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 6
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 6 Title: Time: How We Use and Measure Time
Unit Overview:
Have you ever wondered how long a minute really is? Can you run across the playground in 30 seconds? We become time travelers and explore hours, minutes, and even seconds to better understand how we measure the passing of time. Together, we’ll uncover how keeping track of each moment can help us use our time wisely.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.MD.1-Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units, including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz..; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a twocolumn table.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings
● Units within a measurement system are related, and understanding those relationships allows conversion between different-sized units.
● Knowing how to express measurements in different units helps to compare, organize, and solve problems more effectively.
Essential Questions
● How can I use conversions between different units of time measurement to solve problems?
● How can I organize equivalent measures to help me better understand time conversions?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Relative sizes of time measurement units within a system
● Convert between larger and smaller units of time measurement
● I can read and write the time using an analog clock.
● I can identify and understand the relationships between units of time, such as
Grade 4 Math: Unit 6
Key Vocabulary: No new vocabulary
seconds, minutes, hours, days, and years.
● I can convert measurements from larger units to smaller units.
● I can systematically record time measurement equivalents to compare measurements.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 6 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of converting measurements of time from larger to smaller units.
● Error Analysis: Ava says that “3 hours is the same as 360 seconds because there are 120 seconds in one hour.” Do you agree with Ava?
Explain the mistake she made and show the correct conversion.
● Math Journal: Why is it important to know how to convert and calculate time? Give an example from your day
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Understanding Time
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write the time using an analog clock.
● I can identify and understand the relationships between units of time, such as seconds, minutes, hours, days, and years.
● I can convert measurements from larger units to smaller units.
● I can systematically record time measurement equivalents to compare
Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Essential Questions:
● How can I use conversions between different units of time measurement to solve problems?
● How can I organize equivalent measures to help me better understand time conversions?
Grade 4 Math: Unit 6
measurements.
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: digital stopwatch, analog clock
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Use seconds to describe a duration to understand that time is made up of smaller, measurable units, and it lays the foundation for understanding how time is structured and measured. (TB 4A pg. 211-216, WB 4A pg. 173-174)
● Lesson 2 & 3 Focus: Convert from hours and minutes to minutes/Convert from minutes and seconds to seconds to understand how units of time relate to each other and to prepare them for solving real-world problems. (TB 4A pg. 217-224, WB 4A pg. 175-178)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Find the duration when given the start time and end time/Compare durations of time to understand how time works and support problem-solving in both real-world situations. (TB 4A pg. 225-228, WB 4A pg. 179-184)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Skip
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4A pg. 233 WB 4A pg. 187)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4A pg. 233 WB 4A pg. 188)
● Unit Review (WB 4A pg. 190-192 )
● Cumulative Review 2 (WB 4A pg. 193-196)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 6- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - Time(Answer sheets are available for each month): January, Week 2 and February, Week 4
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from February
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 11
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4- (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Coherence Map Measurement and Data (4.MD.A.2)
● Place value is essential for understanding and comparing decimals
Key Vocabulary: decimal, decimal point, tenth, hundredth
● I can read and write decimals to the hundredths place using place value understanding and explain their value in relation to whole numbers and fractions.
● I can add fractions with denominators of 10 and 100, analyze the sum by representing it as a decimal when appropriate, and determine if my answer is reasonable using a variety of strategies, including estimation, benchmarks, and/or visual models.
● I can change a fraction with a denominator of 10 into an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100.
● I can compare two decimals to the hundredths place using visual models and number lines to explain which is greater, less, or equal using the symbols >, <, or =.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 8 Assessment
● IAB- Number and Operations- Fractions
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of converting fractions to decimals and drawing a model to represent the decimal, converting decimals to fractions, creating equivalent fractions with denominators of 10 or 100, comparing decimals, adding and subtracting decimals to the hundredths place
● Error Analysis: Ethan says, "I think 3/10 is the same as 0.03 because both have a 3 in them." Explain the mistake he made and show the correct decimal for 3/10.
● Math Journal: Using a drawing or model to show that 0.7 is greater than 0.45. Explain how the model supports your thinking.
● Activity Time: Use the decimal notation for fractions with denominators of 100
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Exploring Decimals
Learning Targets:
● I can read and write decimals to the hundredths place using place value understanding and explain their value in relation to whole numbers and fractions.
● I can add fractions with denominators of 10 and 100, analyze the sum by representing it as a decimal when appropriate, and determine if my answer is reasonable using a variety of strategies, including estimation, benchmarks, and/or visual models.
● I can change a fraction with a denominator of 10 into an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100.
● I can compare two decimals to the hundredths place using visual models and number lines to explain which is greater, less, or equal using the symbols >, <, or =.
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● How can I represent fractions and decimals in different ways and show they are equal?
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters, number line template, place value chart, number discs, stop watch
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for addition and subtraction of fractions with like denominators to build a strong foundation for understanding fractions and prepare students for more complex fraction operations. (WB 4B 51-52)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Representing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 10) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 75-78, WB 4B pg. 53-54)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Representing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 10) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 79-82, WB 4B pg. 55-60)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Writing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 100) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 83-88, WB 4B pg. 61-64)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Compare two decimals to hundredths to develop a strong understanding of number size, make meaningful comparisons, and prepare for real-world problem solving. (TB 4B pg. 89-92, WB 4B pg. 65-66)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Adding two decimals to hundredths to develop precision with place value, solve real-world problems involving money and measurement, and build a foundation for more advanced
math. (TB 4B pg. 93-98, WB 4B pg. 67-70)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtracting two decimals to hundredths to develop precision with place value, solve real-world problems involving money and measurement, and build a foundation for more advanced math. (TB 4B pg. 99-104, WB 4B pg. 71-74)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 105, WB 4B pg. 75)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 105, WB 4B pg. 76)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 77-80)
● Cumulative Review 3 (pg. 81-82)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 8- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Decimals (Answer sheets are available for each month): April Week 4
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from April
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 10
● K-5 Resources- Understand Decimal Notation For Fractions And Compare Decimal Fractions (pg. 244-253)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target H
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Numbers and Operations Fractions(4.NF.C.5-7)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 7
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 30
Unit 7 Title: Fractions: Serving Up Fair Shares and Equal Slices
Unit Overview:
Did you know that every time you share a pizza with friends, follow a recipe, or even talk about how much time is left in an hour, you're using fractions? Fractions help us understand parts of a whole in countless ways, making everyday tasks smoother and more accurate! We’ll discover how fractions help us accurately describe, combine, and divide parts of a whole in all sorts of real-world situations.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.NF.1-Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions.
● 4.NF.2- Compare two fractions with different numerators and different denominators, e.g., by creating common denominators or numerators, or by comparing to a benchmark fraction such as 1/2. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
● 4.NF.3- Understand a fraction a/b with a > 1 as a sum of fractions 1/b
● 4.NF.4-Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number.
Understandings
● Equivalent fractions represent the same quantity, even if they look different.
● Adding and subtracting fractions requires understanding the relationship between numerators and denominators.
● Fractions represent parts of a whole that can be compared, ordered, and operated on just like whole numbers.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Essential Questions
● How can I use visual models to demonstrate why equivalent fractions look different?
● What strategies am I using to compare two fractions? How does this build my understanding of the size of fractions?
● How can I break down fractions greater than 1 into smaller parts or sums of unit fractions? How does it help me add and subtract
Grade 4 Math: Unit 7
fractions?
Knowledge
● Fractions can be added and subtracted if they refer to the same whole
● Mixed numbers combine whole numbers and fractions
● Multiplying a fraction by a whole number involves repeated addition
Key Vocabulary: equivalent fraction, mixed number
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can add and subtract fractions with like denominators.
● I can use visual models to explain my solution when multiplying a fraction by a whole number.
● I can analyze and explain why two fractions are equivalent by using visual fraction models
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 7 Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of equivalent fractions, mixed numbers, decomposing fractions, adding fractions with like denominators, subtracting fractions with like denominators, comparing fractions, ordering fractions, multiplying a whole number by a fraction.
● Error Analysis:
○ Sara says that "1/8 is bigger than 1/4 because 8 is more than 4." Do you agree with Sara? Explain why you agree or disagree. If you disagree, use a model or number line to show the correct comparison.
○ Layla says “3 ¼ is the same as 4/4 + ¼ ." Do you agree with Layla? Explain her mistake and write the correct decomposition of 3 ¼.
● Math Journal: Create two equivalent fractions and explain why they are equal.
● Activity Time: Partitioning rectangles into equivalent shapes and Decompose a mixed number into a whole number and a fraction
Grade 4 Math: Unit 7
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs
First Topic: Understanding Fractions
Learning Targets:
● I can add and subtract fractions with like denominators.
● I can use visual models to explain my solution when multiplying a fraction by a whole number.
● I can analyze and explain why two fractions are equivalent by using visual fraction models
Estimated # of Lessons: 25
Essential Questions:
● How can I use visual models to demonstrate why equivalent fractions look different?
● What strategies am I using to compare two fractions? How does this build my understanding of the size of fractions?
● How can I break down fractions greater than 1 into smaller parts or sums of unit fractions? How does it help me add and subtract fractions?
Key: Bold- Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters, unit cubes, fraction area models, paper cut-outs (rectangles), 10-sided dice, fraction discs, number line template, 6-sided dice, fraction bars
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for multiplication and division within 100 to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4B 1-2)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way to build a deep, flexible understanding of how fractions work and to prepare them for more advanced math concepts. (TB 4B pg. 3-8, WB 4B pg. 3-4)
● Lesson 2 & 3 Focus: Adding fractions to understand how parts of a whole combine, develop a strong foundation for higher-level math, and apply math in meaningful real-world situations. (TB 4B pg. 9-16, WB 4B pg. 5-8)
● Lesson 4 & 5 Focus: Subtracting fractions to understand how parts of a whole can be taken away, build deep mathematical reasoning, and solve meaningful, real-world problems. (TB 4B pg. 17-24, WB 4B pg. 9-12)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Write mixed numbers when given the fraction models/Represent mixed numbers on a number line to develop a complete and flexible understanding of numbers, especially how fractions relate to whole numbers. (TB 4B pg. 25-28, WB 4B pg. 13-18)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Recognize and generate equivalent fractions to build a deep understanding of how fractions work, and how they can be expressed in different forms. (TB 4B pg. 29-32, WB 4B pg. 19-22)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Skip
● Lesson 9 Focus: Compare two fractions with different numerators or different denominators,
Grade 4 Math: Unit 7
using the symbols >, =, or <; Recognize that comparisons of fractions are valid only when the fractions refer to the same whole to help students develop a deep, accurate understanding of fractions and their real-world meaning. (TB 4B pg. 37-42, WB 4B pg. 25-28)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Compare and order three fractions with different numerators or different denominators. Recognize that comparisons of fractions are valid only when the fractions refer to the same whole to develop a strong understanding of number size, make meaningful comparisons, and prepare for real-world problem solving. (TB 4B pg. 43-46, WB 4B pg. 29-30)
● Lesson 11 Focus: Decompose a mixed number into a whole number and a fraction to understand the structure of numbers, strengthen their number sense, and prepare for more advanced operations with fractions and equations. (TB 4B pg. 47-50, WB 4B pg. 31-32)
● Lesson 12 Focus: Add mixed numbers with the same denominator to understand how fractional quantities combine or are separated, apply math in real-life contexts, and build a strong foundation for more advanced math. (TB 4B pg. 51-54, WB 4B pg. 33-34)
● Lesson 13 Focus: Subtract mixed numbers with the same denominator to understand how fractional quantities combine or are separated, apply math in real-life contexts, and build a strong foundation for more advanced math. (TB 4B pg. 55-58, WB 4B pg. 35-36)
● Lesson 14 & 15 Focus: Multiplying fractions to understand how to scale and combine fractional quantities, solve real-world problems, and build essential skills for higher-level math. (TB 4B pg. 5966, WB 4B pg. 37-40)
● Lesson 16 Focus: Multiply a mixed number by a whole number to understand how to find total amounts when quantities have both whole and fractional parts. (TB 4B pg. 67-70, WB 4B pg. 4142)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 71, WB 4B pg. 43)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 71, WB 4B pg. 43)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 45-50)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 7- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Fractions (Answer sheets are available for each month): March Week 1
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from March
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Modules 7-9
● Field Trips and Fundraisers CFLM (Context For Learning Mathematics) Lessons 1-5
● K-5 Resources- Number and Operations: Fractions (pages 177-243)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target F and G
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review 4.NF.1 and 2
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review 4.NF.4
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: Colorful Walls
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: Leapfrog Fractions
● Coherence Map Measurement and Data (4.NF.A.1-4)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 8
Course Name: Grade 4 Math Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 8 Title: Decimals: Diving into the Tiny Details
Unit Overview:
Have you ever wondered how we use numbers to show parts of a whole when we're counting money or measuring very precisely? Decimals help us pinpoint exact amounts, making everything from shopping to building more accurate! Let’s investigate how decimals give us a powerful way to represent and calculate with precise amounts, helping us navigate our exact world.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.NF.5- Express a fraction with a denominator of 10 as an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100, and use this technique to add two fractions with respective denominators of 10 and 100
● 4.NF.6-Use decimal notation for fractions with denominators 10 or 100
● 4.NF.7-Compare two decimals to hundredths by reasoning about their size. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two decimals refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual model.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Fractions and decimals are different ways to represent the same part of a whole.
● Decimals with denominators are another way to represent fractions, specifically with denominators of 10 and 100
● Understanding place value is fundamental for reading, writing, and comparing decimals.
● How can I represent fractions and decimals in different ways and show they are equal?
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
Knowledge Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● Place value is essential for understanding and comparing decimals
● I can read and write decimals to the hundredths place using place value understanding and explain their value in relation to whole numbers and fractions.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 8
● I can add fractions with denominators of 10 and 100, analyze the sum by representing it as a decimal when appropriate, and determine if my answer is reasonable using a variety of strategies, including estimation, benchmarks, and/or visual models.
● I can change a fraction with a denominator of 10 into an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100.
Key Vocabulary: decimal, decimal point, tenth, hundredth
● I can compare two decimals to the hundredths place using visual models and number lines to explain which is greater, less, or equal using the symbols >, <, or =.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 8 Assessment
● IAB- Number and Operations- Fractions
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of converting fractions to decimals and drawing a model to represent the decimal, converting decimals to fractions, creating equivalent fractions with denominators of 10 or 100, comparing decimals, adding and subtracting decimals to the hundredths place
● Error Analysis: Ethan says, "I think 3/10 is the same as 0.03 because both have a 3 in them." Explain the mistake he made and show the correct decimal for 3/10.
● Math Journal: Using a drawing or model to show that 0.7 is greater than 0.45. Explain how the model supports your thinking.
● Activity Time: Use the decimal notation for fractions with denominators of 100
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Exploring Decimals
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Learning Targets:
Grade 4 Math: Unit 8
● I can read and write decimals to the hundredths place using place value understanding and explain their value in relation to whole numbers and fractions.
● I can add fractions with denominators of 10 and 100, analyze the sum by representing it as a decimal when appropriate, and determine if my answer is reasonable using a variety of strategies, including estimation, benchmarks, and/or visual models.
● I can change a fraction with a denominator of 10 into an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100.
● I can compare two decimals to the hundredths place using visual models and number lines to explain which is greater, less, or equal using the symbols >, <, or =.
Essential Questions:
● How can I represent fractions and decimals in different ways and show they are equal?
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters, number line template, place value chart, number discs, stop watch
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for addition and subtraction of fractions with like denominators to build a strong foundation for understanding fractions and prepare students for more complex fraction operations. (WB 4B 51-52)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Representing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 10) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 75-78, WB 4B pg. 53-54)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Representing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 10) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 79-82, WB 4B pg. 55-60)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Writing fractions as decimals (with denominator of 100) to understand different ways to express parts of a whole, connect fractions to our base 10 number system, and prepare for real-world applications (TB 4B pg. 83-88, WB 4B pg. 61-64)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Compare two decimals to hundredths to develop a strong understanding of number size, make meaningful comparisons, and prepare for real-world problem solving. (TB 4B pg. 89-92, WB 4B pg. 65-66)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Adding two decimals to hundredths to develop precision with place value, solve real-world problems involving money and measurement, and build a foundation for more advanced math. (TB 4B pg. 93-98, WB 4B pg. 67-70)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtracting two decimals to hundredths to develop precision with place value, solve real-world problems involving money and measurement, and build a foundation for more advanced math. (TB 4B pg. 99-104, WB 4B pg. 71-74)
End of Unit:
Grade 4 Math: Unit 8
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 105, WB 4B pg. 75)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 105, WB 4B pg. 76)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 77-80)
● Cumulative Review 3 (pg. 81-82)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 8- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Decimals (Answer sheets are available for each month): April Week 4
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from April
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 10
● K-5 Resources- Understand Decimal Notation For Fractions And Compare Decimal Fractions (pg. 244-253)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target H
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Numbers and Operations Fractions(4.NF.C.5-7)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 9
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 13
Unit 9 Title: Volume and Mass: Measuring the World Around Us
Unit Overview:
Did you know that volume and mass are all around us, from the water in your water bottle to the weight of your backpack? Volume helps us understand how much space something takes up, while mass tells us how heavy it is. By learning to measure, compare, and estimate volume and mass, we discover how these ideas help us solve real-world problems and make sense of the objects we use every day!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4.MD.1- Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units, including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz.; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a twocolumn table.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Volume and mass can be measured using both metric and customary systems.
● Units within each system are related and can be converted through multiplication or division.
● Precise measurement requires selecting appropriate tools and units.
Knowledge
● The difference between customary and metric units
● Converting between larger and smaller units within the same system
Key Vocabulary: fluid, ounce, cup, pint, quart, gallon, milliliter, liter, ounce, pound, gram, kilogram, convert, volume, mass
● How can I use what I know about measurement units to convert between larger and smaller units within the same system?
● What patterns or rules help me convert between different units within the same measurement system?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure liquid volume and mass using appropriate tools and record the results accurately.
● I can convert between different units of volume and mass by applying knowledge of measurement relationships.
● I can organize and interpret equivalent measurements using a two-column table to identify patterns and relationships.
Grade 4 Math: Unit 9
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 9 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of converting liquid measures, using a 2-column table to convert measures, and knowing the relative weight of objects.
● Error Analysis: Jennifer says that since there are 4 cups in a pint, and 2 pints in a quart, there must be 8 cups in a quart. So 3 quarts = 24 cups. Do you agree with Jennifer? Explain your thinking.
● Math Journal: You are helping at a school kitchen. The recipe calls for 2 liters of milk, but the measuring cup only shows milliliters. Explain how you would figure out how many milliliters you need. Use drawings, models or words to show your thinking.
● Activity Time: Estimate the mass of an object in pounds
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs
First Topic: Measuring and Converting Volume and Mass
Learning Targets:
● I can measure liquid volume and mass using appropriate tools and record the results accurately.
● I can convert between different units of volume and mass by applying knowledge of measurement relationships.
● I can organize and interpret equivalent measurements using a two-column table to identify patterns and relationships.
Estimated # of Lessons: 13
Essential Questions:
● How can I use what I know about measurement units to convert between larger and smaller units within the same system?
● What patterns or rules help me convert between different units within the same measurement system?
Grade 4 Math: Unit 9
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: containers ( 1L, 500mL, 100mL), balance scale, weights
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Measure the volume of a liquid in customary units to understand everyday measurements, make real-world connections, and develop foundational skills for solving problems involving capacity. (TB 4B pg. 109-114, WB 4B pg. 83-84)
● Lesson 2 and 3 Focus (2 days): Converting customary units of volume to understand the relationships between different units, solve real-life problems with accuracy, and build a strong foundation for flexible thinking in measurement. (TB 4B pg. 115-122, WB 4B pg. 85-88)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Measure the volume of a liquid in metric units to understand and use a system of measurement that is widely used around the world. (TB 4B pg. 123-126, WB 4B pg. 89-90)
● Lesson 5 and 6 Focus (2 days): Converting metric units of volume to develop a deep understanding of the metric system and solve real-world problems with precision. (TB 4B pg. 127134, WB 4B pg. 91-94)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Measure the mass of an object in customary units to make real-world comparisons and develop strong measurement skills. (TB 4B pg. 135-138, WB 4B pg. 95-96)
● Lesson 8 and 9 Focus (2 days): Convert customary units of mass to understand the relationships between different units, solve real-life problems with accuracy, and build a strong foundation for flexible thinking in measurement. (TB 4B pg. 139-146, WB 4B pg. 97-100)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Measure the mass of an object in metric units to make real-world comparisons and develop strong measurement skills. (TB 4B pg. 147-150, WB 4B pg. 101-102)
● Lesson 11 Focus: Converting metric units of mass to understand the relationships between different units, solve real-life problems with accuracy, and build a strong foundation for flexible thinking in measurement. (TB 4B pg. 151-154, WB 4B pg. 103-104)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 155, WB 4B pg. 105)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 155, WB 4B pg. 106)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 107-110)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 9- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Measurement (Answer sheets are available for each month): March Week 4
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from May
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) Modules 11
● K-5 Resources- Solve Problems Involving Measurement And Conversion Of Measurements From A Larger Unit To A Smaller Unit (pg. 257-271)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target I
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show Review
● Coherence Map Measurement and Data (4.MD.A.1-2)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 10
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 18
Unit 10 Title: Measurement and Data: From Tiny Inches to Big Ideas
Unit Overview:
Did you know that knowing about area and perimeter helps architects design buildings, farmers plant fields, and even helps you figure out how much fence you need for a garden? Math gives us the power to measure and manage space all around us! Together, we understand how area and perimeter help us measure, plan, and manage space.
1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 4. MD.1-Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units, including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz..; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a twocolumn table.
● 4.MD.3-Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real-world and mathematical problems.
● 4.MD.4-Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions by using information presented in line plots.
Understandings
● Length, area, and perimeter are measurable attributes that can be calculated and compared.
● Data can be represented visually and used to solve problems.
● Choosing appropriate units and tools is essential for accurate measurement and data representation.
Knowledge
● Different units are used to measure different attributes
● Units within a measurement system are
Transfer Goals
● Use precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Essential Questions
● What are the units of measurement the problem is asking for? How do I convert between units of measurement?
● How do I create and analyze line plots to represent a set of data?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can measure objects using appropriate units and tools.
● I can convert between units of length, mass,
STAGE
Grade 4 Math: Unit 10
related and can be converted
● Data can be organized and represented to reveal patterns and relationships
Key Vocabulary: mass, volume, unit conversion and volume.
● I can create line plots to represent measurement data.
● I can solve problems involving measurement and data.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 10 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of area and perimeter, converting linear measures
● Error Analysis: Jesse says that the perimeter of a rectangle that is 8 cm long and 5 cm wide is 40 cm because 8 × 5 = 40. Do you agree with Jesse? Why or why not?
● Math Journal: Explain the difference between area and perimeter using a real-life example (like a garden, a rug, or a room). How would you find the perimeter and the area?
● Activity Time: Find an unknown side length of a rectangle
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs
First Topic: Measurement and Data
Learning Targets:
● I can measure objects using appropriate units and tools.
● I can convert between units of length, mass, and volume.
● I can create line plots to represent measurement data.
● I can solve problems involving measurement and data.
Estimated # of Lessons: 18
Essential Questions
● What are the units of measurement the problem is asking for? How do I convert between units of measurement?
● How do I create and analyze line plots to represent a set of data?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Grade 4 Math: Unit 10
Materials: bean bag, measurement tape
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Measuring length in customary units to understand and apply the measurement system in real-world situations and develop foundational skills in measurement and problemsolving. (TB 4B pg. 159-162, WB 4B pg. 111-112)
● Lessons 2 and 3 Focus (2 days): Converting customary units of length to understand and apply the measurement system in real-world situations and develop foundational skills in measurement and problem-solving. (TB 4B pg. 163-170, WB 4B pg. 113-116)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Measuring length in metric units to give students access to a logical, consistent, and globally used system that supports deep mathematical understanding and practical problemsolving. (TB 4B pg. 171-174, WB 4B pg. 117-118)
● Lessons 5 and 6 Focus (2 day): Converting metric units of length to understand and apply the measurement system in real-world situations and develop foundational skills in measurement and problem-solving. (TB 4B pg. 175-182, WB 4B pg. 119-122)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Finding the perimeter of rectangles to understand the total distance around the outside of a figure. (TB 4B pg. 183-186, WB 4B pg. 123-126)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Finding the area of rectangles to understand how much space a shape covers. (TB 4B pg. 187-190, WB 4B pg. 127-130)
● Lesson 9 Focus (1 day): Solving problems involving perimeter and area to apply math in meaningful, real-world situations. (TB 4B pg. 191-194, WB 4B pg. 131-132)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Making line plots with halves, fourths, sixths, or eighths to build a deeper understanding of fractions, data, and measurement. (TB 4B pg. 195-198, WB 4B pg. 133-134)
● Lesson 11 Focus: Solving problems involving line plots with halves, fourths, sixths, or eighths to apply their knowledge of fractions and data analysis in real-world contexts. (TB 4B pg. 199-202, WB 4B pg. 135-136)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 203, WB 4B pg. 137)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 203, WB 4B pg. 138)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 139-144)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 10- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week -Measurement (Answer sheets are available for each month): March Week 4, April Week 2, June Week 2
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from June
Additional Resources:
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Modules 11
● K-5 Resources
○ Represent and Interpret Data (pg. 279-280)
○ Solve Problems Involving Measurement (pg. 275-278)
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary
Grade 4 Math: Unit 10
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Data Analysis: Target J
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: Donut Party
● Smarter Balanced Performance Task: Fair Play
● Coherence Map Measurement and Data (4.MD.A.1-2)
Grade 4 Math: Unit 11
Course Name: Grade 4 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 12
Unit 11 Title: Word Problems: Solving Big Problems with Everything You Know
Unit Overview:
Did you know that patterns are hidden everywhere, from the rhythm of music to the way plants grow, and even in the numbers we use every day? Math helps us discover these exciting rules and predict what comes next! Let's dig into patterns and explore how uncovering patterns and rules helps us understand the world around us and even predict future events.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
4.OA.2- Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
4.NF.3-Understand a fraction a/b with a > 1 as a sum of fractions 1/b.
4.NF.4- Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number.
4.OA.3-Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies, including rounding.
4.MD.2- Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG:Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Understandings Essential Questions
● The context of the problem helps determine which operations and
● How can I use different math skills to solve a problem?
Grade 4 Math: Unit 11
representations to use.
● Real-world situations can be modeled and solved using mathematics.
● Mathematical concepts are interconnected (additive reasoning to multiplicative reasoning).
Knowledge
● Problem-solving involves applying multiple skills and strategies:
○ Pictures to assist with comprehension
○ Visual Models such as ratio tables, base ten, number lines, and area model
Key Vocabulary: No New Vocabulary
● How do I decide which operation to use in a word problem?
● How can I check if our answers are reasonable?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can solve multi-step word problems and check the reasonableness of the solution.
● I can apply knowledge of operations, fractions, time, money, and measurement to solve problems.
● I can represent and explain solutions clearly.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 4 Unit 11 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Assessing understanding of application word problems using questions drawn from the unit review.
● Error Analysis: Noah solved this problem: “Emma walked 2/3 mile in the morning and 1/3 mile in the afternoon. How far did she walk altogether?” Noah’s answer was: “2/3 + 1/3 = 3/6. So, Emma walked 1/2 mile.” Do you agree with Noah? Explain why his answer is incorrect.
● Math Journal: Describe how you solve a multi-step word problem. What strategies help you figure out what to do first, next, and how to check your answer
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs
Grade 4 Math: Unit 11
First Topic: Understanding Word Problems Estimated # of Lessons: 12
Learning Targets:
● I can solve multi-step word problems and check the reasonableness of the solution.
● I can apply knowledge of operations, fractions, time, money, and measurement to solve problems.
● I can represent and explain solutions clearly.
Essential Questions:
● How can I use different math skills to solve a problem?
● How do I decide which operation to use in a word problem?
● How can I check if our answers are reasonable?
Key: Bold-Lessons, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: sheets of paper
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to build automaticity with basic math facts, which supports higher-level math thinking. (WB 4B 145-146)
● Lessons 1 and 2 Focus (2 days): Solve word problems involving whole numbers and the four operations to model and solve real-life situations. (TB 4B 207-216, WB 4B 147-150)
● Lessons 3 Focus: Solve word problems involving the addition and subtraction of fractions to understand how fractions are used in real-life situations and to develop strong problem-solving skills. (TB 4B 217-220, WB 4B 151-154)
● Lessons 4 Focus: Solve word problems involving the multiplication of fractions to understand how fractions are used in real-life situations and to develop strong problem-solving skills. (TB 4B 221224, WB 4B 155-156)
● Lessons 5 Focus: Solve word problems involving whole numbers and the four operations to model and solve real-life situations. (TB 4B 225-230, WB 4B 157-160)
● Lessons 6 Focus: Solve word problems involving money and the four operations to model and understand how money is used in real-life situations and to develop strong problem-solving skills. (TB 4B 231-234, WB 4B 161-164)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 4B 235, WB 4B pg. 165)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 4B 235, WB 4B pg. 166)
● Unit Review (WB 4B pg. 167-170)
● Cumulative Review 4 (WB 4B pg. 171-174)
● End of Year Review (WB 4B pg. 175-182)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 11- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments.
● Problem of the Week - none are specific to problem solving
● Word Problems of the Week- Choose a problem from those not already completed this year
Additional Resources:
Grade 4 Math: Unit 11
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 15
● K-5 Resources
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 4 (Day, Philpott, Mosesson-Teig, Fosnot)
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Vocabulary: Target A
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials Slide Show
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Problem Solving
● Smarter Balanced Supplemental Materials: Communicate Reasoning
● Coherence Map Operations and Algebraic Thinking (4.OA.A)
Grade 5 Math

Grade 5 Math

Grade 5 Math

Grade 5 Math: Unit 0
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est.
# of Lessons: 10 days
Unit 0 Title: Setting the Culture
Unit Overview:
Creating a collaborative environment where students appreciate productive noise and productive struggle. Learning that communication, perseverance, collaboration, and reflection are key to being successful mathematicians.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
NOTE: This unit is building classroom culture rather than explicit math standards. The lessons in this unit support the development of the following Mathematical Practice Standards:
● MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
● MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
● MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically
● MP6: Attend to precision
● MP7: Look for and make use of structure
● MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Understandings
● Mistakes and challenges help me grow as a math thinker.
● Talking and working with others can lead to stronger ideas, new strategies, and deepen learning.
● Using patterns, tools, and efficient strategies helps us solve problems and understand the world.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 0
Knowledge
● Classroom expectations and routines that support collaborative math learning
● How to select and use mathematical tools and models strategically to support problem solving
● What productive struggle looks like and how to recognize when and how to revise thinking or try a new approach
● How to contribute respectfully and thoughtfully in math discussions by sharing ideas, asking questions, and giving feedback
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can engage in open-ended problem-solving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers and fractions with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
Summative Assessment
Not applicable due to daily practice and observation
First Topic: Establishing Number Corner Routines
Formative Assessment
● Math Journal Entries- Have students respond to questions like “What makes a good math partner?” or “What do I do when I feel stuck in math?”
● Teacher Anecdotal Notes and ChecklistsMonitor during group tasks and partner work (suggested topics could be: who participates and frequency, who uses self-talk, problemsolving strategies)
● Problem Solving Checklist used by students to self-monitor strategy use and reflect on what helped them think.
Estimated # of Lessons: This topic is part of a yearlong focus to strengthen number sense through problem-solving context.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Learning Targets:
Grade 5 Math: Unit 0
● I can recognize and analyze patterns in numbers, shapes, and data to make mathematical generalizations.
● I can solve multi-step problems using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals with strategies and models.
● I can use and explain efficient strategies for computing with fractions, decimals, and whole numbers.
● I can collect, represent, and interpret data using visual models like line plots, bar graphs, and tables.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
Learning Activities:
Essential Questions:
● How can I use patterns and structure to help me make predictions and solve problems in math?
● How can I use strategies and models to solve problems efficiently and accurately?
● How can visual models help me understand and communicate mathematical ideas?
● How do I collect and interpret data to learn about the world around me?
● Daily 15-minute sessions featuring five key workouts: Calendar Grid, Calendar Collector, Solving Problems, Computational Fluency, and Number Strings
● Student-led updates to key displays for hands-on engagement and routine development. Use of manipulatives, math talks, visual models, and discussion to foster deep conceptual understanding.
● Emphasis on mathematical discourse, reasoning, problem solving, and identity as a mathematician.
Second Topic: Setting the Culture through Think! Mathematics Estimated # of Lessons: 10 Days
Learning Targets
● I can engage in open-ended problemsolving with others.
● I can persevere through a challenge and reflect on the process.
● I can use positive self-talk and reflect on what I can do when I feel frustrated or stuck.
● I can communicate my mathematical thinking clearly through discussion, models, and written explanations.
Essential Questions:
● How do effective math partners contribute to productive and meaningful problem solving?
● How can I clearly communicate my reasoning so others can understand, critique, and build on my ideas?
● How can learning from my classmates’ strategies help me improve my own mathematical thinking?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Objective, Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Read The Most Magnificent Thing to foster a growth mindset and self-awareness.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Use the Crazy Colors activity to cultivate metacognition and perseverance.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Using Venn Diagrams to foster communication and embrace differences.
● Lesson 4 Focus: Use activity Disagreeing is Okay! We Can Still Be Friends to support respectful communication in challenging situations.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Initiate Fluency Routines to cultivate independence and collaboration through problem solving.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 0
● Lesson 6 Focus: Try Saving Sam to teach students the power of cooperation and perseverance.
● Lesson 7 Focus: Using the Tax Collector activity to assist students in planning and reflecting so they can understand the foundations of effective group work.
● Lesson 8 Focus: Solve How Many Legs to foster a collaborative classroom culture.
● Lesson 9 Focus: Use the Folding Paper task to shift from speedy calculations to appreciating mathematical insight.
● Lesson 10 Focus: Play the Nine Lives game to empower students to leverage resources independently
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Think Mathematics Online Toolbox
● Meet the Character Videos and Posters Slideshow
Additional Resources:
The Most Magnificent Thing, written by Ashley Spires, Read Aloud
Grade 5 Math: Unit 1
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 10
Unit 1 Title: Place Value and Decimals: Help Tracking Healthy Choices
Unit Overview:
Decimals are everywhere! From money and measurements to sports and even video games, we learn how to represent decimals to the 1000th place. This helps us to compare, round, and estimate real-world challenges such as: snack portions, track exercise time, and manage our money.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.NBT.1- Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.
● 5.NBT.3- Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
● 5.NBT.4-Use place value understanding to round decimals to any given place.
Understandings
● The position of a digit in a number determines its value and the relationship it has to other digits.
● Decimals represent parts of a whole or quantities between whole numbers and can be compared using place value.
● Understanding place value is fundamental for reading, writing, comparing, and rounding decimals.
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
Essential Questions
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 1
Knowledge
● The place value system is based on powers of 10
● Recognize that a digit in one place represents 10X what it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 what it represents in the place to its left
● Decimals can be used to represent parts of a whole
● Rounding decimals provides estimates that are useful when solving problems
● When to round decimals
Key Vocabulary: thousandth
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is multiplied by powers of 10.
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is divided by powers of 10.
● I can use what I know about place value to compare numbers using >, <, and =.
● I can read and write decimals to the thousandths in standard form, word form, and expanded form.
● I can round decimals to any place using place value.
● I can create and use models to compose and decompose decimals.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 1 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of the ten times and 1/10 relationship, comparing decimals to thousandths, and rounding to the nearest tenth and hundredth.
● Error Analysis: A student says 0.53 is greater than 0.7 because .53 has two numbers after the decimal point. What's the mistake? Explain.
● Math Journal: Describe how the value of the digit 7 changes in the numbers 7, 0.7, and 0.07. How does place value help you compare them?
● Activity Time: Compare decimals
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application
Grade 5 Math: Unit 1
opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Place Value and Decimals
Learning Targets:
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is multiplied by powers of 10.
● I can explain and show an example of what happens when a number is divided by powers of 10.
● I can use what I know about place value to compare numbers using >, <, and =.
● I can read and write decimals to the thousandths in standard form, word form, and expanded form.
● I can round decimals to any place using place value.
● I can create and use models to compose and decompose decimals.
Estimated # of Lessons: 10 days
Essential Questions:
● How does the value of a digit change based on its place in a number?
● How does understanding place value help me read, write, and compare numbers accurately?
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: place value chart, number disks, 10-sided die, activity time (lesson 4)
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 and 2 Focus: Understanding Place Value to recognize the relationship between a digit in one place in a multi-digit number and a digit to its right or left. (TB 5A pg. 3-10 WB 5A pg. 1-4)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Writing Decimals to represent decimals to thousandths so students can make sense of and communicate these values accurately. (TB 5A pg. 11-14 WB 5A pg. 5-8)
● Expanded Form SBA practice: (Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, e.g., 347.392 = 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 7 × 1 + 3 × (1/10) + 9 × (1/100) + 2 × (1/1000))
● Lesson 4 Focus: Compare and order decimals to develop number sense and fluency in understanding place value and real-world quantities. (TB 5A pg. 15-18 WB 5A pg. 9-10)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Rounding Decimals to any place helps students make quick estimates in everyday life. (TB 5A pg. 19-22 WB 5A pg.11-12)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 23 WB pg. 13)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 23 WB pg. 14)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 15-16)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
Grade 5 Math: Unit 1
● Tool Kit Unit 1- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: August
● Word Problem of the Week: August
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 1: Understanding Place Value
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NBT
● Expanded form SBA (lesson 3)
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Understand the Place Value System (pages 29-67): games and activities for small group instruction and partner work
Grade 5 Math: Unit 2
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 7
Unit 2 Title: Order of Operations: Plan First Purchase Wisely
Unit Overview:
Ever wondered how online stores calculate your total price or how a chef follows a recipe step by step? Next, we learn why it is important to follow the order of operations, including parentheses, when calculating costs, recipes, or travel time. Like in the real world, interpreting and describing numerical expressions in words help us understand budgets, discounts, and real-life problem-solving.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5. OA. 1- Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
● 5.OA.2-Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings
● The order of operations provides a consistent process for solving mathematical expressions accurately.
● Parentheses and grouping symbols change the interpretation and guide how to solve numerical expressions.
● Being precise with symbols and operations helps to communicate clearly in math.
Knowledge
● The order of operations is a set of rules that ensures consistent results in calculations
Essential Questions
● How does the order of operations help me to simplify and solve complex calculations?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can solve equations that have more than one step using my understanding of the order of operations.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 2
● Parentheses are used to group numbers and operations
● Using parentheses changes the order in which operations are performed
● The difference between evaluating an expression and interpreting an expression
Key Vocabulary: numerical expressions, parentheses
● I can write math expressions to match word problems or mathematical descriptions using parentheses, brackets, and braces
● I can read and explain what a math expression means, even if I don’t solve it.
● I can describe the steps I would take to solve an expression just by looking at it.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 2 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of using parentheses, the correct order of operations, writing, and interpreting numerical expressions.
● Error Analysis: A student solved 5 + 3 × 2 and got 16. What did they do wrong?
● Math Journal: Why are rules important for the order in which we solve math problems? Give an example.
● Activity Time: Complete numerical expressions with parentheses that give a particular value
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Order of Operations
Learning Targets:
● I can solve equations that have more than one step using my understanding of the order of operations.
● I can write math expressions to match word problems or mathematical descriptions using parentheses, brackets, and braces
● I can read and explain what a math
Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Essential Questions:
● How does the order of operations help me to simplify and solve complex calculations?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 2
expression means, even if I don’t solve it.
● I can describe the steps I would take to solve an expression just by looking at it.
Key: Bold- Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: number cards (0-20), unit cubes
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Using Mixed Operations to evaluate expressions with more than one operation to develop critical thinking skills and ensure accurate problem solving in multi-step math situations (TB 5A pg. 27-30 WB 5A pg. 17-18)
● Lesson 2 and 3 Focus: Use the order of operations to evaluate expressions and learn how to use mixed operations to accurately solve complex math problems and build a strong foundation for algebra and real-world problem solving.. (TB 5A pg. 31-40 WB 5A pg. 19-22)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Interpreting expressions: to write simple numerical expressions when given the descriptions and interpret expressions that involve the use of parentheses and the order of operations. (TB 5A pg. 41-44 WB 5A pg. 23-24)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout(TB pg. 45 WB pg. 25)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 45 WB pg. 26)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 27-28)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 2- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: September
● Word Problem of the Week: September
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 2: Writing and Interpreting Numerical Expressions
● Coherence Map Grade 5 OA
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Write and Interpret Numerical Expressions and Analyze Patterns and Expressions(pages 11-24). Games and activities for small groups and partner work.
Context for Learning Mathematics (CFLM)- Due to the complexity of this CFLM unit, students will engage with real-world problems, or “contexts,” that challenge them to apply and extend their learning. Concepts and skills are explicitly taught and then deepened through scaffolded experiences that build on prior lessons within the unit. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and Math Congress discussions, students revisit and refine earlier strategies, strengthen their understanding, and connect new ideas to those already explored. This intentional progression supports the Standards for
Grade 5 Math: Unit 2
Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical concepts, articulate their reasoning, and develop a strong, connected foundation for future learning.
Second Topic: Box Factory (CFLM) Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Learning Targets:
● I can find all the different ways to build a box that holds 24 cubes using rows, columns, and layers.
● I can use multiplication to show how the size and shape of a box can change.
● I can represent and explain my strategies clearly using models and equations.
● I can use parentheses to show how I broke apart a multiplication problem.
● I can use halving and doubling to multiply numbers in a more efficient way.
● I can think about layers in a box to help me understand volume.
Essential Questions:
● How can we use multiplication to find all the ways to build a box that holds 24 cubes?
● How can we use parentheses to show how we broke apart a multiplication problem?
● What do the associative and distributive properties tell us about volume?
● How can halving and doubling help us multiply more efficiently?
● How do rows, columns, and layers help us understand volume in a 3D space?
Materials: Box Factory CFLM Teacher Book, Posters/Work Space for small student groups to explore and collaborate
Learning Activities:
Note: Lessons 1-3 (required) Lesson 4-10 (optional enrichment for advanced students)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Students explore boxes that can each hold 24 items and work to determine all possible rectangular prisms by arranging the items in different combinations of rows, columns, and layers to support the development of multiplication strategies.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Students begin with a mini lesson on halving and doubling to find products using the area model, then continue designing box combinations for 24 cubes by considering layers, and represent their total calculations with parentheses to show how the associative and distributive properties help break apart and combine the parts.
● Lesson 3 Focus: Students share and compare their box designs and calculations, discussing how they used parentheses, the associative and distributive properties, and layering strategies to represent and explain the total number of cubes in their rectangular prisms.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 3
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 18
Unit 3 Title: Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers: Solving Number Mysteries
Unit Overview:
Next, we learn how to multiply by powers of 10 and use the standard algorithm to solve real-world problems like planning big purchases, or figuring out distances. We also practice dividing large numbers using what you know about multiplication to help split costs or pack supplies. Mystery solved!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.NBT.2-Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, and explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when a decimal is multiplied or divided by a power of 10. Use wholenumber exponents to denote powers of 10.
● 5.NBT.5-Fluently multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
● 5.NBT.6-Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Understandings
● The relationship between multiplication and division provides a way to check calculations and solve related problems.
● Multiplying and dividing by powers of 10 results in predictable patterns based on place value.
● Models and visual representations can make operations more concrete and meaningful.
● Estimation is a valuable tool for predicting and checking the reasonableness of answers.
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG:Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How can I use the relationship between multiplication and division to solve problems?
● How does multiplying and dividing by powers of 10 affect this number?
● How can I use estimation to check if my answers are reasonable?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 3
Knowledge
● The relationship between multiplication and division helps to solve problems efficiently
● Multiplying or dividing by powers of 10 changes the position of the digits in a predictable way
● The standard algorithm is an efficient strategy for solving multi-digit multiplication
● Division can be represented and solved using models based on place value
Key Vocabulary: exponent, powers of 10
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can use exponents to show powers of 10 (like writing 10³ instead of 10 × 10 × 10).
● I can describe and show why multiplying by powers of 10 adds zeros to the end of a number.
● I can estimate the answer when multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number, or a 3digit number by a 2-digit number.
● I can multiply multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm.
● I can estimate the answer when dividing a multi-digit number by a 1- or 2-digit number.
● I can divide 3- or 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers to find the whole number answer using strategies.
● I can divide numbers with 2-digit divisors and find both the quotient and the remainder.
● I can use models and visual representations to efficiently and accurately solve calculation problems.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 3 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of using powers of 10, fluently multiplying multi-digit numbers using an algorithm, and dividing multi-digit numbers using strategies
● Error Analysis: A student multiplies 36 by 10 and writes 3600. What error did they make, and how would you help them understand their mistake?
● Math Journal: Explain how estimating can help you decide if your answer to a multiplication or division problem makes sense.
● Activity Time: Divide 4-digit numbers by 2digit divisors
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas
Grade 5 Math: Unit 3
to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Learning Targets:
● I can use exponents to show powers of 10 (like writing 10³ instead of 10 × 10 × 10).
● I can describe and show why multiplying by powers of 10 adds zeros to the end of a number.
● I can estimate the answer when multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number, or a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number.
● I can multiply multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm.
● I can estimate the answer when dividing a multi-digit number by a 1- or 2-digit number.
● I can divide 3- or 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers to find the whole number answer using strategies.
● I can divide numbers with 2-digit divisors and find both the quotient and the remainder.
● I can use models and visual representations to efficiently and accurately solve calculation problems.
Estimated # of Lessons: 18
Essential Questions:
● I can use exponents to show powers of 10 (like writing 10³ instead of 10 × 10 × 10).
● I can describe and show why multiplying by powers of 10 adds zeros to the end of a number.
● I can estimate the answer when multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number, or a 3digit number by a 2-digit number.
● I can multiply multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm.
● I can estimate the answer when dividing a multi-digit number by a 1- or 2-digit number.
● I can divide 3- or 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers to find the whole number answer using strategies.
● I can divide numbers with 2-digit divisors and find both the quotient and the remainder.
● I can use models and visual representations to efficiently and accurately solve calculation problems.
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: number disks, 10-sided die
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for multiplication within 10,000 to strengthen foundational skills needed for efficient multi-digit computation. (TB 5A pg. 29-30)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Understanding powers of 10 and using whole-number exponents to denote powers of 10 and to deepen their grasp of place value and prepare for more advanced concepts in math and science. (TB 5A pg. 49-52 WB 5A pg. 31-32).
● Lesson 2 Focus: Multiplying by powers of 10 and explaining patterns in the number of zeros when multiplying by powers of 10 to recognize place value shifts and strengthen their understanding of how our base-10 system works. (TB 5A pg. 53-56 WB 5A pg. 33-34)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Estimate the product of a 4-digit number and a 1-digit number, or a 3-digit number and a 2-digit number, to reinforce number sense and support students in checking the reasonableness of answers. (TB 5A pg. 57-60 WB 5A pg. 35-36)
Grade 5 Math: Unit 3
● Lesson 4 Focus: Multiplying a multi-digit number and a 1-digit number using area models and number bond representations to support conceptual understanding of multiplication strategies, including partial products. (TB 5A pg. 61-64 WB 5A pg. 37-40)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Multiply a 3-digit number and a 2-digit number to build accuracy and efficiency in solving multi-digit problems and prepare for real-world applications of multiplication (TB 5A pg. 65-70, WB 5A pg. 41-44)
● Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for division within 100. to strengthen foundational skills needed for efficient multi-digit computation. (WB 5A pg. 45-46)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Divide multi-digit numbers by 10 to understand place value shifts and develop a deeper understanding of how decimals and the base-10 system work (TB 5A pg. 71-74, WB 5A pg. 47- 48)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Estimating the quotient when a multi-digit number is divided by a 1- or 2-digit number to develop number sense and choose efficient strategies for solving division problems. (TB 5A pg. 75-78, WB 5A pg. 49-50)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Find whole-number quotients when a 3-digit number is divided by a 2-digit number to build fluency with long division and apply it to real-world problem solving. (TB 5A pg. 79-82 WB 5A pg.51-52)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Find whole-number quotients when a 4-digit number is divided by a 2-digit number to build fluency with long division and apply it to real-world problem solving. (TB 5A pg. 83-86 WB 5A pg. 53-54)
● Lesson 10 Focus: Find whole number quotients and remainders with 2-digit divisors to build fluency with long division and apply it to real-world problem solving. (TB 5A pg. 87-92 WB 5A pg. 55-58)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 93 WB pg. 59)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 93 WB pg. 60)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 61-64)
● Cumulative Review (WB pg. 65-68)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 3- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: October
● Word Problem of the Week: October
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell) -Modules 3 and 4: Multiplying and Dividing with Multidigit Whole Numbers
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NBT
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers (pages 70-106). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 4
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 14
Unit 4 Title: Addition and Subtraction
Unit Overview:
of Decimals: Every Second Counts
Get ready to become a Decimal Superstar! In this unit, you'll build fluency with adding and subtracting decimals to the thousandths, especially with money, measurements, and real-life situations like shopping or splitting a bill. Soon, you’ll confidently tackle tricky problems and use your decimal skills to solve everyday challenges with ease.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5. NBT.7- Add and subtract decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. Relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem.(MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings
● Place value is foundational when adding and subtracting decimals to ensure that like parts are combined or compared correctly.
● Models and visual representations can make decimal operations more concrete and meaningful.
● The relationship between addition and subtraction extends to decimals, providing
Essential Questions
● How does place value guide my problemsolving when adding and subtracting decimals?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve problems involving decimal operations?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 4
a way to check calculations and solve related problems.
Knowledge
● There is a relationship between addition and subtraction that helps to solve problems efficiently
● How adding and subtracting decimals is like adding and subtracting whole numbers
Key Vocabulary: no new vocabulary
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can add and subtract decimals to the hundredths place using place value strategies.
● I can use models or drawings to help me add or subtract decimals to the hundredths place.
● I can use the properties of addition and subtraction to solve problems and justify my approach.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 4 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of adding and subtracting decimals to thousandths using models and strategies for regrouping
● Error Analysis: A student adds 3.45 + 0.7 and writes 3.121. What went wrong?
● Math Journal: Why is it important to line up decimal points when adding or subtracting?
● Activity Time: Subtract decimals to thousandths with regrouping
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Estimated # of Lessons: 14
Learning Targets:
● I can add and subtract decimals to the hundredths place using place value
Essential Questions:
● How does place value guide my problemsolving when adding and subtracting
Grade 5 Math: Unit 4
strategies.
● I can use models or drawings to help me add or subtract decimals to the hundredths place.
● I can use the properties of addition and subtraction to solve problems and justify my approach. decimals?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve problems involving decimal operations?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: counters, base-ten blocks, number disks, place-value chart, number cards (1-9)
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for adding decimals in the form of money to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (WB 5A pg. 69-70)
● Lesson 1 and 2 Focus: Add decimals to thousandths without regrouping to develop precise computational skills, enhance their understanding of decimal place value, and prepare for more complex operations involving decimals in real-life contexts such as money, measurements, and data analysis. (TB 5A pg. 97-104 WB 5A pg. 71-78).
● Lesson 3 Focus: Add decimals to thousandths with regrouping to develop precise computational skills, enhance their understanding of decimal place value, and prepare for more complex operations involving decimals in real-life contexts such as money, measurements, and data analysis. (TB 5A pg. 105-108 WB 5A pg. 79-82).
● Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for subtracting decimals in the form of money to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (WB 5A pg. 83-84)
● Lesson 4 and 5 Focus: Subtracting decimals to thousandths without regrouping. (TB 5A pg. 109116 WB 5A pg. 85-92).
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtracting decimals to thousandths with regrouping to develop precise computational skills, enhance their understanding of decimal place value, and prepare for more complex operations involving decimals in real-life contexts such as money, measurements, and data analysis. (TB 5A pg. 117-122 WB 5A pg. 93-96).
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 123 WB pg. 97)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 123 WB pg. 98)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 99-100)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 4- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: November
● Word Problem of the Week: November
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
Grade 5 Math: Unit 4
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 5: Adding and Subtracting Decimals
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NF.A.1
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Adding and Subtracting Decimals (Pages 109-209). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 5
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
# of Lessons: 15
Unit 5 Title:
Multiplication and Division of Decimals: Small Numbers Big Moves
Unit Overview:
Now that you're a Decimal Dynamo you’ll learn how to multiply and divide decimals in real-world situations like shopping, cooking, and handling money. By exploring patterns with powers of 10, estimating, and solving problems with all kinds of decimals, you’ll build fluency and confidence to tackle any decimal challenge like a math pro!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.NBT.2- Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, and explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when a decimal is multiplied or divided by a power of 10. Use wholenumber exponents to denote powers of 10.
● 5.NBT.7- Multiply and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division, relate the strategy to a written method, and explain the reasoning used.
Transfer Goals
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Place value is the foundation for understanding how and why decimal multiplication and division work.
● Models and visual representations can make decimal operations more concrete and meaningful.
● Estimation is a valuable tool for predicting and checking the reasonableness of answers.
● The relationship between multiplication and division extends to decimals, providing a way to check calculations and solve related problems.
Knowledge
● How does place value guide my problem solving when multiplying and dividing decimals?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve problems involving decimal operations?
● How do I use estimation to check the reasonableness of our answers when multiplying and dividing decimals?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
Grade 5 Math: Unit 5
● Multiplying or dividing by powers of 10 changes the position of the digits in a predictable way
● There is a relationship between multiplication and division that helps to solve problems efficiently
● Multiplying and dividing decimals are like multiplying and dividing whole numbers
Key Vocabulary: no new vocabulary
● I can multiply decimals to the hundredths place using place value strategies.
● I can use models or drawings to help me divide decimals to the hundredths place by a whole number.
● I can explain why the placement of the decimal point “moves” when multiplying or dividing by powers of 10.
● I can use the properties of multiplication and division to solve problems and justify my approach.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 5 Assessment
● IAB- Number and Operations in Base Ten
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of patterns in multiplying and dividing by powers of 10, multiplying and dividing decimals by whole numbers and other decimals using visual models, estimating and solving real-world problems involving multiplication and division of decimals
● Error Analysis: A student multiplies 3.2 × 0.5 and says they estimate the product to be greater than 3.2. Explain the misunderstanding.
● Math Journal: How does multiplying by 0.1 or 0.01 change a number? How is that different from dividing by 0.1?
● Activity Time: Multiply two decimals, divide a decimal by a whole number
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Multiplication and Division of Decimals Estimated # of Lessons: 13
Learning Targets:
Essential Questions:
Grade 5 Math: Unit 5
● I can multiply decimals to the hundredths place using place value strategies.
● I can use models or drawings to help me divide decimals to the hundredths place by a whole number.
● I can explain why the placement of the decimal point “moves” when multiplying or dividing by powers of 10.
● I can use the properties of multiplication and division to solve problems and justify my approach.
Materials: number disks, number cards (0-9)
Learning Activities:
● How does place value guide my problem solving when multiplying and dividing decimals?
● How do visual representations and models help me solve problems involving decimal operations?
● How do I use estimation to check the reasonableness of our answers when multiplying and dividing decimals?
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for multiplication of whole numbers to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (WB 5A pg. 69-70)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Multiplying Decimals by Powers of 10: Explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when the decimal is multiplied by a power of 10. Multiply decimals by a power of 10. (TB 5A pg. 127-132 WB 5A pg. 103-104).
● Lesson 2 Focus: Estimate the product of two decimals: to develop number sense, make reasonable predictions, and efficiently check the reasonableness of their answers in everyday situations involving measurement, money, and data. (TB 5A pg. 133-136, WB 5A pg. 105-106).
● Lesson 3-5 Focus: Multiply a decimal, starting with tenths and up to whole numbers with hundredths to strengthen their understanding of place value in decimal multiplication and apply these skills to practical problems involving measurement, money, and science (TB 5A pg. 137-154 WB 5A pg. 107-116).
● Fluency Practice 2: Develop fluency for division of whole numbers to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (WB 5A pg. 117-118)
● Lesson 6 Focus: Divide decimals by powers of 10 and identify patterns in decimal placement: to understand how the position of the decimal changes, and to strengthen place value understanding when dividing by powers of 10, 0.1, and 0.01. (TB 5A pg. 155-160 WB 5A pg. 119-120).
● Lesson 7 Focus: Skip
● Lesson 8-10 Focus: Dividing decimals and whole numbers: Divide a whole number by a decimal and decimal by a whole number to build flexible problem-solving skills and understand how division applies in real-world contexts like measurements, money, and rates. (TB 5A pg. 165-178 WB 5A pg. 123-128).
● Lesson 11 Focus: Skip
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 183 WB pg. 131)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 184 WB pg. 132)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 133-136)
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Grade 5 Math: Unit 5
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 5- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: December
● Word Problem of the Week: December (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)-Module 6: Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NBT.B.7
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● Performance task: School Supplies ( Uses four operations with decimals to the hundredths)
● K-5 Resources: Multiplying and Dividing Decimals (pages 152-209). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 6
Course Name Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 21
Unit 6 Title: Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: A Fraction Adventure
Unit Overview:
Get ready to become a Fraction Master! In this unit, you’ll learn to add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators, work with mixed numbers, and create equivalent fractions. Whether you're baking, building, or racing, you'll use fractions to solve real-world problems with confidence and ease.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5. NF.1- Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given fractions with equivalent fractions in such a way as to produce an equivalent sum or difference of fractions with like denominators.
● 5. NF.2- Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole, including cases of unlike denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Use benchmark fractions and number sense of fractions to estimate mentally and assess the reasonableness of answers.
Understandings
● A fraction is a more precise part-to-whole representation of a number, to ensure accuracy in calculating answers.
● Equivalent fractions represent the same value, even if they look different.
● Visual models help to envision and efficiently solve problems involving fractional amounts.
● Mathematical reasoning is essential for determining the reasonableness of an answer.
Knowledge
● Common denominators are required to add or subtract fractions
Transfer Goals
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Apply a variety of problem-solving strategies, using manipulatives, drawings, models, and/or equations to represent the situation. (MP 5 Use appropriate tools strategically) (MP 4 Model with mathematics) (VOG: Information Analysts)
Essential Questions
● What strategies can I use to efficiently solve fraction problems with unlike denominators? How can I check if my answer is reasonable?
● How can I use what I know about multiplication to help with finding common denominators?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can develop fluency in finding multiples and equivalent fractions.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 6
● Create equivalent fractions
● Use benchmark fractions (½, ¼, ¾) to make estimations
● Estimate sums and differences of fractions
● Interpret and construct fraction models
● Represent word problems with equations or models
Key Vocabulary: common multiples
● I can add and subtract fractions, including mixed numbers, with unlike denominators using equivalent fractions or models.
● I can solve word problems involving the addition and subtraction of fractions using benchmark fractions with unlike denominators.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 6 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of adding and subtracting fractions with unlike denominators, solving real-world problems with fractions.
● Error Analysis: A student adds 1/4 + 1/3 and gets 2/7. Identify and explain the mistake.
● Math Journal: How do you find a common denominator, and why is it important when adding or subtracting fractions?
● Activity Time: Add mixed fractions with unlike denominators, Subtract mixed fractions with unlike denominators
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Addition and Subtraction of Fractions Estimated # of Lessons: 15
Learning Targets:
● I can develop fluency in finding multiples and equivalent fractions.
● I can add and subtract fractions, including mixed numbers, with unlike denominators using equivalent fractions or models.
● I can solve word problems involving the
Essential Questions:
● What strategies can I use to efficiently solve fraction problems with unlike denominators? How can I check if my answer is reasonable?
● How can I use what I know about multiplication to help with finding common denominators?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 6
addition and subtraction of fractions using benchmark fractions with unlike denominators.
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: fraction area models, number cards (1-10)
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for finding multiples and equivalent fractions to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (WB 5A pg. 137-138)
● Lesson 1-2 Focus: Add fractions with unlike denominators by replacing one given fraction with its equivalent fraction to develop a strong conceptual understanding of fraction equivalence and build accuracy in combining parts of a whole. (TB 5A pg. 189-196 WB 5A pg. 139-146).
● Lesson 3 Focus: Add mixed numbers with unlike denominators to enhance their fraction sense, master converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers, and solve complex real-world problems involving measurements and quantities. (TB 5A pg. 197-200 WB 5A pg. 147-150).
● Lesson 4-5 Focus: Subtract fractions with unlike denominators by replacing the given fractions with their equivalent fractions to deepen their understanding of fraction relationships and accurately solve problems involving parts of a whole.. (TB 5A pg. 201-208 WB 5A pg. 151-156).
● Lesson 6 Focus: Subtract mixed numbers with unlike denominators: to build strong fraction operation skills, improve fluency with whole numbers and fractional parts, and solve real-world problems involving measurement and quantities. (TB 5A pg. 209-214 WB 5A pg. 157-160).
● Lesson 7 Focus: Solve word problems involving the addition and subtraction of fractions with unlike denominators to apply their fraction skills in real-life contexts, develop critical thinking, and strengthen problem-solving strategies. (TB 5A pg. 215-220 WB 5A pg. 161-162).
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB pg. 221 WB pg. 163)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 221 WB pg. 164)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 165-168),
● Cumulative Review 2 (WB pg. 169-172)
● Mid-year Review (WB 5A pg. 173-179)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 6- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: January
● Word Problem of the Week: January (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)-Module 7: Adding and Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NF.A.1
Grade 5 Math: Unit 6
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Adding and Subtracting Fractions (pages 210-261). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Context For Learning Mathematics (CFLM)-Due to the complexity of this CFLM unit, students will engage with real-world problems, or “contexts,” that challenge them to apply and extend their learning. Concepts and skills are explicitly taught and then deepened through scaffolded experiences that build on prior lessons within the unit. Through guided activities such as mini-lessons, group investigations, and Math Congress discussions, students revisit and refine earlier strategies, strengthen their understanding, and connect new ideas to those already explored. This intentional progression supports the Standards for Mathematical Practice by helping students visualize mathematical concepts, articulate their reasoning, and develop a strong, connected foundation for future learning.
First Topic: Best Buys, Ratios, and Rates (CFLM)
Learning Targets:
● I can add and subtract fractions (including mixed numbers) with unlike denominators by finding equivalent fractions.
● I can solve word problems that involve adding and subtracting fractions with unlike denominators by using models or equations.
Estimated # of Lessons: 6
Essential Questions:
● How can we use ratios and rates to solve real-world problems?
● How can we decide which deal is the best buy?
● What strategies can we use to make fair comparisons between different amounts or sizes?
● How do we know when two ratios are equivalent?
Materials: Best Buys, Ratios, and Rates, CFLM Teacher Book, Posters/Work Space for small student groups to explore and collaborate
Learning Activities: Lessons 1-6 (required ), Lessons 7-10 (enrichment)
● Lesson 1 Focus: Introduce proportional reasoning through a real-world context to engage students in exploring ratios and comparisons by shopping for the best deal on cat food, building a foundation for understanding proportions in everyday situations.
● Lesson 2 Focus: Determine which store offers the better deal for 20 cans of cat food by comparing prices using unit rates, equivalent ratios, and fraction strategies to develop proportional reasoning, strengthen problem-solving skills, and justify solutions using models or equations.
● Lesson 3 & 4 Focus: Solve fraction addition and subtraction problems using a common whole (such as money)and explore prices using ratio tables to develop strategies for finding common denominators, understand equivalent ratios and unit prices, and strengthen fraction operations in real-world contexts involving money and measurement.
● Lesson 5 Focus: Use a fraction addition string with the clock as a common whole and create a ratio table to represent ingredients in a fixed ratio to develop skills in finding common denominators and represent proportional relationships in real-world contexts.
● Lesson 6 Focus: Discuss a ratio table showing amounts of multiple ingredients in a fixed ratio and explore addition and subtraction to deepen understanding of proportional relationships and develop strategies for reasoning with ratios using operations.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 7
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 24
Unit 7 Title: Multiplication and Division of Fractions: Multiply the Pieces, Divide the Whole
Unit Overview:
Get ready to multiply and divide fractions in real-life situations! We learn how to use fractions to measure, resize, compare, and share- whether it’s on the soccer field, in the kitchen, or at the amusement park. These skills will help you solve everyday problems with confidence and a bit of fun!
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.NF.3-Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (a/b = a ÷ b). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers,
● 5.NF.4-Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction.
● 5. NF.5- Interpret multiplication as scaling
● 5. NF.6- Solve real-world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem.
● 5.NF.7-Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions.
Understandings
● When multiplying whole numbers, the products increase; when multiplying fractions, the product decreases compared to its factors.
● Dividing fractions and whole numbers can be visualized through sharing and grouping models.
Knowledge
● A fraction can be interpreted as a division of the numerator by the denominator
● Multiplication of fractions can be
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem. (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) (VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Participate in respectful math conversations to share and compare others’ ideas, strategies, and approaches. (MP3 Constructing viable arguments and critiquing the reasoning of others) (VOG: Information Analysts, Responsible Citizens)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● How can I represent and make sense of fractional operations using visual models?
● What do I notice about the product as I multiply fractions? How does it make me a more strategic mathematician?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can interpret and explain how a fraction represents division of the numerator by the denominator.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 7
understood as scaling or resizing a quantity
● Multiply a fraction by a whole number and a fraction by a fraction
● Divide a unit fraction by a whole number and a whole number by a unit fraction using visual representations
● Visual representations, such as area models and number lines, support understanding of fraction multiplication and division
Key Vocabulary: mixed number
● I can multiply a fraction by another fraction and explain why the product is smaller than its factors.
● I can multiply a whole number by a fraction and use a visual representation to explain my answers.
● I can divide a whole number by a unit fraction and use a visual representation to explain my answers.
● I can divide a unit fraction by a whole number and use a visual representation to explain my answer.
● I can compare and discuss the models used by my peers.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 7 Assessment
● IAB- Number and Operations- Fractions
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of multiplying fractions, including fractions by fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, scaling and interpreting multiplication, dividing fractions and whole numbers in real-world contexts, and solving word problems involving all four operations with fractions
● Error Analysis: A student says that 3 ÷ 1/2 = 1.5. What’s their misunderstanding?
● Math Journal: Explain how multiplying a fraction by a whole number is different from dividing a whole number by a fraction.
● Activity Time: Multiply a whole number by a fraction, Compare the size of the product to the size of one factor, Divide a fraction by a whole number
3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
STAGE
Grade 5 Math: Unit 7
First Topic: Multiplication and Division of Fractions
Learning Targets:
● How can I represent and make sense of fractional operations using visual models?
● What do I notice about the product as I multiply fractions? How does it make me a more strategic mathematician?
Estimated # of Lessons: 24
Essential Questions:
● I can interpret and explain how a fraction represents division of the numerator by the denominator.
● I can multiply a fraction by another fraction and explain why the product is smaller than its factors.
● I can multiply a whole number by a fraction and use a visual representation to explain my answers.
● I can divide a whole number by a unit fraction and use a visual representation to explain my answers.
● I can divide a unit fraction by a whole number and use a visual representation to explain my answer.
● I can compare and discuss the models used by my peers.
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages Materials: blank cards, counters, fraction area models, pairs of scissors, dice (6-sided), paper cut-outs (rectangles)
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for multiplication of a fraction and a whole number to help make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (TB 5B pg. 1-2 WB 5B pg. 1-2)
● Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator to understand fractions as representations of equal parts, and build connections between division and fractions. (TB 5B pg. 38 WB 5B pg. 3-6)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Find a fraction of a set by interpreting 1/b × q as one part of a partition of q into b equal parts to help students understand how quantities can be divided into equal parts, laying the foundation for multiplying and dividing with fractions in real-world contexts. (TB 5B pg. 9-12 WB 5B pg. 7-8)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Find a fraction of a set by interpreting a/b × q as a part of a partition of q into b equal parts to develop an understanding of how fractions represent parts of a whole and to prepare students for applying fraction multiplication in real-world contexts. (TB 5B pg. 13-16 WB 5B pg. 9-10)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Multiply a whole number by a fraction to understand how repeated addition of fractional parts relates to multiplication. (TB 5B pg. 17-22 WB 5B pg. 11-12)
● Lesson 5 and 6 Focus: Multiply unit fractions to build a strong foundation for fraction operations, develop flexible thinking, and apply math to real-world situations like sharing, measurement, and scaling. (TB 5B pg. 27-30 WB 5B pg. 13-16)
● Lesson 7 Focus: Multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers to build fluency with fractions, strengthen number sense, and develop the ability to reason abstractly and quantitatively in realworld situations involving measurement, scaling, and problem-solving.(TB 5B pg. 31-34 WB 5B pg.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 7
17-18)
● Lesson 8 Focus: Multiplying mixed numbers to reason abstractly and quantitatively (TB 5B pg. 3538 WB 5B pg. 19-20)
● Lesson 9 Focus: Understanding multiplication as scaling, comparing the size of a product to the size of one factor, and explaining why multiplying a given number by a fraction greater(or less) than 1 results in a product greater (or less) than the given number to see how multiplying by fractions changes a number’s size, which is important for comparing, estimating, and solving reallife problems. (TB 5B pg. 39-42 WB 5B pg. 21-22)
● Lesson 10 and 11 Focus: Solving word problems involving multiplication to apply their math skills to real-life situations, build problem-solving strategies, and deepen their understanding of how fractions work (TB 5B pg. 43-52 WB 5B pg. 23-30)
● Lesson 12 and 13 Focus: Dividing fractions by whole numbers to understand how quantities can be broken into smaller parts, strengthens their grasp of fraction operations, and prepares them to solve real-world problems involving sharing, measuring, and scaling down. (TB 5B pg. 53-60 WB 5B pg. 31-36)
● Lesson 14 Focus: Dividing whole numbers by fractions to understand how many fractional parts fit into a whole, which is essential for real-world problem solving involving measurement, portioning, and scaling up quantities. (TB 5B pg. 61-64 WB 5B pg. 37-38)
● Lesson 15 and 16 Focus: Solving word problems with fraction division to apply their math skills to real-life situations, build problem-solving strategies, and deepen their understanding of how fractions work (TB 5B pg. 65-74 WB 5B pg. 39-42)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 5B pg. 75 WB pg. 43)
● Math Journal (TB pg. 75 WB pg. 44)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 45-48)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 7 - Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: February
● Word Problem of the Week: February (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Modules 9 and 10: Multiplying Fractions by Fractions and Whole Numbers, and Dividing Whole Numbers and Unit Fractions
● Coherence Map Grade 5 NF.B.3
● Exploring Parks and Playgrounds, CFLM (Context For Learning Mathematics) Lesson 6
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● Performance Task: Bake Sale (multiplying fractions and whole numbers)
● Performance Task: Improving Our School (multiplying and dividing fractions and whole numbers)
● Performance Task: Soccer Snacks (division of unit fractions and whole numbers)
● K-5 Resources: Multiply and Divide Fractions (pages 262 - 312). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math:Unit 8
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 11
Unit 8 Title: Measurement and Data: Jump In, Size Up, Track It
Unit Overview:
Next, we learn how to convert measurement units to make sure things fit just right, like your pet’s cage, your backpack’s weight, or even a basketball court setup. Then, we explore how to use line plots with fractional measurements to track how much you’ve grown, compare race times, or see who can jump the farthest. These skills help you make smart decisions and understand the world around you every day.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.MD.1- Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world problems.
● 5.MD.2 - Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Use operations on fractions for this grade to solve problems involving information presented in line plots.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem.(MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Measurement units can be converted within a system to solve real world problems.
● Different measurement units describe the same quantity in different ways.
Knowledge
● Convert between measurement units within the same system
● Create and interpret a line plot
Key Vocabulary: convert, data set
● How can I use conversion between different units of measurement to solve problems?
● How can I use my understanding of fraction operations to solve problems based on data represented on a line plot?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can solve word problems involving conversion of units of measurement.
● I can create a line plot to display a data set of measurements, including fractions.
● I can use fraction operations to answer questions about data shown in a line plot.
● I can show my growth over time (increased sophistication, correction of misconception, more agile use of strategies) around fraction operations using data from a line plot and converting measures.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 8
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 8 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of converting among units of time, length, volume, and mass within systems, solving word problems with measurement conversions, creating and interpreting line plots with fractional measurements
● Error Analysis: A student converts 3 feet to 30 inches. What mistake did they make?
● Math Journal: Why is it useful to be able to convert units of measurement?
● Activity Time: Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Measurement and Data
Learning Targets:
● I can solve word problems involving the conversion of units of measurement.
● I can create a line plot to display a data set of measurements, including fractions.
● I can use fraction operations to answer questions about data shown in a line plot.
● I can show my growth over time (increased sophistication, correction of misconceptions, more agile use of strategies) around fraction operations using data from a line plot and converting measures.
Estimated # of Lessons: 11
Essential Questions:
● How can I use conversion between different units of measurement to solve problems?
● How can I use my understanding of fraction operations to solve problems based on data represented on a line plot?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: measuring tape, weighing scale
Grade 5 Math: Unit 8
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Converting units of time (hours, minutes, and seconds) to solve real-world problems like calculating durations, understanding time relationships, and applying mathematical operations such as multiplication and division (TB 5B pg. 79-82 WB 5B pg. 49-52)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Converting customary units to solve real-world problems, understanding the relationships between different units, and applying mathematical operations such as multiplication and division in everyday contexts like measuring length, weight, and volume. (TB 5B pg. 83-86 WB 5B pg. 53-56)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Converting metric units (like grams and kilograms) to solve real-world problems, understanding how different units relate to each other, solving practical problems in measurement, and applying mathematical operations such as multiplication and division in real-world situations like cooking, science experiments, and comparing weights. (TB 5B pg. 87-90 WB 5B pg. 57-58)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Solve real-world problems involving the conversion of units of measurement: to develop flexibility with measurement units, strengthen problem-solving skills, and apply mathematical reasoning in meaningful, everyday contexts.. (TB 5B pg. 91-94 WB 5B pg. 59-60)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Make line plots to display a data set of measurements in fractions to organize and interpret fractional data, strengthen understanding of measurement and number sense, and draw conclusions in real-world contexts. (TB 5B pg. 95-98 WB 5B pg. 61-62)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Solving problems involving Line Plots to create and interpret line plots with fractional measurements to develop data analysis skills and apply understanding of fraction operations to solve real-world problems. (TB 5B pg. 99-104 WB 5B pg. 63-64)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 5B pg. 105, WB 5B pg. 65)
● Math Journal (TB 5B pg. 106 WB pg. 66)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 67-68)
● Cumulative Review 3 (WB pg. 69-72)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 8- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week March
● Word Problem of the Week March (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)- Module 11: Converting Like Measurements
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: measurement and Data-Convert Like Measurements Within a Given Measurement System (pages 313-325). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 9
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
# of Lessons: 10
Unit 9 Title: Volume and Mass: Think Big Weigh Smart
Unit Overview:
We think big as we learn how to find the area of rectangles using fractions, helping you plan spaces like where to put a rug or set up a garden. Then, we discover how to calculate volume to pack lunch boxes perfectly, stack boxes safely, or build bookshelves that stay strong. Finally, we explore how to find the volume of combined shapes, just like a playground designer creating cool, creative spaces.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.NF.4-Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction.
● 5.MD.3- Recognize volume as an attribute of solid figures and understand concepts of volume measurement.
● 5.MD.4- Measure volumes by counting unit cubes, using cubic cm, cubic in, cubic ft, and improvised units.
● 5.MD.5- Relate volume to the operations of multiplication and addition and solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume.
Transfer Goals
● Understand the meaning of the quantities and create a logical representation of the problem (MP 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively) ( VOG: Critical Thinker)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
● Engage in productive struggle and embrace mistakes as a necessary part of learning. (MP 1 Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Volume measures the amount of space a solid figure occupies and is measured in cubic units.
● Understanding volume helps support problem solving in real-life contexts such as measuring capacity, designing containers, or packing.
Knowledge
● Composite shapes can be broken into right rectangular prisms to find the total volume
● The formula for finding the area of a rectangle and applying it to finding volume, even when the side lengths are fractions
● Multiplying length X width, X height is the formula for volume
● What do I know about volume, and how can I apply that to finding the volume of composite shapes?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can use the area model to find the product of two fractions, including mixed numbers, by multiplying side lengths.
● I can measure volumes by counting cubes.
● I can use what I know about area to extend the relationship to volume by playing with multiple layers.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 9
Key Vocabulary: base area, cubit unit, volume, rectangular prism
● I can apply the formulas V=l x w x h and V= b x h to find the volume of a rectangular prism.
● I can find the volume of solid figures composed of two non-overlapping right rectangular prisms.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 9 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of finding the area of rectangles with fractional side lengths, measuring volume using unit cubes, applying volume formulas for prisms, and solving problems with composite volume.
● Error Analysis: A student finds the volume of a prism by adding length, width, and height. What should they have done instead?
● Math Journal: Describe at least one way to find the volume of a rectangular prism. Bonus points for describing two ways.
● Activity Time: Apply the formula L x W x H to find the volume of a rectangular prism
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Volume and Mass
Learning Targets:
● I can use the area model to find the product of two fractions, including mixed numbers, by multiplying side lengths.
● I can measure volumes by counting cubes.
● I can use what I know about area to extend the relationship to volume by playing with multiple layers.
● I can apply the formulas V=l x w x h and V= b x h to find the volume of a rectangular
Estimated # of Lessons: 10
Essential Questions:
● What do I know about volume, and how can I apply that to finding the volume of composite shapes?
Grade 5 Math: Unit 9
prism.
● I can find the volume of solid figures composed of two non-overlapping right rectangular prisms.
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages Materials: sheets of paper, unit cubes, dice(regular 6-sided)
Learning Activities:
● Fluency Practice 1: Develop fluency for multiplication and finding the areas of a rectangle by tiling.
● Lesson 1 Focus: Multiply side lengths to find the area of rectangles to understand the relationship between multiplication and area, and to apply this understanding to solve problems involving space and measurement. (TB 5B pg. 111-114 WB 5B pg. 75-80)
● Lesson 2 Focus: ChatGPT said:
● Recognize a unit cube and use it to measure volume by counting cubes to develop spatial reasoning, understanding volume as an attribute of solid figures. (TB 5B pg. 115-120 WB 5B pg. 81-84)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Applying the formulas v = l x w x h and v=b x h to find the volume of a rectangular prism. (TB 5B pg. 121-126 WB 5B pg. 85-88)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Find the volumes of solid figures composed of two non-overlapping right rectangular prisms by adding their volumes to build understanding of volume as additive, strengthen spatial reasoning, and solve real-world problems involving composite figures. (TB 5B pg. 127-130 WB 5B pg. 89-92)
● Lesson 5 Focus: Solving word problems to develop a deep understanding of volume as the amount of space a 3D object occupies, allowing students to apply multiplication strategies to solve realworld problems. (TB 5B pg. 131-136 WB 5B pg. 93-96)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 5B pg. 137, WB 5B pg. 97)
● Math Journal (TB 5B pg. 137 WB pg. 98)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 99-102)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 9- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: April
● Word Problem of the Week: April (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)-Module 13: Exploring Volume
● Coherence Map Grade 5 MD.C.3
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Understanding Volume (pages 334-362). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 10
Course Name: Grade 5 Math
Est. # of Lessons: 7
Unit 10 Title: Geometry: Unlocking Secrets of Shapes
Unit Overview:
Polygons are all around us-in tile floors, kites, and bridges. We’ll explore how to identify different polygons, sort triangles and quadrilaterals by their special properties, and find shapes that match perfectly in size and form. Let’s jump in and discover how understanding shapes helps us build and create amazing wonders.
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.G.3-Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category.
● 5.G.4-classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
Understandings
● Classifying shapes helps to make sense of the relationships among different types of figures.
● Shapes can belong to more than one category at the same time based on their properties.
Knowledge
● Triangles and quadrilaterals can be classified by the number of sides, the length of sides, and the types of angles
● Shapes can be sorted into categories and subcategories in a hierarchy
Key Vocabulary: polygons, quadrilaterals, parallelograms, congruent, hierarchy
Transfer Goals
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
● Make sense of problems to build math understanding and reasonableness of the answer. (MP 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them) (VOG: Self-Directed Learners, Critical Thinkers)
Essential Questions
● What attributes help me to classify shapes?
● How does identifying shared attributes help me classify shapes in a hierarchy?
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can explain why a shape (like a square) belongs to more than one category (like a rectangle and a rhombus).
● I can classify shapes into categories and subcategories based on their properties.
● I can create and explain a hierarchy of shapes (like quadrilaterals) using a diagram or chart.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Grade 5 Math: Unit 10
Summative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 10 Assessment
Formative Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of classifying two-dimensional shapes in a hierarchy, identifying regular polygons, and congruent figures
● Error Analysis: A student says all quadrilaterals are squares. How would you correct their thinking?
● Math Journal: How is a square both a rectangle and a rhombus? What does that tell you about geometry?
● Activity Time: Classify quadrilaterals based on their properties
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
First Topic: Geometry
Learning Targets:
● I can explain why a shape (like a square) belongs to more than one category (like a rectangle and a rhombus).
● I can classify shapes and subcategories based on their properties.
● I can create and explain a hierarchy of shapes (like quadrilaterals) using a diagram or chart.
Estimated # of Lessons: 7
Essential Questions:
● What attributes help me to classify shapes?
● How does identifying shared attributes help me classify shapes in a hierarchy?
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Materials: blank cards, protractor, ruler, set square, paper cut-outs (triangles and trapezoids), square grid
Lesson Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Identify regular polygons by defining their attributes, recognizing patterns, and applying geometric reasoning to develop a deeper understanding of shape properties, classify polygons accurately, and strengthen reasoning skills in geometry. (TB 5B pg. 141-144, WB 5B pg. 103-104)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Classify triangles by their sides and angles to analyze geometric properties,
Grade 5 Math: Unit 10
recognize patterns, and build a foundation for reasoning about more complex shapes and relationships in geometry.(TB 5B pg. 145-148, WB 5B pg. 105-106)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Classify quadrilaterals based on their properties to deepen understanding of geometric relationships, recognize shared attributes, and understand the hierarchy among shapes. (TB 5B pg. 149-156, WB 5B pg. 107-108)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Identify figures that have the same shape and size (congruent figures) to build spatial reasoning and develop an understanding of geometric equivalence and transformations. (TB 5B pg. 157-162, WB 5B pg. 109-112)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 5B pg. 163, WB 5B pg. 113)
● Math Journal (TB 5B pg. 164, WB pg. 114)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 115-116)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 10- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: May
● Word Problem of the Week: May (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)-Module 15: Classifying Two-dimensional Figures
● Coherence Map Grade 5 G.B.3
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Classifying Two-Dimensional Figures (pages 375-399). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 11
Course Name: Grade 5
Est. # of Lessons: 13
Unit 11 Title: Expressions and Graphs: Exploring
the World of Numbers and Patterns
Unit Overview:
Ever wanted to track your savings, design cool pixel art, or figure out a game score? Algebra and graphs make all that possible! In this unit, you’ll write and interpret numerical and algebraic expressions, discover relationships between numbers, and create number patterns. You’ll also learn to graph points on the coordinate plane to represent real-world problems and make sense of math in action
STAGE 1: DESIRED RESULTS
Established Goals
● 5.OA.3- Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane.
● 5.G.1-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond.
● 5.G.2- Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation.
Transfer Goals
● Use the precise language of math to effectively communicate their mathematical ideas and articulate their thought processes using numbers, labels, sketches, symbols, and words. (MP 6 Attending to Precision ) (VOG: Effective Communicators)
● Recognize patterns, identify similarities and differences, and understand how different mathematical ideas relate to one another. (MP 7 Look for and make use of structure) (VOG: Critical Thinkers)
Understandings Essential Questions
● Patterns follow rules that can be used to generate ordered pairs.
● Points on a coordinate plane have meaning in context to help solve problems.
● How can I use what I know about the numbers in an ordered pair to describe a location?
● How can graphing points help me understand
Grade 5 Math: Unit 11
patterns or data?
Knowledge
● Plotting ordered pairs on a coordinate plane using x- and y- coordinates
● Graphs can represent relationships between two numerical patterns.
● Patterns can be described using rules and expressions
● Points on a coordinate plane are defined by their distance from the x- and y-axes
Key Vocabulary: coordinate plane, coordinate pair, points
Skills (Framed as Learning Targets)
● I can graph points on the coordinate plane.
● I can identify relationships between two sets of values and write an equation to represent the pattern.
● I can represent real-world and mathematical problems by graphing or interpreting points on the coordinate plane.
STAGE 2: DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
Summative Assessment Formative Assessment
● MDY Grade 5 Unit 11 Assessment
● Exit Ticket: Using questions drawn from the unit review, assess for understanding of writing and interpreting numerical patterns, graphing points on the coordinate plane to solve problems, analyzing relationships between two numerical patterns
● Error Analysis: A student looks at the input 3, 4, 5 and output 6, 8, 10 and says the rule is “add 3.” What's the correct rule and how do you know?
● Math Journal: Describe how you can identify a pattern in a table and write a rule for it.
● Activity Time: Graph points on a coordinate plane
STAGE 3: LEARNING PLAN
Unit Opener & Recall: Used to launch units using a Notice and Wonder format to orient students to the overall topic.
Anchor Task: Begin each lesson with the Anchor Task that activates, engages, and guides students' ideas to create the board plan. Our Friends’ Ideas in each lesson is a tool for teacher-led discussion of various methods of solving the anchor tasks that are coming from students.
Activity Time: Throughout each unit, activity time provides practice, reflection, and application opportunities. Teachers are expected to select guided practice and workbook pages tailored to the student's needs.
Grade 5 Math: Unit 11
First Topic: Expressions and Graphs
Learning Targets:
● I can graph points on the coordinate plane.
● I can identify relationships between two sets of values and write an equation to represent the pattern.
● I can represent real-world and mathematical problems by graphing or interpreting points on the coordinate plane.
Estimated # of Lessons: 13
Essential Questions:
● How can I use what I know about the numbers in an ordered pair to describe a location?
● How can graphing points help me understand patterns or data?
Materials: blank cards, number cards(11 to 20), unit cubes, dice (regular 6-sided), square grid
Learning Activities:
● Lesson 1 Focus: Understanding numerical and algebraic expressions to build a strong foundation in representing and analyzing mathematical relationships. (TB 5B pg. 169-172, WB 5B pg. 117-120)
● Lesson 2 Focus: Identify relationships between two sets of values and generate numerical patterns to recognize and extend patterns, strengthen algebraic thinking, and apply reasoning to solve real-world problems. (TB 5B pg. 173-176, WB 5B pg. 121-122)
● Lesson 3 Focus: Plotting points on a coordinate plane to develop spatial reasoning and use visual models to solve problems involving patterns, distance, and real-world situations. (TB 5B pg. 177182, WB 5B pg. 123-126)
● Lesson 4 Focus: Graph points on a coordinate plane: to understand the relationship between ordered pairs and spatial locations, develop coordinate reasoning, and interpret real-world data visually. (TB 5B pg. 183-188, WB 5B pg. 127-128)
● Lesson 5 and 6 Focus: Solving problems involving graphs to represent real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points on the coordinate plane. (TB pg. 189-200, WB 5B pg. 129-134)
End of Unit:
Note: End-of-unit tasks help teachers assess students' independent understanding, encourage reflection on key concepts, and provide opportunities to apply math skills in meaningful ways before moving on.
● Mind Workout (TB 5B pg. 201, WB 5B pg. 135)
● Math Journal (TB 5B pg. 202, WB pg. 136)
● Unit Review (WB pg. 137-140, Unit Review WB 5B pg. 137-140)
● Cumulative Review 4 (WB pg. 141-146)
● End of the Year Review (WB pg. 147-156)
Think! Mathematics Resources:
● Tool Kit Unit 11- Overview, teaching videos, downloads, and digital access to lessons and assessments
● Problem of the Week: June
● Word Problem of the Week: June (Mild, Medium, Spicy options)
● Multiplication/Division Fluency
Additional Resources: Resources will support tiered instruction and preparation for state assessments
Key: Bold-Lesson, Black: Lesson Purpose, Green: Textbook (TB) and Workbook (WB) pages
Grade 5 Math: Unit 11
● Problem Strings For Fluency and Beyond Grade 5 (Glassco, Fosnot)
● Math in Practice (O’Connell)-Module 14: Understanding the Coordinate System
● Coherence Map Grade 5 MD.B.2
● Coherence Map: Graphing
● Smarter Balance Supplemental Materials
● K-5 Resources: Graphing Points on Coordinate Planes (pages 363-374). Games and activities for small group instruction and partner work.
